Factors Associated with Mortality with Tuberculosis Diagnosis in Indigenous Populations in Peru 2015–2019
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bonachera, J.C.; Gallardo, J.F.M.; Rosique, M.S.B.; Blanco, I.R. Tuberculosis. Diagnóstico y tratamiento. Estudio convencional de contactos. Profilaxis y tratamiento de infección latente. Rev. Neumosur. 2016, 216, 448–538. [Google Scholar]
- PAHO. Tuberculosis in the Americas. 2018. Available online: https://iris.paho.org/handle/10665.2/49510 (accessed on 18 May 2022).
- Tuberculosis—OPS/OMS|Organización Panamericana de la Salud. Available online: https://www.paho.org/es/temas/tuberculosis (accessed on 19 May 2022).
- Organización Panamericana de la Salud. Tuberculosis en las Américas Informe Regional 2019. Available online: https://iris.paho.org/handle/10665.2/52815 (accessed on 29 June 2022).
- Tollefson, D.; Bloss, E.; Fanning, A.; Redd, J.T.; Barker, K.; McCray, E. Burden of tuberculosis in indigenous peoples globally: A systematic review. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2013, 17, 1139–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calixto, R.P.; OPS/OMS Perú—OPS/OMS Perú | OPS/OMS [Internet]. Pan American Health Organization/World Health Organization. 2018. Available online: https://www3.paho.org/per/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=4075:tuberculosis&Itemid=0 (accessed on 19 May 2022).
- Basta, P.C.; Viana, P.V.d.S. Determinants of tuberculosis in Indigenous people worldwide. Lancet Glob. Health 2019, 7, e6–e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank. Indigenous Peoples. Available online: https://www.worldbank.org/en/topic/indigenouspeoples (accessed on 8 June 2022).
- Gracey, M.; King, M. Indigenous health part 1: Determinants and disease patterns. Lancet 2009, 374, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, K.; Lan, Z.; Li, P.; Michelsen, S.W.; Waites, S.; Benedetti, A.; Lejeune, P.; Torrie, J.; Robinson, E.; Vejvoda, B.; et al. Determinants of tuberculosis trends in six Indigenous populations of the USA, Canada, and Greenland from 1960 to 2014: A population-based study. Lancet Public Health 2018, 3, e133–e142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, B.C.M.; Joya, M.C.; Aviles, M.A.G.; Navarro, R.M.; Decroo, T.; Zachariah, R. Tuberculosis among Indigenous Municipalities in Mexico: Analysis of Case Notification and Treatment Outcomes between 2009 and 2013. Available online: https://iris.paho.org/handle/10665.2/28199 (accessed on 8 June 2022).
- Basta, P.C.; Coimbra, C.E., Jr.; Escobar, A.L.; Santos, R.V.; Alves, L.C.C.; Fonseca, L.D.S. Survey for tuberculosis in an indigenous population of Amazonia: The Suruí of Rondônia, Brazil. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2006, 100, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, T.V.; Tegaisa, L.V.; Sarmiento, J.M.H. Tuberculosis en comunidades indígenas del Chocó, Colombia. Análisis epidemiológico y perspectivas para disminuir su incidencia. Enf. Infec. Microbiol. 2020, 38, 104–114. [Google Scholar]
- ISSUU. Estudio de Factores de Riesgo y Percepción de la TB en Comunidades Indígenas Asháninkas by Respira Vida. Available online: https://issuu.com/respiravida/docs/factores_de_riesgo_y_percepciones_- (accessed on 30 June 2022).
- Estudio de Factores de Riesgo y Percepción de la Tuberculosis en Comunidades Indígenas Quechuas: Informe Final. Available online: https://www.gob.pe/institucion/minsa/informes-publicaciones/284967-estudio-de-factores-de-riesgo-y-percepcion-de-la-tuberculosis-en-comunidades-indigenas-quechuas-informe-final (accessed on 29 June 2022).
- Armitage, P.; Colton, T. Encyclopedia of Epidemiologic...—Google Académico [Internet]. Available online: https://scholar.google.com.co/scholar?q=Armitage,+P.%3B+Colton,+T.+Encyclopedia+of+Epidemiologic+Methods&hl=es&as_sdt=0&as_vis=1&oi=scholart (accessed on 25 May 2022).
- Rothman, K.J. Modern Epidemiology. Available online: https://books.google.com/books/about/Modern_Epidemiology.html?id=Z3vjT9ALxHUC (accessed on 25 May 2022).
- Brittain, E.; Schlesselman, J.J.; Stadel, B.V. Cost of case-control studies. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1981, 114, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Métodos estadísticos alternativos y su aplicación a la investigación en Cuidados Intensivos. Med. Intensiv. 2018, 42, 490–499. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosmer, D.W.; Lemeshow, S.; Sturdivant, R.X. Applied Logistic Regression, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- cap03_01.pdf. Available online: https://www.inei.gob.pe/media/MenuRecursivo/publicaciones_digitales/Est/Lib1642/cap03_01.pdf (accessed on 17 June 2022).
- Culqui, D.; Zavaleta, C.; Romero, J.; Bonilla, C.; Trujillo, O.; Cueva, N. Tuberculosis in indigenous populations in Peru: The Aimara of Peru, 2000–2005. Rev. Peru. Epidemiol. 2009, 13, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Fondo para el Desarrollo de los Pueblos Indígenas de América Latina y el Caribe (FILAC). Situación de la Tuberculosis en los Pueblos Indígenas de América Latina y El Caribe | Fondo para el desarrollo de los pueblos indigenas FILAC [Internet]. Available online: https://www.filac.org/3184/ (accessed on 10 November 2022).
- Rios, D.P.G.; Malacarne, J.; Alves, L.C.C.; Sant’Anna, C.C.; Camacho, L.A.B.; Basta, P.C. Tuberculosis in indigenous peoples in the Brazilian Amazon: An epidemiological study in the Upper Rio Negro region. Rev. Panam. Salud Publica 2013, 33, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malacarne, J.; Rios, D.P.G.; Silva, C.M.F.P.D.; Braga, J.U.; Camacho, L.A.B.; Basta, P.C. Prevalence and factors associated with latent tuberculosis infection in an indigenous population in the Brazilian Amazon. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2016, 49, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tb-Indigenas-III-Reunion-Regional-Exitos-Desafios.pdf. Available online: https://www.paho.org/hq/dmdocuments/2011/tb-indigenas-III-Reunion-Regional-Exitos-desafios.pdf (accessed on 17 June 2022).
- Romero-Amaro, Z.; Salazar, P.J.; Bracho, M.A.; Atencio, T.R.; Romero-Gori, N.; Montiel, U.C. Prevalencia de tuberculosis pulmonar en pacientes indígenas y no indígenas del estado Zulia durante el periodo 1996–2005. Kasmera 2008, 36, 159–168. [Google Scholar]
- Mendoza Ticona, A.; Iglesias Quilca, D. Tuberculosis en pacientes con VIH/SIDA. Acta Méd. Peru. 2008, 25, 247–254. [Google Scholar]
- Medina, A.; López, L.; Martínez, C.; Aguirre, S.; Alarcón, E. Factores asociados a la mortalidad por tuberculosis en Paraguay, 2015–2016. Rev. Panam. Salud Publica 2019, 43, e102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, J.D.; Arroyo, L.H.; Arcoverde, M.A.M.; Cartagena-Ramos, D.; Berra, T.Z.; Alves, L.S.; Ramos, A.C.V.; Fuentealba-Torres, M.; de Assis, I.S.; Fiorati, R.C.; et al. Magnitud de los determinantes sociales en el riesgo de mortalidad por tuberculosis en el Centro-Oeste de Brasil. Gac. Sanit. Barc. Ed. Impr. 2020, 34, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salud Pública y algo más. Sesgos, Ventajas y Desventajas en los Estudios de Caso Control. Available online: https://www.madrimasd.org/blogs/salud_publica/2008/04/19/89523 (accessed on 23 May 2022).
- Casadellibro. Epidemiología 5a ED|L. Gordis|Casa del Libro. 2014. Available online: https://www.casadellibro.com/libro-epidemiologia-5-ed/9788490227268/2459270 (accessed on 31 May 2022).
- Oliveira, A.G. Biostatistics Decoded. John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; 480p. [Google Scholar]
- Nájera-Ortiz, J.C.; Sánchez-Pérez, H.J.; Ochoa-Díaz, H.; Arana-Cedeño, M.; Lezama, M.S.; Mateo, M.M. Demographic, health services and socio-economic factors associated with pulmonary tuberculosis mortality in Los Altos Region of Chiapas, Mexico. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2008, 37, 786–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organización Panamericana de la Salud. Lineamientos Para la Prevención y el Control de la Tuberculosis en los Pueblos Indígenas de la Región de las Américas. 2021. Available online: https://irseis.paho.org/handle/10665.2/53308 (accessed on 28 July 2022).
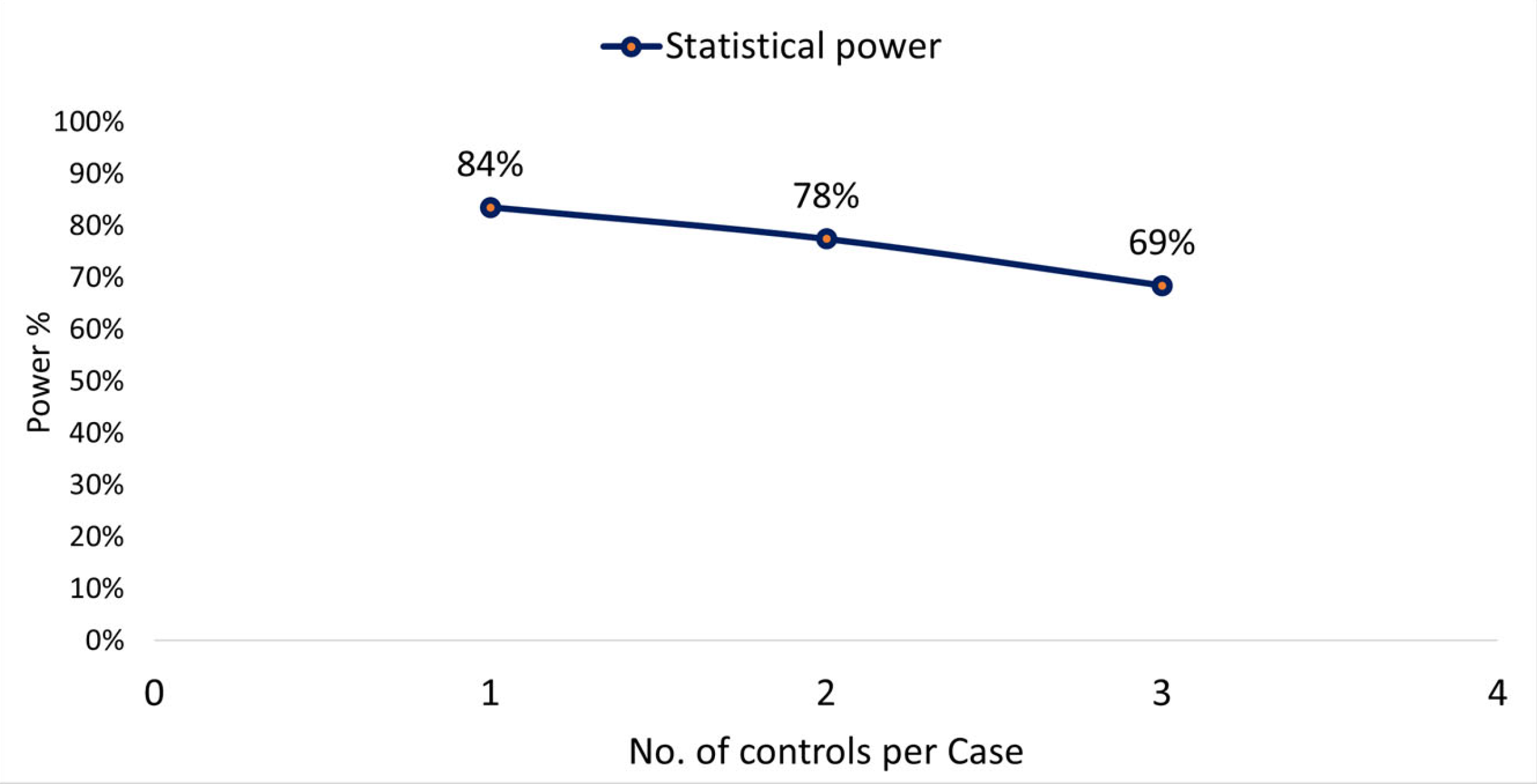
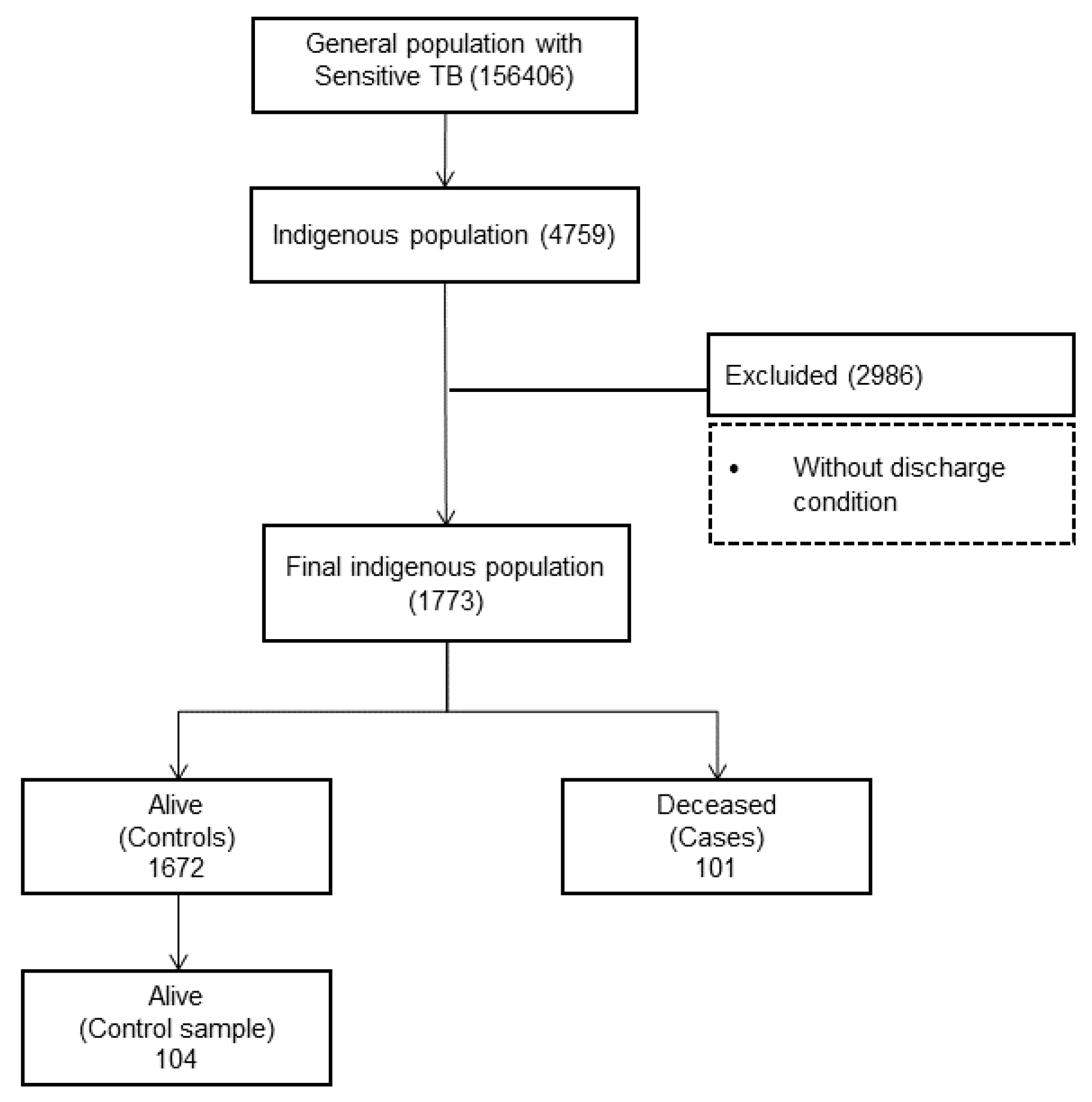
| Mortality Rate | Indigenous Population (2017 Census) | Indigenous Deceased by TB | Total Indigenous d. w/TB | Mortality% by TB | Mortality Rate by TB (100,000 Inhab). |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| General | 5,771,885 | 101 | 1773 | 5.7% | 1.75 |
| Male | 2,801,412 | 76 | 1087 | 7.0% | 2.71 |
| Female | 2,970,473 | 25 | 686 | 3.6% | 0.84 |
| Sociodemographic and Clinical Characteristics | Description | Summary Measure | |
|---|---|---|---|
| n: 1773 | % | ||
| Gender | Female | 686 | 38.7 |
| Male | 1.087 | 61.3 | |
| Age (years) | Median (IQR 1) | 41 (26–55) | |
| Life cycle stage | Childhood/adolescence: (1 to 18 years) | 140 | 8 |
| Youth: (>18 to 26 years) | 327 | 18.4 | |
| Adulthood: (>26 to 59 years) | 940 | 53 | |
| Old age: (>59 years old) | 366 | 20.6 | |
| Ethnic affiliation | Kukama Kukamiria-Yagua | 505 | 28.48 |
| Shipibo-Konibo | 385 | 21.71 | |
| Ashaninka | 298 | 16.8 | |
| Kichwa | 117 | 6.6 | |
| Kukama Kukamiria | 109 | 6.15 | |
| Ticuna | 52 | 2.93 | |
| Shawi | 47 | 2.65 | |
| Harakbut | 37 | 2.09 | |
| Kakataibo | 36 | 2.03 | |
| Bora | 35 | 1.97 | |
| AWAJÚN | 33 | 1.9 | |
| Matsigenka | 32 | 1.8 | |
| Achuar | 18 | 1.02 | |
| Yagua | 18 | 1.02 | |
| Wampis | 16 | 0.9 | |
| Mestizo | 14 | 0.79 | |
| Quechua | 12 | 0.68 | |
| Kandozi | 4 | 0.23 | |
| Sharanahua | 3 | 0.17 | |
| Madija | 2 | 0.11 | |
| Location | Extrapulmonary | 176 | 9.9 |
| Pulmonary | 1597 | 90.1 | |
| Admission status | New | 1631 | 91.99 |
| Relapsed | 78 | 4.40 | |
| Dropout recovered | 61 | 3.44 | |
| Failure | 3 | 0.17 | |
| Discharge status | Cured | 959 | 54.1 |
| Complete treatment | 376 | 21.2 | |
| Dropout | 158 | 8.9 | |
| Deceased | 101 | 5.7 | |
| Failure | 5 | 0.28 | |
| No answer | 174 | 9.8 | |
| Comorbidities and risk factors | |||
| HIV | Positive | 126 | 7.47 |
| Diabetes | Yes | 170 | 11.1 |
| Alcoholism | Yes | 96 | 5.42 |
| Smoking | Yes | 74 | 4.2 |
| Drug addiction | Yes | 44 | 2.5 |
| Treatment regimen 2 | 2HREZ/4(HR)3 | 1629 | 91.9 |
| 2HREZ/10HR | 43 | 2.4 | |
| 2HREZ/7HR | 101 | 5.7 | |
| Characteristics | Deceased (101) | Alive (104) | OR (Crude) | 95% CI | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
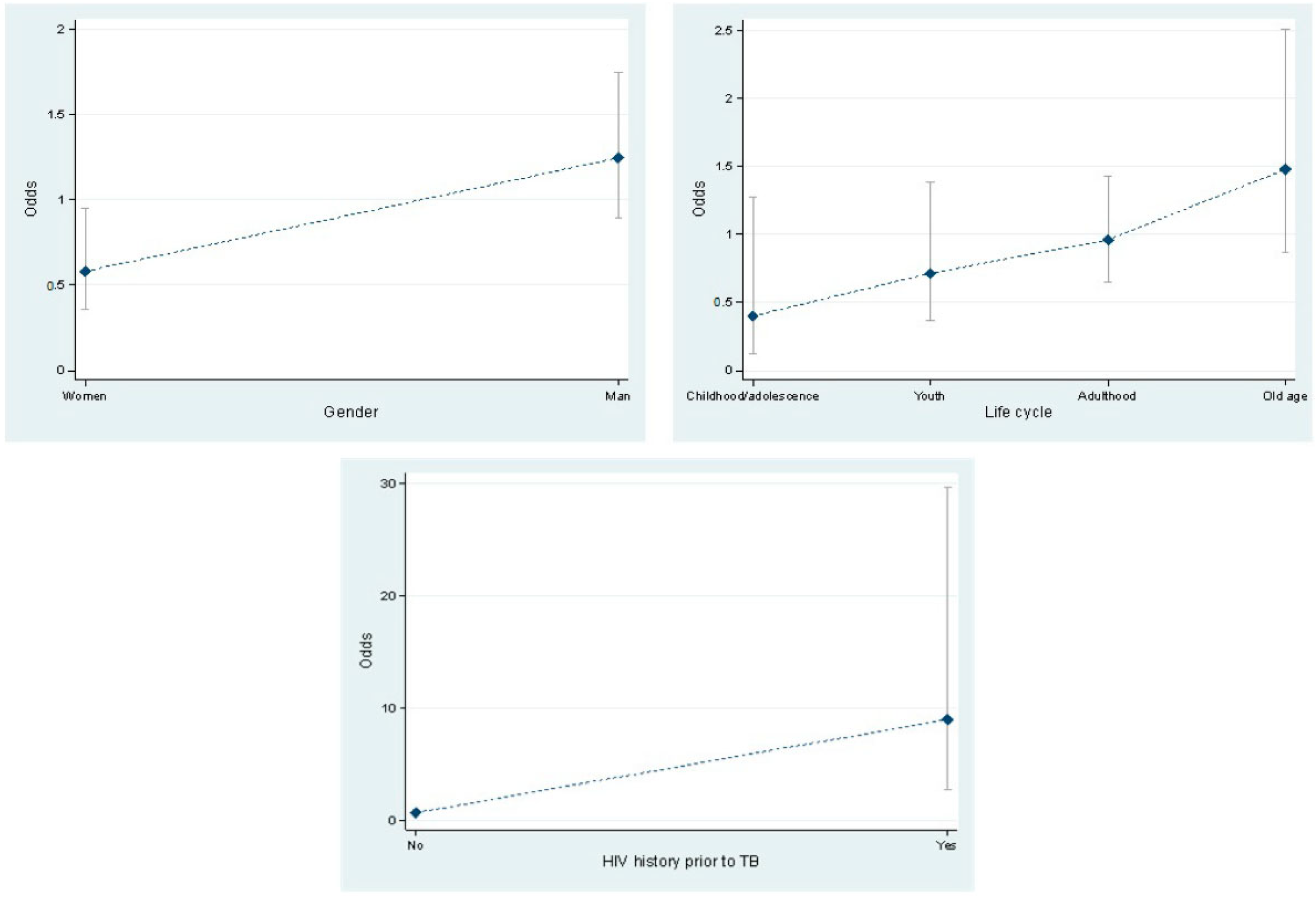
| Gender | Female * | 25 (24.75) | 43 (41.35) | 1 | 0.012 | ||
| Male | 76 (75.25) | 61 (58.65) | 2.14 | 1.8 | 3.9 | ||
| Life cycle stage | Childhood/ adolescence * | 4 (3.96) | 10 (9.6) | 1 | |||
| Youth | 15 (14.8) | 21 (20.2) | 1.78 | 0.47 | 6.8 | 0.395 | |
| Adulthood | 48 (47.5) | 50 (48.1) | 2.4 | 0.7 | 8.2 | 0.16 | |
| Old age | 34 (33.7) | 23 (22.1) | 3.7 | 1.03 | 13.2 | 0.044 | |
| Location of TB | Extrapulmonary * | 16 (15.84) | 11 (10.58) | 1 | |||
| Pulmonary | 85 (84.16) | 93 (89.42) | 0.63 | 0.28 | 1.43 | 0.27 | |
| HIV history prior to TB | No * | 72 (72.73) | 101 (97.12) | 1 | |||
| Yes | 27 (27.27) | 3 (2.88) | 12.6 | 3.7 | 43.2 | 0.000 | |
| DM history prior to TB | No * | 90 (94.74) | 96 (96) | 1 | |||
| Yes | 5 (5.26) | 4 (4) | 1.33 | 0.35 | 5.1 | 0.67 | |
| Diagnosis of DM with glycemia test | Negative * | 71 (88.75) | 81 (87.10) | 1 | 0.74 | ||
| Positive | 9 (11.25) | 12 (12.90) | 0.86 | 0.34 | 2.1 | ||
| Alcoholism | No * | 91 (90.1) | 98 (94.23) | 1 | 0.28 | ||
| Yes | 10 (9.9) | 6 (5.77) | 1.8 | 0.63 | 5.1 | ||
| Smoking | No * | 97 (96.04) | 101 (97.12) | 1 | |||
| Yes | 4 (3.96) | 3 (2.88) | 1.4 | 0.3 | 6.4 | 0.67 | |
| Drug addiction | No * | 100 (99.01) | 103 (99.04) | 1 | 0.98 | ||
| Yes | 1 (0.99) | 1 (0.96) | 1.03 | 0.06 | 16.7 | ||
| Characteristics | Deceased (101) | Alive (104) | OR (Crude) | 95% CI | OR (Adjusted) | 95% CI | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Female * | 25 (24.75) | 43 (41.35) | 1 | 1 | 0.047 | ||||
| Male | 76 (75.25) | 61 (58.65) | 2.14 | 1.8 | 3.9 | 1.94 | 1.001 | 3.7 | ||
| Life cycle stage | Childhood/ Adolescence * | 4 (3.96) | 10 (9.6) | 1 | 0.001 | |||||
| Old age | 34 (33.7) | 23 (22.1) | 3.7 | 1.03 | 13.2 | 2.95 | 1.5 | 5.7 | ||
| VIH history prior to TB | No * | 72 (72.73) | 101 (97.12) | 1 | 1 | 0.000 | ||||
| Yes | 27 (27.27) | 3 (2.88) | 12.6 | 3.7 | 43.2 | 16.7 | 4.7 | 58.7 | ||
| Comparison of logistic regression models | Likelihood | p-value | ||||||||
| Saturated Model (5 covariates) | −119.867 | 0.9846 | ||||||||
| Adjusted Model (3 covariates) | −120.054 | |||||||||
| Hosmer–Lemeshow’s goodness-of-fit test | X2: 0.21 | 0.9949 | ||||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
León-Giraldo, H.; Rivera-Lozada, O.; Castro-Alzate, E.S.; Aylas-Salcedo, R.; Pacheco-López, R.; Bonilla-Asalde, C.A. Factors Associated with Mortality with Tuberculosis Diagnosis in Indigenous Populations in Peru 2015–2019. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 15019. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192215019
León-Giraldo H, Rivera-Lozada O, Castro-Alzate ES, Aylas-Salcedo R, Pacheco-López R, Bonilla-Asalde CA. Factors Associated with Mortality with Tuberculosis Diagnosis in Indigenous Populations in Peru 2015–2019. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(22):15019. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192215019
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeón-Giraldo, Hoover, Oriana Rivera-Lozada, Elvis Siprian Castro-Alzate, Rula Aylas-Salcedo, Robinson Pacheco-López, and César Antonio Bonilla-Asalde. 2022. "Factors Associated with Mortality with Tuberculosis Diagnosis in Indigenous Populations in Peru 2015–2019" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 22: 15019. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192215019
APA StyleLeón-Giraldo, H., Rivera-Lozada, O., Castro-Alzate, E. S., Aylas-Salcedo, R., Pacheco-López, R., & Bonilla-Asalde, C. A. (2022). Factors Associated with Mortality with Tuberculosis Diagnosis in Indigenous Populations in Peru 2015–2019. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(22), 15019. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192215019






