Adverse Childhood Experiences and Oral Health Outcomes in U.S. Children and Adolescents: A Cross-Sectional Study of the 2016 National Survey of Children’s Health
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source, Study Design and Population
2.2. Exposures
2.3. Outcomes
2.4. Covariates
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Child Characteristics
3.2. Caregiver Characteristics
3.3. Household Characteristics
3.4. ACEs and Dental Caries
3.5. ACEs and Bleeding Gums
3.6. ACEs and Fair/Poor Condition of Teeth
4. Discussion
4.1. Implication of Findings
4.2. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Adverse Childhood Experiences. | Mental Illness n = 3392 | Neighborhood Violence, n = 1250 | Financial Hardship n = 7942 | Parental Divorce n = 8943 | Parental Death n = 1108 | Incarceration n = 2272 | Domestic Violence n = 1843 | Substance Abuse n = 3605 | Unfair Treatment due to Race n = 1113 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caregiver characteristics | |||||||||
| Female gender | 8.8 (0.4) | 4.1 (0.3) | 28.5 (0.7) | 27.7 (0.6) | 3.4 (0.2) | 9.2 (0.4) | 6.4 (0.4) | 10.2 (0.4) | 4.0 (0.3) |
| Maternal age at birth, yrs | 28.0 (0.2) | 25.8 (0.3) | 27.7 (0.2) | 27.1 (0.1) | 28.1 (0.4) | 25.7 (0.3) | 26.0 (0.3) | 27.3 (0.2) | 27.8 (0.4) |
| Education | |||||||||
| High School | 8.0 (0.7) | 4.9 (0.6) | 34.1 (1.4) | 30.7 (1.3) | 4.6 (0.5) | 11.2 (0.8) | 7.3 (0.7) | 10.6 (0.8) | 3.0 (0.5) |
| Some college | 9.2 (0.5) | 5.2 (0.5) | 33.8 (1.0) | 33.0 (1.0) | 3.9 (0.4) | 12.1 (0.8) | 8.0 (0.6) | 12.2 (0.7) | 4.5 (0.5) |
| ≥Bachelor’s Degree | 7.0 (0.4) | 1.8 (0.2) | 14.1 (0.5) | 15.6 (0.5) | 1.7 (0.2) | 2.7 (0.3) | 3.0 (0.2) | 6.1 (0.4) | 3.5 (0.3) |
| Child/ Adolescent characteristics | |||||||||
| Age group (yrs.) | |||||||||
| 0–5 | 4.6 (0.4) | 1.1 (0.2) | 23.8 (1.0) | 12.8 (0.7) | 0.9 (0.2) | 4.1 (0.4) | 2.9 (0.3) | 5.0 (0.4) | 1.0 (0.2) |
| 6–11 | 8.8 (0.6) | 3.4 (0.4) | 25.0 (0.9) | 26.4 (0.9) | 2.7 (0.3) | 8.6 (0.6) | 6.1 (0.5) | 9.3 (0.6) | 4.2 (0.5) |
| 12–17 | 10.0 (0.4) | 6.0 (0.4) | 26.5 (0.8) | 33.5 (0.8) | 5.4 (0.4) | 10.0 (0.6) | 7.5 (0.5) | 12.5 (0.6) | 5.4 (0.4) |
| Female gender | 8.3 (0.5) | 3.7 (0.3) | 24.4 (0.8) | 24.7 (0.7) | 2.9 (0.2) | 7.6 (0.5) | 5.3 (0.4) | 9.5 (0.5) | 3.9 (0.4) |
| Race/ethnicity | |||||||||
| NH White | 8.8 (0.3) | 2.5 (0.2) | 21.3 (0.5) | 22.5 (0.5) | 2.5 (0.2) | 5.9 (0.3) | 4.8 (0.3) | 9.6 (0.4) | 0.9 (0.1) |
| NH Black | 6.4 (0.9) | 6.6 (0.9) | 37.2 (1.9) | 35.9 (1.9) | 6.5 (0.8) | 16.2 (1.5) | 9.1 (1.3) | 7.6 (1.1) | 10.1 (1.1) |
| Hispanic | 7.0 (0.8) | 4.7 (0.7) | 29.2 (1.5) | 26.7 (1.4) | 2.8 (0.4) | 8.1 (0.9) | 5.9 (0.7) | 9.6 (0.9) | 4.8 (0.7) |
| NH, Other | 7.4 (0.9) | 3.7 (0.5) | 22.3 (1.4) | 19.1 (1.2) | 3.2 (0.6) | 6.4 (0.9) | 5.0 (0.5) | 7.4 (0.9) | 7.4 (0.9) |
| Fair or Poor teeth | 16.4 (2.3) | 12.3 (2.1) | 49.8 (3.1) | 44.2 (3.1) | 5.9 (1.3) | 18.3 (2.5) | 12.2 (1.9) | 20.8 (2.6) | 10.2 (2.2) |
| Bleeding gums | 12.7 (2.2) | 14.3 (3.3) | 51.4 (4.8) | 40.2 (4.5) | 9.8 (2.7) | 17.7 (3.2) | 15.6 (2.9) | 18.3 (3.8) | 8.3 (2.3) |
| Decayed teeth | 14.0 (1.3) | 8.1 (1.1) | 40.8 (1.9) | 35.5 (1.9) | 5.9 (0.9) | 13.7 (1.4) | 9.9 (1.1) | 15.9 (1.5) | 6.8 (1.3) |
| Anxiety | 22.8 (1.5) | 11.6 (1.3) | 40.3 (2.0) | 43.3 (2.0) | 5.1 (0.7) | 14.2 (1.4) | 13.1 (1.2) | 23.3 (1.8) | 8.6 (1.6) |
| Depression | 25.7 (1.8) | 19.5 (2.3) | 48.2 (2.6) | 53.7 (2.5) | 9.9 (1.6) | 20.5 (2.0) | 16.8 (1.6) | 26.5 (2.1) | 10.8 (1.6) |
| Born in the US | 8.1 (0.3) | 3.6 (0.2) | 25.3 (0.5) | 25.0 (0.5) | 3.1 (0.2) | 7.8 (0.3) | 5.6 (0.3) | 9.1 (0.3) | 3.6 (0.2) |
| Household characteristics | |||||||||
| Language spoken at home | |||||||||
| English | 8.8 (0.3) | 3.7 (0.2) | 25.2 (0.5) | 26.2 (0.5) | 3.4 (0.2) | 8.3 (0.4) | 5.8 (0.3) | 9.8 (0.4) | 3.7 (0.3) |
| Spanish | 2.9 (1.0) | 4.0 (1.0) | 28.6 (2.8) | 17.8 (2.1) | 1.2 (0.4) | 4.6 (1.1) | 3.7 (1.1) | 5.2 (1.3) | 3.7 (0.9) |
| Other | 1.2 (0.3) | 1.3 (0.7) | 17.0 (2.6) | 10.0 (1.7) | 1.9 (0.6) | 2.2 (1.1) | 4.8 (1.6) | 2.4 (1.1) | 2.3 (0.8) |
| Family Structure | |||||||||
| Two parents, married | 5.2 (0.3) | 2.0 (0.2) | 17.4 (0.5) | 8.6 (0.4) | 0.8 (0.1) | 2.7 (0.3) | 2.2 (0.2) | 5.0 (0.3) | 2.7 (0.2) |
| Two parents, unmarried | 10.5 (1.3) | 4.0 (0.6) | 41.1 (2.2) | 44.7 (2.2) | 2.9 (0.7) | 10.0 (1.5) | 9.0 (1.4) | 10.4 (1.2) | 4.2 (1.1) |
| Single mother | 14.1 (0.9) | 8.0 (0.9) | 45.3 (1.5) | 66.3 (1.4) | 8.4 (0.7) | 17.9 (1.1) | 11.7 (0.9) | 16.7 (1.0) | 6.0 (0.7) |
| Other * | 17.3 (1.6) | 9.2 (1.3) | 35.4 (2.3) | 60.7 (2.2) | 13.1 (1.4) | 28.5 (1.9) | 19.3 (1.8) | 28.4 (2.0) | 6.5 (1.2) |
| Number of children | |||||||||
| 1 | 8.7 (0.4) | 4.4 (0.3) | 26.0 (0.8) | 33.0 (0.8) | 5.0 (0.4) | 9.6 (0.5) | 6.6 (0.5) | 10.6 (0.5) | 4.1 (0.3) |
| 2 or 3 | 7.1 (0.3) | 2.8 (0.2) | 23.9 (0.7) | 20.5 (0.6) | 2.4 (0.2) | 6.5 (0.4) | 4.8 (0.3) | 8.1 (0.4) | 2.9 (0.2) |
| ≥4 | 10.8 (1.4) | 5.9 (1.1) | 29.8 (2.0) | 29.2 (2.1) | 2.7 (0.7) | 10.0 (1.4) | 7.7 (1.3) | 11.2 (1.6) | 6.3 (1.4) |
| Family Poverty Ratio | |||||||||
| <100% | 11.5 (0.9) | 7.0 (0.8) | 48.4 (1.7) | 39.4 (1.6) | 5.1 (0.6) | 15.7 (1.1) | 10.8 (0.9) | 13.0 (1.0) | 5.0 (0.6) |
| 100–150% | 8.5 (0.9) | 5.4 (0.9) | 38.2 (1.9) | 29.1 (1.8) | 3.7 (0.5) | 11.7 (1.3) | 7.7 (1.1) | 9.6 (1.0) | 4.7 (1.0) |
| >150% | 6.9 (0.3) | 2.4 (0.2) | 16.8 (0.5) | 20.1 (0.5) | 2.5 (0.2) | 4.9 (0.3) | 3.8 (0.3) | 8.0 (0.4) | 3.1 (0.2) |
References
- Oral Health Coordinating Committee. Oral Health Strategic Framework, 2014–2017. Public Health Rep. 2014, 131, 233–257. Available online: https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/003335491613100208 (accessed on 28 October 2021).
- Eke, P.I.; Thornton-Evans, G.O.; Wei, L.; Borgnakke, W.S.; Dye, B.A.; Genco, R.J. Periodontitis in US adults: National health and nutrition examination survey 2009–2014. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2018, 149, 576–588.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dye, B.A.; Li, X.; Beltran-Aguilar, E.D. Selected oral health indicators in the United States, 2005–2008. NCHS Data Brief 2012, 96, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Dye, B.A.; Harrell, L.; Murphy, D.A.; Belin, T.; Shetty, V. Performance of a quality assurance program for assessing dental health in methamphetamine users. BMC Oral Health 2015, 15, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, S.L.; Vann, W.F.J.; Kotch, J.B.; Pahel, B.T.; Lee, J.Y. Impact of poor oral health on children’s school attendance and performance. Am. J. Public Health 2011, 101, 1900–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinanoff, N.; Baez, R.J.; Diaz Guillory, C.; Donly, K.J.; Feldens, C.A.; McGrath, C.; Phantumvanit, P.; Pitts, N.B.; Seow, W.K.; Sharkov, N.; et al. Early childhood caries epidemiology, aetiology, risk assessment, societal burden, management, education, and policy: Global perspective. Int. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2019, 29, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gift, H.C.; Reisine, S.T.; Larach, D.C. The social impact of dental problems and visits. Am. J. Public Health 1992, 82, 1663–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seirawan, H.; Faust, S.; Mulligan, R. The impact of oral health on the academic performance of disadvantaged children. Am. J. Public Health 2012, 102, 1729–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kragt, L.; van der Tas, J.T.; Moll, H.A.; Elfrink, M.E.; Jaddoe, V.W.; Wolvius, E.B.; Ongkosuwito, E.M. Early caries predicts low oral health-related quality of life at a later age. Caries Res. 2016, 50, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadbent, J.M.; Zeng, J.; Foster Page, L.A.; Baker, S.R.; Ramrakha, S.; Thomson, W.M. Oral health-related beliefs, behaviors, and outcomes through the life course. J. Dent. Res. 2016, 95, 808–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BaniHani, A.; Deery, C.; Toumba, J.; Munyombwe, T.; Duggal, M. The impact of dental caries and its treatment by conventional or biological approaches on the oral health-related quality of life of children and carers. Int. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2018, 28, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Griffin, S.O.; Gooch, B.F.; Espinoza, L.; Wei, L.; Li, C.H.; Thornton-Evans, G.; Junger, M.L.; Robison, V.A.; Fleming, E.B.; et al. Surveillance report trends in dental caries and sealants, tooth retention, and edentulism, United States. J. Dent. Educ. 2016, 81, 100. [Google Scholar]
- Selwitz, R.H.; Ismail, A.I.; Pitts, N.B. Dental caries. Lancet 2007, 369, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim Seow, W. Environmental, maternal, and child factors which contribute to early childhood caries: A unifying conceptual model. Int. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2012, 22, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seow, W.K.; Clifford, H.; Battistutta, D.; Morawska, A.; Holcombe, T. Case-control study of early childhood caries in Australia. Caries Res. 2009, 43, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felitti, V.J.; Anda, R.F.; Nordenberg, D.; Williamson, D.F.; Spitz, A.M.; Edwards, V.; Marks, J.S. Relationship of childhood abuse and household dysfunction to many of the leading causes of death in adults. The Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACE) study. Am. J. Prev. Med. 1998, 14, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Brown, D.S.; Florence, C.S.; Mercy, J.A. The economic burden of child maltreatment in the United States and implications for prevention. Child Abuse Negl. 2012, 36, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, S.M.; Bender, K.; Orsi, R.; McCrae, J.S.; Phillips, J.D.; Rienks, S. Adverse childhood experiences and their relationship to complex health profiles among child welfare-involved children: A classification and regression tree analysis. Health Serv. Res. 2019, 54, 902–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore KA, N.; Ramirez, A. Adverse childhood experience and adolescent well-being: Do protective factors matter? Child Indic. Res. 2016, 9, 299–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinkugbe, A.A.; Hood, K.B.; Brickhouse, T.H. Exposure to adverse childhood experiences and oral health measures in adulthood: Findings from the 2010 behavioral risk factor surveillance system. JDR Clin. Transl. Res. 2018, 4, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bright, M.A.; Alford, S.M.; Hinojosa, M.S.; Knapp, C.; Fernandez-Baca, D.E. Adverse childhood experiences and dental health in children and adolescents. Community Dent. Oral Epidemiol. 2015, 43, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crouch, E.; Radcliff, E.; Nelson, J.; Strompolis, M.; Martin, A. The experience of adverse childhood experiences and dental care in childhood. Community Dent. Oral Epidemiol. 2018, 46, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuyama, Y.; Fujiwara, T.; Aida, J.; Watt, R.G.; Kondo, N.; Yamamoto, T.; Kondo, K.; Osaka, K. Experience of childhood abuse and later number of remaining teeth in older Japanese: A life-course study from Japan Gerontological Evaluation Study project. Community Dent. Oral Epidemiol. 2016, 44, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duda, J.G.; Biss, S.P.; Bertoli, F.M.D.P.; Bruzamolin, C.D.; Pizzatto, E.; Souza, J.F.; Losso, E.M. Oral health status in victims of child abuse: A case-control study. Int. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2017, 27, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabani, F.; Lykens, K.; Tak, H.J. Exploring the relationship between adverse childhood experiences and oral health-related quality of life. J. Public Health Dent. 2018, 78, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghandour, R.M.; Jones, J.R.; Lebrun-Harris, L.A.; Minnaert, J.; Blumberg, S.J.; Fields, J.; Bethell, C.; Kogan, M.D. The Design and Implementation of the 2016 National Survey of Children’s Health. Matern Child Health J 2018, 22, 1093–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locker, D. Measuring oral health: A conceptual framework. Community Dent. Health. 1988, 5, 3–18. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3285972 (accessed on 22 September 2019).
- Slade, G.D.; Spencer, A.J. Development and evaluation of the Oral Health Impact Profile. Community Dent. Health. 1994, 11, 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. Lancet 2007, 370, 1453–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crouch, E.; Radcliff, E.; Brown, M.; Hung, P. Exploring the association between parenting stress and a child’s exposure to adverse childhood experiences (ACEs). Child Youth Serv. Rev. 2019, 102, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher-Owens, S.A.; Lukefahr, F.J.L.; Anupama, F.; Tate, R. American MPH, Dentistry P. 3.03 Child abuse and neglect. J. Hosp. Med. 2020, 15, 100–101. [Google Scholar]
- Manski, R.J.; Macek, M.D.; Moeller, J.F. Private dental coverage: Who has it and how does it influence dental visits and expenditures? J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2002, 133, 1551–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willink, A.; Reed, N.S.; Swenor, B.; Leinbach, L.; DuGoff, E.H.; Davis, K. Dental, vision, and hearing services: Access, spending, and coverage for medicare beneficiaries. Health Aff. 2020, 39, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenney, G.M.; McFeeters, J.R.; Yee, J.Y. Preventive dental care and unmet dental needs among low-income children. Am. J. Public Health 2005, 95, 1360–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lempers, J.D.; Clark-Lempers, D.; Simons, R.L. Economic hardship, parenting, and distress in adolescence. Child Dev. 1989, 60, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLoyd, V.C. The impact of economic hardship on black families and children: Psychological distress, parenting, and socioemotional development. Child Dev. 1990, 61, 311–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vartanian, T.P.; Houser, L. The effects of childhood neighborhood conditions on self-reports of adult health. J. Health Soc. Behav. 2010, 51, 291–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diez Roux, A.V.; Mair, C. Neighborhoods and health. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2010, 1186, 125–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharkey, P.T.; Tirado-Strayer, N.; Papachristos, A.V.; Raver, C.C. The effect of local violence on children’s attention and impulse control. Am. J. Public Health 2012, 102, 2287–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cambron, C.; Kosterman, R.; Catalano, R.F.; Guttmannova, K.; Hawkins, J.D. Neighborhood, family, and peer factors associated with early adolescent smoking and alcohol use. J. Youth Adolesc. 2018, 47, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newacheck, P.W.; Hughes, D.C.; Hung, Y.Y.; Wong, S.; Stoddard, J.J. The unmet health needs of America’s children. Pediatrics 2000, 105 Pt 2, 989–997. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Larijani, H.H.; Guggisberg, M. Improving clinical practice: What dentists need to know about the association between dental fear and a history of sexual violence victimisation. Int. J. Dent. 2015, 2015, 452814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernán, M.A.; Hernández-Díaz, S.; Robins, J.M. A structural approach to selection bias. Epidemiology 2004, 15, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Unweighted n (Weighted %) or Mean (SE) | |
|---|---|
| Caregiver characteristics | |
| Female gender | 28,129 (70.2) |
| Maternal age at birth, yrs. mean (SE) | 29.4 (0.1) |
| Education | |
| High School Diploma | 5566 (26.4) |
| Some College, or Associates Degree | 12,345 (29.2) |
| Bachelor’s Degree or Higher | 23,383 (44.5) |
| Child/ Adolescent characteristics | |
| Age, yrs. mean (SE) | 8.85 (0.05) |
| Age group (yrs.) | |
| 0–5 | 11,458 (30.3) |
| 6–11 | 12,615 (35.1) |
| 12–17 | 17,221 (34.6) |
| Female gender | 21,235 (49.0) |
| Has special healthcare need | 9479 (19.7) |
| Race/ethnicity | |
| White, Non-Hispanic | 29,692 (54.1) |
| Black, Non-Hispanic | 2162 (12.2) |
| Hispanic | 4296 (23.0) |
| Other, Non-Hispanic | 5144 (10.7) |
| Fair/Poor teeth | 1376 (5.2) |
| Bleeding gums | 542 (1.8) |
| Decayed teeth | 3684 (11.2) |
| Anxiety | 3791 (7.4) |
| Depression | 1820 (3.5) |
| Born in United States | 40,137 (96.3) |
| Household characteristics | |
| Number of children | |
| 1 | 17,112 (25.2) |
| 2 or 3 | 22,002 (62.3) |
| ≥4 | 2180 (12.5) |
| Language spoken at home | |
| English | 38,843(86.7) |
| Spanish | 1063 (9.0) |
| Other | 1388 (4.3) |
| Family Structure | |
| Two parents, currently married | 31,410 (68.1) |
| Two parents, not currently married | 2602 (8.6) |
| One mother, married or not married | 4903 (15.5) |
| Other a | 2379 (7.7) |
| Family Poverty Ratio | |
| <100% | 3453 (18.9) |
| 100–150% | 2953 (11.1) |
| >150% | 34,888 (70.0) |
| ACE Measures | Unweighted n (Weighted %) |
|---|---|
| Lived with someone who was mentally ill | 3392 (7.9) |
| Victim of violence/witnessed violence in neighborhood | 1250 (3.6) |
| Hard to cover basics (food/housing) | 7942 (25.2) |
| Parent/guardian divorced/separated | 8943 (24.7) |
| Parent/guardian died | 1108 (3.1) |
| Parent/guardian served time in jail | 2272 (7.7) |
| Parent/guardian were violent toward one another in the home | 1843 (5.6) |
| Lived with someone with a drug/alcohol problem | 3605 (9.1) |
| Treated unfairly because of race/ethnicity | 1113 (3.6) |
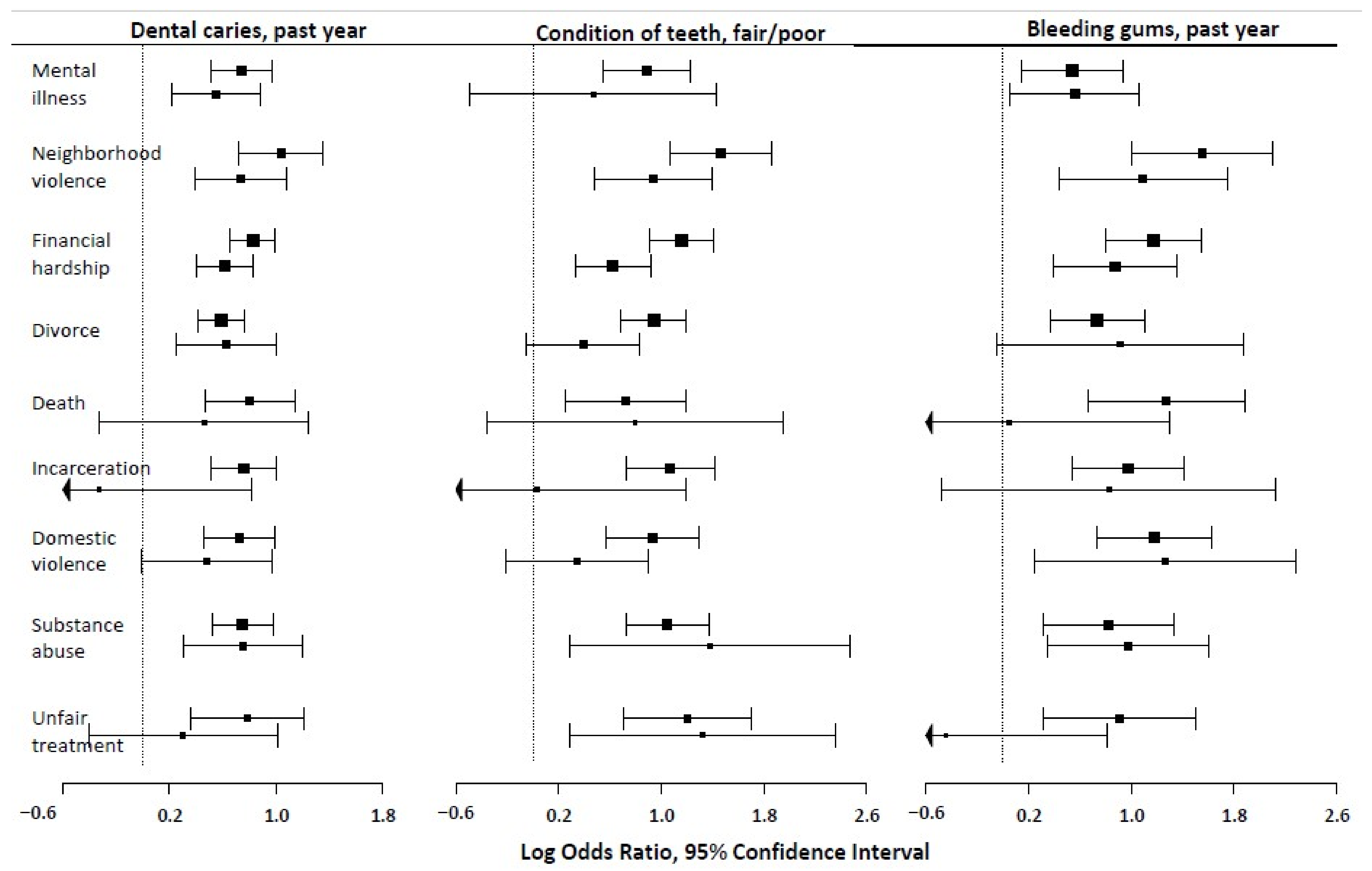
| Decayed Teeth/Cavities | Bleeding Gums a | Fair/Poor Condition of the Teeth | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | AOR b (95% CI) | OR (95% CI) | AOR b (95% CI) | OR (95% CI) | AOR b (95% CI) | |
| Caregiver mental illness | 2.10 (1.67, 2.65) | 1.73 (1.24, 2.42) | 1.71 (1.15, 2.53) | 1.75 (1.06, 2.90) | 2.43 (1.73, 3.41) | 1.60 (0.61, 4.19) |
| Neighborhood violence | 2.82 (2.05, 3.87) | 2.09 (1.48, 2.95) | 4.72 (2.73, 8.16) | 2.97 (1.54, 5.72) | 4.32 (2.91, 6.41) | 2.56 (1.62, 4.06) |
| Financial hardship | 2.28 (1.93, 2.70) | 1.85 (1.50, 2.29) | 3.23 (2.21, 4.71) | 2.39 (1.48, 3.86) | 3.18 (2.48, 4.08) | 1.87 (1.40, 2.51) |
| Caregiver divorce | 1.80 (1.52, 2.14) | 1.87 (1.28, 2.71) | 2.08 (1.44, 3.01) | 2.49 (0.95, 6.51) | 2.56 (1.99, 3.30) | 1.48 (0.95, 2.31) |
| Caregiver death | 2.23 (1.59, 3.14) | 1.58 (0.72, 3.47) | 3.56 (1.93, 6.55) | 1.05 (0.30, 3.66) | 2.06 (1.29, 3.30) | 2.22 (0.70, 7.09) |
| Caregiver incarceration | 2.13 (1.66, 2.74) | 0.72 (0.23, 2.28) | 2.64 (1.71, 4.09) | 2.28 (0.62, 8.37) | 2.92 (2.07, 4.12) | 1.03 (0.32, 3.28) |
| Domestic violence | 2.06 (1.57, 2.70) | 1.62 (0.99, 2.64) | 3.25 (2.08, 5.07) | 3.54 (1.28, 9.77) | 2.53 (1.76, 3.63) | 1.41 (0.81, 2.47) |
| Drug/alcohol problem in household | 2.11 (1.68, 2.66) | 2.11 (1.35, 3.31) | 2.28 (1.37, 3.79) | 2.66 (1.42, 5.00) | 2.85 (2.07, 3.94) | 3.98 (1.33, 11.8) |
| Treated unfairly due to race/ethnicity | 2.19 (1.43, 3.37) | 1.35 (0.66, 2.73) | 2.47 (1.37, 4.47) | 0.64 (0.18, 2.21) | 3.34 (2.04, 5.48) | 3.77 (1.34, 10.6) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Simon, A.; Cage, J.; Akinkugbe, A.A. Adverse Childhood Experiences and Oral Health Outcomes in U.S. Children and Adolescents: A Cross-Sectional Study of the 2016 National Survey of Children’s Health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12313. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182312313
Simon A, Cage J, Akinkugbe AA. Adverse Childhood Experiences and Oral Health Outcomes in U.S. Children and Adolescents: A Cross-Sectional Study of the 2016 National Survey of Children’s Health. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(23):12313. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182312313
Chicago/Turabian StyleSimon, Alyssa, Jamie Cage, and Aderonke A. Akinkugbe. 2021. "Adverse Childhood Experiences and Oral Health Outcomes in U.S. Children and Adolescents: A Cross-Sectional Study of the 2016 National Survey of Children’s Health" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 23: 12313. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182312313
APA StyleSimon, A., Cage, J., & Akinkugbe, A. A. (2021). Adverse Childhood Experiences and Oral Health Outcomes in U.S. Children and Adolescents: A Cross-Sectional Study of the 2016 National Survey of Children’s Health. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(23), 12313. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182312313







