Heavy-Metal Speciation Distribution and Adsorption Characteristics of Cr (VI) in the Soil within Sewage Irrigation Areas
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
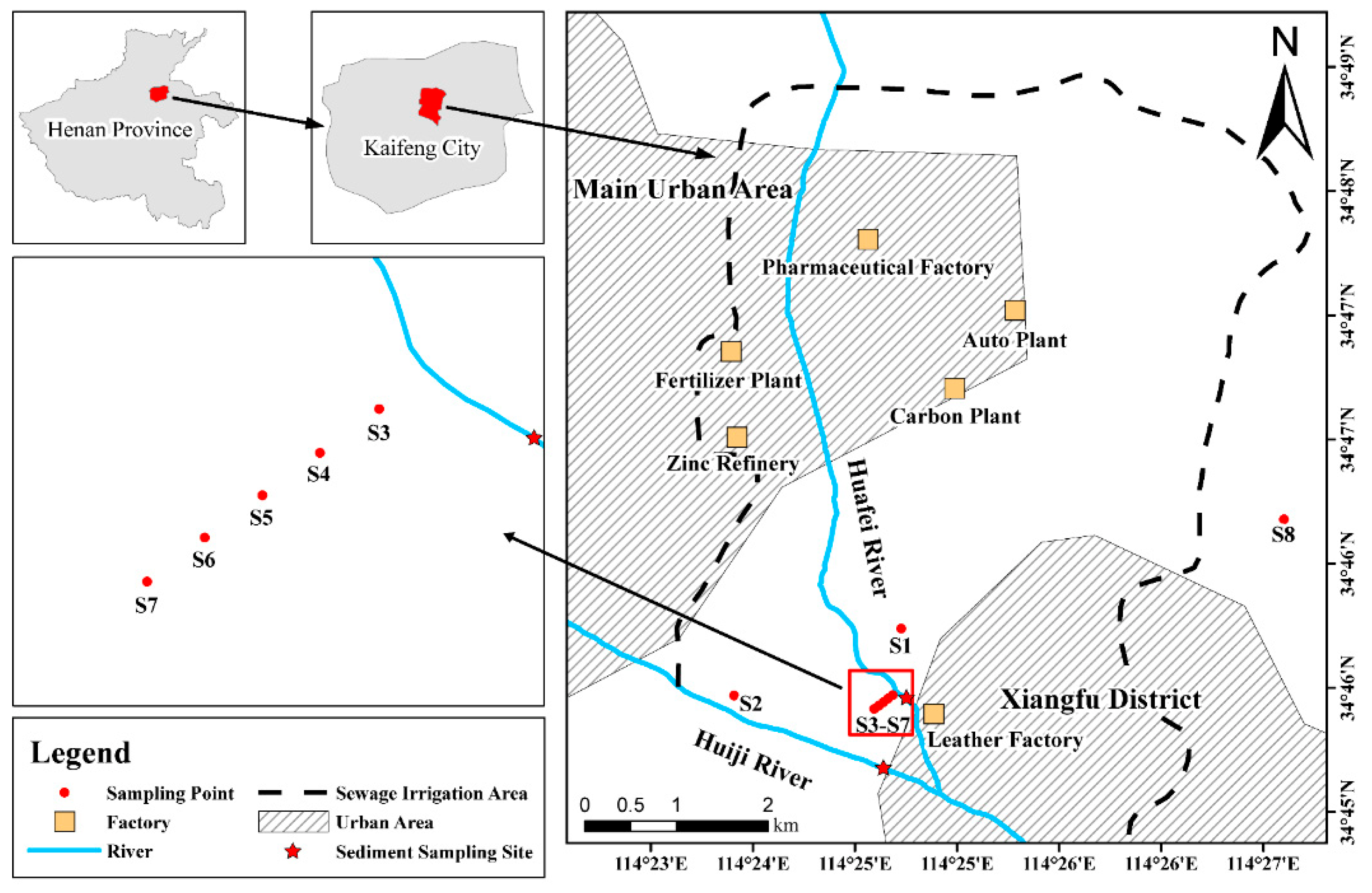
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling and Sample Pretreatment
2.3. Chemical Analysis
2.3.1. Pseudo-Total Concentrations of Heavy Metals
2.3.2. Analysis of Heavy-Metal Speciation
2.3.3. Quality Control and Data Analysis
2.4. Potential Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals
2.5. Adsorption Characteristics of Soil for Cr (VI)
3. Results and Discussion
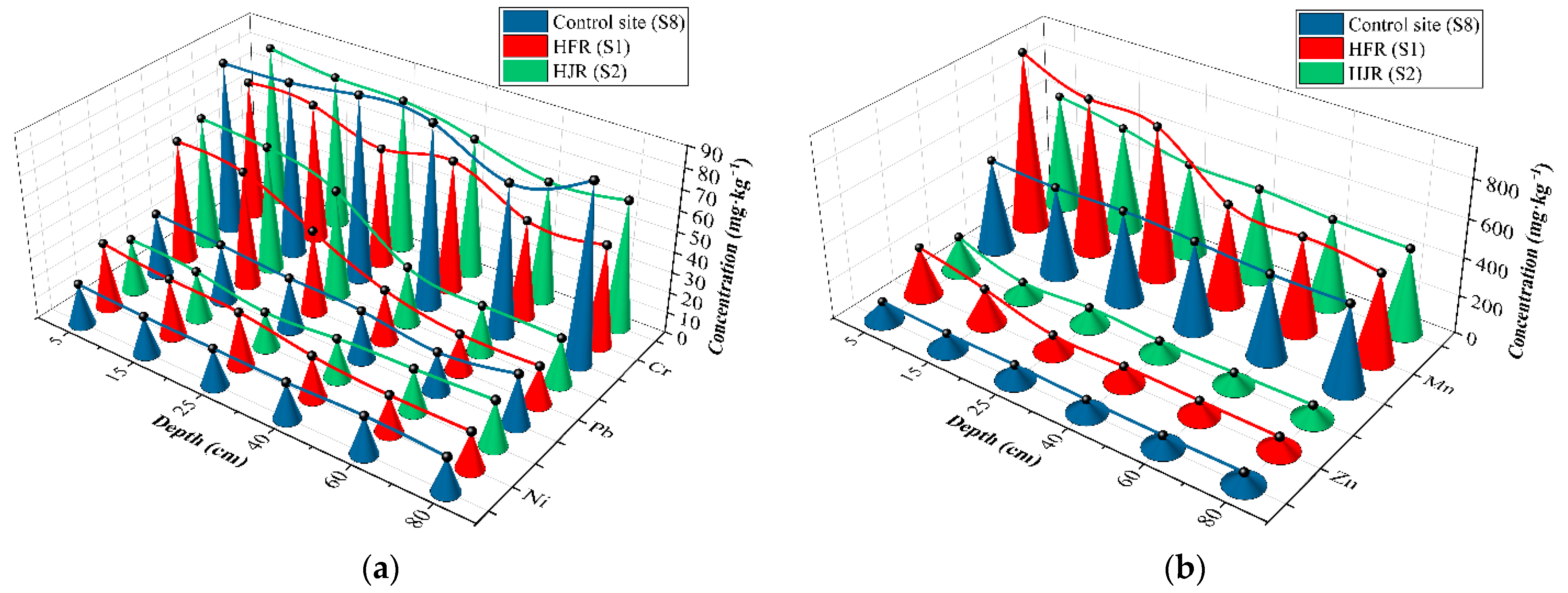
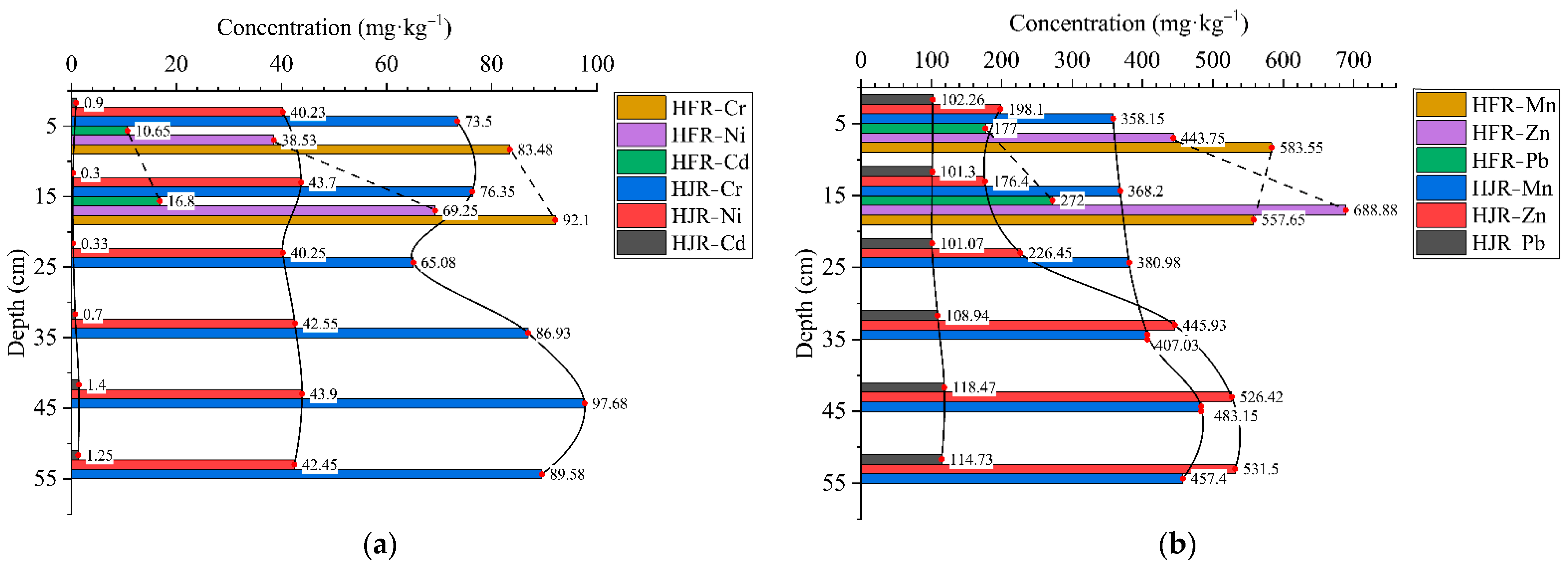
3.1. Vertical Distribution of Heavy Metals
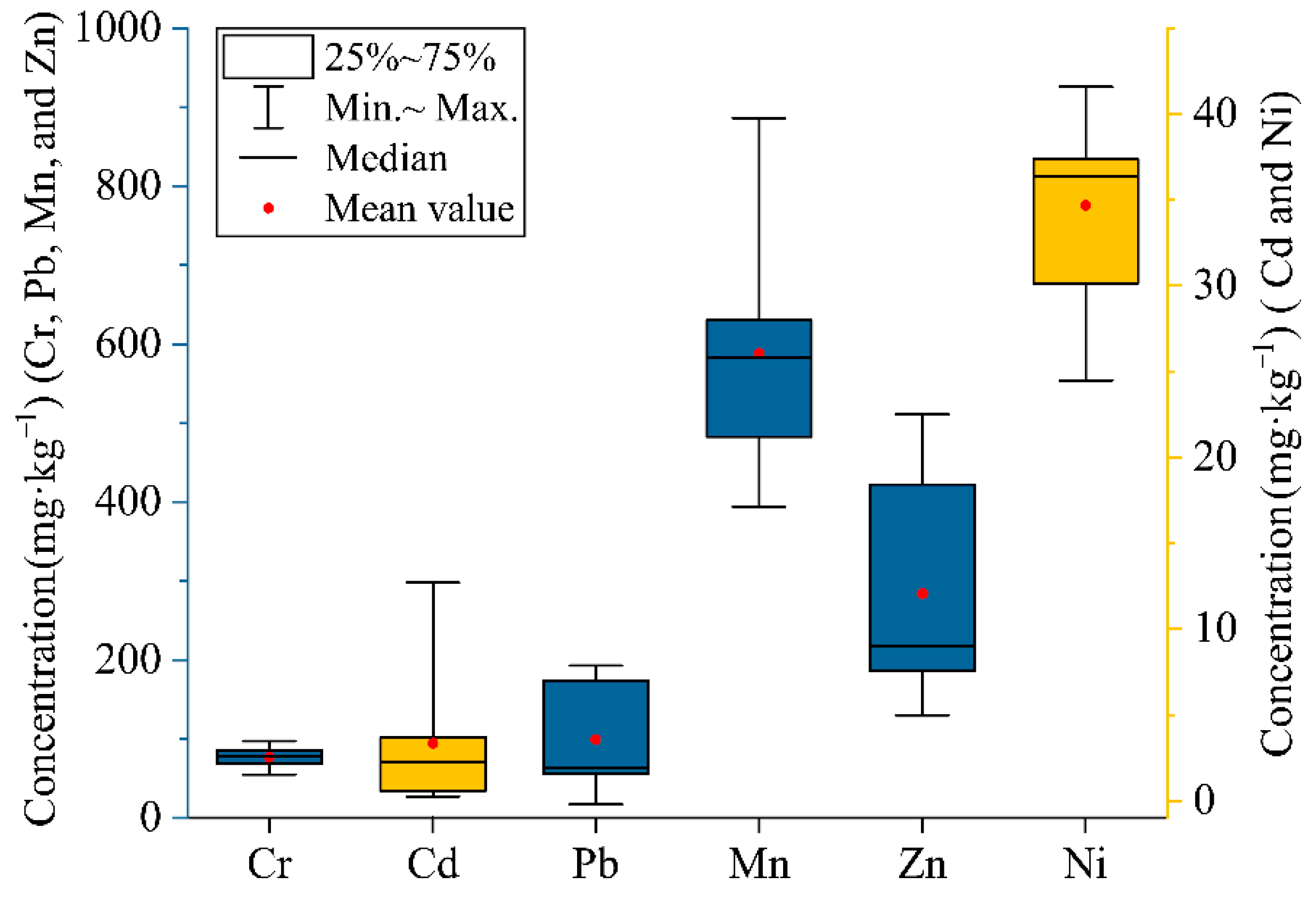
3.2. Heavy Metal Concentrations in Sediment
3.3. Heavy Metal Concentration in Surface Soil
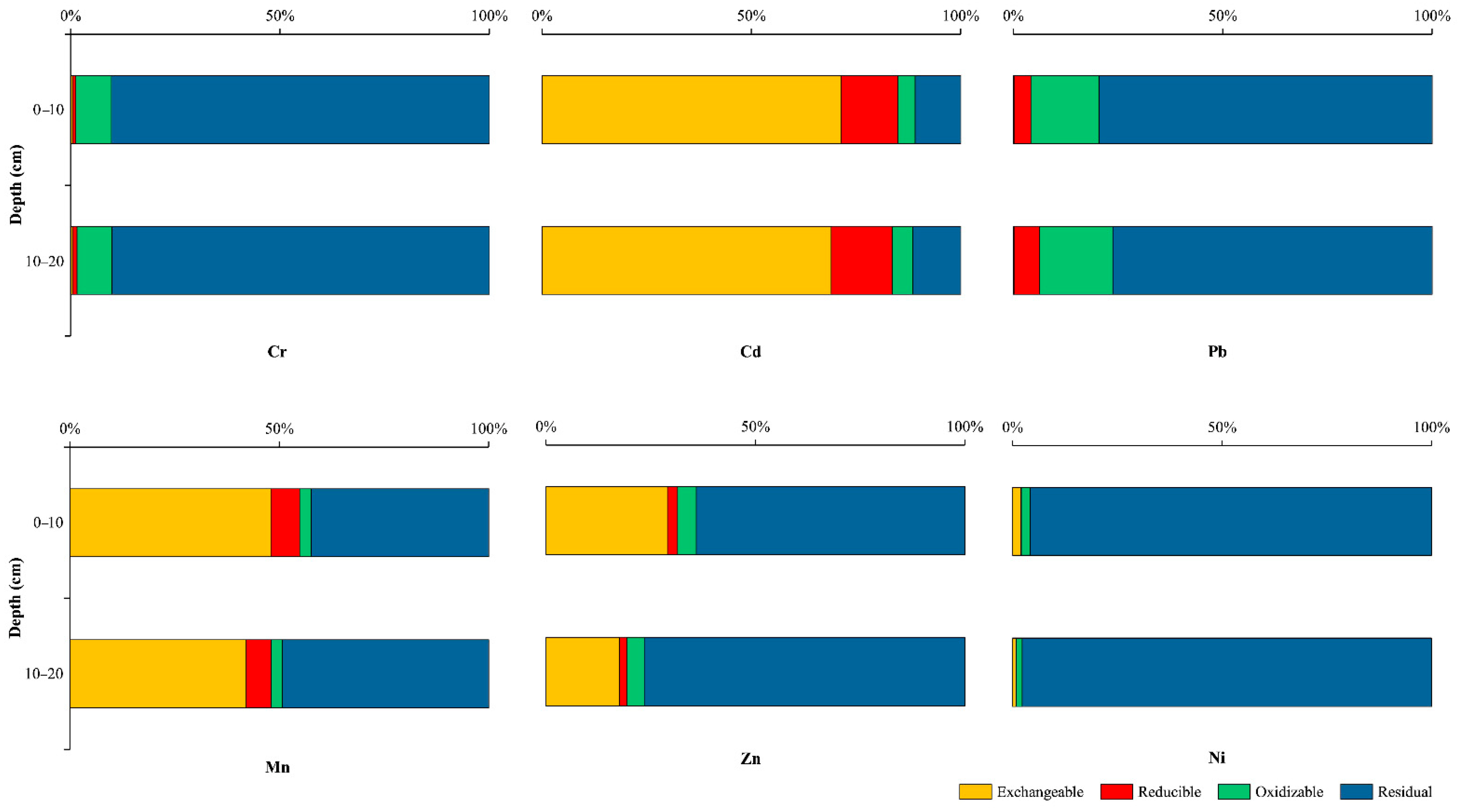
3.4. Distribution of Heavy Metal Speciation in Sediment and Soil
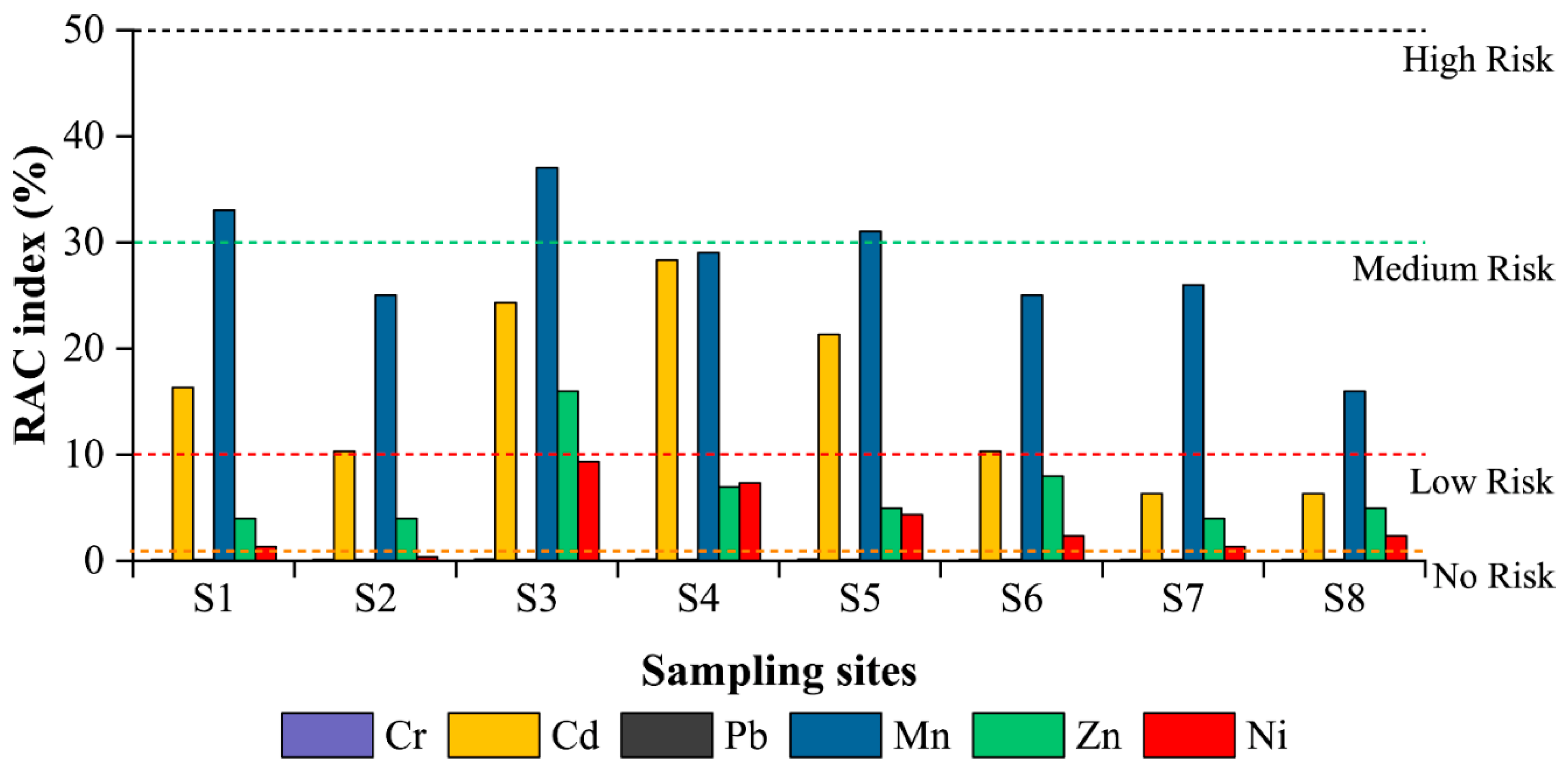
3.5. RAC
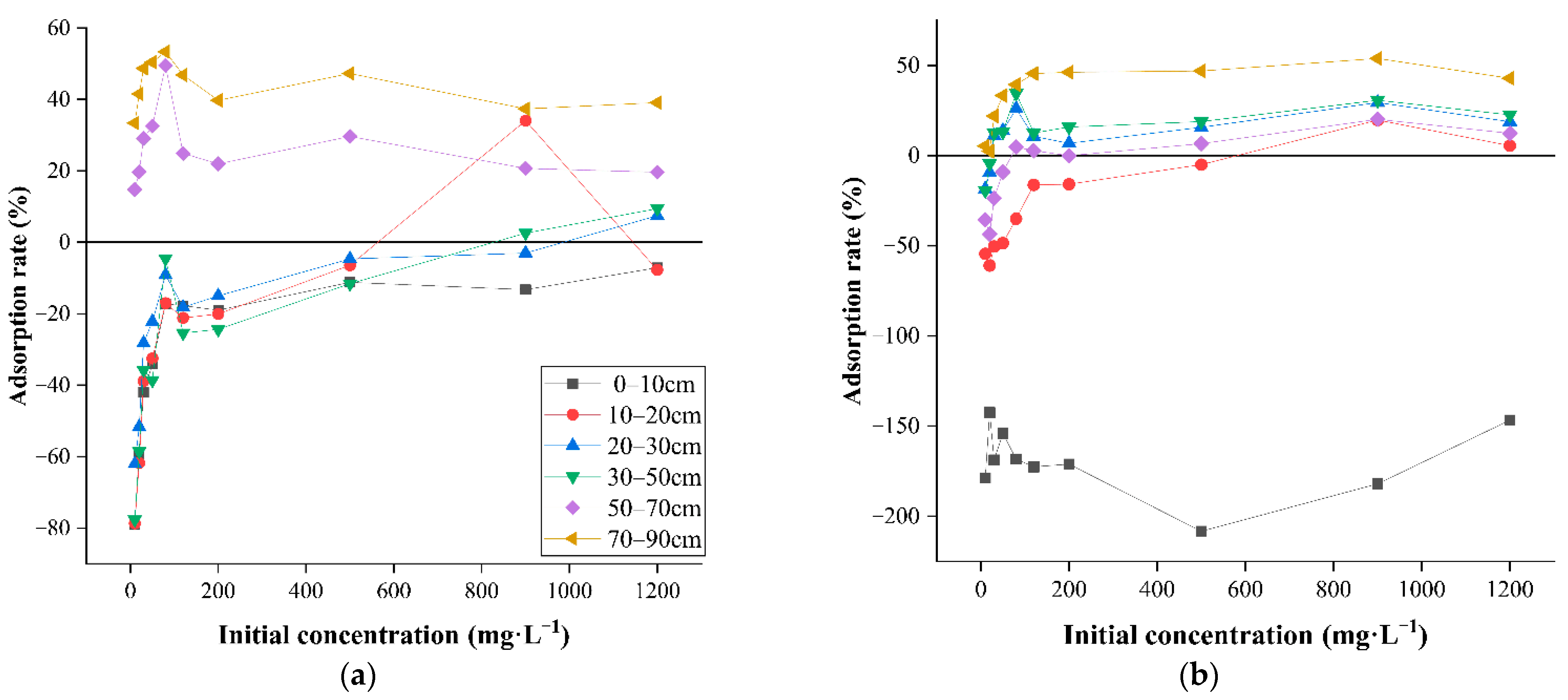
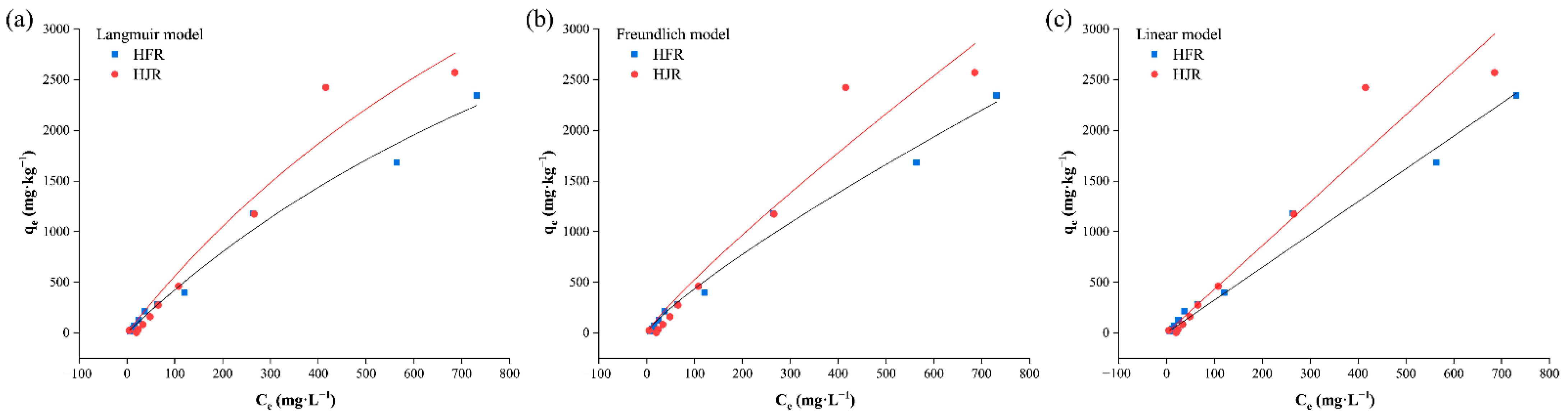
3.6. The Effect of the Initial Concentration of Contaminants on Adsorption
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nzediegwu, C.; Prasher, S.; Elsayed, E.; Dhiman, J.; Mawof, A.; Patel, R. Effect of biochar on heavy metal accumulation in potatoes from wastewater irrigation. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 232, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koehler, A. Water use in LCA: Managing the planet’s freshwater resources. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2008, 13, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pedrero, F.; Kalavrouziotis, I.; Alarcón, J.J.; Koukoulakis, P.; Asano, T. Use of treated municipal wastewater in irrigated agriculture—Review of some practices in Spain and Greece. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 1233–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahat, E.; Linderholm, H.W. The effect of long-term wastewater irrigation on accumulation and transfer of heavy metals in Cupressus sempervirens leaves and adjacent soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 512, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alghobar, M.A. Effect of Sewage Water Irrigation on Soil Properties and Evaluation of the Accumulation of Elements in Grass Crop in Mysore City, Karnataka, India. Am. J. Environ. Prot. 2014, 3, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, H.; Lu, J.; Yuan, X.; Wu, J.; Zhao, J.; Yu, X.H.; Zhou, Y.M. Concentrations, Bioavailability, and Spatial Distribution of Soil Heavy Metals in a Long- Term Wastewater Irrigation Area in North China. Clean-Soil Air Water 2014, 42, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunc, T.; Sahin, U. Red cabbage yield, heavy metal content, water use and soil chemical characteristics under wastewater irrigation. Environ. Sci Pollut. R 2016, 23, 6264–6276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belaid, N.; Neel, C.; Kallel, M.; Ayoub, T.; Ayadi, A.; Baudu, M. Assessment of metal accumulation in calcareous soil and forage crops subjected to long-term irrigation using treated wastewater: Case of El Hajeb-Sfax, Tunisia. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 158, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muchuweti, M.; Birkett, J.W.; Chinyanga, E.; Zvauya, R.; Scrimshaw, M.D.; Lester, J.N. Heavy metal content of vegetables irrigated with mixtures of wastewater and sewage sludge in Zimbabwe: Implications for human health. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2006, 112, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, L.P.; Hu, W.; Wang, X.F.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Meng, Y.B.; Xiao, Q.P.; Guo, X.X.; Zhou, Y.F.; Bi, Y.Y.; et al. Analysis of Heavy Metal Contamination of Agricultural Soils and Related Effect on Population Health-A Case Study for East River Basin in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, A.; Niaz, A.; Ullah, N.; Rehman, A.; Akhlaq, M.; Zakir, M.; Suleman Khan, M. Comparative study of heavy metals in soil and selected medicinal plants. J. Chem. 2013, 17, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelstein, M.; Ben-Hur, M. Heavy metals and metalloids: Sources, risks and strategies to reduce their accumulation in horticultural crops. Sci. Hortic. 2018, 234, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Alamzeb, S.; Begum, S. Accumulation of heavy metals in edible parts of vegetables irrigated with waste water and their daily intake to adults and children, District Mardan, Pakistan. Food Chem. 2013, 136, 1515–1523. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, L.; Liu, X.L.; Hu, J.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.L.; Han, G.L.; Li, S.L.; Liu, C.Q. Heavy Metal Accumulation in Common Aquatic Plants in Rivers and Lakes in the Taihu Basin. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, X.L.; Shen, H.L.; Zhao, Y.J.; Cao, W.X.; Hu, C.W.; Sun, C. Distribution and Potential Ecological Risk of Heavy Metals in Water, Sediments, and Aquatic Macrophytes: A Case Study of the Junction of Four Rivers in Linyi City, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coen, N.; Mothersill, C.; Kadhim, M.; Wright, E.G. Heavy metals of relevance to human health induce genomic instability. J. Pathol. 2001, 195, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Han, Q.; Gui, C.; Ca, O.J.; Liu, Y.; He, X.; He, Y. Differences in the risk assessment of soil heavy metals between newly built and original parks in Jiaozuo, Henan Province, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 676, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Wang, M.; Cao, J.; Gui, C.; Liu, Y. Health risk assessment and bioaccessibilities of heavy metals for children in soil and dust from urban parks and schools of Jiaozuo, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 191, 110157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessier, A.P.; Campbell, P.G.C.; Bisson, M.X. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Anal. Chem. 1979, 51, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sialelli, J.; Urquhart, G.J.; Davidson, C.M.; Hursthouse, A.S. Use of a physiologically based extraction test to estimate the human bioaccessibility of potentially toxic elements in urban soils from the city of Glasgow, UK. Environ. Geochem. Health 2010, 32, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amacher, M.C. Nickel, cadmium, and lead. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 3 Chemical Methods; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1996; Volume 5, pp. 739–768. [Google Scholar]
- Ure, A.; Quevauviller, P.; Muntau, H.; Griepink, B. Speciation of heavy metals in soils and sediments. An account of the improvement and harmonization of extraction techniques undertaken under the auspices of the BCR of the Commission of the European Communities. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 1993, 51, 135–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauret, G.; López-Sánchez, J.; Sahuquillo, A.; Rubio, R.; Davidson, C.; Ure, A.; Quevauviller, P. Improvement of the BCR three step sequential extraction procedure prior to the certification of new sediment and soil reference materials. J. Environ. Monit. 1999, 1, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, S.; Xu, C. Chemical speciation of elements in sediments and soils and their sequential extraction process. Geol. Bull. China 2005, 24, 728–734. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Cid, B.; Lavilla, I.; Bendicho, C. Speeding up of a three-stage sequential extraction method for metal speciation using focused ultrasound. Anal. Chim. Acta 1998, 360, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazos-Capeáns, P.; Barciela-Alonso, M.C.; Bermejo-Barrera, A.; Bermejo-Barrera, P. Chromium available fractions in arousa sediments using a modified microwave BCR protocol based on microwave assisted extraction. Talanta 2005, 65, 678–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, E.; Barahona, E.; Lachica, M.; Mingorance, M. A study of the analytical parameters important for the sequential extraction procedure using microwave heating for Pb, Zn and Cu in calcareous soils. Anal. Chim. Acta 1998, 369, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chomchoei, R.; Shiowatana, J.; Pongsakul, P. Continuous-flow system for reduction of metal readsorption during sequential extraction of soil. Anal. Chim. Acta 2002, 472, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleyzes, C.; Tellier, S.; Astruc, M. Fractionation studies of trace elements in contaminated soils and sediments: A review of sequential extraction procedures. Trends Anal. Chem. 2002, 21, 451–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhiman, J.; Prasher, S.O.; ElSayed, E.; Patel, R.M.; Nzediegwu, C.; Mawof, A. Effect of hydrogel based soil amendments on heavy metal uptake by spinach grown with wastewater irrigation. J. Clean Prod. 2021, 311, 127644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.K.; Singh, K.; Singh, B.; Gautam, N.N. Biomass productivity and nutrient availability of Cynodon dactylon (L.) Pers. growing on soils of different sodicity stress. Biomass Bioenergy 2011, 35, 3440–3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, B.R. Peer reviewed: The challenge of remediating chromium-contaminated soil. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1996, 30, 248A–251A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.K.; Agrawal, M. Biological effects of heavy metals: An overview. J. Environ. Biol. 2005, 26, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bishnoi, N.; Dua, A.; Gupta, V.; Sawhney, S. Effect of chromium on seed germination, seedling growth and yield of peas. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1993, 47, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barceló, J.; Poschenrieder, C.; Gunsé, B. Water relations of chromium VI treated bush bean plants (Phaseolus vulgaris L. cv. Contender) under both normal and water stress conditions. J. Exp. Bot. 1986, 37, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, T.; Sonoda, Y. Comparison of the toxicity of heavy metals to cabbage growth. Plant Soil 1979, 51, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Qadir, M.; Endo, T.; Masunaga, T.; Ahmad, Z. Long-Term Effects of Wastewater Irrigation on Soil Heavy Metal Contamination in Peri-urban Areas of Aleppo, Syria. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2014, 16, 1153–1158. [Google Scholar]
- Sarwar, T.; Shahid, M.; Khalid, S.N.; Shah, A.H.; Ahmad, N.; Naeem, M.A.; ul Haq, Z.; Murtaza, B.; Bakhat, H.F. Quantification and risk assessment of heavy metal build-up in soil-plant system after irrigation with untreated city wastewater in Vehari, Pakistan. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 4281–4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.; Israr, M.; Rehman, S.U.; Azizullah, A.; Gulab, H.; Idrees, M.; Iqbal, R.; Khattak, A.; Hussain, M.; Al-Zuaibr, F.M. Health risk assessment of heavy metals via consumption of dietary vegetables using wastewater for irrigation in Swabi, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0255853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Habahbeh, K.A.; Al-Nawaiseh, M.B.; Al-Sayaydeh, R.S.; Al-Hawadi, J.S.; Albdaiwi, R.N.; Al-Debei, H.S.; Ayad, J.Y. Long-Term Irrigation with Treated Municipal Wastewater from the Wadi-Musa Region: Soil Heavy Metal Accumulation, Uptake and Partitioning in Olive Trees. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, Z.; Wei, Z.; Fan, L.; Zhang, X.; Pei, J. Heavy metal pollution and potential ecological risk assessment in agricultural soils located in the peri-urban area of Kaifeng City. Environ. Chem. 2018, 37, 513–522. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Fan, L.; Chen, Y.; Xing, L.; Yang, Y.; Xiang, Z.; Wang, X. Spatial distribution and source analysis of heavy metals in agricultural soils in a Peri-urban area based on IDW interpolation and chemical fractions: A case study in Henan Province. Acta Sci. Circumst. 2016, 36, 1317–1327. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Han, J.X.; Jian-Hua, M.A. Health Risk Assessment of Wheat Seeds Heavy Metals in the Sewage Irrigation Area of Huafei River, Kaifeng City. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2008, 27, 2332–2337. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, T.; Xue, X.; Rui, L. Application of TOPSIS in Environmental Quality Assessment of Huafei River in Kaifeng. Meteorol. Environ. Sci. 2008, 31, 59–62. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Zhang, M.; Li, K.; Huo, J.; Yu, Q.; Lu, J.; Wang, Q.; Li, Q.; Chen, G. Analysis of Climate Change Characteristics in Kaifeng in the Last 50 Years. Meteorol. Environ. Sci. 2009, 32, 82–86. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.Q. The Distribution, Speciation and the Potential Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in the Pearl River Estuary and Adjacent Shelf. Ph.D. Thesis, Graduate School of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry), Guangzhou, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Nemati, K.; Abu Bakar, N.K.; Abas, M.R.; Sobhanzadeh, E. Speciation of heavy metals by modified BCR sequential extraction procedure in different depths of sediments from Sungai Buloh, Selangor, Malaysia. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 192, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Ramanathan, A.L. Speciation of selected trace metals (Fe, Mn, Cu and Zn) with depth in the sediments of Sundarban mangroves: India and Bangladesh. J. Soils Sediments 2015, 15, 2476–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perin, G.; Craboledda, L.; Lucchese, L.; Cirillo, R.; Orio, A.A. Heavy metal speciation in the sediments of Northern Adriatic Sea. A new approach for environmental toxicity determination. Heavy Met. Environ. 1985, 2, 454–456. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, K.P.; Mohan, D.; Singh, V.K.; Malik, A. Studies on distribution and fractionation of heavy metals in Gomti river sediments—a tributary of the Ganges, India. J. Hydrol. 2005, 312, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, L.; Ruiz, E.; Alonso-Azcárate, J.; Rincón, J. Heavy metal distribution and chemical speciation in tailings and soils around a Pb–Zn mine in Spain. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 1106–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahat, E.A.; Galal, T.M.; Elawa, O.E.; Hassan, L.M. Health risk assessment and growth characteristics of wheat and maize crops irrigated with contaminated wastewater. Environ. Monit Assess. 2017, 189, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.T.; Chen, C.C.; Song, X.L.; Han, Y.L.; Liang, Z.H. Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution in Soil and Plants from Dunhua Sewage Irrigation Area. Int. J. Electrochem Sci. 2011, 6, 5314–5324. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, W.X.; Han, G.L.; Liu, M.; Song, C.; Li, X.Q.; Malem, F. Vertical Distribution and Controlling Factors Exploration of Sc, V, Co, Ni, Mo and Ba in Six Soil Profiles of The Mun River Basin, Northeast Thailand. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ruiz-Fernández, A.; Páez-Osuna, F.; Urrutia-Fucugauchi, J.; Preda, M.; Rehault, I. Historical trace metal fluxes in the Mexico City Metropolitan Zone as evidenced by a sedimentary record from the Espejo de los Lirios lake. Chemosphere 2004, 6, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robbins, J.A. Geochemical and geophysical applications of radioactive lead. In The Biogeochemistry of Lead in the Environment; Nriagu, J.O., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1978; pp. 285–393. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, Y.; Higman, J.; Thompson, J.; O’Toole, T.; Campbell, D. Characterization and spatial distribution of heavy metals in sediment from Cedar and Ortega rivers subbasin. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2002, 54, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, L.Y.; Sun, R.H.; Wang, Z.M.; Yu-He, J.I.; Chen, L.D. Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution in Surface Sediments of Rivers in Northern Area of Haihe River Basin, China. Environ. Sci. 2012, 33, 606–611. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Y.; Fang, M.; Wu, Y.J.; Liu, H.; Tong, X. Pollution characteristics and potential ecological risk of heavy metals in river sediments of Shanghai. China Environ. Sci. 2013, 33, 147–153. [Google Scholar]
- China, E.M. Background Values of Soil Elements in China; China Environment Sciences Press: Beijing, China, 1990; pp. 356–357. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.L.; Ma, X.W.; Ai, S.W.; Zhu, S.Y.; Zhang, W.Y.; Zhang, Y.M. Spatial distribution and source identification of heavy metals in soils under different land uses in a sewage irrigation region, northwest China. J. Soil Sediments 2016, 16, 1547–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadimi, F.; Ghomi, M. Assessment of the effects of municipal wastewater on the heavy metal pollution of water and sediment in Arak Mighan Lake, Iran. J. Tethys 2013, 1, 205–214. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, Y.-T.; Lee, C.-W. Ecological risk assessment of sediment in wastewater discharging area by means of metal speciation. Microchem. J. 2001, 70, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.-H.; Cao, S.-S. Mercury and cadmium contamination of irrigation water, sediment, soil and shallow groundwater in a wastewater-irrigated field in Tianjin, China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2010, 84, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Act, Ontario Environmental Protection. Soil, Ground Water and Sediment Standards for Use under Part XV.1 of the Environmental Protection Act.; Queen’s Printer for Ontario: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Sekiya, N.; Yano, K. Water acquisition from rainfall and groundwater by legume crops developing deep rooting systems determined with stable hydrogen isotope compositions of xylem waters. Field Crops Res. 2002, 78, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.R.; Chaudhary, T.N. Wheat root growth, grain yield and water uptake as influenced by soil water regime and depth of nitrogen placement in a loamy sand soil. Agric. Water Manag. 1983, 6, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akcay, H.; Oguz, A.; Karapire, C. Study of heavy metal pollution and speciation in Buyak Menderes and Gediz river sediments. Water Res. 2003, 37, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattan, R.K.; Datta, S.P.; Chhonkar, P.K.; Suribabu, K.; Singh, A.K. Long-term impact of irrigation with sewage effluents on heavy metal content in soils, crops and groundwater—A case study. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2005, 109, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Ramanathan, A.; Prabha, S.; Ranjan, R.K.; Ranjan, S.; Singh, G. Metal speciation studies in the aquifer sediments of Semria Ojhapatti, Bhojpur District, Bihar. Environ. Monit Assess. 2012, 184, 3027–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, C.H.; Smith, D.; Huitson, A. A general treatment and classification of the solute adsorption isotherm. I. Theoretical. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1974, 47, 755–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnamfard, A.; Salarirad, M.M. Equilibrium and kinetic studies on free cyanide adsorption from aqueous solution by activated carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 170, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Nemr, A. Potential of pomegranate husk carbon for Cr (VI) removal from wastewater: Kinetic and isotherm studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 161, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, K.Y.; Hameed, B.H. Insights into the modeling of adsorption isotherm systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 156, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrzypiec, M.; Wamke, A.; Dopierala, K.; Prochaska, K. Effect of chemical structure of fluorinated polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes on formation of Langmuir monolayers and Langmuir-Blodgett films. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 556, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaraghavan, K.; Padmesh, T.V.N.; Palanivelu, K.; Velan, M. Biosorption of nickel(II) ions onto Sargassum wightii: Application of two-parameter and three-parameter isotherm models. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 133, 304–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparks, D.L. Kinetics of Soil Chemical Processes; Academic Press: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Wei, L.; Yang, S. Effects of humic acids and minerals on adsorption-desorption of atrazine in soil. Acta Pedofil. Sin. 2016, 53, 155–165. [Google Scholar]


| Step | Fraction | Extractant | Shaking Time and Temperature |
|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | Exchangeable | 32 mL of 0.11 M CH3COOH | End-over-end shaking at 22 ± 5 °C for 16 h |
| F2 | Reducible | 32 mL of 0.5 M NH3OH·HCl (pH 1.5) | End-over-end shaking at 22 ± 5 °C for 16 h |
| F3 | Oxidizable | 8 mL of 8.8 M H2O2 (pH 2) | Manual occasional shaking at 22 ± 5 °C for 1 h, then conducting water bath evaporation to 2 mL residue at 85 ± 2 °C |
| 8 mL of 8.8 M H2O2 (pH 2) was added again | Continuing water bath evaporation to 2 mL residue at 85 ± 2 °C | ||
| Cooling was completed, and 32 mL of NH4OAc (pH 2) was added | End-over-end shaking at 22 ± 5 °C for 16 h | ||
| F4 | Residual | 0.2 g air-dried residue was taken | Same digestion scheme as pseudo-total heavy metals |
| RAC Index (%) | Risk Level |
|---|---|
| <1 | No risk |
| 1–10 | Low risk |
| 11–30 | Medium risk |
| 31–50 | High risk |
| >50 | Very high risk |
| Site | Cr | Cd | Pb | Mn | Zn | Ni | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max | Min | Mean | SD | Max | Min | Mean | SD | Max | Min | Mean | SD | Max | Min | Mean | SD | Max | Min | Mean | SD | Max | Min | Mean | SD | |
| S1 | 69 | 47.7 | 59.43 | 8.48 | 2.24 | 0.12 | 1.14 | 0.82 | 59.9 | 18.1 | 36.38 | 17.2 | 952.46 | 451.46 | 672.25 | 191.3 | 256.68 | 62.18 | 110.18 | 69 | 32.13 | 16.46 | 22.23 | 5.5 |
| S2 | 80 | 58.6 | 69.77 | 7.6 | 0.46 | 0.16 | 0.31 | 0.12 | 64.3 | 22.1 | 41.77 | 18 | 612.65 | 442.53 | 503.69 | 60.5 | 184.05 | 66.2 | 92.2 | 41.8 | 25.75 | 17.28 | 21.33 | 2.74 |
| S8 | 91.1 | 73.4 | 85.35 | 5.7 | 0.23 | 0.12 | 0.15 | 0.04 | 30.7 | 18.8 | 25.2 | 3.74 | 483.41 | 434.18 | 458.66 | 18.2 | 97.81 | 62.67 | 75.39 | 12.5 | 20.11 | 16.49 | 18.14 | 1.09 |
| Heavy Metal | Cr | Cd | Pb | Mn | Zn | Ni | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HFR | 87.79 | 13.73 | 224.49 | 570.6 | 566.31 | 53.89 | This study |
| HJR | 74.93 | 0.6 | 101.78 | 363.18 | 187.25 | 41.96 | This study |
| Mighan Lake | 29 | N/V | 12.43 | N/V | 174 | 17.43 | [62] |
| Masan Bay | N/V | 13 | 86 | N/V | N/V | N/V | [63] |
| Beitang River | N/V | 1.73 | 289.1 | N/V | N/V | N/V | [64] |
| Guideline value | 26 | 0.6 | 31 | N/V | 120 | 16 | [65] |
| Heavy Metal | Cr | Cd | Pb | Mn | Zn | Ni |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 68.7 | 2.15 | 58.3 | 886.49 | 217.56 | 30.15 |
| S2 | 77.75 | 0.45 | 62.9 | 583.64 | 130.06 | 24.5 |
| S3 | 85.5 | 12.6 | 193 | 625.15 | 511.04 | 41.62 |
| S4 | 97.2 | 3.57 | 174 | 630.18 | 422.1 | 37.41 |
| S5 | 84 | 2.99 | 137 | 518.7 | 314.92 | 36.4 |
| S6 | 69.8 | 0.85 | 56.1 | 482.6 | 207.62 | 35.77 |
| S7 | 54.9 | 0.12 | 17 | 394.02 | 186.13 | 37.1 |
| Mean | 76.84 | 3.25 | 99.76 | 588.68 | 284.21 | 34.71 |
| C.V. (%) | 0.18 | 1.33 | 0.68 | 0.26 | 0.49 | 0.16 |
| Filter value 1 | 250 | 0.6 | 170 | N/V | N/V | N/V |
| Control value 2 | 1300 | 4 | 1000 | N/V | N/V | N/V |
| Source of Soil | Langmuir Equation | Freundlich Equation | Linear Equation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm | KL | R2 | KF | 1/n | R2 | Kd | R2 | |
| HFR | 7012.198 | 0.0006 | 0.984 | 9.446 | 0.832 | 0.984 | 3.240 | 0.976 |
| HJR | 8399.338 | 0.0007 | 0.950 | 9.225 | 0.878 | 0.937 | 4.306 | 0.937 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, S.; Yu, F.; Zhang, J. Heavy-Metal Speciation Distribution and Adsorption Characteristics of Cr (VI) in the Soil within Sewage Irrigation Areas. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6309. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19106309
Liu S, Yu F, Zhang J. Heavy-Metal Speciation Distribution and Adsorption Characteristics of Cr (VI) in the Soil within Sewage Irrigation Areas. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(10):6309. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19106309
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Songtao, Furong Yu, and Jianuo Zhang. 2022. "Heavy-Metal Speciation Distribution and Adsorption Characteristics of Cr (VI) in the Soil within Sewage Irrigation Areas" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 10: 6309. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19106309
APA StyleLiu, S., Yu, F., & Zhang, J. (2022). Heavy-Metal Speciation Distribution and Adsorption Characteristics of Cr (VI) in the Soil within Sewage Irrigation Areas. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(10), 6309. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19106309






