Global Trends of Nutrition in Cancer Research: A Bibliometric and Visualized Analysis Study over the Past 10 Years
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source and Search Strategy
- (1)
- “nutrition” OR “nutritional therap*” OR “nutritional assessment” OR “nutritional supplement*” OR “nutritional intervention*”
- (2)
- “cancer” OR “cancer care” OR “tumor” OR “neoplasm*” OR “malignanc*” OR “oncology” OR “cancer patient*” OR “cancer management” OR “cancer prevention”
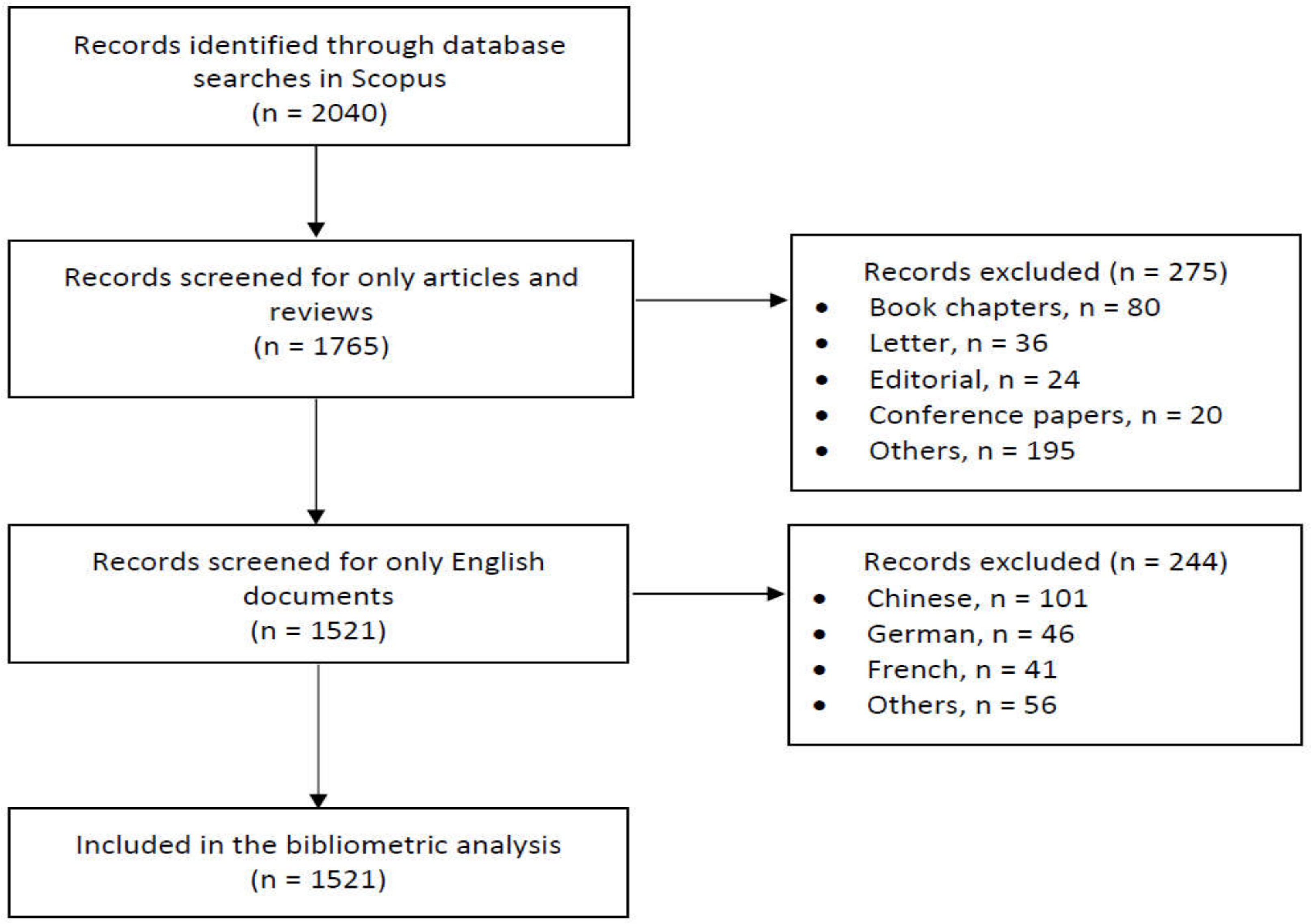
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Data Analysis and Visualization
3. Results
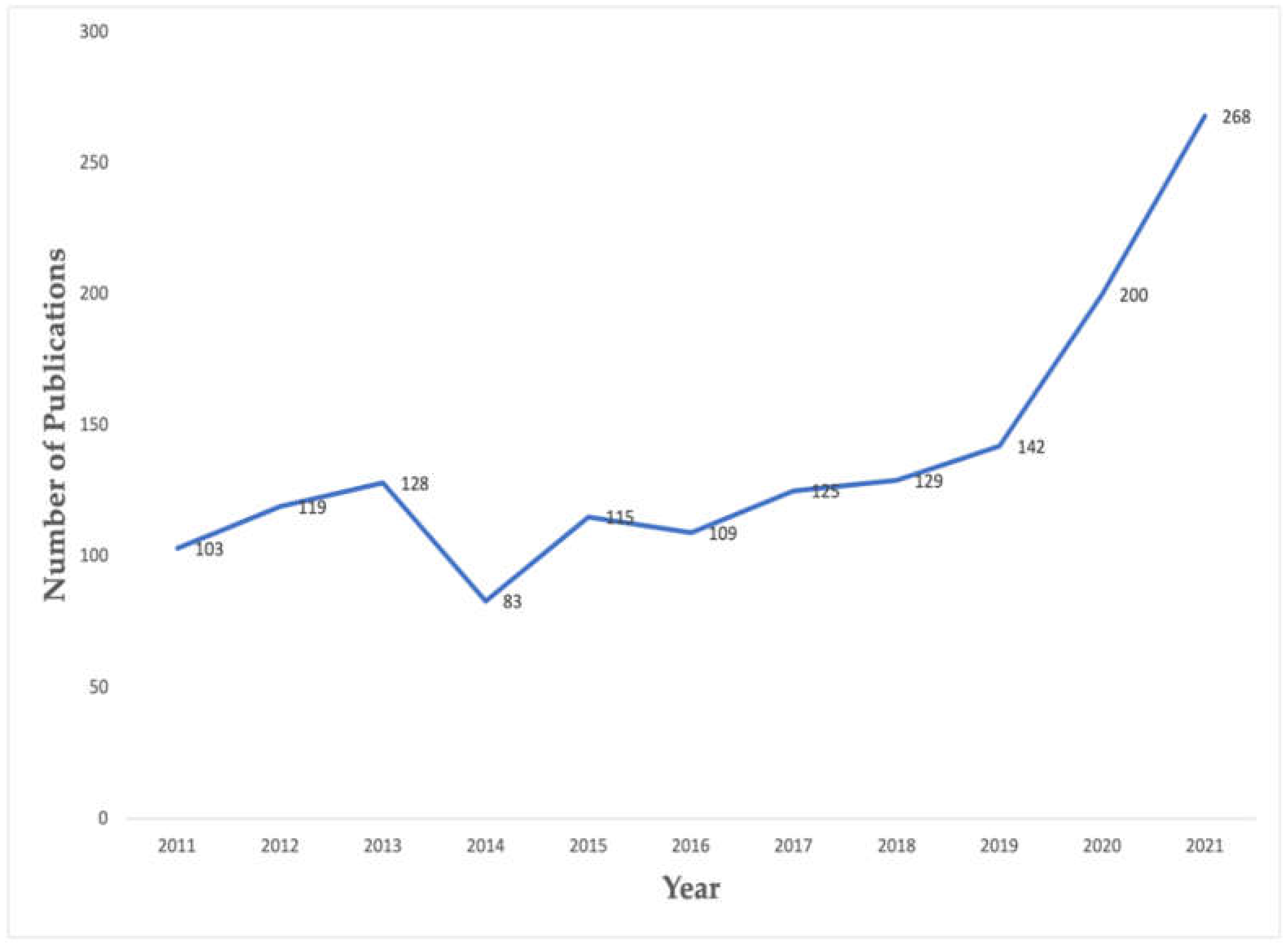
3.1. The Global Publication Trend
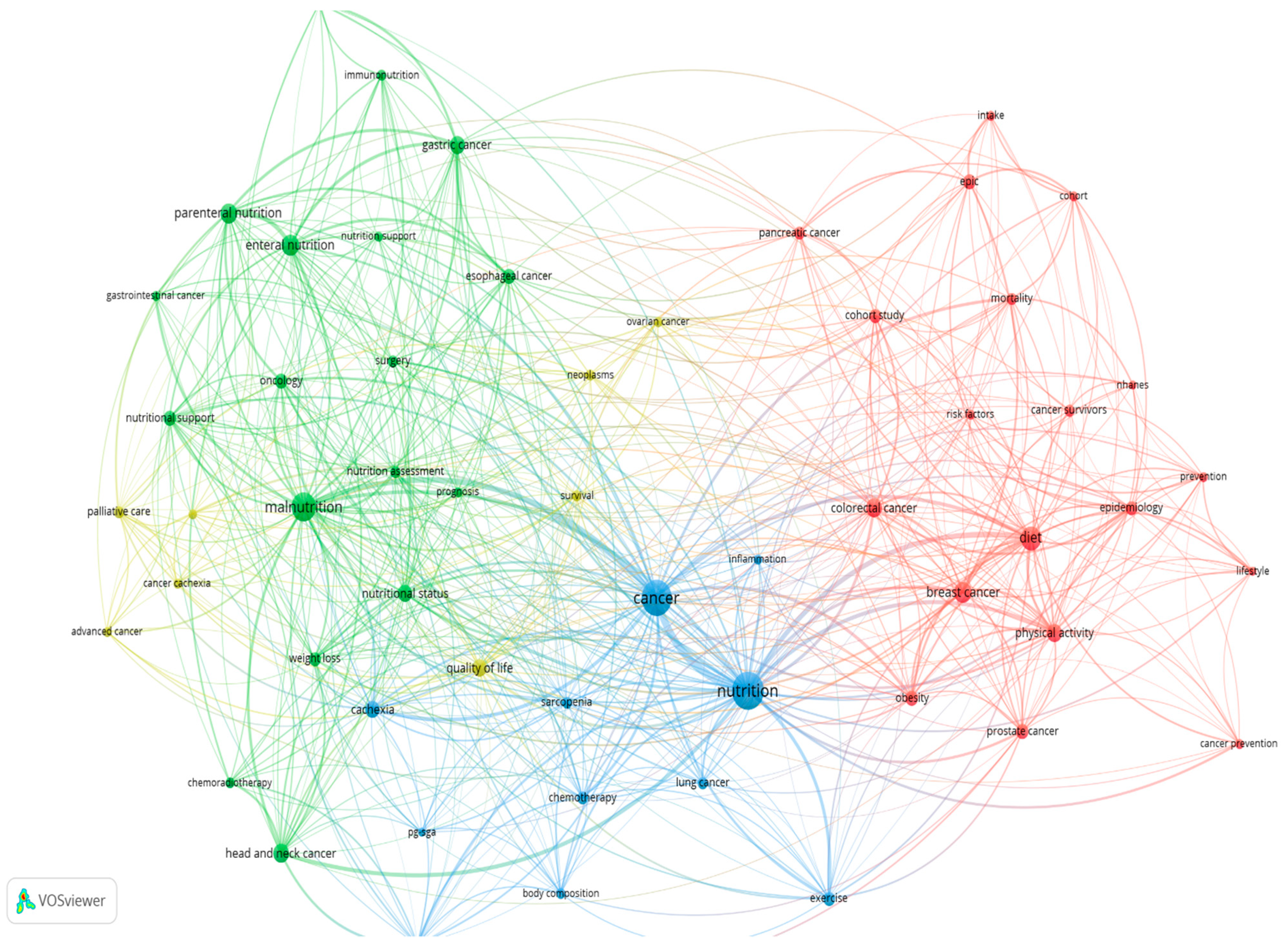
3.2. Authors, Author Keywords, Affiliations
3.3. Journals
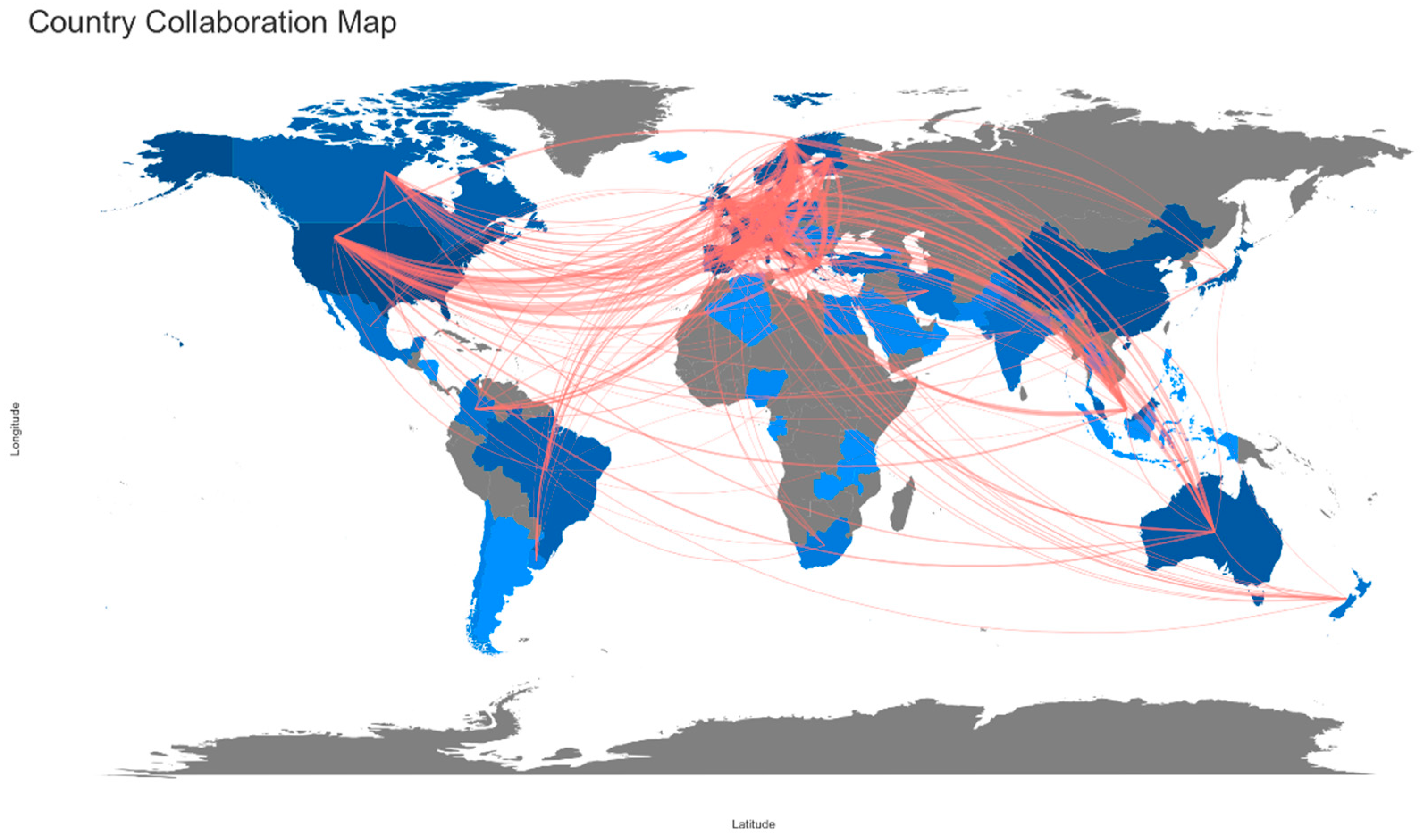
3.4. Country Collaboration
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bianchi, V.E.; Herrera, P.F.; Laura, R. Effect of nutrition on neurodegenerative diseases. A systematic review. Nutr. Neurosci. 2021, 24, 810–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Jeong, K.; Lee, S.; Seo, B.N.; Baek, Y. Low nutritional status links to the prevalence of pre-metabolic syndrome and its cluster in metabolically high-risk Korean adults: A cross-sectional study. Medicine 2021, 100, e25905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsaousi, G.; Panidis, S.; Stavrou, G.; Tsouskas, J.; Panagiotou, D.; Kotzampassi, K. Prognostic indices of poor nutritional status and their impact on prolonged hospital stay in a Greek university hospital. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 924270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffaitin, C.; Lasseur, C.; Chauveau, P.; Barthe, N.; Gin, H.; Combe, C.; Rigalleau, V. Nutritional status in patients with diabetes and chronic kidney disease: A prospective study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Marshall, K.M.; Loeliger, J.; Nolte, L.; Kelaart, A.; Kiss, N.K. Prevalence of malnutrition and impact on clinical outcomes in cancer services: A comparison of two time points. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscaritoli, M.; Krznaric, Z.; Singer, P.; Barazzoni, R.; Cederholm, T.; Golay, A.; Van Gossum, A.; Kennedy, N.; Kreymann, G.; Laviano, A.; et al. Effectiveness and efficacy of nutritional therapy: A systematic review following Cochrane methodology. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 939–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pingili, S.; Ahmed, J.; Sujir, N.; Shenoy, N.; Ongole, R. Evaluation of Malnutrition and Quality of Life in Patients Treated for Oral and Oropharyngeal Cancer. Sci. World J. 2021, 2021, 9936715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, M.B.; Isenring, E.; Brown, B. Nutrition and swallowing therapy strategies for patients with head and neck cancer. Nutrition 2020, 69, 110548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Zhang, X.; Meyerhardt, J.A.; Giovannucci, E.L.; Ogino, S.; Fuchs, C.S.; Chan, A.T. Marine omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid intake and survival after colorectal cancer diagnosis. Gut 2017, 66, 1790–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashi, P.; Popiel, B.; Lammersfeld, C.; Gupta, D. Outcomes of systematic nutritional assessment and medical nutrition therapy in pancreatic cancer. Pancreas 2015, 44, 750–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebuterne, X.; Lemarie, E.; Michallet, M.; de Montreuil, C.B.; Schneider, S.M.; Goldwasser, F. Prevalence of malnutrition and current use of nutrition support in patients with cancer. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2014, 38, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caillet, P.; Liuu, E.; Raynaud Simon, A.; Bonnefoy, M.; Guerin, O.; Berrut, G.; Lesourd, B.; Jeandel, C.; Ferry, M.; Rolland, Y.; et al. Association between cachexia, chemotherapy and outcomes in older cancer patients: A systematic review. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 1473–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilleron, S.; Soto-Perez-de-Celis, E.; Vignat, J.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Bray, F.; Sarfati, D. Estimated global cancer incidence in the oldest adults in 2018 and projections to 2050. Int. J. Cancer 2021, 148, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Pang, L.; Sharma, S.V.; Li, R.; Nyitray, A.G.; Edwards, B.J. Malnutrition and overall survival in older patients with cancer. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 966–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravasco, P. Nurition in cancer patients. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariyanto, T.I.; Kurniawan, A. Appetite problem in cancer patients: Pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Cancer Treat. Res. Commun. 2021, 27, 100336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.S.; Zhao, F.; Fisch, M.J.; O’Mara, A.M.; Cella, D.; Mendoza, T.R.; Cleeland, C.S. Prevalence and characteristics of moderate to severe fatigue: A multicenter study in cancer patients and survivors. Cancer 2014, 120, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotogni, P.; Pedrazzoli, P.; De Waele, E.; Aprile, G.; Farina, G.; Stragliotto, S.; De Lorenzo, F.; Caccialanza, R. Nutritional Therapy in Cancer Patients Receiving Chemoradiotherapy: Should We Need Stronger Recommendations to Act for Improving Outcomes? J. Cancer 2019, 10, 4318–4325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De van der Schueren, M.A.E.; Laviano, A.; Blanchard, H.; Jourdan, M.; Arends, J.; Baracos, V.E. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the evidence for oral nutritional intervention on nutritional and clinical outcomes during chemo(radio)therapy: Current evidence and guidance for design of future trials. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 1141–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arends, J.; Baracos, V.; Bertz, H.; Bozzetti, F.; Calder, P.C.; Deutz, N.E.P.; Erickson, N.; Laviano, A.; Lisanti, M.P.; Lobo, D.N.; et al. ESPEN expert group recommendations for action against cancer-related malnutrition. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 1187–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaldson, M.S. Nutrition and cancer: A review of the evidence for an anti-cancer diet. Nutr. J. 2004, 3, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayne, S.T.; Playdon, M.C.; Rock, C.L. Diet, nutrition, and cancer: Past, present and future. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 13, 504–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhao, D.; Jia, W.; Wang, Y.; Liang, H.; Liu, L.; Wang, W.; Yu, Z.; Guo, F. A bibliometric analysis and review of recent researches on TRPM7. Channels 2020, 14, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doskaliuk, B.; Yatsyshyn, R.; Klishch, I.; Zimba, O. COVID-19 from a rheumatology perspective: Bibliometric and altmetric analysis. Rheumatol. Int. 2021, 41, 2091–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faruk, M.; Rahman, M.; Hasan, S. How digital marketing evolved over time: A bibliometric analysis on scopus database. Heliyon 2021, 7, e08603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akintunde, T.Y.; Chen, S.; Musa, T.H.; Amoo, F.O.; Adedeji, A.; Ibrahim, E.; Tassang, A.E.; Musa, I.H.; Musa, H.H. Tracking the progress in COVID-19 and vaccine safety research—A comprehensive bibliometric analysis of publications indexed in Scopus database. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2021, 17, 3887–3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweileh, W.M. Bibliometric analysis of peer-reviewed literature on antimicrobial stewardship from 1990 to 2019. Glob. Health 2021, 17, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reglero, C.; Reglero, G. Precision nutrition and cancer relapse prevention: A systematic literature review. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baguley, B.J.; Bolam, K.A.; Wright, O.R.; Skinner, T.L. The effect of nutrition therapy and exercise on cancer-related fatigue and quality of life in men with prostate cancer: A systematic review. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, C.C.; Swan, F.; Greenley, S.L.; Lind, M.; Johnson, M.J. Physical activity and nutrition interventions for older adults with cancer: A systematic review. J. Cancer Surviv. 2020, 14, 689–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bye, A.; Sandmael, J.A.; Stene, G.B.; Thorsen, L.; Balstad, T.R.; Solheim, T.S.; Pripp, A.H.; Oldervoll, L.M. Exercise and nutrition interventions in patients with head and neck cancer during curative treatment: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, B.-Y.; Song, H.J.; Yang, K.; Cheon, C.; Ko, Y.; Jang, B.-H.; Shin, Y.-C.; Ko, S.-G. Bibliometric analysis of integrative medicine studies from 2000 to 2019. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2021, 49, 829–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.I.; Ignacio, K.H.; Omar, A.T.; Khu, K.J. Top 100 most cited neurologic and neurosurgical articles on COVID-19: A bibliometric analysis. World Neurosurg. 2022, 157, e137–e147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lastella, M.; Memon, A.R.; Vincent, G.E. Global research output on sleep research in athletes from 1966 to 2019: A bibliometric analysis. Clocks Sleep 2020, 2, 99–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massimo, A.; Corrado, C. Bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. J. Informetr. 2017, 11, 959–975. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Gu, Z.; Zhong, H.; Zha, Q.; Yang, L.; Zhu, C.; Chen, E. A bibliometric analysis using VOSviewer of publications on COVID-19. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 816–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 2010, 84, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fane, M.; Weeraratna, A.T. How the ageing microenvironment influences tumour progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemppainen, L.M.; Kemppainen, T.T.; Reippainen, J.A.; Salmenniemi, S.T.; Vuolanto, P.H. Use of complementary and alternative medicine in Europe: Health-related and sociodemographic determinants. Scand. J. Public Health 2018, 46, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.-L.; Lee, H.-S.; Shin, B.-C.; Liu, J.-P.; Shang, Q.; Yamashita, H.; Lim, B. Traditional medicine in China, Korea, Japan: A brief introduction and comparison. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 429103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asiimwe, J.B.; Nagendrappa, P.B.; Atukunda, E.C.; Kamatenesi, M.M.; Nambozi, G.; Tolo, C.U.; Ogwang, P.E.; Sarki, A.M. Prevalence of the use of herbal medicines among patients with cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2021, 9963038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo-Martínez, L.; Castro-Eguiluz, D.; Copca-Mendoza, E.T.; Pérez-Camargo, D.A.; Reyes-Torres, C.A.; Ávila, E.A.; López-Córdova, G.; Fuentes-Hernández, M.R.; Cetina-Pérez, L.; Milke-García, M.D.P. Nutritional Assessment Tools for the Identification of Malnutrition and Nutritional Risk Associated with Cancer Treatment. Rev. Investig. Clin. 2018, 70, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenlee, H.; Santiago-Torres, M.; McMillen, K.K.; Ueland, K.; Haase, A.M. Helping Patients Eat Better During and Beyond Cancer Treatment: Continued Nutrition Management throughout Care to Address Diet, Malnutrition, and Obesity in Cancer. Cancer J. 2019, 25, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiseman, M.J. Nutrition and cancer: Prevention and survival. Br. J. Nutr. 2019, 122, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Cancer Research Fund International Home Page. Available online: https://www.wcrf.org/nutrition-and-breast-cancer-in-south-africa/ (accessed on 28 January 2022).

| Rank | Author | No. of Articles | % of the Total Number of Articles (1521) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Tumino, R. | 195 | 12.82% |
| 2 | Trichopoulou, A. | 191 | 12.56% |
| 3 | Riboli, E. | 179 | 11.77% |
| 4 | Overvad, K. | 175 | 11.51% |
| 5 | Boeing, H. | 170 | 11.18% |
| 6 | Tjønneland, A. | 152 | 9.99% |
| 7 | Khaw, K-T. | 141 | 9.27% |
| 8 | Kaaks, R. | 135 | 8.88% |
| 9 | Bueno-De-Mesquita, HB. | 129 | 8.48% |
| 10 | Palli, D. | 117 | 7.69% |
| Rank | From | Country | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Imperial College London | United Kingdom | 410 |
| 2 | International Agency for Research on Cancer | France | 392 |
| 3 | University of Oxford | United Kingdom | 342 |
| 4 | University of Athens Medical School | Germany | 258 |
| 5 | University of Cambridge | United Kingdom | 250 |
| 6 | University of Tromso | Norway | 235 |
| 7 | University Medical Center Utrecht | Netherlands | 233 |
| 8 | Umea University | Sweden | 232 |
| 9 | Aarhus University | Denmark | 202 |
| 10 | Lund University | Sweden | 199 |
| Rank | Author Keyword | Occurrences |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Nutrition | 236 |
| 2 | Cancer | 202 |
| 3 | Malnutrition | 135 |
| 4 | Diet | 91 |
| 5 | Breast Cancer | 71 |
| 6 | Enteral Nutrition | 69 |
| 7 | Parenteral Nutrition | 67 |
| 8 | Head and Neck Cancer | 60 |
| 9 | Colorectal Cancer | 58 |
| 10 | Gastric Cancer | 54 |
| Rank | Journal | No. of Articles | Publisher | Aim and Scope |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Nutrients | 70 | MDPI | Nutrients is an international, peer-reviewed open access advanced forum for publishing studies related to Human Nutrition. |
| 2 | International Journal of Cancer | 68 | Wiley | A broad scope of topics relevant to the following categories: Cancer Epidemiology, Cancer Genetics and Epigenetics, Infectious Causes of Cancer, Innovative Tools and Methods, Molecular Cancer Biology Tumor Immunology and Microenvironment, Tumor Markers and Signatures, and Cancer Therapy and Prevention. |
| 3 | Nutrition and Cancer | 59 | Taylor and Francis | This publication reports current findings on the effects of nutrition on the etiology, therapy, and prevention of cancer. Coverage of therapy focuses on research in clinical nutrition and oncology, dietetics, and bioengineering. Prevention approaches include public health recommendations, preventative medicine, behavior modification, education, functional foods, and agricultural and food production policies. |
| 4 | Supportive Care in Cancer | 52 | Springer | This journal covers the physical, psychosocial and spiritual aspects of the cancer patient’s journey from diagnosis through to end-of-life care, with a focus on interventions to mitigate symptoms and side effects during this journey. |
| 5 | American Journal of Clinical Nutrition | 33 | Oxford Academic | Well-controlled clinical studies that describe scientific mechanisms, efficacy, and safety of dietary interventions in the context of disease prevention or a health benefit will be considered. Public health and epidemiologic studies relevant to human nutrition, and innovative investigations of nutritional questions that employ epigenetic, genomic, proteomic, and metabolomic approaches are encouraged. |
| 6 | Clinical Nutrition | 31 | Elsevier | The journal reflects the scientific nature of this multidisciplinary background and encourages the coordination of investigation and research from these disciplines. It also publishes scientific works related to the development of new techniques and their application in the field of clinical nutrition. |
| 7 | British Journal of Nutrition | 28 | Cambridge Core | This journal focuses in nutritional science relevant to human or animal nutrition. The BJN welcomes studies in nutritional epidemiology, nutritional requirements, metabolic studies, body composition, energetics, appetite and obesity. |
| 8 | Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition | 24 | Aspen | This journal is the premier scientific journal of nutrition and metabolic support. It publishes studies that define the cutting edge of basic and clinical research in the field. It explores the science of optimizing the care of patients receiving enteral or IV therapies. |
| 9 | Cancer Epidemiology Biomarkers and Prevention | 23 | AACR | This journal publishes population-based research on cancer etiology, prevention, surveillance, and survivorship. The following topics are of special interest: descriptive, analytical, and molecular epidemiology; biomarkers including assay development, validation, and application; chemoprevention and other types of prevention research in the context of descriptive and observational studies; the role of behavioral factors in cancer etiology and prevention; survivorship studies; risk factors; implementation science and cancer care delivery; and the science of cancer health disparities. |
| 10 | BMC Cancer | 20 | BMC | BMC Cancer considers articles on all aspects of cancer research, including the pathophysiology, prevention, diagnosis and treatment of cancers. The journal also welcomes molecular and cellular biology, genetics, epidemiology, and clinical trials. |
| Rank | Country | No. of Articles |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | United States of America | 239 |
| 2 | China | 170 |
| 3 | United Kingdom | 120 |
| 4 | Spain | 97 |
| 5 | Australia | 85 |
| 6 | Japan | 82 |
| 7 | Italy | 77 |
| 8 | France | 68 |
| 9 | Germany | 62 |
| 10 | Korea | 49 |
| Rank | From | To | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Italy | Germany | 215 |
| 2 | Italy | United Kingdom | 215 |
| 3 | France | Germany | 214 |
| 4 | United Kingdom | Germany | 213 |
| 5 | Italy | France | 212 |
| 6 | United Kingdom | France | 211 |
| 7 | Italy | Spain | 210 |
| 8 | Spain | France | 209 |
| 9 | Spain | Germany | 207 |
| 10 | United Kingdom | Spain | 204 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Youn, B.-Y.; Lee, S.-Y.; Cho, W.; Bae, K.-R.; Ko, S.-G.; Cheon, C. Global Trends of Nutrition in Cancer Research: A Bibliometric and Visualized Analysis Study over the Past 10 Years. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4165. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19074165
Youn B-Y, Lee S-Y, Cho W, Bae K-R, Ko S-G, Cheon C. Global Trends of Nutrition in Cancer Research: A Bibliometric and Visualized Analysis Study over the Past 10 Years. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(7):4165. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19074165
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoun, Bo-Young, Seo-Yeon Lee, Wonje Cho, Kwang-Rok Bae, Seong-Gyu Ko, and Chunhoo Cheon. 2022. "Global Trends of Nutrition in Cancer Research: A Bibliometric and Visualized Analysis Study over the Past 10 Years" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 7: 4165. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19074165
APA StyleYoun, B.-Y., Lee, S.-Y., Cho, W., Bae, K.-R., Ko, S.-G., & Cheon, C. (2022). Global Trends of Nutrition in Cancer Research: A Bibliometric and Visualized Analysis Study over the Past 10 Years. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(7), 4165. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19074165







