Exposure Assessment to Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields in Occupational Military Scenarios: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- Military electromagnetic field;
- Military electromagnetic field exposure;
- Electromagnetic military devices;
- Occupational electromagnetic exposure assessment;
- Electromagnetic exposure in military environments.
- They included any typology of study related to the exposure assessment in military environment to the EMF in the frequency range between 1.5 MHz to 300 GHz;
- They included devices currently used in the armed forces;
- They included information about the exposure conditions;
- They were published in the last 25 years.
3. Results
3.1. Communication Devices
3.2. Localization/Surveillance Devices (Radar)
3.3. Jammers
3.4. EM Directed-Energy Weapons
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Radiofrequency Fields. In Public Consultant Document; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Swedish Radiation Safety Authority SSM. Recent Research on EMF and Health Risk. Tenth Report from SSM’s Scientific Council on Electromagnetic Fields; SSM Report; Strålsäkerhetsmyndigheten: Stockholm, Sweden, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Swedish Radiation Safety Authority SSM. Recent Research on EMF and Health Risk. Eleventh Report from SSM’s Scientific Council on Electromagnetic Fields; SSM Report; Strålsäkerhetsmyndigheten: Stockholm, Sweden, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Swedish Radiation Safety Authority SSM. Recent Research on EMF and Health Risk. Twelfth Report from SSM’s Scientific Council on Electromagnetic Fields; SSM Report; Strålsäkerhetsmyndigheten: Stockholm, Sweden, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- ICNIRP—International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection. Guidelines for limiting exposure to electromagnetic field (100 kHz to 300 GHz). Health Phys. 2020, 118, 483–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geretto, M.; Ferrari, M.; De Angelis, R.; Crociata, F.; Sebastiani, N.; Pulliero, A.; Au, W.; Izzotti, A. Occupational exposures and environmental health hazard of military personnel. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabouis, V.; Arvers, P.; Debouzy, J.C.; Sebbah, C.; Crouzier, D.; Perrin, A. First epidemiological study on occupational radar exposure in the french navy: A 26-year cohort study. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2016, 26, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Amicis, A.; De Sanctis, S.; Di Cristofaro, S.; Franchini, V.; Lista, F.; Regalbuto, E.; Giovenale, E.; Gallerano, G.P.; Nenzi, P.; Bei, R.; et al. Biological effects on in-vitro THz radiation exposure in human foetal fibroblasts. Mutat. Res. 2015, 793, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Tak, J.; Choi, J. Wearable antenna integrated into military berets for indoor/outdoor positioning system. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2017, 16, 1919–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peleg, M.; Nativ, O.; Richter, E.D. Radio frequency radiation-related cancer: Assessing causation in the occupational/military setting. Environ. Res. 2018, 163, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szmiegielski, S. Cancer morbidity in subjects occupationally exposed to high frequency (radiofrequency and microwave) electromagnetic radiation. Sci. Total Environ. 1996, 180, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degrave, E.; Meeusen, B.; Grivegnée, A.R.; Boniol, M.; Autier, P. Causes of death among Belgian professional military radar operators: A 37-year retrospective cohort study. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 4, 945–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobiech, J.; Kieliszek, J.; Puta, R.; Bartczak, D.; Stankiewicz, W. Occupational exposure to electromagnetic field in the polish armed forces. Int. J. Occup. Med. Environ. Health 2017, 4, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ICNIRP—International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection. Guidelines for limiting exposure in time-varying electric, magnetic, and electromagnetic fields (up to 300 GHz). Health Phys. 1998, 74, 494–522. [Google Scholar]
- Directive 2013/35/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 26 June 2013 on the minimum health and safety requirements regarding the exposure of workers to the risks arising from physical agents (electromagnetic fields) (20th individual Directive within the meaning of Article 16(1) of Directive 89/391/EEC) and repealing Directive 2004/40/EC. Off. J. Eur. Union 2013, L-179, 1–21.
- Federal Communications Commission. Evaluating Compliance with FCC Guidelines for Human Exposure to Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields; Supplement C edition 01-01 to OET bulletin 65 edition 97-01; Federal Communications Commission: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, G.; Peng, G. The survey of GSM wireless communication system. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Computer and Information Application, Tianjin, China, 3–5 December 2010; pp. 121–124. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/6141552 (accessed on 14 November 2021).
- Bhargavi, K.; Balachandrudu, K.E.; Nageswar, P. Mobile phone radiation effects on human health. Int. J. Comput. Eng. Res. 2013, 4, 196–203. [Google Scholar]
- Scaffidi, V.P. Military GSM; Defence Science and Technology organization: Canberra, Australia, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Wnuk, M.; Przesmycki, R. Soldier protection of staying in the radiated field generated by antenna of selected military communications systems. Adv. Intell. Syst. Comput. 2018, 604, 236–247. [Google Scholar]
- Karpowicz, J.; Zradzinski, P.; Kieliszek, J.; Gryz, K.; Sobiech, J.; Leszko, W. An in situ and in silico evaluation of biophysical effects of 27 MHz electromagnetic whole body humans exposure expressed by the limb current. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, N.; Kohno, R.; Kubota, S. Research and development of software-defined radio technologies in Japan. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2001, 8, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittium. Bittium Tough SDR Handheld. Available online: https://www.bittium.com/tactical-communications/bittium-tough-sdr-handheld (accessed on 10 November 2021).
- Leonardo. SWave HH-E Handheld Secure Wideband Soldier Radio. Available online: https://www.leonardocompany.com/it/products/swave-hhe-1 (accessed on 10 November 2021).
- THALES. AN/PRC—148 JEM. Available online: https://www.thalesgroup.com/en/markets/defence-and-security/radio-communications/land-communications/tactical-radios/anprc-148-0 (accessed on 10 November 2021).
- RADMOR. VHF/FM Handheld Radio—3501. Available online: https://www.radmor.com.pl/pl_files_to_download/to_download/ulotki/3501_2018_eng.PDF (accessed on 10 November 2021).
- Kaivanto, E.K.; Berg, M.; Salonen, E.; de Maagt, P. Wearable circularly polarized antenna for personal satellite communication and navigation. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2011, 12, 4490–4496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.S.; Sovuthy, C.; Imran, M.A.; Socheatra, S.; Abbasi, Q.; Zainal, A.Z. Recent advances of wearable antennas in materials, fabrication methods, designs and their applications: State-of-the-art. Micromachines 2020, 10, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebaric, J.; Tan, A.-T. Ultra-wideband conformal helmet antenna. In Proceedings of the 2000 Asia-Pacific Microwave Conference, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 3–6 December 2000; pp. 1477–1481. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/926116 (accessed on 14 November 2021).
- Wang, J.J.H. Broadband omnidirectional helmet antennas. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium, Albuquerque, NM, USA, 9–14 July 2006; pp. 2129–2132. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/1711004 (accessed on 10 November 2021).
- Kieliszek, J.; Wyszkowska, J.; Sobiech, J.; Puta, R. Assessment of the electromagnetic field exposure during the use of portable radios in the context of potential health effects. Energies 2020, 23, 6276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paljanos, A.; Miclaus, S.; Munteanu, C. Occupational exposure of personnel operating military radio equipment: Measurements and simulation. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2015, 3, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poonkuzhali, R.; Alex, Z.C.; Balakrishnan, T. Miniaturized wearable fractal antenna for military applications at VHF band. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2016, 62, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salonen, P.; Kim, J.; Rahmat-Samii, Y. Dual-band E-shaped patch wearable textile antenna. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium, Washington, DC, USA, 3–8 July 2005; Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/1551354 (accessed on 10 November 2021).
- Chahat, N.; Zhadobov, M.; Sauleau, R.; Mahdjoubi, K. Improvement of the on-body performance of a dual-band textile antenna using an EBG structure. In Proceedings of the 2010 Loughborough Antennas & Propagations Conference, Loughborough, UK, 8–9 November 2010; Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/5666201 (accessed on 10 November 2021).
- Chahat, N.; Zhadobov, M.; Sauleau, R.; Mahdjoubi, K. Parametric analysis of on-body dual-band antenna performance: Dependence on the human body morphology. In Proceedings of the 5th European Conference on Antennas and Propagations (EUCAP), Rome, Italy, 11–15 April 2011; Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/5782459 (accessed on 14 November 2021).
- Christ, A.; Kainz, W.; Hahn, E.G.; Honegger, K.; Zefferer, M.; Neufeld, E.; Rascher, W.; Janka, R.; Bautz, W.; Chen, J.; et al. The Virtual Family—development of surface-based anatomical models of two adults and two children for dosimetric simulations. Phys. Med. Biol. 2009, 2, N23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michishita, N.; Morishita, H. Helmet antenna design using characteristic mode analysis. ACES J. 2020, 35, 161–166. [Google Scholar]
- Nasim, I.; Kim, S. Human EMF exposure in wearable networks for Internet of Battlefield Things. In Proceedings of the MILCOM 2019—2019 IEEE Military Communication Conference (MILCOM), Norfolk, VA, USA, 12–14 November 2019; pp. 1–6. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9020889 (accessed on 14 November 2021).
- Variani, A.S.; Saboori, S.; Shahsavari, S.; Yasi, S.; Zaroushani, V. Effect of occupational exposure to radar radiation on cancer risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2019, 20, 3211–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, M. Digital Signal Processing, 2nd ed.; Elsevier-Newnes: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 191–200. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.; Kapoor, N. Occupational EMF exposure from radar at X and Ku frequency band and plasma catecholamine levels. Bioelectromagnetics 2015, 36, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Vyonkesh Mani, K.; Kapoor, N. Effect of occupational EMF exposure from radar at two different frequency bands on plasma melatonin and serotonin levels. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2015, 5, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danulescu, R. Assessment of Complex Microwaves Occupational Exposure in Radar Maintenance Activity; International Radiation Protection Association: Vienna, Austria, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Garaj-Vrhovac, V.; Gajiski, G.; Pazanin, S.; Sarolic, A.; Domijan, A.M.; Flajs, D.; Peraica, M. Assessment of cytogenetic damage and oxidative stress in personnel occupationally exposed to the pulsed microwave radiation of marine radar equipment. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2011, 214, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjollund, N.H.; Bonte, J.P. Semen analysis of personnel operating military radar equipment. Reprod. Toxicol. 1997, 11, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsanezhad, M.; Mortazavi, S.; Doohadeh, T.; Jahromi, B.N.; Mozdarani, H.; Zarei, A.; Davari, M.; Amjadi, S.; Soleimani, A.; Haghani, M. Exposure to radiofrequency radiation emitted from mobile phone jammers adversely affects the quality of human sperm. Iran. J. Radiat. Res. 2017, 1, 63–70. [Google Scholar]
- Movahedi, M.M.; Javid-Sharifi, B.; Tavakoli Golpaygani, A.; Mortazavi, S.A.R.; Mortazavi, S.M.J. Short-term exposure to mobile jammer radiofrequency radiation adversely affects the human hearing. Biomed. Res. 2017, 4, 1557–1559. [Google Scholar]
- Shojaeifard, M.B.; Jarideh, S.; Owjfard, M.; Nematollahii, S.; Talaei-Khozani, T.; Malekzadeh, M. Electromagnetic fields on mobile phone jammer exposure on blood factors in rats. J. Biomed. Phys. Eng. 2018, 4, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oke, A.O.; Falohun, A.S.; Adigun, A.A. The design and implementation of a mobile phone detector device with a frequency jamming feature. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2016, 1, 15–19. [Google Scholar]
- Neng-Jing, L.; Zhang, Y.T. A survey of radar ECM and ECCM. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1995, 31, 1110–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selena Electronics. Electronic Warfare System—Jamming Solutions. Available online: www.selenaelectronics.com (accessed on 19 November 2019).
- Yahya, S.I.; Whittow, W.G.; Khaleel, Y.A. Numerical dosimetry of CDMA/GSM, DCS/PCS and 3G signal jammers. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2016, 8, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeVine, S. The Active Denial System—A Revolutionary, Non-Lethal Weapons for Today’s Battlefield; National Defence University Center for Technology and National Security Policy: Washington, DC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kopp, C. The Electromagnetic Bomb—A Weapon of Electrical Mass Destruction; Monash University Clayton: Melbourne, Australia, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson, M.U.; Olsson, F.; Aberg, D.; Jansson, M. Bofors HPM Blackout—A versatile and mobile L-band high power microwave system. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Pulsed Power Conference, Washington, DC, USA, 28 June–2 July 2009; pp. 499–501. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/5386327 (accessed on 14 November 2021).
- Schamiloglu, E. High Power microwave sources and applications. In Proceedings of the 2004 International Microwave Symposium Digest, Fort Worth, TX, USA, 6–11 June 2004; pp. 1001–1004. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/1339150 (accessed on 10 November 2021).
- Hong, K.; Braidwood, S. Stopping car engines using high power electromagnetic pulse. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Electromagnetics in Advanced Applications, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 20–24 September 2010; pp. 378–381. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/5653113 (accessed on 10 November 2021).
- Hamid, F.; Yahya, A.; Tan, T.S.; You, K.Y. Conceptual design of electromagnetic pulse for denied vehicular access application. In Proceedings of the 2nd Joint International Conference on Emerging Computing Technology and Sports, Bandung, Indonesia, 25–27 November 2019; Available online: https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1742-6596/1529/4/042107/meta (accessed on 14 November 2021).
- Valouch, J.; Urbančoková, H. Electromagnetic weapons as means of stopping vehicles. In Proceedings of the SECURWARE 2016: The Tenth International Conference on Emerging Security Information, Systems and Technologies, Nice, France, 24–28 July 2016; Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Jan-Valouch/publication/307571484_Electromagnetic_Weapons_as_Means_of_Stopping_Vehicles_A_Proposal_of_a_Stationary_Electromagnetic_Device_for_Stopping_Vehicles/links/57c95ca308aedb6d6d978de6/Electromagnetic-Weapons-as-Means-of-Stopping-Vehicles-A-Proposal-of-a-Stationary-Electromagnetic-Device-for-Stopping-Vehicles.pdf (accessed on 14 November 2021).
- Urbančoková, H.; Valouch, J.; Kovar, S. Stopping of transport vehicles using the power electromagnetic pulses. Przegląd Elektrotechniczny 2015, 1, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Clemente, F.; Gray, S. The future of the command post: Artificial intelligence could turn data paralysis into information analysis. Signal. Mag. 2018, 73, 29–32. [Google Scholar]
| Destination of Use | Devices |
|---|---|
| Communication devices | GSM systems |
| Radio communication units and SDR systems | |
| Wearable devices | |
| Localization/Surveillance devices | Radar |
| Jammers | Man-portable jammers |
| Land vehicle jammers | |
| Airborne jammers | |
| Stationary jammers | |
| EM Directed-Energy Weapons | HPM—High-power microwave weapons |
| Car stopper devices |
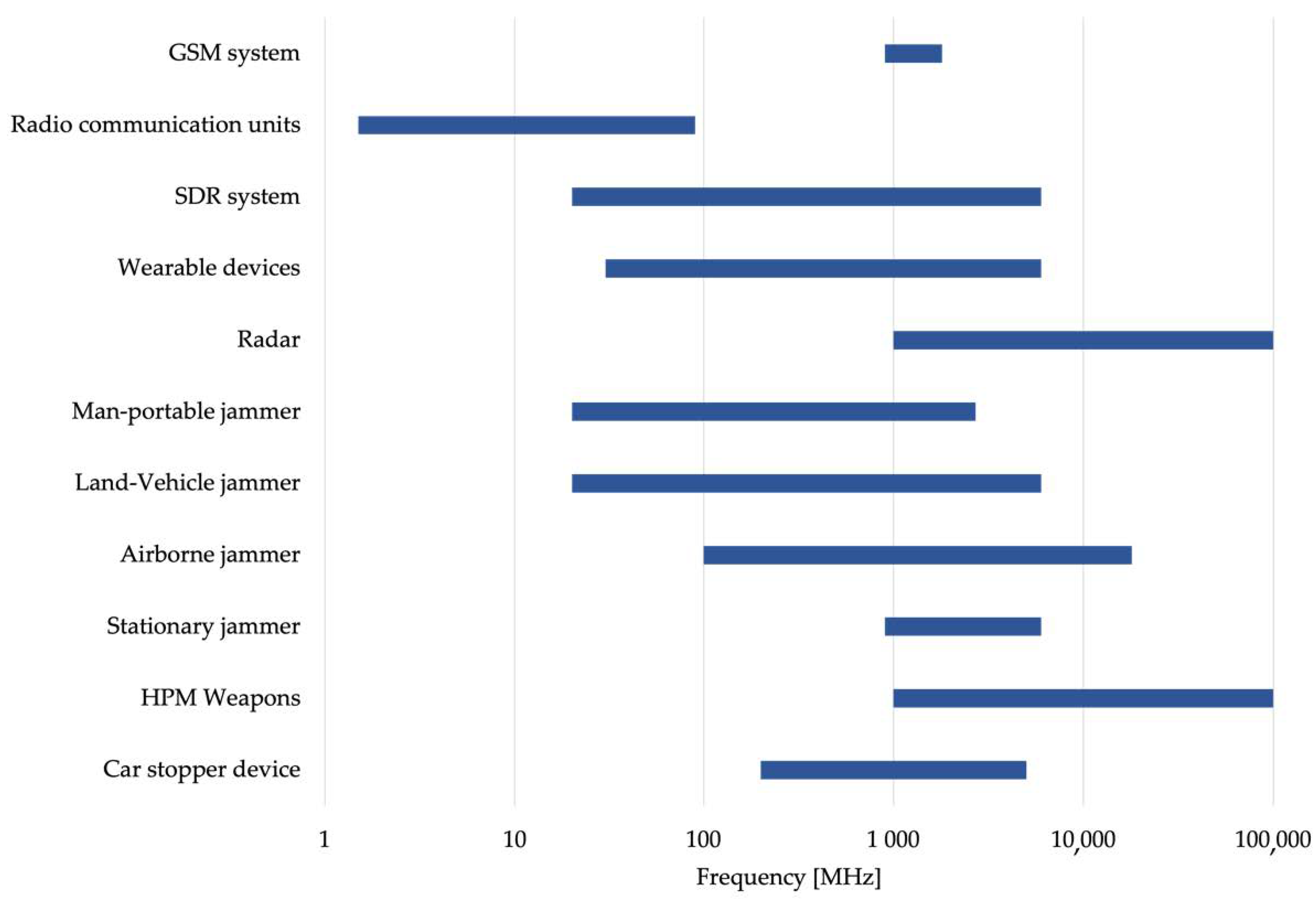
| Devices | Frequency Range |
|---|---|
| GSM systems | 900 MHz–1.8 GHz |
| Radio Communication Units | 1.5 MHz–90 MHz |
| SDR systems | 20 MHz–6 GHz |
| Wearable devices | 30 MHz–6 GHz |
| Device | Frequency Range |
|---|---|
| Radar | 1–300 GHz |
| Device | Frequency Range |
|---|---|
| Man-portable jammers | 20 MHz–2.7 GHz |
| Land vehicle jammers | 20 MHz–6 GHz |
| Airborne jammers | 100 MHz–18 GHz |
| Stationary jammers | 900 MHz–6 GHz |
| Device | Frequency Range |
|---|---|
| HPM—High-power microwave weapons | 1–100 GHz |
| Car stopper devices | 200 MHz–5 GHz |
| Destination of Use | Devices | Configuration |
|---|---|---|
| Communication devices | GSM systems | Near the user |
| Radio communication units | Near the user | |
| SDR systems | Near the user | |
| Wearable devices | Near the user | |
| Localization/surveillance devices | Radar | Far from the user |
| Jammers | Man-portable jammers | Near the user |
| Land vehicle jammers | Near the user | |
| Airborne jammers | Far from the user | |
| Stationary jammers | Far from the user | |
| EM Directed-Energy Weapons | HPM—high-power microwave weapons | Far from the user |
| Car stopper devices | Far from the user |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gallucci, S.; Fiocchi, S.; Bonato, M.; Chiaramello, E.; Tognola, G.; Parazzini, M. Exposure Assessment to Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields in Occupational Military Scenarios: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 920. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19020920
Gallucci S, Fiocchi S, Bonato M, Chiaramello E, Tognola G, Parazzini M. Exposure Assessment to Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields in Occupational Military Scenarios: A Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(2):920. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19020920
Chicago/Turabian StyleGallucci, Silvia, Serena Fiocchi, Marta Bonato, Emma Chiaramello, Gabriella Tognola, and Marta Parazzini. 2022. "Exposure Assessment to Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields in Occupational Military Scenarios: A Review" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 2: 920. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19020920
APA StyleGallucci, S., Fiocchi, S., Bonato, M., Chiaramello, E., Tognola, G., & Parazzini, M. (2022). Exposure Assessment to Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields in Occupational Military Scenarios: A Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(2), 920. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19020920











