Which Non-Pharmaceutical Primary Care Interventions Reduce Inequalities in Common Mental Health Disorders? A Protocol for a Systematic Review of Quantitative and Qualitative Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Questions
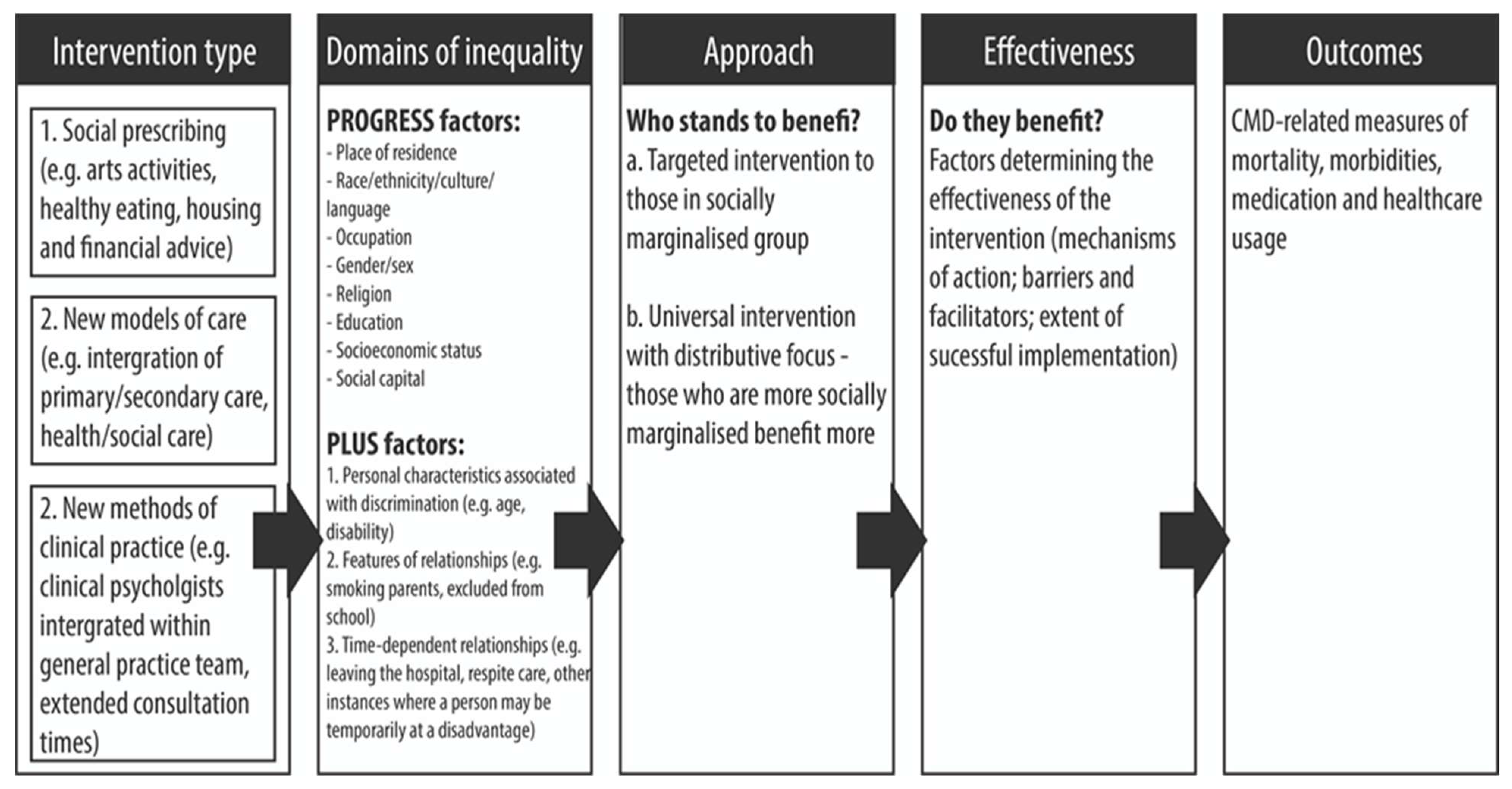
- Which non-pharmaceutical primary care interventions reduce the occurrence of CMD-related adverse health outcomes amongst populations in the most disadvantaged groups in relation to the PROGRESS-Plus framework?
- Which non-pharmaceutical primary care interventions reduce inequalities in CMD- related adverse health outcomes between people from the least and most disadvantaged groups?
- What are the mechanisms by which non-pharmaceutical primary care interventions impact CMD-related adverse health outcomes and inequalities?
- What are the barriers and facilitators to the implementation of non-pharmaceutical primary care interventions in disadvantaged groups?
2.2. Objectives
- Locate studies reporting data for the effects of non-pharmaceutical primary care interventions on CMD-related health outcomes and inequalities, using systematic searches of bibliographic databases and sources of grey literature and systematic screening methods;
- Quantify the effects of non-pharmaceutical primary care interventions on CMD-related health outcomes and inequalities;
- Identify which aspects of the identified interventions influence CMD-related health outcomes and inequalities and the mechanisms (including barriers and facilitators) by which these factors exert their effects;
- Assess the methodological quality of the synthesised evidence;
- Identify policy implications and areas for further research in relation to the review findings.
2.3. Inclusion Criteria
2.3.1. Population
2.3.2. Intervention
2.3.3. Comparators
Population
Intervention
2.3.4. Outcomes
2.3.5. Study Design
2.3.6. Context
2.4. Search Strategy
2.5. Screening and Selection
2.6. Data Extraction
2.7. Quality Appraisal
3. Results
Synthesis
- Developing a theory of how non-pharmaceutical primary care interventions reduce CMD-related adverse health outcomes and inequalities, why and for whom;
- Developing a preliminary synthesis of the data;
- Exploring relationships within and between studies;
- Assessing the robustness of the synthesis.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- The Independent Mental Health Taskforce. The Five Year Forward View for Mental Health. 2016. Available online: https://www.england.nhs.uk/wp-content/uploads/2016/02/Mental-Health-Taskforce-FYFV-final.pdf (accessed on 22 November 2021).
- Kendrick, T.; Burns, T.; Garland, C.; Greenwood, N.; Smith, P. Are specialist mental health services being targeted on the most needy patients? The effects of setting up special services in general practice. Br. J. Gen. Pract. 2000, 50, 121–126. [Google Scholar]
- Reilly, S.T.; Planner, C.; Hann, M.; Reeves, D.; Nazareth, I.; Lester, H. The role of primary care in service provision for people with severe mental illness in the United Kingdom. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundquist, J.; Ohlsson, H.; Sundquist, K.; Kendler, K.S. Common adult psychiatric disorders in Swedish primary care where most mental health patients are treated. BMC Psychiatry 2017, 17, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puschner, B.; Kösters, M.; Bouché, L. The epidemiology, burden and treatment of mental disorders in primary care. Mental Disorders in Primary Care: A Guide to Their Evaluation and Management; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2017; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, I.; Woodward, L. The medicalisation of unhappiness? The management of mental distress in primary care. In Constructions of Health and Illness; Routledge: London, UK, 2017; pp. 124–136. [Google Scholar]
- American Academy of Family Physicians. Mental Health Care Services by Family Physicians (Position Paper). 2021. Available online: https://www.aafp.org/about/policies/all/mental-health-services.html (accessed on 22 November 2021).
- Hálfdánarson, Ó.; Zoega, H.; Aagaard, L.; Bernardo, M.; Brandt, L.; Fusté, A.C.; Furu, K.; Garuoliené, K.; Hoffmann, F.; Huybrechts, K.F.; et al. International trends in antipsychotic use: A study in 16 countries, 2005–2014. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017, 27, 1064–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogowicz, P.; Curtis, H.J.; Walker, A.J.; Cowen, P.; Geddes, J.; Goldacre, B. Trends and variation in antidepressant prescribing in English primary care: A retrospective longitudinal study. BJGP Open 2021, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, R.; Ariti, C.; Bardsley, M. Focus On: Antidepressant Prescribing. 2014. Available online: https://www.nuffieldtrust.org.uk/research/focus-on-antidepressant-prescribing (accessed on 22 November 2021).
- Boyle, S.; Murphy, J.; Rosato, M.; Boduszek, D.; Shevlin, M. Predictors of antidepressant use in the English population: Analysis of the adult psychiatric morbidity survey. Ir. J. Psychol. Med. 2020, 37, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NHS England. Adult Improving Access to Psychological Therapies Programme. 2021. Available online: https://www.england.nhs.uk/mental-health/adults/iapt/ (accessed on 22 November 2021).
- Petersen, I. Integrating task-sharing psychological treatments within primary health care services. In Systems Considerations; SAGE Publications Sage UK: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Drinkwater, C.; Wildman, J.; Moffatt, S. Social prescribing. BMJ 2019, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croxson, C.H.; Ashdown, H.F.; Hobbs, F.R. GPs’ perceptions of workload in England: A qualitative interview study. Br. J. Gen. Pract. 2017, 67, e138–e147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Devastating Cost of Treatment Delays. Available online: https://www.bma.org.uk/news-and-opinion/the-devastating-cost-of-treatment-delays (accessed on 29 November 2021).
- O’Neill, J.; Tabish, H.; Welch, V.; Petticrew, M.; Pottie, K.; Clarke, M.; Evans, T.; Pardo, J.P.; Waters, E.; White, H.; et al. Applying an equity lens to interventions: Using PROGRESS ensures consideration of socially stratifying factors to illuminate inequities in health. J. Clin. Epidemiol 2014, 67, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somers, J.M.; Goldner, E.M.; Waraich, P.; Hsu, L. Prevalence and incidence studies of anxiety disorders: A systematic review of the literature. Can. J. Psychiatry 2006, 51, 100–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabezas-Rodríguez, A.; Utzet, M.; Bacigalupe, A. Which are the intermediate determinants of gender inequalities in mental health?: A scoping review. Int. J. Soc. Psychiatry 2021, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, R.J.; Richardson, E.A.; Shortt, N.K.; Pearce, J.R. Neighborhood environments and socioeconomic inequalities in mental well-being. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2015, 49, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearce, J.; Cherrie, M.; Shortt, N.; Deary, I.; Thompson, C.W. Life course of place: A longitudinal study of mental health and place. Trans. Inst. Br. Geogr. 2018, 43, 555–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sentell, T.; Shumway, M.; Snowden, L. Access to mental health treatment by English language proficiency and race/ethnicity. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2007, 22, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mclean, C.; Campbell, C.; Cornish, F. African-Caribbean interactions with mental health services in the UK: Experiences and expectations of exclusion as (re) productive of health inequalities. Soc. Sci. Med. 2003, 56, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grey, T.; Sewell, H.; Shapiro, G.; Ashraf, F. Mental health inequalities facing UK minority ethnic populations: Causal factors and solutions. J. Psychol. Issues Organ. C 2013, 3, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milner, A.; King, T.; LaMontagne, A.D.; Bentley, R.; Kavanagh, A. Men’s work, women’s work, and mental health: A longitudinal investigation of the relationship between the gender composition of occupations and mental health. Soc. Sci. Med. 2018, 204, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canivet, C.; Aronsson, G.; Bernhard-Oettel, C.; Leineweber, C.; Moghaddassi, M.; Stengård, J.; Westerlund, H.; Östergren, P.-O. The negative effects on mental health of being in a non-desired occupation in an increasingly precarious labour market. SSM - Popul. Heal. 2017, 3, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barr, B.; Kinderman, P.; Whitehead, M. Trends in mental health inequalities in England during a period of recession, austerity and welfare reform 2004 to 2013. Soc. Sci. Med. 2015, 147, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilmaghani, M. Religious identity and health inequalities in Canada. J. Immigr. Minor. Health 2017, 20, 1060–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, A. Religion and mental health: The case of American Muslims. J. Relig. Health 2004, 43, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Social Determinants of Mental Health. 2014. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/112828/9789241506809_eng.pdf (accessed on 22 November 2021).
- Pinxten, W.; Lievens, J. The importance of economic, social and cultural capital in understanding health inequalities: Using a Bourdieu-based approach in research on physical and mental health perceptions. Sociol. Heal. Illn. 2014, 36, 1095–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emerson, E.; Hatton, C. Contribution of socioeconomic position to health inequalities of British children and adolescents with intellectual disabilities. Am. J. Ment. Retard. 2007, 112, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semlyen, J.; King, M.; Varney, J.; Hagger-Johnson, G. Sexual orientation and symptoms of common mental disorder or low wellbeing: Combined meta-analysis of 12 UK population health surveys. BMC Psychiatry 2016, 16, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Health Foundation. Inequalities in Health Care for People with Depression and/or Anxiety. 2021. Available online: https://www.health.org.uk/publications/long-reads/inequalities-in-health-care-for-people-with-depression-and-anxiety (accessed on 22 November 2021).
- World Health Organization. Policy Frameworks. 2021. Available online: https://www.euro.who.int/en/health-topics/noncommunicable-diseases/mental-health/policy-frameworks (accessed on 22 November 2021).
- NHS. NHS Long Term Plan. 2019. Available online: https://www.longtermplan.nhs.uk/ (accessed on 22 November 2021).
- Stevens, S.; Pritchard, A. Third Phase of NHS Response to COVID-19. 2020. Available online: https://www.england.nhs.uk/coronavirus/wp-content/uploads/sites/52/2020/07/20200731-Phase-3-letter-final-1.pdf (accessed on 22 November 2021).
- Tugwell, P.; Petticrew, M.; Kristjansson, E.; Welch, V.; Ueffing, E.; Waters, E.; Bonnefoy, J.; Morgan, A.; Doohan, E.; Kelly, M.P. Assessing equity in systematic reviews: Realising the recommendations of the Commission on Social Determinants of Health. BMJ 2010, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, V.; Petticrew, M.; Petkovic, J.; Moher, D.; Waters, E.; White, H.; Tugwell, P.; Atun, R.; Awasthi, S.; Barbour, V.; et al. Extending the PRISMA statement to equity-focused systematic reviews (PRISMA-E 2012): Explanation and elaboration. J. Clin. Epidemiol 2016, 70, 68–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welch, V.; Petticrew, M.; Tugwell, P.; Moher, D.; O’Neill, J.; Waters, E.; White, H. PRISMA-Equity 2012 extension: Reporting guidelines for systematic reviews with a focus on health equity. PLoS Med. 2012, 9, e1001333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sowden, S.; Nezafat-Maldonado, B.; Wildman, J.; Cookson, R.; Thomson, R.; Lambert, M.; Beyer, F.; Bambra, C. Protocol: Interventions to reduce inequalities in avoidable hospital admissions: Explanatory framework and systematic review protocol. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e035429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kneale, D.; Thomas, J.; Harris, K. Developing and optimising the use of logic models in systematic reviews: Exploring practice and good practice in the use of programme theory in reviews. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142187. [Google Scholar]
- Prady, S.L.; Uphoff, E.P.; Power, M.; Golder, S. Development and validation of a search filter to identify equity-focused studies: Reducing the number needed to screen. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2018, 18, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, S.; Kavanagh, J.; Caird, J.; Lorenc, T.; Oliver, K.; Harden, A. Health Promotion, Inequalities and Young People’s Health. A Systematic Review of Research. 2008. Available online: http://eppi.ioe.ac.uk/cms/LinkClick.aspx?fileticket=lsYdLJP8gBI%3d&tabid=2412&mid=4471&language=en-US (accessed on 8 December 2021).
- Moher, D.; Shamseer, L.; Clarke, M.; Ghersi, D.; Liberati, A.; Petticrew, M.; Shekelle, P.; Stewart, L.A. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst. Rev. 2015, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Which Non-Pharmaceutical Primary Care Interventions Reduce Inequalities in Common Mental Health Disorders? A Protocol for a Systematic Review of Quantitative and Qualitative Studies (PROSPERO 2021 CRD42021281166). 2021. Available online: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?RecordID=281166 (accessed on 29 November 2021).
- The World Bank Group. High Income. 2021. Available online: https://data.worldbank.org/country/XD (accessed on 22 November 2021).
- Cochrane Methods Equity. PROGRESS-Plus. 2021. Available online: https://methods.cochrane.org/equity/projects/evidence-equity/progress-plus (accessed on 22 November 2021).
- Lund, C.; Breen, A.; Flisher, A.J.; Kakuma, R.; Corrigall, J.; Joska, J.; Swartz, L.; Patel, V. Poverty and common mental disorders in low and middle income countries: A systematic review. Soc. Sci. Med. 2010, 71, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spielberger, C.D.; Gorsuch, R.; Lushene, R.; Vagg, P.; Jacobs, G. State-Trait Anxiety Inventory; Mind Garden: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, S.; Kamarck, T.; Mermelstein, R. Perceived stress scale. Measuring stress. In A Guide for Health and Social Scientists; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1994; Volume 10, pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, E.R. Development and validation of an internationally reliable short-form of the positive and negative affect schedule (PANAS). J. Cross-Cultural Psychol. 2007, 38, 227–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tennant, R.; Hiller, L.; Fishwick, R.; Platt, S.; Joseph, S.; Weich, S.; Parkinson, J.; Secker, J.; Stewart-Brown, S. The Warwick-Edinburgh mental well-being scale (WEMWBS): Development and UK validation. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2007, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholte, W.F.; Verduin, F.; Van Lammeren, A.; Rutayisire, T.; Kamperman, A.M. Psychometric properties and longitudinal validation of the self-reporting questionnaire (SRQ-20) in a Rwandan community setting: A validation study. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2011, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sriram, T.; Chandrashekar, C.; Isaac, M.; Shanmugham, V. The general health questionnaire (GHQ). Soc. Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology; Springer International: Cham, Switzerland, 1989; Volume 24, pp. 317–320. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz-García, A.; González-Robles, A.; Mor, S.; Mira, A.; Quero, S.; García-Palacios, A.; Baños, R.M.; Botella, C. Positive and Negative Affect Schedule (PANAS): Psychometric properties of the online Spanish version in a clinical sample with emotional disorders. BMC Psychiatry 2020, 20, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelen, U.; De Peuter, S.; Victoir, A.; Van Diest, U.; Van Den Bergh, O. Further validation of the Positive and Negative Affect Schedule (PANAS) and comparison of two Dutch versions. Gedrag en Gezondheid 2006, 34, 89. [Google Scholar]
- Munnangi, S.; Boktor, S.W. Epidemiology of Study Design; StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Tenny, S.; Brannan, G.D.; Brannan, J.M. Qualitative Study. 2021. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470395/ (accessed on 29 November 2021).
- The Social Prescribing Network. Resources. 2018. Available online: https://www.socialprescribingnetwork.com/resources (accessed on 22 November 2021).
- SIREN (Social Interventions Research and Evaluation Network). Make Health Whole. Integrating Care. Improving Lives. 2017–2021. Available online: https://makehealthwhole.org/resource/siren-social-interventions-research-evaluation-network/ (accessed on 22 November 2021).
- Wilczynski, N.L.; Haynes, R.B.; Hedges, T. Optimal search strategies for identifying mental health content in MEDLINE: An analytic survey. Ann. Gen. Psychiatry 2006, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaner, E.F.; Beyer, F.R.; Muirhead, C.; Campbell, F.; Pienaar, E.D.; Bertholet, N. Effectiveness of brief alcohol interventions in primary care populations. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGowan, J.; Sampson, M.; Salzwedel, D.M.; Cogo, E.; Foerster, V.; Lefebvre, C. PRESS peer review of electronic search strategies: 2015 guideline statement. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2016, 1, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The EndNote Team. EndNote, EndNote X9 ed.; Clarivate: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ouzzani, M.; Hammady, H.; Fedorowicz, Z.; Elmagarmid, A. Rayyan—A web and mobile app for systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. 2016, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CASP. CASP Checklists. 2021. Available online: https://casp-uk.net/casp-tools-checklists/ (accessed on 22 November 2021).
- Long, H.A.; French, D.P.; Brooks, J.M. Optimising the value of the critical appraisal skills programme (CASP) tool for quality appraisal in qualitative evidence synthesis. Res. Methods Med. Health Sci. 2020, 1, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Q.N.; Fàbregues, S.; Bartlett, G.; Boardman, F.; Cargo, M.; Dagenais, P.; Gagnon, M.-P.; Griffiths, F.; Nicolau, B.; O’Cathain, A.; et al. The Mixed Methods Appraisal Tool (MMAT) version 2018 for information professionals and researchers. Educ. Inf. 2018, 34, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downes, M.J.; Brennan, M.; Williams, H.C.; Dean, R. Development of a critical appraisal tool to assess the quality of cross-sectional studies (AXIS). BMJ Open 2016, 6, e011458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Cochrane Collaboration. RoB 2: A Revised Cochrane Risk-of-Bias Tool for Randomized Trials. 2021. Available online: https://methods.cochrane.org/bias/resources/rob-2-revised-cochrane-risk-bias-tool-randomized-trials (accessed on 22 November 2021).
- The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan) [Computer Program], 5.4 ed.; Cochrane: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ogilvie, D.; Fayter, D.; Petticrew, M.; Sowden, A.; Thomas, S.; Whitehead, M. The harvest plot: A method for synthesising evidence about the differential effects of interventions. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2008, 8, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, J.; Harden, A. Methods for the thematic synthesis of qualitative research in systematic reviews. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2008, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popay, J.; Roberts, H.; Sowden, A.; Petticrew, M.; Arai, L.; Rodgers, M. Guidance on the conduct of narrative synthesis in systematic reviews. Prod. ESRC Methods Programm. Vers. 2006, 1, b92. [Google Scholar]
- Petticrew, M.; Roberts, H. Systematic Reviews in the Social Sciences: A Practical Guide; Blackwell Publishing: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- McManus, S.; Bebbington, P.E.; Jenkins, R.; Brugha, T. Mental Health and Wellbeing in England: The Adult Psychiatric Morbidity Survey 2014; NHS Digital: Leeds, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
| Inclusion | Exclusion |
|---|---|
| Population: People with a common mental disorder (CMD) a, who are being treated in primary care. | Population: Studies exclusively involving participants with alternative mental or physical health conditions. |
| Intervention: Non-pharmaceutical interventions delivered by or referred to from primary care teams. These will include:
| Intervention: Studies exclusively investigating the effects of pharmaceutical interventions. |
| Comparators: Population
| |
| Outcomes: Quantitative measures of:
| |
| Study design: Quantitative, qualitative and mixed methods primary studies. | Study design: Editorials and letters. |
| Context: Studies published in English language in an OECD high-income country. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tanner, L.; Sowden, S.; Still, M.; Thomson, K.; Bambra, C.; Wildman, J. Which Non-Pharmaceutical Primary Care Interventions Reduce Inequalities in Common Mental Health Disorders? A Protocol for a Systematic Review of Quantitative and Qualitative Studies. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12978. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182412978
Tanner L, Sowden S, Still M, Thomson K, Bambra C, Wildman J. Which Non-Pharmaceutical Primary Care Interventions Reduce Inequalities in Common Mental Health Disorders? A Protocol for a Systematic Review of Quantitative and Qualitative Studies. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(24):12978. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182412978
Chicago/Turabian StyleTanner, Louise, Sarah Sowden, Madeleine Still, Katie Thomson, Clare Bambra, and Josephine Wildman. 2021. "Which Non-Pharmaceutical Primary Care Interventions Reduce Inequalities in Common Mental Health Disorders? A Protocol for a Systematic Review of Quantitative and Qualitative Studies" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 24: 12978. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182412978
APA StyleTanner, L., Sowden, S., Still, M., Thomson, K., Bambra, C., & Wildman, J. (2021). Which Non-Pharmaceutical Primary Care Interventions Reduce Inequalities in Common Mental Health Disorders? A Protocol for a Systematic Review of Quantitative and Qualitative Studies. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(24), 12978. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182412978