Association between Sleep Duration and Physical Fitness in Children Aged 3–6 Years: A Cross-Sectional Study from China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Method
2.1. Participants
2.2. Measures
2.2.1. Demographic Indicators
2.2.2. Sleep Duration
2.2.3. PF Indicators
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Basic Information and PF Level of Participants
3.2. Description of Sleep Duration Characteristics of Children
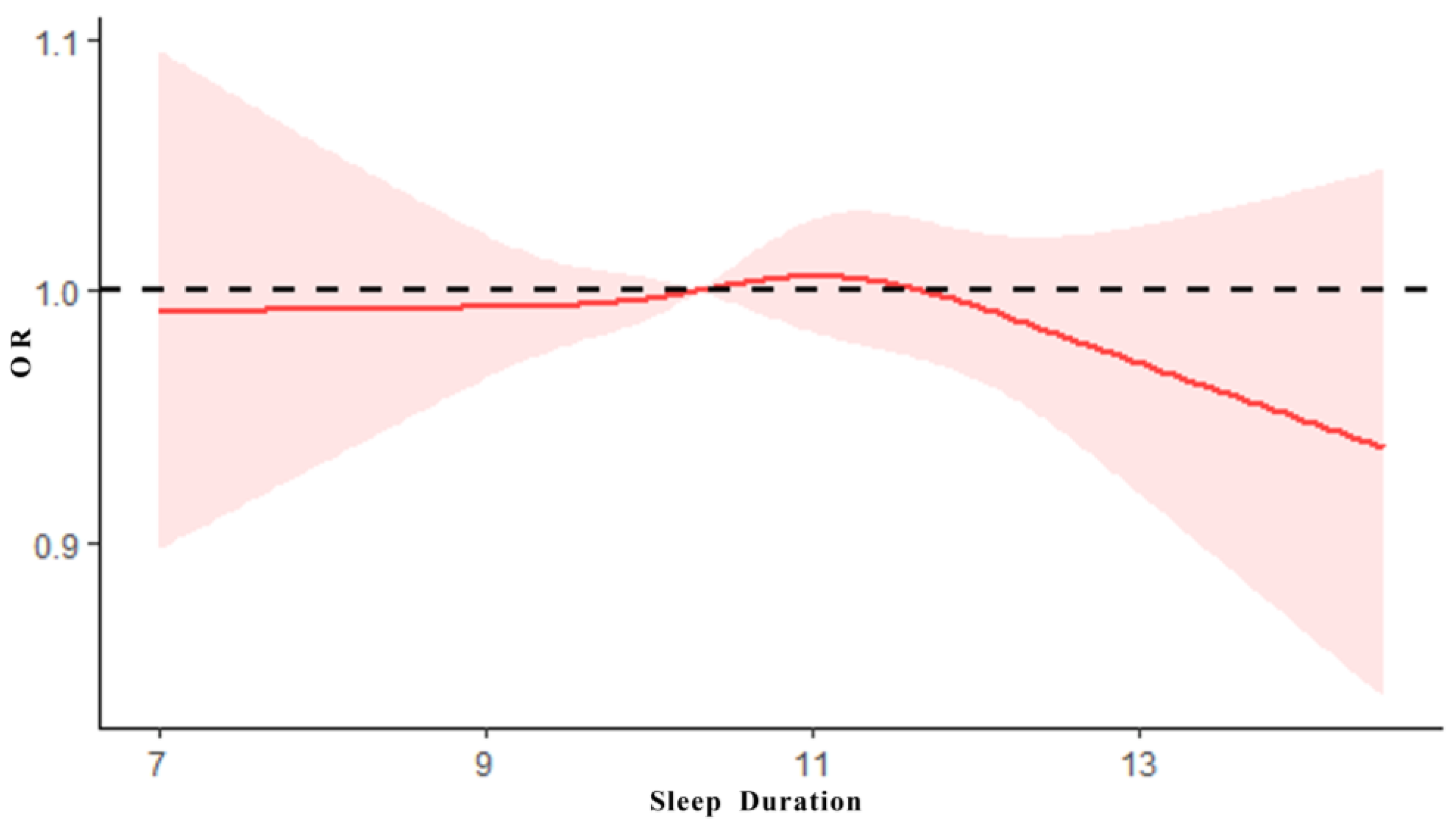
3.3. The Dose–Effect Relationship between Sleep Duration and PF
3.4. The Association between PF Level and Sleep Duration
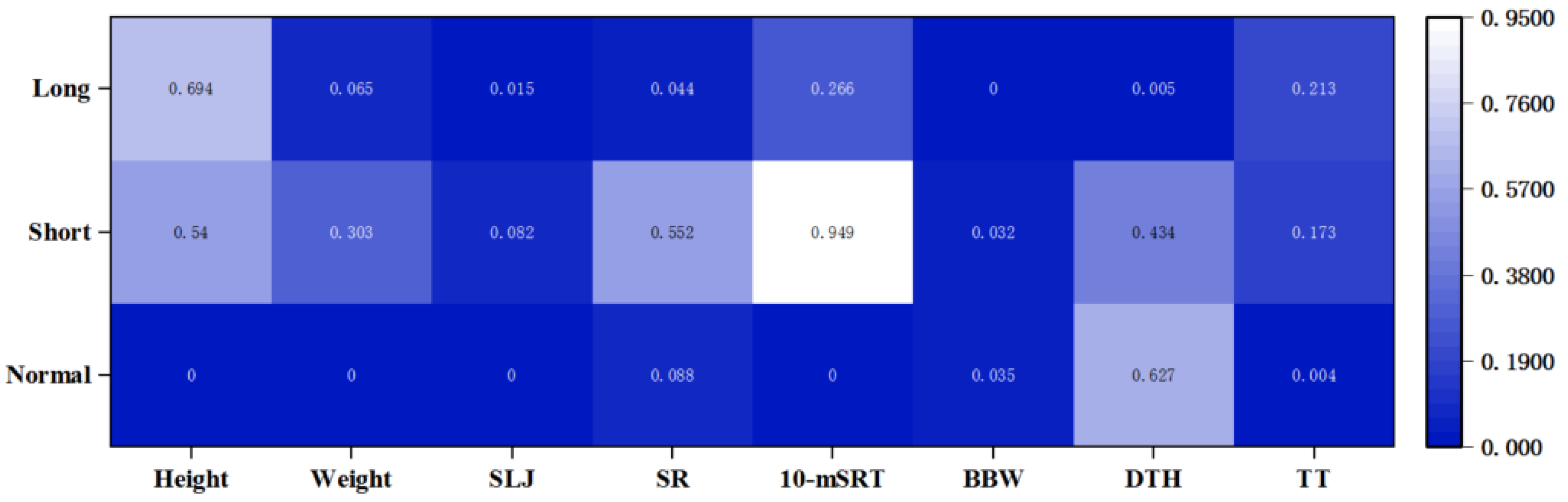
3.5. Correlation of the Components of PF with Sleep Duration
4. Discussion
Limitation and Implication
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- General Administration of Sport China. The 5th National Physical Fitness Monitoring Bulletin of China. Available online: https://www.sport.gov.cn/n20001280/n20001265/n20067533/c23881607/content.html (accessed on 30 December 2021).
- General Administration of Sport China. The National Physical Fitness Monitoring Bulletin of China in 2014. Available online: https://www.sport.gov.cn/n315/n329/c216784/content.html (accessed on 25 November 2015).
- Zhou, Z.; Ren, H.; Yin, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, K. A policy-driven multifaceted approach for early childhood physical fitness promotion: Impacts on body composition and physical fitness in young Chinese children. BMC Pediatrics 2014, 14, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dumuid, D.; Olds, T.; Lewis, L.K.; Martin-Fernández, J.A.; Katzmarzyk, P.T.; Barreira, T.; Broyles, S.T.; Chaput, J.-P.; Fogelholm, M.; Hu, G. Health-related quality of life and lifestyle behavior clusters in school-aged children from 12 countries. J. Pediatrics 2017, 183, 178–183.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shin, D.; Hur, J.; Cho, K.H.; Cho, E.H. Trends of self-reported sleep duration in Korean Adults: Results from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007–2015. Sleep Med. 2018, 52, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Sanders, M.; Feng, W.; Tang, H.; Wang, H.; Jin, X.; Wu, J.; Huang, G.; Sun, J.; Luo, Y.; et al. Using epidemiological data to identify needs for child-rearing support among Chinese parents: A cross-sectional survey of parents of children aged 6 to 35 months in 15 Chinese cities. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quach, J.; Hiscock, H.; Canterford, L.; Wake, M. Outcomes of child sleep problems over the school-transition period: Australian population longitudinal study. Pediatrics 2009, 123, 1287–1292. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sadeh, A.; Mindell, J.A.; Luedtke, K.; Wiegand, B. Sleep and sleep ecology in the first 3 years: A web-based study. J. Sleep Res. 2009, 18, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens-Stively, J.; Frank, N.; Smith, A.; Hagino, O.; Spirito, A.; Arrigan, M.; Alario, A.J. Child temperament, parenting discipline style, and daytime behavior in childhood sleep disorders. J. Dev. Behav. Pediatrics 1997, 18, 314–321. [Google Scholar]
- Sampasa-Kanyinga, H.; Colman, I.; Goldfield, G.S.; Janssen, I.; Wang, J.; Podinic, I.; Tremblay, M.S.; Saunders, T.J.; Sampson, M.; Chaput, J.-P. Combinations of physical activity, sedentary time, and sleep duration and their associations with depressive symptoms and other mental health problems in children and adolescents: A systematic review. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2020, 17, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Guo, X.; Sun, Y. Association between sleep time and depression: A cross-sectional study from countries in rural Northeastern China. J. Int. Med. Res. 2017, 45, 984–992. [Google Scholar]
- De Bruin, E.J.; van Run, C.; Staaks, J.; Meijer, A.M. Effects of sleep manipulation on cognitive functioning of adolescents: A systematic review. Sleep Med. Rev. 2017, 32, 45–57. [Google Scholar]
- Vriend, J.; Davidson, F.; Rusak, B.; Corkum, P. Emotional and cognitive impact of sleep restriction in children. Sleep Med. Clin. 2015, 10, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carson, V.; Lee, E.-Y.; Hewitt, L.; Jennings, C.; Hunter, S.; Kuzik, N.; Stearns, J.A.; Unrau, S.P.; Poitras, V.J.; Gray, C. Systematic review of the relationships between physical activity and health indicators in the early years (0–4 years). BMC Public Health 2017, 17, 33–63. [Google Scholar]
- Woodward, M. Sleep in older people. Rev. Clin. Gerontol. 2012, 22, 130–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beebe, D.W.; Fallone, G.; Godiwala, N.; Flanigan, M.; Martin, D.; Schaffner, L.; Amin, R. Feasibility and behavioral effects of an at-home multi-night sleep restriction protocol for adolescents. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2008, 49, 915–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, S.; Kirov, R. Sleep and its importance in adolescence and in common adolescent somatic and psychiatric conditions. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2011, 4, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Troxel, W.M.; Trentacosta, C.J.; Forbes, E.E.; Campbell, S.B. Negative emotionality moderates associations among attachment, toddler sleep, and later problem behaviors. J. Fam. Psychol. 2013, 27, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- General Administration of Sport of China. The National Physical Fitness Measurement Standards Manual (Preschool Children Version); People’s Physical Culture Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, H.; Yan, J.; Hong, J.-T.; Clark, C.; Yang, X.-N.; Liu, Y.; Chen, S.-T. Prevalence of physical activity and sedentary behavior among Chinese children and adolescents: Variations, gaps, and recommendations. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, A.; De Sanctis, V.; Elalaily, R. Nutrition and pubertal development. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 18, S39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Multicentre Growth Reference Study Group. WHO Child Growth Standards based on length/height, weight and age. Acta Paediatr. Suppl. 2006, 450, 76–85. [Google Scholar]
- National Health and Family Planning Commission of the Peoples Republic of China; China, p.o. Guidelines for Sleep Hygiene for Children Aged 0 to 6 Years. Available online: http://www.nhc.gov.cn/wjw/pqt/201710/e63c5fc4c3d74daf9f5234150c4f400a.shtml (accessed on 12 October 2017).
- Ortega, F.B.; Ruiz, J.R.; Castillo, M.J.; Sjöström, M. Physical fitness in childhood and adolescence: A powerful marker of health. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zong, X.-N.; Li, H. Physical growth of children and adolescents in China over the past 35 years. Bull. World Health Organ. 2014, 92, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Chen, M.; Song, Y.; Ma, J.; Lau, P.W. Geographical Variation in Physical Fitness Among Chinese Children and Adolescents From 2005 to 2014. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 4070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, M.; Tang, A.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, J.; Zhou, G.; Deng, J.; Yang, L.; Li, M.; Chen, J.; Qin, H. The relationship between obesity, sleep and physical activity in Chinese preschool children. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fang, H.; Quan, M.; Zhou, T.; Sun, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Cao, Z.; Zhao, G.; Wang, R.; Chen, P. Relationship between physical activity and physical fitness in preschool children: A cross-sectional study. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 9314026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Shen, X.; Jin, X.; Yan, C.; Wu, S.; Jiang, F.; Yu, X.; Qiu, Y. Sleep habits and sleep disturbance in school-age children of China. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi/Chin. J. Pediatrics 2008, 46, 185–189. [Google Scholar]
- Smiley, A.; King, D.; Bidulescu, A. The association between sleep duration and metabolic syndrome: The NHANES 2013/2014. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, G.; Geng, L.; Luo, J.; Li, N.; Owens, J. Sleep patterns, sleep disturbances, and associated factors among Chinese urban kindergarten children. Behav. Sleep Med. 2016, 14, 100–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zheng, B.; Lv, J.; Guo, Y.; Bian, Z.; Yang, L.; Chen, Y.; Fu, Z.; Guo, H.; Liang, P. Sleep behavior and depression: Findings from the China Kadoorie Biobank of 0.5 million Chinese adults. J. Affect. Disord. 2018, 229, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.H. Prioritizing the integration of sleep into the development and health evaluation system for children and adolescents. Chin. J. Sch. Health 2021, 42, 805–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrios, C.S.; Jay, S.Y.; Smith, V.C.; Alfano, C.A.; Dougherty, L.R. Stability and Predictive Validity of the Parent–Child Sleep Interactions Scale: A Longitudinal Study Among Preschoolers. J. Clin. Child Adolesc. Psychol. 2018, 47, 382–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tham, E.K.; Schneider, N.; Broekman, B.F. Infant sleep and its relation with cognition and growth: A narrative review. Nat. Sci. Sleep 2017, 9, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sluggett, L.; Wagner, S.L.; Harris, R.L. Sleep duration and obesity in children and adolescents. Can. J. Diabetes 2019, 43, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaput, J.-P.; Klingenberg, L.; Sjödin, A. Do all sedentary activities lead to weight gain: Sleep does not. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2010, 13, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.-R.; Spruyt, K.; Chen, W.-J.; Shen, X.-M.; Jiang, F. Somatic growth of lean children: The potential role of sleep. World J. Pediatrics 2014, 10, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.-C.; Hsu, N.-W.; Chou, P. The association between sleep duration and hand grip strength in community-dwelling older adults: The Yilan study, Taiwan. Sleep 2017, 40, zsx021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.; Baek, S.; Park, H.-W.; Kang, E.K. Sleep quality and attention may correlate with hand grip strength: FARM study. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2018, 42, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chien, M.-Y.; Wang, L.-Y.; Chen, H.-C. The relationship of sleep duration with obesity and sarcopenia in community-dwelling older adults. Gerontology 2015, 61, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.; McDonald, C.; McIntyre, A.; Carmody, K.; Donne, B. Effects of acute sleep deprivation and caffeine supplementation on anaerobic performance. Sleep Sci. 2018, 11, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitzman, E.D. Circadian rhythms and episodic hormone secretion in man. Annu. Rev. Med. 1976, 27, 225–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassin, J.; Parker, D.; Mace, J.; Gotlin, R.; Johnson, L.; Rossman, L. Human growth hormone release: Relation to slow-wave sleep and sleep-waking cycles. Science 1969, 165, 513–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skein, M.; Duffield, R.; Edge, J.; Short, M.J.; Mundel, T. Intermittent-sprint performance and muscle glycogen after 30 h of sleep deprivation. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2011, 43, 1301–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Level | Standard | Items | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PF Score | BM Score | MA Score | ||
| L1 (Excellent) | [77.6–100%] | 32–40 | 9–10 | 24–30 |
| L2 (Good) | [67.6–77.5%] | 28–31 | 7–8 | 21–23 |
| L3 (Passing) | [47.6–67.5%] | 20–27 | 5–6 | 15–20 |
| L4 (Fail) | [0–47.5%] | 0–19 | 0–4 | 0–14 |
| Number | Age | Residence (N) | PF Status | Sleep Duration (Hour) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urban | Rural | PF Score | MB Score | MA Score | ||||
| Boys | 11,245 | 4.46 ± 1.04 | 6251 | 5738 | 25.86 ± 4.44 | 7.23 ± 1.89 | 18.61 ± 3.74 | 10.33 ± 1.12 |
| Girls | 10,612 | 4.44 ± 1.04 | 4994 | 4874 | 26.44 ± 4.17 | 7.46 ± 1.72 | 18.99 ± 3.55 | 10.34 ± 1.13 |
| Total | 21,857 | 4.45 ± 1.04 | 11,245 | 10,612 | 26.14 ± 4.33 | 7.34 ± 1.81 | 18.80 ± 3.65 | 10.33 ± 1.12 |
| Characteristic | Total [n = 21,857, Case (%)] | Boys [n = 11,245, Case (%)] | Girls [n = 10,612, Case (%)] | X2 | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 4.037 | 0.258 | ||||
| 3 | 4979 (22.8) | 2507 (22.4) | 2472 (23.3) | |||
| 4 | 6263 (28.6) | 3220 (28.6) | 3043 (28.7) | |||
| 5 | 6445 (29.5) | 3334 (29.6) | 3111 (29.3) | |||
| 6 | 4170 (19.1) | 2184 (19.4) | 1986 (18.7) | |||
| Residence | 5.082 | 0.024 | ||||
| Urban | 11,989 (54.9) | 6251 (55.6) | 5738 (54.1) | |||
| Rural | 9868 (45.1) | 4994 (44.4) | 4874 (45.9) | |||
| PF level | 86.561 | <0.01 | ||||
| L1 | 2344 (10.7) | 1125 (10.0) | 1219 (11.5) | |||
| L2 | 6030 (27.6) | 2988 (26.6) | 3042 (28.7) | |||
| L3 | 12,087 (55.3) | 6262 (55.7) | 5825 (54.8) | |||
| L4 | 1396 (6.4) | 870 (7.7) | 526 (5) | |||
| BM level | 126.773 | <0.01 | ||||
| L1 | 6497 (29.7) | 3336 (29.7) | 3161 (29.8) | |||
| L2 | 9261 (42.3) | 4471 (39.8) | 4790 (45.1) | |||
| L3 | 4077 (18.7) | 2197 (19.5) | 1880 (17.7) | |||
| L4 | 2022 (9.3) | 1241 (11.0) | 781 (7.4) | |||
| MA level | 56.431 | <0.01 | ||||
| L1 | 2168 (9.9) | 1048 (9.3) | 1120 (10.6) | |||
| L2 | 5025 (23.0) | 2530 (22.5) | 2495 (23.5) | |||
| L3 | 11,982 (54.8) | 6114 (54.4) | 5868 (55.3) | |||
| L4 | 2682 (12.3) | 1553 (13.8) | 1129 (10.6) | |||
| Characteristic | Insufficient (<9 h) | Normal (9–13 h) | Excessive (>13 h) | X2 | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | 4.069 | 0.131 | ||||
| Boys (11,245) | 2038 (18.1) | 9051 (80.5) | 156 (1.4) | |||
| Girls (10,612) | 1976 (18.6) | 8518 (80.3) | 118 (1.1) | |||
| Residence | 19.534 | <0.01 | ||||
| Rural (9868) | 1721 (17.4) | 7997 (81.0) | 150 (1.5) | |||
| Urban (11,989) | 2293 (19.1) | 9572 (79.8) | 124 (1.0) | |||
| Age | 564.679 | <0.01 | ||||
| 3 (4979) | 526 (10.6) | 4359 (87.5) | 94 (1.9) | |||
| 4 (6263) | 962 (15.4) | 5186 (82.8) | 115 (1.8) | |||
| 5 (6445) | 1382 (21.4) | 5011 (77.8) | 52 (0.8) | |||
| 6 (4170) | 1144 (27.4) | 3013 (72.3) | 13 (0.3) | |||
| Nutritional status | 3.924 | 0.864 | ||||
| Skinny | 241 (19.6) | 972 (79) | 17 (1.4) | |||
| Thin | 455 (18.9) | 1915 (79.5) | 32 (1.3) | |||
| Normal | 2657 (18.2) | 11,795 (80.6) | 185 (1.3) | |||
| Overweight | 243 (17.7) | 1113 (81.1) | 16 (1.2) | |||
| Obese | 418 (18.9) | 1774 (80.1) | 24 (1.1) | |||
| Total (21,857) | 4014(18.4) | 17,569(80.4) | 274(1.3) | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiong, X.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, C.; Wu, J.; Li, H.; Zhen, Z.; Sun, J. Association between Sleep Duration and Physical Fitness in Children Aged 3–6 Years: A Cross-Sectional Study from China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6902. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19116902
Xiong X, Cui Y, Zhang W, Zhao C, Wu J, Li H, Zhen Z, Sun J. Association between Sleep Duration and Physical Fitness in Children Aged 3–6 Years: A Cross-Sectional Study from China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(11):6902. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19116902
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiong, Xin, Yinchen Cui, Weinan Zhang, Chenlin Zhao, Jiahui Wu, Haifeng Li, Zhiping Zhen, and Jian Sun. 2022. "Association between Sleep Duration and Physical Fitness in Children Aged 3–6 Years: A Cross-Sectional Study from China" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 11: 6902. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19116902
APA StyleXiong, X., Cui, Y., Zhang, W., Zhao, C., Wu, J., Li, H., Zhen, Z., & Sun, J. (2022). Association between Sleep Duration and Physical Fitness in Children Aged 3–6 Years: A Cross-Sectional Study from China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(11), 6902. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19116902





