The Association between Fast Food Outlets and Overweight in Adolescents Is Confounded by Neighbourhood Deprivation: A Longitudinal Analysis of the Millennium Cohort Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants and Setting
2.2. Outcome: Overweight
2.3. Exposure: Fast Food Environment
2.4. Confounder: Neighbourhood Deprivation
2.5. Additional Measures
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Key Findings
4.2. Interpretation
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Swinburn, B.; Egger, G.; Raza, F. Dissecting obesogenic environments: The development and application of a framework for identifying and prioritizing environmental interventions for obesity. Prev. Med. 1999, 29, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgoine, T.; Forouhi, N.G.; Griffin, S.J.; Wareham, N.J.; Monsivais, P. Associations between exposure to takeaway food outlets, takeaway food consumption, and body weight in Cambridgeshire, UK: Population based, cross sectional study. BMJ 2014, 348, g1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moore, L.V.; Diez Roux, A.V.; Nettleton, J.A.; Jacobs, D.R.; Franco, M. Fast-food consumption, diet quality, and neighborhood exposure to fast food: The multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2009, 170, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dornelles, A. Impact of multiple food environments on body mass index. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cavill, N.; Rutter, H. Obesity and the Environment: Regulating the Growth of Fast Food Outlets. 2014. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/296248/Obesity_and_environment_March2014.pdf (accessed on 10 December 2021).
- Nykiforuk, C.I.J.; Campbell, E.J.; Macridis, S.; McKennitt, D.; Atkey, K.; Raine, K.D. Adoption and diffusion of zoning bylaws banning fast food drive-through services across Canadian municipalities. BMC Public Health 2018, 18, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shill, J.; Mavoa, H.; Allender, S.; Lawrence, M.; Sacks, G.; Peeters, A.; Crammond, B.; Swinburn, B. Government regulation to promote healthy food environments--a view from inside state governments. Obes. Rev. 2012, 13, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viner, R.M.; Cole, T.J. Who changes body mass between adolescence and adulthood? Factors predicting change in BMI between 16 year and 30 years in the 1970 British Birth Cohort. Int. J. Obes. 2006, 30, 1368–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fraser, L.; Edwards, K. The association between the geography of fast food outlets and childhood obesity rates in Leeds, UK. Health Place 2010, 16, 1124–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischhacker, S.E.; Evenson, K.R.; Rodriguez, D.A.; Ammerman, A.S. A systematic review of fast food access studies. Obes. Rev. 2011, 12, e460–e471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobb, L.K.; Appel, L.J.; Franco, M.; Jones-Smith, J.C.; Nur, A.; Anderson, C.A.M. The Relationship of the Local Food Environment with Obesity: A Systematic Review of Methods, Study Quality, and Results. Obesity 2015, 23, 1331–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gamba, R.J.; Schuchter, J.; Rutt, C.; Seto, E.Y.W. Measuring the food environment and its effects on obesity in the United States: A systematic review of methods and results. J. Community Health 2015, 40, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkins, E.; Radley, D.; Morris, M.; Hobbs, M.; Christensen, A.; Marwa, W.L.; Morrin, A.; Griffiths, C. A systematic review employing the GeoFERN framework to examine methods, reporting quality and associations between the retail food environment and obesity. Health Place 2019, 57, 186–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widener, M.; Shannon, J. When are food deserts? Integrating time into research on food accessibility. Health Place 2014, 30, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widener, M. Spatial access to food: Retiring the food desert metaphor. Physiol. Behav. 2018, 193, 257–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thornton, L.E.; Lamb, K.; White, S. The use and misuse of ratio and proportion exposure measures in food environment research. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2020, 17, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hobbs, M.; Griffiths, C.; Green, M.A.; Christensen, A.; McKenna, J. Examining longitudinal associations between the recreational physical activity environment, change in body mass index, and obesity by age in 8864 Yorkshire Health Study participants. Soc. Sci. Med. 2019, 227, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, M.A.; Radley, D.; Lomax, N.; Morris, M.A.; Griffiths, C. Is adolescent body mass index and waist circumference associated with the food environments surrounding schools and homes? A longitudinal analysis. BMC Public Health 2018, 18, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mackenbach, J.D.; Charreire, H.; Glonti, K.; Bárdos, H.; Rutter, H.; Compernolle, S.; De Bourdeaudhuij, I.; Nijpels, G.; Brug, J.; Oppert, J.-M.; et al. Exploring the Relation of Spatial Access to Fast Food Outlets With Body Weight: A Mediation Analysis. Environ. Behav. 2018, 51, 401–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hobbs, M.; Green, M.; Roberts, K.; Griffiths, C.; McKenna, J. Reconsidering the relationship between fast-food outlets, area-level deprivation, diet quality and body mass index: An exploratory structural equation modelling approach. J. Epidemiol. Community Heal. 2019, 73, 861–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cummins, S. Neighbourhood food environment and diet: Time for improved conceptual models? Prev. Med. 2007, 44, 196–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaux, M.; Sassi, F. Social inequalities in obesity and overweight in 11 OECD countries. Eur. J. Public Health 2013, 23, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El-Sayed, A.M.; Scarborough, P.; Galea, S. Unevenly distributed: A systematic review of the health literature about socioeconomic inequalities in adult obesity in the United Kingdom. BMC Public Health 2012, 12, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pampel, F.C.; Krueger, P.; Denney, J. Socioeconomic disparities in health behaviors. Annu. Rev. Sociol. 2010, 36, 349–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Franco, M.; Diez Roux, A.V.; Glass, T.A.; Caballero, B.; Brancati, F.L. Neighborhood characteristics and availability of healthy foods in Baltimore. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2008, 35, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macdonald, L.; Cummins, S.; Macintyre, S. Neighbourhood fast food environment and area deprivation-substitution or concentration? Appetite 2007, 49, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westfall, J.; Yarkoni, T. Statistically Controlling for Confounding Constructs Is Harder than You Think. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.A.; Arcaya, M.; Subramanian, S. V Using Internal Migration to Estimate the Causal Effect of Neighborhood Socioeconomic Context on Health: A Longitudinal Analysis, England, 1995–2008. Ann. Am. Assoc. Geogr. 2017, 107, 1266–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cole, T.J.; Bellizzi, M.C.; Flegal, K.M.; Dietz, W.H. Establishing a standard definition for child overweight and obesity worldwide: International survey. BMJ 2000, 320, 1240–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, M.H.; Sovio, U.; Viner, R.M.; Hardy, R.J.; Kinra, S. Overweight in Childhood, Adolescence and Adulthood and Cardiovascular Risk in Later Life: Pooled Analysis of Three British Birth Cohorts. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Royston, P.; Altman, D.G.; Sauerbrei, W. Dichotomizing continuous predictors in multiple regression: A bad idea. Stat. Med. 2006, 25, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamb, K.E.; White, S.R. Categorisation of built environment characteristics: The trouble with tertiles. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2015, 12, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noble, M.; Wright, G.; Smith, G.; Dibben, C. Measuring Multiple Deprivation at the Small-Area Level. Environ. Plan. A 2006, 38, 169–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ONS. 2011 Rural/Urban Classification. 2016. Available online: https://www.ons.gov.uk/methodology/geography/geographicalproducts/ruralurbanclassifications/2011ruralurbanclassification (accessed on 10 December 2021).
- Fraser, L.K.; Edwards, K.L.; Cade, J.E.; Clarke, G.P. Fast food, other food choices and body mass index in teenagers in the United Kingdom (ALSPAC): A structural equation modelling approach. Int. J. Obes. 2011, 35, 1325–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Link, B.G.; Phelan, J. Social Conditions As Fundamental Causes of Disease. J. Health Soc. Behav. 1995, 35, 80–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McAuley, A.; Denny, C.; Taulbut, M.; Mitchell, R.; Fischbacher, C.; Graham, B.; Grant, I.; O’Hagan, P.; McAllister, D.; McCartney, G. Informing Investment to Reduce Inequalities: A Modelling Approach. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, A.P.; Brimblecombe, J.; Eyles, H.; Morris, P.; Vally, H.; O′Dea, K. Food subsidy programs and the health and nutritional status of disadvantaged families in high income countries: A systematic review. BMC Public Health 2012, 12, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wilkins, E.L.; Radley, D.; Morris, M.A.; Griffiths, C. Examining the validity and utility of two secondary sources of food environment data against street audits in England. Nutr. J. 2017, 16, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwan, M.-P. The Uncertain Geographic Context Problem. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 2012, 102, 958–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
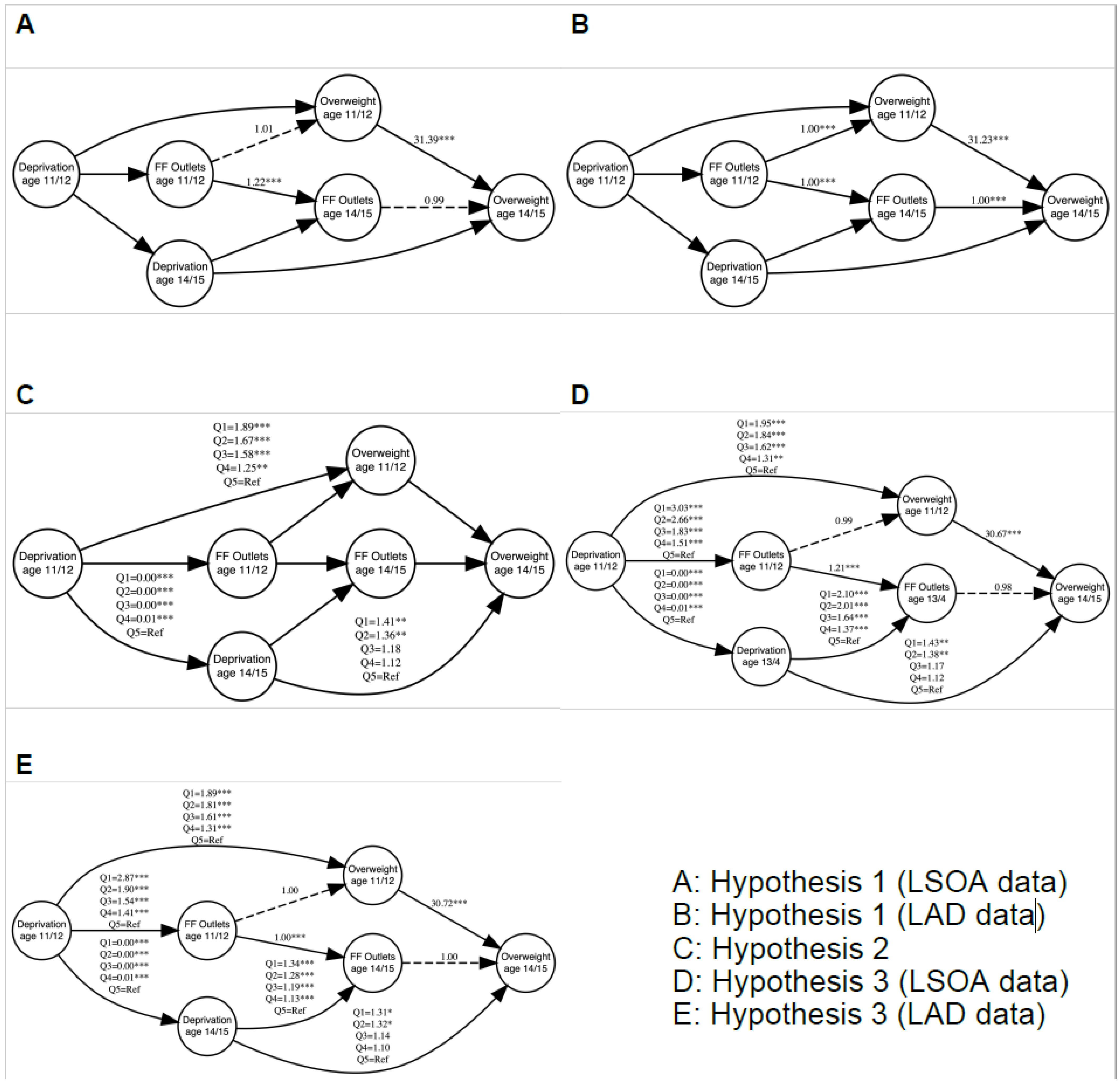
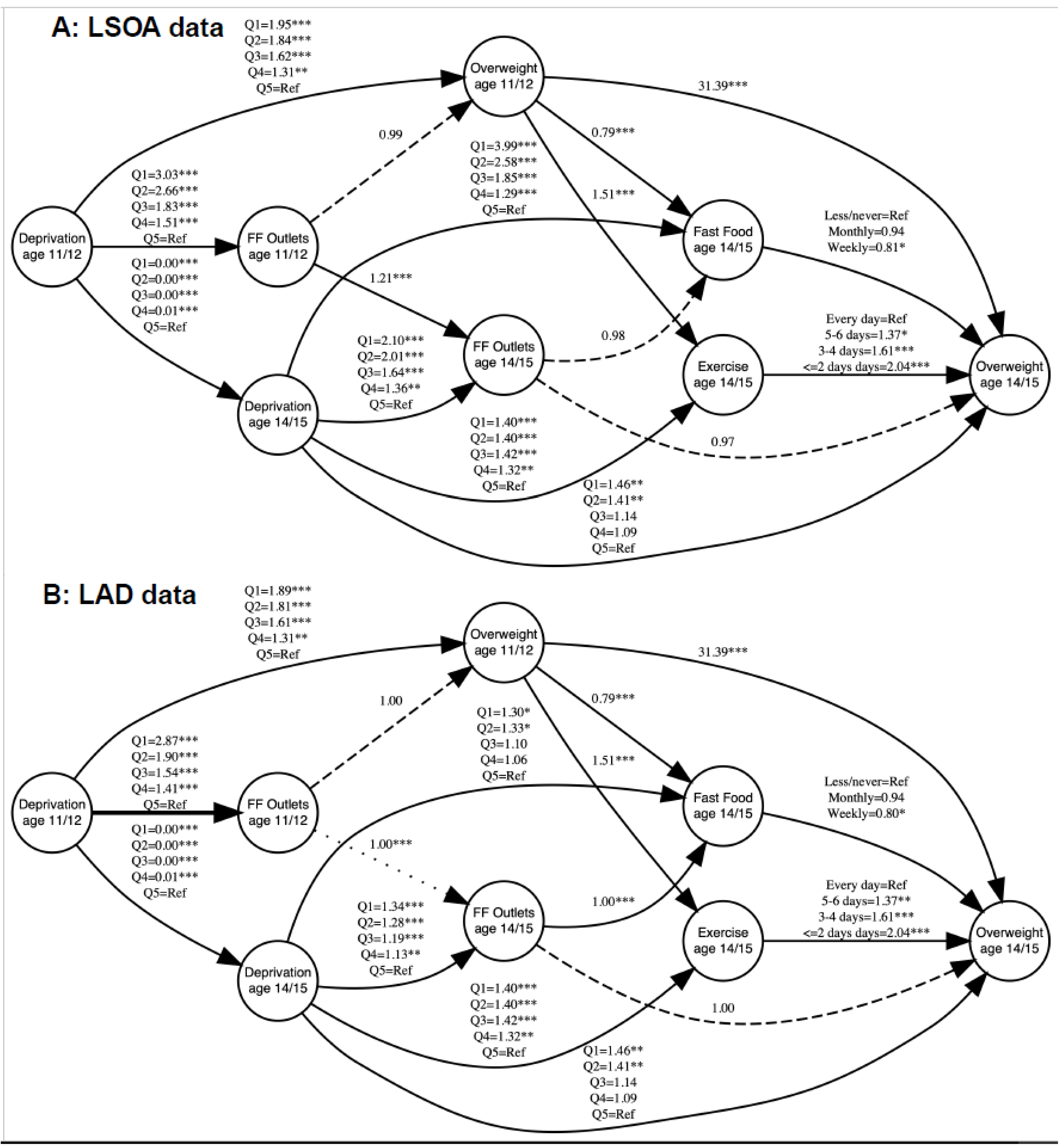
| Measure | Ages 11/12—Wave 5 | Ages 14/15—Waves 6 |
|---|---|---|
| Mean Age | 10.6 | 13.8 |
| Males | 49.4% | 49.4% |
| Females | 50.7% | 50.6% |
| Overweight | 26.4% | 25.4% |
| Mean Fast food outlets in Lower Super Output Area | 1.1 | 1.2 |
| Mean Fast food outlets in Local Authority | 179.2 | 214.1 |
| Deprivation Quintile 1 (Most Deprived) | 23.9% | 23.7% |
| Deprivation Quintile 2 | 19.3% | 19.2% |
| Deprivation Quintile 3 | 18.8% | 18.7% |
| Deprivation Quintile 4 | 18.4% | 18.6% |
| Deprivation Quintile 5 (Least Deprived) | 19.7% | 19.9% |
| Odds Ratio | Lower CI | Upper CI | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model A: Lower Super Output Areas | ||||
| Change in fast food outlets | 0.967 | 0.929 | 1.007 | 0.105 |
| Model B: Local Authority District | ||||
| Change in fast food outlets | 1.0001 | 0.999 | 1.002 | 0.903 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Green, M.A.; Hobbs, M.; Ding, D.; Widener, M.; Murray, J.; Reece, L.; Singleton, A. The Association between Fast Food Outlets and Overweight in Adolescents Is Confounded by Neighbourhood Deprivation: A Longitudinal Analysis of the Millennium Cohort Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 13212. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182413212
Green MA, Hobbs M, Ding D, Widener M, Murray J, Reece L, Singleton A. The Association between Fast Food Outlets and Overweight in Adolescents Is Confounded by Neighbourhood Deprivation: A Longitudinal Analysis of the Millennium Cohort Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(24):13212. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182413212
Chicago/Turabian StyleGreen, Mark A., Matthew Hobbs, Ding Ding, Michael Widener, John Murray, Lindsey Reece, and Alex Singleton. 2021. "The Association between Fast Food Outlets and Overweight in Adolescents Is Confounded by Neighbourhood Deprivation: A Longitudinal Analysis of the Millennium Cohort Study" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 24: 13212. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182413212
APA StyleGreen, M. A., Hobbs, M., Ding, D., Widener, M., Murray, J., Reece, L., & Singleton, A. (2021). The Association between Fast Food Outlets and Overweight in Adolescents Is Confounded by Neighbourhood Deprivation: A Longitudinal Analysis of the Millennium Cohort Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(24), 13212. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182413212







