Comparison of the Effects of Different Forms of Nutrition Education on Adolescent Male Soccer Players
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Subjects
2.2. Questionnaire Studies
2.2.1. Athlete Nutrition Knowledge, Attitude, Eating Behavior Questionnaire (Athlete Nutrition KAP Questionnaire)
2.2.2. Questionnaire of Self-Efficacy
2.3. Nutrition Education
2.4. Statistical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Participants
3.2. Pre-Intervention Questionnaire Test Results for Nutrition Education
3.2.1. Athlete Nutrition KAP Questionnaire Score
3.2.2. Scores of Self-Efficacy Questionnaires
3.3. Intervention Effect and Effect Comparison of Two Forms of Nutrition Education, and Comparison of Effect Persistence
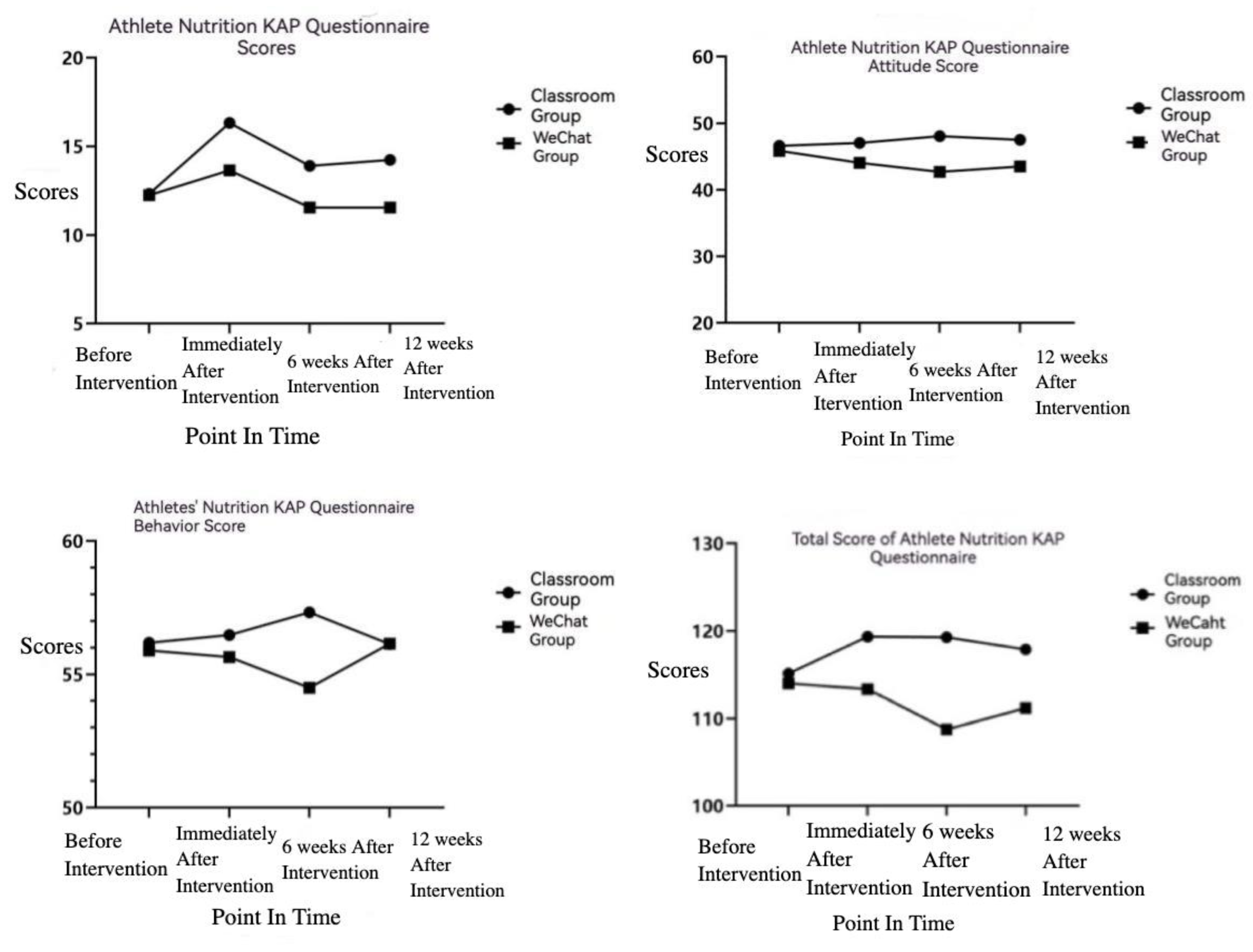
3.3.1. Changes in the Scores of the Athlete Nutrition KAP Questionnaire before the Nutrition Education Intervention, Immediately after the Intervention, and 6 Weeks and 12 Weeks after the Intervention
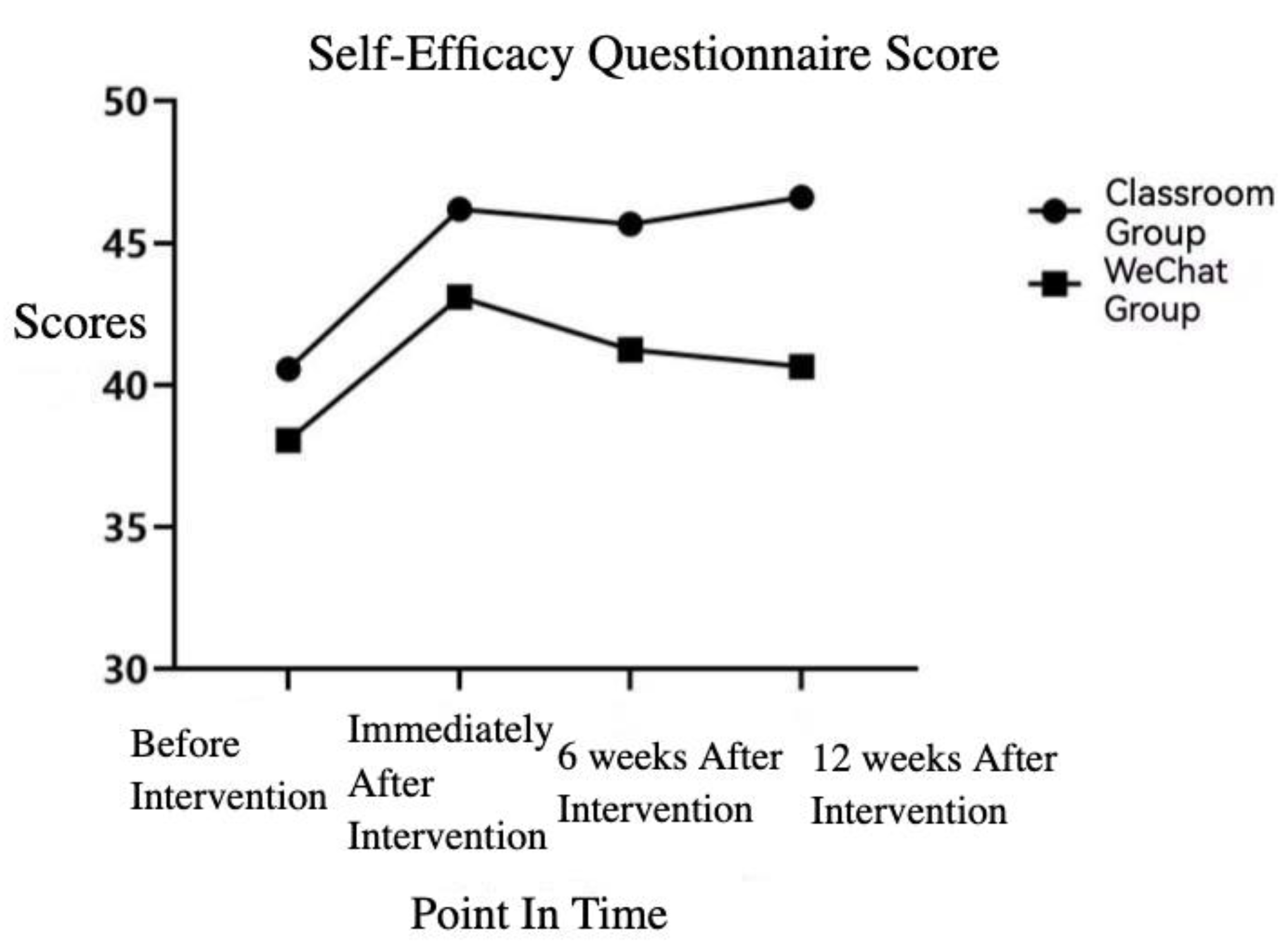
3.3.2. Changes in the Scores of the Self-Efficacy Questionnaire before the Nutrition Education Intervention, Immediately after Intervention, and 6 Weeks and 12 Weeks after Intervention
4. Discussion
4.1. Nutrition Analysis of Young Soccer Players
4.2. Comparative Analysis of the Effect of Two Forms of Nutrition Education Intervention
4.3. Comparative Analysis of the Persistence of the Effects of Two Forms of Nutrition Education
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trakman, G.L.; Forsyth, A.; Middleton, K.; Hoye, R.; Jenner, S.; Keenan, S.; Belski, R. Australian Football Athletes Lack Awareness of Current Sport Nutrition Guidelines. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2018, 28, 644–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davar, V. Nutritional Knowledge and Attitudes towards Healthy Eating of College-Going Women Hockey Players. J. Human Ecol. 2012, 37, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manore, M.M.; Patton-Lopez, M.M.; Meng, Y.; Wong, S.S. Sport Nutrition Knowledge, Behaviors and Beliefs of High School Soccer Players. Nutrients 2017, 9, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, M.; Cartwright, L.; Corish, C.; Sugrue, S.; Wood-Martin, R. The Body Composition, Nutritional Knowledge, Attitudes, Behaviors, and Future Education Needs of Senior Schoolboy Rugby Players in Ireland. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2011, 21, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-McGehee, T.M.; Pritchett, K.L.; Zippel, D.; Minton, D.M.; Cellamare, A.; Sibilia, M. Sports Nutrition Knowledge among Collegiate Athletes, Coaches, Athletic Trainers, and Strength and Conditioning Specialists. J. Athl. Train. 2012, 47, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webb, M.C.; Beckford, S.E. Beckford Nutritional Knowledge and Attitudes of Adolescent Swimmers in Trinidad and Tobago. J. Nutr. Metab. 2014, 2014, 506434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfik, S.; El Koofy, N.; Moawad, E.M.I. Patterns of Nutrition and Dietary Supplements Use in Young Egyptian Athletes: A Community-Based Cross-Sectional Survey. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161252. Available online: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0161252 (accessed on 1 August 2022). [CrossRef]
- Abbey, E.L.; Wright, C.J.; Kirkpatrick, C.M. Nutrition Practices and Knowledge among NCAA Division III Football Players. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2017, 14, 13. Available online: https://jissn.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12970-017-0170-2 (accessed on 1 August 2022). [CrossRef]
- Couture, S.; Lamarche, B.; Morissette, E.; Provencher, V.; Valois, P.; Goulet, C.; Drapeau, V. Evaluation of Sports Nutrition Knowledge and Recommendations among High School Coaches. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2015, 25, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danaher, K.; Curley, T. Nutrition Knowledge and Practices of Varsity Coaches at a Canadian University. Can. J. Diet. Pract. Res. 2014, 75, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cockburn, E.; Fortune, A.; Briggs, M.; Rumbold, P. Nutritional Knowledge of UK Coaches. Nutrients 2014, 6, 1442–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eugene, A.C.; Agwubuike, E.O. The Interface of Nutritional Practices of Selected Basketball Players of Nnamdi Azikiwe University, Awka, On Performance. Global J. Health Sci. 2012, 4, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shriver, L.H.; Betts, N.M.; Wollenberg, G. Dietary Intakes and Eating Habits of College Athletes: Are Female College Athletes Following the Current Sports Nutrition Standards? J. Am. Coll. Health 2013, 61, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, M.; Fernandes, M.J.; Moreira, P.; Teixeira, V.H. Nutritional Supplements Usage by Portuguese Athletes. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2013, 83, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madden, R.F.; Shearer, J.; Legg, D.; Parnell, J.A. Evaluation of Dietary Supplement Use in Wheelchair Rugby Athletes. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wardenaar, F.C.; Ceelen, I.J.M.; Van Dijk, J.-W.; Hangelbroek, R.W.J.; Van Roy, L.; Van der Pouw, B.; De Vries, J.H.M.; Mensink, M.; Witkamp, R.F. Nutritional Supplement Use by Dutch Elite and Sub-Elite Athletes: Does Receiving Dietary Counseling Make a Difference? Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2017, 27, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muwonge, H.; Zavuga, R.; Kabenge, P.A.; Makubuya, T. Nutritional Supplement Practices of Professional Ugandan Athletes: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Int. Soc. Sport. Nutr. 2017, 14, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandura, A. Self-Efficacy: The Exercise of Control; Worth Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Guntzviller, L.M.; King, A.J.; Jensen, J.D.; Davis, L.A. Self-Efficacy, Health Literacy, and Nutrition and Exercise Behaviors in a Low-Income, Hispanic Population. J. Immigr. Minor. Health 2017, 19, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandura, A. Social Cognitive Theory: An Agentic Perspective. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2001, 52, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, A.L.; McArdle, J.J.; Robertson, T.; Dunton, G.F. Nutrition Self-Efficacy Is Unidirectionally Related to Outcome Expectations in Children. Appetite 2015, 84, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, E.S.; Winett, R.A.; Wojcik, J.R. Social-Cognitive Determinants of Nutrition Behavior among Supermarket Food Shoppers: A Structural Equation Analysis. Health Psychol. 2000, 19, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, E.S.; Winett, R.A.; Wojcik, J.R.; Winett, S.G.; Bowden, T. A Computerized Social Cognitive Intervention for Nutrition Behavior: Direct and Mediated Effects on Fat, Fiber, Fruits, and Vegetables, Self-Efficacy, and Outcome Expectations among Food Shoppers. Ann. Behav. Med. 2001, 23, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luszczynska, A.; Gibbons, F.X.; Piko, B.F.; Tekozel, M. Self-Regulatory Cognitions, Social Comparison, and Perceived Peers’ Behaviors as Predictors of Nutrition and Physical Ac-tivity: A Comparison among Adolescents in Hungary, Poland, Turkey, and USA. Psychol. Health 2004, 19, 577–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, E.S.; Winett, R.A.; Wojcik, J.R. Self-Regulation, Self-Efficacy, Outcome Expectations, and Social Support: Social Cognitive Theory and Nutrition Behavior. Ann. Behav. Med. 2007, 34, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trakman, G.L.; Forsyth, A.; Devlin, B.L.; Belski, R. A systematic review of athletes’ and coaches’ nutrition knowledge and reflections on the quality of current nutrition knowledge measures. Nutrients 2016, 8, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, B.L.; Leveritt, M.D.; Kingsley, M.; Belski, R. Dietary intake, body composition, and nutrition knowledge of Australian football and soccer players: Implications for sports nutrition professionals in practice. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2017, 27, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heaney, S.; O’Connor, H.; Michael, S.; Gifford, J.; Naughton, G. Nutrition knowledge in athletes: A systematic review. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2011, 21, 248–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, L.M. Application of the theory of anticipatory guidance to identify nutrition education needs, eating disorder risk, and nutrition knowledge and attitudes of freshmen and sophomore collegiate athletes. Smpte Motion Imag. J. 2011, 69, 470–474. [Google Scholar]
- Bill, H.; Kessler, L.; Jo, E.; Burns-Whitmore, B. Focus groups inform SMS/Text message nutrition education for college athletes. J. Nutr. Educ. Behav. 2016, 48, S39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, A.; Gemming, L.; Baker, D.; Braakhuis, A. Do image-assisted mobile applications improve dietary habits, knowledge, and behaviours in elite athletes? A pilot study. Sports 2017, 5, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, D.; Fang, Z.L.; Qin, L.; Yu, A.Q.; Ren, Y.B.; Xue, B.Y.; Xin, Z.; Zi-Yu, G.; Meng, D.; Nan, A.; et al. Evaluation for the effects of nutritional education on Chinese elite male young soccer players: The application of adjusted dietary balance index (DBI). J. Exerc. Sci. Fit. 2020, 18, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abood, D.A.; Black, D.R.; Birnbaum, R.D. Nutrition Education Intervention for College Female Athletes. J. Nutr. Educ. Behav. 2004, 36, 135–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpinski, C.; Touger-Decker, R.; Denmark, R.; Rigassio-Radler, D.; Rosenbloom, C. Impact of a nine-week interactive Internet-based nutrition education program on nutrition knowledge and dietary behaviors of collegiate athletes. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2012, 112, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, B.L.; Belski, R. Exploring general and sports nutrition and food knowledge in elite male Australian athletes. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2015, 25, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowacka, E.; Leszczyńska, T.; Kopeć, A.; Hojka, D. Nutritional behavior of Polish canoeist’s athletes: The interest of nutritional education. Sci. Sport 2016, 31, e79–e91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Category | Questions | Score Criteria | Range of Scores |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nutritional Knowledge | 1~20 | correct = 1 | 0~20 |
| incorrect = 0 | |||
| Attitude towards Nutrition | 21~30 | A = 5 | 0~50 |
| B = 4 | |||
| C = 3 | |||
| D = 2 | |||
| E = 1 | |||
| No Answer = 0 | |||
| Eating Habits | 34~43 | A = 5 | 0~50 |
| B = 4 | |||
| C = 3 | |||
| D = 2 | |||
| E = 1 | |||
| No Answer = 0 | |||
| 44, 45 | A = 1 | 0~10 | |
| B = 2 | |||
| C = 3 | |||
| D = 4 | |||
| E = 5 | |||
| No Answer = 0 | |||
| 46, 47, 50 | A or no answer = 0 | 0~3 | |
| B = 1 | |||
| 48, 49, 51 | A = 1 | 0~3 | |
| B or no answer = 0 |
| Groups | No. | Age | Height (cm) | Weight (kg) | BMI (kg/m2) | Training Years | Education |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classroom | 21 | 15.0 ± 0.4 | 172.7 ± 4.9 | 56.9 ± 6.0 | 19.1 ± 1.5 | 4.8 ± 1.6 | Middle School |
| 20 | 15.0 ± 0.3 | 170.5 ± 4.7 | 55.0 ± 4.9 | 18.9 ± 1.1 | 4.6 ± 1.8 | Middle School |
| Group | No. | Nutrition Score | Attitude Score | Diet Habit Score | Total Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classroom Group | 21 | 12.3 ± 3.8 | 46.6 ± 4.8 | 56.2 ± 4.3 | 115.14 ± 8.28 |
| 20 | 12.3 ± 4.0 | 45.9 ± 4.7 | 55.9 ± 4.0 | 114.00 ± 9.02 |
| Groups | No. | Scores |
|---|---|---|
| Classroom Group | 21 | 40.57 ± 9.65 |
| WeChat Group | 20 | 38.05 ± 6.16 |
| Before Intervention | After Intervention | 6 Weeks After | 12 Weeks After | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Knowledge Score | Classroom | 12.33 ± 3.8 | 16.33 ± 2.9 *※ | 13.90 ± 3.7 *#※ | 14.24 ± 4.0 *#※ |
| 12.25 ± 4.0 | 13.65 ± 3.0 | 11.55 ± 3.5 | 11.55 ± 3.23 # | ||
| Attitude Score | Classroom | 46.62 ± 4.8 | 47.05 ± 5.4 | 48.05 ± 4.8 * | 47.52 ± 4.8 ※ |
| 45.85 ± 4.7 | 44.05 ± 5.6 | 42.70 ± 12.3 | 43.50 ± 4.5 | ||
| Behavior Score | Classroom | 56.19 ± 4.3 | 56.48 ± 3.7 | 57.33 ± 2.7 | 56.14 ± 3.4 |
| 55.90 ± 4.0 | 55.65 ± 4.7 | 54.50 ± 11.3 | 56.15 ± 3.9 | ||
| Total Score | Classroom | 115.14 ± 8.3 | 119.86 ± 9.3 *※ | 119.29 ± 7.1 * | 117.90 ± 9.7 *※ |
| 114.00 ± 9.0 | 113.35 ± 9.9 | 108.75 ± 25.5 | 111.20 ± 9.5 |
| Groups | Before Intervention | After Intervention | 6 Weeks After | 12 Weeks After |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classroom | 40.57 ± 9.65 | 46.19 ± 6.18 * | 45.67 ± 5.97 * | 46.62 ± 6.04 *※ |
| WeChat Group | 38.05 ± 6.16 | 43.10 ± 7.26 * | 41.25 ± 8.27 * | 40.65 ± 8.13 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, Z.; Wang, S.; Peng, L.; Sun, L.; Qiu, P.; Bai, B.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, J.; Zha, Y.; Zhu, F.; et al. Comparison of the Effects of Different Forms of Nutrition Education on Adolescent Male Soccer Players. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 13803. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192113803
Gao Z, Wang S, Peng L, Sun L, Qiu P, Bai B, Zhang Q, Wu J, Zha Y, Zhu F, et al. Comparison of the Effects of Different Forms of Nutrition Education on Adolescent Male Soccer Players. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(21):13803. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192113803
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Ziyu, Sicheng Wang, Lianlian Peng, Lei Sun, Peng Qiu, Bingyi Bai, Qingqing Zhang, Junyu Wu, Yu Zha, Fenglin Zhu, and et al. 2022. "Comparison of the Effects of Different Forms of Nutrition Education on Adolescent Male Soccer Players" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 21: 13803. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192113803
APA StyleGao, Z., Wang, S., Peng, L., Sun, L., Qiu, P., Bai, B., Zhang, Q., Wu, J., Zha, Y., Zhu, F., & Wang, Q. (2022). Comparison of the Effects of Different Forms of Nutrition Education on Adolescent Male Soccer Players. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(21), 13803. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192113803






