Evaluation of Occupational Health Risk Management and Performance in China: A Case Study of Gas Station Workers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review and Conceptual Paradigm
2.1. Risk Factors
2.1.1. Physical Risks
2.1.2. Chemical Risks
2.1.3. Biological Risks
2.1.4. Physiological Risks
2.1.5. Psychological Risks
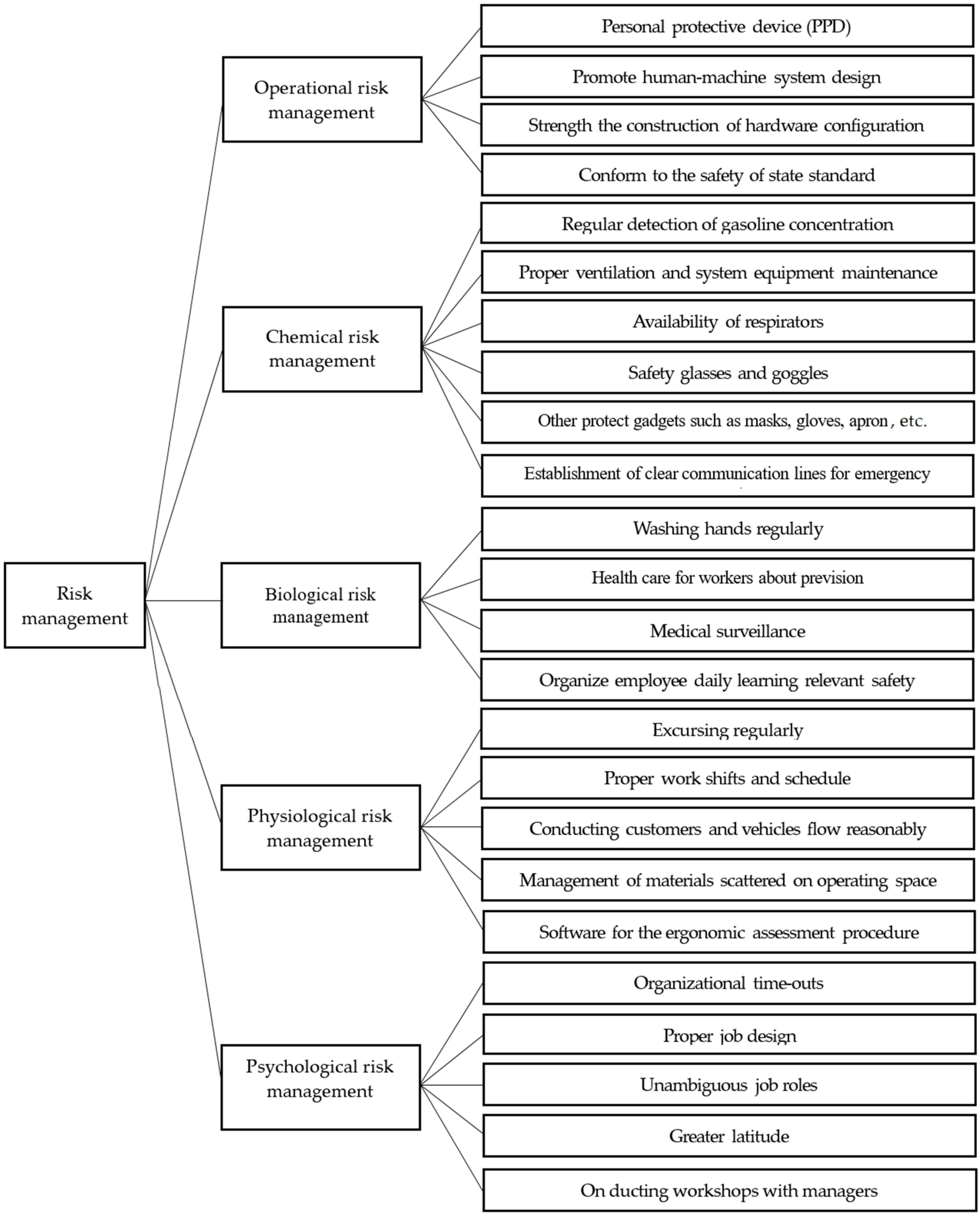
2.2. Risk Response Stratagem
2.2.1. Physical Risk Management
2.2.2. Chemical Risk Management
2.2.3. Biological Risk Management
2.2.4. Physiological Risk Management
2.2.5. Psychological Risk Management
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Research Framework
3.2. Questionnaire Design
3.3. Research Sample
3.4. Fuzzy Theory and Analytic Hierarchy Processes (AHP)
3.5. The Weights of Risk Factors
3.5.1. The Fuzzy Positive Reciprocal Matrix
3.5.2. The Local Weights of Risk Factors
3.5.3. Defuzziness Process
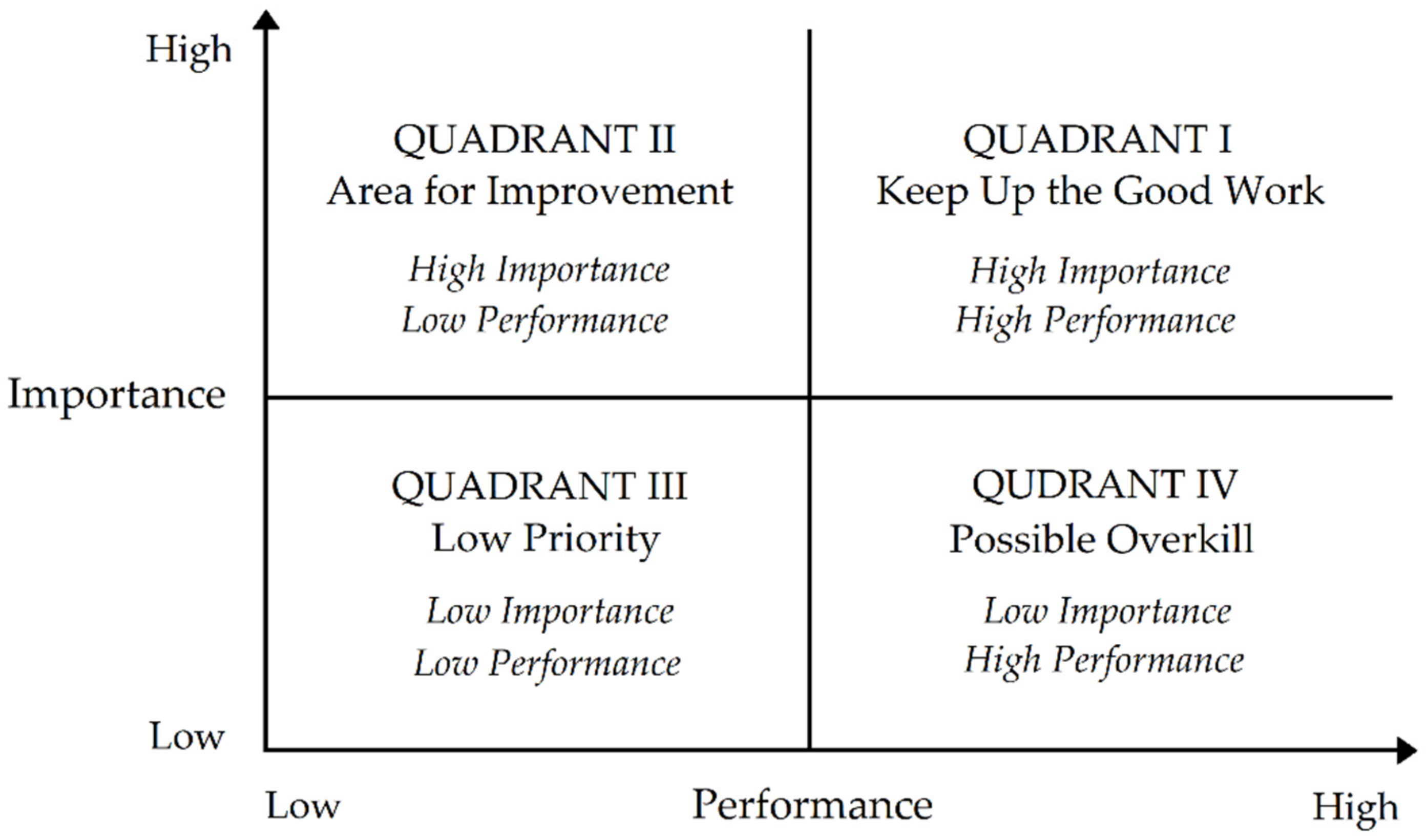
3.6. Performance Evaluation and Importance-Performance Analysis (IPA)
4. Results
4.1. General Characteristics of Research Subjects
4.2. The Relative Importance and Priority Ranking of Main Factors
4.3. The Relative Importance and Priority Ranking of Sub-Factors
4.4. Performance Analysis of Main Factors
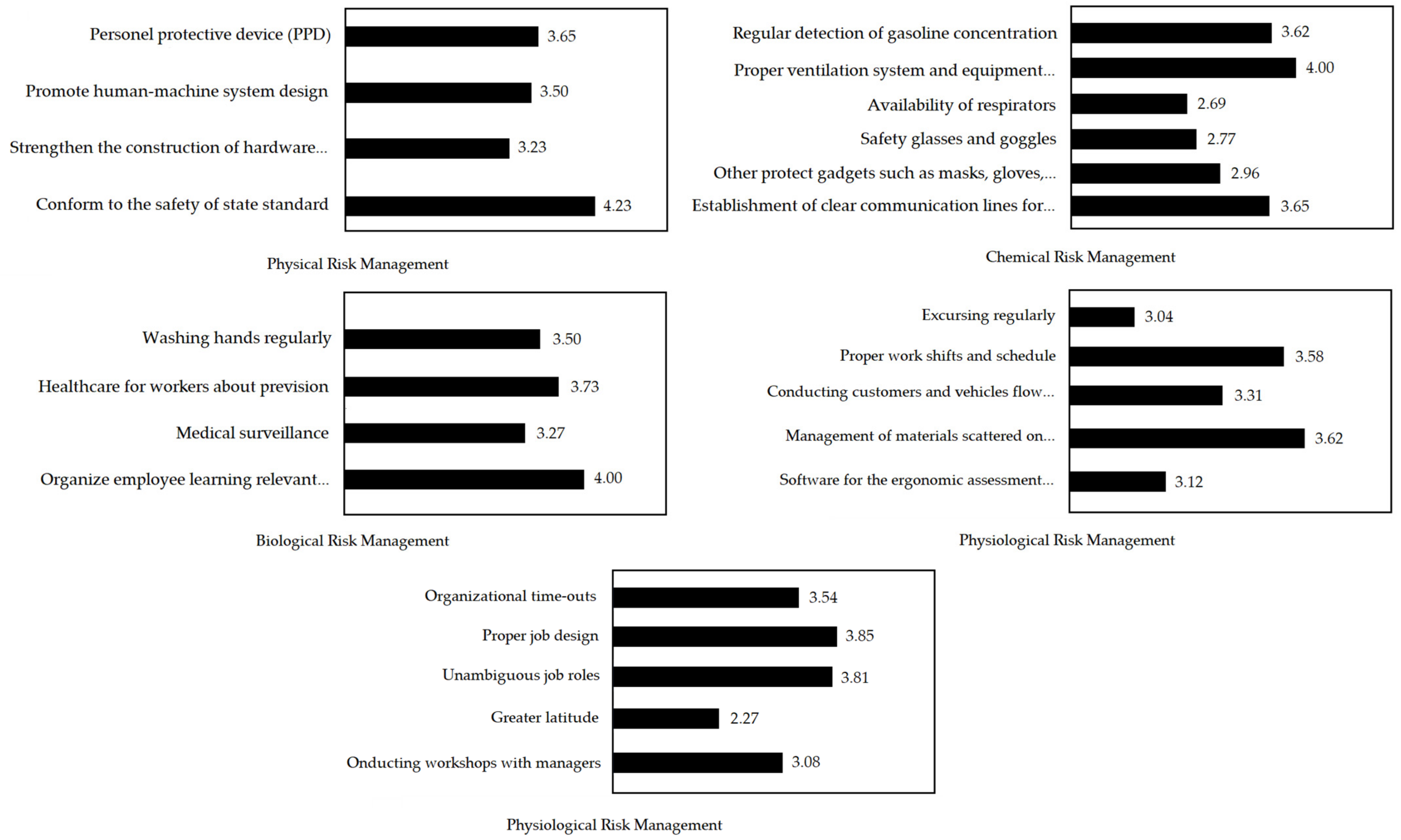
4.5. Performance Analysis of Sub-Factors
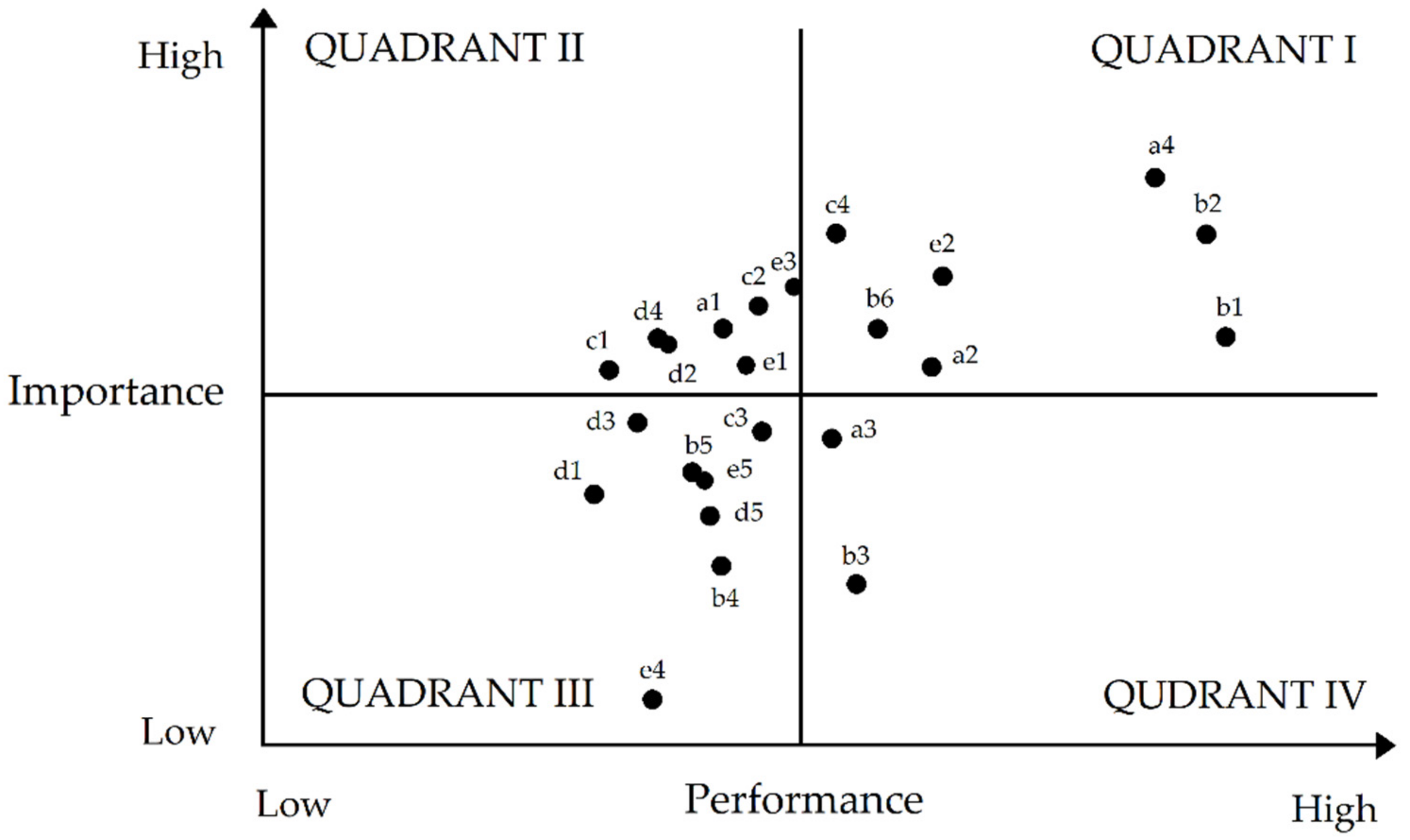
4.6. The Improvement Assessment of Risk Management
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lim, S.K.; Shin, H.S.; Yoon, K.S.; Kwack, S.J.; Um, Y.M.; Hyeon, J.H.; Kwak, H.M.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, T.Y.; Kim, Y.J.; et al. Risk assessment of volatile organic compounds benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, and xylene (BTEX) in consumer products. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2014, 77, 1502–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cezar-Vaz, M.R.; Rocha, L.P.; Bonow, C.A.; Da Silva, M.R.S.; Vaz, J.C.; Cardoso, L.S. Risk perception and occupational accidents: A study of gas station workers in Southern Brazil. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2012, 9, 2362–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pommerehn, J.; dos Santos Filha, V.A.V.; Basso Miolo, S.; Fedosse, E. Noise and quality of life in the perspective of gas station workers. Rev. CEFAC. 2016, 18, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Franzoi, I.G.; Granieri, A.; Sauta, M.D.; Agnesone, M.; Gonella, M.; Cavallo, R.; Lochner, P.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Naldi, A. Anxiety, post-traumatic stress, and burnout in health professionals during the COVID-19 pandemic: Comparing mental health professionals and other healthcare workers. Healthcare 2021, 9, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao-kui, F.; Hong-jun, F. Approaches to gas station firefighting. Saf. Environ. Eng. 2010, 17, 78–80. [Google Scholar]
- Al-ayyadhi, N.; Akhtar, S. Prevalence and risk factors associated with self-rated morbidities among South Asian migrant gas station workers in Kuwait. J. Immigr. Minor. Health 2018, 20, 1324–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, M.J.; Saghi, F.; Alizadeh, E.; Zayeri, F. Relationship between risk perception and occupational accidents: A study among foundry workers. J. Egypt. Public Health Assoc. 2019, 94, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjoberg, L. The methodology of risk perception research. Qual. Quant. 2000, 34, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leoni, T. What drives the perception of health and safety risks in the workplace? Evidence from European labor markets. Empirica 2010, 37, 165–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, M.; Kouhi, F.; Movahedi, M.; Allah-Yari, T. The effect of job safety analysis on risk perception of workers at high risk jobs in a refinery. Iran Occup. Health 2010, 6, 12–25. [Google Scholar]
- Neissi, A.; Hashemi, S.E.; Rahimi, P.T.; Arshadi, N.; Beshlideh, K. Investigating personal, cognitive and organizational variables as predictors of unsafe behaviors among line workers in an industrial company. J. Health Saf. Work 2013, 3, 13–26. [Google Scholar]
- Jahangiri, M.; Zadeh, K.S.; Bashar, O.; Zadeh, H.S. Investigating effective factors on risk perception, safety attitude and safety performance of construction workers of Shiraz city, 2012. J. Health Field 2017, 1, 30–36. [Google Scholar]
- Ghahramani, A.; Abbasi, A. Assessment of the relationship between occupational accident experience and personal and job factors in tar paper manufacturing companies. Iran Occup. Health 2016, 12, 48–57. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, M.C.; Freire, O.N. Carga de Trabalho e Rotatividade na Função de Frentista. RAC 2001, 5, 175–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, W.J.; Medeiros, J.P. Diagnóstico da qualidade de vida no trabalho (qvt) de frentistas de postos de combustíveis e suas interfaces com a qualidade dos serviços prestados. Rev. Gest. USP 2007, 14, 71–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Zhang, Z.; Wan, J.; Gu, S.; Liu, W.; Jin, X. Genetic polymorphisms in hMTH1, hOGG1 and hMYH and risk of chronic benzene poisoning in a Chinese occupational population. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2008, 233, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adami, G.; Larese, F.; Venier, M.; Barbieri, P.; Lo Coco, F.; Reisenhofer, E. Penetration of benzene, toluene and xylenes contained in gasolines through human abdominal skin in vitro. Toxicol. Vitro 2006, 20, 1321–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiwanitkit, V.; Suwansaksri, J.; Nasuan, P. Research note: Urine trans, trans-muconic acid as a biomarker for benzene exposure in gas station attendants in Bangkok, Thailand. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2001, 31, 399–401. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, D.B. Temporal variation in the association between benzene and leukemia mortality. Environ. Health Perspect. 2008, 116, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, D.W.; Anderson, T.E.; Issaragrisil, S. Risk factors for leukemia in Thailand. Ann. Hematol. 2009, 88, 1079–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X. Impact of gasoline upgrade policy on particulate matter pollution in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, S. An empirical analysis on the adoption of alternative fuel vehicles: The case of natural gas vehicles. Energy Policy 2007, 35, 5865–5875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuhui, Z. Discussion on safety status of buried tank in gas station. Oil Depot. Gas Stn. 2010, 3, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Younghwan, P. Research on influencing factors of service interactive experience of digital gas station—The case from China. J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2021, 16, 2151–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shi, X.; Wang, A.; Li, Y. Heavy metals contamination and assessment in gas station dust of Xi’an, a mega-city of China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun-Gi, H. The application of AHP to measure the importance level of managerial factors for e-commerce in SMB. JKAIS 2009, 10, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.P.; Lee, H.C.; Hsieh, Y.K. A multi-criteria approach for the optimal location of gasoline stations being transformed as self-service in Taiwan. Math. Probl. Eng. 2016, 2016, 8341617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shaikh, S.A.; Memon, M.; Kim, K.S. A multi-criteria decision making approach for ideal business location identification. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T.L. A scaling method for priorities in hierarchical structures. J. Math. Psychol. 1977, 3, 234–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wind, Y.; Saaty, T.L. Marketing applications of the analytic hierarchy process. Manag. Sci. 1980, 7, 641–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T.L.; Vargas, L.G. Diagnosis with dependent symptoms: Bayes theorem and the analytic hierarchy process. Oper. Res. 1998, 46, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantaphyllou, E.; Stuart, H.M. Using the analytic hierarchy process for decision making in engineering applications: Some challenges. Int. J. Ind. Eng. Applic. Pract. 1995, 2, 35–44. [Google Scholar]
- Macharis, C.; Springael, J.; De Brucker, K.; Verbeke, A. Promethee and AHP: The design of operational synergies in multi-criteria analysis: Strengthening Promethee with ideas of AHP. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2004, 153, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millet, I.; Wedley, W.C. Modelling risk and uncertainty with the Analytic Hierarchy Process. J. Multi-Cri. Decis. Anal. 2002, 11, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shezi, B.; Street, R.A.; Mathee, A.; Cele, N.; Ndabandaba, S.; Naido, R.N. Ergonomic risk assessment during an informal hand-made cookware operation: Extending an existing model. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghadam, S.R.; Afshari, M.; Ganjali, A.; Moosazadeh, M. Effect of occupational exposure to petrol and gasoline components on liver and renal biochemical parameters among gas station attendants, a review and meta-analysis. Rev. Environ. Health 2020, 35, 517–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, P.A.; Pierce, J.O. Combined effects of heat and noise on human performance: A review. Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. J. 1985, 46, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griefahn, B.; Kuenemund, C.; Neffgen, H.; Sommer, S. Human adaptation to work in two different climates. Int. J. Occup. Saf. Ergon. 1996, 2, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yari, S.; Asadi, A.F.; Nourmohammadi, M. Occupational and environmental cancer. Asian Pac. J. Environ. Cancer 2018, 1, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekpenyong, C.E.; Asuquo, A.E. Recent advances in occupational and environmental health hazards of workers exposed to gasoline compounds. Int. J. Occup. Med. Environ. Health 2017, 30, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witter, R.Z.; Tenney, L.; Clark, S.; Newman, L.S. Occupational exposures in the oil and gas extraction industry: State of the science and research recommendations. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2014, 57, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaiklieng, S.; Suggaravetsiri, P.; Autrup, H. Risk assessment on benzene exposure among gasoline station workers. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2019, 16, 2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoleikha, S.; Mirzaei, R.; Roksana, M. Exposure to chemical hazards in petrol pumps stations in Ahvaz City, Iran. Arch. Environ. Occup. Health 2017, 72, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moolla, R.; Curtis, C.J.; Knight, J. Occupational exposure of diesel station workers to BTEX compounds at a bus depot. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 4101–4115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omoti, A.E.; Waziri-Erameh, J.M.; Enock, M.E. Ocular disorders in a petroleum industry in Nigeria. Eye 2008, 22, 925–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gromadzińska, J.; Wąsowicz, W. Health risk in road transport workers. Part I. Occupational exposure to chemicals, biomarkers of effect. Int. J. Occup. Med. Environ. Health 2019, 32, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Harbi, M.; Alhajri, I.; AlAwadhi, A.; Whalen, J.K. Health symptoms associated with occupational exposure of gasoline station workers to BTEX compounds. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 241, 117847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colman, R.; Coleman, A. Unexpected cause of raised benzene absorption in coke oven by-product workers. Occup. Med. 2006, 56, 269–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Shikdar, A.A. Identification of ergonomic issues that affect workers in oilrigs in desert environments. Int. J. Occup. Saf. Ergon. 2004, 10, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamero, C. Assessing the cost of lost working days associated with job stress: A proposal for Spain. Estud. Econ. Apl. 2010, 28, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Albán-Pérez, G.G.; Pando-Moreno, M.; Laca-Arocena, F.; Colunga-Rodríguez, C.; Verdesoto-Galéas, Á.M.; Sarabia-López, L.E.; León-Navarrete, M.M. Psychosocial factors at work and occupational stress in gas station attendants in Ecuador. Psychology 2017, 8, 2215–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ayoub, M. Ergonomic deficiencies: I. Pain at work. J. Occup. Med. 1990, 32, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shikdar, A.; Al-Araimi, S.; Omurtag, B. Development of a software package for ergonomic assessment of manufacturing industry. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2002, 43, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuranchie, F.A.; Angnunavuri, P.N.; Attiogbe, F.; Nerquaye-Tetteh, E.N. Occupational exposure of benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene and xylene (BTEX) to pump attendants in Ghana: Implications for policy guidance. Cogent Environ. Sci. 2019, 5, 1603418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahangiri, M.; Jalali, M.; Saeidi, C.H. Assessment of occupational exposure to chemicals in order to provide control strategies (case study in polyurethane foam industry). J. Occup. Med. 2012, 5, 33–41. [Google Scholar]
- Far, S.Y.; Mirzaei, R.; Katrini, M.B.; Haghshenas, M.; Sayahi, Z. Assessment of health, safety and environmental risks of Zahedan city gasoline stations. Eng. Technol. Appl. Sci. Res. 2018, 8, 2689–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek, M.D.A.; Mearns, K.; Flin, R. Stress and psychological well-being in UK and Malaysian fire fighters. Int. J. Cross Cult. Manag. 2010, 17, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensah, J.; Amponsah-Tawiah, K. Mitigating occupational stress: The role of psychological capital. J. Workplace Behav. Health. 2016, 31, 189–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konz, S.A. Work Design: Industrial Ergonomics, 4th ed.; Gorsuch Scarisbrick Publishers: Columbus, OH, USA, 1995; pp. 1–557. [Google Scholar]
- Chao, Y.; Jiajia, Z.; Simeng, L.; Shan, Y.; Mingxing, C. Assessment and analysis of regional economic collaborative development within an urban agglomeration: Yangtze river delta as a case study. Habitat Int. 2019, 83, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Shen, G.; Liu, Q.; Li, C.; Zhou, D.; Wang, S. Characteristics and source apportionment of summertime volatile organic compounds in a fast developing city in the Yangtze River delta, China. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.Y. Applications of the extent analysis method on fuzzy AHP. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1996, 95, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, F.T.S.; Kumar, N. Global supplier development considering risk factors using fuzzy extended AHP-based approach. Omega 2007, 35, 417–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsin, M.; Zhan-ao, W.; Shijun, Z.; Weilun, H.; Hengbin, Y. Risk prioritization and management in gas stations by using fuzzy AHP and IPA analysis. Ind. J. Geo-Mar. Sci. 2021, 80, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar]
- Aminbakhsh, S.; Gunduz, M.; Sonmez, M. Safety risk assessment using analytic hierarchy process (AHP) during planning and budgeting of construction projects. J. Saf. Res. 2013, 46, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, J.J. Fuzzy hierarchical analysis. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1985, 17, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, W.K. Assessing the safety factors of ship berthing operations. J. Navig. 2015, 68, 576–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufinami, A.; Gupta, M.M. Introduction to Fuzzy Arithmetic: Theory and Applications; Van Nostrand Reinhold: New York, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Yager, R.R. A procedure for ordering fuzzy subsets of the unit interval. J. Inf. Sci. 2003, 24, 143–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gattás, G.J.F.; Cardoso, L.A.; Medrado-Faria, M.A.; Saldanha, P.H. Frequency of oral mucosa micronuclei in gas station operators after introducing methanol. Occup. Med. 2001, 51, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çelik, A.; Çavas, T.; Ergene-Gözükara, S. Cytogenetic biomonitoring in petrol station attendants: Micronucleus test in exfoliated buccal cells. Mutagenesis 2003, 18, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Li, Y.Q.; Yang, L.J.; Chen, S.H.; Yu, W.; Chen, J.Y.; Liu, W.W. Decreased T-cell receptor excision DNA circles in peripheral blood mononuclear cells among benzene-exposed workers. Int. J. Immunogenet. 2009, 36, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, Q.; Zhang, L.; Shen, M.; Smith, M.T.; Li, G.; Vermeulen, R.; Rappaport, S.M.; Forrest, M.S.; Hayes, R.B.; Linet, M.; et al. Polymorphisms in cytokine and cellular adhesion molecule genes and susceptibility to hematotoxicity among workers exposed to benzene. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 9574–9581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, Q.; Zhang, L.; Li, G.; Vermeulen, R.; Weinberg, R.S.; Dosemeci, M.; Rappaport, S.M.; Shen, M.; Alter, B.P.; Wu, Y.; et al. Hematotoxicity in workers exposed to low levels of benzene. Science 2004, 306, 1774–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitri, S.; Fonseca, A.S.A.; Otero, U.B.; Tabalipa, M.M.; Moreira, J.C.; Sarcinelli, P.D.N. Metabolic polymorphisms and clinical findings related to benzene poisoning detected in exposed Brazilian gas-station workers. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 8434–8447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajapakse, M.Y.; Borras, E.; Fung, A.G.; Yeap, D.; Mccartney, M.M.; Fabia, F.M.; Kenyon, N.J.; Davis, C.E. An environmental air sampler to evaluate personal exposure to volatile organic compounds. Analyst 2021, 146, 636–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamanian, Z.; Sedaghat, Z.; Mehrifar, Y. Harmful outcome of occupational exposure to petrol: Assessment of liver function and blood parameters among gas station workers in Kermanshah city, Iran. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2018, 9, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvestre, R.T.; Delmonico, L.; Bravo, M.; Santiago, F.; Scherrer, L.R.; Moreira, A.; Tabalipa, M.; Otero, U.; Ornellas, M.H.F.; Alves, G. Health survey and assessment of the polymorphisms BRCA1/P871L, BRCA1/Q356R, and BRCA2/N372H in female gas station workers in Rio de Janeiro. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2017, 58, 730–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahemzadih, M.; Abadi, A.; Giahi, O.; Tahmasebi, N. Exposure assessment to benzene, toluene, ethyl benzene and xylene (BTEX) in gas stations in central region of Iran. Asian J. Water Environ. Pollut. 2016, 13, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santillán, S.E. Assessment and control of chemical risk from organic vapors for attendants in a gas station. Enfoqute UTE 2015, 6, 113–123. [Google Scholar]
- Huibin, Y.; Beidou, X.; Xujing, G.; Bo, Y. Case study on environmental risk assessment of petroleum refining and petrochemical project. JEPC 2008, 10, 88–91. [Google Scholar]
- Xianlin, M.; Ding, Z.; Qingxin, F.; Qingguo, W.; Liping, J. Risk Representation in Risk Assessment of Petrochemical Industry. J. Harbin Inst. Technol. 1998, 5, 55–61. [Google Scholar]
- Xiaoran, L.; Gang, L.; Qiuling, Z.; Chenggang, W. Application of risk assessment method in the evaluation of the effect of occupational disease hazard control in a petrochemical project. Chin. J. Ind. Med. 2012, 25, 58–60. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira-Martins, C.R.; Grisolia, C.K. Toxicity and genotoxicity of wastewater from gasoline stations. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2009, 32, 853–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, M.M.S.; Perez, M.E.T.; Castro, L.A.S.; Delgado, E.G. Occupational diseases from exposure to benzene in gas station workers. RSAN 2020, 40, 157–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, S.O.D.; De Seta, M.H. Health surveillance in worker’s health in floating gas stations in Manaus, Amazonas. Vigil. Sanit. Em Debate-Soc. Cienc. Tecnol. 2020, 8, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Chen, Y.; Wei, Y.; Li, J. Detection of Specific Building in Remote Sensing Images Using a Novel YOLO-S-CIOU Model. Case: Gas Station Identification. Sensors 2021, 21, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Ji, Z.; Liu, P.; Wu, Z.Q.; Li, G.; Cui, D.S.; Wu, Y.Z.; Xu, S. Gas station recognition method based on monitoring data of heavy-duty vehicles. Energies 2022, 14, 8011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezrodny, A.A.; Yunushev, R.R.; Korolenok, A.M.; Zaytsev, O.S. Structure models and control algorithms for technical maintenance of gas station nets. Nauka I Tehnol. Truboprov. Transp. Nefti I Nefteprod.-Sci. Technol.-Oil Oil Prod. Pipeline Transp. 2020, 10, 535–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, K.; Kato, E.; Tsunemi, K. Does risk information change the acceptance of hydrogen refueling stations in the general Japanese population? Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2019, 44, 16038–16047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura-Correa, M.J.; Jacobina, A.; Santos, S.; Pinheiro, R.; Pinto, N.F. Exposure to benzene in gas stations in Brazil: Occupational health surveillance (VISAT) network. Cien. Saude Colet. 2014, 19, 4637–4648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezrodny, A.A.; Tszin, V.; Korolenok, A.M. Gas station control system structure improvement. Nauka I Tehnol. Truboprov. Transp. Nefti I Nefteprod.-Sci. Technol.-Oil Oil Prod. Pipeline Transp. 2019, 9, 710–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezrodny, A.A.; Yunushev, R.R.; Korolyonok, A.M. System cause-and-effect approach to structure development and control of gas station nets. Nauka I Tehnol. Truboprov. Transp. Nefti I Nefteprod.-Sci. Technol.-Oil Oil Prod. Pipeline Transp. 2019, 9, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Lee, K.; Kim, J.; Lee, Y.; Park, J.; Moon, I. Development of Korean hydrogen fueling station codes through risk analysis. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2011, 36, 13122–13131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, Z. Countermeasures for safe production problems in petroleum enterprises. Surf. Eng. Oil Gas Fields 2011, 30, 90. [Google Scholar]
- Rongxue, K.; Mingyu, Z.; Junsheng, B.; Zongzhi, W.; Liangquan, S.; Haibo, G.; Xue, L. Development and application of gas station safety monitoring and early warning system. Chin. J. Saf. Sci. 2008, 7, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Mindez, G.G.; Rodriguez-Garza, C.A.; Rosas-Castro, J.A. Organizational change in service stations: Implications of energy reform. Rev. Investig. Univ. Quindio 2020, 32, 59–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youcheng, W.; Wenzhang, L.; Hongkun, S.; Zhigang, J.; Quan, G. Practice and discussion of HSE risk classification prevention and control in foreign petroleum and petrochemical enterprises. J. Saf. Sci. Technol. 2017, 13, 151–155. [Google Scholar]
- Karthikeya, R.; Venkatesan, K.G.S.; Chandrasekar, A. A comparison of strengths and weaknesses for analytical hierarchy process. J. Chem. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 9, 12–15. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Aurum, A.K.; Gorton, I.; Jeffery, R. Tradeoff and sensitivity analysis in software architecture evaluation using analytic hierarchy process. Softw. Qual. J. 2005, 13, 357–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobczak, A.; Berry, D.M. Distributed priority ranking of strategic preliminary requirements for management information systems in economic organizations. Inform. Software Technol. 2007, 49, 960–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Category | Frequency | Percent | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Marital status | Single | 64 | 30.8 |
| Married | 144 | 69.2 | |
| Gender | Male | 144 | 69.2 |
| Female | 64 | 30.8 | |
| Working Experience | 1~3 | 80 | 38.5 |
| Over 3 years | 128 | 61.5 | |
| Region | Zhejiang Province | 96 | 46.2 |
| Shanghai | 56 | 26.9 | |
| Jiangsu Province | 56 | 26.9 | |
| Work shifts and schedule | Day time | 168 | 80.8 |
| Night time | 40 | 19.2 | |
| Schooling | Middle School | 16 | 7.70 |
| High School | 56 | 26.9 | |
| Higher education, incomplete | 136 | 65.4 | |
| Total | 208 | 100.0 | |
| Category | Importance | Ranking |
|---|---|---|
| Physical risk management | 0.219 | 2 |
| Chemical risk management | 0.341 | 1 |
| Biological risk management | 0.137 | 4 |
| Physiological risk management | 0.116 | 5 |
| Psychological risk management | 0.186 | 3 |
| Category | Average | Ranking |
|---|---|---|
| Physical risk management | 3.19 | 4 |
| Chemical risk management | 3.81 | 1 |
| Biological risk management | 3.65 | 2 |
| Physiological risk management | 3.50 | 3 |
| Psychological risk management | 2.85 | 5 |
| Code | Factor | Importance Weights (%) | Performance Weights (%) | Quadrant |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a1 | Personal protective device (PPD) | 0.033 | 3.654 | IV |
| a2 | Promote human–machine system design | 0.058 | 3.500 | I |
| a3 | Strength the construction of hardware configuration | 0.045 | 3.231 | II |
| a4 | Conform to the safety of state standard | 0.084 | 4.231 | I |
| b1 | Regular detection of gasoline concentration | 0.092 | 3.615 | I |
| b2 | Proper ventilation system and equipment maintenance | 0.090 | 4.000 | I |
| b3 | Availability of respirators | 0.048 | 2.692 | II |
| b4 | Safety glasses and goggles | 0.031 | 2.769 | III |
| b5 | Other protective gadgets such as masks, gloves, apron and boots | 0.030 | 2.962 | III |
| b6 | Establishment of clear communication lines for emergency preparedness | 0.051 | 3.654 | I |
| c1 | Washing hands regularly | 0.020 | 3.500 | IV |
| c2 | Healthcare for workers about prevision | 0.036 | 3.731 | IV |
| c3 | Medical surveillance | 0.035 | 3.269 | III |
| c4 | Organize employee daily learning relevant safety knowledge | 0.046 | 4.000 | I |
| d1 | Excursing regularly | 0.016 | 3.038 | III |
| d2 | Proper work shifts and schedule | 0.027 | 3.577 | IV |
| d3 | Conducting customers and vehicles flow reasonably | 0.021 | 3.308 | III |
| d4 | Management of materials scattered on operating space | 0.025 | 3.615 | IV |
| d5 | Software for the ergonomic assessment procedure | 0.028 | 3.115 | III |
| e1 | Organizational time-outs | 0.034 | 3.538 | IV |
| e2 | Proper job design | 0.059 | 3.846 | I |
| e3 | Unambiguous job roles | 0.041 | 3.808 | IV |
| e4 | Greater latitude | 0.023 | 2.269 | III |
| e5 | Conducting workshops with managers | 0.029 | 3.077 | III |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohsin, M.; Yin, H.; Huang, W.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, L.; Mehak, A. Evaluation of Occupational Health Risk Management and Performance in China: A Case Study of Gas Station Workers. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3762. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19073762
Mohsin M, Yin H, Huang W, Zhang S, Zhang L, Mehak A. Evaluation of Occupational Health Risk Management and Performance in China: A Case Study of Gas Station Workers. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(7):3762. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19073762
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohsin, Muhammad, Hengbin Yin, Weilun Huang, Shijun Zhang, Luyao Zhang, and Ana Mehak. 2022. "Evaluation of Occupational Health Risk Management and Performance in China: A Case Study of Gas Station Workers" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 7: 3762. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19073762
APA StyleMohsin, M., Yin, H., Huang, W., Zhang, S., Zhang, L., & Mehak, A. (2022). Evaluation of Occupational Health Risk Management and Performance in China: A Case Study of Gas Station Workers. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(7), 3762. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19073762








