The Microbiome–Gut–Brain Axis and Dementia: A Bibliometric Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
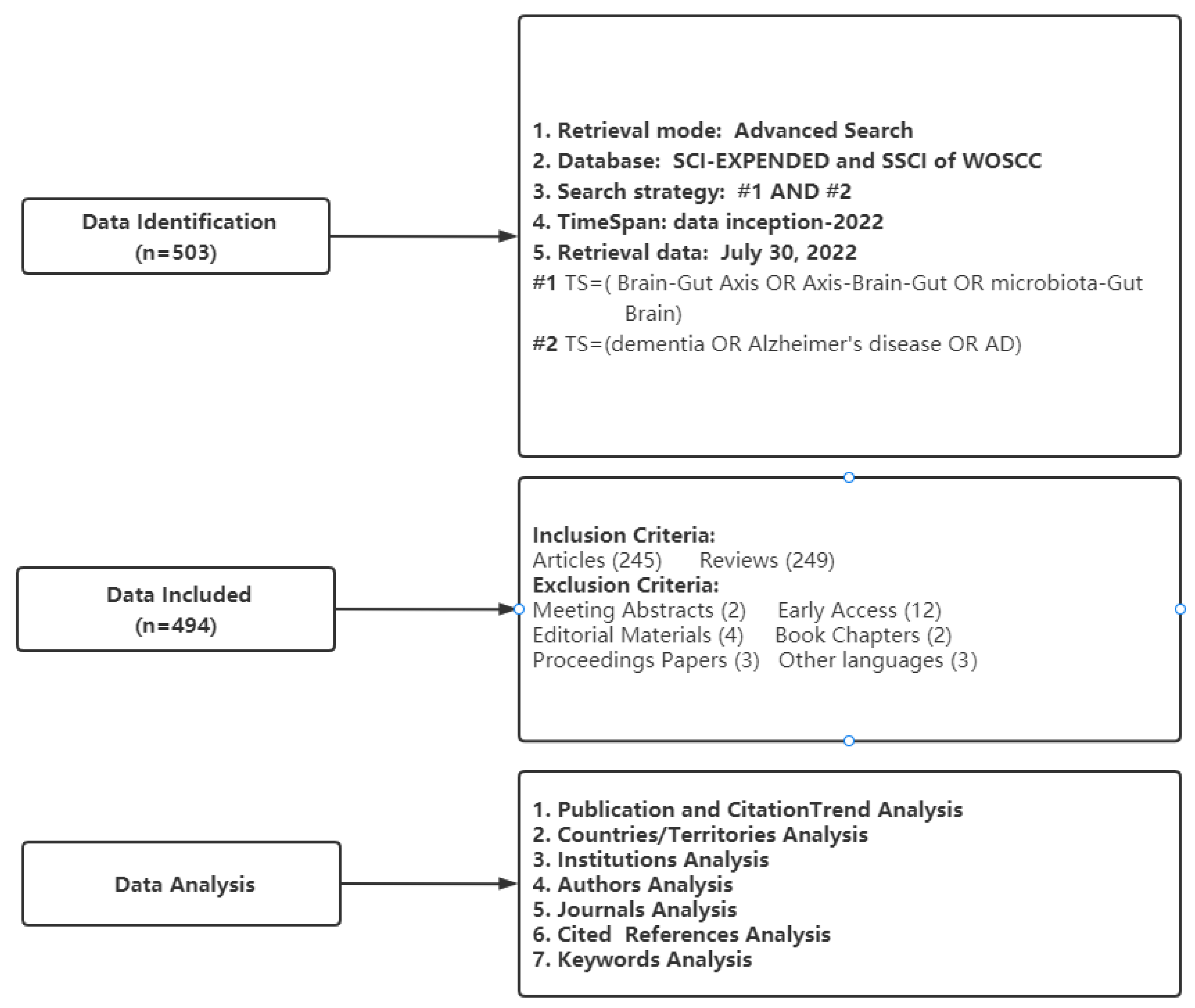
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Data Analysis
3. Results
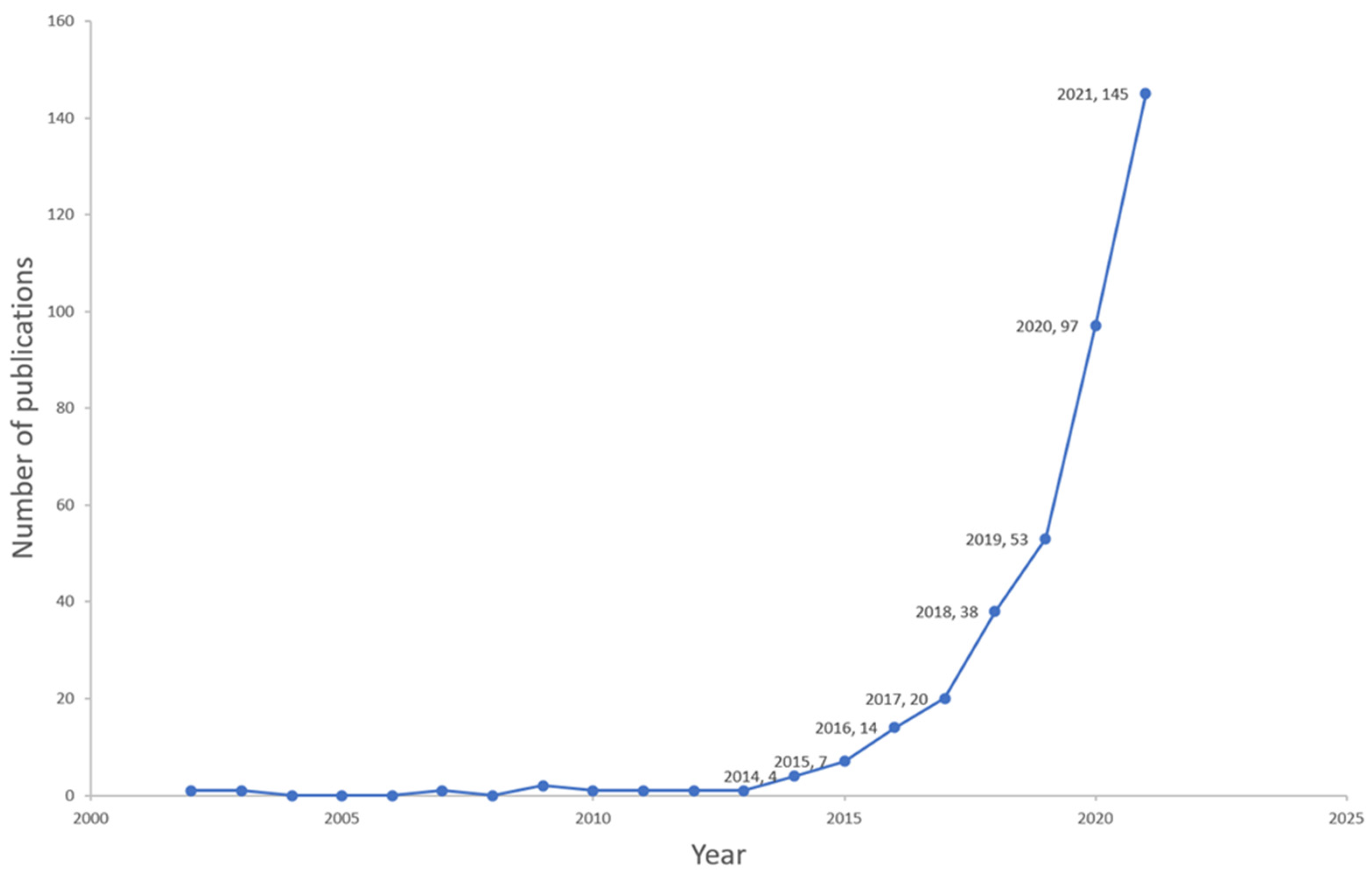
3.1. General Features of Publications
3.2. Top Cited Papers
3.3. Journal Analysis
3.4. Author Analysis
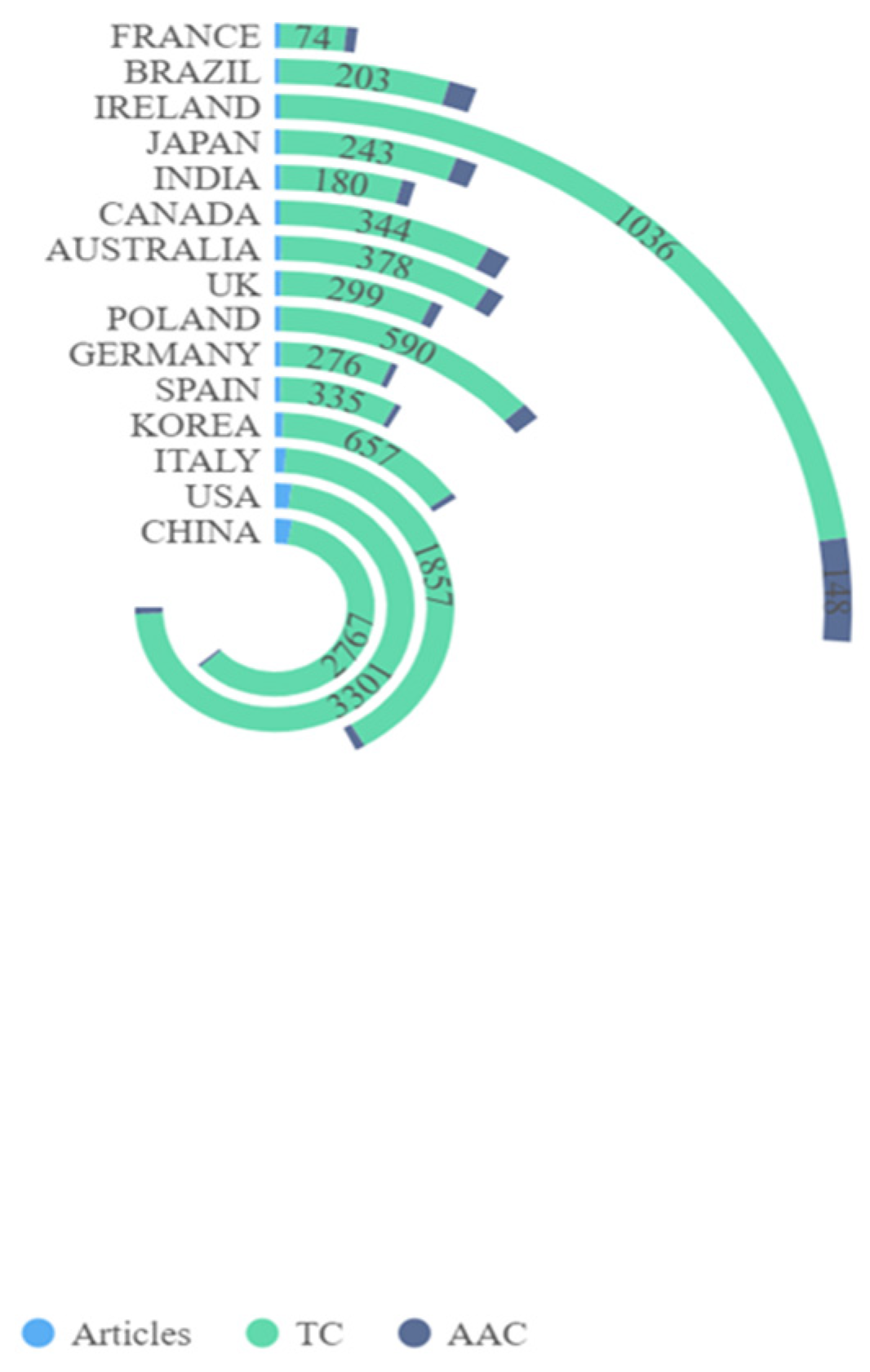
3.5. Country/Territory Analysis
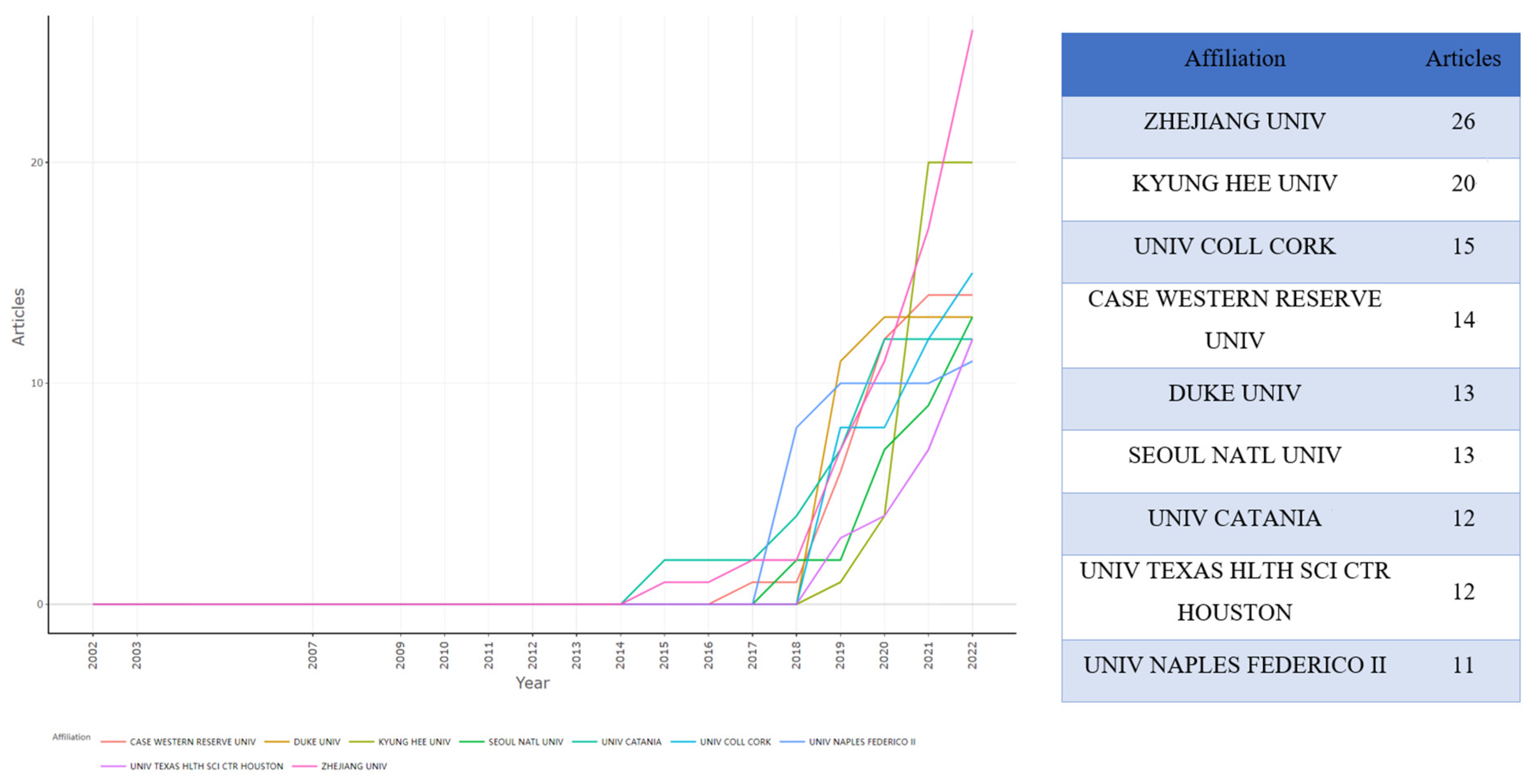
3.6. Institution Analysis
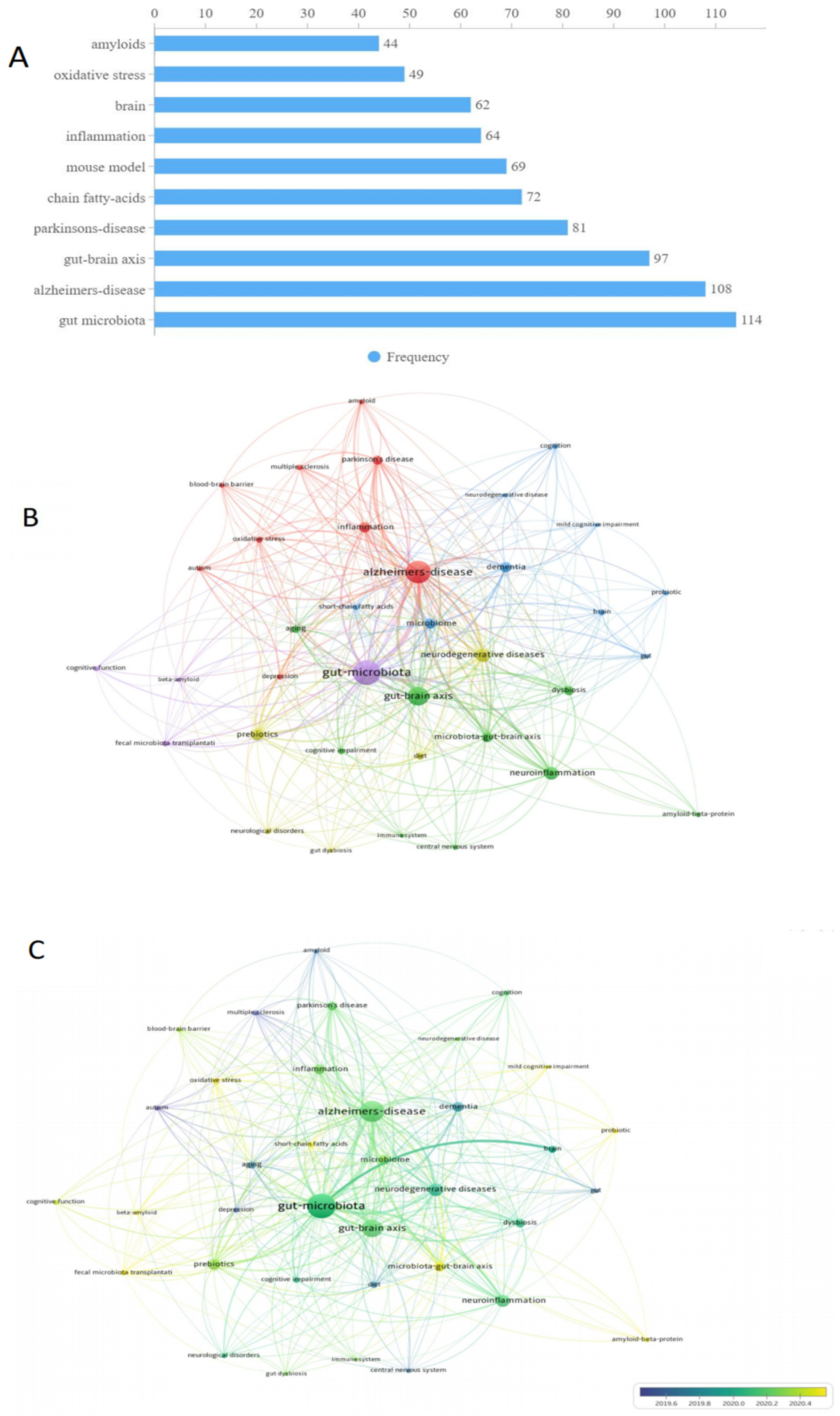
3.7. Keyword Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Claesson, M.J.; O’Toole, P.W. Evaluating the latest high-throughput molecular techniques for the exploration of microbial gut communities. Gut Microbes 2010, 1, 277–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, A.; Fonseca, S.; Carding, S.R. Gut microbes and metabolites as modulators of blood-brain barrier integrity and brain health. Gut Microbes 2020, 11, 135–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelucci, F.; Cechova, K.; Amlerova, J.; Hort, J. Antibiotics, gut microbiota, and Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, C.R.; Osadchiy, V.; Kalani, A.; Mayer, E.A. The Brain-Gut-Microbiome Axis. Cell Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 6, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharon, G.; Sampson, T.R.; Geschwind, D.H.; Mazmanian, S.K. The Central Nervous System and the Gut Microbiome. Cell 2016, 167, 915–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandilyan, M.B.; Dening, T. What is dementia. In Evidence-Based Practice in Dementia for Nurses and Nursing Students; Jessica Kingsley: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gale, S.A.; Acar, D.; Daffner, K.R. Dementia. Am. J. Med. 2018, 131, 1161–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Global Action Plan on the Public Health Response to Dementia 2017–2025; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Alzheimer’s Disease Facts and Figures. 2020 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2020, 16, 391–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Guo, J.; Shen, Y.; Huang, L.; Leng, B.; Fan, D.; Shui, L.; Chen, C. Probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics for the treatment of dementia: Protocol for a systematic review. Medicine 2020, 99, e18608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, S.M.; Surette, M.; Bercik, P. The interplay between the intestinal microbiota and the brain. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampson, T.R.; Mazmanian, S.K. Control of brain development, function, and behavior by the microbiome. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 17, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, H.E.; Bai, Y.M.; Tsai, S.J.; Su, T.P.; Chen, T.J.; Wang, Y.P.; Chen, M.H. Inflammatory bowel disease is associated with higher dementia risk: A nationwide longitudinal study. Gut 2021, 70, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fröhlich, E.E.; Farzi, A.; Mayerhofer, R.; Reichmann, F.; Jačan, A.; Wagner, B.; Zinser, E.; Bordag, N.; Magnes, C.; Fröhlich, E.; et al. Cognitive impairment by antibiotic-induced gut dysbiosis: Analysis of gut microbiota-brain communication. Brain Behav. Immun. 2016, 56, 140–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Hu, X.; Liang, S.; Li, W.; Wu, X.; Wang, L.; Jin, F. Lactobacillus fermentum NS9 restores the antibiotic induced physiological and psychological abnormalities in rats. Benef. Microbes 2015, 6, 707–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durieux, V.; Gevenois, P.A. Bibliometric indicators: Quality measurements of scientific publication. Radiology 2010, 255, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokol, P.; Blažun Vošner, H.; Završnik, J. Application of bibliometrics in medicine: A historical bibliometrics analysis. Health Info. Libr. J. 2021, 38, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Gu, D.; Zhao, T.; Zhao, Z.; Xiong, Y.; Sun, M.; Xin, C.; Zhang, Y.; Pei, L.; Sun, J. Trends in Piezo Channel Research Over the Past Decade: A Bibliometric Analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 668714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabanillas-Lazo, M.; Quispe-Vicuña, C.; Barja-Ore, J.; Fernandez-Giusti, A.; Munive-Degregori, A.; Retamozo-Siancas, Y.; Guerrero, M.E.; Mayta-Tovalino, F. A 10-Year Bibliometric Analysis of Global Research on Gut Microbiota and Parkinson’s Disease: Characteristics, Impact, and Trends. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 4144781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Hu, J.; Deng, S.; Tan, Y.; Qiu, C.; Zhang, M.; Ni, X.; Lu, H.; Wang, Z.; Li, L.; et al. Bibliometric and Visual Analysis of Research on the Links Between the Gut Microbiota and Depression From 1999 to 2019. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 587670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Long, T.; You, J.; Li, P.; Xu, Q. Bibliometric Visualization Analysis of Microbiome-Gut-Brain Axis from 2004 to 2020. Med. Sci. Monit. 2022, 28, e936037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince, M.; Bryce, R.; Albanese, E.; Wimo, A.; Ribeiro, W.; Ferri, C.P. The global prevalence of dementia: A systematic review and metaanalysis. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2013, 9, 63–75.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aria, M.; Cuccurullo, C. bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. J. Informetr. 2017, 11, 959–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 2010, 84, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittemore, R.; Chao, A.; Jang, M.; Minges, K.E.; Park, C. Methods for knowledge synthesis: An overview. Heart Lung 2014, 43, 453–461. [Google Scholar]
- Cryan, J.F.; O’Riordan, K.J.; Cowan, C.S.M.; Sandhu, K.V.; Bastiaanssen, T.F.S.; Boehme, M.; Codagnone, M.G.; Cussotto, S.; Fulling, C.; Golubeva, A.V.; et al. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 1877–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, K.; Mulak, A. Brain-Gut-Microbiota Axis in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2019, 25, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksnes, D.W.; Langfeldt, L.; Wouters, P. Citations, citation indicators, and research quality: An overview of basic concepts and theories. Sage Open 2019, 9, 2158244019829575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, S.; Lukiw, W.J. Alzheimer’s disease and the microbiome. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2013, 7, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Gut instincts: Microbiota as a key regulator of brain development, ageing and neurodegeneration. J. Physiol. 2017, 595, 489–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itzhaki, R.F.; Lathe, R.; Balin, B.J.; Ball, M.J.; Bearer, E.L.; Braak, H.; Bullido, M.J.; Carter, C.; Clerici, M.; Cosby, S.L.; et al. Microbes and Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2016, 51, 979–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, E.R.; Kemp, M.; Nguyen, T.T. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Review of Taxonomic Alterations and Potential Avenues for Interventions. Arch. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2022, 37, 595–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Lin, C.L.; Kao, C.H. Irritable Bowel Syndrome Is Associated with an Increased Risk of Dementia: A Nationwide Population-Based Study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0144589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bornmann, L.; Daniel, H.D. What do we know about the h index? J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2007, 58, 1381–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.L.; Bai, W.; Li, X.H.; Huang, H.; Cui, X.L.; Cheung, T.; Su, Z.H.; Yuan, Z.; Ng, C.H.; Xiang, Y.T. Schizophrenia and Inflammation Research: A Bibliometric Analysis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 907851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiraz, M. A Holistic Investigation of Global Outputs of COVID-19 Publications in Neurology and Neurosurgery. 2020, 4, 506–512. Eurasian J. Med. Investig. 2020, 4, 506–512. [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, J.; Garges, S.; Giovanni, M.; McInnes, P.; Wang, L.; Schloss, J.A.; Bonazzi, V.; McEwen, J.E.; Wetterstrand, K.A.; Deal, C.; et al. The NIH Human Microbiome Project. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 2317–2323. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, T.; Schloss, P.D. Dynamics and associations of microbial community types across the human body. Nature 2014, 509, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, R.E.; Lozupone, C.A.; Hamady, M.; Knight, R.; Gordon, J.I. Worlds within worlds: Evolution of the vertebrate gut microbiota. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 776–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lai, H.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yang, N.; Wang, C.; Liang, Z.; Zeng, J.; Yang, J. Visualization and Analysis in the Field of Pan-Cancer Studies and Its Application in Breast Cancer Treatment. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 635035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, C.A.; Hardy, J.; Schott, J.M. Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Neurol. 2018, 25, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, M.P.; LeVine, H., 3rd. Alzheimer’s disease and the amyloid-beta peptide. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2010, 19, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megur, A.; Baltriukienė, D.; Bukelskienė, V.; Burokas, A. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis and Alzheimer’s Disease: Neuroinflammation Is to Blame? Nutrients 2020, 13, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salminen, S.; Bouley, C.; Boutron-Ruault, M.C.; Cummings, J.H.; Franck, A.; Gibson, G.R.; Isolauri, E.; Moreau, M.C.; Roberfroid, M.; Rowland, I. Functional food science and gastrointestinal physiology and function. Br. J. Nutr. 1998, 80 (Suppl. 1), S147–S171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goswami, A.; Wendt, F.R.; Pathak, G.A.; Tylee, D.S.; De Angelis, F.; De Lillo, A.; Polimanti, R. Role of microbes in the pathogenesis of neuropsychiatric disorders. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2021, 62, 100917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cattaneo, A.; Cattane, N.; Galluzzi, S.; Provasi, S.; Lopizzo, N.; Festari, C.; Ferrari, C.; Guerra, U.P.; Paghera, B.; Muscio, C.; et al. Association of brain amyloidosis with pro-inflammatory gut bacterial taxa and peripheral inflammation markers in cognitively impaired elderly. Neurobiol. Aging 2017, 49, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minter, M.R.; Zhang, C.; Leone, V.; Ringus, D.L.; Zhang, X.; Oyler-Castrillo, P.; Musch, M.W.; Liao, F.; Ward, J.F.; Holtzman, D.M.; et al. Antibiotic-induced perturbations in gut microbial diversity influences neuro-inflammation and amyloidosis in a murine model of Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagyinszky, E.; Giau, V.V.; Shim, K.; Suk, K.; An, S.S.A.; Kim, S. Role of inflammatory molecules in the Alzheimer’s disease progression and diagnosis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 376, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, Y.P.; Bernardi, A.; Frozza, R.L. The Role of Short-Chain Fatty Acids From Gut Microbiota in Gut-Brain Communication. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.H.; Xie, R.Y.; Liu, X.L.; Chen, S.D.; Tang, H.D. Mechanisms of Short-Chain Fatty Acids Derived from Gut Microbiota in Alzheimer’s Disease. Aging Dis. 2022, 13, 1252–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueira, J.; Jonsson, P.; Nordin Adolfsson, A.; Adolfsson, R.; Nyberg, L.; Öhman, A. NMR analysis of the human saliva metabolome distinguishes dementia patients from matched controls. Mol. Biosyst. 2016, 12, 2562–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, A.; Geddes, T.; Han, B.; Bahado-Singh, R.O.; Wilson, G.D.; Imam, K.; Maddens, M.; Graham, S.F. Diagnostic Biomarkers of Alzheimer’s Disease as Identified in Saliva using 1H NMR-Based Metabolomics. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2017, 58, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaie, A.; Parker, R.D.; Abdollahi, M. Oxidative Stress and Pathogenesis of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: An Epiphenomenon or the Cause? Dig. Dis. Sci. 2007, 52, 2015–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momtaz, Y.A.; Hamid, T.A.; Ibrahim, R. Gastritis May Boost Odds of Dementia. Am. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. Other Demen. 2014, 29, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doulberis, M.; Kotronis, G.; Gialamprinou, D.; Polyzos, S.A.; Papaefthymiou, A.; Katsinelos, P.; Kountouras, J. Alzheimer’s disease and gastrointestinal microbiota; impact of Helicobacter pylori infection involvement. Int. J. Neurosci. 2021, 131, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adewuyi, E.O.; O’Brien, E.K.; Nyholt, D.R.; Porter, T.; Laws, S.M. A large-scale genome-wide cross-trait analysis reveals shared genetic architecture between Alzheimer’s disease and gastrointestinal tract disorders. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caputi, V.; Giron, M.C. Microbiome-Gut-Brain Axis and Toll-Like Receptors in Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1689. [Google Scholar]
- Fasano, A.; Visanji, N.P.; Liu, L.W.; Lang, A.E.; Pfeiffer, R.F. Gastrointestinal dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 625–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeiffer, R.F. Gastrointestinal dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2011, 17, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Yang, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Jiang, H. Meta-analysis: Association of Helicobacter pylori infection with Parkinson’s diseases. Helicobacter 2017, 22, e12398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjarnason, I.T.; Charlett, A.; Dobbs, R.J.; Dobbs, S.M.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Kerwin, R.W.; Mahler, R.F.; Oxlade, N.L.; Peterson, D.W.; Plant, J.M.; et al. Role of chronic infection and inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract in the etiology and pathogenesis of idiopathic parkinsonism. Part 2: Response of facets of clinical idiopathic parkinsonism to Helicobacter pylori eradication. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled efficacy study. Helicobacter 2005, 10, 276–287. [Google Scholar]
- Brandscheid, C.; Schuck, F.; Reinhardt, S.; Schäfer, K.H.; Pietrzik, C.U.; Grimm, M.; Hartmann, T.; Schwiertz, A.; Endres, K. Altered Gut Microbiome Composition and Tryptic Activity of the 5xFAD Alzheimer’s Mouse Model. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2017, 56, 775–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Nie, S.; Cao, M.; Marshall, C.; Gao, J.; Xiao, N.; Hu, G.; Xiao, M. Characterization of AD-like phenotype in aged APPSwe/PS1dE9 mice. Age 2016, 38, 303–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, S.A.; Sarkar, S.; Schmued, L.C. Longitudinal behavioral changes in the APP/PS1 transgenic Alzheimer’s Disease model. Behav. Brain Res. 2013, 242, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.W.; Liong, M.T.; Tsai, Y.C. New perspectives of Lactobacillus plantarum as a probiotic: The gut-heart-brain axis. J. Microbiol. 2018, 56, 601–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donthu, N.; Kumar, S.; Mukherjee, D.; Pandey, N.; Lim, W.M. How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: An overview and guidelines. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 133, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiraz, S.; Demir, E. Global Scientific Outputs of Schizophrenia Publications From 1975 to 2020: A Bibliometric Analysis. Psychiatr. Q. 2021, 92, 1725–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| SCR | Title (N = 494) | Year | Journal | FA | CA | TC | TC/Y |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis | 2019 | Psychological Review | John F. Cryan | Timothy G. Dinan | 894 | 223.50 |
| 2 | Interactions between the microbiota, immune and nervous systems in health and disease | 2017 | Nature Neuroscience | Thomas C Fung | Elaine Y Hsiao | 764 | 127.33 |
| 3 | The Gut Microbiota and Alzheimer’s Disease | 2017 | Journal of Alzheimers Disease | Chunmei Jiang | Bin Zhao | 329 | 54.83 |
| 4 | Brain-Gut-Microbiota Axis in Alzheimer’s Disease | 2019 | Journal of Neurogastroenterology and Motility | Karol Kowalski | Agata Mulak | 277 | 69.25 |
| 5 | Microbiota-Microbiome-Gut-Brain Axis and Neurodegenerative Diseases | 2017 | Current Neurology and Neuroscience Reports | Eamonn M M Quigley | Eamonn M M Quigley | 263 | 43.83 |
| 6 | Gut microbiome in health and disease: Linking the microbiome-gut-brain axis and environmental factors in the pathogenesis of systemic and neurodegenerative diseases | 2016 | Pharmacology & Therapeutics | Shivani Ghaisas | Anumantha Kanthasamy | 252 | 36.00 |
| 7 | Role of gut microbiota and nutrients in amyloid formation and pathogenesis of Alzheimer disease | 2016 | Nutrition Review | Francesca Pistollato | Maurizio Battino | 250 | 35.71 |
| 8 | The bowel and beyond: the enteric nervous system in neurological disorders | 2016 | Psychiatry Research | Meenakshi Rao | Michael D Gershon | 230 | 32.86 |
| 9 | Neuropeptide Y: A stressful review | 2016 | Neuropeptides | Florian Reichmann | Peter Holzer | 227 | 32.43 |
| 10 | Microbiome, probiotics and neurodegenerative diseases: deciphering the gut brain axis | 2017 | Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences | Susan Westfall | Satya Prakash | 211 | 35.17 |
| SCR | Journal (N = 246) | h_index | TC | NP | IF | JCR | Research Domain |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Journal of Alzheimers Disease | 8 | 620 | 23 | 4.160 | Q1 | Psychology |
| 2 | Nutrients | 9 | 423 | 19 | 6.706 | Q1 | Agricultural and Biological Sciences |
| 3 | International Journal of Molecular Sciences | 7 | 237 | 18 | 6.208 | Q1 | Chemistry |
| 4 | Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience | 9 | 386 | 14 | 5.702 | Q1 | Neuroscience |
| 5 | Frontiers in Neuroscience | 5 | 103 | 12 | 5.152 | Q2 | Neuroscience |
| 6 | Microorganisms | 6 | 83 | 8 | 4.926 | Q3 | Medicine |
| 7 | Antioxidants | 4 | 45 | 7 | 7.675 | Q1 | Agricultural and Biological Sciences |
| 8 | Current Alzheimer Research | 4 | 155 | 7 | 3.040 | Q1 | Medicine |
| 9 | Frontiers in Immunology | 3 | 82 | 7 | 8.786 | Q1 | Medicine |
| 10 | Aging-Us | 4 | 159 | 6 | 5.955 | Q2 | Biochemistry, Genetics and Molecular Biology |
| 11 | Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology | 4 | 164 | 6 | 6.073 | Q2 | Medicine |
| 12 | Frontiers in Nutrition | 4 | 32 | 6 | 6.590 | Q1 | Food Science |
| 13 | Frontiers in Pharmacology | 2 | 49 | 6 | 5.988 | Q1 | Medicine |
| 14 | Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry | 3 | 62 | 6 | 5.895 | Q1 | Agricultural and Biological Sciences |
| 15 | Scientific Reports | 4 | 385 | 6 | 4.996 | Q1 | Multidisciplinary |
| Name | Institution | h_index | NP | TC | ATC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Johnson K Katerina V.-A. Johnson | University of Oxford | 4 | 4 | 552 | 138 |
| Park S Sunmin Park | Hoseo University | 4 | 5 | 178 | 35.6 |
| Goebel Stengel M Miriam Goebel-Stengel | Martin-Luther-Krankenhaus | 5 | 5 | 105 | 21.0 |
| Kobelt P Peter Kobelt | Charité—Universitätsmedizin Berlin | 5 | 5 | 105 | 21.0 |
| Rose M | Philipps-Universität | 5 | 5 | 105 | 21.0 |
| Stengel A Andreas Stengel | University Hospital Tübingen | 5 | 5 | 105 | 21.0 |
| Liu X Xiaofei Liu | South China University of Technology | 4 | 5 | 96 | 19.2 |
| Perry G George Perry | The University of Texas at San Antonio | 5 | 5 | 89 | 17.8 |
| Obrenovich M Mark Obrenovich | Cleveland State University | 5 | 5 | 82 | 16.4 |
| Zhang M Meng Zhang | Beijing Gene Tangram Technology | 3 | 5 | 78 | 15.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, H.-L.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Li, J.-X.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Su, Z.; Cheung, T.; Jackson, T.; Sha, S.; Xiang, Y.-T. The Microbiome–Gut–Brain Axis and Dementia: A Bibliometric Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16549. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192416549
Sun H-L, Feng Y, Zhang Q, Li J-X, Wang Y-Y, Su Z, Cheung T, Jackson T, Sha S, Xiang Y-T. The Microbiome–Gut–Brain Axis and Dementia: A Bibliometric Analysis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(24):16549. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192416549
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, He-Li, Yuan Feng, Qinge Zhang, Jia-Xin Li, Yue-Ying Wang, Zhaohui Su, Teris Cheung, Todd Jackson, Sha Sha, and Yu-Tao Xiang. 2022. "The Microbiome–Gut–Brain Axis and Dementia: A Bibliometric Analysis" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 24: 16549. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192416549
APA StyleSun, H.-L., Feng, Y., Zhang, Q., Li, J.-X., Wang, Y.-Y., Su, Z., Cheung, T., Jackson, T., Sha, S., & Xiang, Y.-T. (2022). The Microbiome–Gut–Brain Axis and Dementia: A Bibliometric Analysis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(24), 16549. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192416549







