Single Slow-Paced Breathing Session at Six Cycles per Minute: Investigation of Dose-Response Relationship on Cardiac Vagal Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Material and Measures
2.2.1. Cardiac Vagal Activity
2.2.2. Slow-Paced Breathing
2.2.3. TV Neutral Documentary
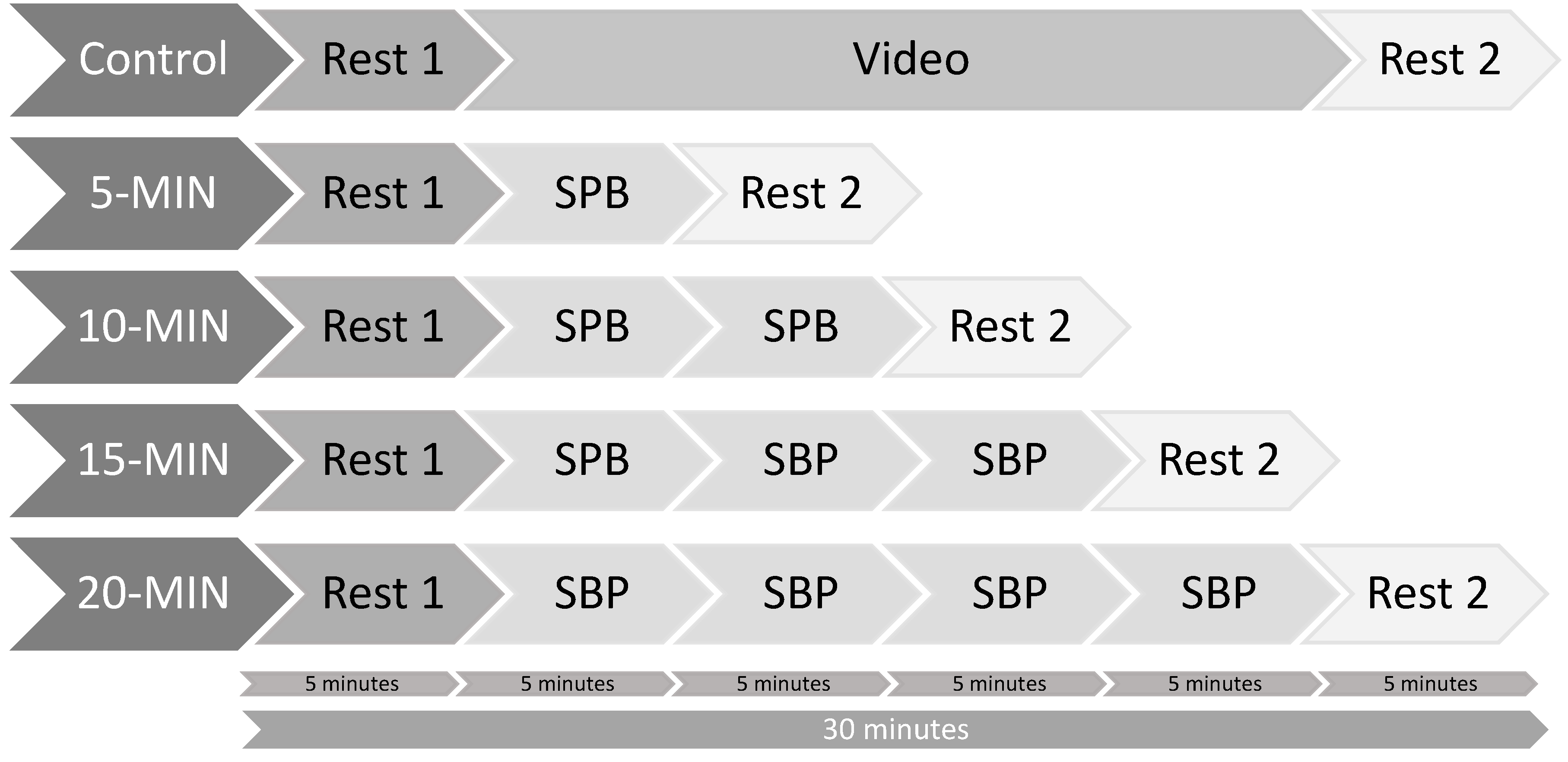
2.3. Procedure
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Main Dependent Variable of Interest: Root Mean Square of Successive Differences (RMSSD)
3.2. Manipulation Check: Respiratory Frequency (RF)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Russo, M.A.; Santarelli, D.M.; O’Rourke, D. The physiological effects of slow breathing in the healthy human. Breathe 2017, 13, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaccaro, A.; Piarulli, A.; Laurino, M.; Garbella, E.; Menicucci, D.; Neri, B.; Gemignani, A. How Breath-Control Can Change Your Life: A Systematic Review on Psycho-Physiological Correlates of Slow Breathing. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gerritsen, R.J.S.; Band, G.P.H. Breath of Life: The Respiratory Vagal Stimulation Model of Contemplative Activity. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Diest, I.; Verstappen, K.; Aubert, A.E.; Widjaja, D.; Vansteenwegen, D.; Vlemincx, E. Inhalation/Exhalation ratio modulates the effect of slow breathing on heart rate variability and relaxation. Appl. Psychophysiol. Biofeedback 2014, 39, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laborde, S.; Iskra, M.; Zammit, N.; Borges, U.; You, M.; Sevoz-Couche, C.; Dosseville, F. Slow-Paced Breathing: Influence of Inhalation/Exhalation Ratio and of Respiratory Pauses on Cardiac Vagal Activity. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, D.; Matthews, J.J.L.; Chen, J.J.; Mah, L. Increased exhalation to inhalation ratio during breathing enhances high-frequency heart rate variability in healthy adults. Psychophysiology 2021, 58, e13905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altshuler, B. Modeling of dose-response relationships. Environ. Health Perspect. 1981, 42, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherwood, L. Fundamentals of Physiology: A Human Perspective, 3rd ed.; Brooks/Cole: Belmont, CA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Tortora, G.J.; Derrickson, B.H. Principles of Anatomy and Physiology; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bernardi, L.; Gabutti, A.; Porta, C.; Spicuzza, L. Slow breathing reduces chemoreflex response to hypoxia and hypercapnia, and increases baroreflex sensitivity. J. Hypertens. 2001, 19, 2221–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehrer, P.M.; Gevirtz, R. Heart rate variability biofeedback: How and why does it work? Front. Psychol. 2014, 5, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Noble, D.J.; Hochman, S. Hypothesis: Pulmonary afferent activity patterns during slow, deep breathing contribute to the neural induction of physiological relaxation. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mather, M.; Thayer, J.F. How heart rate variability affects emotion regulation brain networks. Cur. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2018, 19, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodal, P. The Central Nervous System—Structure and Function, 5th ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Appelhans, B.M.; Luecken, L.J. Heart rate variability as an index of regulated emotional responding. Rev. Gen. Psychol. 2006, 10, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thayer, J.F.; Ahs, F.; Fredrikson, M.; Sollers, J.J.; Wager, T.D. A meta-analysis of heart rate variability and neuroimaging studies: Implications for heart rate variability as a marker of stress and health. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2012, 36, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thayer, J.F.; Hansen, A.L.; Saus-Rose, E.; Johnsen, B.H. Heart rate variability, prefrontal neural function, and cognitive performance: The neurovisceral integration perspective on self-regulation, adaptation, and health. Annal. Behav. Med. 2009, 37, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R.; Thayer, J.F.; Khalsa, S.S.; Lane, R.D. The hierarchical basis of neurovisceral integration. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 75, 274–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benarroch, E.E. The central autonomic network: Functional organization, dysfunction, and perspective. Mayo Clin. Proc. 1993, 68, 988–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M. Heart rate variability: Standards of measurement, physiological interpretation, and clinical use: Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology. Eur. Heart J. 1996, 17, 354–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berntson, G.G.; Bigger, J.T.; Eckberg, D.L.; Grossman, P.; Kaufmann, P.G.; Malik, M.; Nagaraja, H.N.; Porges, S.W.; Saul, J.P.; Stone, P.H.; et al. Heart rate variability: Origins, methods, and interpretive caveats. Psychophysiology 1997, 34, 623–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laborde, S.; Mosley, E.; Thayer, J.F. Heart Rate Variability and Cardiac Vagal Tone in Psychophysiological Research—Recommendations for Experiment Planning, Data Analysis, and Data Reporting. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- You, M.; Laborde, S.; Salvotti, C.; Zammit, N.; Mosley, E.; Dosseville, F. Influence of a Single Slow-Paced Breathing Session on Cardiac Vagal Activity in Athletes. Int. J. Mental Health Addict. 2021, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laborde, S.; Hosang, T.; Mosley, E.; Dosseville, F. Influence of a 30-day slow paced breathing intervention compared to social media use on subjective sleep quality and cardiac vagal activity. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Laborde, S.; Allen, M.S.; Borges, U.; Iskra, M.; Zammit, N.; You, M.; Hosang, T.; Mosley, E.; Dosseville, F. Psychophysiological effects of slow-paced breathing at six cycles per minute with or without heart rate variability biofeedback. Psychophysiology 2021, e13952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, M.; Andrasik, F. Biofeedback, Fourth Edition: A Practitioner’s Guide; The Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Shaffer, F.; Meehan, Z.M. A practical guide to resonance frequency assessment for heart rate variability biofeedback. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, B.; Friedman, B.H. Positive emotion reduces dyspnea during slow paced breathing. Psychophysiology 2012, 49, 690–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.S.; Lehrer, P.M. The effects of specific respiratory rates on heart rate and heart rate variability. Appl. Psychophysiol. Biofeedback 2003, 28, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, M.; Laborde, S.; Zammit, N.; Iskra, M.; Borges, U.; Dosseville, F.; Vaughan, R.S. Emotional Intelligence Training: Influence of a Brief Slow-Paced Breathing Exercise on Psychophysiological Variables Linked to Emotion Regulation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, S.; Jendreizik, L.; Ettinger, U.; Laborde, S. Keeping the pace: The effect of slow-paced breathing on error monitoring. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2019, 146, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laborde, S.; Allen, M.S.; Borges, U.; Hosang, T.J.; Furley, P.; Mosley, E.; Dosseville, F. The Influence of Slow-Paced Breathing on Executive Function. J. Psychophysiol. 2021, 35, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, R.; Outhred, T.; Heathers, J.A.; Quintana, D.S.; Kemp, A.H. Matter over mind: A randomised-controlled trial of single-session biofeedback training on performance anxiety and heart rate variability in musicians. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintana, D.S.; Heathers, J.A. Considerations in the assessment of heart rate variability in biobehavioral research. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Buchner, A.; Lang, A.G. Statistical power analyses using G*Power 3.1: Tests for correlation and regression analyses. Behav. Res. Methods 2009, 41, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Penttila, J.; Helminen, A.; Jartti, T.; Kuusela, T.; Huikuri, H.V.; Tulppo, M.P.; Coffeng, R.; Scheinin, H. Time domain, geometrical and frequency domain analysis of cardiac vagal outflow: Effects of various respiratory patterns. Clin. Physiol. 2001, 21, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarvainen, M.P.; Niskanen, J.P.; Lipponen, J.A.; Ranta-Aho, P.O.; Karjalainen, P.A. Kubios HRV—Heart rate variability analysis software. Comput. Methods Progr. Biomed. 2014, 113, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laborde, S.; Allen, M.S.; Gohring, N.; Dosseville, F. The effect of slow-paced breathing on stress management in adolescents with intellectual disability. J. Intellect. Disabil. Res. 2017, 61, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorig, T. The respiratory system. In The Handbook of Psychophysiology; Cacioppo, J.T., Tassinary, L.G., Berntson, G.G., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 231–244. [Google Scholar]
- Zelano, C.; Jiang, H.; Zhou, G.; Arora, N.; Schuele, S.; Rosenow, J.; Gottfried, J.A. Nasal Respiration Entrains Human Limbic Oscillations and Modulates Cognitive Function. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 12448–12467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Biskamp, J.; Bartos, M.; Sauer, J.F. Organization of prefrontal network activity by respiration-related oscillations. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maric, V.; Ramanathan, D.; Mishra, J. Respiratory regulation & interactions with neuro-cognitive circuitry. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2020, 112, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagevik Olsen, M.; Lannefors, L.; Westerdahl, E. Positive expiratory pressure—Common clinical applications and physiological effects. Respir. Med. 2015, 109, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Strauss-Blasche, G.; Moser, M.; Voica, M.; McLeod, D.R.; Klammer, N.; Marktl, W. Relative timing of inspiration and expiration affects respiratory sinus arrhythmia. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2000, 27, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laborde, S.; Lentes, T.; Hosang, T.J.; Borges, U.; Mosley, E.; Dosseville, F. Influence of slow-paced breathing on inhibition after physical exertion. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Urbaniak, G.C.; Plous, S. Research Randomizer; Version 4.0; Social Psychology Network: Middletown, CT, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Van Eekelen, A.P.; Houtveen, J.H.; Kerkhof, G.A. Circadian variation in cardiac autonomic activity: Reactivity measurements to different types of stressors. Chronobiol. Int. 2004, 21, 107–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehrer, P.M.; Kaur, K.; Sharma, A.; Shah, K.; Huseby, R.; Bhavsar, J.; Zhang, Y. Heart Rate Variability Biofeedback Improves Emotional and Physical Health and Performance: A Systematic Review and Meta Analysis. Appl. Psychophysiol. Biofeedback 2020, 45, 109–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strohmaier, S. The Relationship Between Doses of Mindfulness-Based Programs and Depression, Anxiety, Stress, and Mindfulness: A Dose-Response Meta-Regression of Randomized Controlled Trials. Mindfulness 2020, 11, 1315–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, C.H.; Medeiros, R.A.; Pinheiro, D.G.; Marinho Mde, J. Spontaneous respiratory modulation improves cardiovascular control in essential hypertension. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2007, 88, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tharion, E.; Samuel, P.; Rajalakshmi, R.; Gnanasenthil, G.; Subramanian, R.K. Influence of deep breathing exercise on spontaneous respiratory rate and heart rate variability: A randomised controlled trial in healthy subjects. Indian J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2012, 56, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Narkiewicz, K.; van de Borne, P.; Montano, N.; Hering, D.; Kara, T.; Somers, V.K. Sympathetic neural outflow and chemoreflex sensitivity are related to spontaneous breathing rate in normal men. Hypertension 2006, 47, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shea, S.A. Behavioural and arousal-related influences on breathing in humans. Exp. Physiol. 1996, 81, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tipton, M.J.; Harper, A.; Paton, J.F.R.; Costello, J.T. The human ventilatory response to stress: Rate or depth? J. Physiol. 2017, 595, 5729–5752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homma, I.; Masaoka, Y. Breathing rhythms and emotions. Exp. Physiol. 2008, 93, 1011–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grassmann, M.; Vlemincx, E.; von Leupoldt, A.; Mittelstadt, J.M.; van den Bergh, O. Respiratory Changes in Response to Cognitive Load: A Systematic Review. Neural Plast. 2016, 2016, 8146809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nicolo, A.; Massaroni, C.; Schena, E.; Sacchetti, M. The Importance of Respiratory Rate Monitoring: From Healthcare to Sport and Exercise. Sensors 2020, 20, 6396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, M.E.B.; Scott, A.B.; Boggero, I.A.; Carlson, C.R. Inclusion of a rest period in diaphragmatic breathing increases high frequency heart rate variability: Implications for behavioral therapy. Psychophysiology 2017, 54, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kromenacker, B.W.; Sanova, A.A.; Marcus, F.I.; Allen, J.J.B.; Lane, R.D. Vagal Mediation of Low-Frequency Heart Rate Variability During Slow Yogic Breathing. Psychosom. Med. 2018, 80, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| PRE | DURING | POST | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | SD | M | SD | M | SD | ||
| RMSSD | Control | 60.58 | 38.55 | 58.56 | 35.87 | 57.52 | 36.07 |
| 5-MIN | 56.82 | 32.10 | 82.68 | 35.37 | 60.64 | 30.75 | |
| 10-MIN | 55.61 | 34.02 | 83.35 | 37.52 | 60.34 | 35.47 | |
| 15-MIN | 58.15 | 35.04 | 86.13 | 37.14 | 63.24 | 32.78 | |
| 20-MIN | 57.91 | 34.79 | 83.95 | 37.64 | 62.33 | 34.52 | |
| Control (Log) | 1.71 | 0.25 | 1.70 | 0.24 | 1.68 | 0.27 | |
| 5-MIN (Log) | 1.69 | 0.24 | 1.88 | 0.19 | 1.73 | 0.22 | |
| 10-MIN (Log) | 1.67 | 0.25 | 1.88 | 0.19 | 1.71 | 0.25 | |
| 15-MIN (Log) | 1.69 | 0.26 | 1.90 | 0.19 | 1.74 | 0.23 | |
| 20-MIN (Log) | 1.69 | 0.25 | 1.88 | 0.19 | 1.73 | 0.24 | |
| Respiratory Frequency | Control | 17.09 | 2.61 | 16.90 | 2.73 | 17.02 | 2.53 |
| 5-MIN | 16.78 | 3.03 | 6.58 | 0.28 | 14.18 | 3.02 | |
| 10-MIN | 16.71 | 2.93 | 6.57 | 0.27 | 13.16 | 2.70 | |
| 15-MIN | 17.05 | 2.67 | 6.53 | 0.30 | 12.16 | 2.57 | |
| 20-MIN | 16.91 | 2.78 | 6.50 | 0.28 | 11.14 | 2.30 | |
| Control (Log) | 1.23 | 0.07 | 1.22 | 0.08 | 1.23 | 0.07 | |
| 5-MIN (Log) | 1.22 | 0.08 | 0.82 | 0.02 | 1.14 | 0.10 | |
| 10-MIN (Log) | 1.22 | 0.08 | 0.82 | 0.02 | 1.11 | 0.09 | |
| 15-MIN (Log) | 1.23 | 0.07 | 0.81 | 0.02 | 1.08 | 0.09 | |
| 20-MIN (Log) | 1.22 | 0.08 | 0.81 | 0.02 | 1.04 | 0.09 | |
| Heart Rate | Control | 66.18 | 10.61 | 67.62 | 10.32 | 67.39 | 10.36 |
| 5-MIN | 67.70 | 10.44 | 69.13 | 7.90 | 67.88 | 9.21 | |
| 10-MIN | 66.18 | 10.33 | 67.76 | 7.58 | 67.70 | 10.33 | |
| 15-MIN | 65.41 | 10.98 | 67.78 | 8.37 | 68.02 | 10.05 | |
| 20-MIN | 66.79 | 10.46 | 67.61 | 8.65 | 67.57 | 10.40 | |
| Control (Log) | 1.82 | 0.07 | 1.83 | 0.07 | 1.82 | 0.07 | |
| 5-MIN (Log) | 1.83 | 0.07 | 1.84 | 0.05 | 1.83 | 0.06 | |
| 10-MIN (Log) | 1.82 | 0.07 | 1.83 | 0.05 | 1.83 | 0.07 | |
| 15-MIN (Log) | 1.81 | 0.07 | 1.83 | 0.06 | 1.83 | 0.06 | |
| 20-MIN (Log) | 1.82 | 0.07 | 1.83 | 0.06 | 1.82 | 0.07 | |
| Difference PRE/DURING | Difference PRE/POST | Difference DURING/POST | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cohen’s d | p | Cohen’s d | p | Cohen’s d | p | ||
| RMSSD | Control | 0.167 | 0.204 | 0.292 | 0.029 | 0.203 | 0.124 |
| 5-MIN | −1.305 | <0.001 | −0.363 | 0.007 | 1.349 | <0.001 | |
| 10-MIN | −1.445 | <0.001 | −0.284 | 0.033 | 1.262 | <0.001 | |
| 15-MIN | −1.219 | <0.001 | −0.411 | 0.003 | 1.062 | <0.001 | |
| 20-MIN | −1.350 | <0.001 | −0.383 | 0.005 | 1.104 | <0.001 | |
| Respiratory frequency | Control | 0.185 | 0.162 | 0.024 | 0.857 | −0.148 | 0.260 |
| 5-MIN | 4.696 | <0.001 | 1.308 | <0.001 | −3.317 | <0.001 | |
| 10-MIN | 4.710 | <0.001 | 1.745 | <0.001 | −3.147 | <0.001 | |
| 15-MIN | 5.459 | <0.001 | 2.014 | <0.001 | −2.774 | <0.001 | |
| 20-MIN | 4.987 | <0.001 | 2.963 | <0.001 | −2.468 | <0.001 | |
| Heart Rate | Control | −0.199 | 0.131 | −0.179 | 0.174 | 0.025 | 0.846 |
| 5-MIN | −0.245 | 0.065 | −0.049 | 0.711 | 0.196 | 0.138 | |
| 10-MIN | −0.217 | 0.101 | −0.151 | 0.250 | 0.062 | 0.634 | |
| 15-MIN | −0.269 | 0.043 | −0.389 | 0.004 | −0.003 | 0.984 | |
| 20-MIN | −0.126 | 0.338 | −0.098 | 0.452 | 0.037 | 0.776 | |
| PRE | DURING | POST | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cohen’s d | p | Cohen’s d | p | Cohen’s d | p | ||
| RMSSD | Control—5-MIN | 0.152 | 0.249 | −1.218 | <0.001 | −0.370 | 0.006 |
| Control—10-MIN | 0.248 | 0.062 | −1.137 | <0.001 | −0.194 | 0.142 | |
| Control—15-MIN | 0.149 | 0.256 | −1.255 | <0.001 | −0.402 | 0.003 | |
| Control—20-MIN | 0.127 | 0.335 | −1.173 | <0.001 | −0.376 | 0.005 | |
| 5-MIN—10-MIN | 0.113 | 0.389 | −0.014 | 0.915 | 0.179 | 0.173 | |
| 5-MIN—15-MIN | 0.001 | 0.992 | −0.221 | 0.095 | −0.143 | 0.278 | |
| 5-MIN—20-MIN | −0.030 | 0.818 | −0.058 | 0.655 | −0.037 | 0.780 | |
| 10-MIN—15-MIN | −0.141 | 0.282 | −0.211 | 0.110 | −0.306 | 0.022 | |
| 10-MIN—20-MIN | −0.175 | 0.185 | −0.035 | 0.790 | −0.247 | 0.063 | |
| 15-MIN—20-MIN | −0.037 | 0.778 | 0.202 | 0.125 | 0.108 | 0.411 | |
| Respiratory frequency | Control—5-MIN | 0.217 | 0.102 | 5.456 | <0.001 | 1.352 | <0.001 |
| Control—10-MIN | 0.294 | 0.028 | 5.342 | <0.001 | 1.733 | <0.001 | |
| Control—15-MIN | 0.032 | 0.804 | 5.160 | <0.001 | 2.102 | <0.001 | |
| Control—20-MIN | 0.135 | 0.304 | 5.190 | <0.001 | 2.836 | <0.001 | |
| 5-MIN—10-MIN | 0.046 | 0.723 | 0.047 | 0.722 | 0.897 | <0.001 | |
| 5-MIN—15-MIN | −0.188 | 0.155 | 0.170 | 0.196 | 1.528 | <0.001 | |
| 5-MIN—20-MIN | −0.126 | 0.337 | 0.274 | 0.040 | 1.924 | <0.001 | |
| 10-MIN—15-MIN | −0.253 | 0.057 | 0.152 | 0.247 | 0.943 | <0.001 | |
| 10-MIN—20-MIN | −0.204 | 0.122 | 0.298 | 0.026 | 1.604 | <0.001 | |
| 15-MIN—20-MIN | 0.111 | 0.398 | 0.114 | 0.384 | 1.069 | <0.001 | |
| Heart Rate | Control—5-MIN | −0.195 | 0.139 | −0.242 | 0.068 | −0.067 | 0.610 |
| Control—10-MIN | −0.009 | 0.942 | −0.057 | 0.666 | −0.009 | 0.945 | |
| Control—15-MIN | 0.103 | 0.431 | −0.041 | 0.755 | −0.070 | 0.594 | |
| Control—20-MIN | −0.084 | 0.522 | −0.029 | 0.827 | −0.008 | 0.951 | |
| 5-MIN—10-MIN | 0.163 | 0.216 | 0.239 | 0.071 | 0.058 | 0.657 | |
| 5-MIN—15-MIN | 0.239 | 0.071 | 0.189 | 0.153 | −0.017 | 0.897 | |
| 5-MIN—20-MIN | 0.102 | 0.436 | 0.267 | 0.045 | 0.047 | 0.717 | |
| 10-MIN—15-MIN | 0.113 | 0.389 | 0.009 | 0.948 | −0.054 | 0.679 | |
| 10-MIN—20-MIN | −0.085 | 0.516 | 0.047 | 0.719 | <0.001 | 1.000 | |
| 15-MIN—20-MIN | −0.210 | 0.112 | 0.027 | 0.839 | 0.063 | 0.632 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
You, M.; Laborde, S.; Zammit, N.; Iskra, M.; Borges, U.; Dosseville, F. Single Slow-Paced Breathing Session at Six Cycles per Minute: Investigation of Dose-Response Relationship on Cardiac Vagal Activity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12478. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182312478
You M, Laborde S, Zammit N, Iskra M, Borges U, Dosseville F. Single Slow-Paced Breathing Session at Six Cycles per Minute: Investigation of Dose-Response Relationship on Cardiac Vagal Activity. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(23):12478. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182312478
Chicago/Turabian StyleYou, Min, Sylvain Laborde, Nina Zammit, Maša Iskra, Uirassu Borges, and Fabrice Dosseville. 2021. "Single Slow-Paced Breathing Session at Six Cycles per Minute: Investigation of Dose-Response Relationship on Cardiac Vagal Activity" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 23: 12478. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182312478
APA StyleYou, M., Laborde, S., Zammit, N., Iskra, M., Borges, U., & Dosseville, F. (2021). Single Slow-Paced Breathing Session at Six Cycles per Minute: Investigation of Dose-Response Relationship on Cardiac Vagal Activity. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(23), 12478. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182312478






