The Effect of Juingong Meditation on the Theta to Alpha Ratio in the Temporoparietal and Anterior Frontal EEG Recordings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
- -
- provide valid informed consent prior to any study procedure
- -
- male or female subjects age 18 to 80 years
- -
- acute or chronic disorders (cardio-vascular, respiratory, neurologic, psychiatric)
- -
- drinking before experiment
- -
- took psychotropic drugs or were judged to be physically and mentally unsuitable for EEG
2.3. Setting and Samples
2.4. Procedure
2.5. Data Collection
2.6. Data Processing
2.7. Statistics
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, M.; Utama, N.P. Meditation Effect on human Brain compared with psychological questionnaire. Int. J. Inf. Educ. Technol. 2014, 4, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cardoso, R.; de Souza, E.; Camano, L.; Leite, J.R. Meditation in health: An operational definition. Brain Res. Protoc. 2004, 14, 58–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, N.-S. Teaching Transnational Buddhist Meditation with Vipassanā (Neiguan) and Mindfulness (Zhengnian) for Healing Depression in Contemporary China. Religions 2021, 12, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.H. Analysis of trends in meditation Education-related articles. Korean J. Ethics 2018, 1, 275–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milton, I. What Does Mindfulness Really Mean? Clarifying Key Terms and Definitions—Part I. Psychother. Aust. 2011, 17, 78–81. Available online: https://searchinformitorg/doi/103316/informit311352245148408.
- Braboszcz, C.; Cahn, B.R.; Levy, J.; Fernandez, M.; Delorme, A. Increased Gamma Brainwave Amplitude Compared to Control in Three Different Meditation Traditions. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otani, A. Eastern Meditative Techniques and Hypnosis: A New Synthesis. Am. J. Clin. Hypn. 2003, 46, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Daehaeng. No River to Cross: Trusting the Enlightenment That’s Always Right Here, 1st ed.; Wisdom Publications: Somerville, MA, USA, 2012; pp. 15–18. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, H. Über das Elektrenkephalogramm des Menschen. Arch. Für Psychiatr. Und Nervenkrankh. 1938, 108, 407–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, N.N.; Gastaut, H. Variations de l’activite electrique du cerveau, du coeur et des muscles squelettiques au cours de la meditation et de l’extase yogique. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1955, 6, 211–219. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.-Y.; Leve, L.D. A translational neuroscience perspective on mindfulness meditation as a prevention strategy. Transl. Behav. Med. 2016, 6, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLosAngeles, D.; Williams, G.; Burston, J.; Fitzgibbon, S.P.; Lewis, T.W.; Grummett, T.S.; Clark, C.R.; Pope, K.J.; Willoughby, J.O. Electroencephalographic Correlates of States of Concentrative Meditation. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2016, 110, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, W.; Camfield, D.A.; Woods, W.; Sarris, J.; Pipingas, A. Spectral Power and Functional Connectivity Changes During Mindfulness Meditation with Eyes Open: A Magnetoencephalography (MEG) Study in Long-Term Meditators. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2015, 98, 95–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauswald, A.; Übelacker, T.; Leske, S.; Weisz, N. What It Means to Be Zen: Marked Modulations of Local and Interareal Synchronization During Open Monitoring Meditation. Neuroimage 2015, 108, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benca, R.M.; Obermeyer, W.H.; Larson, C.L.; Yun, B.; Dolski, I.; Kleist, K.D.; Weber, S.M.; Davidson, R.J. EEG Alpha power and Alpha power asymmetry in sleep and wakefulness. Psyhophysiology 1999, 36, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabourin, M.E.; Cutcomb, S.D.; Crawford, H.J.; Pribram, K. EEG correlates of hypnotic susceptibility and hyp-notic trance: Spectral analysis and coherence. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 1990, 10, 125–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillard, B.; El-Baz, A.S.; Sears, L.; Tasman, A.; Sokhadze, E.M. Neurofeedback Training Aimed to Improve Focused Attention and Alertness in Children With ADHD: A Study of Relative Power of EEG Rhythms Using Custom-Made Software Application. Clin. EEG Neurosci. 2013, 44, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peniston, E.G.; Kulkosky, P.J. Alpha-theta brainwave neuro-feedback therapy for Vietnam veterans with combat-related post-traumatic stress disorder. Med. Psychother. 1991, 4, 47–60. [Google Scholar]
- Saxby, E.; Peniston, E.G. Alpha-theta brainwave neurofeedback training: An effective treatment for male and female alcoholics with depressive symptoms. J. Clin. Psychol. 1995, 51, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauregard, M.; Courtemanche, J.; Paquette, V. Brain activity in near-death experiencers during a meditative state. Resuscitation 2009, 80, 1009–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martial, C.; Mensen, A.; Charland-Verville, V.; Vanhaud-enhuyse, A.; Rentmeister, D.; Bahri, M.A.; Cassol, H.; Englebert, J.; Gosseries, O.; Laureys, S.; et al. Neurophenomenology of near-death experience memory in hypnotic recall: A within-subject EEG study. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmieri, A.; Calvo, V.; Johann, R.K.; Meconi, F.; Ma-rangoni, M.; Barilaro, P.; Broggio, A.; Sambin, M.; Sessa, P. “Reality” of near-death-experience memories: Evidence from a psychodynamic and electrophysio-logical integrated study. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahani, A.; Wahbeh, H.; Nezamfar, H.; Miller, M.; Erdogmus, D.; Oken, B. Quantitative change of EEG and respiration signals during mindfulness meditation. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2014, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagopoulos, J.; Xu, J.; Rasmussen, I.; Vik, A.; Gin, S.M.; Carl, F.E.; Ingrid, E.A.; Jardar, G.S.; Hollup, S.; Holen, A.; et al. Increased Theta and Alpha EEG Activity During Nondirective Meditation. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2009, 15, 1187–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habibabad, A.S.; MahdiNejad, J.E.D.; Azemati, H. Recording the Users’ Brain Waves in Manmade Religious Environments Based on Psychological Assessment of Form in Cre-ation/Enhancement of Spiritual Sense. Integr. Psychol. Behav. Sci. 2020, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MahdiNejad, J.-E.-D.; Azemati, H.; Matracchi, P. Investigating the effect of age and gender of users on improving spirituality by using EEG. Cogn. Neurodynamics 2021, 15, 637–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeng-Mi, S.; Joo-Hyun, K.; Jong-Hoon, K. The Experiences of Recovery from Disease in Patients doing Meditation. J. Korean Acad. Nurs. 2005, 35, 1025–1035. [Google Scholar]
- Daehaeng. Wake Up and Laugh: The Dharma Teaching of Zen Master Daehaeng, 1st ed.; Wisdom Publications: Somerville, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 86–87. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson, C.M.; Burrell, J.I.; Kuziek, J.W.; Thirunavukkarasu, S.; Buck, B.H.; Mathewson, K.E. Application of the Muse portable EEG system to aid in rapid diagnosis of stroke. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockman, C. Can a technology teach meditation? Experiencing the EEG headband interaxon muse as a meditation guide. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Learn. 2020, 15, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dkhil, M.B.; Wali, A.; Alimi, A.M. Drowsy driver detection by EEG analysis using Fast Fourier Transform. In Proceedings of the 2015 15th International Conference on Intelligent Systems Design and Applications (ISDA), Marrakech, Morocco, 14–16 December 2015; pp. 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nussbaumer, H.J. The Fast Fourier Transform. In Fast Fourier Transform and Convolution Algorithms; Springer Series in Information Sciences; Springer: Wien, Austria, 1981; Volume 2, pp. 80–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, S.; Bush, G.; Gollub, R.; Fricchione, G.; Khalsa, G.; Benson, H. Functional brain mapping of the relaxation response and meditation. Neuro Rep. 2000, 11, 1581–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, F.A.A.; Shapiai, M.I.; Setiawan, N.A.; Mitsukura, Y. Classification of Human Concentration in EEG Signals using Hilbert Huang Transform. Int. J. Simul. Syst. Sci. Technol. 2017, 18, 10.1–10.11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.J.; Park, Y.B. Clinical utility of paced breathing as a concentration meditation practice. Complement. Ther. Med. 2012, 20, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mark, L.J.P.; Bodenhamer-Davis, E.; Laurie, J.B.; Michael, S.G. Spectral Dynamics and Therapeutic Implications of the Theta/Alpha Crossover in Alpha-Theta Neurofeedback. J. Neurother. 2013, 17, 3–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa, L.L.; Dragos, H.; Pantelemon, C.; Rosu, O.V.; Strilciuc, S. The Role of Quantitative EEG in the Diagnosis of Neuropsychiatric Disorders. J. Med. Life 2020, 13, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
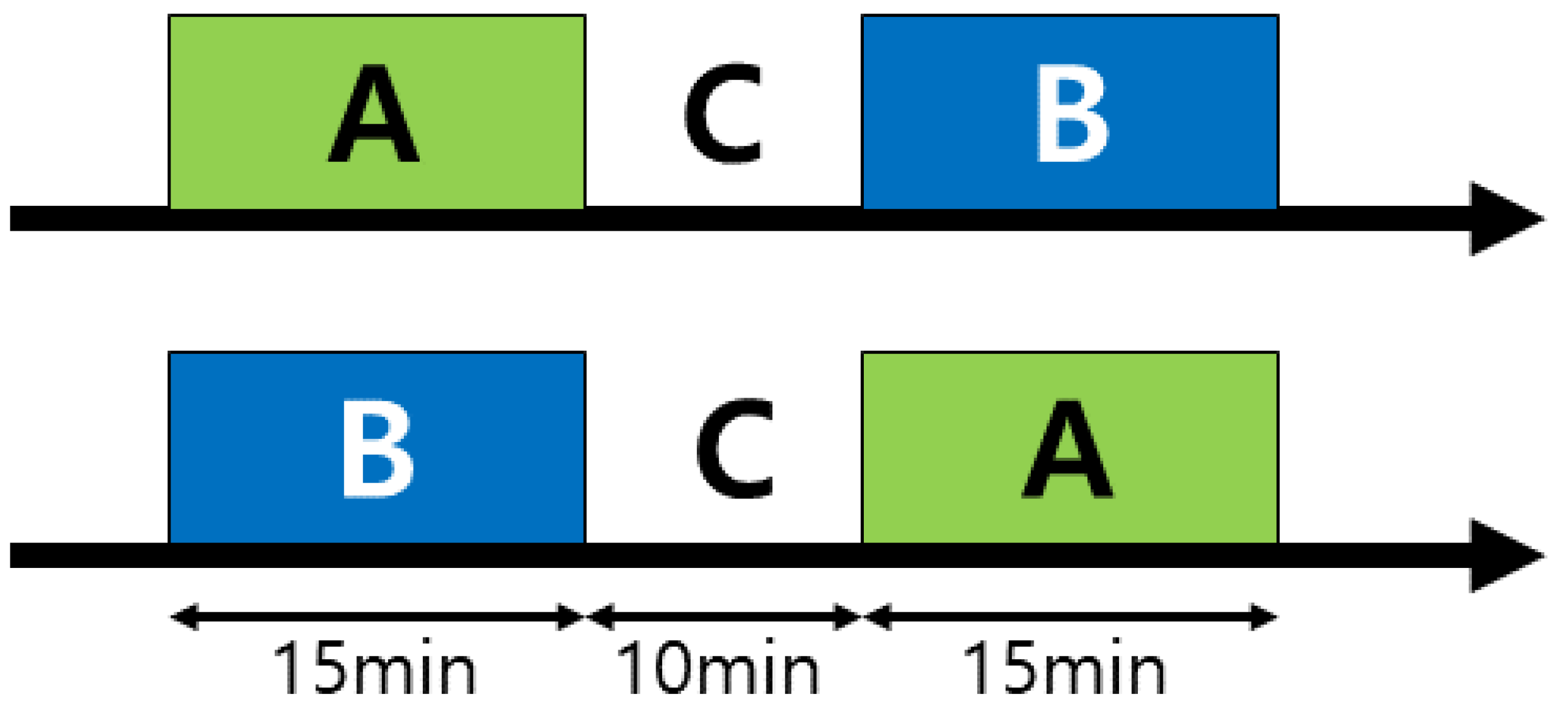
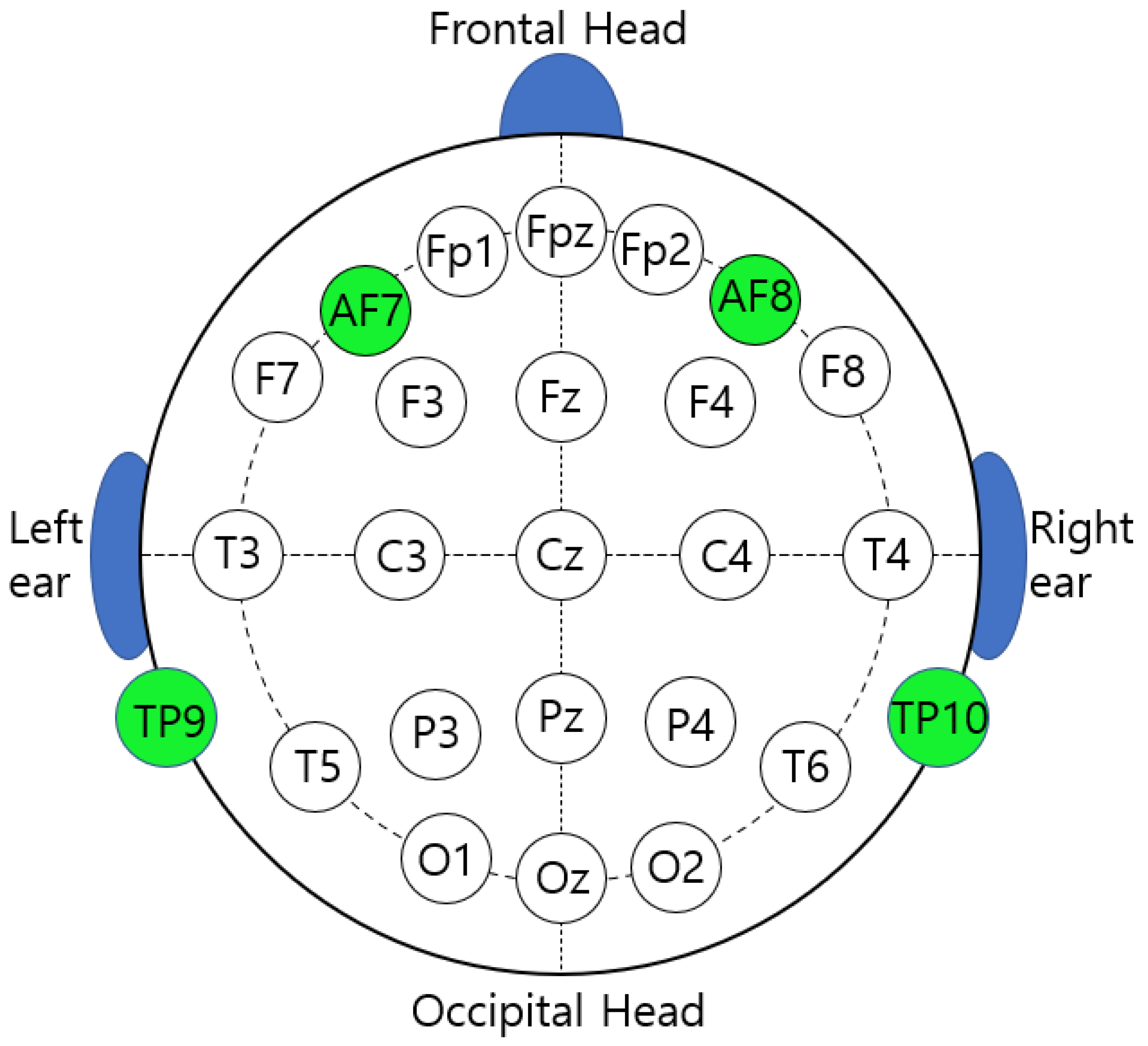
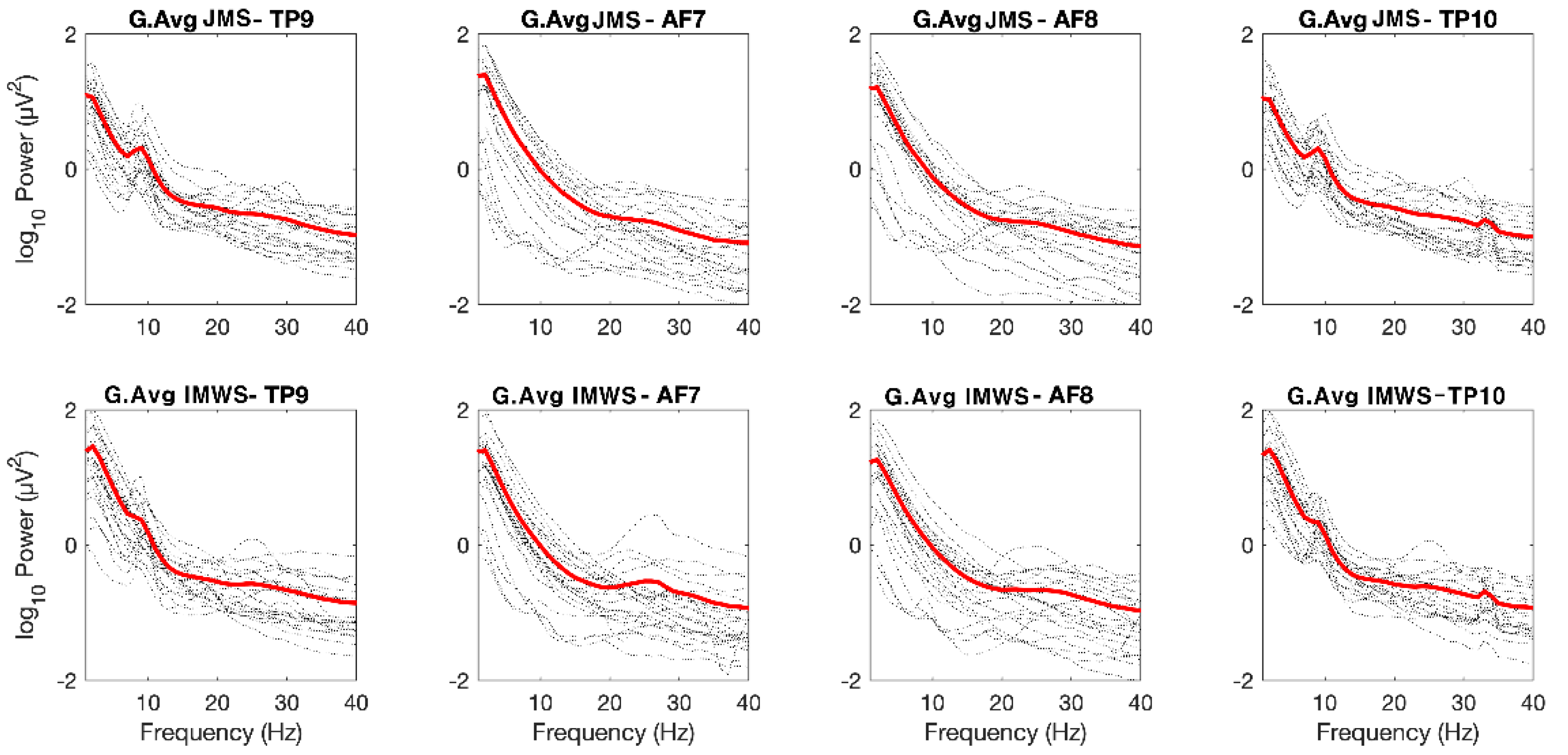
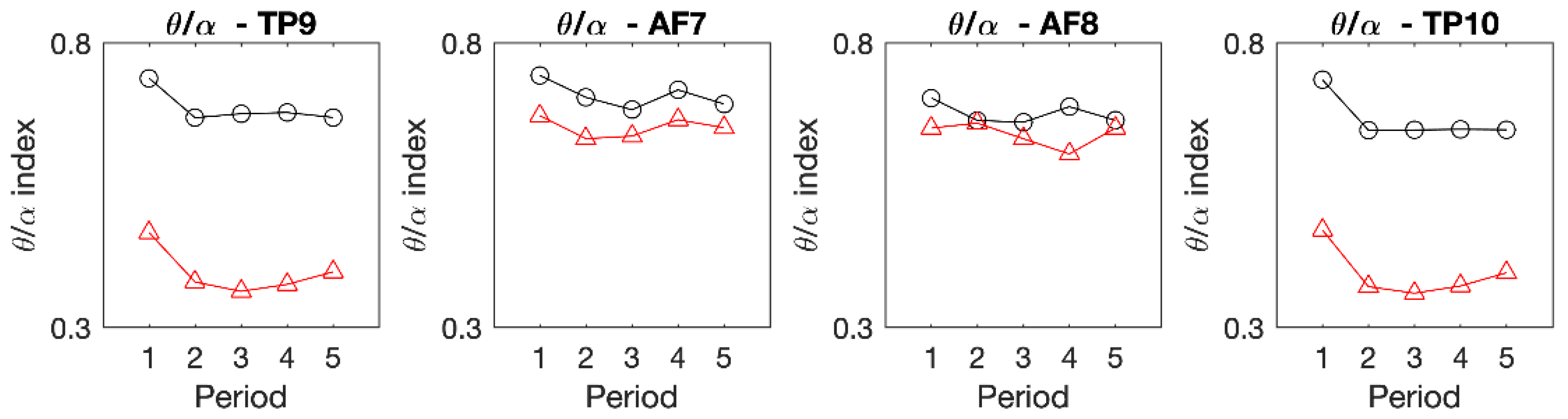
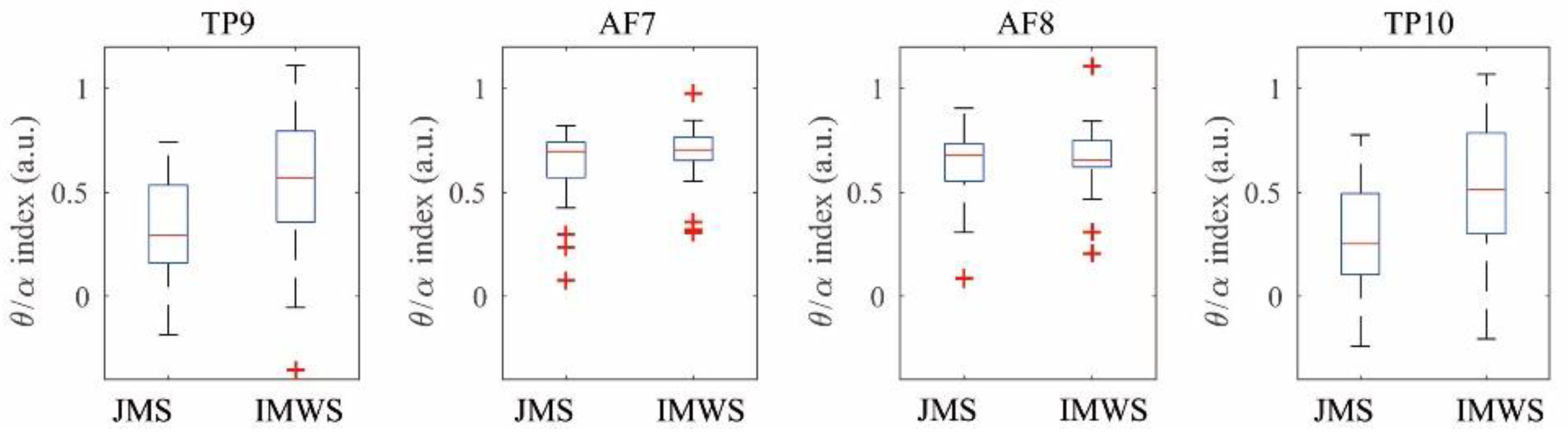
| Channel | States | M ± SD | Paired T | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TP9 | JMS | 0.31 ± 0.28 | −3.73 | 0.001 |
| IMWS | 0.55 ± 0.37 | |||
| AF7 | JMS | 0.63 ± 0.20 | 0.166 | |
| IMWS | 0.68 ± 0.16 | |||
| AF8 | JMS | 0.60 ± 0.21 | 0.347 | |
| IMWS | 0.65 ± 0.20 | |||
| TP10 | JMS | 0.30 ± 0.27 | −4.22 | <0.000 |
| IMWS | 0.54 ± 0.33 |
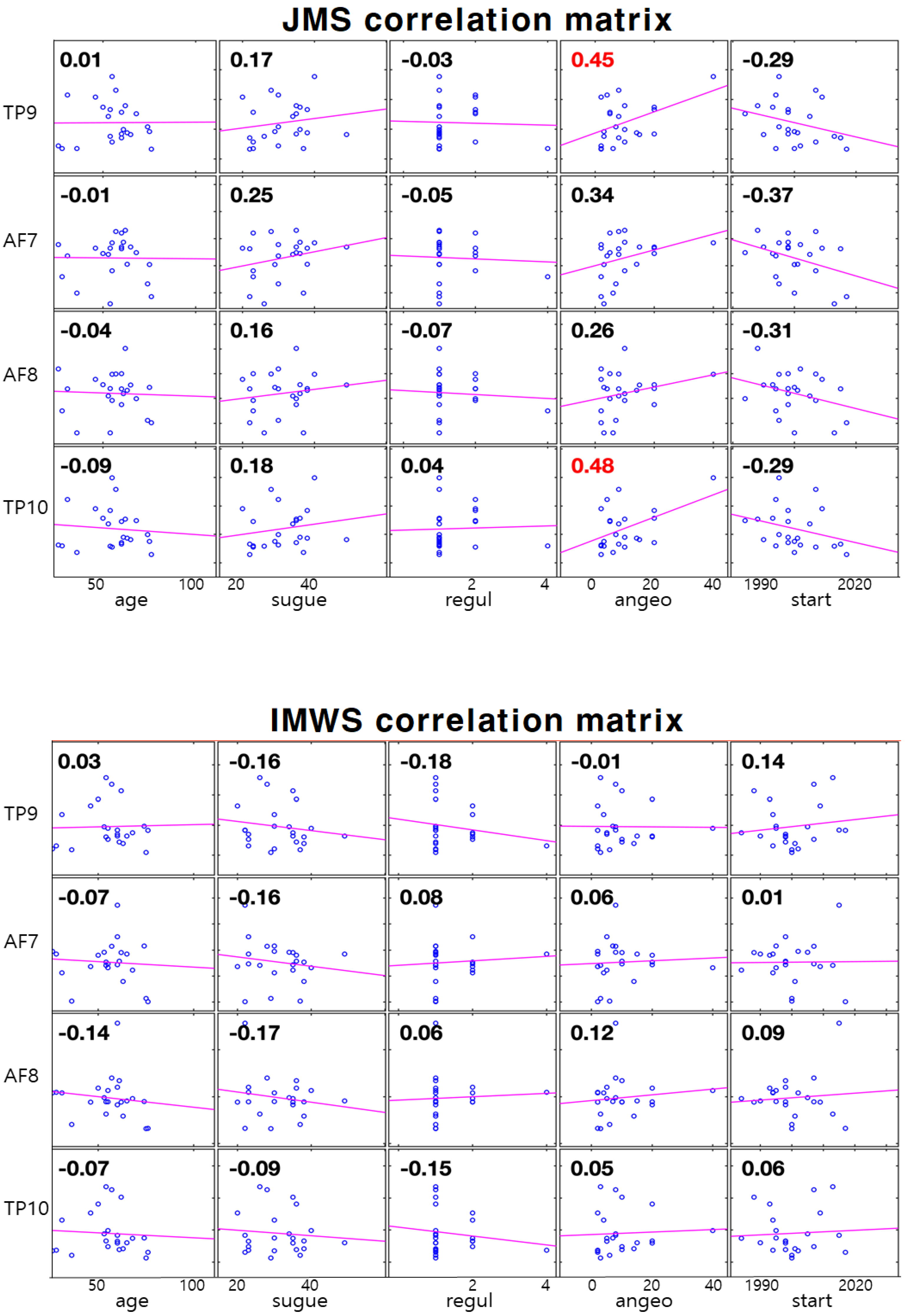
| JMS | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pearson-r | Age | Sugye | Regul | Angeo | Start |
| TP9 | 0.01 | 0.17 | −0.03 | 0.45 | −0.29 |
| AF7 | −0.01 | 0.25 | −0.05 | 0.34 | −0.37 |
| AF8 | −0.04 | 0.16 | −0.07 | 0.26 | −0.31 |
| TP10 | −0.09 | 0.18 | 0.04 | 0.48 | −0.29 |
| IMWS | |||||
| Pearson-r | Age | Sugye | Regul | Angeo | Start |
| TP9 | 0.03 | −0.16 | −0.18 | −0.01 | 0.14 |
| AF7 | −0.07 | −0.16 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.01 |
| AF8 | −0.14 | −0.17 | 0.06 | 0.12 | 0.09 |
| TP10 | −0.07 | −0.09 | −0.15 | 0.05 | 0.06 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.; Kim, M.; Jang, M.; Lee, J. The Effect of Juingong Meditation on the Theta to Alpha Ratio in the Temporoparietal and Anterior Frontal EEG Recordings. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1721. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031721
Kim J, Kim M, Jang M, Lee J. The Effect of Juingong Meditation on the Theta to Alpha Ratio in the Temporoparietal and Anterior Frontal EEG Recordings. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(3):1721. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031721
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Joohyun, Miji Kim, Miran Jang, and Junyeop Lee. 2022. "The Effect of Juingong Meditation on the Theta to Alpha Ratio in the Temporoparietal and Anterior Frontal EEG Recordings" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 3: 1721. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031721
APA StyleKim, J., Kim, M., Jang, M., & Lee, J. (2022). The Effect of Juingong Meditation on the Theta to Alpha Ratio in the Temporoparietal and Anterior Frontal EEG Recordings. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(3), 1721. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031721







