Lifestyle Factors Associated with Undernutrition in Older People after the Great East Japan Earthquake: A Prospective Study in the Fukushima Health Management Survey
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
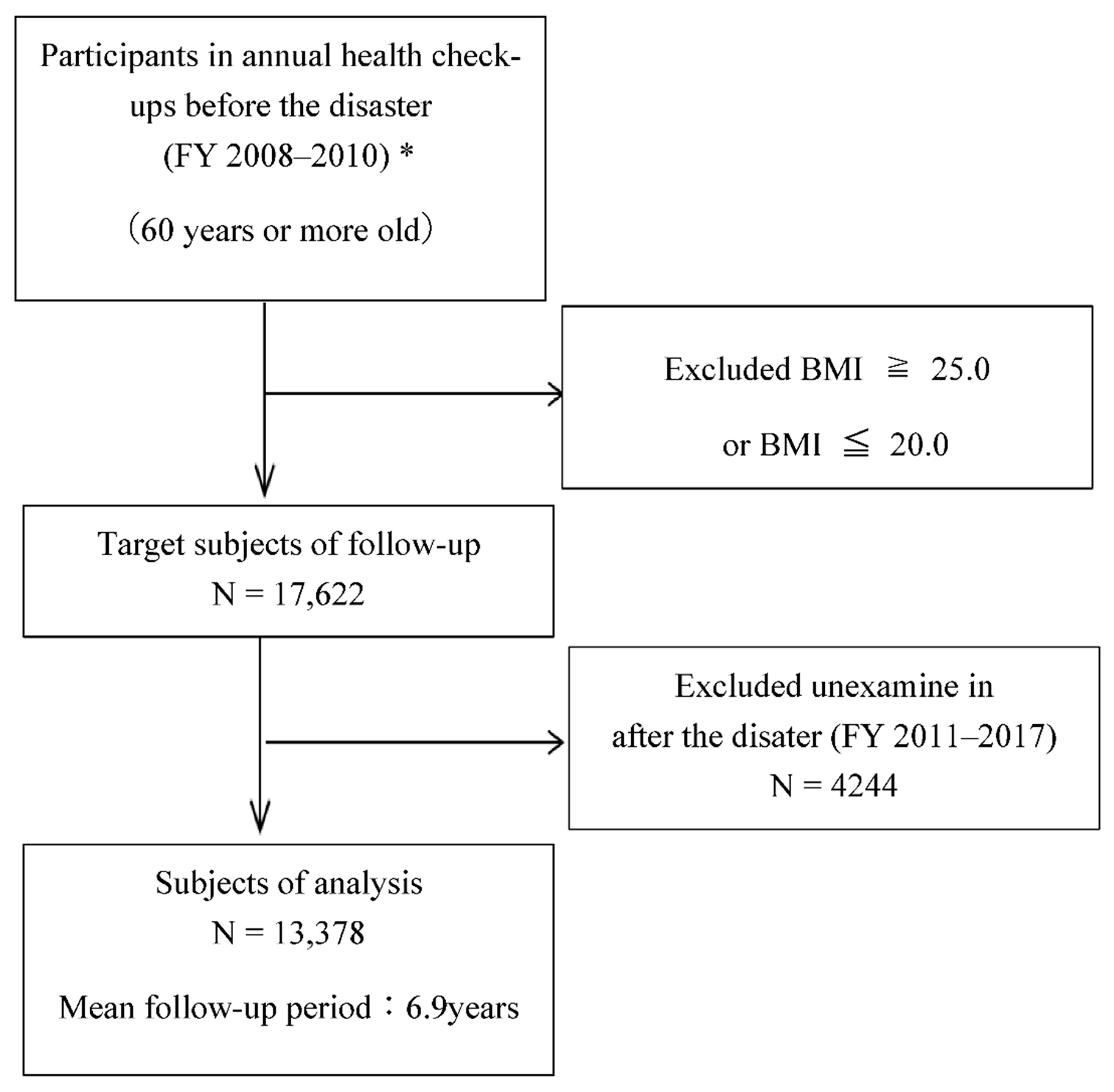
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Measurements/Definitions and Data Collection
2.2.1. Undernutrition
2.2.2. Weight Loss Amount
2.2.3. Lifestyle Status
2.2.4. Medical History
2.2.5. Evacuees
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Frequency and Characteristics of Undernutrition after the Disaster
3.2. Lifestyle Factors Associated with Undernutrition
4. Discussion
4.1. Exercise Habits and Physical Activities
4.2. Relationship between Exercise Habits and BMI
4.3. Association with Evacuation
4.4. Late Meals
4.5. Comparison between the Affected Areas and the Rest of Japan
4.6. Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akiyama, H. Concept of science and society in the age of longevity. Kagaku 2010, 80, 59–64. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Q.L.; Bandeen-Roche, K.; Varadhan, R.; Zhou, J.; Fried, L.P. Initial manifestations of frailty criteria and the development of frailty phenotype in the women’s health and aging study II. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2008, 63, 984–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fried, L.P.; Walston, J. Frailty and failure to thrive. In Principles of Geriatric Medicine and Gerontology; Hazzard, W.R., Blass, J.P., Ettinger, W.H., Jr., Halter, J.B., Ouslander, J., Eds.; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 1387–1402. [Google Scholar]
- Shimada, H.; Makizako, H.; Doi, T.; Yoshida, D.; Tsutsumimoto, K.; Anan, Y.; Uemura, K.; Ito, T.; Lee, S.; Park, H.; et al. Combined prevalence of frailty and mild cognitive impairment in a population of elderly Japanese people. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2013, 14, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, G.; Iliffe, S.; Taniguchi, Y.; Shimada, H.; Rakugi, H.; Walters, K. Prevalence of frailty in Japan: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 27, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare. Summary of the Results of the 2017 National Health and Nutrition Survey. 11 September 2018. Available online: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/content/10904750/000351576.pdf (accessed on 11 September 2019).
- Yasumura, S.; Abe, M. Fukushima health management survey and related issues. Asia Pac. J. Public Health 2017, 29, 29S–35S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utsukushima Fukushima Future Support Center. Report on the Survey and Research Project on the Necessary Support by Analyzing the Causes of the Increase in the Number of People Certified as Needing Long-Term Care in Fukushima Prefecture. National University Corporation Fukushima University, 2015. Available online: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/file/06-Seisakujouhou-12300000-Roukenkyoku/0000140299.pdf (accessed on 28 October 2019).
- Shimizu, S.; Tamamura, K. The elderly people and the Great East Japan disaster of March 11, 2011. Bull. Nara Univ. Educ. 2013, 62, 59–70. [Google Scholar]
- Tanba, F. Current Status and Issues of Evacuees in the Accident at TEPCO’s Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. 32nd Atomic Energy Commission: Document 1–3. Available online: http://www.aec.go.jp/jicst/NC/iinkai.teirei/siryo2013/siryo32/siryo1-3.pdf (accessed on 20 December 2019).
- Mihara, M.; Harada, M.; Oka, J.; Tsuboyama-Kasaoka, N. The effect of lunch box provision and mass feeding on energy and nutrient supply at emergency shelters after the Great East Japan Earthquake. Nihon Koshu Eisei Zasshi 2019, 66, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohira, T.; Hosoya, M.; Yasumura, S.; Satoh, H.; Suzuki, H.; Sakai, A.; Ohtsuru, A.; Kawasaki, Y.; Takahashi, A.; Ozasa, K.; et al. Effect of evacuation on body weight after the Great East Japan Earthquake. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2016, 50, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohira, T.; Hosoya, M.; Yasumura, S.; Satoh, H.; Suzuki, H.; Sakai, A.; Ohtsuru, A.; Kawasaki, Y.; Takahashi, A.; Ozasa, K.; et al. Evacuation and risk of hypertension after the Great East Japan Earthquake: The Fukushima Health Management Survey. Hypertension 2016, 68, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satoh, H.; Ohira, T.; Hosoya, M.; Sakai, A.; Watanabe, T.; Ohtsuru, A.; Kawasaki, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Takahashi, A.; Kobashi, G.; et al. Evacuation after the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant accident is a cause of diabetes: Results from the Fukushima health management survey. J. Diabetes Res. 2015, 2015, 627390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satoh, H.; Ohira, T.; Nagai, M.; Hosoya, M.; Sakai, A.; Watanabe, T.; Ohtsuru, A.; Kawasaki, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Takahashi, A.; et al. Hypo-high-density lipoprotein cholesterolemia caused by evacuation after the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant accident: Results from the Fukushima Health Management Survey. Intern. Med. 2016, 55, 1967–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hashimoto, S.; Nagai, M.; Fukuma, S.; Ohira, T.; Hosoya, M.; Yasumura, S.; Satoh, H.; Suzuki, H.; Sakai, A.; Ohtsuru, A.; et al. Influence of Post-disaster Evacuation on Incidence of Metabolic Syndrome. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2017, 24, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, A.; Ohira, T.; Hosoya, M.; Yasumura, S.; Nagai, M.; Ohira, H.; Hashimoto, S.; Satoh, H.; Sakai, A.; Ohtsuru, A.; et al. Effect of evacuation on liver function after the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident: The Fukushima Health Management Survey. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 27, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Ohira, T.; Abe, M.; Kamiya, K.; Yamashita, S.; Yasumura, S.; Ohtsuru, A.; Masaharu, M.; Harigane, M.; Horikoshi, N.; et al. Evacuation after the Great East Japan Earthquake was associated with poor dietary intake: The Fukushima Health Management Survey. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 27, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsubota-Utsugi, M.; Yonekura, Y.; Tanno, K.; Nozue, M.; Shimoda, H.; Nishi, N.; Sakata, K.; Kobayashi, S.; RIAS Study. Association between health risks and frailty in relation to the degree of housing damage among elderly survivors of the great East Japan earthquake. BMC Geriatr. 2018, 18, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa-Silva, M.C. Subjective and objective nutritional assessment methods: What do they really assess? Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2008, 11, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasazuki, S.; Inoue, M.; Tsuji, I.; Sugawara, Y.; Tamakoshi, A.; Matsuo, K.; Wakai, K.; Nagata, C.; Tanaka, K.; Mizoue, T.; et al. Body Mass Index and Mortality from All Causes and Major Causes in Japanese: Results of a Pooled Analysis of 7 Large-Scale Cohort studies. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 21, 417–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoyama, Y.; Sasaki, M.; Sato, K. Nutrition intake among the Japanese elderly: An intergenerational comparison based on national health and nutrition survey scores. Ann. Hum. Biol. 2019, 46, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, Z.; Kirk, S.; Lawrenson, S.; Sandford, S. Use of BMI in the assessment of undernutrition in older subjects: Reflecting on practice. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2005, 64, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, Y.; Kitamura, A.; Kawano, Y.; Shinkai, S. Dietary intake and nutritional status among Japanese elderly participants in the National health and nutritional survey Japan 2003–2011. J. Jpn. Soc. Shokuiku 2018, 12, 33–40. [Google Scholar]
- Japan Geriatrics Society. Statement of the Japan Geriatrics Society on Frailty. 13 May 2014. Available online: https://www.jpn-geriat-soc.or.jp/info/topics/pdf/20140513_01_01.pdf (accessed on 3 December 2019).
- Fried, L.P.; Tangen, C.M.; Walston, J.; Newman, A.B.; Hirsch, C.; Gottdiener, J.; Seeman, T.; Tracy, R.; Kop, W.J.; Burke, G.; et al. Frailty in older adults: Evidence for a phenotype. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2001, 56, M146–M157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaddey, H.L.; Holder, K. Unintentional weight loss in older adults. Am. Fam. Physician 2014, 89, 718–722. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare. Standard health screening and health Guidance Program. Final Version. Part 2 Medical Examination Attachment 3 Standard Questionnaire. 2007; pp. 45–46. Available online: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/bunya/kenkou/seikatsu/pdf/02.pdf (accessed on 4 January 2020).
- Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare. Physical Activity Reference for Health Promotion 2013. 2013. Available online: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/content/000306883.pdf (accessed on 10 January 2020).
- Hubner, S.; Boron, J.B.; Koehler, K. The effects of exercise on appetite in older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 734267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianfredi, V.; Blandi, L.; Cacitti, S.; Minelli, M.; Signorelli, C.; Amerio, A.; Odone, A. Depression and objectively measured physical activity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, T.; Tsumura, K.; Suematsu, C.; Okada, K.; Fujii, S.; Endo, G. Walking to work and the risk for hypertension in men: The Osaka Health Survey. Ann. Intern. Med. 1999, 131, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, S.; Kojima, M.; Tokudome, S.; Mori, M.; Sakauchi, F.; Fujino, Y.; Wakai, K.; Lin, Y.; Kikuchi, S.; Tamakoshi, K.; et al. Effect of physical activity on breast cancer risk: Findings of the Japan collaborative cohort study. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2008, 17, 3396–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Takahashi, H.; Kuriyama, S.; Tsubono, Y.; Nakaya, N.; Fujita, K.; Nishino, Y.; Shibuya, D.; Tsuji, I. Time spent walking and risk of colorectal cancer in Japan: The Miyagi Cohort study. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2007, 16, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbaum, S.; Sherrington, C. Is exercise effective in promoting mental well-being in older age? A systematic review. Br. J. Sports Med. 2011, 45, 1079–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.A.; Pence, B.D.; Woods, J.A. Exercise and respiratory tract viral infections. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2009, 37, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, I.D.; Fairhall, N.; Langron, C.; Lockwood, K.; Monaghan, N.; Aggar, C.; Sherrington, C.; Lord, S.R.; Kurrle, S.E. A multifactorial interdisciplinary intervention reduces frailty in older people: Randomized trial. BMC Med. 2013, 11, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazuhiro, N. Current status of diets and nutritional issues in disaster areas: Report on the areas affected by the Great East Japan Earthquake (Kesennuma City, Miyagi Prefecture). J. Jpn. Diabetes Soc. 2011, 54, 724–726. [Google Scholar]
- Ishida, Y.; Yoshida, D.; Honda, T.; Hirakawa, Y.; Shibata, M.; Sakata, S.; Furuta, Y.; Oishi, E.; Hata, J.; Kitazono, T.; et al. Influence of the accumulation of unhealthy eating habits on obesity in a general japanese population: The Hisayama study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubota, K.; Okubo, T.; Satoh, Y.; Hirose, T.; Imai, Y. Reasons for not receiving the specific health examination and health attitudes of those who have not received the examination in Hanamaki City, Iwate Prefecture. J. Health Welf. Stat. 2021, 57, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Goto, M.; Takeda, M.; Kainuma, Y.; Suijo, Y. Factors and Countermeasures for undiagnosed patients based on questionnaire survey of undiagnosed patients for specific health examination. Indic. Health Welf. 2022, 58, 34–39. [Google Scholar]
| Total | Undernutrition | Non-Undernutrition | p Values * | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Participants | n | 13,378 | 1712 | (12.8) | 11,666 | (87.2) | |||
| Follow-up period, (years) | 13,378 | 6.9 | (2.2) | 4.9 | (2.0) | 7.2 | (2.1) | <0.001 | |
| Evacuee, (%) | 13,378 | 4586 | (34.3) | 489 | (28.6) | 4097 | (35.1) | <0.001 | |
| Sex(men), n(%) | 13,378 | 6351 | (47.5) | 631 | (36.9) | 5720 | (49.0) | <0.001 | |
| Age, (years) | 13,378 | 68.4 | (6.2) | 68.8 | (6.3) | 68.3 | (6.2) | 0.003 | |
| 75 years old or older, n (%) | 13,378 | 2796 | (20.9) | 389 | (22.7) | 2407 | (20.6) | 0.047 | |
| 80 years old or older, n (%) | 13,378 | 659 | (4.9) | 99 | (5.8) | 560 | (4.8) | 0.08 | |
| Body weight, (kg) | 13,378 | 54.7 | (6.8) | 50.7 | (6.0) | 55.2 | (6.7) | <0.001 | |
| Body mass index, (kg/m2) | 13,378 | 22.7 | (1.3) | 21.3 | (1.0) | 22.9 | (1.3) | <0.001 | |
| Amount of weight loss, (kg) | 13,378 | 0.53 | (3.8) | 4.65 | (3.0) | −0.07 | (3.5) | <0.001 | |
| Rate of weight loss, (%) | 13,378 | 1.01 | (7.0) | 9.02 | (5.4) | −0.16 | (6.4) | <0.001 | |
| Rate of weight loss, (kg/year) | 13,378 | 0.12 | (0.7) | 1.05 | (0.8) | −0.02 | (0.6) | <0.001 | |
| Rate of weight loss, (%/year) | 13,378 | 0.22 | (1.4) | 2.06 | (1.6) | −0.05 | (1.1) | <0.001 | |
| Weight loss ≥ 5 kg, n (%) | 13,378 | 1422 | (10.6) | 645 | (37.7) | 777 | (6.7) | <0.001 | |
| Weight loss ≥ 5 %, n (%) | 13,378 | 3560 | (26.6) | 1268 | (74.1) | 2292 | (19.7) | <0.001 | |
| Exercise habits, n (%) | <30 min/2times/week | 12,488 | 8061 | (64.6) | 1065 | (67.0) | 6996 | (64.2) | 0.03 |
| Physical activities, n (%) | <1 h/day | 12,495 | 7556 | (60.5) | 1010 | (63.5) | 6546 | (60.0) | 0.01 |
| Walking speed, n (%) | fast | 12,490 | 5543 | (44.4) | 693 | (43.6) | 4850 | (44.5) | 0.51 |
| Insufficient sleep, n (%) | yes | 12,532 | 9768 | (77.9) | 1212 | (76.1) | 8556 | (78.2) | 0.06 |
| Weight change from age 20, n (%) | ≥10 kg | 12,493 | 2760 | (22.1) | 161 | (10.1) | 2599 | (23.8) | <0.001 |
| Weight change in 1 year, n (%) | ≥±3 kg | 12,492 | 2055 | (16.5) | 201 | (12.7) | 1854 | (17.0) | <0.001 |
| Meals before going to bed, n (%) | ≥3 times/week | 12,498 | 2835 | (22.7) | 294 | (18.5) | 2541 | (23.3) | <0.001 |
| Snack after dinner, n (%) | ≥3 times/week | 12,514 | 913 | (7.3) | 116 | (7.3) | 797 | (7.3) | 0.98 |
| Lack of breakfast, n (%) | ≥3 times/week | 12,502 | 445 | (3.6) | 60 | (3.8) | 385 | (3.5) | 0.61 |
| Smoking status, n (%) | Current smoker | 13,378 | 1762 | (13.2) | 194 | (11.3) | 1568 | (13.4) | 0.02 |
| Drinking status, n (%) | Non-drinker | 13,378 | 7553 | (56.5) | 1098 | (64.1) | 6455 | (55.3) | <0.001 |
| Current drinker, <44 g/day | 5164 | (38.6) | 547 | (32.0) | 4617 | (39.6) | |||
| Current drinker, <44 g/day | 661 | (4.9) | 67 | (3.9) | 594 | (5.1) | |||
| Digestive surgery, n (%) | yes | 13,378 | 821 | (6.1) | 120 | (7.0) | 701 | (6.0) | 0.11 |
| Lifestyle-related diseases, n (%) | yes | 13,378 | 5586 | (41.8) | 797 | (46.6) | 4789 | (41.1) | <0.001 |
| Subjective symptoms, n (%) | nothing | 13,378 | 10,543 | (78.8) | 1339 | (78.2) | 9204 | (78.9) | 0.04 |
| 1 symptom | 2077 | (15.5) | 254 | (14.8) | 1823 | (15.6) | |||
| 2 or more | 758 | (5.7) | 119 | (7.0) | 639 | (5.5) | |||
| Sex-Age-Adjustment | Multivariable Adjustment (Model 1) * | Multivariable Adjustment (Model 2) *2 | Multivariable Adjustment (Model 3) *3 | Multivariable Adjustment (Model 4) *4 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factor | Reference | HR (95% CI) | P Values | HR (95% CI) | p Values | HR (95% CI) | P Values | HR (95% CI) | p Values | HR (95% CI) | p Values |
| Sex (Women) | Men | 1.63 (1.48–1.80) | <0.001 | 1.64 (1.45–1.85) | <0.001 | 1.63 (1.44–1.84) | <0.001 | 1.42 (1.26–1.61) | <0.001 | 1.42 (1.25–1.61) | <0.001 |
| Age | 1 SD (6.2 years) | 1.24 (1.18–1.31) | <0.001 | 1.25 (1.18–1.32) | <0.001 | 1.24 (1.18–1.31) | <0.001 | 1.23 (1.17–1.30) | <0.001 | 1.23 (1.17–1.25) | <0.001 |
| Age (≥75 years old) | <75 years old | 1.60 (1.43–1.79) | <0.001 | ||||||||
| Age (≥80 years old) | <80 years old | 1.96 (1.60–2.41) | <0.001 | ||||||||
| BMI at baseline | −1 SD (1.35 kg/m2) | 0.24 (0.23–0.26) | <0.001 | 0.24 (0.23–0.26) | <0.001 | 0.24 (0.23–0.26) | <0.001 | ||||
| Evacuation (no) | Yes | 1.44 (1.29–1.60) | <0.001 | 1.40 (1.26–1.56) | <0.001 | 1.40 (1.26–1.55) | <0.001 | 1.38 (0.12–1.54) | <0.001 | 1.39 (1.25–1.54) | <0.001 |
| Walking speed (fast) | Slow | 0.94 (0.85–1.03) | 0.18 | ||||||||
| Insufficient sleep (yes) | No | 1.11 (0.99–1.25) | 0.08 | ||||||||
| Exercise habits (<30 min/2 times/week) | ≥30 min/2times/week | 1.16 (1.04–1.29) | 0.006 | 1.14 (1.03–1.27) | 0.02 | 1.11 (1.00–1.24) | |||||
| Physical activities (<1 h/day) | ≥1 h/day | 1.15 (1.04–1.27) | 0.009 | 1.12 (1.01–1.25) | 0.03 | 1.08 (0.98–1.20) | 0.14 | ||||
| Smoking status (yes) | No | 1.20 (1.02–1.41) | 0.03 | 1.16 (0.99–1.37) | 0.07 | 1.16 (0.99–1.37) | 0.07 | 1.01 (0.86–1.19) | 0.93 | 1.01 (0.85–1.18) | 0.95 |
| Drinking status (<44 g/day) | Non-drinker | 0.87 (0.77–0.97) | 0.02 | 0.89 (0.79–1.00) | 0.05 | 0.89 (0.79–1.00) | 0.04 | 0.90 (0.79–1.01) | 0.07 | 0.89 (0.79–1.00) | 0.06 |
| (≥44 g/day) | Non-drinker | 1.03 (0.79–1.34) | 0.86 | 1.07 (0.82–1.39) | 0.64 | 1.06 (0.81–1.39) | 0.66 | 0.96 (0.73–1.25) | 0.75 | 0.95 (0.73–1.25) | 0.71 |
| Meals before going to bed (<3 times/week) | ≥3 times/week | 1.27 (1.12–1.44) | <0.001 | 1.26 (1.11–1.43) | <0.001 | 1.25 (1.10–1.42) | <0.001 | 1.19 (1.05–1.35) | <0.01 | 1.18 (1.04–1.35) | <0.01 |
| Snack after dinner (≥3 time/week) | <3 times/week | 1.01 (0.84–1.22) | 0.90 | ||||||||
| Digestive surgery (yes) | No | 1.27 (1.05–1.53) | 0.01 | 1.24 (1.03–1.50) | 0.02 | 1.24 (1.02–1.49) | 0.03 | 1.02 (0.84–1.23) | 0.85 | 1.02 (0.85–1.23) | 0.83 |
| Lifestyle-related diseases (yes) | No | 1.29 (1.17–1.42) | <0.001 | 1.27 (1.16–1.40) | <0.001 | 1.28 (1.16–1.41) | <0.001 | 1.02 (0.92–1.12) | 0.76 | 1.02 (0.93–1.12) | 0.69 |
| Subjective symptoms (1 symptom) | No symptoms | 0.96 (0.84–1.10) | 0.54 | 0.98 (0.86–1.13) | 0.85 | 0.98 (0.86–1.13) | 0.86 | 0.996 (0.87–1.14) | 0.95 | 0.997(0.87–1.14) | 0.96 |
| (2 or more symptoms) | No symptoms | 1.25 (1.04–1.51) | 0.02 | 1.26 (1.04–1.53) | 0.02 | 1.26 (1.04–1.52) | 0.02 | 1.36 (1.12–1.64) | <0.01 | 1.36 (1.12–1.64) | <0.01 |
| Exercise Habit | Physical Activity | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≥30 min/2times/Week | <30 min/2times/Week | ≥1 h/Day | <1 h/Day | ||||||
| Number of participants | 4427 | 8061 | 4939 | 7556 | |||||
| Number of undernutrition | 525 | 1065 | 580 | 1010 | |||||
| follow-up years | 7.09 | 6.98 | 7.02 | 7.01 | |||||
| Total person years | 31,381 | 56,249 | 34,678 | 53,004 | |||||
| Incidence rate of undernutrition (1000 person years) | 16.7 | 18.9 | 16.7 | 19.1 | |||||
| HR (95% CI) | p values *1 | p for interaction | HR (95% CI) | p values *2 | p for interaction | ||||
| Sex | Men | Reference | 1.21 (1.02–1.44) | 0.03 | 0.48 | Reference | 1.08 (0.92–1.28) | 0.34 | 0.42 |
| Women | Reference | 1.10 (0.96–1.25) | 0.18 | Reference | 1.15 (1.01–1.31) | 0.04 | |||
| Age group | ≥68 years old | Reference | 1.05 (0.90–1.22) | 0.54 | 0.98 | Reference | 1.07 (0.92–1.24) | 0.40 | 0.87 |
| <68 years old | Reference | 1.22 (1.05–1.42) | <0.001 | Reference | 1.16 (1.01–1.34) | 0.04 | |||
| BMI | ≥22.7 | Reference | 0.98 (0.73–1.32) | 0.91 | <0.001 | Reference | 1.04 (0.77–1.39) | 0.81 | 0.87 |
| <22.7 | Reference | 1.15 (1.03–1.29) | 0.02 | Reference | 1.11 (0.99–1.24) | 0.07 | |||
| Evacuation | No | Reference | 1.19 (1.05–1.35) | 0.01 | 0.29 | Reference | 1.10 (0.97–1.24) | 0.13 | 0.37 |
| Yes | Reference | 1.02 (0.85–1.24) | 0.81 | Reference | 1.18 (0.98–1.43) | 0.09 | |||
| Smoking status | No | Reference | 1.10 (0.98–1.23) | 0.09 | 0.08 | Reference | 1.14 (1.02–1.27) | 0.02 | 0.33 |
| Yes | Reference | 1.54 (1.10–2.14) | 0.01 | Reference | 0.98 (0.73–1.32) | 0.90 | |||
| Drinking status | Non-drinker | Reference | 1.09 (0.95–1.24) | 0.22 | Reference | 1.19 (1.05–1.36) | 0.01 | ||
| <44 g/day | Reference | 1.22 (1.02–1.46) | 0.03 | 0.38 | Reference | 1.04 (0.87–1.25) | 0.65 | 0.34 | |
| ≥44 g/day | Reference | 1.46 (0.84–2.54) | 0.18 | 0.35 | Reference | 0.98 (0.59–1.62) | 0.93 | 0.56 | |
| Meals before going to bed | <3 times/week | Reference | 1.16 (0.90–1.47) | 0.25 | 0.67 | Reference | 1.19 (0.94–1.51) | 0.15 | 0.49 |
| ≥3 times/week | Reference | 1.14 (1.02–1.28) | 0.03 | Reference | 1.11 (0.99–1.25) | 0.07 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Okazaki, K.; Ohira, T.; Sakai, A.; Shimabukuro, M.; Kazama, J.J.; Takahashi, A.; Nakano, H.; Hayashi, F.; Nagao, M.; Yasumura, S.; et al. Lifestyle Factors Associated with Undernutrition in Older People after the Great East Japan Earthquake: A Prospective Study in the Fukushima Health Management Survey. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3399. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19063399
Okazaki K, Ohira T, Sakai A, Shimabukuro M, Kazama JJ, Takahashi A, Nakano H, Hayashi F, Nagao M, Yasumura S, et al. Lifestyle Factors Associated with Undernutrition in Older People after the Great East Japan Earthquake: A Prospective Study in the Fukushima Health Management Survey. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(6):3399. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19063399
Chicago/Turabian StyleOkazaki, Kanako, Tetsuya Ohira, Akira Sakai, Michio Shimabukuro, Junichiro J. Kazama, Atsushi Takahashi, Hironori Nakano, Fumikazu Hayashi, Masanori Nagao, Seiji Yasumura, and et al. 2022. "Lifestyle Factors Associated with Undernutrition in Older People after the Great East Japan Earthquake: A Prospective Study in the Fukushima Health Management Survey" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 6: 3399. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19063399
APA StyleOkazaki, K., Ohira, T., Sakai, A., Shimabukuro, M., Kazama, J. J., Takahashi, A., Nakano, H., Hayashi, F., Nagao, M., Yasumura, S., Ohto, H., & Kamiya, K. (2022). Lifestyle Factors Associated with Undernutrition in Older People after the Great East Japan Earthquake: A Prospective Study in the Fukushima Health Management Survey. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(6), 3399. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19063399






