Abstract
Background: The purpose of this study is to investigate the effect of Taekwondo training on body composition and to evaluate the magnitude of the effect. Methods: Databases were used to select studies related to the effectiveness of Taekwondo training, and the inclusion criteria were as follows. Results: Thirty-seven studies were selected. We found statistically significant differences from the control group in weight, body mass index (BMI), waist circumference (WC), waist–hip ratio (WHR), body fat mass, body fat percentage, lean mass, and muscle mass. Also, the age group was statistically significant in control variables on weight, BMI, and body fat percentage. Conclusions: Taekwondo training had a positive effect on body composition, and these results suggest that Taekwondo training is an effective exercise method to lower obesity.
1. Introduction
Insufficient physical activity was reported as the fourth most important risk factor among the causes of death worldwide [1]. For this reason, Korea has set physical activity goals for all age groups through the 3rd National Health Promotion Plan (HP2020) and is creating various policies and environments to promote physical activity [2]. According to the Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention report in 2019, the rate of aerobic exercise among adolescents increased by 3.0% p from 10.9% in 2009 to 13.9% in 2018. On the other hand, the rate of aerobic exercise among adults over the age of 19 and older decreased by 9.8% from 58.3% in 2014 to 48.5% in 2017, and the rate of walking among adults over the age of 19 and older decreased by 6.7% p from 45.7% in 2007 to 39.0% in 2017 [3]. However, according to the study of Guthold et al. [4], a 2016 survey of 298 schools in 146 countries found that 81.0% of 11–17 year olds were not getting enough physical activity. On the other hand, in the case of Korea, 94.2% of adolescents showed insufficient amount of physical activity, which made Korea recognized as the country with the most insufficient amount of physical activity for adolescents in the world. Since such a decrease in physical activity can cause a decrease in physical strength and muscle mass [5] and an increase in body fat mass, thereby causing metabolic diseases [6], efforts to increase physical activity are required.
Taekwondo is a traditional martial art from Korea and is recognized as a global martial arts and sport with more than 100 million practitioners in 210 countries worldwide [1]. Taekwondo as an exercise has positive effects on the psychological and physiological areas for the growth and development of children and adolescents. In addition, Taekwondo training prevents or positively improves obesity, dyslipidemia, diabetes, hypertension, cerebrovascular, and cardiovascular diseases in adults and the elderly [7,8,9,10]. In addition, it is expected to improve various physical strengths, including aerobic capacity, muscle strength, muscular endurance, flexibility, speed, and agility through the physiological effects of Taekwondo practice [11,12,13,14]. For this reason, Taekwondo is considered suitable as an essential exercise for improving the physical activity of Koreans and preventing and improving various diseases. However, although multiple studies have been conducted to verify the effectiveness of Taekwondo training, the results are not consistent, and depend on the study subject, method and duration of interventions, making it difficult to generalize the results. Therefore, it is necessary to present the best evidence to prove the effect of physical activity through Taekwondo among Koreans [15]. Thus, this study shows the effects of Taekwondo training on changes in body composition comprehensively and quantitatively to serve as evidence for the development of Taekwondo training as a war to improve obesity caused by lack of exercise in modern people including not only Koreans but people worldwide.
2. Materials and Methods
This study was conducted with reference to the Preferred Reporting for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) guidelines [16].
2.1. Search Strategy
In this study, we searched the literature in electronic databases, including the Cochrane Library, EMBASE, and PubMed, and used RISS (Research Information Sharing Service), NDSL (National Science and Technology Information Center) in Korea. The keyword used in the literature search was “Taekwondo”. In addition, we included gray literature such as dissertations to reduce publication bias. The language of the papers was limited to Korean and English. The publication year was not limited to the default setting. The reason we used only ‘taekwondo’ as a keyword is to prevent the omission of literature related to this topic as much as possible.
2.2. Selection of Studies
We selected literature according to the following PICO (participants, interventions, comparisons, outcomes) criteria. We included studies where the study subjects were the general public and excluded studies where the study subjects were not the general public (athletes, disabled people, hypertensive patients, diabetic patients, etc.). In addition, we selected studies where the intervention method was Taekwondo training and excluded studies that added interventions other than Taekwondo. Also, we included only studies with a control group who did not practice Taekwondo. We selected studies that presented actual measurements of body composition and studies with an RCT (randomized controlled trial) study design.
2.3. Moderator
The effects of Taekwondo intervention were analyzed by looking at how the results were influenced by the differences in the moderators, including gender, age, training period, research method, types of literature, and quality evaluation. Age was divided into three groups: students who attend elementary, middle, and high school, adults, and the elderly. The training periods were divided into 12 weeks or less and more than 12 weeks. Publication types were identified by dividing them into degree thesis and journal publications.
2.4. Quality Assessment
For the qualitative evaluation of the selected literature, the Cochrane Collaboration’s RoB (Risk of Bias) tool [16] was used. The evaluation consists of 7 items, including: (1) generating order of random assignment; (2) hiding assignment order; (3) blinding study participants and researchers; (4) blinding outcome evaluation; (5) insufficient result data; (6) selective reporting; and (7) other biases. The evaluation was rated as low risk, high risk, and uncertain.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
The effect size of the Taekwondo intervention and the heterogeneity were analyzed using the R program (version 3.6.2, R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria) [17]. The outcome variables were all continuous variables and included Height, weight, BMI, WC, WHR, fat mass, lean mass, body fat percentage, and muscle mass. The overall effect size was analyzed when there were three or more outcome variables. The measurement unit was the same, expressed as mean difference (MD) and 95% confidence intervals (Cls). The random effects model was used under the assumption that the outcome variables of each study were heterogeneous [18]. Meta-ANOVA and meta-regression were performed for the moderating variables, and both continuous variables (sample sizes) and categorical variables (gender, age, study period, publication type) were estimated using the Restricted Maximum Likelihood (REML) method [19].
2.6. Assessment of Heterogeneity
Heterogeneity was assessed using the Cochrane Q test and Higgins’ I2 statistics. When the p-value of the Cochrane Q test was 0.1 or less or the Higgins’ I2 was 50% or more, it was considered that there was statistically significant heterogeneity.
2.7. Publication Bias
For the publication bias analysis, we applied a funnel plot using standard error and MD, additionally applied Egger’s test and Begg’s test [20].
3. Result
3.1. Inclusion of Studies
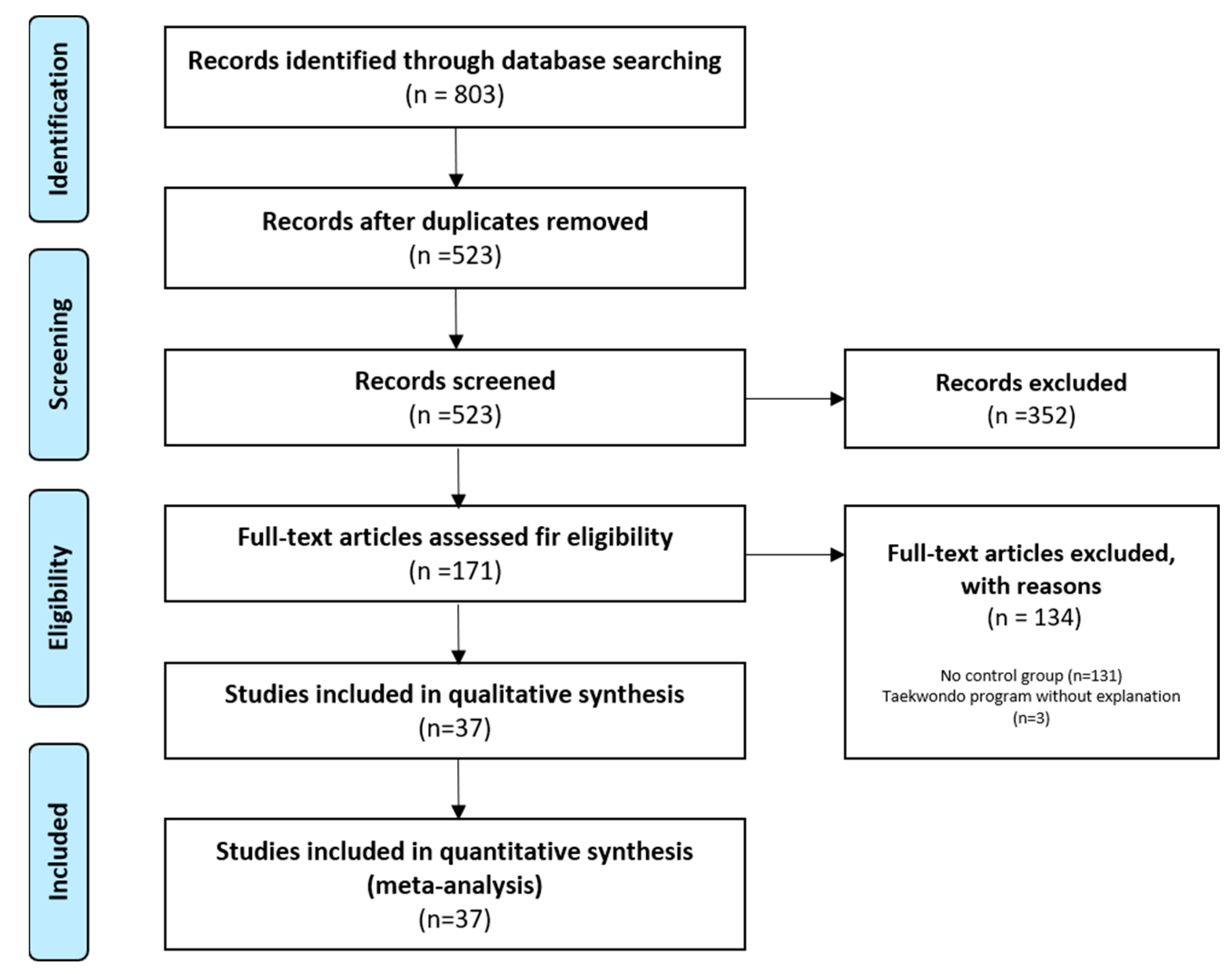
Of the 803 studies, we selected 171 studies, excluding duplicate studies (280) and those unrelated to this study (352). Then, as a result of full-text screening according to the PICO criteria, 131 studies without a control group and three studies that did not explain the Taekwondo training program were excluded. Therefore, we finally selected 37 studies for meta-analysis. All 37 papers were satisfied for both qualitative and quantitative analysis. The detailed process is shown in Figure 1.
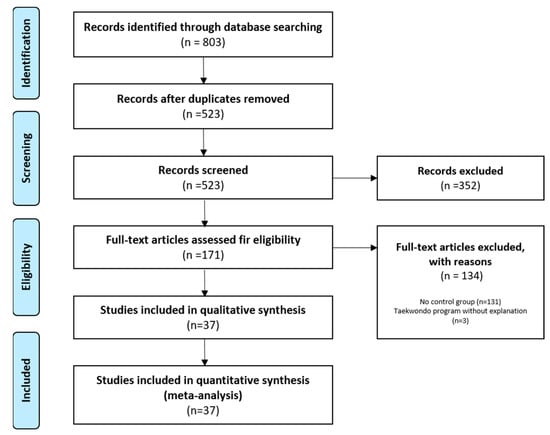
Figure 1.
PRISMA flow diagram.
3.2. Characteristics of the Included Studies
The total sample size was 801. The average age of the participants was 32.19 years old, ranging from 7.46 to 75.07, and 54.2% of the participants were male. 18 studies [21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37] were for students, 12 studies [38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49] were for adults, and 7 studies were for seniors [50,51,52,53,54,55,56], and the training period was 8–24 months. According to the publication type, 15 were for dissertations studies, and 22 studies were for journal publication. The characteristics of the included studies are summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Characteristics of included studies.
3.3. Quality Assessment
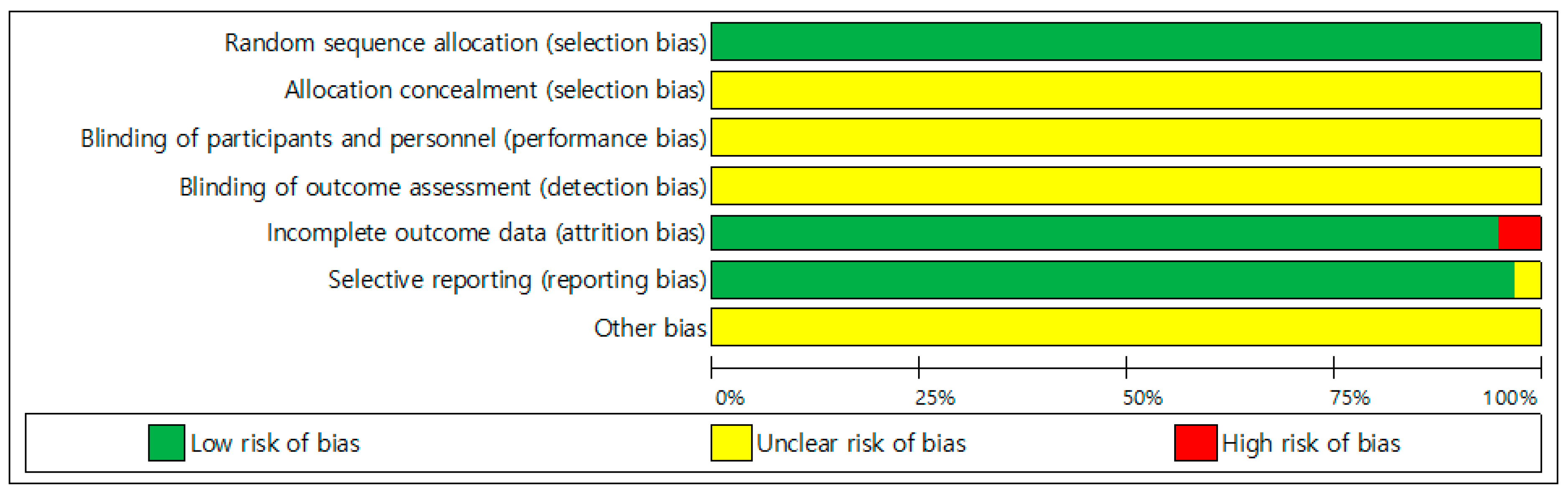
Two independent researchers (S.B., S.N.) performed quality assessment as shown in Figure 2, based on the criteria of the Cochrane Collaboration. All 37 studies were randomized control studies, and all studies analyzed the results, excluding participants who dropped out during the intervention.
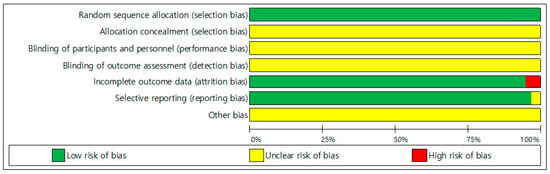
Figure 2.
Assessment of risk of bias in included studies.
3.4. Outcome Findings
3.4.1. Height
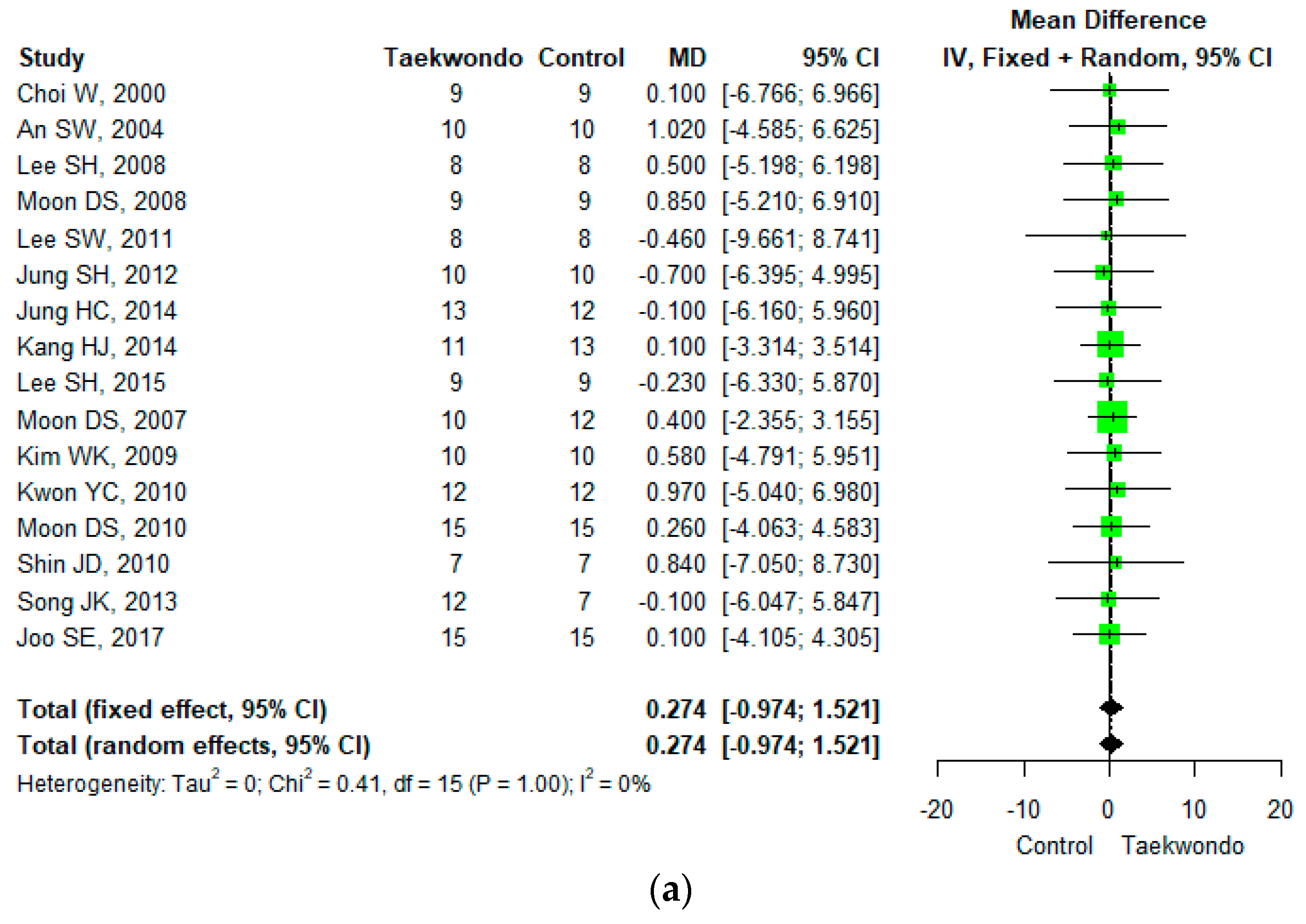
Sixteen studies reported height (total n = 184; taekwondo training group n = 168, control group n = 166). The mean difference (MD) in heights between the Taekwondo training and the control group was 0.274 (95% CI; −0.974, 1.521), and no statistically significant difference was found. For the heterogeneity test, the results of Cochrane Q were p = 1.00, and Higgins’ I2 was 0% (Figure 3a).
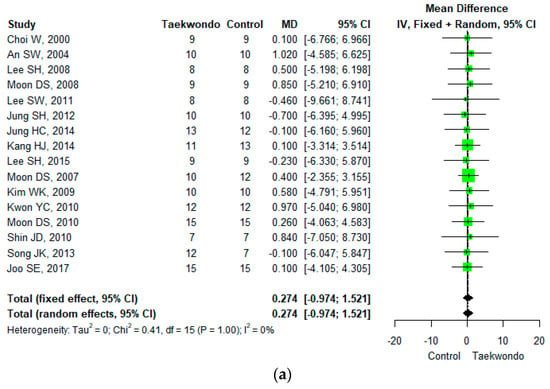
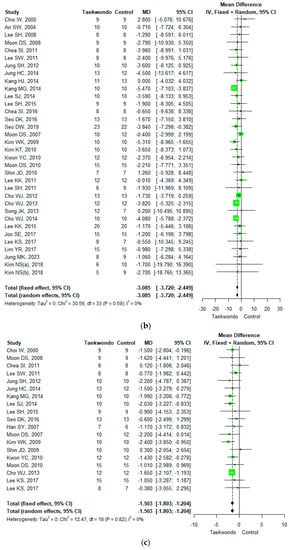
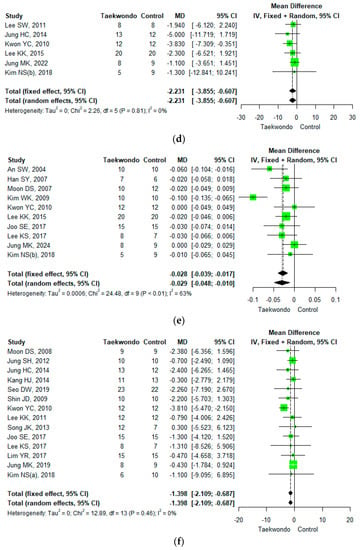
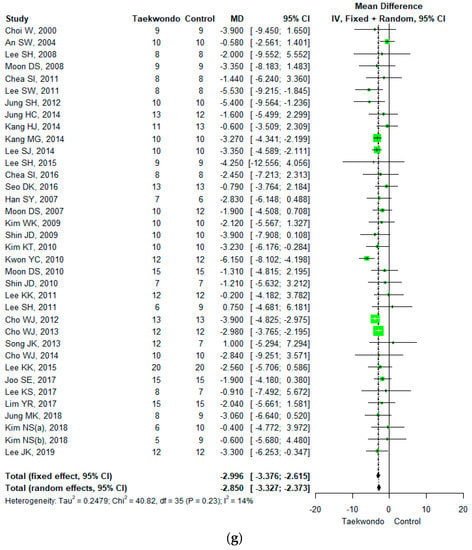
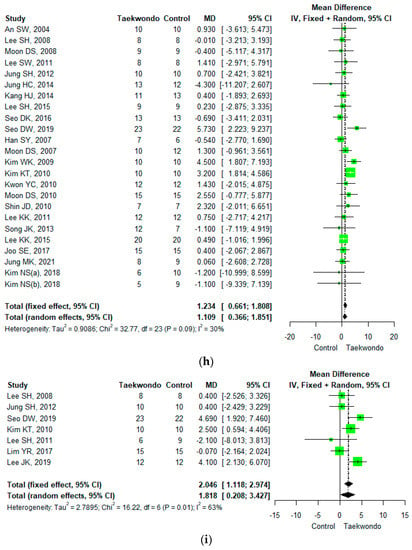
Figure 3.
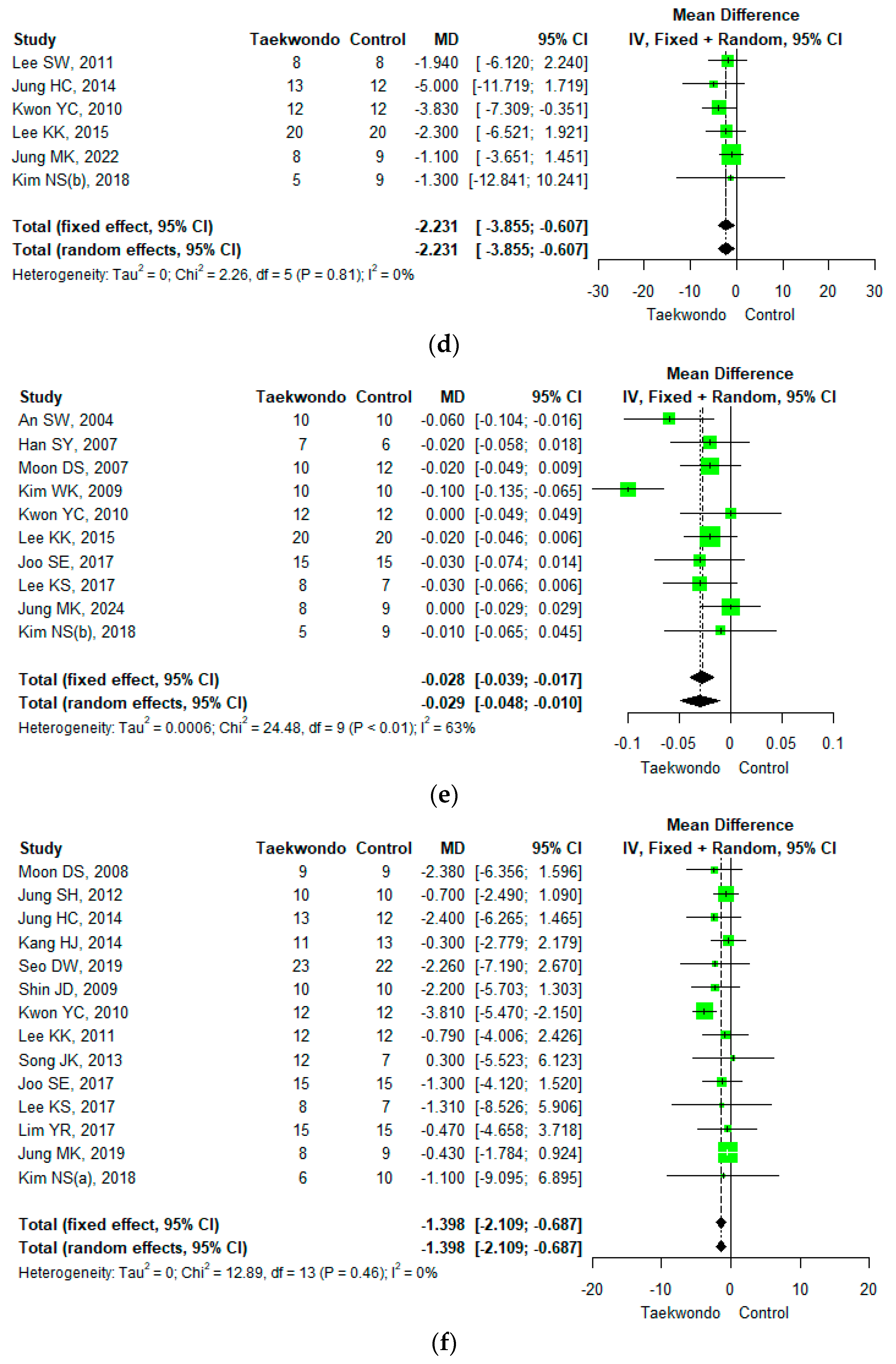
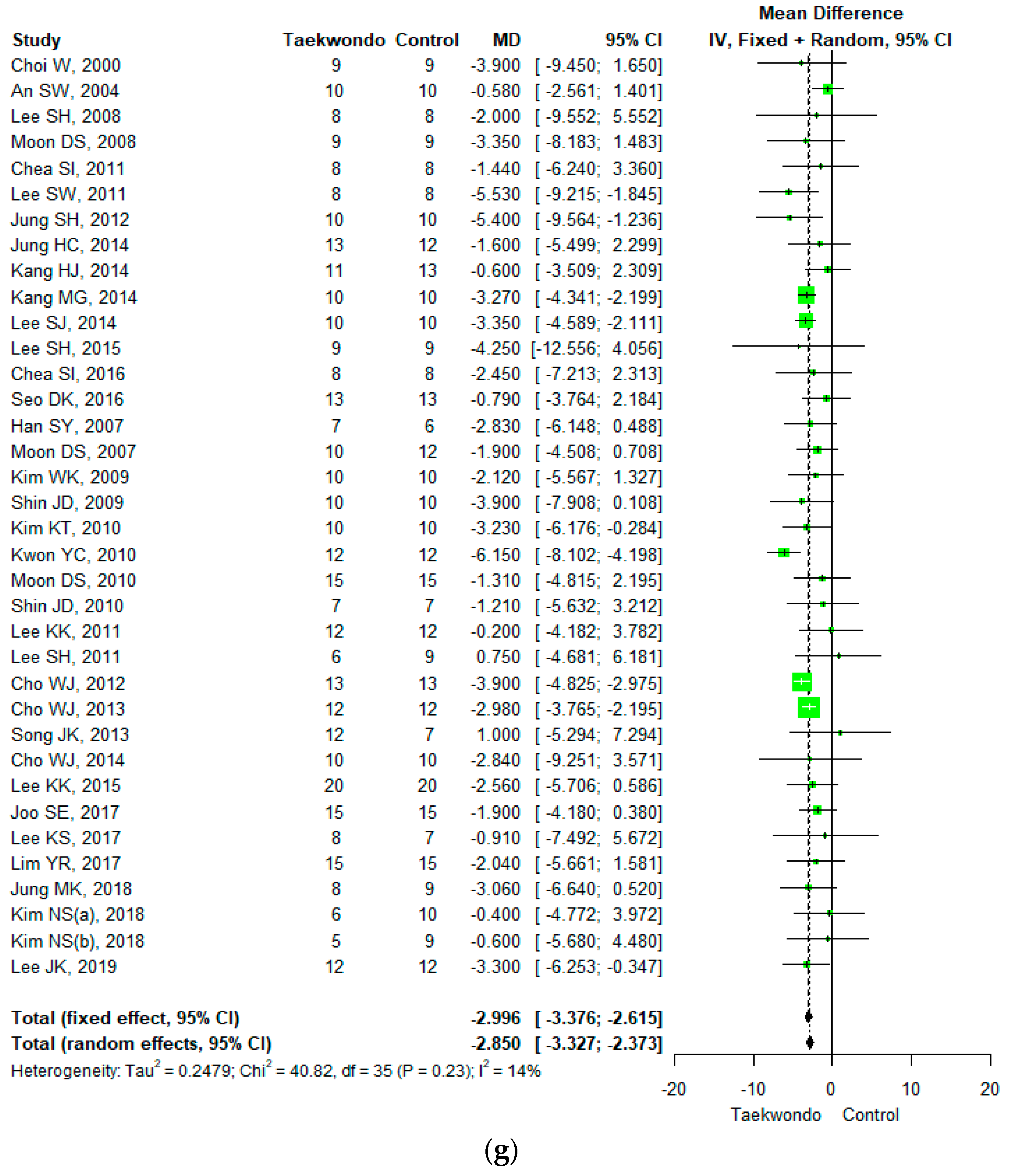
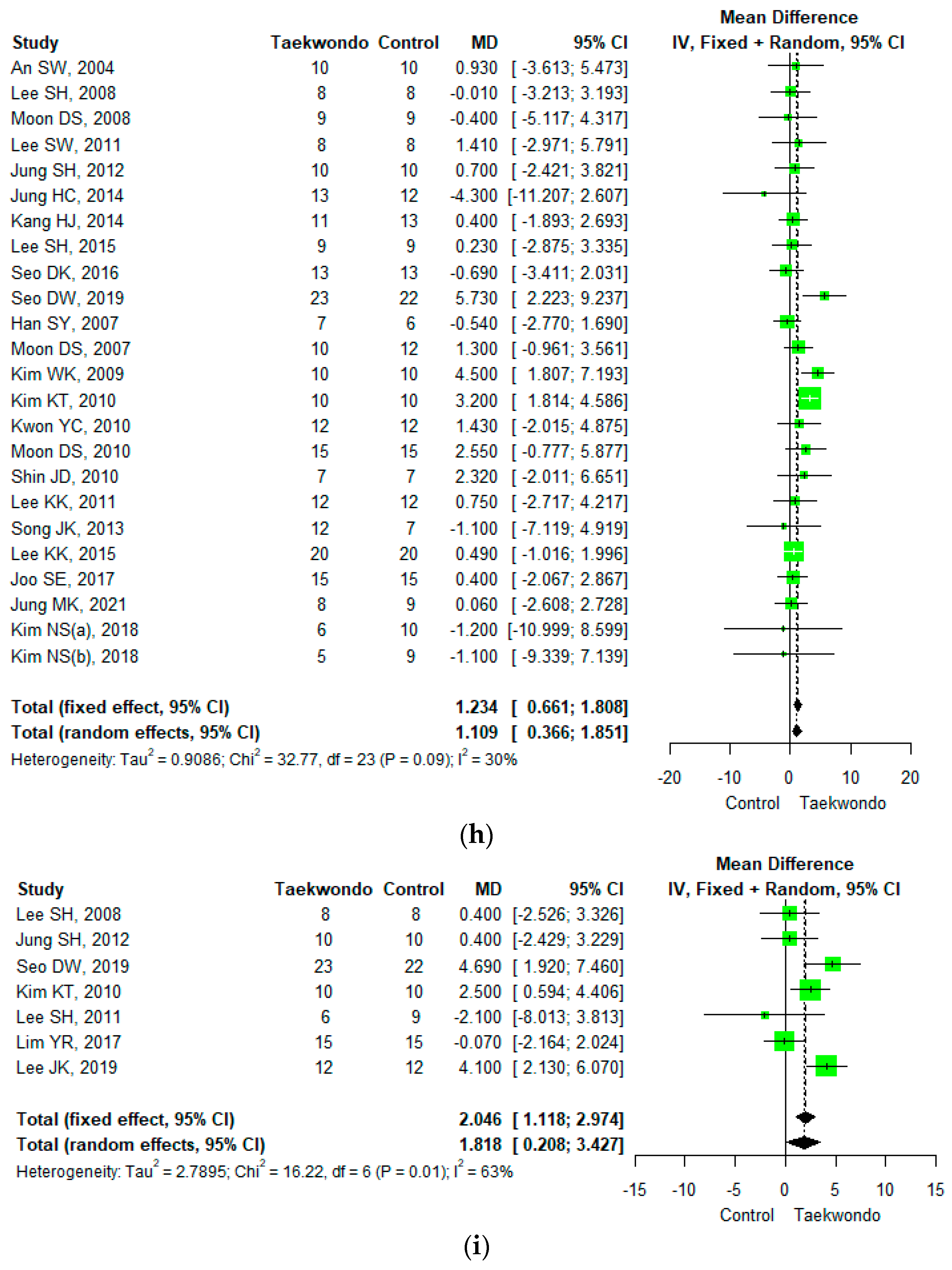
Forest plot of the mean difference in physique and body composition. (a) Height; (b) weight; (c) body mass index; (d) waist circumference; (e) waist-hip ratio; (f) body fat mass; (g) body fat percentage; (h) lean mass; (i) muscle mass.
3.4.2. Weight
A total of 34 studies reported body weight (total n = 738; taekwondo training group n= 365, control group n = 373). The mean difference (MD) in body weight between the Taekwondo training and the control group was −3.085 (95% CI; −3.720, −2.449). That is, the weight of the Taekwondo training group decreased by 3.1 kg compared to the control group, which was statistically significant (p < 0.001). For the heterogeneity test, the results of Cochrane Q were p = 0.59, and Higgins’ I2 was 0% (Figure 3b).
3.4.3. Body Mass Index
Eighteen studies reported body mass index (total n = 395; 198 Taekwondo training group, 197 control group). The mean difference (MD) of body mass index between the Taekwondo training and the control group was −1.503 (95% CI; −1.803, −1.204). The Body mass index of the Taekwondo training group decreased by 1.5 compared to the control group, and there was a statistically significant difference (p < 0.001). For the heterogeneity test, the results of Cochrane Q were p = 0.82, and Higgins’ I2 was 0% (Figure 3c).
3.4.4. Waist Circumference
Six studies reported waist circumference (total n = 136; taekwondo training group n = 66, control group n = 70). The mean difference (MD) in waist circumference between the Taekwondo training and the control group was −2.231 (95% CI; −3.855, −0.607). The waist circumference of the Taekwondo training group decreased by 2.2 cm compared to the control group, and there was a statistically significant difference (p < 0.05). For the heterogeneity test, the results of Cochrane Q were p = 0.81, and Higgins’ I2 was 0% (Figure 3d).
3.4.5. Waist–Hip Ratio
Ten studies reported the waist–hip ratio (total n = 215; Taekwondo training group n= 105, control group n = 110). The mean difference (MD) in the waist–hip ratio between the Taekwondo training and the control groups was −0.029 (95% CI; −0.015, −0.010). The waist–hip ratio of the Taekwondo training group decreased by 0.03 compared to the control group, and there was a statistically significant difference (p < 0.05). For the heterogeneity test, the results of Cochrane Q were p <0.01, and Higgins’ I2 was 0% (Figure 3e).
3.4.6. Body Fat Mass
Fourteen studies reported body fat mass (total n = 327; Taekwondo training group n = 164, the control group n = 163). The average difference (MD) in body fat mass between the Taekwondo training and the control group was −1.398 (95% CI; −2.109, −0.687). The body fat mass of the Taekwondo training group decreased by 1.40 kg compared to the control group, and there was a statistically significant difference (p < 0.01). For the heterogeneity test, the results of Cochrane Q were p = 0.46, and Higgins’ I2 was 0% (Figure 3f).
3.4.7. Body Fat Percentage
Thirty-six studies reported body fat percentage (total n = 750; taekwondo training group n= 371, control group n = 379). The mean difference (MD) in body fat percentage between the Taekwondo training and the control group was −2.850 (95% CI; −3.327, −2.373). The body fat percentage of the Taekwondo training group decreased by −2.90% compared to the control group, and there was a statistically significant difference (p < 0.001). For the heterogeneity test, the results of Cochrane Q were p = 0.23, and Higgins’ I2 was 14% (Figure 3g).
3.4.8. Lean Mass
Twenty-four studies reported lean mass (total n = 531; taekwondo training group n = 263, control group n = 268). The average difference (MD) in lean mass between the Taekwondo training and the control groups was 1.109 (95 % CI; 0.366, 1.851). The lean mass of the Taekwondo training group increased by 1.11 kg compared to the control group, and there was a statistically significant difference (p < 0.05). For the heterogeneity test, the results of Cochrane Q were p = 0.09, and Higgins’ I2 was 30% (Figure 3h).
3.4.9. Muscle Mass
Seven studies reported muscle mass (total n = 170; Taekwondo training group n = 84, control group n = 86). The mean difference (MD) in muscle mass between the Taekwondo training and the control group was 1.818 (95% CI; 0.208, 3.427). The muscle mass of the Taekwondo training group increased by 1.82 kg compared to the control group, and there was a statistically significant difference (p < 0.05). For the heterogeneity test, the results of Cochrane Q were p = 0.01, and Higgins’ I2 was 63% (Figure 3i).
3.5. Moderator Analyses
The results of meta-ANOVA with categorical variables (gender, age, study period, publication type) are shown in Table 2 and Table 3. No statistical significance was reported on moderating variables of height, WC, WHR, body fat mass, lean mass, and muscle mass. Meanwhile, in the case of body weight (p = 0.044), BMI (p = 0.036), and body fat percentage (p = 0.026), the age group was confirmed as a statistically significant moderating variable. It was confirmed that the decrease rate of weight and BMI was the highest among the student group, and the decrease rate of body fat percentage was highest among the elderly group.

Table 2.
Effects of moderators on height, weight, BMI, WC, WHR.

Table 3.
Effects of moderators on fat mass, % fat, lean mass, muscle mass.
3.6. Publication Bias
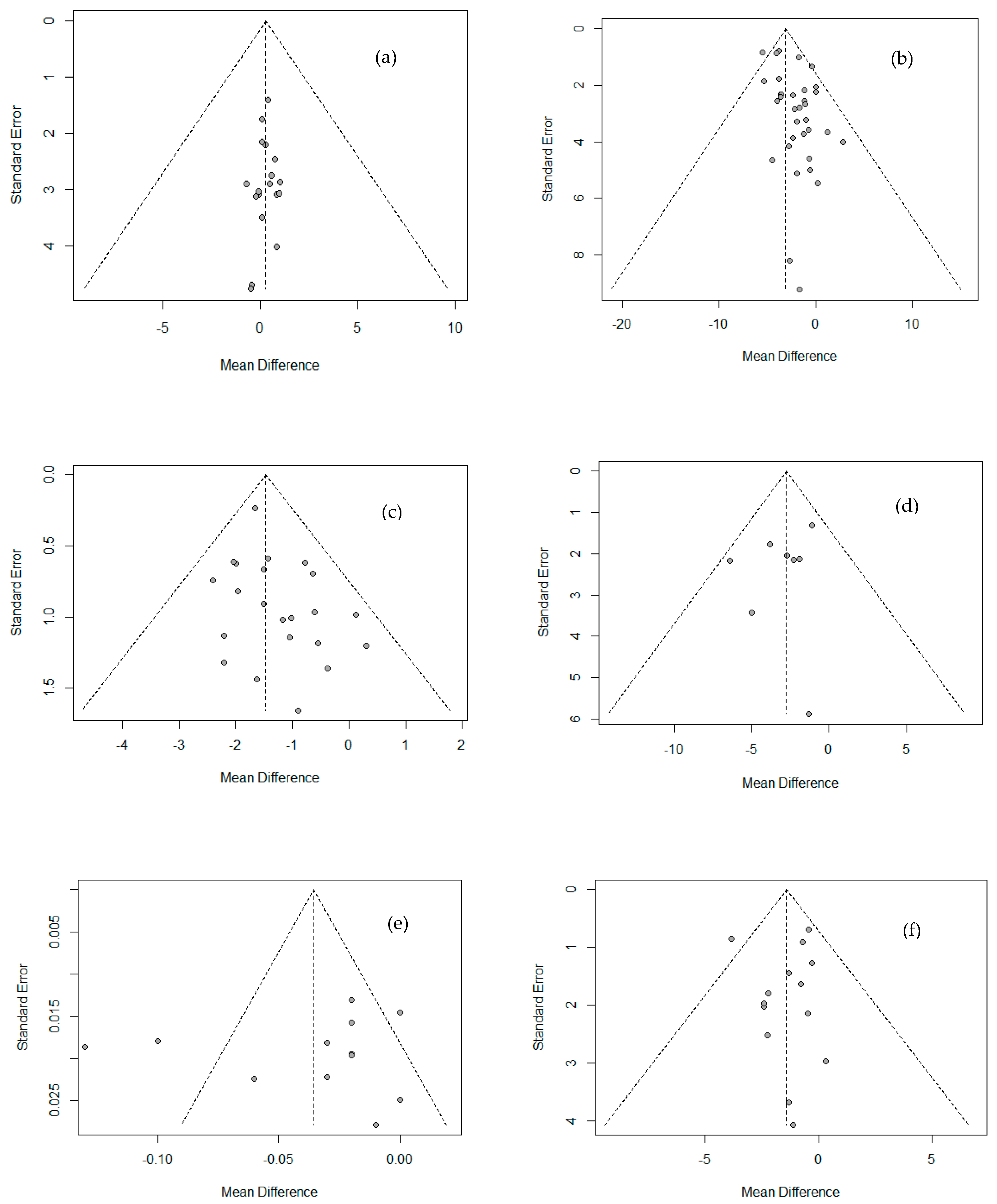
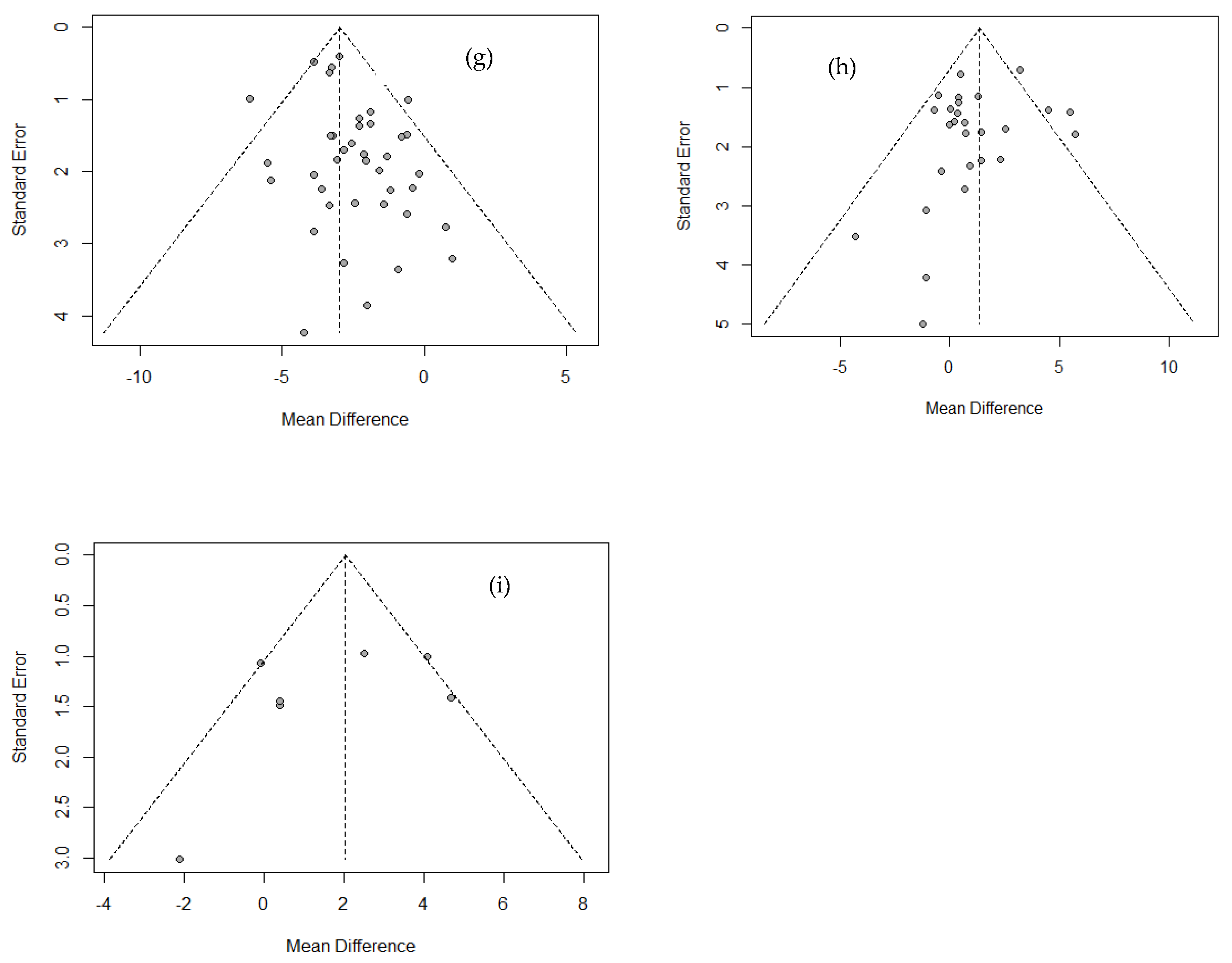
Funnel plots were used to analyze publication bias or effects of small-sized research, as shown in Figure 4. No publication bias was found from Egger’s linear regression test among all variables except weight and body fat percentage, excluding small-sized studies (WC, muscle mass). Also, as a result of Begg’s test using a rank correlation test, no factor showed a significant difference, so the publication bias of the literature used in this study could not be confirmed.
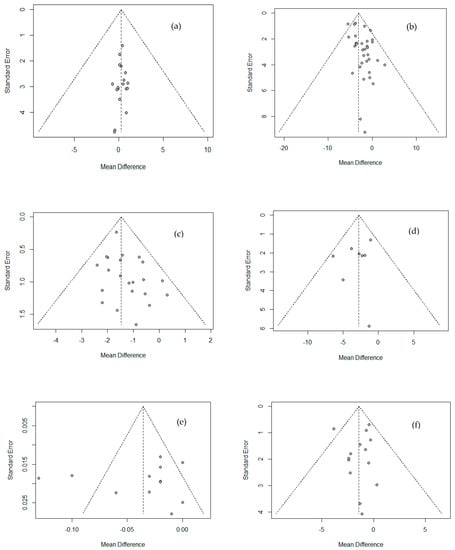
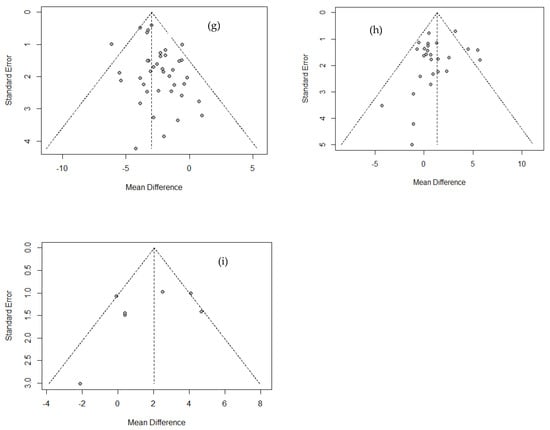
Figure 4.
Funnel plot showing the publication bias of Physique and body composition. (a) Height; (b) weight; (c) BMI; (d) WC; (e) WHR; (f) fat mass.; (g) % body fat; (h) lean mass; (i) muscle mass.
4. Discussion
Since changes in body composition occur throughout the lifespan due to growth, maturation and aging, as well as factors such as diseases and behaviors, it is a representative indicator for determining the level of body development [58]. Observing changes in body composition is an important factor in determining health, disease, exercise, and nutrition. It is also a very important factor in physique and athletic performance [59].
In general, Taekwondo training in Korea consists of 5 sessions per week, 1 h per session [60]. The training period is about 12 weeks, which we present in Table 1. Taekwondo exercise consists of 5 min each of warm-up and cool-down routines, followed by 50 min of exercise including basic Taekwondo movements, Poomsae, and Gyeorugi (fighting simulation) as the main exercises. Most taekwondo training centers apply a similar method. Therefore, the effect of taekwondo training in this study has very suitable conditions for meta-analysis.
As a result of analyzing the effect of Taekwondo training on changes in body composition, statistically significant differences were found in body weight, BMI, WC, body fat mass, body fat percentage, lean mass, and muscle mass, excluding height. Especially in the case of students, body weight and body fat percentage decreased significantly, and lean mass and muscle mass also tended to increase. In the elderly, a significant decrease in body fat percentage and an increase in muscle mass were found.
According to ACSM guidelines, exercise intensity 40–70% VO2R (oxygen uptake reserve) is recommended for overweight and obesity management [61]. Taekwondo’s basic movements, kicks, and Poomsae movements have an exercise intensity of 84% HRmax and 56.8~82.2% VO2max [62]. Taekwondo competition is a high-intensity exercise with an exercise intensity of 10 METs [63]. As such, Taekwondo exhibits anaerobic exercise patterns during matches and competitions and aerobic exercise patterns during taekwondo aerobics, Poomsae, sparring steps, basic movements, and moving kicks.
Therefore, the results of this study are clear evidence that the type of exercise and intensity of Taekwondo has positive effects on reducing body weight and body fat and increasing lean mass. In addition, there is a disadvantage that long and tedious exercise time is required to obtain meaningful exercise effects with general aerobic exercise such as walking or running [64]. In contrast, Taekwondo is an interval training type that alternates high- and low-intensity exercise repeatedly. In addition, Taekwondo gives interest and has higher exercise effects within the same amount of exercise time than other exercise types such as walking or moderate running [65]. Therefore, the exercise program using Taekwondo will positively improve obesity, the most severe health issue in Korea, and contribute significantly to preventing chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disease.
We found one unfortunate thing while conducting this study. That is, many studies reporting on the effectiveness of Taekwondo training do not apply an RCT design or even have no control group. In fact, there were many documents excluded from the analysis because there was no control group during this study. Therefore, if researchers who want to explain the effects of Taekwondo training in the future follow the RCT design well, follow-up researchers will find clearer results.
5. Conclusions
We found that taekwondo training at a frequency of five times per week for more than 12 weeks positively improved the obesity factor through this study. These findings are clear evidence that Taekwondo training is an effective exercise that can prevent or positively improve obesity. In addition, it shows that Taekwondo has value as a lifestyle sport that can contribute to the promotion of human health, not just bounded in the field of martial arts and sports.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.B. and S.-S.N.; methodology, S.B., J.-D.L. and S.-S.N.; software, S.B.; validation, S.B., J.-B.P. and S.-S.N.; formal analysis, S.B. and S.-S.N.; investigation, S.B., S.-H.C. and J.-B.P.; resources, S.B. and J.-D.L.; data creation, S.B. and J.-D.L.; writing original draft preparation, S.B. and S.-S.N.; writing—review and editing, S.B., J.-D.L. and S.-S.N.; visualization, S.B.; supervision, S.-H.C., J.-B.P. and S.-S.N.; project administration, S.B. and S.-S.N.; funding acquisition, J.-D.L., S.-H.C., J.-B.P. and S.-S.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by Taekwondo Research Institute of Kukkiwon.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of SungShin Women’s University SSWUIRB-2021-030 and 06-12-2021).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
All authors sincerely thank Kukkiwon President Lee Dongsub for supporting this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- World Taekwondo Federation. Vision, Mission, Strategy; World Taekwondo Federation: Seoul, Korea, 2021; Available online: http://www.worldtaekwondo.org/about-wt/about.html (accessed on 10 August 2021).
- Ministry of Health and Welfare. The 3rd National Health Plan (2011–2020); Ministry of Health and Welfare: Seoul, Korea, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Korea Center for Disease Control Trend of Physical Activity Practice Rate, 2007–2017. 2019. Available online: http://www.kdca.go.kr/filepath/boardDownload.es?bid=0034&list_no=364483&seq=1 (accessed on 10 August 2021).
- Guthold, R.; Stevens, G.A.; Riley, L.M.; Bull, F.C. Global trends in insufficient physical activity among adolescents: A pooled analysis of 298 population-based surveys with 1· 6 million participants. Lancet Child. Adolesc. Health 2020, 4, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, S.K.; Smuder, A.J.; Criswell, D.S. Mechanistic links between oxidative stress and disuse muscle atrophy. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 15, 2519–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swift, D.L.; Johannsen, N.M.; Lavie, C.J.; Earnest, C.P.; Church, T.S. The role of exercise and physical activity in weight loss and maintenance. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2014, 56, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Byun, J.C. body composition, Cholesterol, Lumbar and femur BMD and bone marker hormones by Taekwondo training in children. Korean J. Growth Dev. 2005, 13, 41–51. [Google Scholar]
- Song, E. The Effects of a 10-Week Taekwon Diet Program on Body Composition, Blood Pressure, Blood Glucose and Physical Self-Description of Obese Women. Ph.D. Thesis, Kyung Hee University, Yongin, Korea, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.M. Effects of Taekwondo training on left ventricular function and cardiovascular disease risk factor in hypertensive obese elderly women. Ph.D. Thesis, Dong-A University, Busan, Korea, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.B. The effects of Poomsae training of Taekwondo on senile demantia factor and physical fitness in the elderly. Master’s Thesis, Dong-A University, Busan, Korea, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Marković, G.; Mišigoj-Duraković, M.; Trninić, S. Fitness profile of elite Croatian female taekwondo athletes. Coll. Antropol. 2005, 29, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Heller, J.; Peric, T.; Dlouha, R.; Kohlikova, E.; Melichna, J.; Novakova, H. Physiological profiles of male and female taekwon-do (ITF) black belts. J. Sports Sci. 1998, 16, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhlel, E.; Jouini, A.; Gmada, N.; Nefzi, A.; Abdallah, K.B.; Tabka, Z. Heart rate and blood lactate responses during Taekwondo training and competition. Sci. Sports 2006, 21, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.D. Easy-to-Understand Meta-Analysis; Hakjisa Publishing: Seoul, Korea, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Moher, D.; Shamseer, L.; Clarke, M.; Ghersi, D.; Liberati, A.; Petticrew, M.; Shekelle, P.; Stewart, L.A. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst. Rev. 2015, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thomas, J.; Chandler, J.; Cumpston, M.; Li, T.; Page, M.J.; Welch, V.A. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, S.R.; Kim, S. Intervention meta-analysis: Application and practice using R software. Epidemiol. Health 2019, 41, e2019008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DerSimonian, R.; Laird, N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control. Clin. Trials 1986, 7, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, S.R. R Meta-Analysis for Medical and Health Researchers; Hannarae Publishing: Seoul, Korea, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Shim, S.R.; Shin, I.S.; Bae, J.M. Intervention meta-analysis using STATA software. J. Health Inform. Stat. 2016, 41, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W. The Effect of Taekwondo Training Activity on the Development of Physical Strength toward Obesity Children. Master’s Thesis, Dong-A University, Busan, Korea, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.H. Effect of Taekwondo Program and Calcium Intake on Body Composition, Physical Fitness, Growth Hormone, and IGF-1 in Elementary School Male Students. Master’s Thesis, Pusan National University, Busan, Korea, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.W. Effects of Taekwondo Training on Physical Fitness and Immune System Function in Infantile Obesity. Master’s Thesis, Pusan National University, Busan, Korea, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, S.H. Effect of Official Rhythmic Poomsae Training Program on Body Composition, Physical Fitness and Growth Factor in Elementary Students. Master’s Thesis, Dong-A University, Busan, Korea, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.J. The Effect of Taekwondo Training on Body Composition, Physical Fitness, and Balance Ability in Obese Grade-Schooler. Master’s Thesis, Chosun University, Gwangju, Korea, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.H. The effects of Taekwondo training on PAPS, Growth Factor and Attention concentration in Children. Master’s Thesis, Dong-A University, Busan, Korea, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, D.W. Effect of Taekwondo Training on Body Composition, Bone Mineral Density and Isokinetic Concentric/Eccentric Contractions of Teenagers for 12 Weeks. Ph.D. Thesis, Woosuk University, Wanju-gun, Korea, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- An, S.W. The Effects of Taekwondo Training on Physical Fitness and Insulin in Obese Adolescents. Master’s Thesis, Dong-A University, Busan, Korea, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, D.K. The Effect of Taekwondo Training on Body Composition, Physical Fitness and Growth Factors in Female Students after Menarche. Master’s Thesis, Dong-A University, Busan, Korea, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, H.C. Effects of 16 Weeks of Taekwondo Training on Abdominal Fat, Adipocytokines, Bone Mineral Density, Bone Turnover Markers, and Health-Related Fitness in Obese Male Adolescents. Ph.D. Thesis, Kyunghee University, Yongin, Korea, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, M.G. The Effects of Taekwondo Training on Body Composition, Blood Lipid, and Adiponectin in Obese Middle School Girls. Ph.D. Thesis, Chosun University, Gwangju, Korea, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, D.S.; Kim, D.Y. The Effect of Taekwondo on Body Composition, Physical Fitness and Growth Factors in Elderly Women. Korea Sport Res. 2007, 18, 495–506. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, W.K.; Kwon, Y.C. The Effect of Taekwondo Training on Physical Fitness and Growth Hormone, IGF-1 or DHEAs Concentration in Obesity Adolescent. Korean J. Sports Sci. 2009, 18, 1007–1018. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, Y.C.; Park, S.K.; Kim, E.H.; Park, J.K.; Jang, J.H. Effects of Taekwondo Training on Body Composition, Physical Fitness and Serum Adiponectin in Children Obesity. J. Korean Alliance Martial Arts 2010, 12, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Baek, Y.H. The Effect of Taekwondo and Allium Tuberosum Intake on Body Composition, Blood Lipids and C-Reactive Protein. J. Life Sci. 2011, 21, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, W.J.; Jeoung, J.H. Effects of Taekwondo Poomsae Training on Body Composition, Blood Lipid, and Adiponectin in Obese Children. J. Korean Alliance Martial Arts 2013, 15, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.K.; Kim, H.B.; Kang, H.J.; Jung, H.C. Effect of 12 weeks Taekwondo Poomsae training on body composition, health-related fitness and dietary intake in male adolescents. Taekwondo J. Kukkiwon 2013, 4, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, W.J.; Yoon, O.N. The Effect of 12Weeks Taekwondo Training Program on Blood Lipid and Growth Hormone in Obese Children. Korean J. Growth Dev. 2014, 22, 267–272. [Google Scholar]
- Chea, S.I. Effects on Lipid Metabolic-related Hormones, Inflammatory Markers and Metabolic Syndrome of Intermittent High Intensity Interval Training Using Taekwondo and Continuous Aerobic Training in Middle-Aged Obese Women. Ph.D. Thesis, Hanyang University, Ansan, Korea, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, D.K. The Effect of Taekwondo Exercise on Body Composition, Neurotransmitter and Brain Nerve Growth Factor in Middle-aged Women. Ph.D. Thesis, Pukyong National University, Busan, Korea, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Han, S.Y.; Kim, H.; Lee, S.H. Effects of Basic Taekwondo Movement Training on Body Composition, Cardiorespiratory of Middle-aged Women. Korean J. Sports Sci. 2007, 16, 667–681. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.T. Influence of Taekwondo and Combined Strength Exercise on Health-Related Physical Fitness and Blood Lipid in Private Security Guards. J. Korean Alliance Martial Arts 2010, 12, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.K. The Effect of Taekwondo Training on Electrophysiological Stress, Stress Hormone and Body Composition (BIA & CT) in Middle-Aged Women. Korean J. Sports Sci. 2011, 20, 1029–1039. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.K. Effects of Taekwondo Training on Body Composition, Blood Lipid and Bone Mineral Density in Postmenopausal Women. J. Sport Leis. Stud. 2015, 61, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, S.E.; Jung, H.C.; Kang, H.J.; Jung, S.W.; Seo, M.W.; Kim, S.W.; Song, J.K. Effect of 12 weeks of Taekwondo training on body fatness, health-related fitness and isokinetic muscle strength in obese women aged 35–55 years. Korean Soc. Sports Sci. 2017, 26, 879–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.S.; An, Y.J.; Kim, T.W.; Son, H.J.; Yang, J.H.; Mo, K.W.; Kim, S.K.; Jang, C.H. The Effect of 8 Weeks Rope-Skipping Exercise and Taekwondo Exercise on Blood lipids, Vascular Compliance, Oxidant Stress and Antioxidant Capacity in Middle Aged Men. Korean J. Phys. Educ. 2017, 56, 651–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, M.K.; Ryu, J.K.; Jung, H.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Park, S.K. Effects of Taekwondo aerobic and Combined Exercise Program on Health-related Physical Fitness and Physical Activity and Depression Scale in Menopausal Obesity Women. Korean Soc. Sports Sci. 2018, 27, 1199–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.G.; Lee, S.H. Effects of Taekwondo Exercise on Body Composition, Lipid Profile and Leptin in Obese Middle-aged Women. J. World Soc. Taekwondo Cult. 2019, 10, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.S.; Lee, J.Y. The Effect of 12 weeks Taekwondo Training on Body-Composition, Blood Irisin, Adiponectin, and Lipids Levels in Obese College Students. Korean Soc. Sports Sci. 2018, 27, 1081–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.S.; Lee, J.Y. The Effect of Long-Term Taekwondo Participation on Blood Glucose, Insulin, CRP levels, HOMA-IR, and Body-Composition in Obese Male College Students. Korean J. Sports Sci. 2018, 27, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chea, S.I. A Study on the Effect of Functional Fitness, Body composition and Vascular Compliance before and after 12 weeks Taekwondo Training in Elder Women. Master’s Thesis, Hanyang University, Ansan, Korea, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, H.J. Effects of 12 Weeks of Taekwondo and Resistance Training on Bone Mineral Density, Bone Turnover Markers, Functional Fitness, and Arterial Compliance in Elderly Women. Ph.D. Thesis, Kyunghee University, Yongin, Korea, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, J.D.; Kim, W.K. Effects of taekwondo poomsae training on body composition, β-amyloid and DHEAs concentration in elderly women. Korean J. Phys. Educ. 2009, 48, 503–511. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, D.S.; Kwon, Y.C. The effect of Taekwondo Exercise on Health-Related Physical Fitness, Cognitive Ability and Dementia-induced Factors in Frail Elderly Women. Korean J. Sports Sci. 2010, 19, 875–887. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, J.D. Effects of Difference Exercise Type on Taekwondo Poomsae Training and Walking exercise on Body Compositon, Serum Cholesterol and Dementia Risk Factors in Elderly Obese Women. Korean J. Sports Sci. 2010, 19, 1069–1080. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, W.J. The Effects of Taekwondo Poomsae Training on Body Composition, hs-CRP, TNF-α and Adiponectin in Old obese Women. Korean J. Sport 2012, 10, 567–578. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, Y.R.; Lee, G.H. The Influence of 12-week Taekwondo Aerobics on Healthy Physical Fitness and Blood Composition in the Middle Ages Woman. Korean J. Sport 2017, 15, 547–555. [Google Scholar]
- Zemel, B. Body composition during growth and development. In Human Growth and Development; Elsevier Science: Orando, FL, USA, 2002; pp. 271–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchard, C.E.; Shephard, R.J.; Stephens, T.E. Physical Activity, Fitness, and Health: International Proceedings and Consensus Statement. International Consensus Symposium on Physical Activity, Fitness, and Health, 2nd, Toronto, ON, Canada, May 1992; Human Kinetics Publishers: Champaign, IL, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, S.; Lim, K. Effects of Taekwondo training on physical fitness factors in Korean elementary students: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Exerc. Nutr. Biochem. 2019, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riebe, D.; Ehrman, J.K.; Liguori, G.; Magal, M. American College of Sports Medicine. ACSM’s Guidelines for Exercise Testing and Prescription; Wolters Kluwer: Alphen aan den Rijn, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.K.; Kong, M.A.; Kang, H.S. Measurement of exercise intensity during basic movement, kicking and Poomsae of Taekwondo. Korean Soc. Exerc. Physiol. 2003, 12, 727–734. [Google Scholar]
- Ainsworth, B.E.; Haskell, W.L.; Herrmann, S.D.; Meckes, N.; Bassett, D.R.; Tudor-Locke, C.; Greer, J.L.; Vezina, J.; Whitt-Glover, M.C.; Leon, A.S. 2011 Compendium of Physical Activities: A second update of codes and MET values. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2011, 43, 1575–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alkahtani, S. Comparing fat oxidation in an exercise test with moderate-intensity interval training. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2014, 13, 51. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Helgerud, J.; Høydal, K.; Wang, E.; Karlsen, T.; Berg, P.; Bjerkaas, M.; Simonsen, T.; Helgesen, C.; Hjorth, N.; Bach, R. Aerobic high-intensity intervals improve VO2max more than moderate training. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2007, 39, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).