Heart Rate Does Not Reflect the %VO2max in Recreational Runners during the Marathon
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. The Incremental Maximal Test and the Marathon Race
2.3. The Experimental Measurements
2.4. The Variables Used in the Analysis of Results
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Maximal Values of O2 and Heart Rate in the Test UM-TT
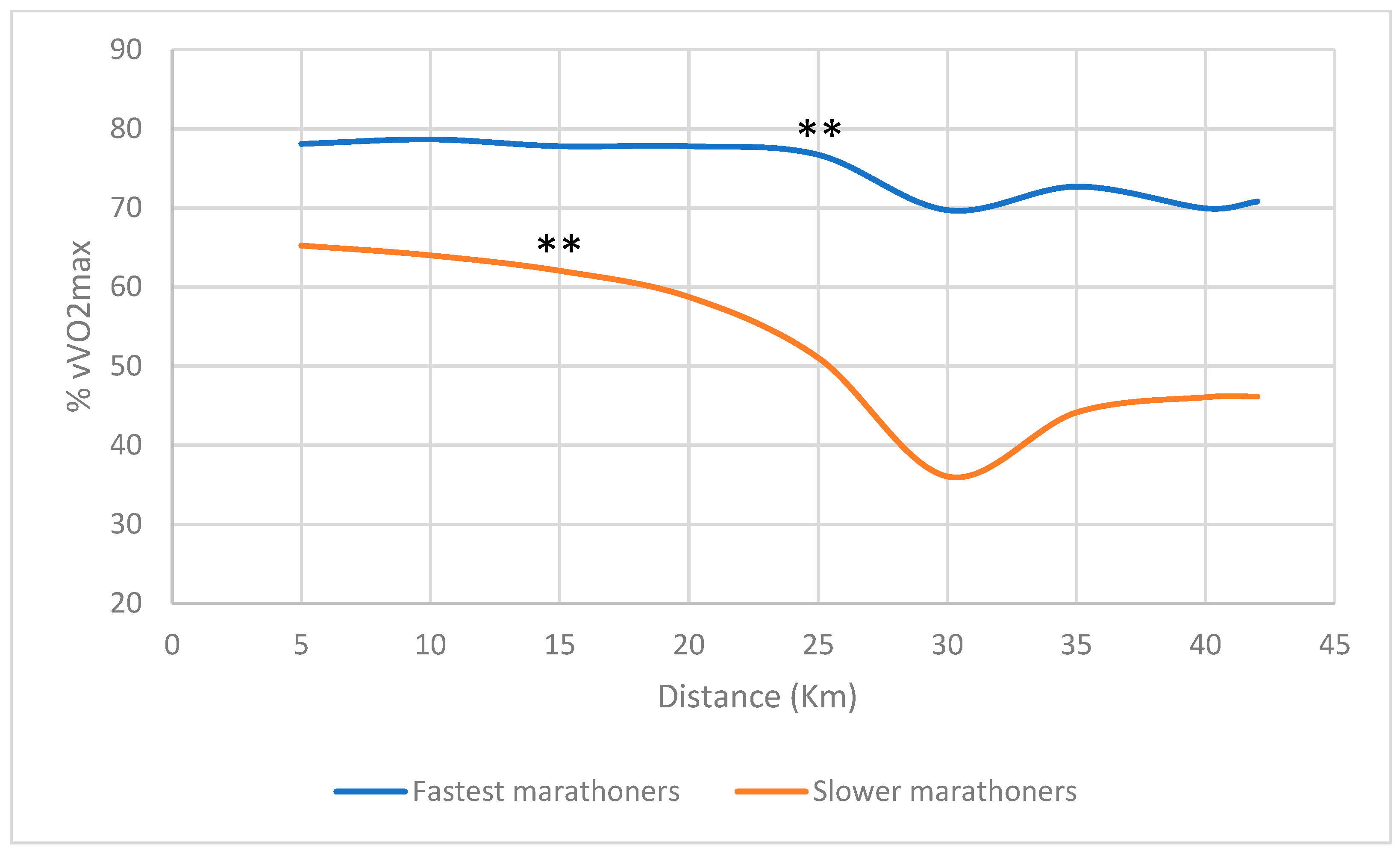
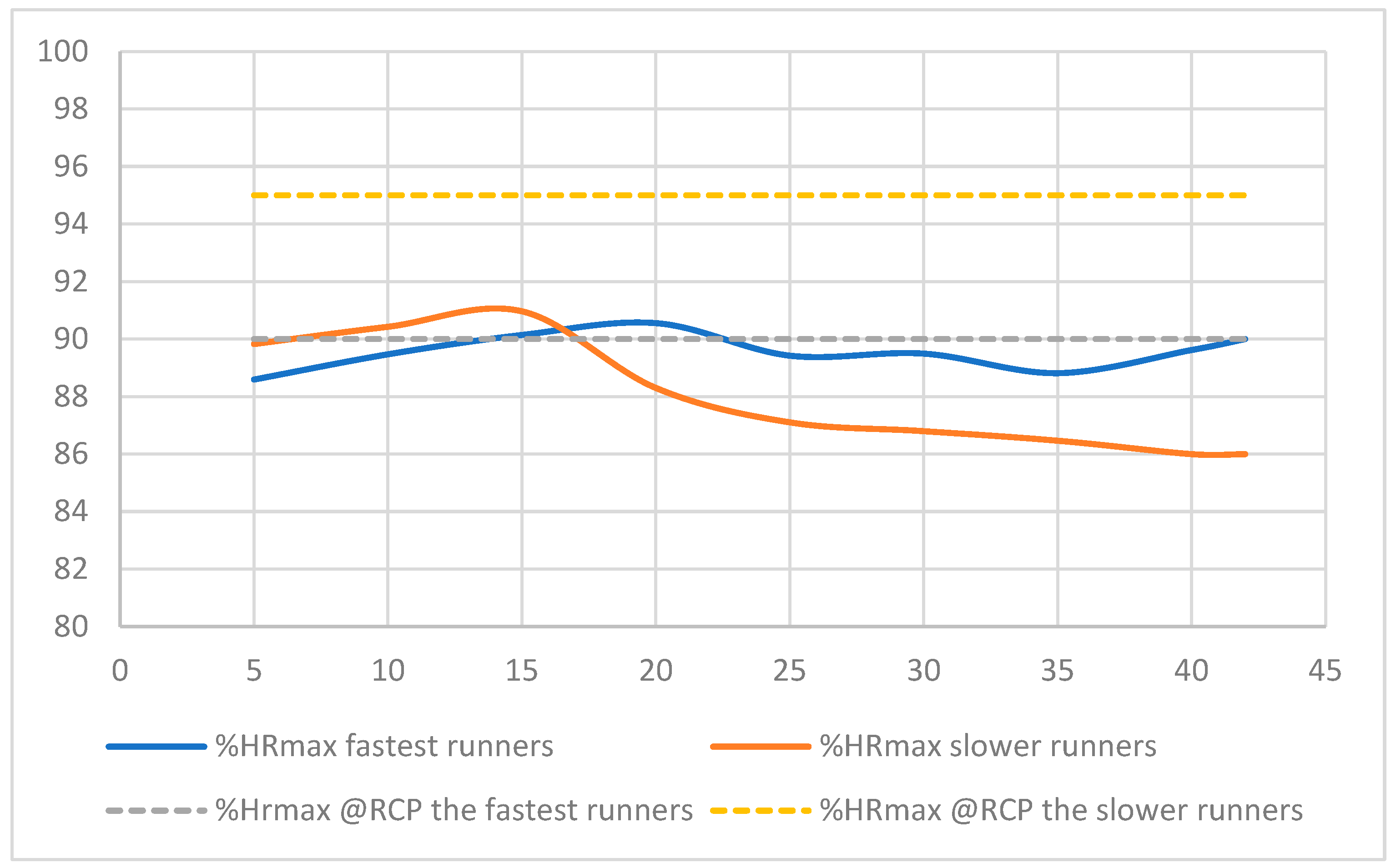
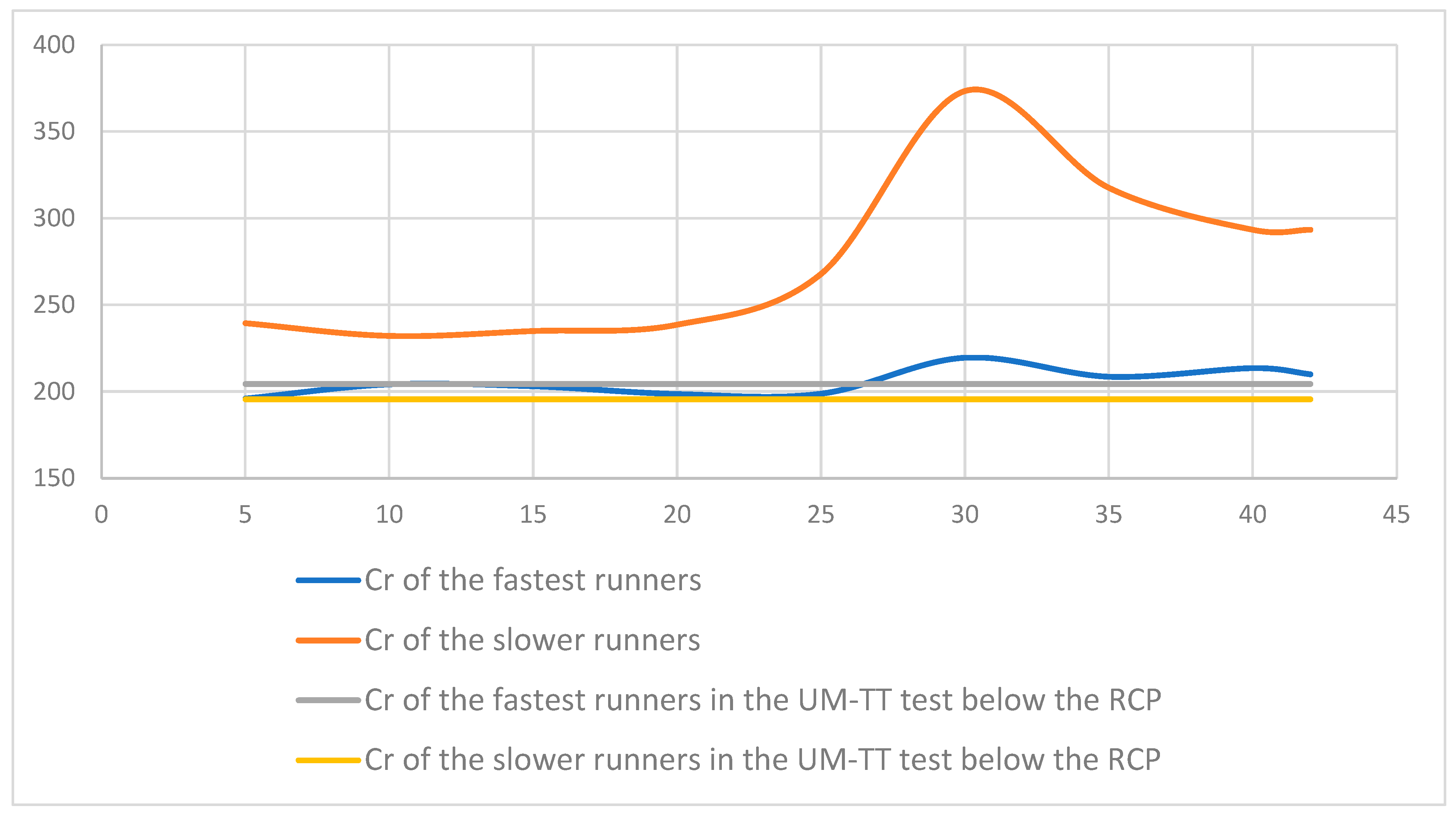
3.2. VO2 and Heart Rate in the Marathon Race
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Limits of this Study
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Costill, D.L.; Fox, E.L. Energetics of marathon running. Med. Sci. Sports 1969, 1, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maron, M.B.; Horvath, S.M. The Marathon: A History and Review of the Literature. Med. Sci. Sports 1978, 10, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vitti, A.; Nikolaidis, P.T.; Villiger, E.; Onywera, V.; Knechtle, B. The “New York City Marathon”: Participation and performance trends of 1.2M runners during half-century. Res. Sports Med. 2020, 28, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breen, D.; Norris, M.; Healy, R.; Anderson, R. Marathon Pace Control in Masters Athletes. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2018, 13, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, D.; Wightman, S.; Basevitch, I.; Johnstone, J.; Espejo-Sanchez, C.; Beckford, C.; Boal, M.; Scruton, A.; Ferrandino, M.; Merzbach, V. Physiological and training characteristics of recreational marathon runners. Open Access J. Sports Med. 2017, 8, 231–241. [Google Scholar]
- Myrkos, A.; Smilios, I.; Kokkinou, E.M.; Rousopoulos, E.; Douda, H. Physiological and Race Pace Characteristics of Medium and Low-Level Athens Marathon Runners. Sports 2020, 9, 116. [Google Scholar]
- Ashley, M. Everything You Need to Know About the 10 Most Popular Marathon Training Plans. Available online: https://www.shape.com/fitness/training-plans/marathon-training-for-beginners (accessed on 15 April 2022).
- Smyth, B. Fast Starters and Slow Finishers: A Large-Scale Data Analysis of Pacing at the Beginning and End of the Marathon for Recreational Runners. J. Sports Anal. 2018, 4, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buman, M.P.; Brewer, B.W.; Cornelius, A.E.; Van Raalte, J.L.; Petitpas, A.J. Hitting the wall in the marathon: Phenomenological characteristics and associations with expectancy, gender, and running history. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2008, 9, 177–190. [Google Scholar]
- Maron, M.; Horvath, S.M.; Wilkerson, J.E.; Gliner, J.A. Oxygen Uptake Measurements During Competitive Marathon Running. J. Appl. Physiol. 1976, 40, 836–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinari, C.A.; Edwards, J.; Billat, V. Maximal Time Spent at VO2max from Sprint to the Marathon. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billat, V.; Poinsard, L.; Palacin, F.; Pycke, R.J.; Maron, M. Oxygen Uptake Measurements and Rate of Perceived Exertion During a Marathon. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjödin, B.; Svedenhag, J. Applied Physiology of Marathon Running. Sports Med. 1985, 2, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coyle, E.F. Physiological Regulation of Marathon Performance. Sports Med. 2007, 37, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagan, R.D.; Upton, S.J.; Duncan, J.J.; Gettman, L.R. Marathon performance in relation to maximal aerobic power and training indices in female distance runners. Br. J. Sports Med. 1987, 21, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- di Prampero, P.E.; Atchou, G.; Brückner, J.C.; Moia, C. The energetics of endurance running. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occup. Physiol. 1986, 55, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapoport, B.I. Metabolic factors limiting performance in marathon runners. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2010, 6, e1000960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, B.; Sollevi, A.; Jansson, E. Increased IMP content in glycogen-depleted muscle fibres during submaximal exercise in man. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1988, 133, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahlin, K.; Tonkonogi, M.; Söderlund, K. Energy supply and muscle fatigue in humans. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1997, 162, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oficial-Casado, F.; Uriel, J.; Jimenez-Perez, I.; Goethel, M.F.; Pérez-Soriano, P.; Priego-Quesada, J.I. Consistency of pacing profile according to performance level in three different editions of the Chicago, London, and Tokyo marathons. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 10780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micklewright, D.; Papadopoulou, E.; Swart, J.; Noakes, T. Previous experience influences pacing during 20 km time trial cycling. Br. J. Sports Med. 2010, 44, 952–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billat, V.; Petot, H.; Landrain, M.; Meilland, R.; Koralsztein, J.P.; Hamard, L. Cardiac Output and Performance during a Marathon Race in Middle-Aged Recreational Runners. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 810859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, B.; Giles, D.; Draper, N.; Hoos, O.; Gronwald, T. A new detection method defining the aerobic threshold for endurance exercise and training prescription based on fractal correlation properties of heart rate variability. Front. Physiol. 2021, 11, 596567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coyle, E.F.; González-Alonso, J. Cardiovascular Drift During Prolonged Exercise: New Perspectives. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2001, 29, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Billat, V.L.; Palacin, F.; Correa, M.; Pycke, J.R. Pacing Strategy Affects the Sub-Elite Marathoner’s Cardiac Drift and Performance. Front. Psychol. 2020, 10, 3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schena, F.; Pellegrini, B.; Tarperi, C.; Calabria, E.; Salvagno, G.L.; Capelli, C. Running Economy During a Simulated 60-km Trial. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2014, 9, 604–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, L.; Costill, D.L. A Comparison of Two Middle-Aged Ultramarathon Runners, Research Quarterly. Am. Assoc. Health Phys. Educ. Recreat. 1970, 41, 135–139. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, A.M.; Kirby, B.S.; Clark, I.E.; Rice, H.M.; Fulkerson, E.; Wylie, L.J.; Wilkerson, D.P.; Vanhatalo, A.; Wilkins, B.W. Physiological demands of running at 2-hour marathon race pace. J. Appl. Physiol. 2021, 130, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyner, M.J.; Hunter, S.K.; Lucia, A.; Jones, A.M. Physiology and fast marathons. J. Appl. Physiol. 2020, 128, 1065–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmaidi, S.; Collomp, K.; Caillaud, C.; Prefaut, C. Maximal and Functional Aerobic Capacity as Assessed by Two Graduated Field Methods in Comparison to Laboratory Exercise Testing in Moderately Trained Subject. Int. J. Sports Med. 1992, 13, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Léger, L.; Boucher, R. An indirect continuous running multistage field test: The Université de Montréal track test. Can. J. Appl. Sport Sci. 1980, 5, 77–84. [Google Scholar]
- Beaver, W.L.; Wasserman, K.; Whipp, B.J. A new method for detecting anaerobic threshold by gas exchange. J. Appl. Physiol. 1986, 60, 2020–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraft, G.L.; Roberts, R.A. Validation of the garmin forerunner 920XT fitness watch VO2peak test. Ijier 2017, 5, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karvonen, J.; Vuorimaa, T. Heart rate and exercise intensity during sports activities. Practical application. Sports Med. 1988, 5, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loftin, M.; Sothern, M.; Koss, C.; Tuuri, G.; Vanvrancken, C.; Kontos, A.; Bonis, M. Energy expenditure and influence of physiologic factors during marathon running. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2007, 21, 1188–1191. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Costill, D.L.; Thomason, H.; Roberts, E. Fractional utilization of the aerobic capacity during distance running. Med. Sci. Sports 1973, 5, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achten, J.; Jeukendrup, A.E. Heart rate monitoring: Applications and limitations. Sports Med. 2003, 33, 517–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lounana, J.; Campion, F.; Noakes, T.D.; Medelli, J. Relationship between %HRmax, %HR reserve, %VO2max, and %VO2 reserve in elite cyclists. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2007, 39, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, T.; Lamberts, R.P.; Lambert, M.I. Methods of prescribing relative exercise intensity: Physiological and practical considerations. Sports Med. 2013, 43, 613–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, C.; Figueroa, A.; Fernhall, B.; Kanaley, J.A. Energy expenditure of walking and running comparison with prediction equations. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2004, 36, 2128–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minetti, A.E.; Ardigò, L.P.; Saibene, F. The transition between walking and running in humans: Metabolic and mechanical aspects at different gradients. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1994, 150, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharhag-Rosenberger, F.; Meyer, T.; Gässler, N.; Faude, O.; Kindermann, W. Exercise at given percentages of VO2max: Heterogeneous metabolic responses between individuals. J. Sci. Med. Sports 2010, 13, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pycke, J.R.; Billat, V. Marathon Performance Depends on Pacing Oscillations between Non Symmetric Extreme Values. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marino, F. The limitations of the constant load and self-paced exercise models of exercise physiology. Comp. Exerc. Physiol. 2012, 8, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Koning, J.; Foster, C.; Bakkum, A.; Kloppenburg, S.; Thiel, C.; Joseph, T.; Cohen, J.; Porcari, J. Regulation of Pacing Strategy during Athletic Competition. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e15863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binkley, S.; Foster, C.; Cortis, C.; de Koning, J.J.; Dodge, C.; Doberstein, S.T.; Fusco, A.; Jaime, S.J.; Porcari, J.P. Summated Hazard Score as a Powerful Predictor of Fatigue in Relation to Pacing Strategy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, H.A. Comparison between field research and controlled laboratory research. Arch. Clin. Biomed. Res. 2017, 1, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira Damasceno, V.; Costa, A.D.S.; Campello, M.C.A.; Souza, D.E.; Gonçalves, R.; Campos, E.Z.; Santos, T.M. Criterion validity and accuracy of a heart rate monitor. Hum. Mov. 2022, 23, 60–68. [Google Scholar]
- Tabata, I.; Kawakami, A. Effects of blood glucose concentration on ratings of perceived exertion during prolonged low-intensity physical exercise. JPN J. Physiol. 1991, 41, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Subjects | Level | Age (years) | Weight (kg) | Height (cm) | BMI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | High | 47 | 71 | 175 | 23.1 |
| 2 | High | 44 | 82 | 183 | 24.5 |
| 3 | High | 33 | 71 | 177 | 22.7 |
| 4 | High | 34 | 68 | 181 | 20.8 |
| 5 | High | 37 | 74 | 193 | 19.9 |
| 6 | Low | 50 | 71 | 170 | 24.6 |
| 7 | Low | 37 | 66 | 173 | 22.1 |
| 8 | Low | 33 | 77 | 180 | 23.8 |
| 9 | Low | 53 | 75 | 186 | 21.7 |
| 10 | Low | 49 | 77 | 187 | 22.0 |
| Mean | 41.7 | 73.2 | 180.5 | 22.5 | |
| SD | 7.7 | 4.8 | 7.0 | 1.5 |
| Level | vO2max (km·h−1) | HRmax (bpm) | O2max (mL·kg−1·min−1) | v@RCP%vO2max | CR (mL·kg−1·km−1) %v@RCP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High | 15.9 | 176 | 53 | 96% | 214 |
| High | 16.5 | 179 | 52 | 92% | 204 |
| High | 16.8 | 174 | 57 | 86% | 203 |
| High | 18.5 | 169 | 63 | 87% | 212 |
| High | 17.0 | 170 | 48 | 91% | 189 |
| Low | 16.5 | 183 | 49 | 92% | 180 |
| Low | 16.5 | 178 | 53 | 81% | 191 |
| Low | 16.0 | 188 | 52 | 91% | 217 |
| Low | 16.0 | 175 | 45 | 94% | 187 |
| Low | 16.0 | 184 | 53 | 83% | 203 |
| Mean High Level | 16.9 | 174 | 55 | 90% | 204 |
| SD Group 1 | 1.0 | 4 | 6 | 4% | 10 |
| Mean Level Low | 16.2 | 182 | 50 | 89% | 196 |
| SD Level Low | 0.3 | 5 | 4 | 6% | 15 |
| p value | 0.2 | 0.06 | 0.22 | 0.840 | 0.333 |
| Mean All the runners | 16.6 | 178 | 52 | 89% | 200 |
| SD All the runners | 0.8 | 6 | 5 | 5% | 13 |
| Level |
Marathon Times (s) | Vmarathon (km·h−1) | Vmarathon %vO2max |
HRmarathon (bpm) |
HRmarathon %HRmax | HRmarathon %HR RCP |
Vmarathon %vO2max | O2 Marathon %O2max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High | 12694 | 12.0 | 75% | 169 | 96% | 105% | 75% | 83% |
| High | 12897 | 11.8 | 71% | 162 | 90% | 98% | 71% | 77% |
| High | 12160 | 12.5 | 74% | 160 | 92% | 110% | 74% | 78% |
| High | 10200 | 14.9 | 80% | 148 | 88% | 104% | 80% | 80% |
| High | 13449 | 11.3 | 66% | 139 | 82% | 84% | 66% | 77% |
| Low | 18700 | 8.1 | 49% | 155 | 85% | 89% | 49% | 82% |
| Low | 17795 | 8.5 | 52% | 161 | 90% | 92% | 52% | 72% |
| Low | 16161 | 9.4 | 59% | 159 | 85% | 91% | 59% | 74% |
| Low | 17650 | 8.6 | 54% | 148 | 85% | 89% | 54% | 73% |
| Low | 18382 | 8.3 | 52% | 173 | 94% | 99% | 52% | 76% |
| Mean High Level | 12280 | 12.5 | 74% | 156 | 90% | 100% | 74% | 79% |
| SD Group 1 | 1250 | 1.4 | 5% | 12 | 5% | 10% | 5% | 3% |
| Mean Level Low | 17737 | 8.6 | 53% | 159 | 88% | 92% | 53% | 76% |
| SD Level Low | 979 | 0.5 | 4% | 9 | 4% | 4% | 7% | 4% |
| p value | 0.008 | 0.008 | 0.008 | 0.999 | 0.548 | 0.222 | 0.841 | 0.1000 |
| Mean All therunners | 15008 | 10.5 | 63% | 157 | 89% | 96% | 63% | 77% |
| SD All the runners | 3065 | 2.3 | 12% | 10 | 5% | 8% | 12% | 4% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Billat, V.; Palacin, F.; Poinsard, L.; Edwards, J.; Maron, M. Heart Rate Does Not Reflect the %VO2max in Recreational Runners during the Marathon. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12451. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912451
Billat V, Palacin F, Poinsard L, Edwards J, Maron M. Heart Rate Does Not Reflect the %VO2max in Recreational Runners during the Marathon. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(19):12451. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912451
Chicago/Turabian StyleBillat, Véronique, Florent Palacin, Luc Poinsard, Johnathan Edwards, and Michael Maron. 2022. "Heart Rate Does Not Reflect the %VO2max in Recreational Runners during the Marathon" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 19: 12451. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912451
APA StyleBillat, V., Palacin, F., Poinsard, L., Edwards, J., & Maron, M. (2022). Heart Rate Does Not Reflect the %VO2max in Recreational Runners during the Marathon. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(19), 12451. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912451









