A Subject-Tailored Variability-Based Platform for Overcoming the Plateau Effect in Sports Training: A Narrative Review
Abstract
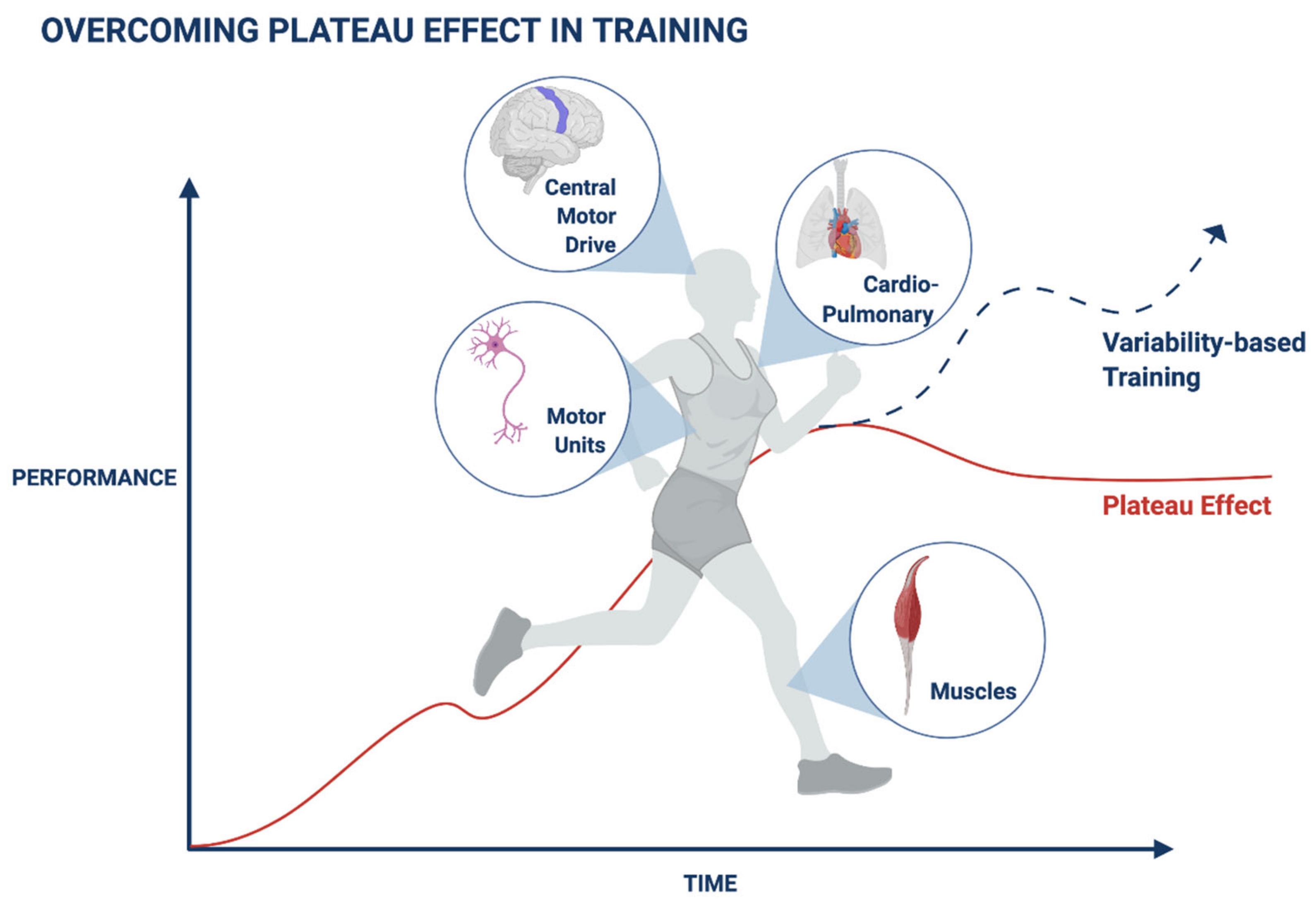
1. Introduction
2. Adaptation Mechanisms Are Associated with a Plateau in Muscle Performance during Exercise
3. Adaptation Mechanisms Are Associated with a Plateau in the Cardiovascular Parameters during Exercise
4. Adaptation Prevents Progress during Recovery in Patients with Neurological Diseases
5. Mechanisms Associated with the Exercise-Related Plateau
6. Maneuvers for Overcoming the Plateau Effect in Health and Disease
7. Entropy, Variability, and Randomness Characterize Biological Systems: A Basis for Designing Methods for Overcoming Plateaus
8. Variability in Biological Systems Characterizes the Typical Trajectory of the Body’s Response to Triggers: A Platform for Overcoming Plateaus
9. Overcoming Plateaus in Muscle Training by Introducing Subject-Tailored Variability Patterns
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Disclosure
Abbreviations
References
- Storniolo, J.L.; Cairo, B.; Porta, A.; Cavallari, P. Symbolic Analysis of the Heart Rate Variability during the Plateau Phase Following Maximal Sprint Exercise. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 632883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niemeyer, M.; Leithäuser, R.; Beneke, R. Effect of intensive prior exercise on muscle fiber activation, oxygen uptake kinetics, and oxygen uptake plateau occurrence. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2020, 120, 2019–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebisz, P.; Hebisz, R.; Borkowski, J.; Zatoń, M. Time of VO2max Plateau and Post-Exercise Oxygen Consumption during Incremental Exercise Testing in Young Mountain Bike and Road Cyclists. Physiol. Res. 2018, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, Y.-E.; Lin, Z.-M.; Hua, D.-M.; Jiang, Y.; Huo, Y.-T.; Luo, Q.; Chen, R.-C. Evaluation of carbon dioxide rebreathing during exercise assisted by noninvasive ventilation with plateau exhalation valve. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2017, 12, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Finn, H.T.; Brennan, S.L.; Gonano, B.M.; Knox, M.F.; Ryan, R.C.; Siegler, J.C.; Marshall, P.W. Muscle Activation Does Not Increase after a Fatigue Plateau Is Reached during 8 Sets of Resistance Exercise in Trained Individuals. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2014, 28, 1226–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, D.; Mehter, M.; Gernigon, M.; Caddy, O.; Keiller, D.; Barnes, R. The effects of exercise modality on the incidence of plateau at V·O2max. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2012, 32, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, D.; Schaitel, K.; Pennefather, A.; Gernigon, M.; Keiller, D.; Barnes, R. The incidence of plateau at 2max is affected by a bout of prior-priming exercise. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2011, 32, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gacesa, J.Z.P.; Klasnja, A.V.; Grujic, N.G. Changes in Strength, Endurance, and Fatigue during a Resistance–Training Program for the Triceps Brachii Muscle. J. Athl. Train. 2013, 48, 804–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paton, C.D.; Hopkins, W.G. Combining Explosive and High-Resistance Training Improves Performance in Competitive Cyclists. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2005, 19, 826–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falvo, M.J.; Sirevaag, E.J.; Rohrbaugh, J.W.; Earhart, G.M. Resistance training induces supraspinal adaptations: Evidence from movement-related cortical potentials. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 109, 923–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weavil, J.C.; Sidhu, S.K.; Mangum, T.S.; Richardson, R.S.; Amann, M. Intensity-dependent alterations in the excitability of cortical and spinal projections to the knee extensors during isometric and locomotor exercise. Am. J. Physiol. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2015, 308, R998–R1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Vecchio, A.; Casolo, A.; Negro, F.; Scorcelletti, M.; Bazzucchi, I.; Enoka, R.; Felici, F.; Farina, D. The increase in muscle force after 4 weeks of strength training is mediated by adaptations in motor unit recruitment and rate coding. J. Physiol. 2019, 597, 1873–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundstrup, E.; Jakobsen, M.D.; Andersen, C.H.; Zebis, M.K.; Mortensen, O.S.; Andersen, L.L. Muscle Activation Strategies during Strength Training with Heavy Loading vs. Repetitions to Failure. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2012, 26, 1897–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrese, A.L.; Ostáriz, E.S.; Mallen, J.C.; Izquierdo, D.M. The changes in running performance and maximal oxygen uptake after long-term training in elite athletes. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2005, 45, 435–440. [Google Scholar]
- Hofstetter, S.; Assaf, Y. The rapid development of structural plasticity through short water maze training: A DTI study. Neuroimage 2017, 155, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boone, J.; Vandekerckhove, K.; Coomans, I.; Prieur, F.; Bourgois, J.G. An integrated view on the oxygenation responses to incremental exercise at the brain, the locomotor and respiratory muscles. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2016, 116, 2085–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Høydal, M.A.; Wisløff, U.; Kemi, O.J.; Ellingsen, Ø. Running speed and maximal oxygen uptake in rats and mice: Practical implications for exercise training. Eur. J. Cardiovasc. Prev. Rehabil. 2007, 14, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamagishi, T.; Babraj, J. Effects of reduced-volume of sprint interval training and the time course of physiological and performance adaptations. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2017, 27, 1662–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandbakk, Ø.; Skålvik, T.F.; Spencer, M.; Van Beekvelt, M.; Welde, B.; Hegge, A.M.; Gjøvaag, T.; Ettema, G. The physiological responses to repeated upper-body sprint exercise in highly trained athletes. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2015, 115, 1381–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izem, O.; Maufrais, C.; Obert, P.; Rupp, T.; Schuster, I.; Nottin, S. Kinetics of Left Ventricular Mechanics during Transition from Rest to Exercise. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2019, 51, 1838–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimenez, P.; Kerhervé, H.; Messonnier, L.A.; Féasson, L.; Millet, G.Y. Changes in the Energy Cost of Running during a 24-h Treadmill Exercise. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2013, 45, 1807–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Lezaun, E.; Schumann, M.; Mäkinen, T.; Kyröläinen, H.; Walker, S. Effects of resistance training frequency on cardiorespiratory fitness in older men and women during intervention and follow-up. Exp. Gerontol. 2017, 95, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Racinais, S.; Buchheit, M.; Girard, O. Breakpoints in ventilation, cerebral and muscle oxygenation, and muscle activity during an incremental cycling exercise. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossiter, H.B.; Kowalchuk, J.M.; Whipp, B.J. A test to establish maximum O2uptake despite no plateau in the O2uptake response to ramp incremental exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 2006, 100, 764–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munch, G.D.W.; Svendsen, J.H.; Damsgaard, R.; Secher, N.H.; González-Alonso, J.; Mortensen, S.P. Maximal heart rate does not limit cardiovascular capacity in healthy humans: Insight from right atrial pacing during maximal exercise. J. Physiol. 2013, 592, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammer, S.M.; Alexander, A.M.; Didier, K.; Smith, J.R.; Caldwell, J.T.; Sutterfield, S.L.; Ade, C.J.; Barstow, T.J. The noninvasive simultaneous measurement of tissue oxygenation and microvascular hemodynamics during incremental handgrip exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 2018, 124, 604–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, J.; McEvoy, A.; Pyke, K.E. Can a combination of handgrip exercise and prolonged forearm occlusion elicit a maximal brachial artery FMD response? Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2014, 114, 1297–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stöcker, F.; Von Oldershausen, C.; Paternoster, F.K.; Schulz, T.; Oberhoffer, R. Relationship of post-exercise muscle oxygenation and duration of cycling exercise. BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2016, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocker, F.; Von Oldershausen, C.; Paternoster, F.K.; Schulz, T.; Oberhoffer, R. End-exercise ΔHHb/ΔVO2 and post-exercise local oxygen availability in relation to exercise intensity. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2015, 37, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyberg, S.K.; Berg, O.K.; Helgerud, J.; Wang, E. Blood flow regulation and oxygen uptake during high-intensity forearm exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 2017, 122, 907–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murias, J.M.; Spencer, M.D.; Keir, D.A.; Paterson, D.H. Systemic and vastus lateralis muscle blood flow and O2 extraction during ramp incremental cycle exercise. Am. J. Physiol. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2013, 304, R720–R725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lintu, N.; Tompuri, T.; Viitasalo, A.; Soininen, S.; Laitinen, T.; Savonen, K.; Lindi, V.; Lakka, T.A. Cardiovascular fitness and haemodynamic responses to maximal cycle ergometer exercise test in children 6–8 years of age. J. Sports Sci. 2013, 32, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spee, R.F.; Niemeijer, V.M.; Wessels, B.; Jansen, J.P.; Wijn, P.F.; Doevendans, P.A.; Kemps, H.M. Characterization of exercise limitations by evaluating individual cardiac output patterns: A prospective cohort study in patients with chronic heart failure. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2015, 15, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kojima, M.S.; Noda, A.; Miyata, S.; Kojima, J.; Hara, Y.; Minoshima, M.; Murohara, T. The Effect of Habitual Physical Training on Left Ventricular Function during Exercise Assessed by Three-Dimensional Echocardiography. Echocardiography 2015, 32, 1670–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.E.N.; Conlee, R.K.; Jensen, R.O.B.E.R.T.; Fellingham, G.W.; George, J.D.; Fisher, A.G. Stroke volume does not plateau during graded exercise in elite male distance runners. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2001, 33, 1849–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mcnarry, M.A.; Farr, C.; Middlebrooke, A.; Welford, D.; Breese, B.; Armstrong, N.; Barker, A.R. Aerobic Function and Muscle Deoxygenation Dynamics during Ramp Exercise in Children. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2015, 47, 1877–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Howden, E.J.; Perhonen, M.; Peshock, R.M.; Zhang, R.; Arbab-Zadeh, A.; Adams-Huet, B.; Levine, B.D. Females have a blunted cardiovascular response to one year of intensive supervised endurance training. J. Appl. Physiol. 2015, 119, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keiller, D.R.; Gordon, D.A. The plateau at V˙ O2max is associated with anaerobic alleles. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2019, 23, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-J.; Kilbreath, S.L.; Singh, M.F.; Zeman, B.; Davis, G.M. Effect of Progressive Resistance Training on Muscle Performance after Chronic Stroke. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2010, 42, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosbie, J.; Russold, M.; Raymond, J.; Middleton, J.W.; Davis, G.M. Functional Electrical Stimulation-Supported Interval Training Following Sensorimotor-Complete Spinal Cord Injury: A Case Series. Neuromodulation 2009, 12, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, H.R.; Perret, C.; Saunders, B.A.; Kakebeeke, T.H.; Donaldson, N.D.N.; Allan, D.B.; Hunt, K.J. Cardiorespiratory and Power Adaptations to Stimulated Cycle Training in Paraplegia. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2008, 40, 1573–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wymbs, N.F.; Grafton, S.T. The Human Motor System Supports Sequence-Specific Representations over Multiple Training-Dependent Timescales. Cereb. Cortex 2014, 25, 4213–4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirasawa, A.; Sato, K.; Yoneya, M.; Sadamoto, T.; Bailey, D.M.; Ogoh, S. Heterogeneous Regulation of Brain Blood Flow during Low-Intensity Resistance Exercise. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2016, 48, 1829–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popovic, B.; Popovic, D.; Macut, D.; Antić, I.B.; Isailovic, T.; Ognjanović, S.; Bogavac, T.; Kovačević, V.E.; Ilic, D.; Petrovic, M.; et al. Acute Response to Endurance Exercise Stress: Focus on Catabolic/Anabolic Interplay Between Cortisol, Testosterone, and Sex Hormone Binding Globulin in Professional Athletes. J. Med. Biochem. 2019, 38, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, A.; Dutheil, F.; Drapeau, V.; Metz, L.; Lesour, B.; Chapier, R.; Pereira, B.; Verney, J.; Baker, J.S.; Vinet, A.; et al. Long-term effects of high-intensity resistance and endurance exercise on plasma leptin and ghrelin in overweight individuals: The RESOLVE Study. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2019, 44, 1172–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knez, W.; Jenkins, D.; Coombes, J. The Effect of an Increased Training Volume on Oxidative Stress. Int. J. Sports Med. 2013, 35, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzulla, M.; Volterman, K.A.; Packer, J.E.; Wooding, D.J.; Brooks, J.C.; Kato, H.; Moore, D.R. Whole-body net protein balance plateaus in response to increasing protein intakes during post-exercise recovery in adults and adolescents. Nutr. Metab. 2018, 15, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira-Coelho, F.; Fonseca, C.G.; Barbosa, N.H.S.; Vaz, F.F.; Cordeiro, L.M.D.S.; Coimbra, C.C.; Pires, W.; Soares, D.; Wanner, S.P. Effects of manipulating the duration and intensity of aerobic training sessions on the physical performance of rats. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirthalingam, T.; Mavros, Y.; Wilson, G.C.; Clarke, J.L.; Mitchell, L.; Hackett, D. Effects of a Modified German Volume Training Program on Muscular Hypertrophy and Strength. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2017, 31, 3109–3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Signorile, J.F.; Carmel, M.P.; Lai, S.; Roos, B.A. Early plateaus of power and torque gains during high- and low-speed resistance training of older women. J. Appl. Physiol. 2005, 98, 1213–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santtila, M.; Häkkinen, K.; Nindl, B.C.; Kyröläinen, H. Cardiovascular and Neuromuscular Performance Responses Induced by 8 Weeks of Basic Training Followed by 8 Weeks of Specialized Military Training. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2012, 26, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strzała, M.; Ostrowski, A.; Szygula, Z. Altitude Training and its Influence on Physical Endurance in Swimmers. J. Hum. Kinet. 2011, 28, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wernbom, M.; Aagaard, P. Muscle fibre activation and fatigue with low-load blood flow restricted resistance exercise—An integrative physiology review. Acta Physiol. 2019, 228, e13302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Midgley, A.; McNaughton, L.R.; Wilkinson, M. Is There an Optimal Training Intensity for Enhancing the Maximal Oxygen Uptake of Distance Runners? Sports Med. 2006, 36, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mier, C.M.; Alexander, R.P.; Mageean, A.L. Achievement of V Combining Dot AboveO2max Criteria during a Continuous Graded Exercise Test and a Verification Stage Performed by College Athletes. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2012, 26, 2648–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.L.; Roth, E.J.; Killian, C.; Hornby, T.G. Locomotor Training Improves Daily Stepping Activity and Gait Efficiency in Individuals Poststroke Who Have Reached a “Plateau” in Recovery. Stroke 2010, 41, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-H.; Shin, Y.-I.; You, J.H.; Park, M.S. Comparative effects of robotic-assisted gait training combined with conventional physical therapy on paretic hip joint stiffness and kinematics between subacute and chronic hemiparetic stroke. NeuroRehabilitation 2018, 42, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, Y.; Kondo, I.; Sonoda, S.; Miyasaka, H.; Teranishi, T.; Nagai, S.; Saitoh, E. Preliminary Trial to Increase Gait Velocity with High Speed Treadmill Training for Patients with Hemiplegia. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2010, 89, 683–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Shin, Y.; Park, J.-H.; Cha, Y.J.; You, J.H. Effects of Walkbot gait training on kinematics, kinetics, and clinical gait function in paraplegia and quadriplegia. NeuroRehabilitation 2018, 42, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byl, N.N. Mobility training using a bionic knee orthosis in patients in a post-stroke chronic state: A case series. J. Med Case Rep. 2012, 6, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.D.O.; Dutra, M.T.; de Moraes, W.M.A.M.; Funghetto, S.S.; de Farias, D.L.; dos Santos, P.H.F.; Vieira, D.C.L.; Nascimento, D.D.C.; Orsano, V.S.M.; Schoenfeld, B.J.; et al. Resistance training-induced gains in muscle strength, body composition, and functional capacity are attenuated in elderly women with sarcopenic obesity. Clin. Interv. Aging 2018, 13, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabat, Y. Overcoming randomness does not rule out the importance of inherent randomness for functionality. J. Biosci. 2019, 44, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Ilan, Y. Generating randomness: Making the most out of disordering a false order into a real one. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilan, Y. Advanced Tailored Randomness: A Novel Approach for Improving the Efficacy of Biological Systems. J. Comput. Biol. 2020, 27, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilan, Y. Order Through Disorder: The Characteristic Variability of Systems. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabat, Y.; Lichtenstein, Y.; Ilan, Y. Short-Term Cohousing of Sick with Healthy or Treated Mice Alleviates the Inflammatory Response and Liver Damage. Inflammation 2020, 44, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Haj, M.; Kanovitch, D.; Ilan, Y. Personalized inherent randomness of the immune system is manifested by an individualized response to immune triggers and immunomodulatory therapies: A novel platform for designing personalized immunotherapies. Immunol. Res. 2019, 67, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lorenzo, V.; Schmidt, M. Biological standards for the Knowledge-Based BioEconomy: What is at stake. New Biotechnol. 2018, 40, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gsponer, J.; Babu, M.M. The rules of disorder or why disorder rules. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2009, 99, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckle, A.M.; Borg, N.A. Integrating Experiment and Theory to Understand TCR-pMHC Dynamics. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodygin, D.; Flügel, A. Intravital real-time analysis of T-cell activation in health and disease. Cell Calcium 2017, 64, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilan, Y. Randomness in microtubule dynamics: An error that requires correction or an inherent plasticity required for normal cellular function? Cell. Biol. Int. 2019, 43, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilan, Y. Microtubules: From understanding their dynamics to using them as potential therapeutic targets. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 234, 7923–7937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilan-Ber, T.; Ilan, Y. The role of microtubules in the immune system and as potential targets for gut-based immunotherapy. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 111, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forkosh, E.; Kenig, A.; Ilan, Y. Introducing variability in targeting the microtubules: Review of current mechanisms and future directions in colchicine therapy. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2020, 8, e00616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albanna, B.F.; Hillar, C.; Sohl-Dickstein, J.; Deweese, M.R. Minimum and Maximum Entropy Distributions for Binary Systems with Known Means and Pairwise Correlations. Entropy 2017, 19, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richman, J.S.; Moorman, J.R. Physiological time-series analysis using approximate entropy and sample entropy. Am. J. Physiol. -Heart Circ. Physiol. 2000, 278, H2039–H2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajdl, K.; Lansky, P.; Kostal, L. Entropy factor for randomness quantification in neuronal data. Neural Netw. 2017, 95, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatef, B.; Ghanjal, A.; Motaqi, M.; Arab, Z. Force variability in the short- and long-term type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Med. Signals Sens. 2019, 9, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilan, Y. Overcoming Compensatory Mechanisms toward Chronic Drug Administration to Ensure Long-Term, Sustainable Beneficial Effects. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2020, 18, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, S.; Roy, K.; Zangle, T.; Hoffmann, A. Nongenetic origins of cell-to-cell variability in B lymphocyte proliferation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E2888–E2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yizhak, K.; Aguet, F.; Kim, J.; Hess, J.M.; Kübler, K.; Grimsby, J.; Frazer, R.; Zhang, H.; Haradhvala, N.J.; Rosebrock, D.; et al. RNA sequence analysis reveals macroscopic somatic clonal expansion across normal tissues. Science 2019, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.D.; Henriques, T.; Munshi, M.N.; Segal, A.R.; Goldberger, A.L. Dynamical glucometry: Use of multiscale entropy analysis in diabetes. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 2014, 24, 033139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez-Villegas, J.F.; Lam-Espinosa, E.; Ramirez-Moreno, D.F.; Calvo-Echeverry, P.C.; Agredo-Rodriguez, W. Heart Rate Variability Dynamics for the Prognosis of Cardiovascular Risk. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plews, D.J.; Laursen, P.B.; Le Meur, Y.; Hausswirth, C.; Kilding, A.E.; Buchheit, M. Monitoring Training with Heart-Rate Variability: How Much Compliance Is Needed for Valid Assessment? Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2014, 9, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elgart, V.; Lin, J.-R.; Loscalzo, J. Determinants of drug-target interactions at the single cell level. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2018, 14, e1006601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leino, A.D.; King, E.C.; Jiang, W.; Vinks, A.; Klawitter, J.; Christians, U.; Woodle, E.S.; Alloway, R.R.; Rohan, J.M. Assessment of tacrolimus intrapatient variability in stable adherent transplant recipients: Establishing baseline values. Am. J. Transplant. 2018, 19, 1410–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gueta, I.; Markovits, N.; Yarden-Bilavsky, H.; Raichlin, E.; Freimark, D.; Lavee, J.; Loebstein, R.; Peled, Y. High tacrolimus trough level variability is associated with rejections after heart transplant. Am. J. Transplant. 2018, 18, 2571–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gueta, I.; Markovits, N.; Yarden-Bilavsky, H.; Raichlin, E.; Freimark, D.; Lavee, J.; Loebstein, R.; Peled, Y. Intrapatient variability in tacrolimus trough levels after solid organ transplantation varies at different postoperative time periods. Am. J. Transplant. 2018, 19, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Bello, A.; Congy-Jolivet, N.; Danjoux, M.; Muscari, F.; Lavayssière, L.; Esposito, L.; Hebral, A.-L.; Bellière, J.; Kamar, N. High tacrolimus intra-patient variability is associated with graft rejection, and de novo donor-specific antibodies occurrence after liver transplantation. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 1795–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stergiou, N.; Harbourne, R.T.; Cavanaugh, J.T. Optimal movement variability: A new theoretical perspective for neurologic physical therapy. J. Neurol. Phys. Ther. 2006, 30, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofori, E.; Shim, J.; Sosnoff, J.J. The influence of lower leg configurations on muscle force variability. J. Biomech. 2018, 71, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stergiou, N.; Decker, L.M. Human movement variability, nonlinear dynamics, and pathology: Is there a connection? Hum. Mov. Sci. 2011, 30, 869–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, T.J. The influence of aging and sex on skeletal muscle mass and strength. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2001, 4, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martel, G.F.; Roth, S.M.; Ivey, F.M.; Lemmer, J.T.; Tracy, B.L.; Hurlbut, D.E.; Metter, E.J.; Hurley, B.F.; Rogers, M.A. Age and sex affect human muscle fibre adaptations to heavy-resistance strength training. Exp. Physiol. 2006, 91, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cignetti, F.; Schena, F.; Rouard, A. Effects of fatigue on inter-cycle variability in cross-country skiing. J. Biomech. 2009, 42, 1452–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, M.P.; Walsh, D. Mechanisms of fatigue. J. Support Oncol. 2010, 8, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Samani, A.; Srinivasan, D.; Mathiassen, S.E.; Madeleine, P. Variability in spatio-temporal pattern of trapezius activity and coordination of hand-arm muscles during a sustained repetitive dynamic task. Exp. Brain Res. 2016, 235, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.W.; Goodpaster, B.H.; Strotmeyer, E.S.; de Rekeneire, N.; Harris, T.B.; Schwartz, A.V.; Tylavsky, F.A.; Newman, A.B. Decreased Muscle Strength and Quality in Older Adults with Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes 2006, 55, 1813–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatef, B.; Bahrpeyma, F.; Tehrani, M.R.M. The comparison of muscle strength and short-term endurance in the different periods of type 2 diabetes. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2014, 13, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harbourne, R.T.; Stergiou, N. Movement Variability and the Use of Nonlinear Tools: Principles to Guide Physical Therapist Practice. Phys. Ther. 2009, 89, 267–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilan, Y. β-Glycosphingolipids as Mediators of Both Inflammation and Immune Tolerance: A Manifestation of Randomness in Biological Systems. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury, T.; Ilan, Y. Introducing Patterns of Variability for Overcoming Compensatory Adaptation of the Immune System to Immunomodulatory Agents: A Novel Method for Improving Clinical Response to Anti-TNF Therapies. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenig, A.; Ilan, Y. A Personalized Signature and Chronotherapy-Based Platform for Improving the Efficacy of Sepsis Treatment. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Horin, S.; Chowers, Y. Review article: Loss of response to anti-TNF treatments in Crohn’s disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 33, 987–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalden, J.R.; Schulze-Koops, H. Immunogenicity and loss of response to TNF inhibitors: Implications for rheumatoid arthritis treatment. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2017, 13, 707–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehdizadeh, A.; Barzegar, M.; Negargar, S.; Yahyavi, A.; Raeisi, S. The current and emerging therapeutic approaches in drug-resistant epilepsy management. Acta Neurol. Belg. 2019, 119, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrone, L.; Scuteri, D.; Rombola, L.; Mizoguchi, H.; Bagetta, G. Opioids Resistance in Chronic Pain Management. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2017, 15, 444–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Testani, J.; Collins, S. Diuretic Resistance in Heart Failure. Curr. Hear. Fail. Rep. 2019, 16, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennabi, D.; Aouizerate, B.; El-Hage, W.; Doumy, O.; Moliere, F.; Courtet, P.; Nieto, I.; Bellivier, F.; Bubrovsky, M.; Vaiva, G.; et al. Risk factors for treatment resistance in unipolar depression: A systematic review. J. Affect. Disord. 2015, 171, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mezza, T.; Cinti, F.; Cefalo, C.M.A.; Pontecorvi, A.; Kulkarni, R.N.; Giaccari, A. β-Cell Fate in Human Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes: A Perspective on Islet Plasticity. Diabetes 2019, 68, 1121–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoury, T.; Ilan, Y. Platform introducing individually tailored variability in nerve stimulations and dietary regimen to prevent weight regain following weight loss in patients with obesity. Obes. Res. Clin. Pr. 2021, 15, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilan, Y. Improving Global Healthcare and Reducing Costs Using Second-Generation Artificial Intelligence-Based Digital Pills: A Market Disruptor. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolben, Y.; Weksler-Zangen, S.; Ilan, Y. Adropin as a potential mediator of the metabolic system-autonomic nervous system-chronobiology axis: Implementing a personalized signature-based platform for chronotherapy. Obes. Rev. 2020, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilan, Y.; Spigelman, Z. Establishing patient-tailored variability-based paradigms for anti-cancer therapy: Using the inherent trajectories which underlie cancer for overcoming drug resistance. Cancer Treat. Res. Commun. 2020, 25, 100240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, A.; Weksler-Zangen, S.; Ilan, Y. Role of the Immune System and the Circadian Rhythm in the Pathogenesis of Chronic Pancreatitis. Pancreas 2020, 49, 1024–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potruch, A.; Khoury, S.T.; Ilan, Y. The role of chronobiology in drug-resistance epilepsy: The potential use of a variability and chronotherapy-based individualized platform for improving the response to anti-seizure drugs. Seizure 2020, 80, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelman, R.; Bayatra, A.; Kessler, A.; Schwartz, A.; Ilan, Y. Targeting SARS-CoV-2 receptors as a means for reducing infectivity and improving antiviral and immune response: An algorithm-based method for overcoming resistance to antiviral agents. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 1397–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishay, Y.; Kolben, Y.; Kessler, A.; Ilan, Y. Role of circadian rhythm and autonomic nervous system in liver function: A hypothetical basis for improving the management of hepatic encephalopathy. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2021, 321, G400–G412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenig, A.; Kolben, Y.; Asleh, R.; Amir, O.; Ilan, Y. Improving Diuretic Response in Heart Failure by Implementing a Patient-Tailored Variability and Chronotherapy-Guided Algorithm. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 695547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmanov, H.; Ross, E.L.; Ilan, Y. Establishment of an Individualized Chronotherapy, Autonomic Nervous System, and Variability-Based Dynamic Platform for Overcoming the Loss of Response to Analgesics. Pain Physician 2021, 24, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Isahy, Y.; Ilan, Y. Improving the long-term response to antidepressants by establishing an individualized platform based on variability and chronotherapy. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 59, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilan, Y. Why targeting the microbiome is not so successful: Can randomness overcome the adaptation that occurs following gut manipulation? Clin. Exp. Gastroenterol. 2019, 12, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishay, Y.; Potruch, A.; Schwartz, A.; Berg, M.; Jamil, K.; Agus, S.; Ilan, Y. A digital health platform for assisting the diagnosis and monitoring of COVID-19 progression: An adjuvant approach for augmenting the antiviral response and mitigating the immune-mediated target organ damage. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 143, 112228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurvitz, N.; Azmanov, H.; Kesler, A.; Ilan, Y. Establishing a second-generation artificial intelligence-based system for improving diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring of patients with rare diseases. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2021, 29, 1485–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilan, Y. Second-Generation Digital Health Platforms: Placing the Patient at the Center and Focusing on Clinical Outcomes. Front. Digit. Health 2020, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rensing, N.; Han, L.; Wong, M. Intermittent dosing of rapamycin maintains antiepileptogenic effects in a mouse model of tuberous sclerosis complex. Epilepsia 2015, 56, 1088–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strik, A.; Berends, S.; Mould, D.; Mathôt, R.; Ponsioen, C.; van den Brande, J.; Jansen, J.; Hoekman, D.; Brandse, J.; Löwenberg, M.; et al. Dashboard driven vs. conventional dosing of infliximab in inflammatory bowel disease patients: The PRECISION trial. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2019, 13, S063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakral, M.; Walker, R.; Saunders, J.K.; Shortreed, S.M.; Dublin, S.; Parchman, M.; Hansen, R.N.; Ludman, E.; Sherman, K.J.; Von Korff, S.M. Impact of Opioid Dose Reduction and Risk Mitigation Initiatives on Chronic Opioid Therapy Patients at Higher Risk for Opioid-Related Adverse Outcomes. Pain Med. 2017, 19, 2450–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, J.W.; Lovejoy, T.I.; Becker, W.C.; Morasco, B.J.; Koenig, C.J.; Hoffecker, L.; Dischinger, H.R.; Dobscha, S.K.; Krebs, E. Patient Outcomes in Dose Reduction or Discontinuation of Long-Term Opioid Therapy. Ann. Intern. Med. 2017, 167, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsini, C.; Dankulov, M.M.; Colomer-De-Simón, P.; Jamakovic, A.; Mahadevan, P.; Vahdat, A.; Bassler, K.E.; Toroczkai, Z.; Boguñá, M.; Caldarelli, G.; et al. Quantifying randomness in real networks. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gelman, R.; Berg, M.; Ilan, Y. A Subject-Tailored Variability-Based Platform for Overcoming the Plateau Effect in Sports Training: A Narrative Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1722. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031722
Gelman R, Berg M, Ilan Y. A Subject-Tailored Variability-Based Platform for Overcoming the Plateau Effect in Sports Training: A Narrative Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(3):1722. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031722
Chicago/Turabian StyleGelman, Ram, Marc Berg, and Yaron Ilan. 2022. "A Subject-Tailored Variability-Based Platform for Overcoming the Plateau Effect in Sports Training: A Narrative Review" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 3: 1722. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031722
APA StyleGelman, R., Berg, M., & Ilan, Y. (2022). A Subject-Tailored Variability-Based Platform for Overcoming the Plateau Effect in Sports Training: A Narrative Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(3), 1722. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031722






