A New Sight of Influencing Effects of Major Factors on Cd Transfer from Soil to Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.): Based on Threshold Regression Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of the Study Area
2.2. Sampling and Preparation
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.4. Data Analysis
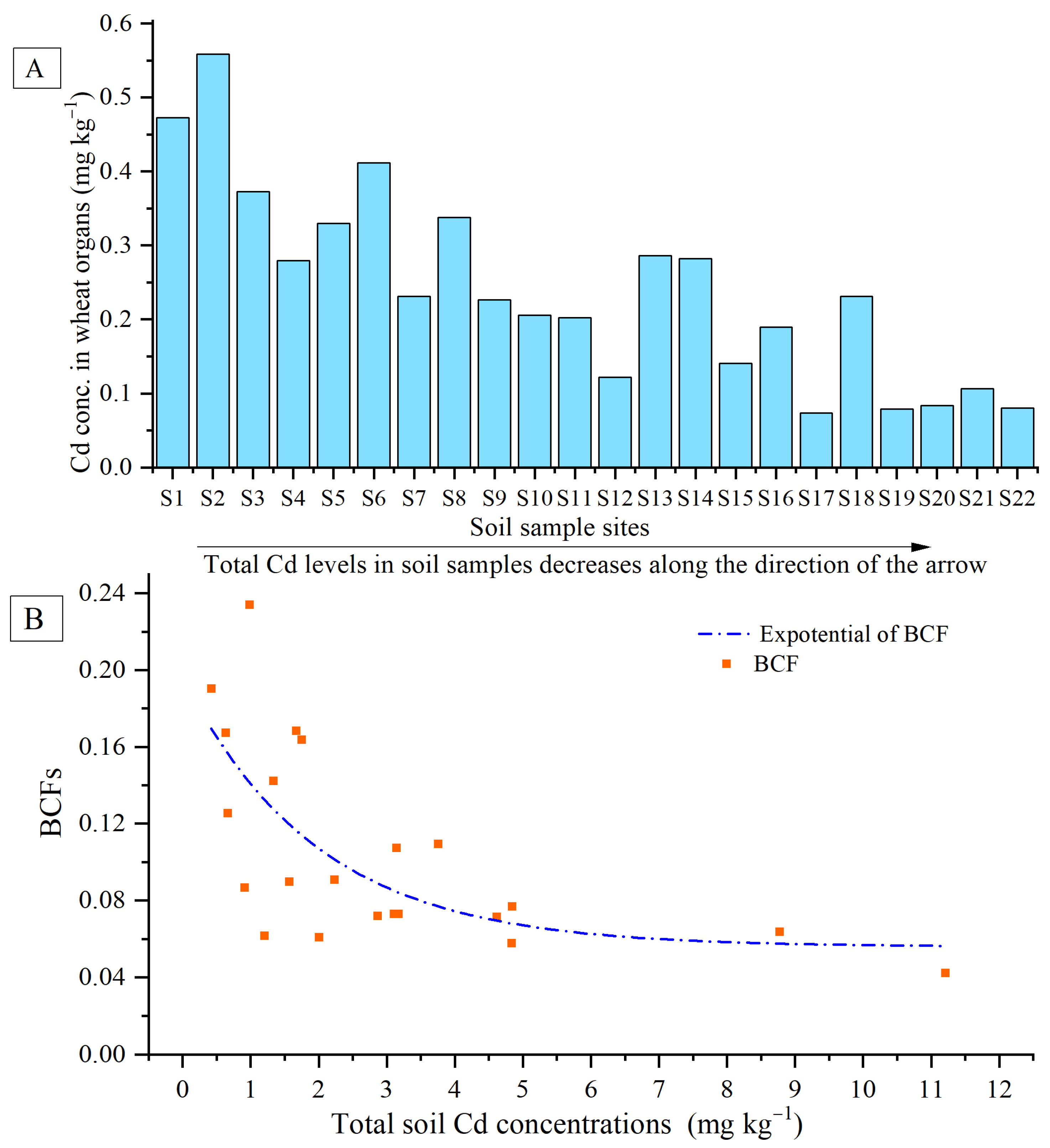
2.4.1. Bioconcentration Factor (BCF)
2.4.2. Threshold Regression Analysis
2.4.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cd Concentration and Soil Properties
3.2. Chemical Speciation of Cd under Sequential Extraction
3.3. Cadmium Accumulation in Wheat Grains, and Correlation with Soil Parameters
3.4. Threshold Effects of Main Soil Factors under Different Soil Cd and pH Levels
4. Discussions
4.1. Effects of pH, Ex-Cd, and OM on Cd Uptake, and Transfer from Soil to Wheat
4.2. Effects of Several Main Elements on Cd Uptake and Transfer from Soil to Wheat
4.3. Impacts of Different Soil Particle Sizes on Cd Uptake and Transfer from Soil to Wheat
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Genchi, G.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Lauria, G.; Carocci, A.; Catalano, A. The Effects of Cadmium Toxicity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gramlich, A.; Tandy, S.; Gauggel, C.; Lopez, M.; Perla, D.; Gonzalez, V.; Schulin, R. Soil cadmium uptake by cocoa in Honduras. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 612, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Ren, Q.; Zheng, K.X.; Jiao, Z.Q.; Ruan, X.L.; Wang, Y.Y. Migration of heavy metals in the soil-grape system and potential health risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Li, Z.J.; Lu, L.; Long, J.; Liang, Y.C. Cross-species extrapolation of prediction models for cadmium transfer from soils to corn grain. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, M.L.; Zhao, F.J.; McGrath, S.P.; Nicholson, F.A.; Chambers, B.J. Predicting cadmium concentrations in wheat and barley grain using soil properties. J. Environ. Qual. 2004, 33, 532–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brus, D.J.; De Gruijter, J.J.; Römkens, P.F.A.M. Probabilistic quality standards for heavy metal in soil derived from quality standards in crop. Geoderma 2005, 128, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Lv, J.L.; He, W.X.; Zhang, H.; Cao, Y.F.; Dai, Y.C. Major factors influencing cadmium uptake from the soil into wheat plants. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 113, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viala, Y.; Laurette, J.; Denaix, L.; Gourdain, E.; Meleard, B.; Nguyen, C.; Schneider, A.; Sappin-Didier, V. Predictive statistical modeling of cadmium content in durum wheat grain based on soil parameters. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 20641–20654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.D.; Ye, X.Z.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, D.; Hu, J.; Gao, N. Evaluation of cadmium transfer from soil to leafy vegetables: Influencing factors, transfer models, and indication of soil threshold contents. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 164, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.F.; Su, Y.; Lu, S.G. Predicting accumulation of Cd in rice (Oryza sativa L.) and soil threshold concentration of Cd for rice safe production. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 738, 139805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 15618-1995; National Environmental Protection Bureau Environmental Quality Standard for Soils. SAC: Beijing, China, 1995.
- Tong, H. On a threshold model. In Pattern Recoginition and Signal Processing; Chen, C.H., Ed.; Sijthoff & Noordhoff: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1978; pp. 575–586. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, H. Threshold Models in Nonlinear Time Series analysis. In Lecture Notes in Statistics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, H.; Lim, K.S. Threshold autoregression, limit cycles and cyclical data. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1980, 42, 245–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, H. Non-Linear Time Series: A Dynamics System Approach; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, H. Threshold models in time series analysis-30 years on. Stat. Interface 2011, 4, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, B.E. Threshold autoregression in economics. Stat. Interface 2011, 4, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, K. Measuring fixed costs for firms’ use of a free trade agreement: Threshold regression approach. Econ. Lett. 2011, 113, 301–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chen, C.R. Analysts’ forecast dispersion and stock returns: A panel threshold regression analysis based on conditional limited market participation hypothesis. Financ. Res. Lett. 2016, 18, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.L.T.; Whitmore, G.A.; Laden, F.; Hart, J.E.; Garshick, E. A case-control study relating railroad worker mortality to diesel exhaust exposure using a threshold regression model. J. Stat. Plan. Inference 2009, 139, 1633–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.L.T.; Whitmore, G.A.; Rosner, B. Threshold regression for survival data with time-varying covariates. Stat. Med. 2010, 29, 896–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.H.; Chuang, H.Y.; Lee, M.L. A threshold regression model to predict return to work after traumatic limb injury. Injury 2016, 47, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.Y.; Duan, W.S.; Li, Y.; Mao, J.Y. A timescale decomposed threshold regression downscaling approach to forecasting south China early summer rainfall. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2016, 33, 1071–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.L.; Chang, X.L.; Huang, C.F. Impact of population strecture of carbon emissions based on spatial dobbin model and threshold regression model. Environ. Sci. Manag. 2022, 47, 6. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Feng, F.; Feng, X.G.; Hou, J.C.; Hou, J.C.; Huo, D.M.; Tang, R. Effectiveness of regional environmental regulation, economic growth and environmental pollution: An emprical study of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. Resour. Sci. 2020, 42, 2341–2353. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.F.; Zhang, S.; Geng, W.C.; Ding, Y.F.; Jiang, X.Y. Use of geographically weighted regression (GWR) to reveal spatially varying relationships between Cd Accumulation and soil properties at field scale. Land 2022, 11, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.F.; Fan, L.D.; Chen, Y.Z.; Xing, L.T.; Yang, Y.J.; Xiang, Z.T.; Wang, X.L. Spatial distribution and source analysis of heavy metals in agricultural soils in a Peri-urban area based on IDW interpolation and chemical fractions: A case study in Henan province. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2016, 36, 1317–1327. [Google Scholar]
- NY/T 1121.1-2006; The Agricultural Industry Standards of the People’s Republic of China. Soil Sampling Processing and Reposition. Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2006.
- Lu, R.S. Soil and Agro-Chemistry Analysis; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.C.; Chi, P.H.; Shiue, M.Y. Comparison of different digestion methods for total decomposition of siliceous and organic environmental samples. Anal. Sci. 2001, 17, 1395–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- HJ 1068-2019; Soil—Determination of Particle Size Distribution—Pipette Method and Hydrometer Method. The Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2019.
- Chen, Z.F.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, L.D.; Xing, L.T.; Yang, Y.J. Cadmium (Cd) Localization in Tissues of Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.), and Its Phytoremediation Potential for Cd-Contaminated Soils. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 95, 784–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.F.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Q.; Qiao, J.J.; Tian, Q.; Liu, X.T. Heavy metal contents and chemical speciations in sewage-irrigated soils from the eastern suburb of Beijing, China. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2009, 7, 690–695. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.F.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, Y.E.; Yang, X.; Qiao, J.J.; Tian, Q.; Zhang, Q. Health risks of HMs in sewage-irrigated soils and edible seeds in Langfang of Hebei province, China. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 90, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, B.E. Inference when a nuisance parameter is not identified under the null hypothesis. Econometrica 1996, 64, 413–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, B.E. Sample splitting and threshold estimation. Econometrica 2000, 68, 575–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Environmental Monitoring Station. Background Values of the Elements in Soil in China; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- GB 2762-2017; National Food Safety Standard Limits of Contaminants in Food. National Food Safety Standard: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Liu, K.; He, W.X.; Zhang, H.; Cao, Y.F.; Dai, Y.C.; Lv, J.L. Cadmium accumulation and translocation in wheat and grain Cd prediction. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2015, 34, 1441–1448. [Google Scholar]
- Ran, J.; Wang, D.; Wang, C.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, H. Heavy metal contents, distribution, and prediction in a regional soil-wheat system. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 544, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.Z.; Zhong, H.; Liu, G.X.; Dai, Z.M.; Brookes, P.C.; Xu, J.M. Remediation of heavy metal contaminated soils by biochar: Mechanisms, potential risks and applications in China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 846855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.Y.; Yang, W.W.; Cheng, P.; Zhang, S.W.; Jiao, W.T.; Sun, Y.H. Adsorption characteristics of cadmium onto microplastics from aqueous solutions. Chemosphere 2019, 235, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Y.; Wang, Y.L.; Jiang, L.N.; Zhang, D.J. Effect of cadmium stress on wheat rhizoshpere environment in three soil textures during filling stage. Acta Agric. Boreali-Occident. Sin. 2012, 21, 167–171. [Google Scholar]
- Garrett, R.G.; MacLaurin, A.I.; Gawalko, E.J.; Tkachuk, R.; Hall, G.E.M. A prediction model for estimating the cadmium content of durum wheat from soil chemistry. J. Geochem. Explor. 1998, 64, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, C.W.; McLaren, R.G.; Roberts, A.H.C. Cadmium concentrations in some New Zealand wheat grain. N. Z. J. Crop Hortic. Sci. 2001, 29, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norvell, W.A.; Wu, J.; Hopkins, D.G.; Welch, R.M. Association of cadmium in durum wheat grain with soil chloride and chelate-extractable soil cadmium. Soil. Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 2162–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, M.; Zhou, W.; Lin, B. Subcellular and molecular distribution of cadmium in two wheat genotypes differing in shoot/root Cd partitioning. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2003, 36, 671–675. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, X.L.; Wang, C.; Wang, R.J.; Peng, F.; Xiao, X.; Zeng, J.; Fan, X.; Kang, H.Y.; Sha, L.N.; et al. Proteomic profiling of the interactions of Cd/Zn in the roots of dwarf polish wheat (Triticum polonicum L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, N.; Ishaq, W.; Farid, G.; Shaheen, M.R.; Imran, M.; Geng, M.J.; Hussain, S. Zinc-cadmium interactions: Impact on wheat physiology and mineral acquisition. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 122, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saifullah; Sarwar, N.; Bibi, S.; Ahmad, M.; Yong, S.O. Effectiveness of zinc application to minimize cadmium toxicity and accumulation in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 1663–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, S.J.; Li, F.S.; Wang, Q.H.; Guo, G.L. Adsorption characteristics of cadmium on particle-sized aggregates from black soil. Res. Environ. Sci. 2012, 25, 447–452. [Google Scholar]



| Mean | Median | Min. | Max. | CV | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil Cd (mg kg−1) | 2.99 ± 2.67 | 2.12 | 0.42 | 11.21 | 89.40% |
| pH | 7.88 ± 0.38 | 7.90 | 6.82 | 8.78 | 4.82% |
| CaCO3 (g kg−1) | 67.86 ± 18.79 | 72.79 | 43.32 | 106.07 | 27.69% |
| OM (%) | 3.02 ± 0.56 | 2.93 | 2.26 | 4.08 | 18.60% |
| Clay, 0–2 μm (%) | 1.20 ± 0.39 | 1.10 | 0.75 | 2.08 | 32.39% |
| Silt, 2–50 μm (%) | 67.80 ± 7.14 | 69.48 | 51.96 | 78.82 | 10.54% |
| Sand, 50 μm (%) | 31.00 ± 7.33 | 29.48 | 19.11 | 46.97 | 23.64% |
| Soil Ca (g kg−1) | 31.78 ± 6.10 | 31.61 | 22.52 | 42.93 | 19.19% |
| Soil Fe (g kg−1) | 30.11 ± 2.87 | 29.69 | 26.17 | 38.14 | 9.52% |
| Soil Mn (g kg−1) | 0.57 ± 0.05 | 0.56 | 0.50 | 0.72 | 9.08% |
| Soil P (g kg−1) | 1.23 ± 0.26 | 1.16 | 0.93 | 1.77 | 21.58% |
| Soil Zn (mg kg−1) | 488.44 ± 836.58 | 198.96 | 110.64 | 4057.14 | 171.28% |
| Grain Cd | BCF | Log[BCF] | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Soil Cd | 0.847 ** | −0.588 ** | −0.661 ** |
| Ex-Cd | 0.802 ** | −0.616 ** | −0.675 ** |
| Soil Ca | −0.206 | 0.331 | 0.291 |
| Soil Fe | 0.283 | −0.017 | −0.023 |
| Soil Mn | −0.182 | −0.025 | −0.065 |
| Soil P | 0.357 | −0.669 ** | −0.726 ** |
| Soil Zn | 0.586 ** | −0.428 * | −0.541 ** |
| pH | −0.534 * | 0.363 | 0.426 * |
| CaCO3 | −0.118 | 0.295 | 0.237 |
| OM | −0.230 | −0.381 | −0.409 |
| Log[OM] | −0.219 | −0.403 | −0.427 * |
| Clay (<2 μm) | −0.374 | 0.472 * | 0.408 |
| silt (2–50 μm) | −0.593 ** | 0.298 | 0.323 |
| Sand (>50 μm) | 0.598 ** | −0.316 | −0.337 |
| Model No. | Controlling Factor | Threshold Estimate | Prediction Models | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | pH | 7.98 | Log[BCF] = −3.337 + 0.292 pH pH ≤ 7.98 | 0.354 |
| Log[BCF] = 4.186 − 0.615 pH pH > 7.98 | 0.500 | |||
| (2) | Log[OM] | 7.98 | Log[BCF] = −0.608 − 0.998 log[OM] pH ≤ 7.98 | 0.321 |
| Log[BCF] = −0.496 − 0.831 log[OM] pH > 7.98 | 0.066 | |||
| (3) | Soil P | 7.98 | Log[BCF] = −0.606 − 0.375 [soil P] pH ≤ 7.98 | 0.488 |
| Log[BCF] = 0.252 − 1.008 [soil P] pH > 7.98 | 0.766 | |||
| (4) | Soil Ca | 7.81 | Log[BCF] = −0.926 − 0.008 [soil Ca] pH ≤ 7.81 | 0.204 |
| Log[BCF] = −1.325 − 0.012 [soil Ca] pH > 7.81 | 0.155 | |||
| (5) | Soil Zn | 1.75 | Log[BCF] = −0.698 − 0.001 [soil Zn] soil Cd ≤ 1.75 | 0.037 |
| Log[BCF] = −1.081 − 0.0001 [soil Zn] soil Cd > 1.75 | 0.504 | |||
| (6) | Soil P | 2.01 | Log[BCF] = 0.217 − 1.044 [soil P] soil Cd ≤ 2.01 | 0.557 |
| Log[BCF] = −0.759 − 0.272 [soil P] soil Cd > 2.01 | 0.412 | |||
| (7) | Ex-Cd | 1.20 | Log[BCF] = −0.761 − 3.898 [ex-Cd] soil Cd ≤ 1.20 | 0.509 |
| Log[BCF] = −0.911 − 0.245 [ex-Cd] soil Cd >1.20 | 0.490 | |||
| (8) | Clay (<2 μm) | 1.67 | Log[BCF] = −1.205 + 0.219 [Clay] soil Cd ≤ 1.67 | 0.309 |
| Log[BCF] = −0.366 − 0.731 [Clay] soil Cd > 1.67 | 0.739 | |||
| (9) | Silt (2–50 μm) | 1.75 | Log[BCF] = −0.685 + 0.003 [Silt] soil Cd ≤ 1.75 | 0.013 |
| Log[BCF] = −1.537 − 0.006 [Silt] soil Cd > 1.75 | 0.091 | |||
| (10) | Sand (>50 μm) | 1.75 | Log[BCF] = −0.928 + 0.002 [Sand] soil Cd ≤ 1.75 | 0.007 |
| Log[BCF] = −0.948 − 0.006 [Sand] soil Cd > 1.75 | 0.078 |
| Considered Controlling Factor | Prediction Models | R2 | p | Conditions | Literature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH, Lg[Cdtotal] | Lg[Cdgrain] = 0.28 + 0.44 Lg[Cdtotal] − 0.18 pH | 0.42 | <0.05 | N = 162, pH 5.2–8.3 | [5] |
| pH, Lg[Cdtotal], Lg[SOM] | Lg[Cdgrain] = 1.022 + 0.749 Lg[Cdtotal] − 0.257 pH − 0.277 Lg[SOM] | 0.44 | <0.05 | N = 84, pH 4.4–7.4 | [6] |
| pH, control Cd * | Lg[BCF] = −0.081 pH − 0.254 | 0.728 | <0.001 | N = 17, pH = 4.90–8.80, OM = 8.57–47.69 g kg−1 | [4] |
| pH, low Cd * | Lg[BCF] = −0.104 pH − 0.170 | 0.811 | <0.001 | ||
| pH, high Cd * | Lg[BCF] = −0.079 pH − 0.280 | 0.713 | <0.001 | ||
| pH, Lg[Cdtotal] | Lg[Cdgrain] = 1.386 + Lg[Cdtotal] − 0.279 pH | 0.85 | <0.001 | N = 14, pH 5.74–8.37, OC 6.78–27.66 g kg−1 | [7] |
| pH, Lg[Cdtotal] | Lg[Cdgrain] = 0.703 + 1.04 Lg[Cdtotal] − 0.175 pH | 0.61 | <0.001 | N = 99, pH 5.0–8.6, OM 8.49–57.9 g kg−1 | [41] |
| pH, LgCsoil | LgCgrain * = −0.257 pH + 1.203 + LgCsoil * | 0.85 | <0.001 | N = 14, pH 5.74–8.65, OC 4.97–27.7 g kg−1 | [40] |
| pH, Lg[OC], LgCsoil | LgCgrain = −0.280 pH − 0.446Lg[OC] * + 1.848 + LgCsoil | 0.93 | <0.001 | ||
| pHCaCl2 *, Lg[CdDGT *] | Lg[Cdgrain] = 7.359 + 0.697 Lg[CdDGT] − 1.014 pHCaCl2 | 0.66 | <0.001 | N = 26, pH = 8.0–8.7, OC 9.21–40.3 g kg−1 | [8] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Z.; Geng, W.; Jiang, X.; Ruan, X.; Wu, D.; Li, Y. A New Sight of Influencing Effects of Major Factors on Cd Transfer from Soil to Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.): Based on Threshold Regression Model. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12363. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912363
Chen Z, Geng W, Jiang X, Ruan X, Wu D, Li Y. A New Sight of Influencing Effects of Major Factors on Cd Transfer from Soil to Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.): Based on Threshold Regression Model. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(19):12363. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912363
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Zhifan, Wencai Geng, Xingyuan Jiang, Xinling Ruan, Di Wu, and Yipeng Li. 2022. "A New Sight of Influencing Effects of Major Factors on Cd Transfer from Soil to Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.): Based on Threshold Regression Model" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 19: 12363. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912363
APA StyleChen, Z., Geng, W., Jiang, X., Ruan, X., Wu, D., & Li, Y. (2022). A New Sight of Influencing Effects of Major Factors on Cd Transfer from Soil to Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.): Based on Threshold Regression Model. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(19), 12363. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912363






