Prevalence and Factors Associated with Mental and Emotional Health Outcomes among Africans during the COVID-19 Lockdown Period—A Web-based Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Setting and Study Participants
2.2. Survey Design
2.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.4. Consent and Ethical Consideration
2.5. Data Analysis
2.5.1. Outcome Variables
2.5.2. Confounding Variables
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sample Characteristics
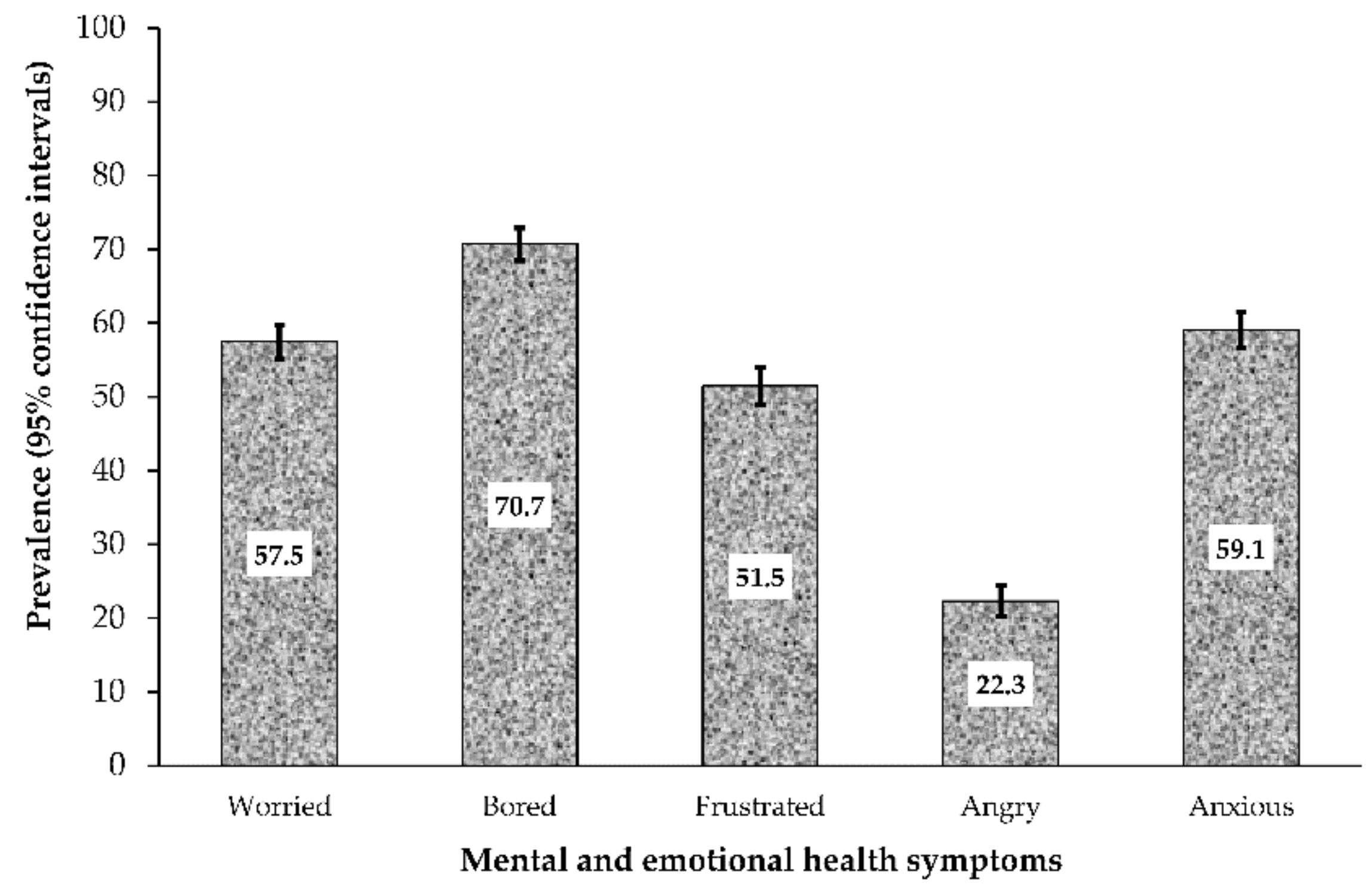
3.2. Prevalence of Mental Health/Emotional Symptoms
3.3. Univariate Analysis of Factors Associated with Mental Health Symptoms
3.4. Multivariate Analysis of Factors Associated with Mental Health/Emotional Symptoms
4. Discussion
5. Limitations and Strengths
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Questionnaire for the effect of COVID-19 on family welfare.
- Country of origin
- Country of residence
- Province/State/County
- Gender
- MALE
- FEMALE
- OTHERS
- Age (Years)
- Marital Status
- SINGLE
- MARRIED
- SEPARATED/DIVORCED
- WIDOW/WIDOWER
- Religion
- MUSLIM
- CHRISTIAN
- AFRICAN TRADITIONALIST
- OTHERS
- Highest level of education
- PRIMARY SCHOOL
- HIGH/SECONDARY SCHOOL
- POLYTHECNIC/DIPLOMA
- UNIVERSITY DEGREE (Bachelors/Professional)
- POSTGRADUATE DEGREE (Masters/PhD)
- Employment Status
- SELF EMPLOYED
- EMPLOYED
- UNEMPLOYED
- STUDENT/NON-STUDENT
- Occupation
- Do you live alone?
- YES
- NO
- If you live with family/friends, how many of you live together?
- PERCEPTION OF RISK OF INFECTION
- Risk of becoming infected.
- VERY HIGH
- HIGH
- LOW
- VERY LOW
- UNLIKELY
- Risk of becoming severely infected
- VERY HIGH
- HIGH
- LOW
- VERY LOW
- UNLIKELY
- Risk of dying from the infection
- VERY HIGH
- HIGH
- LOW
- VERY LOW
- UNLIKELY
- How do you feel about the COVID-19 lockdown measures? (Tick the option that best describes how you feel. You can choose more than one option)
- WORRIED (Yes/No)
- BORED (Yes/No)
- FRUSTRATED (Yes/No)
- ANGRY (Yes/No)
- ANXIOUS (Yes/No)
- How likely do you think Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) will continue in your country?
- VERY LIKELY
- LIKELY
- NEITHER LIKELY, NOR UNLIKELY
- UNLIKELY
- VERY UNLIKELY
- If Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) continues in your country, how concerned would you be that you or your family would be directly affected?
- EXTREMELY CONCERNED
- CONCERNED
- NEITHER CONCERNED, NOR UNCONCERNED
- UNCONCERNED
- EXTREMELY UNCONCERNED
- PUBLIC ATTITUDE TOWARDS COMPLIANCE WITH COVID-19 RECOMMENDED PRACTICES
- In recent days, have you gone to any crowded place including religious events
- ALWAYS
- SOMETIMES
- RARELY
- NOT AT ALL
- NOT SURE
- In recent days, have you worn a mask when leaving home?
- ALWAYS
- SOMETIMES
- RARELY
- NOT AT ALL
- NOT SURE
- In recent days, have you been washing your hands with soap and running water for at least 20 seconds each time?
- ALWAYS
- SOMETIMES
- RARELY
- NOT AT ALL
- NOT SURE
- Are you currently or have you been in (domestic/home) quarantine because of COVID-19?
- YES
- NO
- Are you currently or have you been in self-isolation because of COVID-19?
- YES
- NO
- Have you travelled outside your home in recent days using the public transport
- YES
- NO
References
- Chen, S.; Cheng, Z.; Wu, J. Risk factors for adolescents’ mental health during the COVID-19 pandemic: A comparison between Wuhan and other urban areas in China. Glob. Health 2020, 16, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buheji, M.; da Costa Cunha, K.; Beka, G.; Mavric, B.; de Souza, Y.; da Costa Silva, S.S.; Hanafi, M.; Yein, T.C. The extent of covid-19 pandemic socio-economic impact on global poverty. a global integrative multidisciplinary review. Am. J. Econ. 2020, 10, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bherwani, H.; Nair, M.; Musugu, K.; Gautam, S.; Gupta, A.; Kapley, A.; Kumar, R. Valuation of air pollution externalities: Comparative assessment of economic damage and emission reduction under COVID-19 lockdown. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2020, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozamiz-Etxebarria, N.; Idoiaga Mondragon, N.; Dosil Santamaría, M.; Picaza Gorrotxategi, M. Psychological symptoms during the two stages of lockdown in response to the COVID-19 outbreak: An investigation in a sample of citizens in Northern Spain. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Miao, M.; Lim, J.; Li, M.; Nie, S.; Zhang, X. Is lockdown bad for social anxiety in COVID-19 Regions?: A national study in the SOR perspective. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semo, B.-w.; Frissa, S.M. The mental health impact of the COVID-19 pandemic: Implications for sub-Saharan Africa. Psychol. Res. Behav. Manag. 2020, 13, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. WHO survey shows COVID-19 disrupting mental health services in most countries, WHO survey. In World Mental Health Day on 10 October to Highlight Urgent Need to Increase Investment in Chronically Underfunded Sector; Brunier, A., Drysdale, C., Eds.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020; Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/05-10-2020-covid-19-disrupting-mental-health-services-in-most-countries-who-survey#:~:text=The%20survey%20of%20130%20countries,urgent%20need%20for%20increased%20funding (accessed on 10 November 2020).
- Agberotimi, S.F.; Akinsola, O.S.; Oguntayo, R.; Olaseni, A.O. Interactions between socioeconomic status and mental health outcomes in the nigerian context amid COVID-19 pandemic: A comparative study. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 559819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Zhang, F.; Wei, C.; Jia, Y.; Shang, Z.; Sun, L.; Wu, L.; Sun, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y. Prevalence and predictors of PTSS during COVID-19 outbreak in China hardest-hit areas: Gender differences matter. Psychiatry Res. 2020, 287, 112921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Mental Health and Psychosocial Considerations during the COVID-19 Outbreak, 18 March 2020; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Zhao, N. Generalized anxiety disorder, depressive symptoms and sleep quality during COVID-19 outbreak in China: A web-based cross-sectional survey. Psychiatry Res. 2020, 288, 112954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, T.-J. Telehealth & Mental Healthcare of Older Adults. Health 2020, 26, 571–573. [Google Scholar]
- Mahase, E. Covid-19: EU states report 60% rise in emergency calls about domestic violence. BMJ 2020, 11, 369. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. New WHO Estimates: Up to 190000 People Could Die of COVID-19 in Africa If Not Controlled; Oka, S., Ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.; Roy, M.D.; Sinha, C.P.T.M.K.; Parveen, C.P.T.M.S.; Sharma, C.P.T.G.; Joshi, C.P.T.G. Impact of COVID-19 and lockdown on mental health of children and adolescents: A narrative review with recommendations. Psychiatry Res. 2020, 293, 113429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, W.E.; Dumas, T.M.; Forbes, L.M. Physically isolated but socially connected: Psychological adjustment and stress among adolescents during the initial COVID-19 crisis. Can. J. Behav. Sci./Rev. Can. Sci. Comport. 2020, 52, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yang, L.; Zhang, C.; Xiang, Y.-T.; Liu, Z.; Hu, S.; Zhang, B. Online mental health services in China during the COVID-19 outbreak. Lancet Psychiatry 2020, 7, e17–e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, I. Covid-19 and Tourism in Africa: An Unprecedented Shock; Italian Institute for International Political Studies: Milan, Italy, 2020; Available online: https://www.ispionline.it/en/pubblicazione/covid-19-and-tourism-africa-unprecedented-shock-27640 (accessed on 2 October 2020).
- Ovenseri-Ogbomo, G.; Ishaya, T.; Osuagwu, U.L.; Abu, E.K.; Nwaeze, O.; Oloruntoba, R.; Ekpenyong, B.; Mashige, K.P.; Chikasirimobi, T.; Langsi, R.; et al. Factors associated with the myth about 5G network during COVID-19 pandemic in sub-Saharan Africa. J. Glob. Health Rep. 2020, 4, e2020094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayston, R.; Frissa, S.; Tekola, B.; Hanlon, C.; Prince, M.; Fekadu, A. Explanatory models of depression in sub-Saharan Africa: Synthesis of qualitative evidence. Soc. Sci. Med. 2020, 246, 112760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abir, T.; Kalimullah, N.A.; Osuagwu, U.L.; Yazdani, D.M.N.-A.; Al Mamun, A.; Husain, T.; Basak, P.; Permarupan, P.Y.; Agho, K. Factors Associated with Perception of Risk and Knowledge of Contracting the Novel COVID-19 among Adults in Bangladesh: Analysis of Online Surveys. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duthé, G.; Rossier, C.; Bonnet, D.; Soura, A.B.; Corker, J. Mental health and urban living in sub-Saharan Africa: Major depressive episodes among the urban poor in Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso. Popul. Health Metr. 2016, 14, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Yu, X.; Yan, J.; Yu, Y.; Kou, C.; Xu, X.; Lu, J. Prevalence of mental disorders in China: A cross-sectional epidemiological study. Lancet Psychiatry 2019, 6, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Zheng, P.; Jia, Y.; Chen, H.; Mao, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, Y.; Fu, H.; Dai, J. Mental health problems and social media exposure during COVID-19 outbreak. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchal, N.; Kamal, R.; Orgera, K.; Cox, C.; Garfield, R.; Hamel, L.; Chidambaram, P. The Implications of COVID-19 for Mental Health and Substance Use. Available online: https://www.kff.org/coronavirus-covid-19/issue-brief/the-implications-of-covid-19-for-mental-health-and-substance-use/view/footnotes/ (accessed on 21 August 2020).
- Pandey, D.; Bansal, S.; Goyal, S.; Garg, A.; Sethi, N.; Pothiyill, D.I.; Sreelakshmi, E.S.; Sayyad, M.G.; Sethi, R. Psychological impact of mass quarantine on population during pandemics—The COVID-19 Lock-Down (COLD) study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorillo, A.; Sampogna, G.; Giallonardo, V.; Del Vecchio, V.; Luciano, M.; Albert, U.; Carmassi, C.; Carrà, G.; Cirulli, F.; Dell’Osso, B. Effects of the lockdown on the mental health of the general population during the COVID-19 pandemic in Italy: Results from the COMET collaborative network. Eur. Psychiatry 2020, 63, e87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, E.A.; O’Connor, R.C.; Perry, V.H.; Tracey, I.; Wessely, S.; Arseneault, L.; Ballard, C.; Christensen, H.; Silver, R.C.; Everall, I. Multidisciplinary research priorities for the COVID-19 pandemic: A call for action for mental health science. Lancet Psychiatry 2020, 7, 547–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfefferbaum, B.; North, C.S. Mental Health and the Covid-19 Pandemic. New Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 510–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafini, G.; Parmigiani, B.; Amerio, A.; Aguglia, A.; Sher, L.; Amore, M. The psychological impact of COVID-19 on the mental health in the general population. QJM Int. J. Med. 2020, 113, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Pan, R.; Wan, X.; Tan, Y.; Xu, L.; Ho, C.S.; Ho, R.C. Immediate psychological responses and associated factors during the initial stage of the 2019 coronavirus disease (COVID-19) epidemic among the general population in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braunack-Mayer, A.; Tooher, R.; Collins, J.E.; Street, J.M.; Marshall, H. Understanding the school community’s response to school closures during the H1N1 2009 influenza pandemic. BMC Public Health 2013, 13, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Xu, X.; Xiao, S.; Wu, X.; Shu, Y. Household transmission of COVID-19-a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Infect. 2020, 81, 979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed Said, J.; Jibril, A.; Isah, R.; Beida, O. Pattern of Presentation and Utilization of Services for Mental and Neurological Disorders in Northeastern Nigeria: A Ten-Year Study. Psychiatry J. 2015, 2015, 328432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Odejide, O.; Morakinyo, J. Mental health and primary care in Nigeria. World Psychiatry 2003, 2, 164. [Google Scholar]
- Hjort, J.; Poulsen, J. The arrival of fast internet and employment in Africa. Am. Econ. Rev. 2019, 109, 1032–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effenberger, M.; Kronbichler, A.; Shin, J.I.; Mayer, G.; Tilg, H.; Perco, P. Association of the COVID-19 pandemic with Internet Search Volumes: A Google TrendsTM Analysis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 95, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadler, J.T.; Weston, R.; Voyles, E.C. Stuck in the Middle: The Use and Interpretation of Mid-Points in Items on Questionnaires. J. Gen. Psychol. 2015, 142, 71–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawel, A.; Shou, Y.; Smithson, M.; Cherbuin, N.; Banfield, M.; Calear, A.L.; Farrer, L.M.; Gray, D.; Gulliver, A.; Housen, T. The effect of COVID-19 on mental health and wellbeing in a representative sample of Australian adults. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variables | Number | Percentages |
|---|---|---|
| Sociodemographic characteristics | ||
| Place of Origin (n = 1969) | ||
| West Africa | 1108 | 56.27 |
| East Africa | 209 | 10.61 |
| Central Africa | 251 | 12.75 |
| Southern Africa | 401 | 20.37 |
| Place of residence | ||
| Africa | 1855 | 92.52 |
| Diaspora | 150 | 7.48 |
| Age in years (n = 1988) | ||
| 18–28 years | 775 | 38.98 |
| 29–38 | 530 | 26.66 |
| 39–48 | 441 | 22.18 |
| 49+ years | 242 | 12.17 |
| Sex (n = 1991) | ||
| Men | 1099 | 55.20 |
| Women | 892 | 44.80 |
| Marital Status (n = 1995) | ||
| Married | 879 | 44.06 |
| Not married † | 1116 | 55.94 |
| Highest level of Education (n = 1997) | ||
| Postgraduate Degree (Masters/PhD) | 642 | 32.15 |
| Bachelor’s degree | 1090 | 54.58 |
| Secondary/Primary | 265 | 13.27 |
| Employment status (n = 2000) | ||
| Employed | 1321 | 66.05 |
| Unemployed | 679 | 33.95 |
| Occupation type (n = 1904) | ||
| Non-healthcare | 1471 | 77.26 |
| Healthcare | 433 | 22.74 |
| Religion (n = 1995) | 1995 | |
| Christianity | 1763 | 88.37 |
| Islam/others † | 232 | 11.63 |
| Household factors | ||
| Do you live alone during COVID-19 (n = 1996) | ||
| No | 1624 | 81.36 |
| Yes | 372 | 18.64 |
| Number living together (n = 1775) | ||
| 1–3 people | 506 | 28.83 |
| 4–6 people | 908 | 51.74 |
| 6+ people | 341 | 19.43 |
| Public attitudes toward compliance with COVID-19 | ||
| Practiced self-isolation (n = 1801) | ||
| No | 1237 | 68.68 |
| Yes | 564 | 31.32 |
| Home quarantined due to COVID-19 (n = 1798) | ||
| No | 1091 | 60.68 |
| Yes | 707 | 39.32 |
| Gone to a crowded event (n = 1797) | ||
| No | 1550 | 86.25 |
| Yes | 247 | 13.75 |
| Perception of risk | ||
| Risk of becoming infected (n = 1821) | ||
| High | 674 | 37.01 |
| Not high | 1147 | 62.99 |
| Risk of becoming severely infected (n = 1823) | ||
| High | 471 | 25.84 |
| Not high | 1352 | 74.16 |
| Risk of dying from infection (n = 1818) | ||
| High | 352 | 19.36 |
| Not high | 1466 | 80.64 |
| Possibility of you/family member being affected (n = 1794) | ||
| Concerned | 1692 | 94.31 |
| Not Concerned | 102 | 5.69 |
| Likelihood of COVID-19 continuing (n = 1827) | ||
| Likely | 1167 | 63.88 |
| Not Likely | 660 | 36.12 |
| Variables | Worried | Bored | Frustrated | Angry | Anxious | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | OR | 95% CI | OR | 95% CI | OR | 95% CI | OR | 95% CI | |
| Demography | ||||||||||
| Place of Origin | ||||||||||
| West Africa | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | - | ||||
| East Africa | 1.34 | [0.97, 1.85] | 0.61 | [0.43, 0.86] | 1.56 | [1.12, 2.18] | 1.27 | [0.85, 1.89] | 1.09 | [0.78, 1.52] |
| Central Africa | 1.19 | [0.89, 1.60] | 1.56 | [1.06, 2.30] | 1.64 | [1.20, 2.24] | 2.38 | [1.69, 3.35] | 1.98 | [1.41, 2.79] |
| Southern Africa | 1.21 | [0.95, 1.54] | 0.60 | [0.4, 0.79] | 1.48 | [1.14, 1.92] | 1.05 | [0.76, 1.46 | 0.99 | [0.76, 1.28] |
| Place of residence | ||||||||||
| Africa | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |||||
| Diaspora | 0.76 | [0.53, 1.08] | 1.23 | [0.80, 1.89] | 0.82 | [0.56, 1.19] | 0.90 | [0.56, 1.44] | 0.84 | [0.57, 1.24] |
| Age in years | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 18–28 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |||||
| 29–38 | 1.17 | [0.91, 1.51] | 1.12 | [0.83, 1.50] | 0.86 | [0.66, 1.13] | 0.85 | [0.61, 1.18] | 0.92 | [0.70, 1.21] |
| 39–48 | 1.09 | [0.81, 1.48] | 1.03 | [0.72, 1.48] | 1.10 | [0.80, 1.53] | 0.91 | [0.61, 1.35] | 0.75 | [0.54, 1.04] |
| 49+ | 1.04 | [0.83, 1.32] | 0.13 | [0.71, 1.21] | 0.84 | [0.66, 1.08] | 0.95 | [0.71, 1.29] | 0.96 | [0.75, 1.24] |
| Sex | ||||||||||
| Men | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - |
| Women | 0.98 | [0.82, 1.19] | 1.28 | [1.02, 1.59] | 0.98 | [0.80, 1.20] | 0.89 | [0.70, 1.14] | 1.24 | [1.02, 1.53] |
| Marital Status | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Married | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - |
| Not married† | 1.06 | [0.88, 1.28] | 1.12 | [0.90, 1.40] | 1.25 | [1.02, 1.52] | 1.30 | [1.02, 1.66] | 1.16 | [0.95, 1.42] |
| Highest level of Education | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Postgraduate Degree (Masters /PhD) | 1.00 | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | |
| Bachelor’s degree | 1.24 | [1.01, 1.52] | 0.72 | [0.56, 0.91] | 1.12 | [0.90, 1.40] | 0.94 | [0.72, 1.23] | 1.03 | [0.82, 1.29] |
| Secondary/Primary | 1.02 | [0.75, 1.39] | 1.04 | [0.72, 1.51] | 1.23 | [0.89, 1.69] | 0.74 | [0.49, 1.12] | 0.98 | [0.71, 1.36] |
| Employment status | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Employed | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - |
| Unemployed | 1.09 | [0.90, 1.33] | 1.02 | [0.81, 1.28] | 1.29 | [1.04, 1.59] | 1.01 | [0.78, 1.30] | 1.01 | [0.81, 1.24] |
| Occupation type | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Non-healthcare | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - |
| Healthcare | 1.10 | [0.88, 1.39] | 0.90 | [0.70, 1.17] | 0.78 | [0.61, 0.99] | 0.64 | [0.46, 0.88] | 1.17 | [0.91, 1.49] |
| Religion | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Christianity | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Islam/others† | 1.20 | [0.89, 1.61] | 0.91 | [0.65, 1.28] | 0.89 | [0.65, 1.22] | 1.02 | [0.70, 1.49] | 0.89 | [0.65, 1.22] |
| Household factors | ||||||||||
| Number living together | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 1–3 people | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| 4–6 people | 1.13 | [0.90, 1.43] | 1.15 | [0.89, 1.49] | 1.07 | [0.83, 1.36] | 1.27 | [0.93, 1.72] | 1.14 | [0.89, 1.46] |
| 6+ people | 0.97 | [0.73, 1.29] | 1.57 | [1.11, 2.23] | 1.42 | [1.04, 1.95] | 1.64 | [1.12, 2.37] | 1.39 | [1.01, 1.93] |
| Attended crowded event | ||||||||||
| No | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - |
| Yes | 1.15 | [0.87, 1.51] | 1.02 | [0.73, 1.42] | 1.06 | [0.78, 1.42] | 0.99 | [0.68, 1.43] | 1.20 | [0.87, 1.68] |
| Public attitudes towards compliance to COVID-19 | ||||||||||
| Self-Isolation | ||||||||||
| No | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - |
| Yes | 1.07 | [0.87, 1.31] | 0.96 | [0.75, 1.22] | 0.97 | [0.77, 1.21] | 0.80 | [0.60, 1.06] | 0.85 | [0.67, 1.06] |
| Home quarantined due to COVID-19 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| No | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - |
| Yes | 1.03 | [0.85, 1.25] | 1.04 | [0.82, 1.31] | 1.01 | [0.81, 1.25] | 0.86 | [0.66, 1.11] | 0.96 | [0.77, 1.20] |
| Perception of risk | ||||||||||
| Risk of becoming infected | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| High | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - |
| Not high | 0.34 | [0.27, 0.41] | 1.16 | [0.92, 1.46] | 1.22 | [0.99, 1.52] | 1.51 | [1.15, 1.99] | 1.12 | [0.90, 1.39] |
| Risk of becoming severely infected | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| High | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - |
| Not high | 0.26 | [0.20, 0.33] | 1.11 | [0.86, 1.43] | 1.05 | [0.83, 1.33] | 1.14 | [0.85, 1.53] | 1.06 | [0.84, 1.35] |
| Risk of dying from infection | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| High | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - |
| Not high | 0.18 | [0.14, 0.25] | 1.30 | [0.98, 1.72] | 1.12 | [0.86, 1.46] | 1.06 | [0.77, 1.47] | 1.08 | [0.83, 1.41] |
| Possibility of you/family member being affected | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Concerned | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - |
| Not Concerned | 0.17 | [0.10, 0.27] | 0.92 | [0.58, 1.48] | 0.80 | [0.51, 1.24] | 0.70 | [0.39, 1.26] | 0.63 | [0.40, 0.98] |
| Likelihood of COVID-19 continuing | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Likely | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - |
| Not Likely | 0.62 | [0.51,0.75] | 1.12 | [0.58, 1.48] | 1.17 | [0.94, 1.45] | 1.40 | [1.08, 1.81] | 1.08 | [0.86, 1.34] |
| Variables | Worried | Bored | Frustrated | Angry | Anxious | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| aOR | 95% CI | aOR | 95% CI | aOR | 95% CI | aOR | 95% CI | aOR | 95% CI | |
| Demography | ||||||||||
| Place of Origin | ||||||||||
| West Africa | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - |
| East Africa | 1.13 | [0.77, 1.66] | 0.48 | [0.32, 0.72] | 1.16 | [0.78, 171] | 1.05 | [0.65, 1.70] | 0.99 | [0.67, 1.47] |
| Central Africa | 1.07 | [0.74, 1.56] | 1.37 | [0.85, 2.21] | 1.49 | [1.01, 2.19] | 2.12 | [1.37, 3.29] | 1.60 | [1.05, 2.43] |
| Southern Africa | 1.17 | [0.87, 1.58] | 0.59 | [0.42, 0.82] | 1.46 | [1.06, 2.00] | 0.87 | [0.58, 1.31] | 0.90 | [0.65, 1.23] |
| Place of residence | ||||||||||
| Africa | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - |
| Diaspora | 1.00 | [0.59, 1.69] | 1.70 | [0.86, 3.38] | 0.94 | [0.53, 1.64] | 0.86 | [0.42, 1.78] | 0.88 | [0.49, 1.58] |
| Age in years | ||||||||||
| 18–28 | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - |
| 29–38 | 1.12 | [0.76, 1.65] | 1.27 | [0.83, 1.96] | 1.56 | [1.03, 2.34] | 1.11 | [0.69, 1.79 | 0.93 | [0.62, 1.40] |
| 39–48 | 1.49 | [0.94, 2.35] | 1.81 | [1.05, 3.10] | 1.95 | [1.20, 3.19] | 1.01 | [0.56, 1.81] | 0.93 | [0.57,1.52] |
| 49+ | 1.19 | [0.72, 1.98] | 1.58 | [0.87, 2.81] | 2.09 | [1.22, 3.56] | 0.95 | [0.49, 1.82] | 0.69 | [0.40, 1.17] |
| Sex | ||||||||||
| Men | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - |
| Women | 1.05 | [0.82, 1.33] | 1.15 | [0.88, 1.52] | 0.78 | [0.60,1.00] | 0.68 | [0.50, 0.93] | 1.17 | [0.90, 1.51] |
| Marital Status | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Married | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - |
| Not married † | 1.10 | [0.79, 1.52] | 1.53 | [1.04, 2.42] | 1.65 | [1.16, 2.33] | 1.81 | [1.19, 2.75] | 1.40 | [0.99, 1.99] |
| Highest level of Education | ||||||||||
| Postgraduate Degree (Masters/PhD) | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - |
| Bachelor’s degree | 1.29 | [0.96, 1.74] | 0.79 | [0.56, 1.11] | 1.19 | [0.87, 1.63] | 1.01 | [0.69, 1.49] | 0.94 | [0.69, 1.28] |
| Secondary/Primary | 1.12 | [0.70, 1.80] | 1.24 | [0.72, 2.14] | 1.01 | [0.62, 1.64] | 0.55 | [0.29, 1.04] | 0.64 | [0.40, 1.05] |
| Employment status | ||||||||||
| Employed | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - |
| Unemployed | 1.44 | [1.03, 2.02] | 0.94 | [0.64, 1.37] | 1.45 | [1.01, 2.07] | 0.81 | [0.53, 1.24] | 0.78 | [0.54, 1.13] |
| Occupation type | ||||||||||
| Non-healthcare | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - |
| Healthcare | 1.02 | [0.77, 1.36] | 0.98 | [0.71, 1.34] | 0.75 | [0.55, 1.00] | 0.60 | [0.41, 0.90] | 1.18 | [0.87,1.59] |
| Religion | ||||||||||
| Christianity | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Islam/others† | 1.15 | [0.78, 1.69] | 0.93 | [0.60, 1.45] | 0.99 | [0.66, 1.47] | 1.26 | [0.77, 2.05] | 0.89 | [0.59, 1.34] |
| Household factors | ||||||||||
| Number living together | ||||||||||
| <3 people | 1.00 | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | |
| 4–6 people | 1.12 | [0.85,1.47] | 1.27 | [0.94, 1.72] | 1.03 | [0.78, 1.38] | 1.17 | [0.81, 1.66] | 1.23 | [0.92, 1.63] |
| 6+ people | 0.94 | [0.66, 1.32] | 1.70 | [1.13, 2.56] | 1.42 | [0.99, 2.05] | 1.20 | [0.77, 1.87] | 1.31 | [0.90, 1.90] |
| Attended crowded event | ||||||||||
| No | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - |
| Yes | 1.09 | [0.76, 1.56] | 1.02 | [0.68, 1.56] | 1.11 | [0.76, 1.60] | 0.88 | [0.55, 1.40] | 1.06 | [0.72, 1.57] |
| Public attitudes toward compliance to COVID-19 | ||||||||||
| Self-Isolation | ||||||||||
| No | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Yes | 0.96 | [0.72, 1.28] | 0.86 | [0.62, 1.18] | 0.86 | [0.64, 1.15] | 0.69 | [0.48, 1.00] | 0.85 | [0.63, 1.14] |
| Home quarantined due to COVID-19 | ||||||||||
| No | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - |
| Yes | 1.01 | [0.77, 1.31] | 0.95 | [0.70, 1.29] | 1.05 | [0.79, 1.38] | 1.16 | [0.83, 1.63] | 0.97 | [0.73, 1.29] |
| Perception of risk | ||||||||||
| Risk of becoming infected | ||||||||||
| High | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - |
| Not high | 0.57 | [0.45, 0.80] | 0.94 | [0.64, 1.39] | 1.32 | [0.93, 1.88] | 1.84 | [1.16, 2.93] | 1.11 | [0.78, 1.59] |
| Risk of becoming severely infected | ||||||||||
| High | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Not high | 0.60 | [0.39, 0.93] | 0.91 | [0.57, 1.48] | 0.84 | [0.54, 1.88] | 0.84 | [0.47, 1.48] | 0.98 | [0.63, 1.52] |
| Risk of dying from infection | ||||||||||
| High | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - |
| Not high | 0.38 | [0.25, 0.58] | 1.49 | [0.97, 2.30] | 1.18 | [0.79, 1.76] | 0.89 | [0.53, 1.48] | 1.19 | [0.80, 1.78] |
| Possibility of you/family member being affected | ||||||||||
| Concerned | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - |
| Not Concerned | 0.17 | [0.09, 0.33] | 1.06 | [0.57, 1.97] | 0.82 | [0.46, 1.45] | 0.89 | [0.45, 1.79] | 0.64 | [0.36, 1.14] |
| Likelihood of COVID-19 continuing | ||||||||||
| Likely | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - |
| Not Likely | 0.76 | [0.59, 0.97] | 1.08 | [0.81, 1.45] | 1.27 | [0.98, 1.66] | 1.49 | [1.08, 2.04] | 1.17 | [0.89, 1.53] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Langsi, R.; Osuagwu, U.L.; Goson, P.C.; Abu, E.K.; Mashige, K.P.; Ekpenyong, B.; Ovenseri-Ogbomo, G.O.; Chikasirimobi G, T.; Miner, C.A.; Ishaya, T.; et al. Prevalence and Factors Associated with Mental and Emotional Health Outcomes among Africans during the COVID-19 Lockdown Period—A Web-based Cross-Sectional Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 899. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18030899
Langsi R, Osuagwu UL, Goson PC, Abu EK, Mashige KP, Ekpenyong B, Ovenseri-Ogbomo GO, Chikasirimobi G T, Miner CA, Ishaya T, et al. Prevalence and Factors Associated with Mental and Emotional Health Outcomes among Africans during the COVID-19 Lockdown Period—A Web-based Cross-Sectional Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(3):899. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18030899
Chicago/Turabian StyleLangsi, Raymond, Uchechukwu L Osuagwu, Piwuna Christopher Goson, Emmanuel Kwasi Abu, Khathutshelo P Mashige, Bernadine Ekpenyong, Godwin O Ovenseri-Ogbomo, Timothy Chikasirimobi G, Chundung Asabe Miner, Tanko Ishaya, and et al. 2021. "Prevalence and Factors Associated with Mental and Emotional Health Outcomes among Africans during the COVID-19 Lockdown Period—A Web-based Cross-Sectional Study" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 3: 899. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18030899
APA StyleLangsi, R., Osuagwu, U. L., Goson, P. C., Abu, E. K., Mashige, K. P., Ekpenyong, B., Ovenseri-Ogbomo, G. O., Chikasirimobi G, T., Miner, C. A., Ishaya, T., Oloruntoba, R., Nwaeze, O., Charwe, D. D., & Agho, K. E. (2021). Prevalence and Factors Associated with Mental and Emotional Health Outcomes among Africans during the COVID-19 Lockdown Period—A Web-based Cross-Sectional Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(3), 899. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18030899








