The Slope Safety, Heavy Metal Leaching, and Pollutant Diffusion Prediction Properties under the Influence of Unclassified Cemented Paste Backfill in an Open Pit
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
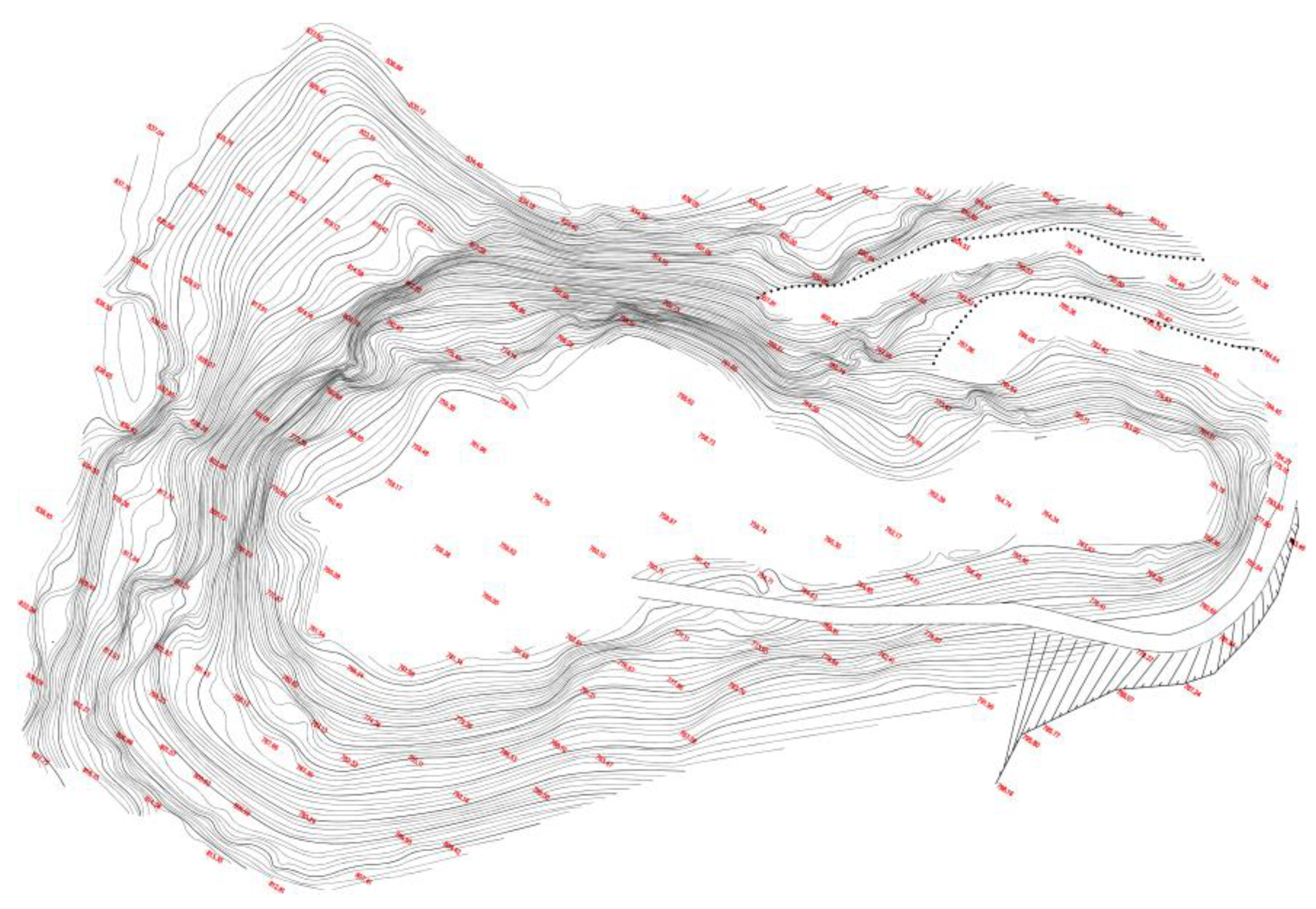
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Backfilling Implementation
2.3. Experiments
2.3.1. Physical Tests
- (1)
- Physical properties of rock and CPB sample
- (2)
- Physical properties of unclassified tailings
2.3.2. Slope Stability Research Program
2.3.3. Heavy Metals Leaching Experiment
2.3.4. Groundwater Safety Monitoring
2.3.5. Prediction Method
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Safety of the Slope
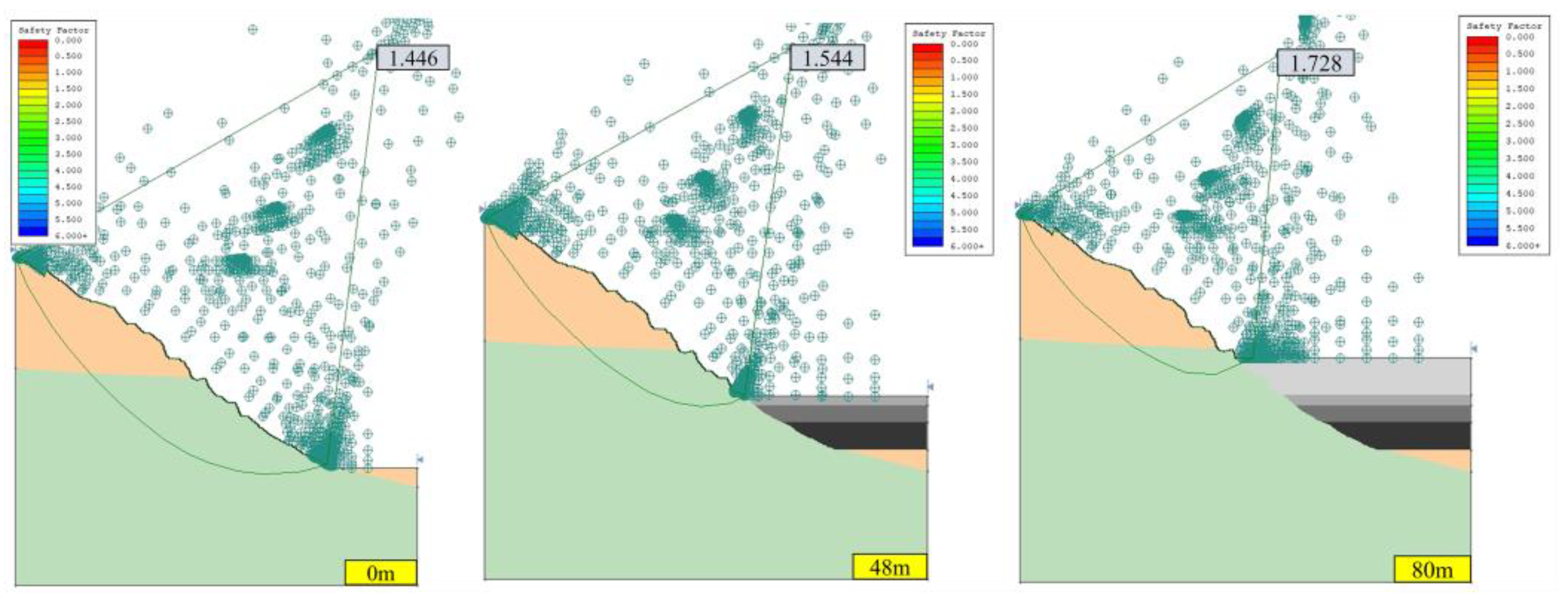
3.1.1. Stability Analysis of Open-Pit Slope without Seepage Field
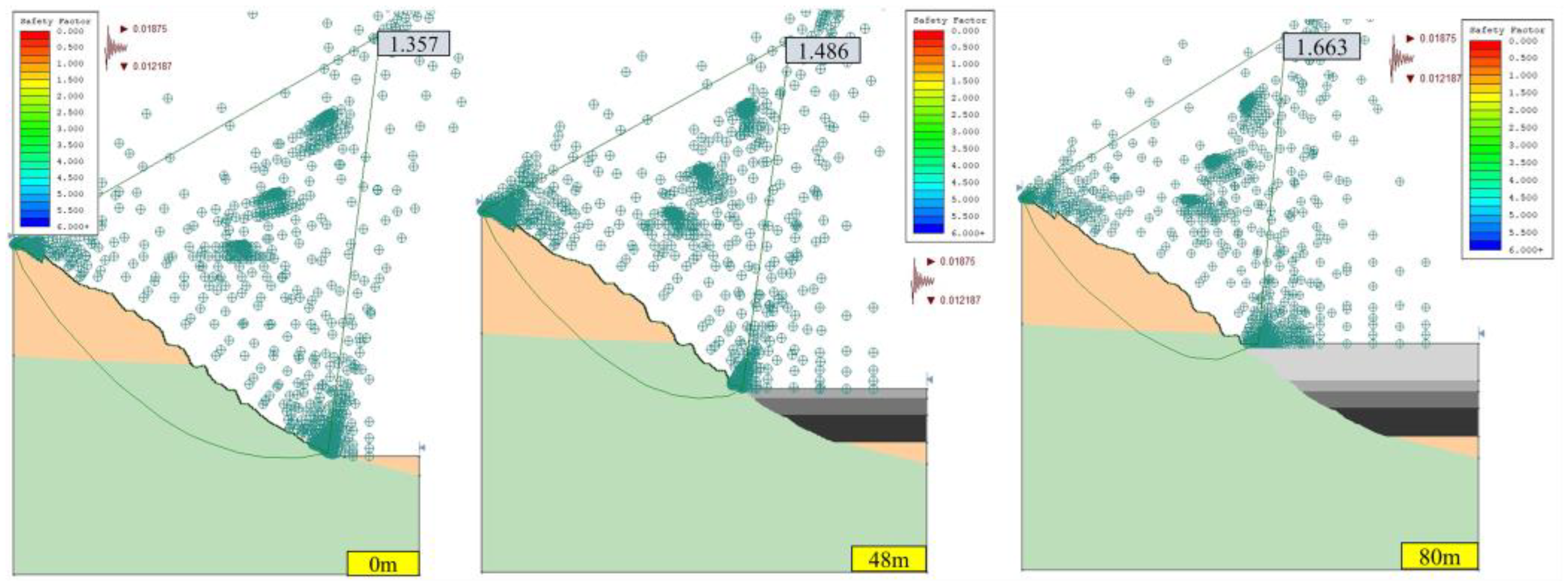
3.1.2. Stability Analysis of Open-Pit Slope under Seepage Field
3.2. Leaching Properties
3.3. Groundwater Safety Monitoring
3.4. Groundwater Safety Monitoring
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The safety factor of the open pit slope was proportional to the height of OPUCPB. Under the conditions of seismic forces and seepage fields, the safety factor of slope B was increased from 1.188 to 1.574 using OPUCPB.
- (2)
- According to the results of acid and water leaching of tailings and backfilling cement bodies, CPB can effectively capture and fix the heavy metals so that the leaching concentration in tailings changes from exceeding the groundwater class III standard to meeting the standard.
- (3)
- The groundwater monitoring results showed that the groundwater around the open pit conformed to the national groundwater class III limit requirements and OPUCPB had no significant impact on the groundwater.
- (4)
- Considering extreme conditions, a failure of the cementitious material conveying system occurs, and a small number of tailings enter the open pit without consolidation in a short time, thus polluting the groundwater. It was found that the pollution process was very slow, even just 50 m away from the leak point, and the minimum time required for pollutants to reach the standard limit was 232 d. Therefore, the long-term influence of tailings solidification by backfilling in an open pit on the groundwater environment can be controlled. In addition, the heavy metal diffusion in the groundwater should be investigate in the future.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ruan, Z.; Wu, A.; Bürger, R.; Betancourt, F.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jiao, H.; Wang, S. Effect of interparticle interactions on the yield stress of thickened flocculated copper mineral tailings slurry. Powder Technol. 2021, 392, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.; Ruan, Z.; Wang, J. Rheological behavior of paste in metal mines. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2022, 29, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Qi, C.; Chen, Q.; Gan, D.; Xue, Z.; Hu, Y. A new procedure for recycling waste tailings as cemented paste backfill to underground stopes and open pits. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 188, 601–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Tao, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y. Utilization of modified copper slag activated by Na2SO4 and CaO for unclassified lead/zinc mine tailings based cemented paste backfill. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 290, 112608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Qi, C. The carbon uptake and mechanical property of cemented paste backfill carbonation curing for low concentration of CO2. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 852, 158516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.-L.; Li, Y.-T.; Chen, Q.-S.; Liu, Y.-K.; Feng, Y.; Wang, D.-L. Effects of temperatures and pH values on rheological properties of cemented paste backfill. J. Cent. South Univ. 2021, 28, 1707–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.W.; Wang, Y.B.; Zhang, F.; Feng, L.Z.; Zhou, Y. Janbu Method Application in Jianshan Iron Mine. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 524, 608–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H. Upper Bound Solution of Rationalized Janbu Method. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2011, 90, 2393–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.-M.; Li, D.-Q.; Cao, Z.-J.; Xu, D.-S.; Fu, X.-Y. Reliability-based monitoring sensitivity analysis for reinforced slopes using BUS and subset simulation methods. Eng. Geol. 2021, 293, 106331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, P.; Qiu, P.; Liu, B.; Chen, W.; Su, S. Stability prediction and optimal angle of high slope in open-pit mine based on two-dimension limit equilibrium method and three-dimension numerical simulation. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2022, 127, 103151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Dalconi, M.C.; Molinari, S.; Valentini, L.; Wang, Y.; Sun, S.; Wang, P.; Artioli, G. Retention of phosphorus and fluorine in phosphogypsum for cemented paste backfill: Experimental and numerical simulation studies. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 113775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Dalconi, M.C.; Molinari, S.; Valentini, L.; Wang, Y.; Sun, S.; Wang, P.; Artioli, G. Enhancing the sustainable immobilization of phosphogypsum by cemented paste backfill with the activation of γ-Al2O3. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 347, 128624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Clavier, K.A.; Spreadbury, C.; Townsend, T.G. Limitations of the TCLP fluid determination step for hazardous waste characterization of US municipal waste incineration ash. Waste Manag. 2019, 87, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuppusamy, V.K.; Holuszko, M. Sulfuric acid baking and water leaching of rare earth elements from coal tailings. Fuel 2022, 319, 123738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, E.E.; Chiang, P.C.; Lu, P.H.; Ko, Y.W. Comparisons of metal leachability for various wastes by extraction and leaching methods. Chemosphere 2001, 45, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzano, C.; Pertis, M.D.; Perillo, G.; Cioffi, R. Treatment and Reuse of Ash from Municipal Solid Waste Incineration. Mater. Contact Characterisation X 2021, 133, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, B.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, M. Risk assessment of groundwater with multi-source pollution by a long-term monitoring programme for a large mining area. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2018, 128, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singha, S.; Pasupuleti, S.; Singha, S.S.; Singh, R.; Kumar, S. Prediction of groundwater quality using efficient machine learning technique. Chemosphere 2021, 276, 130265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamovic, D.; Ishiyama, D.; Kawaraya, H.; Ogawa, Y.; Stevanovic, Z. Geochemical characteristics and estimation of groundwater pollution in catchment areas of Timok and Pek Rivers, Eastern Serbia: Determination of early-stage groundwater pollution in mining areas. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2022, 16, 100719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, Z. Site prioritization and performance assessment of groundwater monitoring network by using information-based methodology. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singha, S.; Pasupuleti, S.; Singha, S.S.; Kumar, S. Effectiveness of groundwater heavy metal pollution indices studies by deep-learning. J. Contam. Hydro.l 2020, 235, 103718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghaddam, H.K.; Rajaei, A.; Rahimzadeh Kivi, Z.; Moghaddam, H.K. Prediction of qualitative parameters concentration in the groundwater resources using the Bayesian approach. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2022, 17, 100758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Technical Guidelines for Environmental Impact Assessment Groundwater Environment. 2016. Available online: https://english.mee.gov.cn/Resources/standards/others1/Technical_Guideline_EIA/201603/t20160303_331190.shtml (accessed on 4 June 2022).
- Chen, Q.; Tao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Qi, C. The rheological, mechanical and heavy metal leaching properties of cemented paste backfill under the influence of anionic polyacrylamide. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loáiciga, H.A. Groundwater and earthquakes: Screening analysis for slope stability. Eng. Geol. 2015, 193, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senneca, O.; Cortese, L.; Di Martino, R.; Fabbricino, M.; Ferraro, A.; Race, M.; Scopino, A. Mechanisms affecting the delayed efficiency of cement based stabilization/solidification processes. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 261, 121230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Cement-Tailings Ratio | γ (t/m3) | Rc (MPa) | Rt (MPa) | C (MPa) | φ (º) | K (m/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1:10 | 1.67 | 2.38 | 0.056 | 0.37 | 72.56 | 0.8 × 10−4 |
| 1:14 | 1.64 | 1.67 | 0.048 | 0.28 | 70.76 | 1.0 × 10−4 |
| 1:16 | 1.66 | 1.52 | 0.041 | 0.25 | 70.69 | 1.1 × 10−4 |
| 1:20 | 1.70 | 0.88 | 0.036 | 0.18 | 67.13 | 1.3 × 10−4 |
| Material | γ (t/m3) | Rc (MPa) | C/MPa | φ (º) | K (m/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metamorphic Quartz Sandstone | 26.46 | 145.64 | 44.00 | 27.84 | 1.86 × 10−4 |
| Fine-grained Granite | 25.48 | 99.68 | 27.46 | 32.24 | 6.59 × 10−6 |
| Marble | 28.59 | 88.65 | 22.79 | 35.66 | 3.47 × 10−6 |
| Particle Size (μm) | +150 | −150~+74 | −74~+45 | −45~+37 | −37 | Recovery Percent |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content (%) | 10.82 | 11.97 | 19.37 | 6.88 | 50.96 | 100% |
| Test Items | T1/mg·L−1 | T2/mg·L−1 | T3/mg·L−1 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | D2 | D3 | D1 | D2 | D3 | D1 | D2 | D3 | |
| PH | 6.21 | 6.22 | 6.24 | 6.31 | 6.35 | 6.33 | 7.36 | 7.36 | 7.38 |
| Cu | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Pb | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Zn | 0.09 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Cd | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| As | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Mn | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Fe | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, K.; Zhang, Q.; Tao, Y.; Luo, K.; Chen, Q. The Slope Safety, Heavy Metal Leaching, and Pollutant Diffusion Prediction Properties under the Influence of Unclassified Cemented Paste Backfill in an Open Pit. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12772. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912772
Chen K, Zhang Q, Tao Y, Luo K, Chen Q. The Slope Safety, Heavy Metal Leaching, and Pollutant Diffusion Prediction Properties under the Influence of Unclassified Cemented Paste Backfill in an Open Pit. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(19):12772. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912772
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Ke, Qinli Zhang, Yunbo Tao, Kai Luo, and Qiusong Chen. 2022. "The Slope Safety, Heavy Metal Leaching, and Pollutant Diffusion Prediction Properties under the Influence of Unclassified Cemented Paste Backfill in an Open Pit" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 19: 12772. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912772
APA StyleChen, K., Zhang, Q., Tao, Y., Luo, K., & Chen, Q. (2022). The Slope Safety, Heavy Metal Leaching, and Pollutant Diffusion Prediction Properties under the Influence of Unclassified Cemented Paste Backfill in an Open Pit. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(19), 12772. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912772






