Human Body Burden of Heavy Metals and Health Consequences of Pb Exposure in Guiyu, an E-Waste Recycling Town in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Review Methodology
3. Body Burden of HMs in Guiyu
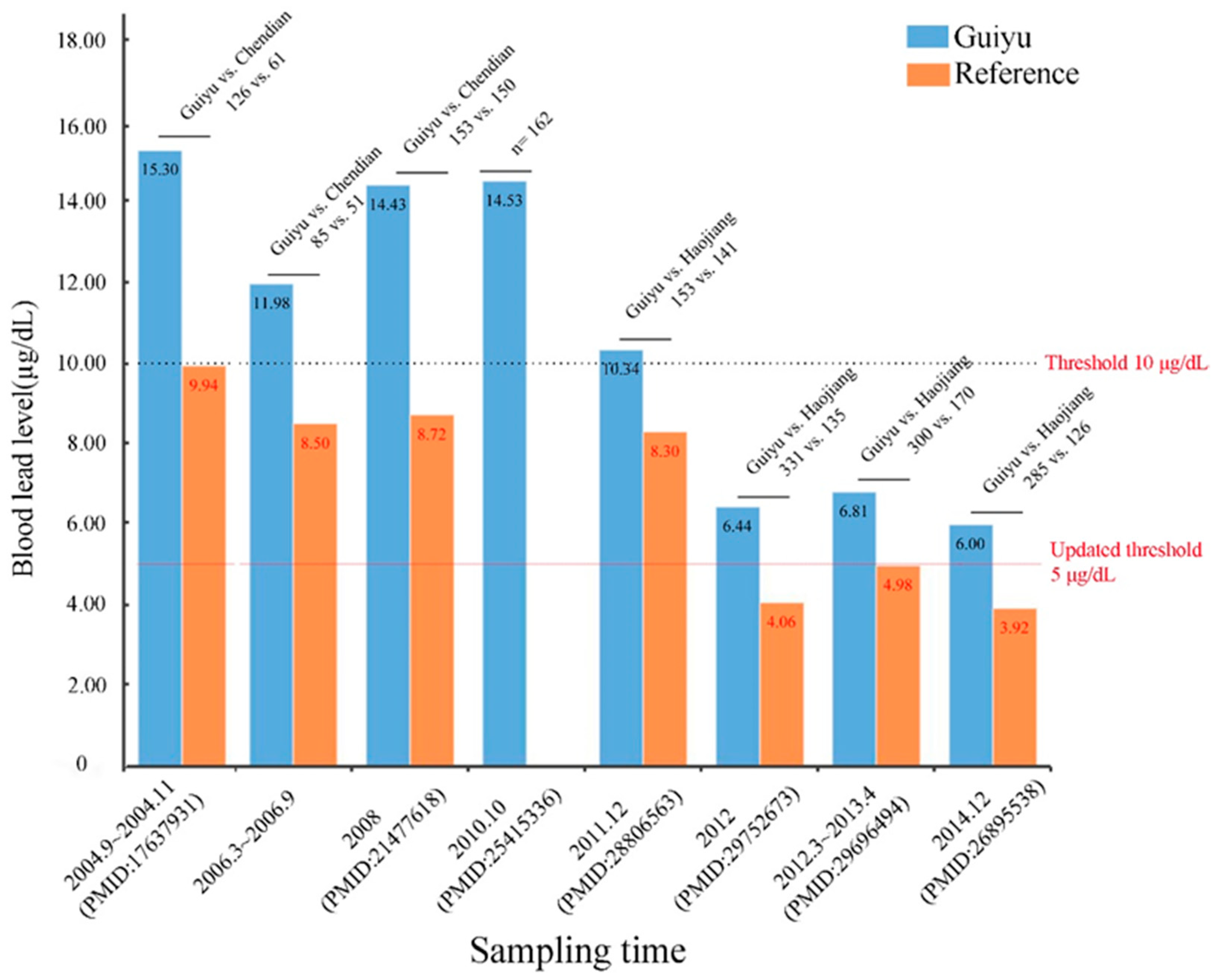
3.1. Total Blood
3.2. Umbilical Cord Blood (UCB)
3.3. Placenta
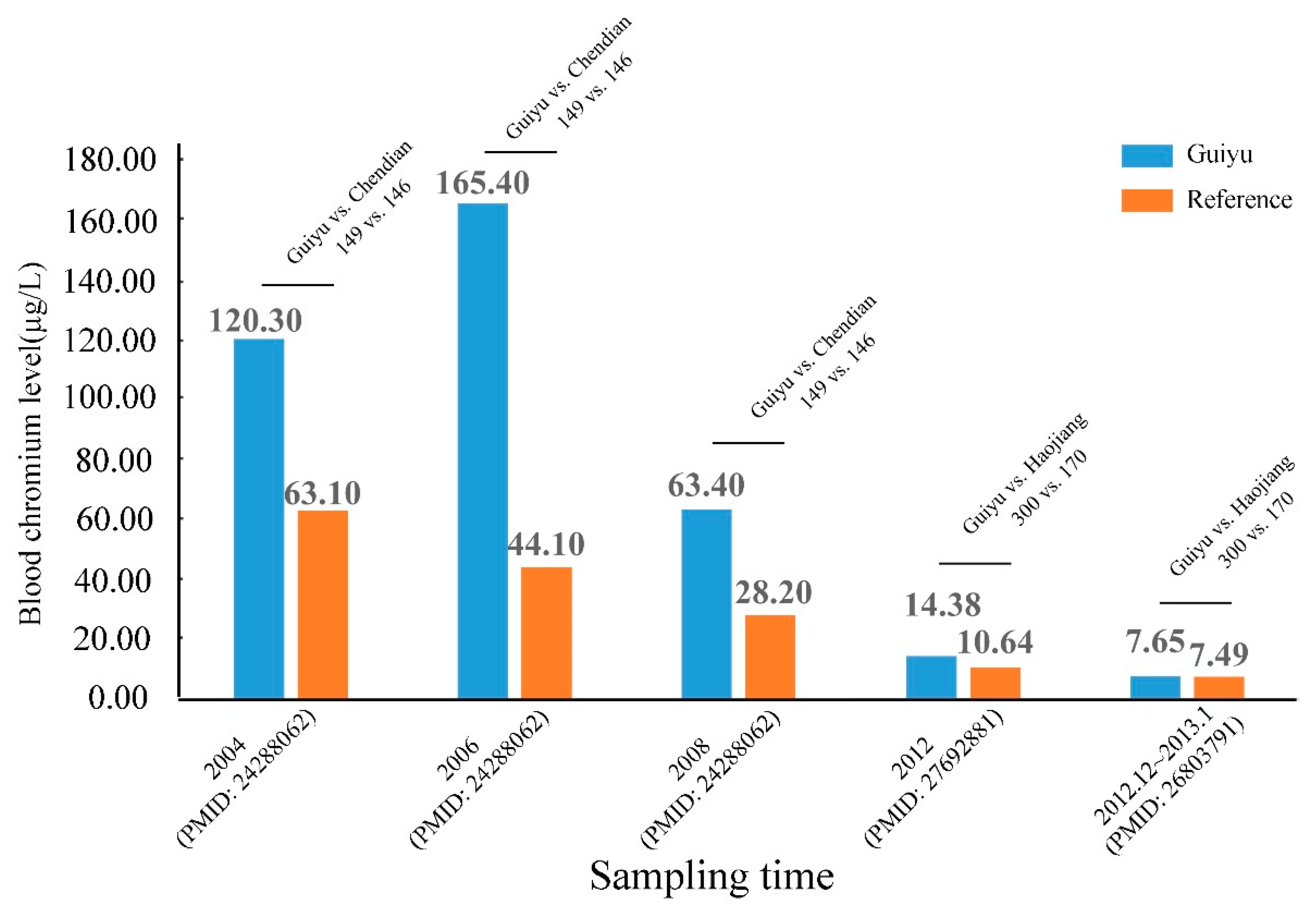
3.4. Erythrocyte
3.5. Urine
3.6. Hair
3.7. Meconium
4. Health Effects of Pb Exposure in Guiyu
4.1. Nervous System
4.2. Cardiovascular System
4.3. Immune System
4.4. Hematologic System
4.5. Growth Effects
4.6. Adverse Birth Outcomes
4.7. Chromosome and DNA Damage
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, J.; Lopez, B.N.; Liu, L.; Zhao, N.; Yu, K.; Zheng, L. Regional or global WEEE recycling. Where to go? Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 923–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breivik, K.; Armitage, J.M.; Wania, F.; Jones, K.C. Tracking the global generation and exports of e-waste. Do existing estimates add up? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 8735–8743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, X.; Gong, R.; Chen, W.Q.; Li, J. Uncovering the Recycling Potential of “New” WEEE in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 1347–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suciu, N.; Capri, E.; Trevisan, M.; Tanaka, T.; Tien, H.; Heise, S.; Schuhmacher, M.; Nadal, M.; Rovira, J.; Seguí, X.; et al. Human and Environmental Impact Produced by E-Waste Releases at Guiyu Region (China). In Global Risk-Based Management of Chemical Additives II; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 349–384. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Q.; Xu, X.; Dai, Q.; Ye, K.; Wang, C.; Huo, X. Air pollution and body burden of persistent organic pollutants at an electronic waste recycling area of China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2018, 41, 93–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Children’s Health and the Environment: A Global Perspective (A Resource Manual for the Health Sector). Adolescence 2009, 44, 248–249.
- Wong, C.S.; Duzgoren-Aydin, N.S.; Aydin, A.; Wong, M.H. Evidence of excessive releases of metals from primitive e-waste processing in Guiyu, China. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 148, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.H.; Wu, S.C.; Deng, W.J.; Yu, X.Z.; Luo, Q.; Leung, A.O.; Wong, C.S.; Luksemburg, W.J.; Wong, A.S. Export of toxic chemicals—A review of the case of uncontrolled electronic-waste recycling. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 149, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Centers for Disease Control (CDC). Preventing lead poisoning in young children. Kans. Med. 1992, 93, 358–359. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, L.; Wu, K.; Li, Y.; Qi, Z.; Han, D.; Zhang, B.; Gu, C.; Chen, G.; Liu, J.; Chen, S.; et al. Blood lead and cadmium levels and relevant factors among children from an e-waste recycling town in China. Environ. Res. 2008, 108, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xu, X.; Wu, K.; Piao, Z.; Huang, J.; Guo, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, A.; Huo, X. Association between lead exposure from electronic waste recycling and child temperament alterations. Neurotoxicology 2011, 32, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Liu, J.; Huang, C.; Lu, F.; Chiung, Y.M.; Huo, X. Association of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and lead co-exposure with child physical growth and development in an e-waste recycling town. Chemosphere 2015, 139, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Liu, J.; Zeng, X.; Lu, F.; Chen, A.; Huo, X. Elevated serum polybrominated diphenyl ethers and alteration of thyroid hormones in children from Guiyu, China. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Sun, D.; Cao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Huo, X. Alteration of the number and percentage of innate immune cells in preschool children from an e-waste recycling area. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 145, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Xu, X.; Yekeen, T.A.; Lin, K.; Li, W.; Huo, X. Assessment of association between the dopamine D2 receptor (DRD2) polymorphism and neurodevelopment of children exposed to lead. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 22, 1786–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, B.; Lin, K.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Huo, X. Thyroid disruption and reduced mental development in children from an informal e-waste recycling area: A mediation analysis. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, X.; Peng, L.; Xu, X.; Zheng, L.; Qiu, B.; Qi, Z.; Zhang, B.; Han, D.; Piao, Z. Elevated blood lead levels of children in Guiyu, an electronic waste recycling town in China. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 1113–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Huo, X.; Zheng, L.; Li, Y. Investigation on blood lead and intelligence levels of children in electronic waste recycling area. J. Shantou Univ. Med. Coll. 2007, 20, 170–175. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Peng, L.; Li, W.; Qiu, B.; Huo, X. Investigation of blood lead level of children aged 1~6 in electronic waste disposing district. J. Environ. Health 2006, 23, 58–60. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Peng, L.; Huo, X.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Qiu, B. Effects of electronic waste recycling disposing contamination on children’s blood lead level. J. Shantou Univ. Med. Coll. 2005, 18, 48–50. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, X.; Xu, X.; Zheng, X.; Reponen, T.; Chen, A.; Huo, X. Heavy metals in PM 2.5 and in blood, and children’s respiratory symptoms and asthma from an e-waste recycling area. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 210, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y. Pollution: Centralized pilot for e-waste processing. Nature 2016, 538, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cao, J.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Hylkema, M.N.; Huo, X. Increased memory T cell populations in Pb-exposed children from an e-waste-recycling area. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616–617, 988–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Huo, X.; Cao, J.; Yang, T.; Xu, L.; Xu, X. Elevated lead levels and adverse effects on natural killer cells in children from an electronic waste recycling area. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 213, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellinger, D.C. Lead. Pediatrics 2004, 113 (Suppl. 4), 1016–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betts, K.S. CDC updates guidelines for children’s lead exposure. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, a268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.; Huo, X.; Liu, D.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X. S100beta in heavy metal-related child attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder in an informal e-waste recycling area. Neurotoxicology 2014, 45, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Xu, X.; Zeng, X.; Xu, L.; Zeng, Z.; Huo, X. Decreased vaccine antibody titers following exposure to multiple metals and metalloids in e-waste-exposed preschool children. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 220 Pt A, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.; Xu, X.; Boezen, H.M.; Vonk, J.M.; Wu, W.; Huo, X. Decreased lung function with mediation of blood parameters linked to e-waste lead and cadmium exposure in preschool children. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 230, 838–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Yang, H.; Liao, W.; Qiu, S.; Huo, X.; Xu, X. Study on blood chromium levels and behavior effects of children in electronic waste recycling area. J. Shantou Univ. Med. Coll. 2011, 24, 26–29. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Yekeen, T.A.; Liu, J.; Zhuang, B.; Li, W.; Huo, X. Chromium exposure among children from an electronic waste recycling town of China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 22, 1778–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.A.; Kozlovsky, A.S. Chromium intake, absorption and excretion of subjects consuming self-selected diets. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1985, 41, 1177–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomiyama, H.; Yotoriyama, M.; Nomiyama, K. Normal chromium levels in urine and blood of Japanese subjects determined by direct flameless atomic absorption spectrophotometry, and valency of chromium in urine after exposure to hexavalent chromium. Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. J. 1980, 41, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.; Xu, X.; Qin, Q.; Ye, K.; Wu, W.; Huo, X. Heavy metal exposure has adverse effects on the growth and development of preschool children. Environ. Geochem. Health 2018, 41, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, G.; Xu, X.; Li, B.; Wu, K.; Yekeen, T.A.; Huo, X. Association between lung function in school children and exposure to three transition metals from an e-waste recycling area. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2013, 23, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Liu, R.; Dietrich, K.; Reponen, T.; Ho, S.M.; Xie, C.; Sucharew, H.; et al. Metal concentrations in pregnant women and neonates from informal electronic waste recycling. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2018, 29, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, X.; Liu, J.; Wu, K.; Gu, C.; Shao, G.; Chen, S.; Chen, G.; Huo, X. The hazard of chromium exposure to neonates in Guiyu of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 403, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, W.; Huang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Wu, K. Associations of neonatal lead, cadmium, chromium and nickel co-exposure with DNA oxidative damage in an electronic waste recycling town. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 472, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Huo, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hylkema, M.N.; Wu, Y.; Xu, X. Differential DNA methylation in newborns with maternal exposure to heavy metals from an e-waste recycling area. Environ. Res. 2019, 171, 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Yang, H.; Chen, A.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, K.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Huo, X. Birth outcomes related to informal e-waste recycling in Guiyu, China. Reprod. Toxicol. 2012, 33, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, X.; Wu, K.; Chen, G.; Liu, J.; Chen, S.; Gu, C.; Zhang, B.; Zheng, L.; Zheng, M.; et al. Monitoring of lead load and its effect on neonatal behavioral neurological assessment scores in Guiyu, an electronic waste recycling town in China. J. Environ. Monit. 2008, 10, 1233–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, X.; Peng, L.; Qiu, B.; Zheng, L.; Yekeen, T.A.; Xu, X. ALAD genotypes and blood lead levels of neonates and children from e-waste exposure in Guiyu, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2014, 21, 6744–6750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Huo, X.; Liu, J.; Peng, L.; Li, W.; Xu, X. Assessment of cadmium exposure for neonates in Guiyu, an electronic waste pollution site of China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 177, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, B.; Lu, F.; Fu, Y.; LIu, Y.; Huo, X.; Xu, X. Analysis of prenatal mercury exposure in neonates. J. Shantou Univ. Med. Coll. 2015, 28, 10–12. [Google Scholar]
- Gude, N.M.; Roberts, C.T.; Kalionis, B.; King, R.G. Growth and function of the normal human placenta. Thromb. Res. 2004, 114, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llanos, M.N.; Ronco, A.M. Fetal growth restriction is related to placental levels of cadmium, lead and arsenic but not with antioxidant activities. Reprod. Toxicol. 2009, 27, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myllynen, P.; Pasanen, M.; Pelkonen, O. Human placenta: A human organ for developmental toxicology research and biomonitoring. Placenta 2005, 26, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban-Vasallo, M.D.; Aragones, N.; Pollan, M.; Lopez-Abente, G.; Perez-Gomez, B. Mercury, cadmium, and lead levels in human placenta: A systematic review. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 1369–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, S.; Huo, X.; Zhang, Q.; Fan, X.; Du, L.; Xu, X.; Qiu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gu, J. Short placental telomere was associated with cadmium pollution in an electronic waste recycling town in China. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Y.; Huo, X.; Li, Y.; Wu, K.; Liu, J.; Huang, J.; Zheng, G.; Xiao, Q.; Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; et al. Monitoring of lead, cadmium, chromium and nickel in placenta from an e-waste recycling town in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 3113–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhou, T.; Xu, X.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhu, M.; Li, W.; Yi, D.; Huo, X. Downregulation of placental S100P is associated with cadmium exposure in Guiyu, an e-waste recycling town in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 410-411, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Huo, X.; Wu, K.-s.; Liu, J.-x.; Ban, H.; Xu, X.-j. Placental cadmium concentration and the levels of metallothionein expression in an electronic waste environmental polluted site. Carcinog. Teratog. Mutagen. 2010, 2, 010. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Chiung, Y.M.; Lu, F.; Qiu, S.; Ji, M.; Huo, X. Associations of cadmium, bisphenol A and polychlorinated biphenyl co-exposure in utero with placental gene expression and neonatal outcomes. Reprod. Toxicol. 2015, 52, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, S. Lead and Cadmium Occurrence in Placenta and Associated Factors in Guiyu, China. QSci. Proc. 2012, 2012, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Huo, X.; Liu, J.; LI, B.; Akangbe, Y.T.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X. Association between Prenatal Lead and Cadmium Exposure from Electronic Waste Recycling and the Development of Neonate. J. Shantou Univ. Med. Coll. 2012, 25, 138–140. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Ge, J.; Huo, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lau, A.T.Y.; Xu, X. Differential proteomic expression of human placenta and fetal development following e-waste lead and cadmium exposure in utero. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 550, 1163–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.; Huo, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, T.; Li, M.; Xu, X. Elevated lead levels and changes in blood morphology and erythrocyte CR1 in preschool children from an e-waste area. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 592, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Huo, X.; Lin, P.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Xu, X. Association between blood erythrocyte lead concentrations and hemoglobin levels in preschool children. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 22, 9233–9240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, X.; Dai, Y.; Yang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Xu, X. Decreased erythrocyte CD44 and CD58 expression link e-waste Pb toxicity to changes in erythrocyte immunity in preschool children. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 664, 690–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Shih, R.; Rothenberg, S.; Schwartz, B.S. The epidemiology of lead toxicity in adults: Measuring dose and consideration of other methodologic issues. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarup, L.; Akesson, A. Current status of cadmium as an environmental health problem. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 238, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huo, X.; Xu, L.; Wei, X.; Wu, W.; Wu, X.; Xu, X. Hearing loss in children with e-waste lead and cadmium exposure. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 624, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Chen, A.; Davuljigari, C.B.; Zheng, X.; Kim, S.S.; Dietrich, K.N.; Ho, S.M.; Reponen, T.; Huo, X. Maternal urinary cadmium levels during pregnancy associated with risk of sex-dependent birth outcomes from an e-waste pollution site in China. Reprod. Toxicol. 2018, 75, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Huo, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, Q.; Xu, X. Hearing loss risk and DNA methylation signatures in preschool children following lead and cadmium exposure from an electronic waste recycling area. Chemosphere 2020, 246, 125829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, J.L.; Batista, B.L.; Nunes, J.A.; Passos, C.J.; Barbosa, F., Jr. Evaluation of the use of human hair for biomonitoring the deficiency of essential and exposure to toxic elements. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 405, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, W.; Chenb, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, G.; Luo, J.; Wu, K. Hair mercury concentrations and associated factors in an electronic waste recycling area, Guiyu, China. Environ. Res. 2014, 128, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Ni, W.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Wu, K. Levels and risk factors of antimony contamination in human hair from an electronic waste recycling area, Guiyu, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 7112–7119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, X.; Liu, J.; Zheng, L.; Chen, G.; Chen, S.; Huo, X. Determination of Meconium Lead Level of Newborn by Graphite Furnace Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. Spectrosc. Spectral Anal. 2008, 28, 447–449. [Google Scholar]
- Berglund, M.; Akesson, A.; Bjellerup, P.; Vahter, M. Metal-bone interactions. Toxicol. Lett. 2000, 112–113, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Huo, X.; Xu, L.; Cheng, Z.; Cong, X.; Lu, X.; Xu, X. Elevated lead levels from e-waste exposure are linked to decreased olfactory memory in children. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231 Pt 1, 1112–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, R.; Peng, Z.; Chen, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, H.; Cai, Z.; Qin, S.; Liu, B.; Huo, X.; et al. Effects of lead exposure on attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children from an e-waste recycling area. Beijing Med. J. 2013, 35, 249–252. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Huo, X.; Ho, G.; Chen, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, T.; Ma, L. Attention-deficit/hyperactivity symptoms in preschool children from an e-waste recycling town: Assessment by the parent report derived from DSM-IV. BMC Pediatr. 2015, 15, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, H.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Cong, X.; Lu, X.; Huo, X. Elevated lead levels from e-waste exposure are linked to sensory integration difficulties in preschool children. Neurotoxicology 2019, 71, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Miller, G.; Ding, G.; Lou, X.; Cai, D.; Chen, Z.; Meng, J.; Tang, J.; Chu, C.; Mo, Z.; et al. Health risk assessment of lead for children in tinfoil manufacturing and e-waste recycling areas of Zhejiang Province, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 426, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, N.; Wang, X.; Weisskopf, M.G.; Sparrow, D.; Schwartz, J.; Hu, H.; Park, S.K. Lead-Related Genetic Loci, Cumulative Lead Exposure and Incident Coronary Heart Disease: The Normative Aging Study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prokopowicz, A.; Sobczak, A.; Szula-Chraplewska, M.; Zaciera, M.; Kurek, J.; Szoltysek-Boldys, I. Effect of occupational exposure to lead on new risk factors for cardiovascular diseases. Occup. Environ. Med. 2017, 74, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Huo, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X. Cardiovascular endothelial inflammation by chronic coexposure to lead (Pb) and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from preschool children in an e-waste recycling area. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 246, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Huo, X. Elevated inflammatory Lp-PLA2 and IL-6 link e-waste Pb toxicity to cardiovascular risk factors in preschool children. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Huo, X.; Zhang, S.; Cheng, Z.; Huang, Y.; Xu, X. Relations of blood lead levels to echocardiographic left ventricular structure and function in preschool children. Chemosphere 2021, 268, 128793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Xu, X.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Huo, X. Considerable decrease of antibody titers against measles, mumps, and rubella in preschool children from an e-waste recycling area. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 760–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Guo, P.; Fu, T.; Dai, Y.; Lin, S.L.; Huo, X. Decreased blood hepatitis B surface antibody levels linked to e-waste lead exposure in preschool children. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 298, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Zhang, J.; Huang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Huo, X. Effect of Lead and Cadmium Exposure on the Levels of Innate Immune Cells in Preschool Children. J. Shantou Univ. Med. Coll. 2012, 25, 193–195. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Huo, X.; Lu, X.; Zeng, Z.; Faas, M.M.; Xu, X. Exposure to multiple heavy metals associate with aberrant immune homeostasis and inflammatory activation in preschool children. Chemosphere 2020, 257, 127257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Xu, X.; Lu, F.; Wang, Q.; Zeng, Z.; Huo, X. High serum IgG subclass concentrations in children with e-waste Pb and Cd exposure. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 764, 142806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, X.; Zeng, Z.; Lin, X.; Qin, Q.; Huo, X. Blood lead and cadmium levels associated with hematological and hepatic functions in patients from an e-waste-polluted area. Chemosphere 2018, 220, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Huo, X.; Huang, J.; Zheng, G.; Xu, X. Relationship between Blood Cadmium and Red Blood Cell Parameters in Children aged 3~ 7 Years in Guiyu Area of Guangdong Province. J. Shantou Univ. Med. Coll. 2010, 23, 100–102. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Huang, P.; Zhang, R.; Feng, X.; Tang, Q.; Liu, S.; Wen, F.; Zeng, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, T.; et al. Effect of lead exposure from electronic waste on haemoglobin synthesis in children. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2021, 94, 911–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Huo, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X. Lead exposure is associated with risk of impaired coagulation in preschool children from an e-waste recycling area. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 20670–20679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, R.; Hu, H.; Rotnitzky, A.; Bellinger, D.; Needleman, H. A longitudinal study of chronic lead exposure and physical growth in Boston children. Environ. Health Perspect. 1995, 103, 952–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Huo, X.; Yekeen, T.A.; Zheng, Q.; Zheng, M.; Xu, X. Effects of lead and cadmium exposure from electronic waste on child physical growth. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2013, 20, 4441–4447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huo, X.; Xiao, Q.; Li, B.; Qiu, S.; Liu, J.; Xijin, X. Analysis of DNA Damage of Umbilical Cord Blood Lymphocytes and Related Factors in Neonates from an E-waste Recycling Area. J. Shantou Univ. Med. Coll. 2011, 24, 20–22. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Liao, W.; Lin, Y.; Dai, Y.; Shi, Z.; Huo, X. Blood concentrations of lead, cadmium, mercury and their association with biomarkers of DNA oxidative damage in preschool children living in an e-waste recycling area. Environ. Geochem. Health 2017, 40, 1481–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, W.; Shi, X.; Wu, K. Human Body Burden of Heavy Metals and Health Consequences of Pb Exposure in Guiyu, an E-Waste Recycling Town in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12428. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182312428
Huang W, Shi X, Wu K. Human Body Burden of Heavy Metals and Health Consequences of Pb Exposure in Guiyu, an E-Waste Recycling Town in China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(23):12428. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182312428
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Wenlong, Xiaoling Shi, and Kusheng Wu. 2021. "Human Body Burden of Heavy Metals and Health Consequences of Pb Exposure in Guiyu, an E-Waste Recycling Town in China" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 23: 12428. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182312428
APA StyleHuang, W., Shi, X., & Wu, K. (2021). Human Body Burden of Heavy Metals and Health Consequences of Pb Exposure in Guiyu, an E-Waste Recycling Town in China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(23), 12428. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182312428






