Mortality Related to Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease during the COVID-19 Pandemic: An Analysis of Multiple Causes of Death through Different Epidemic Waves in Veneto, Italy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
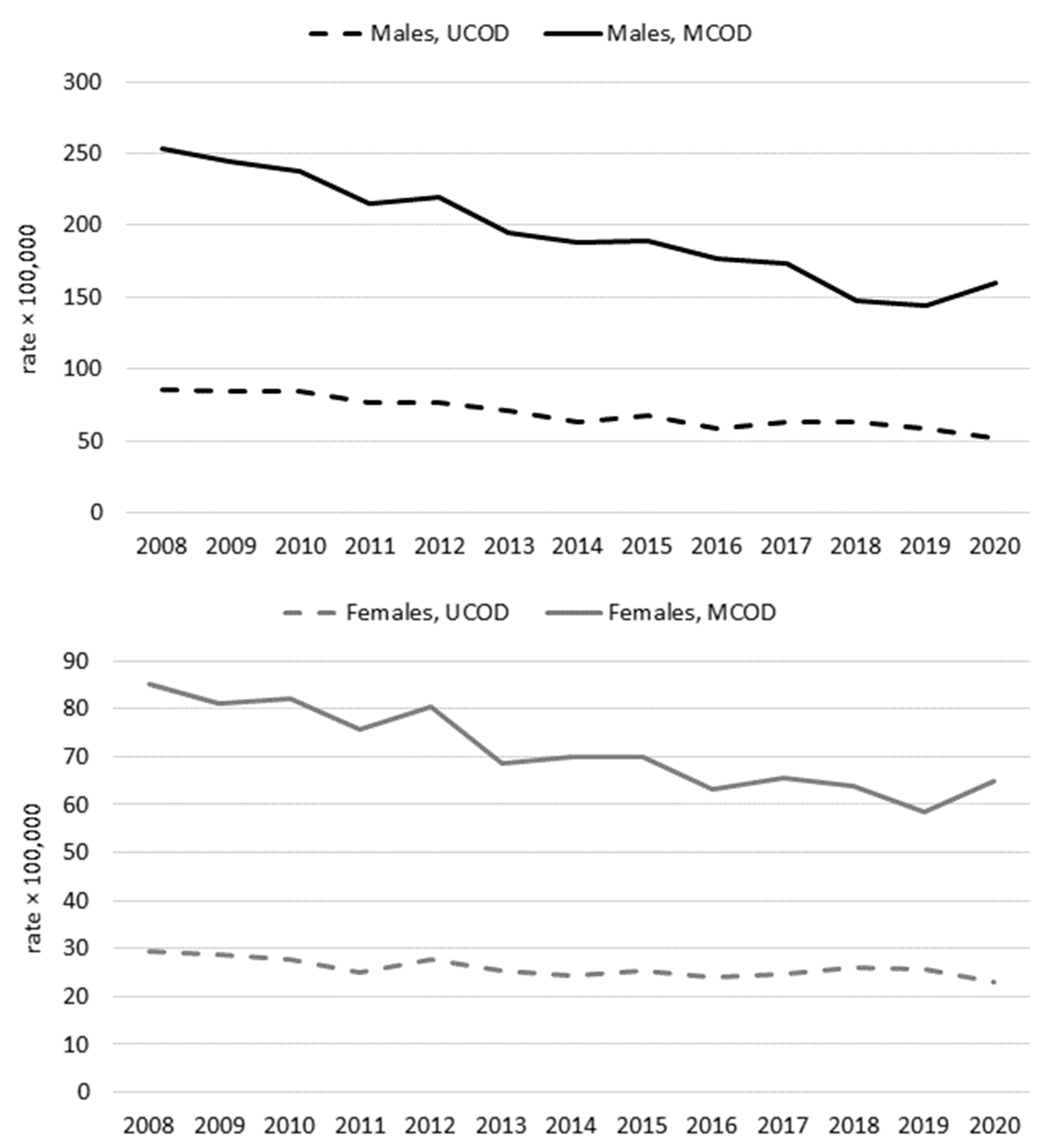
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- López-Campos, J.L.; Ruiz-Ramos, M.; Soriano, J.B. Mortality trends in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in Europe, 1994–2010: A joinpoint regression analysis. Lancet Respir. Med. 2014, 2, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrabian, B.; Mirsaeidi, M. A Trend Analysis of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Mortality in the United States by Race and Sex. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2021, 18, 1138–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, S.A.; Wheaton, A.G.; Watson, K.B.; Liu, Y.; Croft, J.B.; Greenlund, K.J. Geographic Differences in Sex-Specific Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Mortality Rate Trends Among Adults Aged ≥ 25 Years—United States, 1999–2019. MMWR Morb/ Mortal Wkly. Rep. 2022, 71, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2015 Chronic Respiratory Disease Collaborators. Global, regional, and national deaths, prevalence, disability-adjusted life years, and years lived with disability for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma, 1990–2015: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet Respir. Med. 2017, 5, 691–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/chronic-obstructive-pulmonary-disease-(copd) (accessed on 31 August 2022).
- Lindberg, A.; Lindberg, L.; Sawalha, S.; Nilsson, U.; Stridsman, C.; Lundbäck, B.; Backman, H. Large underreporting of COPD as cause of death-results from a population-based cohort study. Respir. Med. 2021, 186, 106518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcon, A.; Saugo, M.; Fedeli, U. COPD-Related Mortality and Co-morbidities in Northeastern Italy, 2008–2012: A Multiple Causes of Death Analysis. COPD 2016, 13, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannino, D.M.; Brown, C.; Giovino, G.A. Obstructive lung disease deaths in the United States from 1979 through 1993. An analysis using multiple-cause mortality data. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1997, 156, 814–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obi, J.; Mehari, A.; Gillum, R. Mortality Related to Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Co-morbidities in the United States, A Multiple Causes of Death Analysis. COPD 2018, 15, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santo, A.H.; Fernandes, F.L.A. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease-Related Mortality in Brazil, 2000–2019: A Multiple-Cause-of-Death Study. COPD 2022, 19, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansell, A.L.; Walk, J.A.; Soriano, J.B. What do chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients die from? A multiple cause coding analysis. Eur. Respir. J. 2003, 22, 809–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldacre, M.J.; Duncan, M.; Cook-Mozaffari, P.; Griffith, M. Mortality rates for common respiratory diseases in an English population 1979–1998: Artefact and substantive trends. J. Public Health 2004, 26, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fuhrman, C.; Jougla, E.; Nicolau, J.; Eilstein, D.; Delmas, M.C. Deaths from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in France, 1979–2002: A multiple cause analysis. Thorax 2006, 61, 930–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-García, A.; Pérez-Ríos, M.; Fernández-Villar, A.; Naveira, G.; Candal-Pedreira, C.; Santiago-Pérez, M.I.; Represas-Represas, C.; Malvar-Pintos, A.; Cerdeira-Caramés, S.; Ruano-Raviña, A. Four Decades of COPD Mortality Trends: Analysis of Trends and Multiple Causes of Death. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Han, X.; Luo, Y.; Weiguo, X. Deaths of obstructive lung disease in the Yangpu district of Shanghai from 2003 through 2011: A multiple cause analysis. Chin. Med. J. 2014, 127, 1619–1625. [Google Scholar]
- Fearnley, E.; Li, S.Q.; Guthridge, S. Trends in chronic disease mortality in the Northern Territory Aboriginal population, 1997–2004: Using underlying and multiple causes of death. Aust. N. Z. J. Public Health 2009, 33, 551–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardhan, S.; Wood, S.; Vaughan, M.; Trott, M. The Risk of COVID-19 Related Hospitalsation, Intensive Care Unit Admission and Mortality in People with Underlying Asthma or COPD: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 668808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsallakh, M.A.; Sivakumaran, S.; Kennedy, S.; Vasileiou, E.; Lyons, R.A.; Robertson, C.; Sheikh, A.; Davies, G.A.; EAVE II Collaborators. Impact of COVID-19 lockdown on the incidence and mortality of acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: National interrupted time series analyses for Scotland and Wales. BMC Med. 2021, 19, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, G.; Zhu, L.; Hayen, A.; Bell, K.J.L. Learning from the pandemic: Mortality trends and seasonality of deaths in Australia in 2020. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2022, 51, 718–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.B.; Anderson, R.N. The Leading Causes of Death in the US for 2020. JAMA 2021, 325, 1829–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luck, A.N.; Preston, S.H.; Elo, I.T.; Stokes, A.C. The unequal burden of the Covid-19 pandemic: Capturing racial/ethnic disparities in US cause-specific mortality. SSM Popul. Health 2022, 17, 101012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soriano, J.B.; Peláez, A.; Fernández, E.; Moreno, L.; Ancochea, J. The Emergence of COVID-19 as a Cause of Death in 2020 and its Effect on Mortality by Diseases of the Respiratory System in Spain: Trends and Their Determinants Compared to 2019. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2022, 58, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, F.; Pitter, G.; Da Re, F.; Tonon, M.; Avossa, F.; Bellio, S.; Fedeli, U.; Gubian, L.; Monetti, D.; Saia, M.; et al. Epidemiology and public health response in early phase of COVID-19 pandemic, Veneto Region, Italy, 21 February to 2 April 2020. Euro. Surveill. 2020, 25, 2000548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, T.H.; Hsu, P.Y.; Bjorkenstam, C.; Anderson, R.N. Certifying diabetes-related cause-of-death: A comparison of inappropriate certification statements in Sweden, Taiwan and the USA. Diabetologia 2006, 49, 2878–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orsi, C.; Navarra, S.; Frova, L.; Grande, E.; Marchetti, S.; Pappagallo, M.; Grippo, F. Impact of the implementation of ICD-10 2016 version and Iris software on mortality statistics in Italy. Epidemiol. Prev. 2019, 43, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fedeli, U.; Casotto, V.; Barbiellini Amidei, C.; Saia, M.; Tiozzo, S.N.; Basso, C.; Schievano, E. Parkinson’s disease related mortality: Long-term trends and impact of COVID-19 pandemic waves. Park. Relat. Disord. 2022, 98, 75–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazick, A.; Gergonne, B.; Nielsen, J.; Wuillaume, F.; Virtanen, M.J.; Fouillet, A.; Uphoff, H.; Sideroglou, T.; Paldy, A.; Oza, A.; et al. Excess mortality among the elderly in 12 European countries, February and March 2012. Euro. Surveill. 2012, 17, 20138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de’ Donato, F.K.; Leone, M.; Noce, D.; Davoli, M.; Michelozzi, P. The Impact of the February 2012 Cold Spell on Health in Italy Using Surveillance Data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61720. [Google Scholar]
- Gayle, A.V.; Axson, E.L.; Bloom, C.I.; Navaratnam, V.; Quint, J.K. Changing causes of death for patients with chronic respiratory disease in England, 2005–2015. Thorax 2019, 74, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raknes, G.; Strøm, M.S.; Sulo, G.; Øverland, S.; Roelants, M.; Juliusson, P.B. Lockdown and non-COVID-19 deaths: Cause-specific mortality during the first wave of the 2020 pandemic in Norway: A population-based register study. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e050525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grande, E.; Fedeli, U.; Pappagallo, M.; Crialesi, R.; Marchetti, S.; Minelli, G.; Iavarone, I.; Frova, L.; Onder, G.; Grippo, F. Variation in Cause-Specific Mortality Rates in Italy during the First Wave of the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Study Based on Nationwide Data. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voci, D.; Fedeli, U.; Farmakis, I.T.; Hobohm, L.; Keller, K.; Valerio, L.; Schievano, E.; Barbiellini Amidei, C.; Konstantinides, S.V.; Kucher, N.; et al. Deaths related to pulmonary embolism and cardiovascular events before and during the 2020 COVID-19 pandemic: An epidemiological analysis of data from an Italian high-risk area. Thromb. Res. 2022, 212, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacedonia, D.; Scioscia, G.; Santomasi, C.; Fuso, P.; Carpagnano, G.E.; Portacci, A.; Mastroianni, F.; Larizza, G.; Sabato, E.; Profilo, E.; et al. Impact of smoking, COPD and comorbidities on the mortality of COVID-19 patients. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerayeli, F.V.; Milne, S.; Cheung, C.; Li, X.; Yang, C.W.T.; Tam, A.; Choi, L.H.; Bae, A.; Sin, D.D. COPD and the risk of poor outcomes in COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. EClinicalMedicine 2021, 33, 100789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, H.H.; Godtfredsen, N.S.; Lange, P.; Vestbo, J. Potential misclassification of causes of death from COPD. Eur. Respir. J. 2006, 28, 781–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diab, N.; Gershon, A.S.; Sin, D.D.; Tan, W.C.; Bourbeau, J.; Boulet, L.P.; Aaron, S.D. Underdiagnosis and Overdiagnosis of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 198, 1130–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| UCOD | MCOD | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | n | Proportional Mortality | n | Proportional Mortality |
| 2008 | 1179 | 2.7% | 3538 | 8.2% |
| 2009 | 1176 | 2.7% | 3475 | 8.0% |
| 2010 | 1190 | 2.7% | 3476 | 8.0% |
| 2011 | 1118 | 2.5% | 3340 | 7.6% |
| 2012 | 1240 | 2.7% | 3645 | 7.9% |
| 2013 | 1168 | 2.6% | 3273 | 7.3% |
| 2014 | 1123 | 2.5% | 3347 | 7.5% |
| 2015 | 1241 | 2.6% | 3473 | 7.2% |
| 2016 | 1142 | 2.4% | 3264 | 6.9% |
| 2017 | 1219 | 2.5% | 3361 | 6.9% |
| 2018 | 1290 | 2.7% | 3088 | 6.4% |
| 2019 | 1265 | 2.6% | 3022 | 6.3% |
| 2020 | 1175 | 2.1% | 3478 | 6.2% |
| 2008–2020 | 15,526 | 2.6% | 43,780 | 7.2% |
| 2008–2012 | 2013–2017 | 2018–2019 | 2020 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COPD (J40–J44, J47) | UCOD MCOD | 34% 100% | 35% 100% | 42% 100% | 34% 100% |
| Ischemic heart diseases (I20–I25) | UCOD | 16% | 13% | 10% | 8% |
| MCOD | 30% | 25% | 23% | 21% | |
| Cerebrovascular diseases (I60–I69) | UCOD | 5% | 4% | 4% | 4% |
| MCOD | 15% | 12% | 11% | 11% | |
| Ipertensive disesases (I10–I13) | UCOD | 6% | 7% | 6% | 6% |
| MCOD | 28% | 27% | 27% | 27% | |
| Diabetes (E10–E14) | UCOD | 2% | 2% | 2% | 2% |
| MCOD | 15% | 15% | 15% | 17% | |
| Neoplasms (C00–D48) | UCOD | 14% | 15% | 14% | 12% |
| MCOD | 23% | 22% | 22% | 21% | |
| Dementia/Alzheimer (F01, F03, G30) | UCOD | 3% | 3% | 3% | 3% |
| MCOD | 9% | 9% | 10% | 10% | |
| Infectious diseases (A00–B99, others *) | UCOD | 2% | 3% | 1% | 1% |
| MCOD | 23% | 24% | 25% | 30% | |
| COVID-19 (U07.1, U07.2) | UCOD | - | - | - | 13% |
| MCOD | - | - | - | 15% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fedeli, U.; Barbiellini Amidei, C.; Marcon, A.; Casotto, V.; Grippo, F.; Grande, E.; Gaisl, T.; Barco, S. Mortality Related to Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease during the COVID-19 Pandemic: An Analysis of Multiple Causes of Death through Different Epidemic Waves in Veneto, Italy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12844. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912844
Fedeli U, Barbiellini Amidei C, Marcon A, Casotto V, Grippo F, Grande E, Gaisl T, Barco S. Mortality Related to Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease during the COVID-19 Pandemic: An Analysis of Multiple Causes of Death through Different Epidemic Waves in Veneto, Italy. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(19):12844. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912844
Chicago/Turabian StyleFedeli, Ugo, Claudio Barbiellini Amidei, Alessandro Marcon, Veronica Casotto, Francesco Grippo, Enrico Grande, Thomas Gaisl, and Stefano Barco. 2022. "Mortality Related to Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease during the COVID-19 Pandemic: An Analysis of Multiple Causes of Death through Different Epidemic Waves in Veneto, Italy" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 19: 12844. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912844
APA StyleFedeli, U., Barbiellini Amidei, C., Marcon, A., Casotto, V., Grippo, F., Grande, E., Gaisl, T., & Barco, S. (2022). Mortality Related to Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease during the COVID-19 Pandemic: An Analysis of Multiple Causes of Death through Different Epidemic Waves in Veneto, Italy. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(19), 12844. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912844







