Pesticide Research on Environmental and Human Exposure and Risks in Sub-Saharan Africa: A Systematic Literature Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Article Selection
2.3. Data Extraction
- Year of publication, year of data collection, and over how many years the data were collected
- Country where the study was conducted, the region where the study was conducted (when more than one region only one was reported (i.e., the first one which was mentioned)) and GPS coordinates of the study site (if the specific site was not mentioned, a random GPS point in the region was taken; in case no region was stated, the GPS of the capital city of the country was taken).
- Any organochlorine pesticides (OCPs), dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT),
- Any current-used pesticides (CUP; all pesticides other than OCPs), type of CUP (herbicides, fungicides, insecticides), chemical group of CUP insecticides (organophosphates, pyrethroids or others), and if no pesticides were mentioned by type or chemical group.
- Information on the matrices collected (e.g., water, soil, or air)
- Health risks assessment conducted for consumption, ingestion, inhalation, or dermal exposure.
- Environmental risk assessment conducted.
- Study design (i.e., intervention study, cross-sectional, longitudinal, retrospective, and case report)
- Study population (i.e., general population or occupational population)
- Sex of participants
- Number of individuals in the study population
- Human health outcomes: human health outcome group (e.g., signs and symptoms of acute poisoning, respiratory health) and outcome diagnosis method (i.e., objective measures, self-reported, or doctor-diagnosed)
- Human pesticide exposure: self-reported exposure, exposure algorithm, objective exposure marker (e.g., biomarkers in urine or blood and active ingredients in wristband)
- KAP and training of pesticide user
2.4. Analysis
3. Results
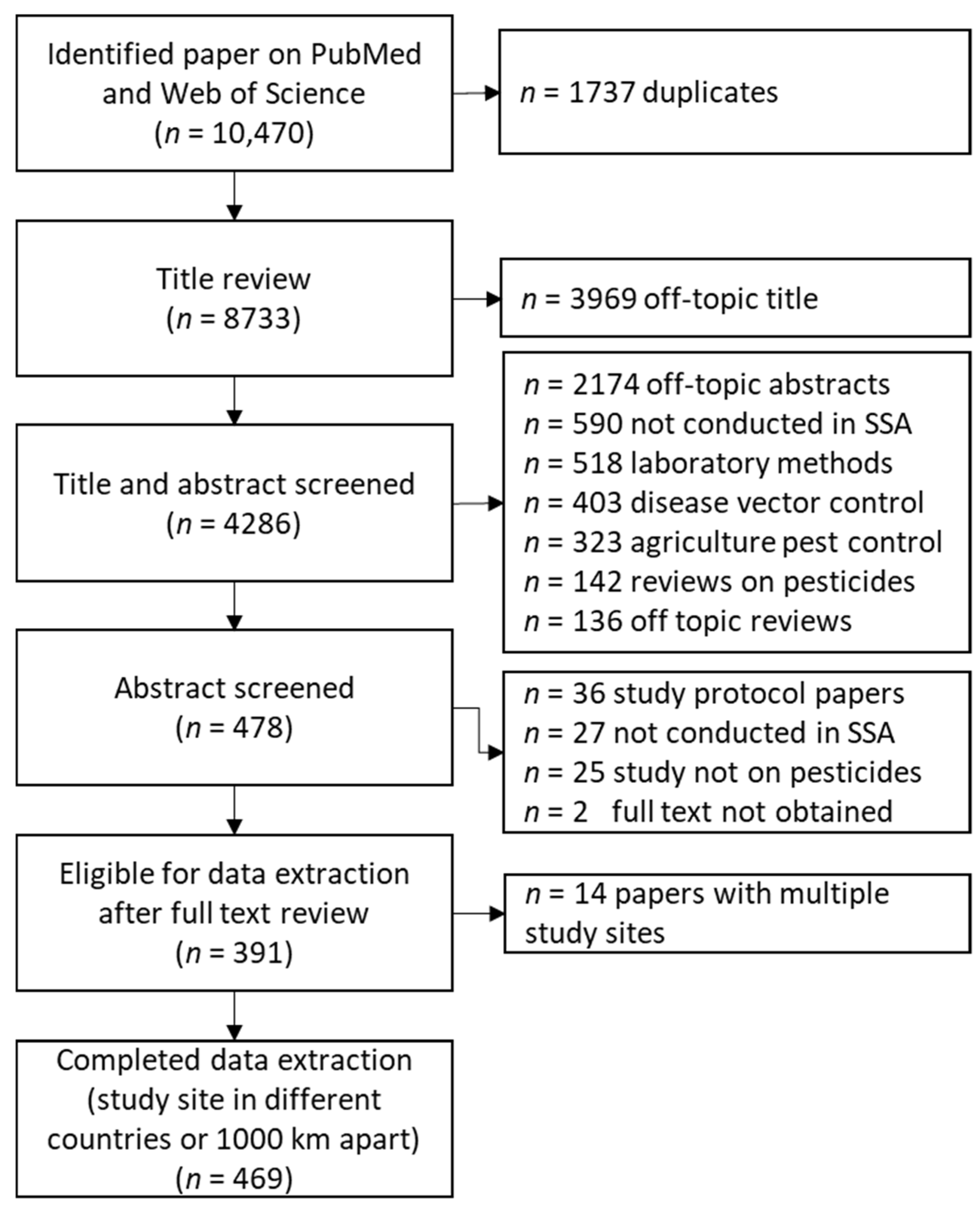
3.1. Identified Research Articles
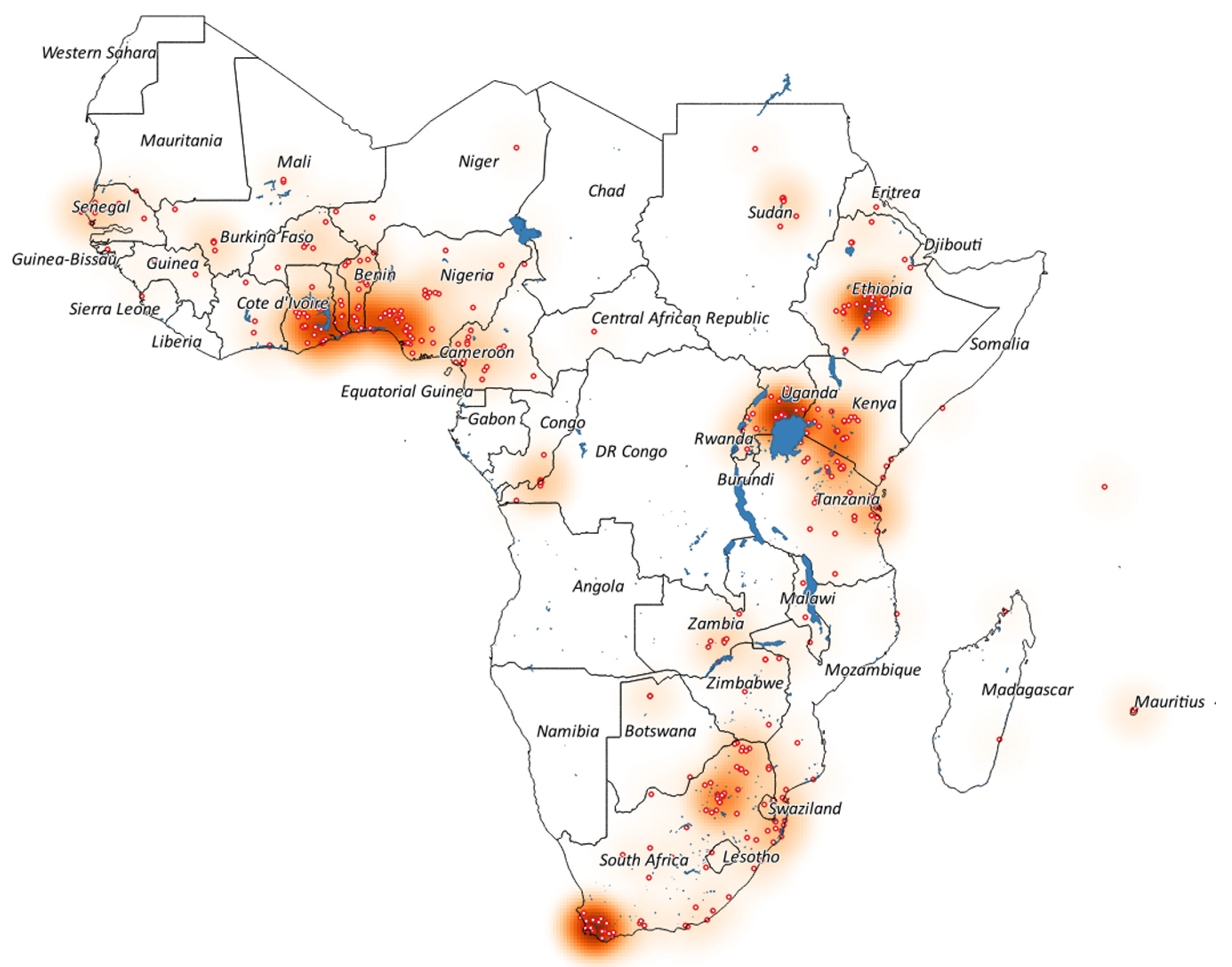
3.2. Spatial Distribution of the Research Studies across Sub-Saharan Africa
3.3. Pesticides Investigated
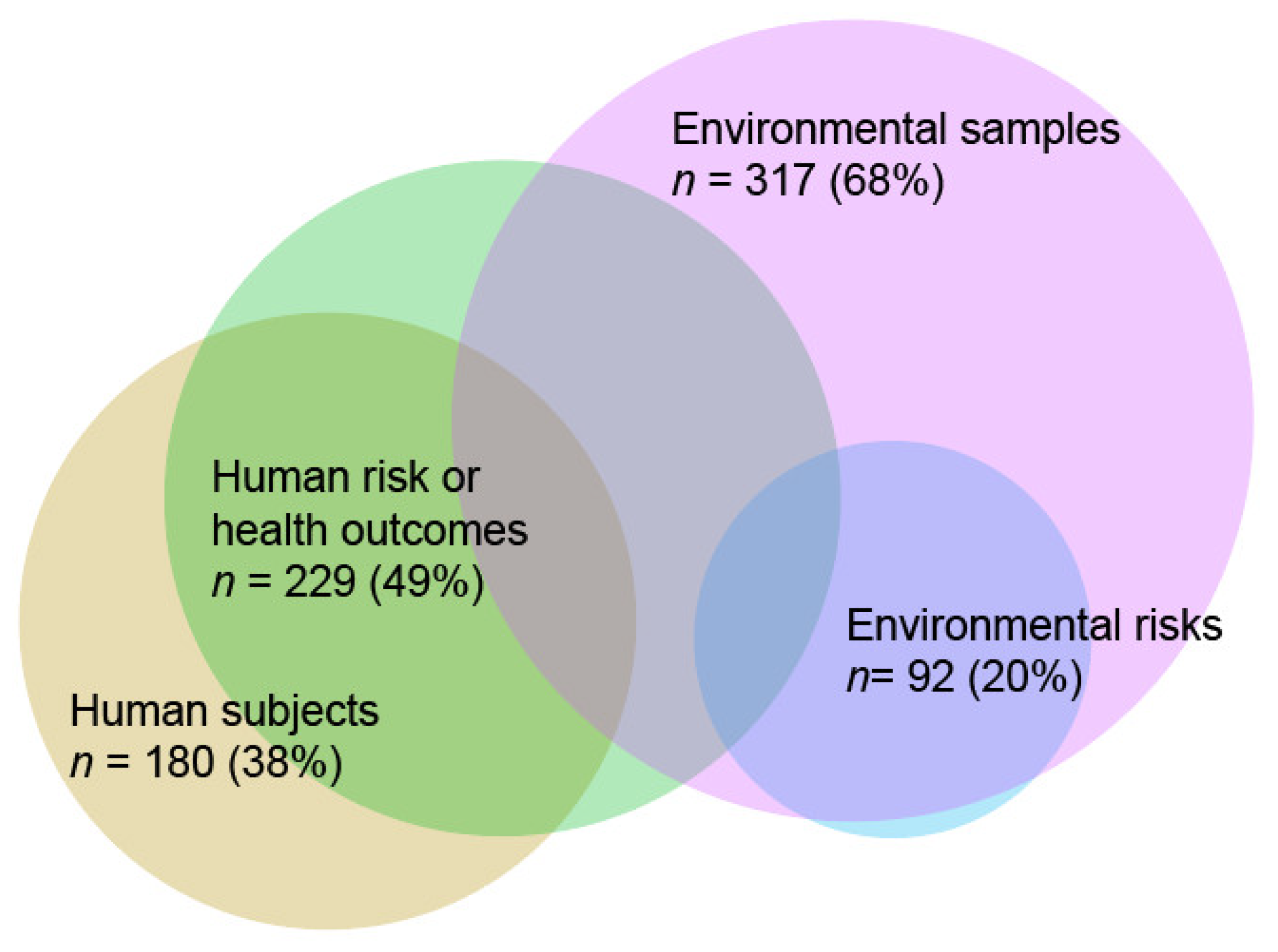
3.4. Extracted Human Subject and Environmental Sample Information
3.5. Human Subjects
3.5.1. Human Health Outcomes
3.5.2. Human Exposure and KAP of Pesticide Use
3.6. Environmental Samples
3.7. Duration and Temporal Distribution of Data Collection
3.8. Authors and Research Institutions
4. Discussion
Strength and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- OECD; FAO. OECD-FAO Agricultural Outlook 2018–2027; OECD Publishing: Paris, France; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Delcour, I.; Spanoghe, P.; Uyttendaele, M. Literature review: Impact of climate change on pesticide use. Food Res. Int. 2015, 68, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, D.K.; Mueller, N.D.; West, P.C.; Foley, J.A. Yield Trends Are Insufficient to Double Global Crop Production by 2050. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Transforming Food and Agriculture to Achieve the SDGs; Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2018; ISBN 9789251306260. [Google Scholar]
- Grote, U.; Fasse, A.; Nguyen, T.T.; Erenstein, O. Food Security and the Dynamics of Wheat and Maize Value Chains in Africa and Asia. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2021, 4, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mottaleb, K.A.; Fatah, F.A.; Kruseman, G.; Erenstein, O. Projecting food demand in 2030: Can Uganda attain the zero hunger goal? Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 28, 1140–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, M.; Pingali, P. Transforming Smallholder Agriculture to Achieve the SDGs. In The Role of Smallholder Farms in Food and Nutrition Security; Gomez y Paloma, S., Riesgo, L., Louhichi, K., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- FAO Statistics and Database of the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAOSTAT). Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/EP/visualize; http://www.webcitation.org/723qXCJRz (accessed on 28 October 2021).
- Jepson, P.C.; Murray, K.; Bach, O.; Bonilla, M.A.; Neumeister, L. Selection of pesticides to reduce human and environmental health risks: A global guideline and minimum pesticides list. Lancet Planet. Health 2020, 4, e56–e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jepson, P.C.; Guzy, M.; Blaustein, K.; Sow, M.; Sarr, M.; Mineau, P.; Kegley, S. Measuring pesticide ecological and health risks in West African agriculture to establish an enabling environment for sustainable intensification. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 369, 20130491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabrowski, J.M.; Shadung, J.M.; Wepener, V. Prioritizing agricultural pesticides used in South Africa based on their environmental mobility and potential human health effects. Environ. Int. 2014, 62, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hough, R.L. A world view of pesticides. Nat. Geosci. 2021, 14, 181–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.H.M.; Lenzen, M.; McBratney, A.; Maggi, F. Risk of pesticide pollution at the global scale. Nat. Geosci. 2021, 14, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siviter, H.; Bailes, E.J.; Martin, C.D.; Oliver, T.R.; Koricheva, J.; Leadbeater, E.; Brown, M.J.F. Agrochemicals interact synergistically to increase bee mortality. Nature 2021, 596, 389–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, N.; Thierfelder, C. Weed control under conservation agriculture in dryland smallholder farming systems of southern Africa. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2017, 37, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negatu, B.; Kromhout, H.; Mekonnen, Y.; Vermeulen, R. Use of chemical pesticides in Ethiopia: A cross-sectional comparative study on knowledge, attitude and practice of farmers and farm workers in three farming systems. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2016, 60, 551–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabrowski, J.M. Development of pesticide use maps for South Africa. S. Afr. J. Sci. 2015, 111, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, R.M.; Seibert, D.; Quesada, H.B.; de Jesus Bassetti, F.; Fagundes-Klen, M.R.; Bergamasco, R. Occurrence, impacts and general aspects of pesticides in surface water: A review. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020, 135, 22–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, R.; Scheidegger, R.; Doppler, T.; Dietzel, A.; Fenicia, F.; Stamm, C. A review of long-term pesticide monitoring studies to assess surface water quality trends. Water Res. X 2020, 9, 100064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohlander, J.; Fuhrimann, S.; Basinas, I.; Cherrie, J.W.; Galea, K.S.; Povey, A.; van Martie, T.; Harding, A.-H.; Jones, K.; Vermeulen, R.; et al. A systematic review of methods used to assess exposure to pesticides in occupational epidemiology studies, 1993-2017. Occup. Environ. Med. 2020, 77, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curchod, L.; Oltramare, C.; Junghans, M.; Stamm, C.; Dalvie, M.A.; Röösli, M.; Fuhrimann, S. Temporal variation of pesticide mixtures in rivers of three agricultural watersheds during a major drought in the Western Cape, South Africa. Water Res. X 2019, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degrendele, C.; Klanova, J.; Prokes, R.; Pribylová, P.; Senk, P.; Sudoma, M.; Röösli, M.; Dalvie, M.A.; Fuhrimann, S. Current use pesticides in soil and air from two agricultural sites in South Africa: Implications for environmental fate and human exposure. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 807, 150455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalvie, M.A.; Sosan, M.B.; Africa, A.; Cairncross, E.; London, L. Environmental monitoring of pesticide residues from farms at a neighbouring primary and pre-school in the Western Cape in South Africa. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 466–467, 1078–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrimann, S.; Van den Brenk, I.; Atuhaire, A.; Mubeezi, R.; Staudacher, P.; Huss, A.; Kromhout, H. Recent pesticide exposure affects sleep: A cross-sectional study among smallholder farmers in Uganda. Environ. Int. 2021, 158, 106878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.; Jørs, E.; Sandbæk, A.; Sekabojja, D.; Ssempebwa, J.; Mubeezi, R.; Staudacher, P.; Fuhrimann, S.; Sigsgaard, T.; Burdorf, A.; et al. Organophosphate and carbamate insecticides is related to decreased pulmonary function among smallholder farmers in Uganda: A short-term follow-up study with three rounds of examinations. Thorax 2021, 75, 780–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietler, D.; Leuenberger, A.; Bempong, N.; Cramer, C.; Eggen, R.I.L.; Erismann, S.; Ferazzi, S.; Flahault, A.; Fletcher, H.A.; Fuhrer, B.; et al. Health in the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development: From framework to action, transforming challenges into opportunities. J. Glob. Health 2019, 9, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; Altman, D.; Antes, G.; Atkins, D.; Barbour, V.; Barrowman, N.; Berlin, J.A.; et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chetty-Mhlanga, S.; Basera, W.; Fuhrimann, S.; Probst-Hensch, N.; Delport, S.; Mugari, M.; Van Wyk, J.; Roosli, M.; Dalvie, M.A.; Röösli, M.; et al. A prospective cohort study of school-going children investigating reproductive and neurobehavioral health effects due to environmental pesticide exposure in the Western Cape, South Africa: Study protocol. BMC Public Health 2018, 18, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chetty-Mhlanga, S.; Fuhrimann, S.; Basera, W.; Eeftens, M.; Röösli, M.; Dalvie, M. Association of activities related to pesticide exposure on headache severity and neurodevelopment of school-children in the rural agricultural farmlands of the Western Cape of South Africa. Environ. Int. 2020, 146, 106237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrimann, S.; Klánová, J.; Přibylová, P.; Kohoutek, J.; Dalvie, M.A.; Röösli, M.; Degrendele, C. Qualitative assessment of 27 current-use pesticides in air at 20 sampling sites across Africa. Chemosphere 2020, 258, 127333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batterman, S.A.; Chernyak, S.M.; Gounden, Y.; Matooane, M.; Naidoo, R.N. Organochlorine pesticides in ambient air in Durban, South Africa. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 397, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riana Bornman, M.S.; Bouwman, H. Environmental pollutants and diseases of sexual development in humans and wildlife in South Africa: Harbingers of impact on overall health? Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2012, 47, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauch, S.; Bradman, A.; Coker, E.; Chevrier, J.; An, S.; Bornman, R.; Eskenazi, B. Determinants of Exposure to Pyrethroid Insecticides in the VHEMBE Cohort, South Africa (vol 52, pg 12108, 2018). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delport, R.; Bornman, R.; MacIntyre, U.E.; Oosthuizen, N.M.; Becker, P.J.; Aneck-Hahn, N.H.; de Jager, C. Changes in retinol-binding protein concentrations and thyroid homeostasis with nonoccupational exposure to DDT. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 647–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fuhrimann, S.; Farnham, A.; Staudacher, P.; Atuhaire, A.; Manfioletti, T.; Niwagaba, C.; Namirembe, S.; Mugweri, J.; Winkler, M.; Portengen, L.; et al. Exposure to multiple pesticides and neurobehavioral outcomes among smallholder farmers in Uganda. Environ. Int. 2021, 152, 106477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staudacher, P.; Fuhrimann, S.; Farnham, A.; Mora, A.M.; Atuhaire, A.; Niwagaba, C.; Stamm, C.; Eggen, R.I.L.; Winkler, M.S. Comparative Analysis of Pesticide Use Determinants Among Smallholder Farmers from Costa Rica and Uganda. Environ. Health Insights 2020, 14, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diemer, N.; Staudacher, P.; Atuhaire, A.; Fuhrimann, S.; Inauen, J. Smallholder farmers’ information behavior differs for organic versus conventional pest management strategies: A qualitative study in Uganda. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 257, 120465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrimann, S.; Winkler, M.S.; Staudacher, P.; Weiss, F.T.; Stamm, C.; Eggen, R.I.L.; Lindh, C.H.; Menezes-Filho, J.A.; Baker, J.M.; Ramírez-Muñoz, F.; et al. Exposure to pesticides and health effects on farm owners and workers from conventional and organic agricultural farms in Costa Rica: Protocol for a cross-sectional study. JMIR Res. Protoc. 2019, 8, e10914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, K.; Basinas, I.; Kromhout, H.; Van Tongeren, M.; Harding, A.H.; Cherrie, J.W.; Povey, A.; Ahmad, Z.N.S.; Fuhrimann, S.; Ohlander, J.; et al. Improving exposure assessment methodologies for epidemiological studies on pesticides: Study protocol. JMIR Res. Protoc. 2020, 9, 8–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, W.A.H.; Schlüssem, V.; Jors, E.; Sekabojja, D.; Ssempebwa, C.; Mubeezi, R.; Staudacher, P.; Fuhrimann, S.; Hansen, M.R.H. Precision and accuracy of FEV 1 measurements from the Vitalograph copd-6 mini-spirometer in a healthy Ugandan population. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0253319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otieno, P.O.; Schramm, K.-W.W.; Pfister, G.; Lalah, J.O.; Ojwach, S.O.; Virani, M. Spatial distribution and temporal trend in concentration of carbofuran, diazinon and chlorpyrifos ethyl residues in sediment and water in Lake Naivasha, Kenya. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2012, 88, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negatu, B.; Kromhout, H.; Mekonnen, Y.; Vermeulen, R. Occupational pesticide exposure and respiratory health: A large-scale cross-sectional study in three commercial farming systems in Ethiopia. Thorax 2017, 72, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fix, J.; Annesi-Maesano, I.; Baldi, I.; Boulanger, M.; Cheng, S.; Cortes, S.; Dalphin, J.-C.; Dalvie, M.A.; Degano, B.; Douwes, J.; et al. Gender differences in respiratory health outcomes among farming cohorts around the globe: Findings from the AGRICOH consortium. J. Agromed. 2020, 26, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negatu, B.; Vermeulen, R.; Mekonnen, Y.; Kromhout, H. Neurobehavioural symptoms and acute pesticide poisoning: A cross-sectional study among male pesticide applicators selected from three commercial farming systems in Ethiopia. Occup. Environ. Med. 2018, 75, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teklu, B.M. Environmental Risk Assessment of Pesticides in Ethiopia: A Case of Surface Water Systems. Ph.D. Thesis, Wageningen University, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ezemonye, L.I.; Ikpesu, T.; Isioma, D. Distribution of propoxurin in water, sediment and fish from warri river, Niger Delta, Nigeria. Turk. J. Biochem. 2009, 34, 121–127. [Google Scholar]
- Bogdal, C.; Scheringer, M.; Abad, E.; Abalos, M.; van Bavel, B.; Hagberg, J.; Fiedler, H. Worldwide distribution of persistent organic pollutants in air, including results of air monitoring by passive air sampling in five continents. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 46, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, E.A.D.; Mulhauser, B.; Mulot, M.; Mutabazi, A.; Glauser, G.; Aebi, A. A worldwide survey of neonicotinoids in honey. Science 2017, 358, 109–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, H.M.; Armstrong, G.; Barton, M.; Bergmann, A.J.; Bondy, M.; Halbleib, M.L.; Hamilton, W.; Haynes, E.; Herbstman, J.; Hoffman, P.; et al. Discovery of common chemical exposures across three continents using silicone wristbands. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2019, 6, 181836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomenson, J.A.; Matthews, G.A. Causes and types of health effects during the use of crop protection chemicals: Data from a survey of over 6,300 smallholder applicators in 24 different countries. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2009, 82, 935–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christie, M.E.; van Houweling, E.; Zseleczky, L. Mapping gendered pest management knowledge, practices, and pesticide exposure pathways in Ghana and Mali. Agric. Human Values 2015, 32, 761–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, S.; Ball, A.; Pretty, J. Trends in pesticide use and drivers for safer pest management in four African countries. Crop Prot. 2008, 27, 1327–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaccher, V.; Ingenbleek, L.; Adegboye, A.; Hossou, S.E.; Koné, A.Z.; Oyedele, A.D.; Kisito, C.S.K.J.; Dembélé, Y.K.; Hu, R.; Adbel Malak, I.; et al. Levels of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in foods from the first regional Sub-Saharan Africa Total Diet Study. Environ. Int. 2020, 135, 105413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munschy, C.; Vigneau, E.; Bely, N.; Héas-Moisan, K.; Olivier, N.; Pollono, C.; Hollanda, S.; Bodin, N. Legacy and emerging organic contaminants: Levels and profiles in top predator fish from the western Indian Ocean in relation to their trophic ecology. Environ. Res. 2020, 188, 109761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Maartens, F.; Vega, H.; Kunene, S.; Gumede, J.; Krieger, R.I. 2,2-bis(4-chlorophenyl)acetic acid (dda), a water-soluble urine biomarker of DDT metabolism in humans. Int. J. Toxicol. 2009, 28, 528–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, K.A.; Seck, D.; Hobbie, K.A.; Traore, A.N.; McCartney, M.A.; Ndaye, A.; Forsberg, N.D.; Haigh, T.A.; Sower, G.J. Passive sampling devices enable capacity building and characterization of bioavailable pesticide along the Niger, Senegal and Bani Rivers of Africa. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 369, 20130110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogata, Y.; Takada, H.; Mizukawa, K.; Hirai, H.; Iwasa, S.; Endo, S.; Mato, Y.; Saha, M.; Okuda, K.; Nakashima, A.; et al. International Pellet Watch: Global monitoring of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in coastal waters. 1. Initial phase data on PCBs, DDTs, and HCHs. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 1437–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harner, T.; Pozo, K.; Gouin, T.; Macdonald, A.; Hung, H.; Cainey, J.; Peters, A. Global pilot study for persistent organic pollutants (POPs) using PUF disk passive air samplers. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 144, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isogai, N.; Hogarh, J.N.; Seike, N.; Kobara, Y.; Oyediran, F.; Wirmvem, M.J.; Ayonghe, S.N.; Fobil, J.; Masunaga, S. Atmospheric monitoring of organochlorine pesticides across some West African countries. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 31828–31835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, J.; Eskenazi, B.; Bornman, R.; Gaspar, F.W.; Crause, M.; Obida, M.; Chevrier, J. Exposure to DDT and hypertensive disorders of pregnancy among South African women from an indoor residual spraying region: The VHEMBE study. Environ. Res. 2018, 162, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebremichael, S.; Birhanu, T.; Tessema, D.A. Analysis of organochlorine pesticide residues in human and cow’s milk in the towns of Asendabo, Serbo and Jimma in South-Western Ethiopia. Chemosphere 2013, 90, 1652–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manfo, F.P.T.; Mboe, S.A.; Nantia, E.A.; Ngoula, F.; Telefo, P.B.; Moundipa, P.F.; Cho-Ngwa, F. Evaluation of the Effects of Agro Pesticides Use on Liver and Kidney Function in Farmers from Buea, Cameroon. J. Toxicol. 2020, 2020, 2305764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.R.H.; Jørs, E.; Sandbæk, A.; Sekabojja, D.; Ssempebwa, J.C.; Mubeezi, R.; Staudacher, P.; Fuhrimann, S.; Burdorf, A.; Bibby, B.M.; et al. Exposure to cholinesterase inhibiting insecticides and blood glucose level in a population of Ugandan smallholder farmers. Occup. Environ. Med. 2020, 77, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rother, H.A. Pesticide suicides: What more evidence is needed to ban highly hazardous pesticides? Lancet Glob. Health 2021, 9, e225–e226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, K.A.; Tzilivakis, J.; Warner, D.J.; Green, A. An international database for pesticide risk assessments and management. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2016, 22, 1050–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonga, H.E. Assessment of farming practices and uses of agrochemicals in Lake Manyara basin, Tanzania. J. Agric. Res. 2011, 6, 2216–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damte, T.; Tabor, G. Small-scale vegetable producers’ perception of pests and pesticide uses in East Shewa zone, Ethiopia. Int. J. Pest Manag. 2015, 61, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidoo, S.; London, L.; Burdorf, A.; Naidoo, R.N.; Kromhout, H. Agricultural activities, pesticide use and occupational hazards among women working in small scale farming in Northern Kwazulu-Natal, South Africa. Int. J. Occup. Environ. Health 2008, 14, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandie, F.J.; Krauss, M.; Massei, R.; Ganatra, A.; Fillinger, U.; Becker, J.; Liess, M.; Torto, B.; Brack, W. Multi-compartment chemical characterization and risk assessment of chemicals of emerging concern in freshwater systems of western Kenya. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2020, 32, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houbraken, M.; Habimana, V.; Senaeve, D.; López-Dávila, E.; Spanoghe, P. Multi-residue determination and ecological risk assessment of pesticides in the lakes of Rwanda. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 576, 888–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veludo, A.; Figueiredo, D.; Degrendele, C.; Röösli, M.; Fuhrimann, F. Seasonal variations in air concentrations of 27 organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) and 25 current-use pesticides (CUPs) across three agricultural areas of South Africa. Chemosphere 2021, 289, 133162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandie, F.J.; Krauss, M.; Beckers, L.M.; Massei, R.; Fillinger, U.; Becker, J.; Liess, M.; Torto, B.; Brack, W. Occurrence and risk assessment of organic micropollutants in freshwater systems within the Lake Victoria South Basin, Kenya. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 714, 136748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrimann, S.; Mol, H.G.J.; Dias, J.; Dalvie, M.A.; Röösli, M.; Degrendele, C.; Figueiredo, D.M.; Huss, A.; Portengen, L.; Vermeulen, R. Quantitative assessment of multiple pesticides in silicone wristbands of children/guardian pairs living in agricultural areas in South Africa. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 152330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelmel, J.P.; Lin, E.Z.; Delay, K.; Williams, A.J.; Zhou, Y.; Bornman, R.; Obida, M.; Chevrier, J.; Pollitt, K. Assessing the external exposome of South African children using wearable passive samplers and high-resolution mass spectrometry. Expo. Health 2021, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donald, C.E.; Scott, R.P.; Blaustein, K.L.; Halbleib, M.L.; Sarr, M.; Jepson, P.C.; Anderson, K.A. Silicone wristbands detect individuals’ pesticide exposures in West Africa. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2016, 3, 160433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschet, C.; Wittmer, I.; Simovic, J.; Junghans, M.; Piazzoli, A.; Singer, H.; Stamm, C.; Leu, C.; Hollender, J. How a complete pesticide screening changes the assessment of surface water quality. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 5423–5432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barr, D.B. Biomonitoring of exposure to pesticides. J. Chem. Health Saf. 2008, 15, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhaert, V.; Newmark, N.; D’Hollander, W.; Covaci, A.; Vlok, W.; Wepener, V.; Addo-Bediako, A.; Jooste, A.; Teuchies, J.; Blust, R.; et al. Persistent organic pollutants in the Olifants River Basin, South Africa: Bioaccumulation and trophic transfer through a subtropical aquatic food web. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 792–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogbeide, O.; Tongo, I.; Enuneku, A.; Ogbomida, E.; Ezemonye, L. Human Health Risk Associated with Dietary and Non-Dietary Intake of Organochlorine Pesticide Residues from Rice Fields in Edo State Nigeria. Expo. Health 2016, 8, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groffen, T.; Rijnders, J.; van Doorn, L.; Jorissen, C.; de Borger, S.M.; Luttikhuis, D.O.; de Deyn, L.; Covaci, A.; Bervoets, L. Preliminary study on the distribution of metals and persistent organic pollutants (POPs), including perfluoroalkylated acids (PFAS), in the aquatic environment near Morogoro, Tanzania, and the potential health risks for humans. Environ. Res. 2021, 192, 110299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnhoorn, I.E.J.; Bornman, M.S.; Jansen van Rensburg, C.; Bouwman, H. DDT residues in water, sediment, domestic and indigenous biota from a currently DDT-sprayed area. Chemosphere 2009, 77, 1236–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sichilongo, K.; Banda, D. GC-MS determination of targeted pesticides in environmental samples from the Kafue Flats of Zambia. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2013, 91, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shunthirasingham, C.; Mmereki, B.T.; Masamba, W.; Oyiliagu, C.E.; Lei, Y.D.; Wania, F. Fate of pesticides in the arid subtropics, Botswana, Southern Africa. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 8082–8088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otieno, P.; Okinda Owuor, P.; Lalah, J.O.; Pfister, G.; Schramm, K.W. Monitoring the occurrence and distribution of selected organophosphates and carbamate pesticide residues in the ecosystem of Lake Naivasha, Kenya. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2015, 97, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanyika-Mbewe, C.; Thole, B.; Makwinja, R.; Kaonga, C.C. Monitoring of carbaryl and cypermethrin concentrations in water and soil in Southern Malawi. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogbeide, O.; Tongo, I.; Ezemonye, L. Risk assessment of agricultural pesticides in water, sediment, and fish from Owan River, Edo State, Nigeria. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nibamureke, U.M.C.; Barnhoorn, I.E.J.; Wagenaar, G.M. Health assessment of freshwater fish species from Albasini Dam, outside a DDT-sprayed area in Limpopo province, South Africa: A preliminary study. Afr. J. Aquat. Sci. 2016, 41, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, M.H.B.; Polder, A.; Brynildsrud, O.B.; Karimi, M.; Lie, E.; Manyilizu, W.B.; Mdegela, R.H.; Mokiti, F.; Murtadha, M.; Nonga, H.E.; et al. Organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in human breast milk and associated health risks to nursing infants in Northern Tanzania. Environ. Res. 2017, 154, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horn, S.; Pieters, R.; Bøhn, T. May agricultural water sources containing mixtures of agrochemicals cause hormonal disturbances? Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 711, 134862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mawussi, G.; Scorza Júnior, R.P.; Dossa, E.L.; Alaté, K.-K.A. Insecticide residues in soil and water in coastal areas of vegetable production in Togo. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 7379–7385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teklu, B.M.; Haileslassie, A.; Mekuria, W. Pesticides as water pollutants and level of risks to environment and people: An example from Central Rift Valley of Ethiopia. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekonen, S.; Argaw, R.; Simanesew, A.; Houbraken, M.; Senaeve, D.; Ambelu, A.; Spanoghe, P. Pesticide residues in drinking water and associated risk to consumers in Ethiopia. Chemosphere 2016, 162, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojemaye, C.C.Y.; Onwordi, C.T.; Pampanin, D.M.; Sydnes, M.O.; Petrik, L. Presence and risk assessment of herbicides in the marine environment of Camps Bay (Cape Town, South Africa). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 738, 140346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelbagi, A.O.; Ismail, R.E.A.; Ishag, A.E.S.A.; Hammad, A.M.A. Pesticide residues in eggplant fruit from Khartoum State, Sudan. J. Health Pollut. 2020, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapeleka, J.A.; Sauli, E.; Sadik, O.; Ndakidemi, P.A. Co-exposure risks of pesticides residues and bacterial contamination in fresh fruits and vegetables under smallholder horticultural production systems in Tanzania. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0235345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omwenga, I.; Kanja, L.; Zomer, P.; Louisse, J.; Rietjens, I.M.C.M.; Mol, H. Organophosphate and carbamate pesticide residues and accompanying risks in commonly consumed vegetables in Kenya. Food Addit. Contam. Part B Surveill. 2021, 14, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atabila, A.; Phung, D.T.; Hogarh, J.N.; Fobil, J.N.; Sadler, R.; Connell, D.; Chu, C. Probabilistic health risk assessment of chlorpyrifos exposure among applicators on rice farms in Ghana. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 67555–67564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornman, M.S.; Chevrier, J.; Rauch, S.; Crause, M.; Obida, M.; Sathyanarayana, S.; Barr, D.B.; Eskenazi, B. Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane exposure and anogenital distance in the Venda Health Examination of Mothers, Babies and their Environment (VHEMBE) birth cohort study, South Africa. Andrology 2016, 4, 608–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaspar, F.W.; Chevrier, J.; Bornman, R.; Crause, M.; Obida, M.; Barr, D.B.; Bradman, A.; Bouwman, H.; Eskenazi, B. Undisturbed dust as a metric of long-term indoor insecticide exposure: Residential DDT contamination from indoor residual spraying and its association with serum levels in the VHEMBE cohort. Environ. Int. 2015, 85, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atabila, A.; Sadler, R.; Phung, D.T.; Hogarh, J.N.; Carswell, S.; Turner, S.; Patel, R.; Connell, D.; Chu, C. Biomonitoring of chlorpyrifos exposure and health risk assessment among applicators on rice farms in Ghana. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 20854–20867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalvie, M.A.; Naik, I.; Channa, K.; London, L. Urinary dialkyl phosphate levels before and after first season chlorpyrifos spraying amongst farm workers in the Western Cape, South Africa. J. Environ. Sci. Health B. 2011, 46, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linderholm, L.; Biague, A.; Månsson, F.; Norrgren, H.; Bergman, Å.; Jakobsson, K. Human exposure to persistent organic pollutants in West Africa—A temporal trend study from Guinea-Bissau. Environ. Int. 2010, 36, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sosan, M.B.; Akingbohungbe, A.E.; Durosinmi, M.A.; Ojo, I.A.O. Erythrocyte cholinesterase enzyme activity and hemoglobin values in cacao farmers of southwestern Nigeria as related to insecticide exposure. Arch. Environ. Occup. Health 2010, 65, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clausen, A.; Thomsen, J.; Atuhaire, A.; Jors, E. Effect of Integrated Pest Management Training on Ugandan Small-Scale Farmers. Environ. Health Insights 2017, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Settle, W.; Soumaré, M.; Sarr, M.; Garba, M.H.; Poisot, A.S. Reducing pesticide risks to farming communities: Cotton farmer field schools in Mali. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 369, 20120277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naidoo, S.; London, L.; Rother, H.-A.; Burdorf, A.; Naidoo, R.N.; Kromhout, H. Pesticide safety training and practices in women working in small-scale agriculture in South Africa. Occup. Environ. Med. 2010, 67, 823–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sibani, C.; Jessen, K.K.; Tekin, B.; Nabankema, V.; Jørs, E. Effects of Teaching Health Care Workers on Diagnosis and Treatment of Pesticide Poisonings in Uganda. Environ. Health Insights 2017, 11, 117863021772677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Investigated Pesticides | All Studies n (%) |
|---|---|
| Total studies | 469 (100) |
| Assessed pesticide not specified | 36 (7.7) |
| OCPs and CUPs together | 101 (21.5) |
| Only organochlorine pesticides (OCP) | 180 (38.4) |
| Only current-used pesticides (CUP) | 152 (32.4) |
| All OCP | 281 (59.9) |
| OCP (DDT) | 241 (85.8) |
| All CUP | 253 (53.9) |
| All CUP mixtures (I, F, and H together) | 68 (26.9) |
| All insecticides (I) | 233 (92.1) |
| I Organophosphates | 180 (77.3) |
| I Pyrethroids | 106 (45.5) |
| All herbicides (H) | 110 (43.5) |
| All fungicides (F) | 89 (35.2) |
| Studies including human subjects [study sites n (%)] | 180 (38.4) | |
| Overarching topics assessed along with studies with human subjects | Intervention studies (includes also health outcomes) | 4 (2.2) |
| Health outcomes assessed (can include exposure or KAP) | 123 (68.3) | |
| Only exposure (can include KAP) | 49 (27.2) | |
| Only KAP assessed | 4 (2.2) | |
| Type of study population | ||
| Occupational | 108 (60) | |
| Environmental | 40 (22.2) | |
| Occupational and environmental | 29 (16.1) | |
| Self-inflicted poisoning | 3 (1.7) | |
| Study design | ||
| Cross-sectional | 151 (83.9) | |
| Prospective longitudinal | 18 (10) | |
| Retrospective | 6 (3.3) | |
| Case report | 5 (2.8) | |
| Age groups | ||
| Adults | 164 (91.1) | |
| Adults and children | 7 (3.9) | |
| Children | 9 (5) | |
| Gender of the study population | ||
| Both gender | 111 (61.7) | |
| Male only | 39 (21.7) | |
| Female only | 20 (11.1) | |
| Gender not assessed | 10 (5.6) | |
| Number of participants (median (range)) | ||
| Cross-sectional studies | 183 (7–1496) | |
| Prospective longitudinal studies | 310 (15–1461) | |
| Retrospective studies | 797 (96–7427) | |
| All health outcomes assessments | All health outcomes | 127 (70.6) |
| Analysis method of outcomes | ||
| Regression model to assess exposure/outcome | 36 (28.3) | |
| Significant positive associations observed | 28 (77.8) | |
| Descriptive reporting of outcomes | 77 (60.6) | |
| Model-based risks | 14 (11) | |
| Self-reported signs and symptoms of acute poisoning | 38 (29.9) | |
| Doctor-diagnosed pesticide poisoning | 24 (18.9) | |
| Neurological assessment | 17 (13.4) | |
| Reproductive health | 14 (11) | |
| Respiratory health | 11 (8.7) | |
| Unspecific human health risks | 12 (9.4) | |
| Kidney and/or liver problems | 6 (4.7) | |
| Other: Diabetes, hypertension, cancer | 1 (0.8) | |
| Assessment method | ||
| Self-reported | 58 (45.7) | |
| Objective measures | 41 (32.3) | |
| Doctor-diagnosed | 16 (12.6) | |
| Model-based risks | 12 (9.4) | |
| Human exposure assessments | All human exposure assessments | 171 (95) |
| Objective exposure markers and self-reported exposure data | 45 (26.3) | |
| Only objective exposure markers | 15 (8.8) | |
| Exposure algorithms based on self-reported data | 4 (2.3) | |
| Only self-reported exposure data | 107 (62.6) | |
| All matrices objective human exposure markers were assessed | 60 (35.1) | |
| Blood | 36 (60) | |
| Urine | 14 (23.3) | |
| Wristbands | 5 (8.3) | |
| Breast milk | 4 (6.7) | |
| Other | 5 (8.3) | |
| KAP | All knowledge, attitude, and practice (KAP) | 149 (82.8) |
| Training on pesticide use | 40 (26.8) | |
| All environmental samples [study sites n (%)] | 317 (67.6) | |
| Integrative assessment | 1 matrix | 217 (68.4) |
| 2 matrices | 55 (17.4) | |
| 3 or more matrices | 45 (14.2) | |
| Individual matrices collected (overlaps between matrices) | Water | 93 (29.4) |
| Aquatic species | 79 (25) | |
| Sediment | 73 (23.1) | |
| Agricultural produce | 72 (22.8) | |
| Air | 57 (18) | |
| Soil | 39 (12.3) | |
| Other matrices | 34 (10.4) | |
| Dust | 2 (0.6) | |
| Envrionmental risk assessment (among collected samples) | All environmental risk assessments | 89 (28.2) |
| Levels of at least one pesticide above risk threshold | 76 (85.4) | |
| Water | 41 (44.1) | |
| Sediment | 33 (45.2) | |
| Aquatic species | 27 (34.2) | |
| Agricultural produce | 24 (33.3) | |
| Other matrices | 14 (42.4) | |
| Soil | 9 (23.1) | |
| Human health risk assessment | All human health risk assessments | 112 (35.4) |
| Levels of at least one pesticide above risk threshold | 53 (47.3) | |
| Human health outcomes investingated | ||
| Unspecific human health risks | 78 (69.6) | |
| Cancer | 14 (12.5) | |
| Pesticide poisoning | 13 (11.6) | |
| Reproductive health | 5 (4.5) | |
| Neurological assessment | 2 (1.8) | |
| Exposure pathways | ||
| Consumption | 107 (95.5) | |
| Ingestion | 2 (1.8) | |
| Inhalation | 3 (2.7) | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fuhrimann, S.; Wan, C.; Blouzard, E.; Veludo, A.; Holtman, Z.; Chetty-Mhlanga, S.; Dalvie, M.A.; Atuhaire, A.; Kromhout, H.; Röösli, M.; et al. Pesticide Research on Environmental and Human Exposure and Risks in Sub-Saharan Africa: A Systematic Literature Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 259. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19010259
Fuhrimann S, Wan C, Blouzard E, Veludo A, Holtman Z, Chetty-Mhlanga S, Dalvie MA, Atuhaire A, Kromhout H, Röösli M, et al. Pesticide Research on Environmental and Human Exposure and Risks in Sub-Saharan Africa: A Systematic Literature Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(1):259. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19010259
Chicago/Turabian StyleFuhrimann, Samuel, Chenjie Wan, Elodie Blouzard, Adriana Veludo, Zelda Holtman, Shala Chetty-Mhlanga, Mohamed Aqiel Dalvie, Aggrey Atuhaire, Hans Kromhout, Martin Röösli, and et al. 2022. "Pesticide Research on Environmental and Human Exposure and Risks in Sub-Saharan Africa: A Systematic Literature Review" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 1: 259. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19010259
APA StyleFuhrimann, S., Wan, C., Blouzard, E., Veludo, A., Holtman, Z., Chetty-Mhlanga, S., Dalvie, M. A., Atuhaire, A., Kromhout, H., Röösli, M., & Rother, H.-A. (2022). Pesticide Research on Environmental and Human Exposure and Risks in Sub-Saharan Africa: A Systematic Literature Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(1), 259. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19010259








