S-Fertilizer (Elemental Sulfur) Improves the Phytoextraction of Cadmium through Solanum nigrum L.
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil Sampling and Analysis
2.2. Experimental Plan
2.3. Plant Harvesting
2.4. Determination of Photosynthetic Pigments and Gas Exchange Parameters
2.5. Determination of Oxidative Stress Biomarkers
2.6. Determination of Antioxidant Enzyme Activities
2.7. Cd Determination in Plants
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Result
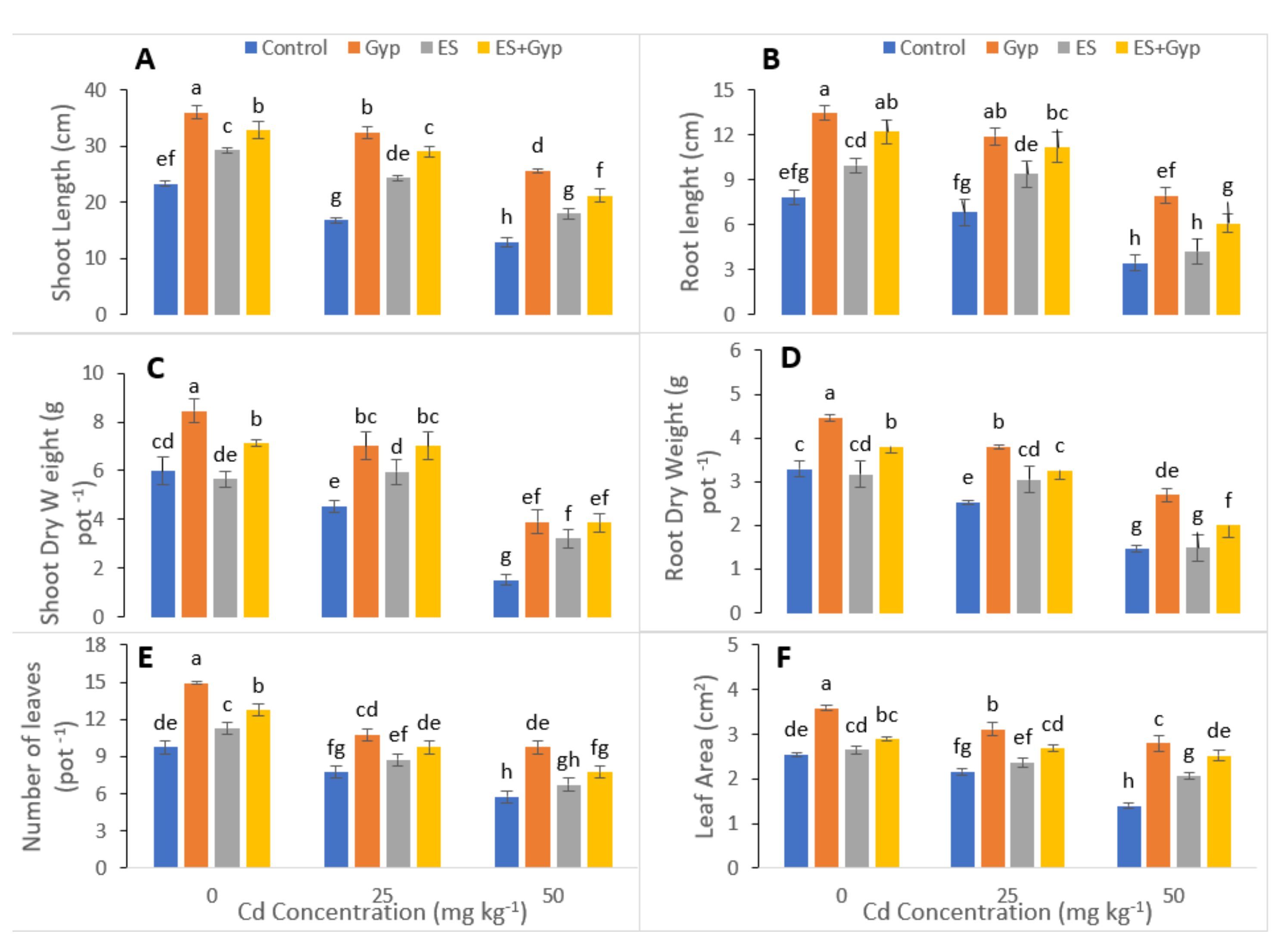
3.1. Effect of S-Fertilizer on Biomass and Growth of the Plants under Cd Contaminated Soil
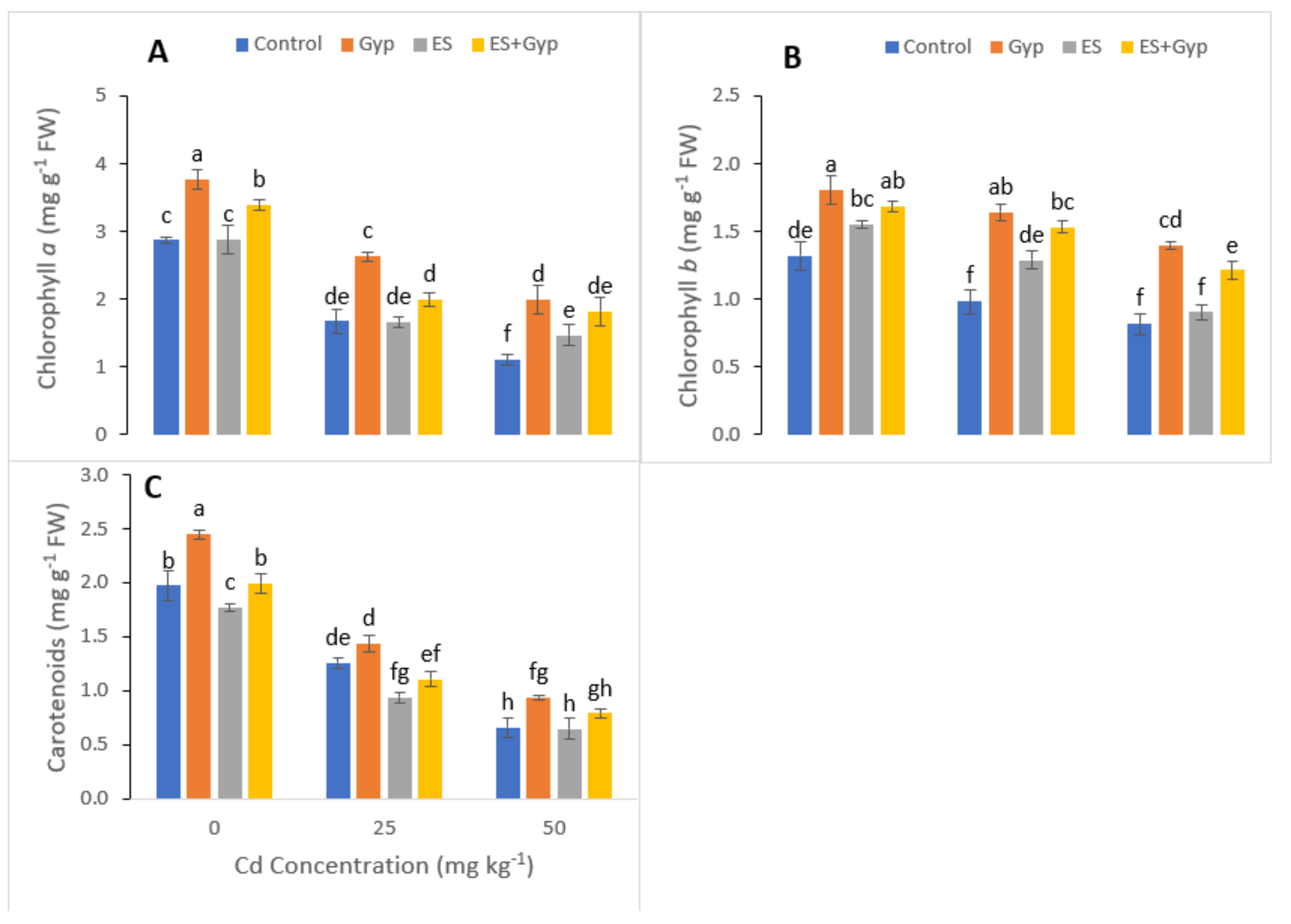
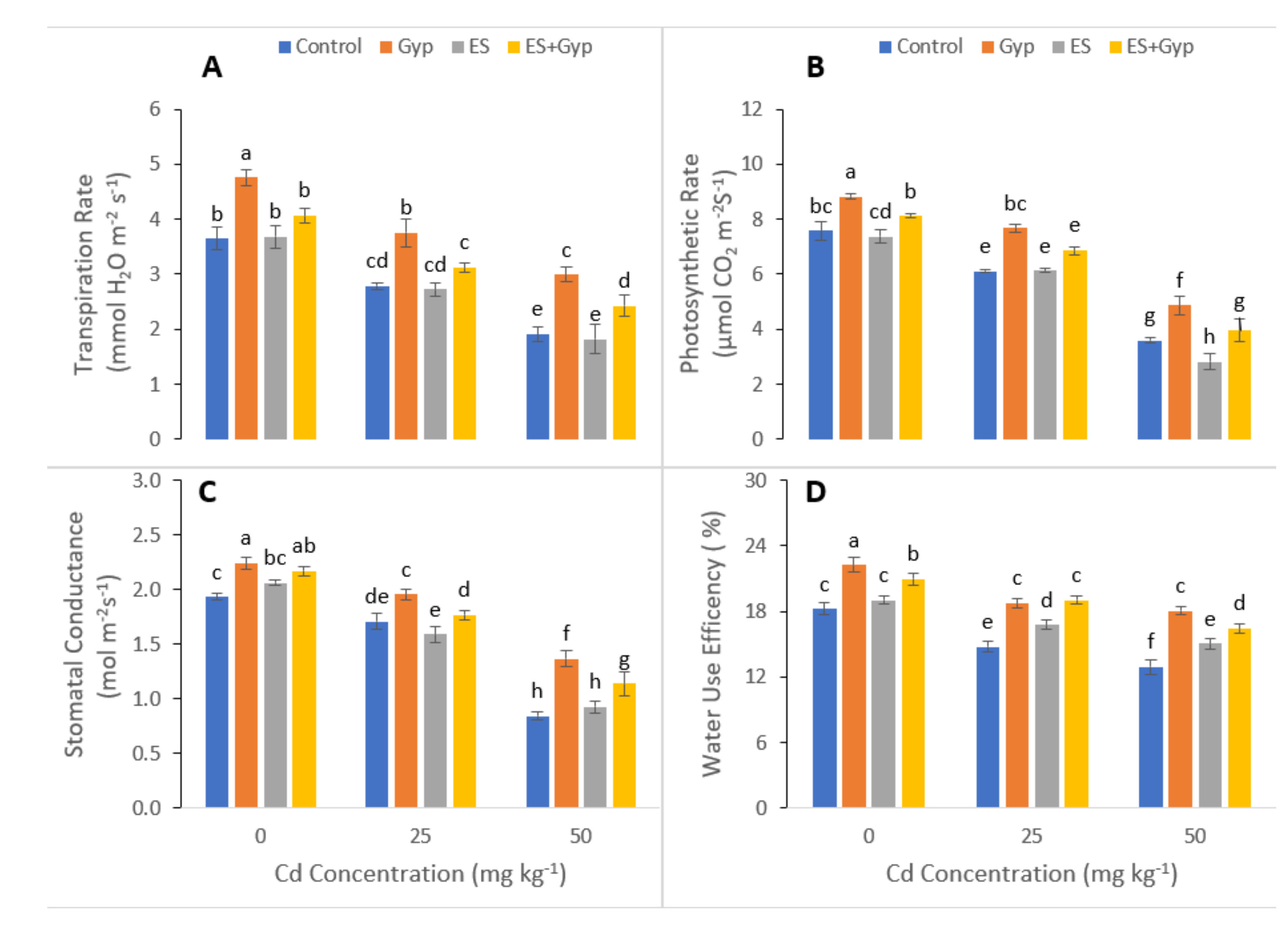
3.2. Effect of S-Fertilizer on Photosynthetic Pigments and Gas Exchange Characteristics of the Plants under Cd Contaminated Soil
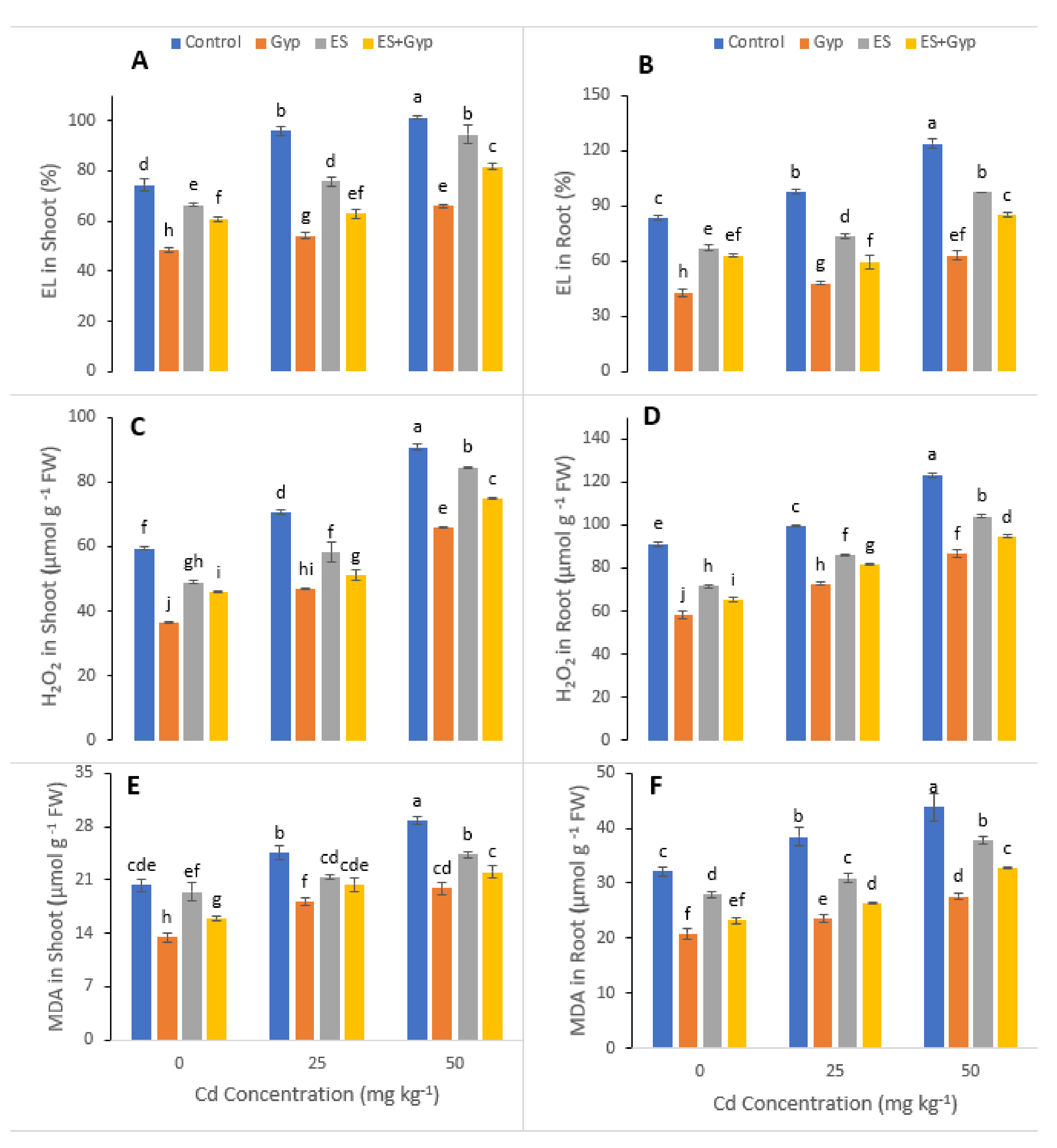
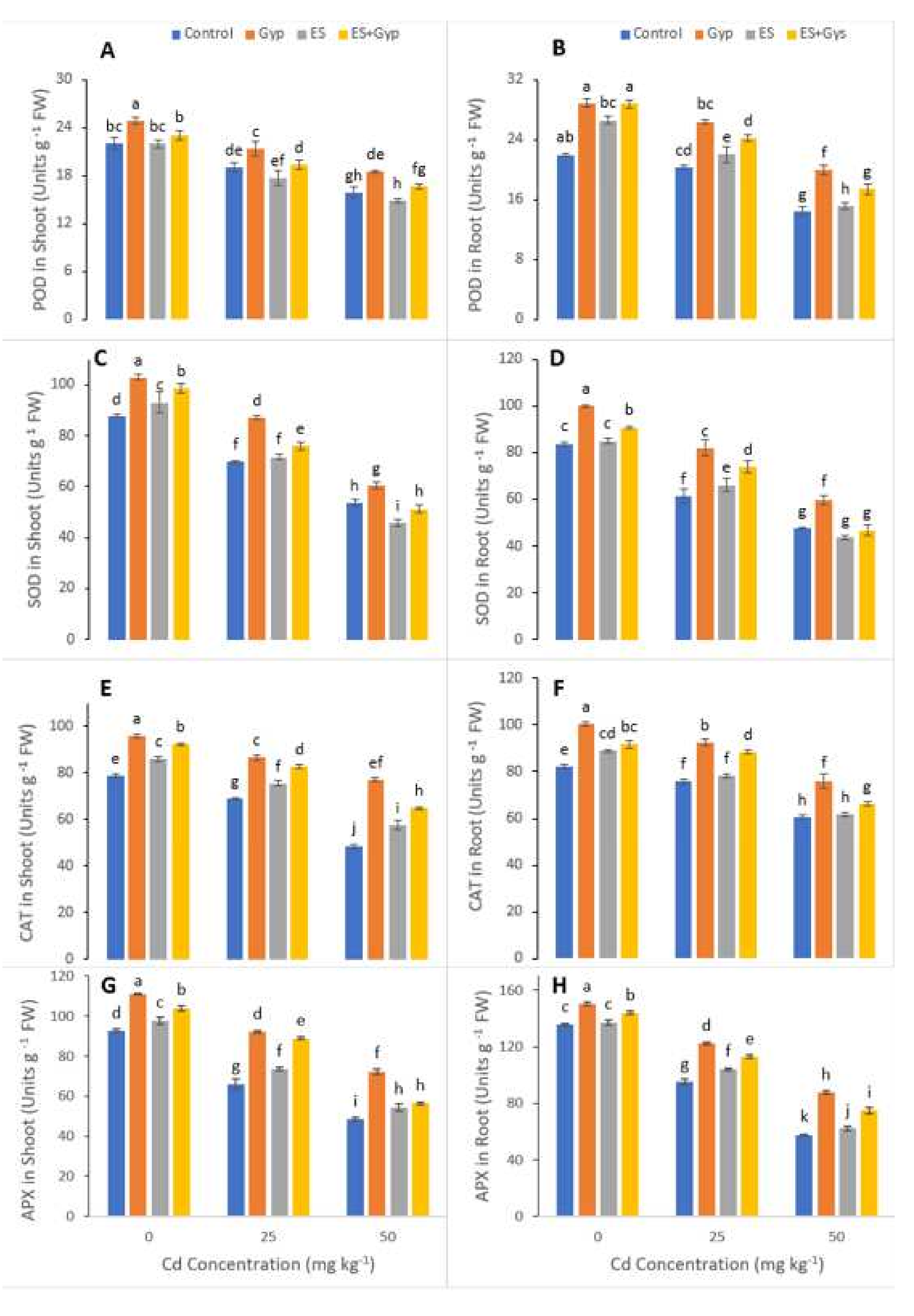
3.3. Effect of S-Fertilizer on Oxidative Stress Indicators and Response of Antioxidative Enzymes of the Plants under Cd Contaminated Soil
3.4. Effect of S-Fertilizer on Cd Accumulation of the Plants under Cd Contaminated Soil
3.5. Correlation between Various Growth and Physiological Parameters with Cd Uptake and Accumulation
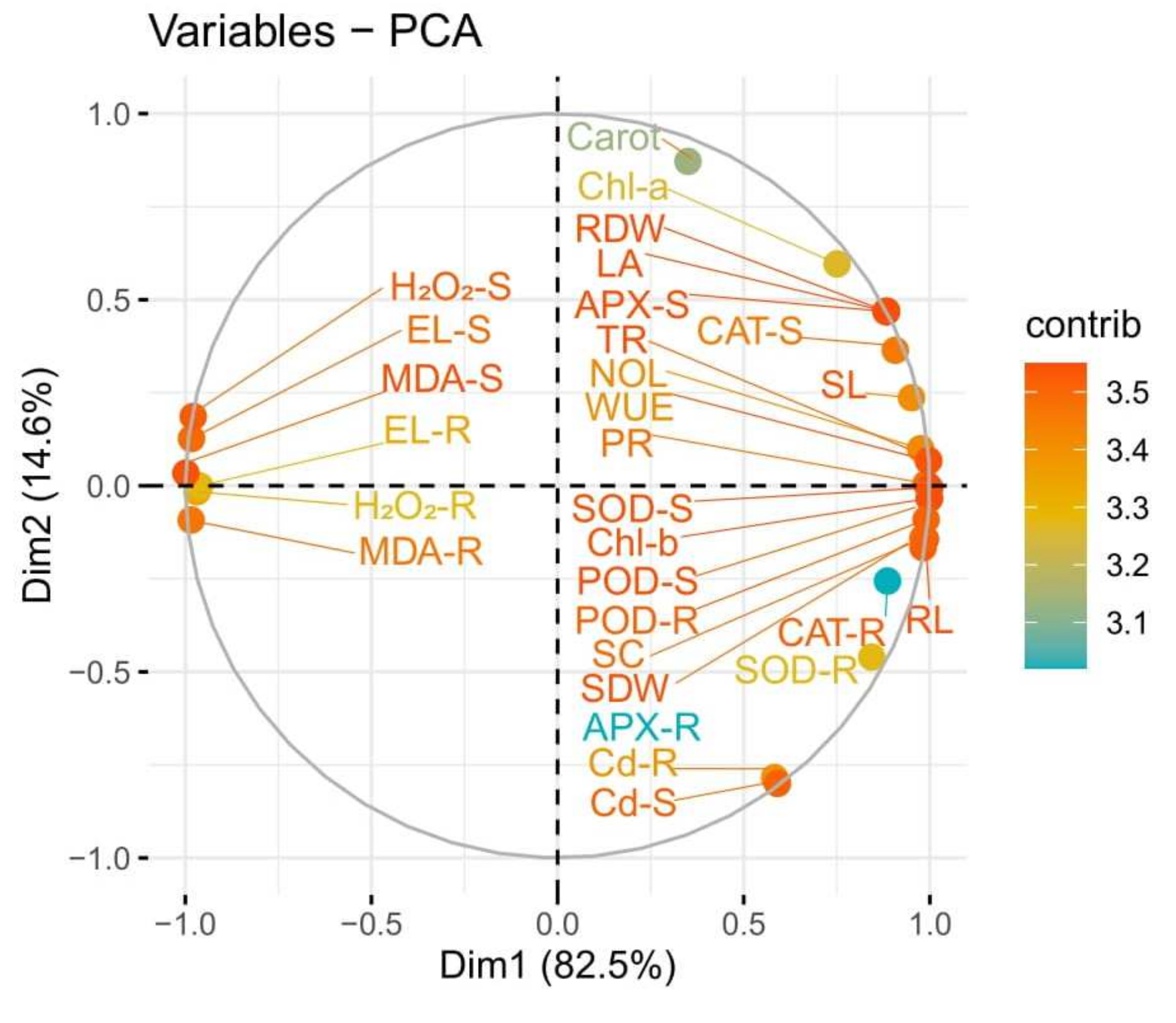
3.6. Principal Component Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, Z.I.; Mansha, A.; Saleem, M.H.; Tariq, F.; Ahmad, K.; Ahmad, T.; Farooq Awan, M.U.; Abualreesh, M.H.; Alatawi, A.; Ali, S. Trace metal accumulation in rice variety kainat irrigated with canal water. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtaza, G.; Riaz, U.; Aziz, H.; Shaheen, N.; Sohail, M.I.; Saleem, M.H.; Abualreesh, M.H.; Alatawi, A.; Ali, S. Health risk assessment, pore water chemistry, and assessment of trace metals transfer from two untreated sewage sludge types to tomato crop (Lycopersicon esculentum) at different application levels. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Mfarrej, M.F.B.; El-Esawi, M.A.; Waseem, M.; Alatawi, A.; Nafees, M.; Saleem, M.H.; Rizwan, M.; Yasmeen, T.; Anayat, A.; et al. Chromium-resistant Staphylococcus aureus alleviates chromium toxicity by developing synergistic relationships with zinc oxide nanoparticles in wheat. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 230, 113142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tariq, F.; Wang, X.; Saleem, M.H.; Khan, Z.I.; Ahmad, K.; Saleem Malik, I.; Munir, M.; Mahpara, S.; Mehmood, N.; Ahmad, T.; et al. Risk assessment of heavy metals in basmati rice: Implications for public health. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.H.; Kamran, M.; Zhou, Y.; Parveen, A.; Rehman, M.; Ahmar, S.; Malik, Z.; Mustafa, A.; Anjum, R.M.A.; Wang, B. Appraising growth, oxidative stress and copper phytoextraction potential of flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) grown in soil differentially spiked with copper. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 257, 109994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaheer, I.E.; Ali, S.; Saleem, M.H.; Arslan Ashraf, M.; Ali, Q.; Abbas, Z.; Rizwan, M.; El-Sheikh, M.A.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Wijaya, L. Zinc-lysine supplementation mitigates oxidative stress in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) by preventing phytotoxicity of chromium, when irrigated with tannery wastewater. Plants 2020, 9, 1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.H.; Rehman, M.; Kamran, M.; Afzal, J.; Noushahi, H.A.; Liu, L. Investigating the potential of different jute varieties for phytoremediation of copper-contaminated soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 30367–30377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.H.; Ali, S.; Irshad, S.; Hussaan, M.; Rizwan, M.; Rana, M.S.; Hashem, A.; Abd Allah, E.F.; Ahmad, P. Copper uptake and accumulation, ultra-structural alteration, and bast fibre yield and quality of fibrous jute (Corchorus capsularis L.) plants grown under two different soils of China. Plants 2020, 9, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rehman, M.; Saleem, M.H.; Fahad, S.; Maqbool, Z.; Peng, D.; Deng, G.; Liu, L. Medium nitrogen optimized Boehmeria nivea L. growth in copper contaminated soil. Chemosphere 2020, 266, 128972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Lei, M.; Chen, T. Cost–benefit calculation of phytoremediation technology for heavy-metal-contaminated soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 563, 796–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, M.; Malik, Z.; Parveen, A.; Huang, L.; Riaz, M.; Bashir, S.; Mustafa, A.; Abbasi, G.H.; Xue, B.; Ali, U. Ameliorative effects of biochar on rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) growth and heavy metal immobilization in soil irrigated with untreated wastewater. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2019, 39, 266–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhu, P.M.; Sadagopan, R.S. Effect of heavy metals on growth and development of cultivated plants with reference to cadmium, chromium and lead–A review. J. Stress Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 16, 84–102. [Google Scholar]
- Nagajyoti, P.C.; Lee, K.D.; Sreekanth, T. Heavy metals, occurrence and toxicity for plants: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2010, 8, 199–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Heng, S.; Munis, M.F.H.; Fahad, S.; Yang, X. Phytoremediation of heavy metals assisted by plant growth promoting (PGP) bacteria: A review. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2015, 117, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.; Hussain, S.; El-Esawi, M.A.; Rana, M.S.; Saleem, M.H.; Riaz, M.; Ashraf, U.; Potcho, M.P.; Duan, M.; Rajput, I.A. Molybdenum supply alleviates the cadmium toxicity in fragrant rice by modulating oxidative stress and antioxidant gene expression. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.; Hussain, S.; Rana, M.S.; Saleem, M.H.; Rasul, F.; Ali, K.H.; Potcho, M.P.; Pan, S.; Duan, M.; Tang, X. Molybdenum improves 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline, grain quality traits and yield attributes in fragrant rice through efficient nitrogen assimilation under cadmium toxicity. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 211, 111911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, J.; Wang, X.; Saleem, M.-H.; Sun, X.; Hussain, S.; Khan, I.; Rana, M.-S.; Ahmed, S.; Awan, S.-A.; Fiaz, S.; et al. Application of ferrous sulfate alleviates negative impact of cadmium in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Biocell 2021, 45, 1631–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, J.; Saleem, M.H.; Batool, F.; Elyamine, A.M.; Rana, M.S.; Shaheen, A.; El-Esawi, M.A.; Tariq Javed, M.; Ali, Q.; Arslan Ashraf, M.; et al. Role of ferrous sulfate (FeSO4) in resistance to cadmium stress in two rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, M.; Ali, S.; Abbas, T.; Zia-ur-Rehman, M.; Hannan, F.; Keller, C.; Al-Wabel, M.I.; Ok, Y.S. Cadmium minimization in wheat: A critical review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 130, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoseini, S.M.; Zargari, F. Cadmium in plants: A review. Int. J. Farming Allied Sci. 2013, 2, 579–581. [Google Scholar]
- Shanying, H.; Xiaoe, Y.; Zhenli, H.; Baligar, V.C. Morphological and physiological responses of plants to cadmium toxicity: A review. Pedosphere 2017, 27, 421–438. [Google Scholar]
- Heile, A.O.; Zaman, Q.U.; Aslam, Z.; Hussain, A.; Aslam, M.; Saleem, M.H.; Abualreesh, M.H.; Alatawi, A.; Ali, S. Alleviation of cadmium phytotoxicity using silicon fertilization in wheat by altering antioxidant metabolism and osmotic adjustment. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, M.T.; Saleem, M.H.; Aslam, S.; Rehman, M.; Iqbal, N.; Begum, R.; Ali, S.; Alsahli, A.A.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Wijaya, L. Elucidating silicon-mediated distinct morpho-physio-biochemical attributes and organic acid exudation patterns of cadmium stressed ajwain (Trachyspermum ammi L.). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 157, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, D.K.; Singh, V.P.; Kumar, D.; Chauhan, D.K. Rice seedlings under cadmium stress: Effect of silicon on growth, cadmium uptake, oxidative stress, antioxidant capacity and root and leaf structures. Chem. Ecol. 2012, 28, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.H.; Ali, S.; Rehman, M.; Rana, M.S.; Rizwan, M.; Kamran, M.; Imran, M.; Riaz, M.; Soliman, M.H.; Elkelish, A. Influence of phosphorus on copper phytoextraction via modulating cellular organelles in two jute (Corchorus capsularis L.) varieties grown in a copper mining soil of Hubei Province, China. Chemosphere 2020, 248, 126032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleem, M.H.; Ali, S.; Rehman, M.; Rizwan, M.; Kamran, M.; Mohamed, I.A.; Bamagoos, A.A.; Alharby, H.F.; Hakeem, K.R.; Liu, L. Individual and combined application of EDTA and citric acid assisted phytoextraction of copper using jute (Corchorus capsularis L.) seedlings. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 19, 100895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parveen, A.; Saleem, M.H.; Kamran, M.; Haider, M.Z.; Chen, J.-T.; Malik, Z.; Rana, M.S.; Hassan, A.; Hur, G.; Javed, M.T. Effect of citric acid on growth, ecophysiology, chloroplast ultrastructure, and phytoremediation potential of jute (Corchorus capsularis L.) seedlings exposed to copper stress. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, M.; Danish, M.; Saleem, M.H.; Malik, Z.; Parveen, A.; Abbasi, G.H.; Jamil, M.; Ali, S.; Afzal, S.; Riaz, M. Application of abscisic acid and 6-benzylaminopurine modulated morpho-physiological and antioxidative defense responses of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) by minimizing cobalt uptake. Chemosphere 2020, 263, 128169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.H.; Fahad, S.; Adnan, M.; Ali, M.; Rana, M.S.; Kamran, M.; Ali, Q.; Hashem, I.A.; Bhantana, P.; Ali, M.; et al. Foliar application of gibberellic acid endorsed phytoextraction of copper and alleviates oxidative stress in jute (Corchorus capsularis L.) plant grown in highly copper-contaminated soil of China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 37121–37133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.H.; Fahad, S.; Khan, S.U.; Ahmar, S.; Khan, M.H.U.; Rehman, M.; Maqbool, Z.; Liu, L. Morpho-physiological traits, gaseous exchange attributes, and phytoremediation potential of jute (Corchorus capsularis L.) grown in different concentrations of copper-contaminated soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 189, 109915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, P.; Abdel Latef, A.A.; Abd Allah, E.F.; Hashem, A.; Sarwat, M.; Anjum, N.A.; Gucel, S. Calcium and potassium supplementation enhanced growth, osmolyte secondary metabolite production, and enzymatic antioxidant machinery in cadmium-exposed chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, P.; Ahanger, M.A.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Wijaya, L.; Alam, P. Exogenous application of nitric oxide modulates osmolyte metabolism, antioxidants, enzymes of ascorbate-glutathione cycle and promotes growth under cadmium stress in tomato. Protoplasma 2018, 255, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleem, M.H.; Ali, S.; Rehman, M.; Hasanuzzaman, M.; Rizwan, M.; Irshad, S.; Shafiq, F.; Iqbal, M.; Alharbi, B.M.; Alnusaire, T.S. Jute: A potential candidate for phytoremediation of metals—A review. Plants 2020, 9, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saleem, M.H.; Ali, S.; Hussain, S.; Kamran, M.; Chattha, M.S.; Ahmad, S.; Aqeel, M.; Rizwan, M.; Aljarba, N.H.; Alkahtani, S. Flax (Linum usitatissimum L.): A potential candidate for phytoremediation? Biological and economical points of view. Plants 2020, 9, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saleem, M.H.; Fahad, S.; Rehman, M.; Saud, S.; Jamal, Y.; Khan, S.; Liu, L. Morpho-physiological traits, biochemical response and phytoextraction potential of short-term copper stress on kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) seedlings. PeerJ 2020, 8, e8321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhantana, P.; Rana, M.S.; Sun, X.-C.; Moussa, M.G.; Saleem, M.H.; Syaifudin, M.; Shah, A.; Poudel, A.; Pun, A.B.; Bhat, M.A. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and its major role in plant growth, zinc nutrition, phosphorous regulation and phytoremediation. Symbiosis 2021, 84, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, W.J.; Bozzo, G.G.; Carlow, C.; MacDonald, W.N.; Shelp, B.J. Strategic timing and rate of sulphur fertilization improves sulphur use efficiency in subirrigated greenhouse-grown chrysanthemums. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2019, 99, 654–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irshad, S.; Xie, Z.; Kamran, M.; Nawaz, A.; Mehmood, S.; Gulzar, H.; Saleem, M.H.; Rizwan, M.; Malik, Z.; Parveen, A.; et al. Biochar composite with microbes enhanced arsenic biosorption and phytoextraction by Typha latifolia in hybrid vertical subsurface flow constructed wetland. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 291, 118269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganie, M.A.; Akhter, F.; Bhat, M.; Najar, G. Growth, yield and quality of French bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) as influenced by sulphur and boron application on inceptisols of Kashmir. Bioscan 2014, 9, 513–518. [Google Scholar]
- Capaldi, F.R.; Gratão, P.L.; Reis, A.R.; Lima, L.W.; Azevedo, R.A. Sulfur metabolism and stress defense responses in plants. Trop. Plant Biol. 2015, 8, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saito, K. Sulfur assimilatory metabolism. The long and smelling road. Plant Physiol. 2004, 136, 2443–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qayyum, M.F.; ur Rehman, M.Z.; Ali, S.; Rizwan, M.; Naeem, A.; Maqsood, M.A.; Khalid, H.; Rinklebe, J.; Ok, Y.S. Residual effects of monoammonium phosphate, gypsum and elemental sulfur on cadmium phytoavailability and translocation from soil to wheat in an effluent irrigated field. Chemosphere 2017, 174, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, M.; Akmal, M.; Ullah, S.; Hassan, M.; Farooq, S. Effectiveness of zinc and gypsum application against cadmium toxicity and accumulation in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2017, 48, 1659–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UdDin, I.; Bano, A.; Masood, S. Chromium toxicity tolerance of Solanum nigrum L. and Parthenium hysterophorus L. plants with reference to ion pattern, antioxidation activity and root exudation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 113, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fidalgo, F.; Azenha, M.; Silva, A.F.; de Sousa, A.; Santiago, A.; Ferraz, P.; Teixeira, J. Copper-induced stress in Solanum nigrum L. and antioxidant defense system responses. Food Energy Secur. 2013, 2, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.R.; Ullah, I.; Khan, A.L.; Hong, S.-J.; Waqas, M.; Park, G.-S.; Kwak, Y.; Choi, J.; Jung, B.-K.; Park, M. Phytostabilization and physicochemical responses of Korean ecotype Solanum nigrum L. to cadmium contamination. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2014, 225, 2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, H.; Zia-ur-Rehman, M.; Naeem, A.; Khalid, M.U.; Rizwan, M.; Ali, S.; Umair, M.; Sohail, M.I. Solanum nigrum L.: A novel hyperaccumulator for the phyto-management of cadmium contaminated soils. In Cadmium Toxicity and Tolerance in Plants; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 451–477. [Google Scholar]
- Bouyoucos, G.J. Hydrometer method improved for making particle size analyses of soils 1. Agron. J. 1962, 54, 464–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amacher, M.C. Nickel, cadmium, and lead. Methods Soil Anal. Part 3 Chem. Methods 1996, 5, 739–768. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, M.L. Soil Chemical Analysis; Constable and Co Ltd.: London, UK, 1962; p. 497. [Google Scholar]
- Moodie, C.; Smith, H.; McCreery, R. Laboratory Manual for Soil Fertility (Mimeographed); Washington State College: Washington, DC, USA, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Arnon, D.I. Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. Polyphenoloxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol. 1949, 24, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Austin, R.B. Prospects for Genetically Increasing the Photosynthetic Capacity of Crops; CIMMYT: Veracruz, Mexico, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Dionisio-Sese, M.L.; Tobita, S. Antioxidant responses of rice seedlings to salinity stress. Plant Sci. 1998, 135, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, R.L.; Packer, L. Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts: I. Kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1968, 125, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, S.; Choudhuri, M.A. Glycolate metabolism of three submersed aquatic angiosperms: Effect of heavy metals. Aquat. Bot. 1981, 11, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-N.; Pan, S.-M. Assay of superoxide dismutase activity by combining electrophoresis and densitometry. Bot. Bull. Acad. Sin. 1996, 37, 107–111. [Google Scholar]
- Sakharov, I.Y.; Ardila, G.B. Variations of peroxidase activity in cocoa (Theobroma cacao L.) beans during their ripening, fermentation and drying. Food Chem. 1999, 65, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aebi, H. vitro. In Methods in Enzymology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1984; Volume 105, pp. 121–126. [Google Scholar]
- Nakano, Y.; Asada, K. Hydrogen peroxide is scavenged by ascorbate-specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts. Plant Cell Physiol. 1981, 22, 867–880. [Google Scholar]
- Jezek, M.; Geilfus, C.-M.; Mühling, K.-H. Glutamine synthetase activity in leaves of Zea mays L. as influenced by magnesium status. Planta 2015, 242, 1309–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, S.; Jamshieed, S.; Rasool, S.; Ashraf, M.; Akram, N.A.; Ahmad, P. Modulation of plant growth and metabolism in cadmium-enriched environments. In Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2014; pp. 51–88. [Google Scholar]
- El-Esawi, M.A.; Elkelish, A.; Soliman, M.; Elansary, H.O.; Zaid, A.; Wani, S.H. Serratia marcescens BM1 enhances cadmium stress tolerance and phytoremediation potential of soybean through modulation of osmolytes, leaf gas exchange, antioxidant machinery, and stress-responsive genes expression. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rizwan, M.; Ali, S.; ur Rehman, M.Z.; Maqbool, A. A critical review on the effects of zinc at toxic levels of cadmium in plants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 6279–6289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saifullah Khan, M.N.; Iqbal, M.; Naeem, A.; Bibi, S.; Waraich, E.A.; Dahlawi, S. Elemental sulfur improves growth and phytoremediative ability of wheat grown in lead-contaminated calcareous soil. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2016, 18, 1022–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaheer, I.E.; Ali, S.; Saleem, M.H.; Ali, M.; Riaz, M.; Javed, S.; Sehar, A.; Abbas, Z.; Rizwan, M.; El-Sheikh, M.A.; et al. Interactive role of zinc and iron lysine on Spinacia oleracea L. growth, photosynthesis and antioxidant capacity irrigated with tannery wastewater. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2020, 26, 2435–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, I.A.; Shalby, N.; El-Badri, A.M.; Saleem, M.H.; Khan, M.N.; Nawaz, M.A.; Qin, M.; Agami, R.A.; Kuai, J.; Wang, B. Stomata and xylem vessels traits improved by melatonin application contribute to enhancing salt tolerance and fatty acid composition of Brassica napus L. plants. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.H.; Wang, X.; Ali, S.; Zafar, S.; Nawaz, M.; Adnan, M.; Fahad, S.; Shah, A.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Hefft, D.I.; et al. Interactive effects of gibberellic acid and NPK on morpho-physio-biochemical traits and organic acid exudation pattern in coriander (Coriandrum sativum L.) grown in soil artificially spiked with boron. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 167, 884–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghani, M.A.; Abbas, M.M.; Ali, B.; Aziz, R.; Qadri, R.W.K.; Noor, A.; Azam, M.; Bahzad, S.; Saleem, M.H.; Abualreesh, M.H.; et al. Alleviating role of gibberellic acid in enhancing plant growth and stimulating phenolic compounds in carrot (Daucus carota L.) under lead stress. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, I.; Saleem, M.H.; Mumtaz, S.; Rasheed, R.; Ashraf, M.A.; Maqsood, F.; Rehman, M.; Yasmin, H.; Ahmed, S.; Ishtiaq, M. Choline chloride mediates chromium tolerance in spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) by restricting its uptake in relation to morpho-physio-biochemical attributes. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2021, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, A.; Rizwan, M.; Ali, S.; ur Rehman, M.Z.; Ishaque, W.; Riaz, M.A.; Maqbool, A. Effect of foliar-applied iron complexed with lysine on growth and cadmium (Cd) uptake in rice under Cd stress. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 20691–20699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.H.; Fahad, S.; Khan, S.U.; Din, M.; Ullah, A.; Sabagh, A.E.L.; Hossain, A.; Llanes, A.; Liu, L. Copper-induced oxidative stress, initiation of antioxidants and phytoremediation potential of flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) seedlings grown under the mixing of two different soils of China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 5211–5221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaheer, I.E.; Ali, S.; Saleem, M.H.; Noor, I.; El-Esawi, M.A.; Hayat, K.; Rizwan, M.; Abbas, Z.; El-Sheikh, M.A.; Alyemeni, M.N. Iron–lysine mediated alleviation of chromium toxicity in spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) plants in relation to morpho-physiological traits and iron uptake when irrigated with tannery wastewater. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.; Yang, M.; Fahad, S.; Saleem, M.H.; Liu, L.; Liu, F.; Deng, G. Morpho-physiological traits, antioxidant capacity, and nitrogen metabolism in ramie under nitrogen fertilizer. Agron. J. 2020, 112, 2988–2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, S.A.; Hayat, S.; Ahmad, A. Brassinosteroids protect photosynthetic machinery against the cadmium induced oxidative stress in two tomato cultivars. Chemosphere 2011, 84, 1446–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaheer, I.E.; Ali, S.; Saleem, M.H.; Yousaf, H.S.; Malik, A.; Abbas, Z.; Rizwan, M.; Abualreesh, M.H.; Alatawi, A.; Wang, X. Combined application of zinc and iron-lysine and its effects on morpho-physiological traits, antioxidant capacity and chromium uptake in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0262140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, M.T.; Tanwir, K.; Abbas, S.; Saleem, M.H.; Iqbal, R.; Chaudhary, H.J. Chromium retention potential of two contrasting Solanum lycopersicum Mill. cultivars as deciphered by altered pH dynamics, growth, and organic acid exudation under Cr stress. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 27542–27554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, M.; Saleem, M.H.; Fahad, S.; Bashir, S.; Peng, D.; Deng, G.; Alamri, S.; Siddiqui, M.H.; Khan, S.M.; Shah, R.A. Effects of rice straw biochar and nitrogen fertilizer on ramie (Boehmeria nivea L.) morpho-physiological traits, copper uptake and post-harvest soil characteristics, grown in an aged-copper contaminated soil. J. Plant Nutr. 2021, 45, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumtaz, S.; Saleem, M.H.; Hameed, M.; Batool, F.; Parveen, A.; Amjad, S.F.; Mahmood, A.; Arfan, M.; Ahmed, S.; Yasmin, H. Anatomical adaptations and ionic homeostasis in aquatic halophyte Cyperus laevigatus L. under high salinities. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 2655–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perveen, R.; Wang, X.; Jamil, Y.; Ali, Q.; Ali, S.; Zakaria, M.Q.; Afzaal, M.; Kasana, R.A.; Saleem, M.H.; Fiaz, S. Quantitative determination of the effects of he–ne laser irradiation on seed thermodynamics, germination attributes and metabolites of safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) in relation with the activities of germination enzymes. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.; Amjad, S.F.; Saleem, M.H.; Yasmin, H.; Imran, M.; Riaz, M.; Ali, Q.; Joyia, F.A.; Ahmed, S.; Ali, S. Foliar application of ascorbic acid enhances salinity stress tolerance in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) through modulation of morpho-physio-biochemical attributes, ions uptake, osmo-protectants and stress response genes expression. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 4276–4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, H.; Wang, X.; Murtaza, G.; Ashar, A.; Hussain, S.; Abid, M.; Murtaza, B.; Saleem, M.H.; Fiaz, S.; Ali, S. Evaluation of Compost and Biochar to Mitigate Chlorpyrifos Pollution in Soil and Their Effect on Soil Enzyme Dynamics. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, A.; Akram, N.A.; Saleem, M.H.; Ashraf, M.; Ahmed, S.; Ali, S.; Abdullah Alsahli, A.; Alyemeni, M.N. Seed treatment with α-tocopherol regulates growth and key physio-biochemical attributes in carrot (Daucus carota L.) plants under water limited regimes. Agronomy 2021, 11, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, M.; Ali, S.; Adrees, M.; Rizvi, H.; Zia-ur-Rehman, M.; Hannan, F.; Qayyum, M.F.; Hafeez, F.; Ok, Y.S. Cadmium stress in rice: Toxic effects, tolerance mechanisms, and management: A critical review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 17859–17879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Soil | Units |
|---|---|
| Textural Class | Sandy Clay Loam |
| Sand | 63.7% |
| Silt | 14.4% |
| Clay | 21.9% |
| pH | 7.71 |
| EC | 1.93 dS m−1 |
| HCO3−1 | 3.1 mmol L−1 |
| Total nitrogen | 0.06% |
| Available P | 2.7 mg kg−1 |
| K+ | 0.08 mmol L−1 |
| Cl−1 | 5 mmol L−1 |
| Ca+2 + Mg+2 | 14.34 mmol L−1 |
| Available Cd | 0.03 mg kg−1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alatawi, A.; Wang, X.; Maqbool, A.; Saleem, M.H.; Usman, K.; Rizwan, M.; Yasmeen, T.; Arif, M.S.; Noreen, S.; Hussain, A.; et al. S-Fertilizer (Elemental Sulfur) Improves the Phytoextraction of Cadmium through Solanum nigrum L. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031655
Alatawi A, Wang X, Maqbool A, Saleem MH, Usman K, Rizwan M, Yasmeen T, Arif MS, Noreen S, Hussain A, et al. S-Fertilizer (Elemental Sulfur) Improves the Phytoextraction of Cadmium through Solanum nigrum L. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(3):1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031655
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlatawi, Aishah, Xiukang Wang, Arosha Maqbool, Muhammad Hamzah Saleem, Kamal Usman, Muhammad Rizwan, Tahira Yasmeen, Muhammad Saleem Arif, Shamaila Noreen, Afzal Hussain, and et al. 2022. "S-Fertilizer (Elemental Sulfur) Improves the Phytoextraction of Cadmium through Solanum nigrum L." International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 3: 1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031655
APA StyleAlatawi, A., Wang, X., Maqbool, A., Saleem, M. H., Usman, K., Rizwan, M., Yasmeen, T., Arif, M. S., Noreen, S., Hussain, A., & Ali, S. (2022). S-Fertilizer (Elemental Sulfur) Improves the Phytoextraction of Cadmium through Solanum nigrum L. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(3), 1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031655










