The Removal of Meat Exudate and Escherichia coli from Stainless Steel and Titanium Surfaces with Irregular and Regular Linear Topographies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Equipment and Material Suppliers
2.2. Production of Surfaces
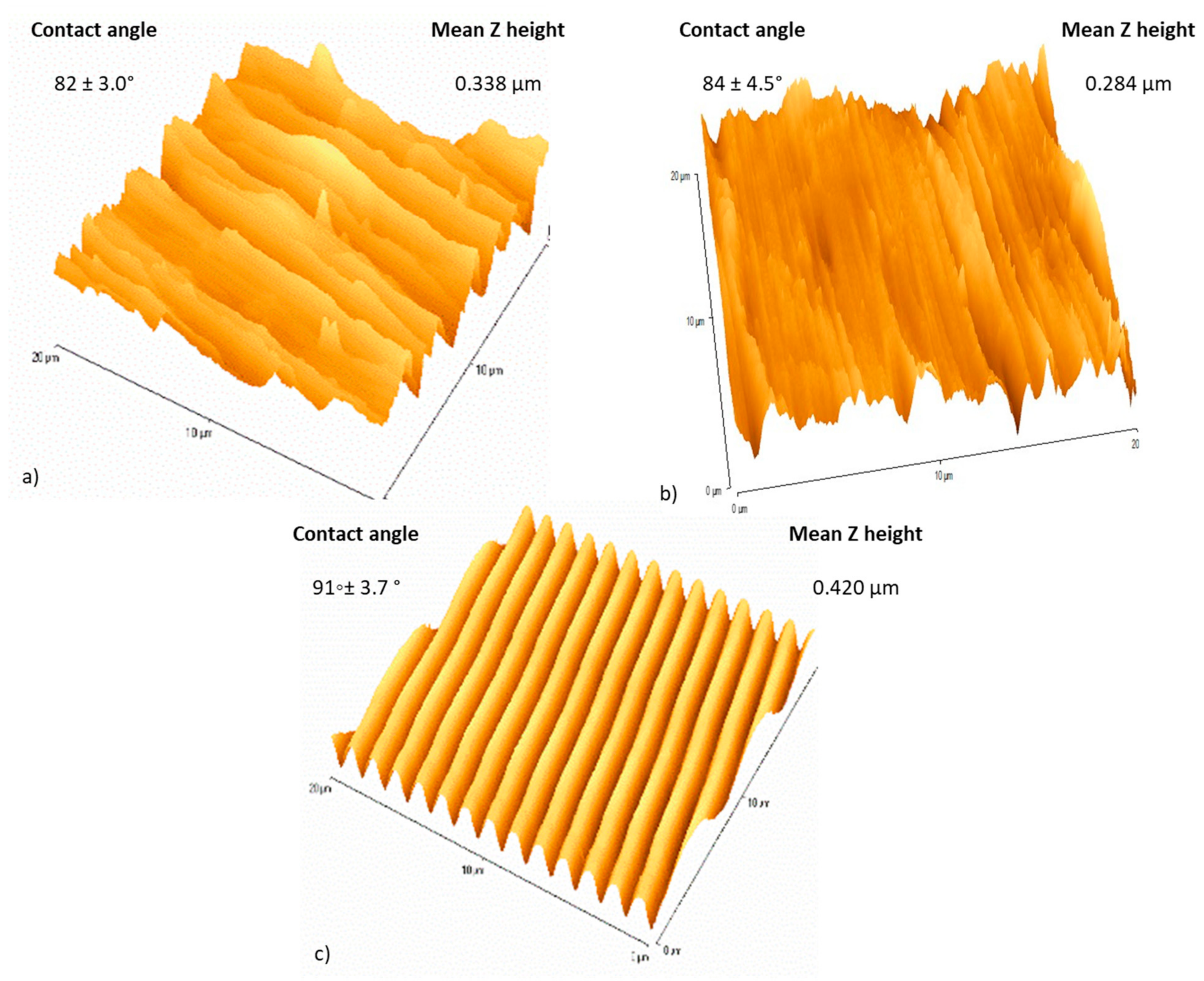
2.3. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
2.4. Sample Organisms
2.5. Bacterial Stock and Working Cultures
2.6. Meat Exudates
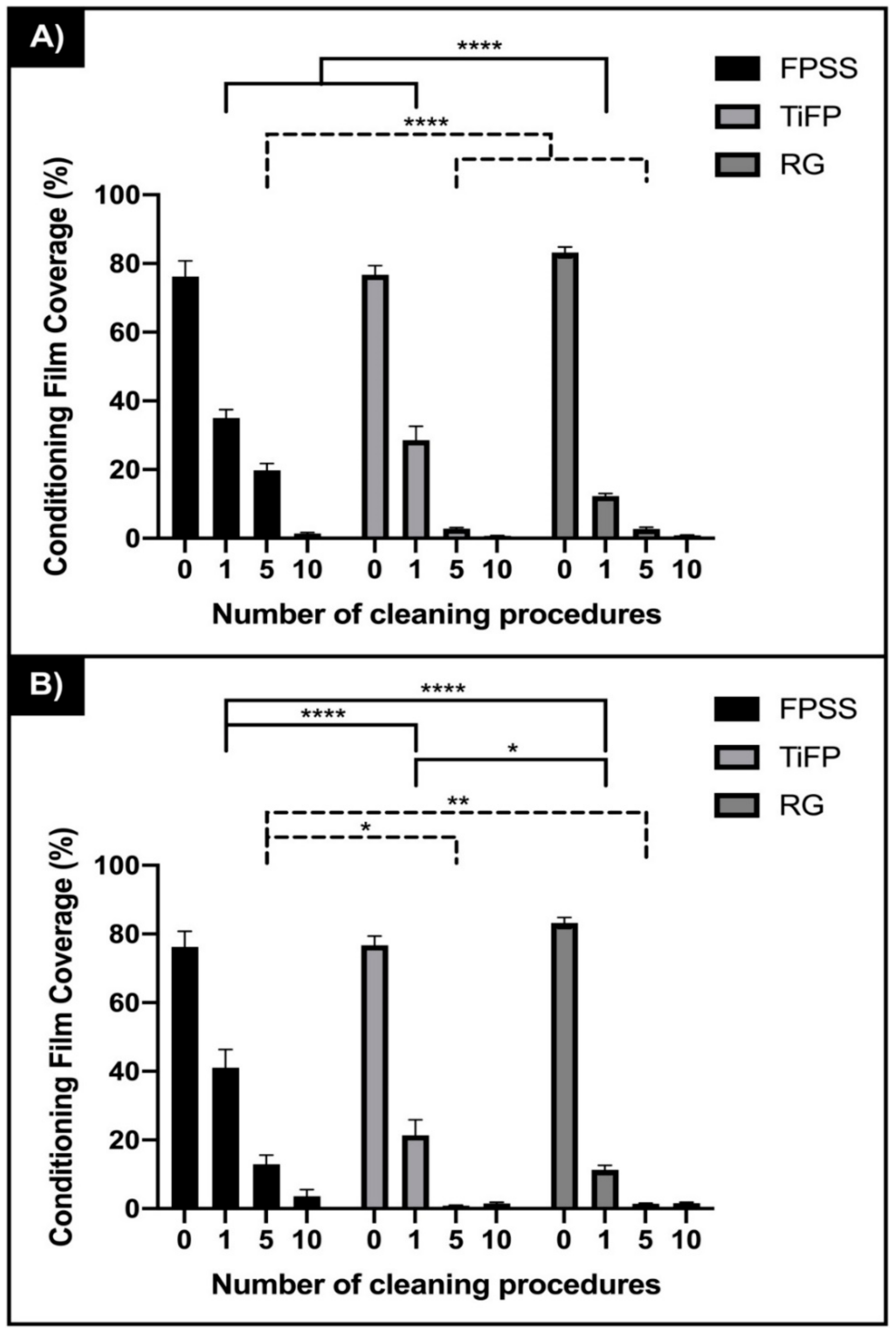
2.7. Cleaning Assays
2.8. Preparation of Stains
2.9. Differential Staining of Meat Exudate and E. coli
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results

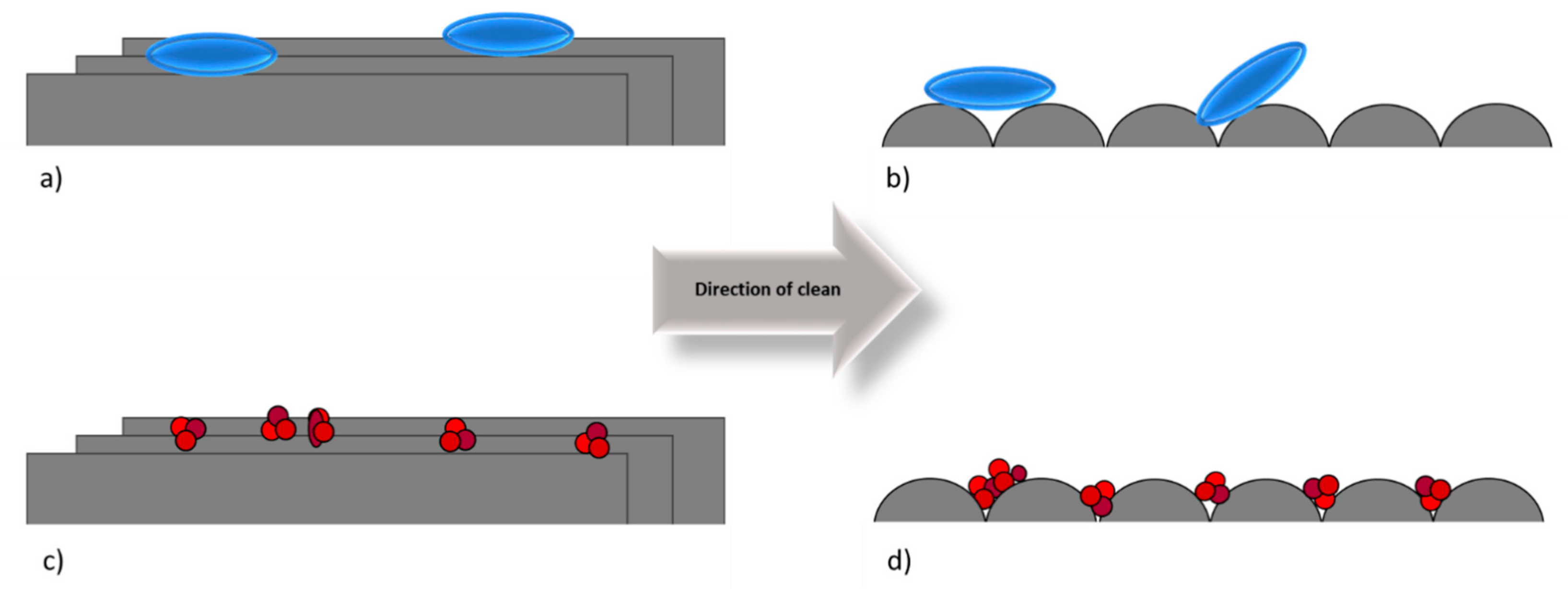
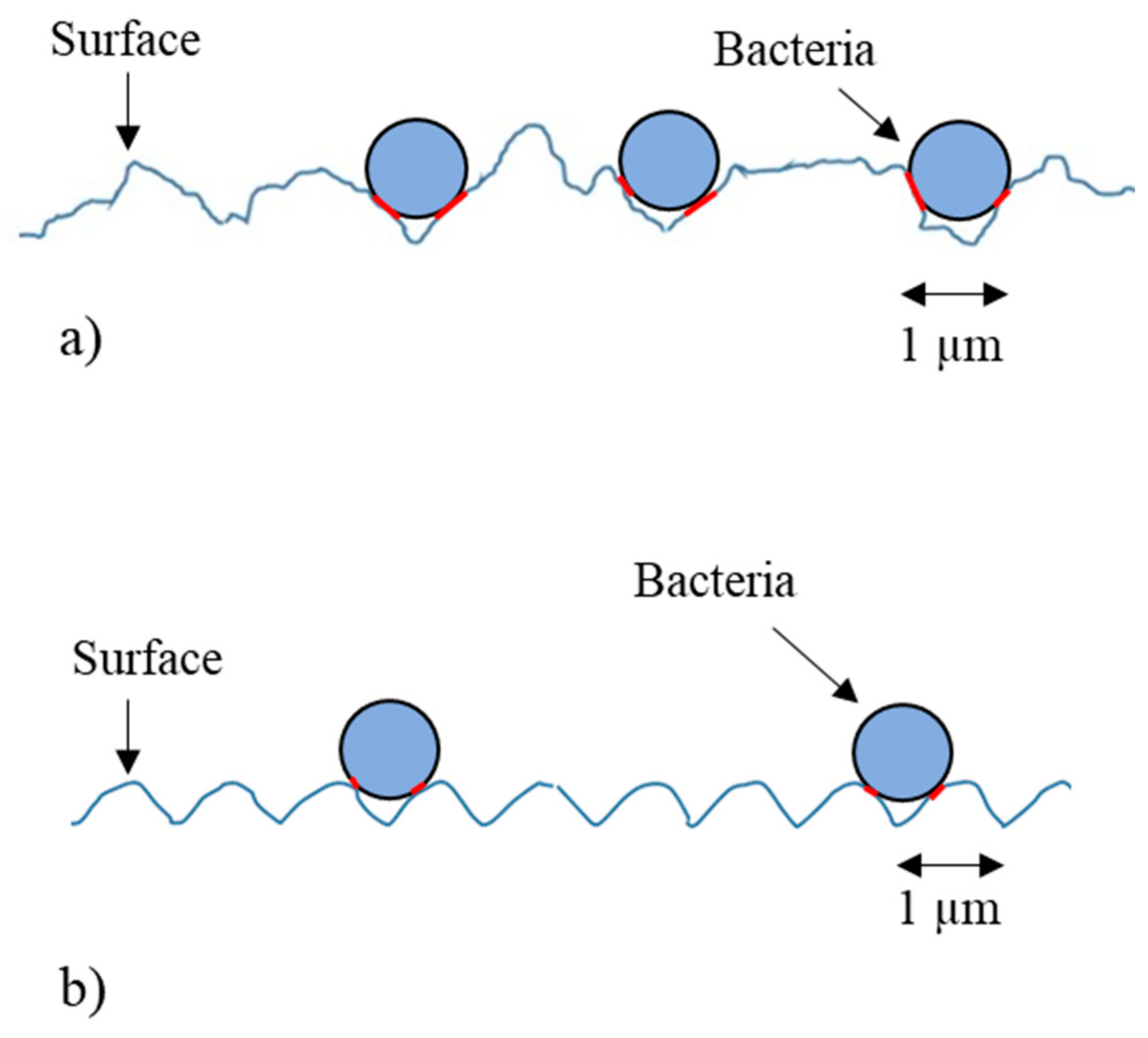
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lindsay, D.; von Holy, A. What food safety professionals should know about bacterial biofilms. Br. Food J. 2006, 108, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Hansen, M.F.; Røder, H.L.; Wang, N.; Burmølle, M.; He, G. Mixed-species biofilms in the food industry: Current knowledge and novel control strategies. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 2277–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitehead, K.A.; Benson, P.; Verran, J. Developing application and detection methods for Listeria monocytogenes and fish extract on open surfaces in order; to optimize cleaning protocols. Food Bioprod. Process. 2015, 93, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bintsis, T. Foodborne pathogens. AIMS Microbiol. 2017, 3, 529–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Houdt, R.; Michiels, C.W. Biofilm formation and the food industry, a focus on the bacterial outer surface. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 109, 1117–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chlebicz, A.; Śliżewska, K. Campylobacteriosis, salmonellosis, yersiniosis, and listeriosis as zoonotic foodborne diseases: A review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food Standard Agency. Foodborne Disease Strategy 2010–2015: An FSA Programme for the Reduction of Foodborne Disease in the UK; Food Standard Agency: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Yemmireddy, V.K.; Hung, Y.C. Using photocatalyst metal oxides as antimicrobial surface coatings to ensure food safety—Opportunities and challenges. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2017, 16, 617–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genigeorgis, C. Biofilms: Their Significance to Cleaning in the Meat Sector. In New Challenges in Meat Hygiene: Specific Problems in Cleaning and Disinfection; Bart, S.A., Bauer, F., Eds.; ECCEAMST: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 1995; pp. 29–49. [Google Scholar]
- CDC. Multistate Out Break of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli O157:H7 Infections Linked to Ground Beef; CDC: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Pordesimo, L.O.; Wilkerson, G.; Womac, R.; Cutter, N. Process Engineering Variables in the Spray Washing of Meat. J. Food Prot. 2002, 65, 222–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gristina, A.G. Biomaterial-centered infection: Microbial adhesion versus tissue integration. Science 1987, 237, 1588–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, R.; Van der Mei, H.C.; Busscher, H.J. Physico-chemistry of initial microbial adhesive interactions—its mechanisms and methods for study. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 1999, 23, 179–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, K.; Matsumoto, S. Bacterial adhesion: From mechanism to control. Biochem. Eng. J. 2010, 48, 424–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slate, A.J.; Wickens, D.; Wilson-Nieuwenhuis, J.; Dempsey-Hibbert, N.; West, G.; Kelly, P.; Verran, J.; Banks, C.E.; Whitehead, K.A. The effects of blood conditioning films on the antimicrobial and retention properties of zirconium-nitride silver surfaces. Colloids Surf. B 2019, 173, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorite, G.S.; Rodrigues, C.M.; De Souza, A.A.; Kranz, C.; Mizaikoff, B.; Cotta, M.A. The role of conditioning film formation and surface chemical changes on Xylella fastidiosa adhesion and biofilm evolution. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 359, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokare, C.; Chakraborty, S.; Khopade, A.; Mahadik, K.R. Biofilm: Importance and Applications. Indian J. Biotechnol. 2009, 8, 159–168. [Google Scholar]
- Moreira, J.; Gomes, L.; Whitehead, K.; Lynch, S.; Tetlow, L.; Mergulhão, F. Effect of surface conditioning with cellular extracts on Escherichia coli adhesion and initial biofilm formation. Food Bioprod. Process. 2017, 104, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyard-Nicodème, M.; Tresse, O.; Houard, E.; Jugiau, F.; Courtillon, C.; El Manaa, K.; Laisney, M.J.; Chemaly, M. Characterization of Campylobacter spp. transferred from naturally contaminated chicken legs to cooked chicken slices via a cutting board. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 164, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birk, T.; Ingmer, H.; Andersen, M.T.; Jørgensen, K.; Brøndsted, L. Chicken juice a food-based model system suitable to study survival of Campylobacter jejuni. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 38, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, H.L.; Reuter, M.; Salt, L.J.; Cross, K.L.; Betts, R.P.; van Vliet, A.H.M. Chicken juice enhances surface attachment and biofilm formation of Campylobacter Jejuni. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 7053–7060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, C.; Zahn, S.; Rost, F.; Zahn, P.; Jaros, D.; Rohm, H. Physical Methods for Cleaning and Disinfection of Surfaces. Food Eng. Rev. 2011, 3, 171–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, H.; Taylor, J.H.; Hall, K.E.; Holah, J.T. Effectiveness of cleaning techniques used in the food industry in terms of the removal of bacterial biofilms. J. Appl. Microbiol. 1999, 87, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, H.; He, A.; Tran, F. Microbial efficacy and impact on the population of Escherichia coli of a routine sanitation process for the fabrication facility of a beef packing. Plant Food Control 2017, 71, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Badoni, M.; Youssef, M.K.; Gill, C.O. Enhanced control of microbiological contamination of product at a large beef packing plant. J. Food Prot. 2012, 75, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youssef, M.K.; Badoni, M.; Yang, X.; Gill, C.O. Sources of Escherichia coli deposited on beef during breaking of carcasses carrying few E. coli at two packing plants. Food Control 2013, 31, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genigeorgis, C.; Rosales, J.; Verder-Elepano, M. Affect of selected sanitizer cleaners and soaps on Listeria spp., S. typhimurium, E. coli, and P. aeruginosa in the presence or absence of organic matter. In Proceedings of the International Conference Listeria and Food Safety—ASEPT, Laval, France, 13–14 June 1991; p. 186. [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead, K.A.; Verran, J. The effect of surface topography on the retention of microorganisms. Food Bioprod. Process. 2006, 84, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jullien, C.; Bénézech, T.; Carpentier, B.; Lebret, V.; Faille, C. Identification of surface characteristics relevant to the hygienic status of stainless steel for the food industry. J. Food Eng. 2003, 56, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mettler, E.; Carpentier, B. Hygienic quality of floors in relation to surface texture. Food Bioprod. Process. 1999, 77, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, K.A.; Verran, J. The effect of application method on the retention of Pseudomonas aeruginosa on stainless steel, and titanium coated stainless steel of differing topographies. Inter. Biodeter. Biodeg. 2007, 60, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, K.; Benson, P.; Smith, L.; Verran, J. The use of physicochemical methods to detect organic food soils on stainless steel surfaces. Biofouling 2009, 25, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jullien, C.; Benezech, T.; Le Gentil, C.; Boulange-Petermann, L.; Dubois, P.; Tissier, J.P.; Traisnel, M.; Faille, C. Physico-chemical and hygienic property modifications of stainless steel surfaces induced by conditioning with food and detergent. Biofouling 2008, 24, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuson, H.H.; Weibel, D.B. Bacteria-surface interactions. Soft Matter. 2013, 9, 4368–4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Koo, H.; Ren, D. Effects of material properties on bacterial adhesion and biofilm formation. J. Dent. Res. 2015, 94, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zhang, B.; Liu, Y.; Suo, X.; Li, H. Influence of surface topography on bacterial adhesion: A review. Biointerphases 2018, 13, 060801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, K.A.; Colligon, J.; Verran, J. Retention of microbial cells in substratum surface features of micrometer and sub-micrometer dimensions. Colloids Surf. B 2005, 41, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, L.C.; Fang, J.; Borca-Tasciuc, D.A.; Worobo, R.W.; Moraru, C.I. Effect of micro- and nanoscale topography on the adhesion of bacterial cells to solid surfaces. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 2703–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verran, J. Testing surface cleanability in food processing. In Handbook of Hygiene Control in the Food Industry; Lelieveld, A.H.L.M., Holah Mostert, J.T., Eds.; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 556–571. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Feng, G.; Moraru, C.I. Micro and Nanotopography Sensitive Bacterial Attachment Mechanisms: A Review. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Pascal, M.A. Effect of micro-pattern topography on the attachment and survival of foodborne microorganisms on food contact surfaces. Food Saf. 2018, 38, e12379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamerud, K.L.; Hobbie, K.A.; Anderson, K.A. Stainless steel leaches nickel and chromium into foods during cooking. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 9495–9501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Winslow, C.J.; Logan, B.E. Spectral force analysis using atomic force microscopy reveals the importance of surface heterogeneity in bacterial; and colloid adhesion to engineered surfaces. Colloids Surf. B 2008, 62, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, C.F.; Cogo-Müller, K.; Franco, G.C.; Silva-Concílio, L.R.; Campos, M.S.; de Mello Rode, S.; Neves, A.C.C. Initial oral biofilm formation on titan;ium implants with different surface treatments: An in vivo study. Arch. Oral. Biol. 2016, 69, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhidime, I.D.; Saubade, F.; Benson, P.S.; Butler, J.A.; Olivier, S.; Kelly, P.; Verran, J.; Whitehead, K.A. The antimicrobial effect of metal substrates on food pathogens. Food Bioprod. Process. 2019, 113, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lausmaa, J. Surface spectroscopic characterization of titanium implant materials. J. Electron. Spectros. Relat. Phenom. 1996, 81, 343–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verran, J.; Packer, A.; Kelly, P.; Whitehead, K.A. The retention of bacteria on hygienic surfaces presenting scratches of microbial dimensions. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 50, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitehead, K.A.; Olivier, S.; Benson, P.S.; Arneborg, N.; Verran, J.; Kelly, P. The effect of surface properties of polycrystalline, single phase metal coatin;gs on bacterial retention. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 197, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caballero, L.; Whitehead, K.; Allen, N.; Verran, J. Inactivation of Escherichia coli on immobilized TiO2 using fluorescent light. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2009, 202, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, K.; Benson, P.; Verran, J. The detection of food soils on stainless steel using energy dispersive X-ray and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Biofouling 2011, 27, 907–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, K.A.; Benson, P.; Verran, J. Differential fluorescent staining of Listeria monocytogenes and a whey food soil for quantitative analysis of surfac;e hygiene. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 135, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, R.D.; Verran, J.; Jones, M.; Bhakoo, M. Use of the atomic force microscope to determine the effect of substratum surface topography on bacterial adhesion. Langmuir 2002, 18, 2343–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slate, A.J.; Wickens, D.J.; El Mohtadi, M.; Dempsey-Hibbert, N.; West, G.; Banks, C.E.; Whitehead, K.A. Antimicrobial activity of Ti-ZrN/Ag coatings for use in biomaterial applications. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGaffey, M.; zur Linden, A.; Bachynski, N.; Oblak, M.; James, F.; Weese, J.S. Manual polishing of 3D printed metals produced by laser powder bed fusion reduces biofilm formation. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, C.; Lukowicz, R.; Merchant, S.; Valquier-Flynn, H.; Caballero, J.; Sandoval, J.; Okuom, M.; Huber, C.; Brooks, T.D.; Wilson, E.; et al. Quantitative and qualitative assessment methods for biofilm growth: A mini-review. Res. Rev. J. Eng. Technol. 2017, 6, 30214915. [Google Scholar]
- Jeyachandran, Y.; Venkatachalam, S.; Karunagaran, B.; Narayandass, S.K.; Mangalaraj, D.; Bao, C.; Zhang, C. Bacterial adhesion studies on titanium, titanium nitride and modified hydroxyapatite thin films. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2007, 27, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spriano, S.; Chandra, V.S.; Cochis, A.; Uberti, F.; Rimondini, L.; Bertone, E.; Vitale, A.; Scolaro, C.; Ferrari, M.; Cirisano, F. How do wettability, zeta potential and hydroxylation degree affect the biological response of biomaterials? Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 74, 542–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassmann, T.; Kreis, S.; Behr, M.; Buergers, R. The influence of surface texture and wettability on initial bacterial adhesion on titanium and zirconium oxide dental implants. Int. J. Implant. Dent. 2017, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scwach, T.S.; Zottola, E.A. Scanning electron microscopic study on some effects of sodium hypochloride on attachment of bacteria to stainless steel. J. Food. Prot. 1984, 47, 656–759. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Feng, J.; Ma, L.; de la Fuente Núñez, C.; Gölz, G.; Lu, X. Effects of meat juice on biofilm formation of Campylobacter and Salmonella. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 253, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakanishi, K.; Sakiyama, T.; Imamura, K. On the adsorption of proteins on solid surfaces, a common but very complicated phenomenon. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2001, 91, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rechendorff, K.; Hovgaard, M.B.; Foss, M.; Zhdanov, V.; Besenbacher, F. Enhancement of protein adsorption induced by surface roughness. Langmuir 2006, 22, 10885–10888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thyparambil, A.A.; Wei, Y.; Latour, R.A. Experimental characterization of adsorbed protein orientation, conformation, and bioactivity. Biointerphases 2015, 10, 019002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saubade, F.J.; Hughes, S.; Wickens, D.J.; Wilson-Nieuwenhuis, J.; Dempsey-Hibbert, N.; Crowther, G.S.; West, G.; Kelly, P.; Banks, C.E.; Whitehead, K.A. Effectiveness of titanium nitride silver coatings against Staphylococcus spp. in the presence of BSA and whole blood conditioning agents. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2019, 141, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, J.S.; Koohmaraie, M. Cell surface charge characteristics and their relationship to bacterial attachment to meat surfaces. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1989, 55, 832–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Weyer, A.; Devleeschouwer, M.J.; Dony, J. Bactericidal activity of disinfectants on Listeria. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1993, 74, 480–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spurlock, A.T.; Zottola, E.A. Growth and attachment of Listeria monocytogenes to cast iron. J. Food Prot. 1991, 54, 925–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jessen, B.; Lammert, L. Biofilm and disinfection in meat processing plants. Int. Biodeter. Biodeg. 2003, 51, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, G.U.; Kitajima, M.; Sherchan, S.P.; Sexton, J.D.; Sifuentes, L.Y.; Gerba, C.P.; Reynolds, K.A. Impact of disinfectant wipes on the risk of Campylobacter jejuni infection during raw chicken preparation in domestic kitchens. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 119, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloomfield, S.F.; Carling, P.C.; Exner, M. A unified framework for developing effective hygiene procedures for hands, environmental surfaces and laundry in healthcare, domestic, food handling and other settings. GMS Hyg. Infect. Control 2017, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Evans, A.; Slate, A.J.; Akhidime, I.D.; Verran, J.; Kelly, P.J.; Whitehead, K.A. The Removal of Meat Exudate and Escherichia coli from Stainless Steel and Titanium Surfaces with Irregular and Regular Linear Topographies. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3198. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18063198
Evans A, Slate AJ, Akhidime ID, Verran J, Kelly PJ, Whitehead KA. The Removal of Meat Exudate and Escherichia coli from Stainless Steel and Titanium Surfaces with Irregular and Regular Linear Topographies. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(6):3198. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18063198
Chicago/Turabian StyleEvans, Adele, Anthony J. Slate, I. Devine Akhidime, Joanna Verran, Peter J. Kelly, and Kathryn A. Whitehead. 2021. "The Removal of Meat Exudate and Escherichia coli from Stainless Steel and Titanium Surfaces with Irregular and Regular Linear Topographies" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 6: 3198. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18063198
APA StyleEvans, A., Slate, A. J., Akhidime, I. D., Verran, J., Kelly, P. J., & Whitehead, K. A. (2021). The Removal of Meat Exudate and Escherichia coli from Stainless Steel and Titanium Surfaces with Irregular and Regular Linear Topographies. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(6), 3198. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18063198





