Seasonal Water Quality and Algal Responses to Monsoon-Mediated Nutrient Enrichment, Flow Regime, Drought, and Flood in a Drinking Water Reservoir
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
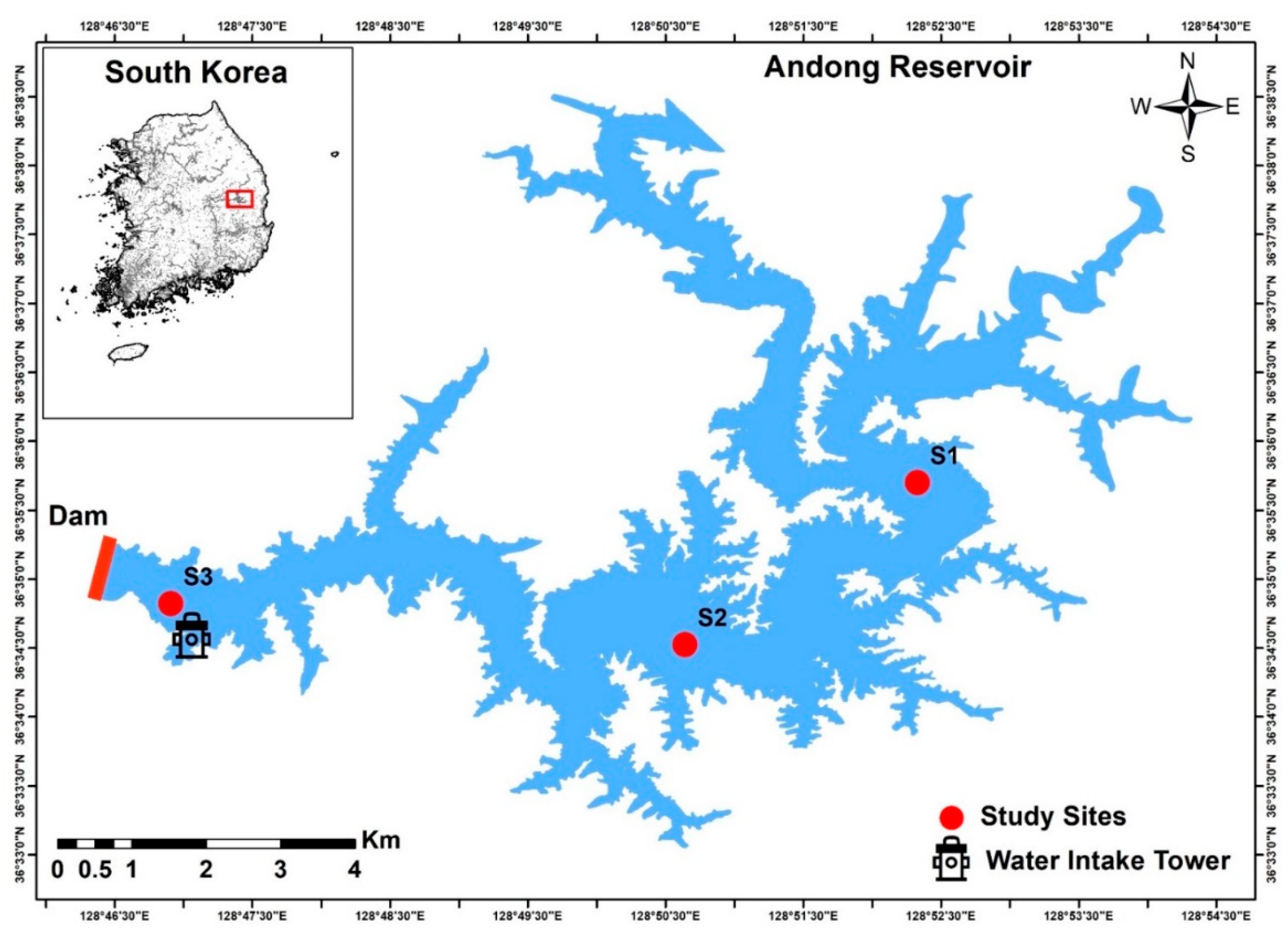
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Analyses of Water Chemistry
2.3. Flood-Drought Dynamics, Flow Regime, and Rainfall Data
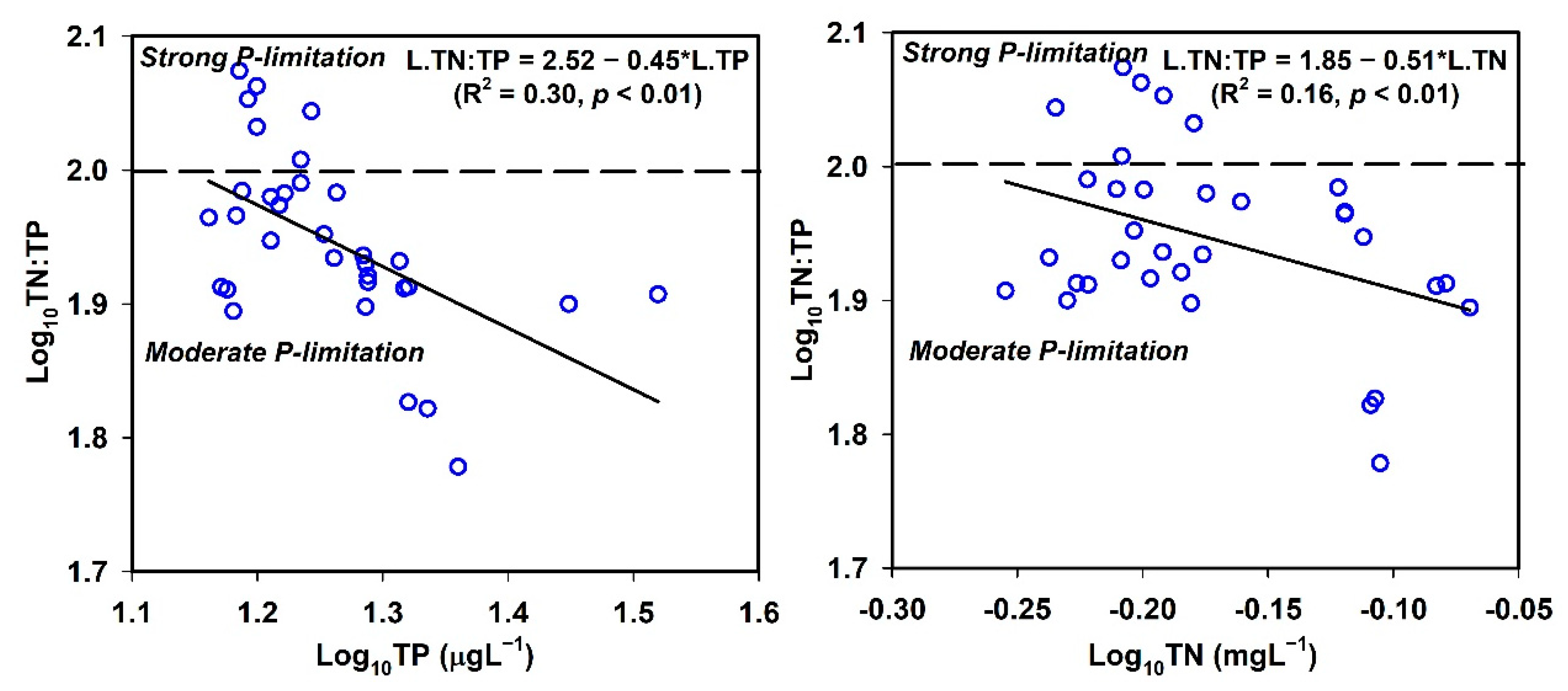
2.4. Establishment of Trophic Status and Nutrient Enrichment
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Spatio-Seasonal Trends in Reservoir Water Chemistry and Nutrient Classification
3.2. Correlation Analysis of Physicochemical Water Quality
3.3. Long-Term Trends in Water Chemistry
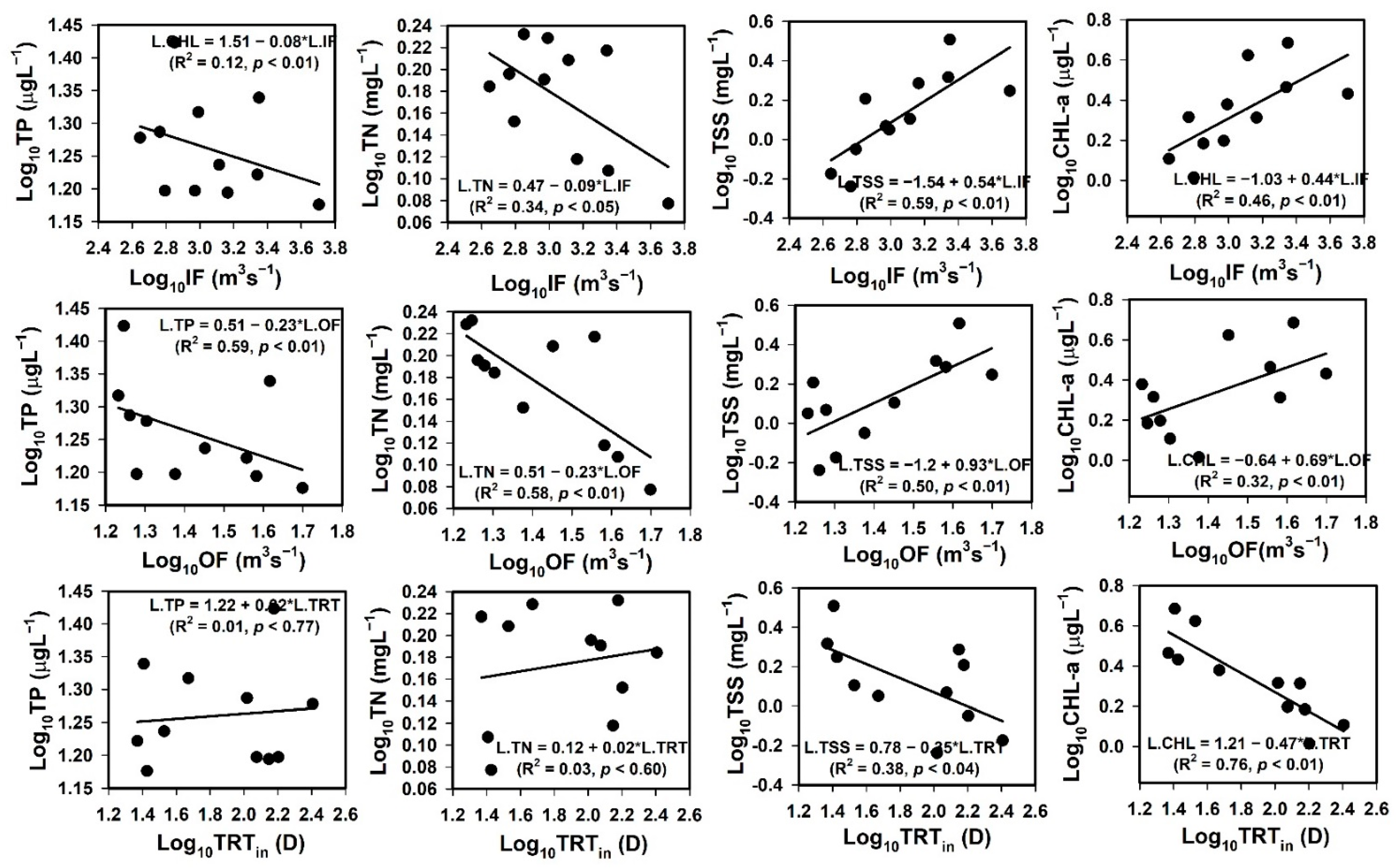
3.4. Impact of Flood and Drought Dynamics
3.5. Relationships between Flow Regime, Nutrients, TSS, and Sestonic Chl-a
3.6. Empirical Modelling of Nutrients and Sestonic CHL-a
3.7. Organic Pollutants, Transparency, and Nonalgal Light Attenuation
3.8. Seasonal Multivariate Water Quality Evaluation
3.8.1. The PCA/FA Results
3.8.2. The DA of Seasonal Variations
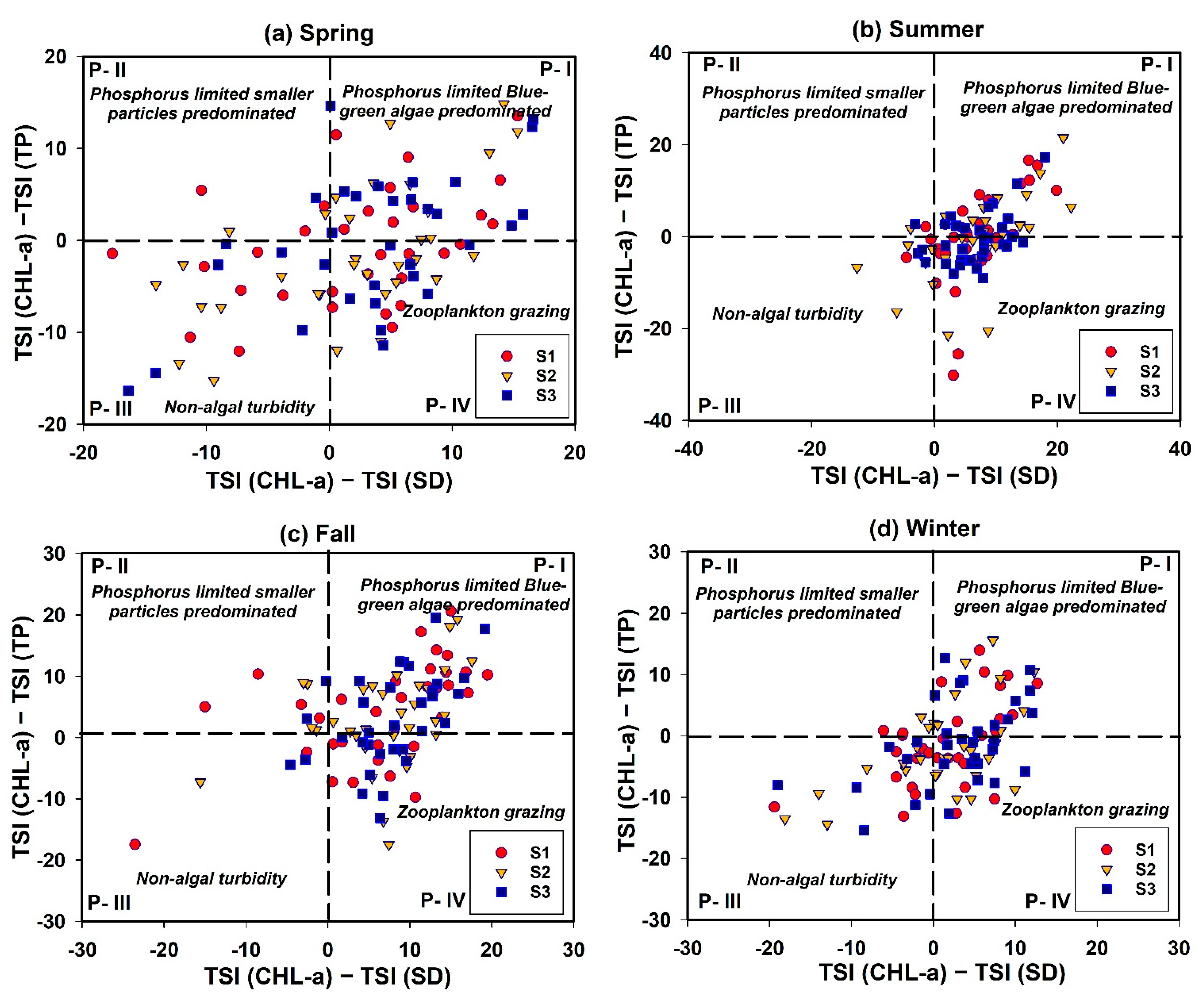
3.9. Seasonal Trophic Status Assessment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hutchins, M.G.; Abesser, C.; Prudhomme, C.; Elliott, J.A.; Bloomfield, J.P.; Mansour, M.M.; Hitt, O.E. Combined impacts of future land-use and climate stressors on water resources and quality in groundwater and surface waterbodies of the upper Thames river basin, UK. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 962–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atique, U.; An, K.G. Reservoir water quality assessment based on chemical parameters and the chlorophyll dynamics in relation to nutrient regime. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2019, 28, 1043–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinotti, V.; Balordi, M.; Ciceri, G. A flow injection analyser conductometric coupled system for the field analysis of free dissolved CO2 and total dissolved inorganic carbon in natural waters. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 403, 1083–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Schoups, G.; van de Giesen, N. Organic pollution of rivers: Combined threats of urbanization, livestock farming and global climate change. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vörösmarty, C.J.; McIntyre, P.B.; Gessner, M.O.; Dudgeon, D.; Prusevich, A.; Green, P.; Glidden, S.; Bunn, S.E.; Sullivan, C.A.; Reidy Lierman, C.; et al. Global threats to human water security and river biodiversity. Nature 2010, 467, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, D.-Y.; Atique, U.; Yoon, J.; Lim, B.; An, K.-G. Ecological Risk Assessment of Urban Streams Using Fish Biomarkers of DNA Damages and Physiological Responses. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2020, 29, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, W.-K.; Atique, U.; An, K.-G. Ecological risk assessments and eco-toxicity analyses using chemical, biological, physiological responses, DNA damages and gene-level biomarkers in Zebrafish (Danio rerio) in an urban stream. Chemosphere 2020, 239, 124754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hering, D.; Carvalho, L.; Argillier, C.; Beklioglu, M.; Borja, A.; Cardoso, A.C.; Duel, H.; Ferreira, T.; Globevnik, L.; Hanganu, J.; et al. Managing aquatic ecosystems and water resources under multiple stress—An introduction to the MARS project. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 503–504, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyeste, K.; Dobrocsi, P.; Czeglédi, I.; Czédli, H.; Harangi, S.; Baranyai, E.; Simon, E.; Nagy, S.A.; Antal, L. Age and diet-specific trace element accumulation patterns in different tissues of chub (Squalius cephalus): Juveniles are useful bioindicators of recent pollution. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 101, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgieva, E.; Yancheva, V.; Stoyanova, S.; Velcheva, I.; Iliev, I.; Vasileva, T.; Bivolarski, V.; Petkova, E.; László, B.; Nyeste, K.; et al. Which Is More Toxic? Evaluation of the Short-Term Toxic Effects of Chlorpyrifos and Cypermethrin on Selected Biomarkers in Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio, Linnaeus 1758). Toxics 2021, 9, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atique, U.; Kwon, S.; An, K.-G. Linking weir imprints with riverine water chemistry, microhabitat alterations, fish assemblages, chlorophyll-nutrient dynamics, and ecological health assessments. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamun, M.; Kim, J.Y.; An, K.G. Multivariate statistical analysis of water quality and trophic state in an artificial dam reservoir. Water 2021, 13, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagenhoff, A.; Townsend, C.R.; Matthaei, C.D. Macroinvertebrate responses along broad stressor gradients ofdeposited fine sediment and dissolved nutrients: A stream mesocosm experiment. J. Appl. Ecol. 2012, 49, 892–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atique, U.; Iqbal, S.; Khan, N.; Qazi, B.; Javeed, A.; Anjum, K.M.; Haider, M.S.; Khan, T.A.; Mahmood, S.; Sherzada, S. Multivariate Assessment of Water Chemistry and Metals in a River Impacted by Tanning Industry. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2020, 29, 3013–3025. [Google Scholar]
- Haque, M.A.; Jewel, M.A.S.; Atique, U.; Paul, A.K.; Iqbal, S. Seasonal and spatial variation of flagellate communities in a tropical river. Limnologica 2020, 85, 125824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.A.; Jewel, M.A.S.; Akhi, M.M.; Atique, U.; Paul, A.K.; Iqbal, S.; Islam, M.S.; Das, S.K.; Alam, M.M. Seasonal dynamics of phytoplankton community and functional groups in a tropical river. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-J.; Atique, U.; An, K.-G. Long-term ecological health assessment of a restored urban stream based on chemical water quality, physical habitat conditions and biological integrity. Water 2019, 11, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Atique, U.; An, K.-G. Relative abundance and invasion dynamics of alien fish species linked to chemical conditions, ecosystem health, native fish assemblage, and stream order. Water 2021, 13, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, V.H.; Schindler, D.W. Eutrophication science: Where do we go from here? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2009, 24, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, E.; Søndergaard, M.; Jensen, J.P.; Havens, K.E.; Anneville, O.; Carvalho, L.; Coveney, M.F.; Deneke, R.; Dokulil, M.T.; Foy, B.; et al. Lake responses to reduced nutrient loading—An analysis of contemporary long-term data from 35 case studies. Freshw. Biol. 2005, 50, 1747–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spears, B.M.; Carvalho, L.; Dudley, B.; May, L. Variation in chlorophyll a to total phosphorus ratio across 94 UK and Irish lakes: Implications for lake management. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 115, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atique, U.; An, K.-G. Stream health evaluation using a combined approach of multi-metric chemical pollution and biological integrity models. Water 2018, 10, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atique, U.; Byungjin, L.; Johee, Y.; An, K.-G. Biological Health Assessments of Lotic Waters by Biotic Integrity Indices and their Relations to Water Chemistry. Water 2019, 11, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, J.; Atique, U.; An, K.G. Multiyear links between water chemistry, algal chlorophyll, drought-flood regime, and nutrient enrichment in a morphologically complex reservoir. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Atique, U.; Mamun, M.; An, K.-G. Long-Term Interannual and Seasonal Links between the Nutrient Regime, Sestonic Chlorophyll and Dominant Bluegreen Algae under the Varying Intensity of Monsoon Precipitation in a Drinking Water Reservoir. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, G.; Pietiläinen, O.P.; Carvalho, L.; Solimini, A.; Lyche Solheim, A.; Cardoso, A.C. Chlorophyll-nutrient relationships of different lake types using a large European dataset. Aquat. Ecol. 2008, 42, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamun, M.; Kwon, S.; Kim, J.E.; An, K.G. Evaluation of algal chlorophyll and nutrient relations and the N:P ratios along with trophic status and light regime in 60 Korea reservoirs. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 140451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, N.M.; Deemer, B.R.; Corman, J.R.; Razavi, N.R.; Strock, K.E. Key differences between lakes and reservoirs modify climate signals: A case for a new conceptual model. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2017, 2, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ma, J.; Guo, J.; Paerl, H.W.; Brookes, J.D.; Xiao, Y.; Lunhui, L. Water quality trends in the Three Gorges Reservoir region before and after impoundment (1992–2016). Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2018, 19, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atique, U.; An, K.-G. Landscape heterogeneity impacts water chemistry, nutrient regime, organic matter and chlorophyll dynamics in agricultural reservoirs. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 110, 105813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamun, M.; Kim, J.Y.; An, K.-G. Trophic Responses of the Asian Reservoir to Long-Term Seasonal and Interannual Dynamic Monsoon. Water 2020, 12, 2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdiyan, O.; Filazzola, A.; Molot, L.A.; Gray, D.; Sharma, S. Drivers of water quality changes within the Laurentian Great Lakes region over the past 40 years. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2021, 66, 237–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Rocha, C.A.N., Jr.; da Costa, M.R.A.; Menezes, R.F.; Attayde, J.L.; Becker, V. Water volume reduction increases eutrophication risk in tropical semi-arid reservoirs. Acta Limnol. Bras. 2018, 30, e106. [Google Scholar]
- Brasil, J.; Attayde, J.L.; Vasconcelos, F.R.; Dantas, D.D.F.; Huszar, V.L.M. Drought induced water-level reduction favors cyanobacteria blooms in tropical shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 2016, 770, 145–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, K.G.; Park, S.S. Indirect influence of the summer monsoon on chlorophyll-total phosphorus models in reservoirs: A case study. Ecol. Model. 2002, 152, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, K.-G.; Park, S.S.; Ahn, K.Y.; Urchin, C.G. Dynamics of nitrogen, phosphorus, algal biomass, and suspended solids in an artificial lentic ecosystem and significant implications of regional hydrology on trophic status. J. Environ. Biol. 2003, 24, 29–38. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.J.; An, K.-G. The development and application of multi-metric water quality assessment model for reservoir managements in Korea. Korean J. Limnol. 2009, 42, 242–252. [Google Scholar]
- K-Water. Working Reference on Dam Operations; K-Water: Daejeon, Korea, 2019. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- K-Water. Specification of the Andong Dam; K-Water: Daejeon, Korea, 2020. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Kwak, J.; Joo, H.; Jung, J.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.S. A case study: Bivariate drought identification on the Andong dam, South Korea. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2020, 35, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, A.; Franson, M.A. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Crumpton, W.G.; Isenhart, T.M.; Mitchell, P.D. Nitrate and organic N analyses with second-derivative spectroscopy. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1992, 37, 907–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prepas, E.E.; Rigler, F.H. Improvements in quantifying the phosphorus concentration in lake water. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1982, 39, 822–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA (American Public Health Association); American Water Works Association (AWWA); Water Environment Federation (WEF). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; AWWA: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; ISBN 9780875530130. [Google Scholar]
- MOE (Ministry of Environment). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water Quality Contamination; The Ministry of Environments (MOE): Gwacheon, Korea, 2000.
- Carlson, R.E. A Trophic State Index for Lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1977, 22, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratzer, C.R.; Brezonik, P.L. A Carlson-type trophic state index for nitrogen in Florida lakes. Water Resour. Bull. 1981, 17, 713–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, R.E.; Havens, K.E. Simple graphical methods for the interpretation of relationships between trophic state variables. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2005, 21, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, W.W. An empirical analysis of phosphorus, nitrogen, and turbidity effects on reservoir chlorophyll-A levels. Can. Water Resour. J. 1982, 7, 88–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Helsel, D.R.; Mueller, D.K.; Slack, J.R. Computer Program for the Kendall Family of Trend Tests; Scientific Investigations Report 2005–5275; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2006.
- Singh, A.; Maichle, R. ProUCL V. 5.1. Statistical Software for Environmental Applications for Data Sets with and without Nondetect Observations; USEPA: Washington, WA, USA, 2016.
- Hammer, Ø.; Harper, D.A.T.; Ryan, P.D. PAST: Paleontological Statistics Software Package for Education and Data Analysis. Palaeontol. Electron. 2001, 4, 9. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. Eutrophication of Waters: Monitoring Assessment and Control; OECD: Paris, France, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Driedger, A.G.J.; Dürr, H.H.; Mitchell, K.; VanCappellen, P. Plastic debris in the Laurentian Great Lakes: A review. J. Great Lakes Res. 2015, 41, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhateria, R.; Jain, D. Water quality assessment of lake water: A review. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 2, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, Y.S.; Patil, S.K.; Dhande, A.D.; Pawar, N.S. Water quality of river Tapti at Bhusawal Town. Indian J. Environ. Protect. 2003, 23, 620–623. [Google Scholar]
- Dixit, A.; Siddaiah, N.S.; Joshi, P. Hydrogeochemical assessment of wetlands of Gurugram, Haryana, India: Implications for natural processes and anthropogenic changes. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, S.; Pilon, P.; Cavadias, G. Power of the Mann ± Kendall and Spearman s rho tests for detecting monotonic trends in hydrological series. J. Hydrol. 2002, 259, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caissie, D. The thermal regime of rivers—A review. Freshw. Biol. 2006, 51, 1389–1406. [Google Scholar]
- Jeppesen, E.; Brucet, S.; Naselli-Flores, L.; Papastergiadou, E.; Stefanidis, K.; Nõges, T.; Nõges, P.; Attayde, J.L.; Zohary, T.; Coppens, J.; et al. Ecological impacts of global warming and water abstraction on lakes and reservoirs due to changes in water level and related changes in salinity. Hydrobiologia 2015, 750, 201–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; McLean, C.E.; Long, D.T.; Steinman, A.D.; Stevenson, R.J. Eutrophication and recovery of a Lake inferred from sedimentary diatoms originating from different habitats. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 628, 1352–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhagwat, T.; Klein, I.; Huth, J.; Leinenkugel, P. Volumetric Analysis of Reservoirs in Drought-Prone Areas Using Remote Sensing Products. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atique, U.; Mamun, M.; An, K.G. Links between land use patterns, chlorophyll-nutrients regime, organic matter, water clarity and trophic state dynamics along with empirical models development in agricultural reservoirs. In Proceedings of the 2020 Korea Institute of Environmental Biology Spring E-Conference, Jeju Island, Korea, 10 July 2020; p. 167. [Google Scholar]
- Rueda, F.; Moreno-Ostos, E.; Armengol, J. The residence time of river water in reservoirs. Ecol. Model. 2006, 191, 260–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, M.; Wang, K.; Yang, N.; Li, F.; Zou, Y.; Chen, X.; Deng, Z.; Xie, Y. Evaluation and variation trends analysis of water quality in response to water regime changes in a typical river-connected lake (Dongting Lake), China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poff, N.L.R.; Schmidt, J.C. How dams can go with the flow. Science 2016, 353, 1099–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maavara, T.; Chen, Q.; Van Meter, K.; Brown, L.E.; Zhang, J.; Ni, J.; Zarfl, C. River dam impacts on biogeochemical cycling. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, D.S.; Hwang, S.J.; An, K.G. Nutrients and chlorophyll-a dynamics in a temperate reservoir influenced by Asian monsoon along with in situ nutrient enrichment bioassays. Limnology 2010, 11, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.-H.; Kim, B.; Kim, C.; An, K.-G. Ecosystem health evaluation of agricultural reservoirs using multi-metric lentic ecosystem health assessment (LEHA) model. Paddy Water Environ. 2014, 12, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamun, M.; Lee, S.J.; An, K.G. Roles of nutrient regime and N:P ratios on algal growth in 182 Korean agricultural reservoirs. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2018, 27, 1175–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowlton, M.F.; Jones, J.R. Temporal and spatial dynamics of suspended sediment, nutrients, and algal biomass in Mark Twain Lake, Missouri. Arch. Hydrobiol. 1995, 135, 145–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.R.; Obrecht, D.V.; Perkins, B.D.; Knowlton, M.F.; Thorpe, A.P.; Watanabe, S.; Bacon, R.R. Nutrients, seston, and transparency of missouri reservoirs and oxbow lakes: An analysis of regional limnology. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2008, 24, 155–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muangthong, S.; Shrestha, S. Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: Case study of the Nampong River and Songkhram River, Thailand. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheela, A.M.; Letha, J.; Joseph, S.; Ramachandran, K.K.; Sanalkumar, S.P. Trophic state index of a lake system using IRS (P6-LISS III) satellite imagery. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 177, 575–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markad, A.T.; Landge, A.T.; Nayak, B.B.; Inamdar, A.B.; Mishra, A.K. A multivariate statistical approach for the evaluation of spatial and temporal dynamics of surface water quality from the small reservoir located in the drought-prone area of South-West India: A case study of Tiru reservoir (India). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 31013–31031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palácio, S.M.; Espinoza-Quiñones, F.R.E.; de Pauli, A.R.; Queiroz, C.B.; Fabris, S.C.; Fagundes-Klen, M.R.; Veit, M.; Piana, P.A. Assessment of anthropogenic impacts on the water quality of Marreco River, Brazil, based on principal component analysis and toxicological assays. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Aziz, T.N.; Del Giudice, D.; Hall, N.S.; Obenour, D.R. Exploring nutrient and light limitation of algal production in a shallow turbid reservoir. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 269, 116210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmudi, M.; Serihollo, L.G.; Herawati, E.Y.; Lusiana, E.D.; Buwono, N.R. A count model approach on the occurrences of harmful algal blooms (HABs) in Ambon Bay. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2020, 46, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodds, W.K.; Bouska, W.W.; Eitzmann, J.L.; Pilger, T.J.; Pitts, K.L.; Riley, A.J.; Schloesser, J.T.; Thornbrugh, D.J. Eutrophication of U.S. freshwaters: Analysis of potential economic damages. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jargal, N.; Atique, U.; Mamun, M.; An, K.G. Seasonal and long-term connections between trophic status, sestonic chlorophyll, nutrients, organic matter, and monsoon rainfall in a multipurpose reservoir. Water 2021, 13, 1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Water Quality Parameters | Mean ± SD (Min–Max) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter | |||||||||
| S1 | S2 | S3 | S1 | S2 | S3 | S1 | S2 | S3 | S1 | S2 | S3 | |
| pH | 7.46 ± 0.34 | 7.38 ± 0.33 | 7.29 ± 0.28 | 7.46 ± 0.52 | 7.41 ± 0.41 | 7.30 ± 0.45 | 7.20 ± 0.39 | 7.18 ± 0.35 | 6.98 ± 0.40 | 7.21 ± 0.30 | 7.18 ± 0.34 | 7.02 ± 0.33 |
| (6.8–8.2) | (6.9–8.3) | (6.8–7.9) | (6.2–9.1) | (6.6–8.8) | (6.1–8.2) | (6.5–8.2) | (6.6–8) | (6.0–7.8) | (6.1–7.7) | (5.9–8.1) | (5.9–7.7) | |
| WT | 7.44 ± 2.66 | 6.68 ± 2.14 | 6.29 ± 1.60 | 15.87 ± 3.19 | 14.45 ± 2.68 | 12.53 ± 1.92 | 16.74 ± 2.19 | 15.70 ± 1.91 | 14.34 ± 2.19 | 7.33 ± 3.35 | 6.97 ± 2.79 | 6.76 ± 2.63 |
| (3.7–13) | (4–12.3) | (3.8–9.3) | (11–24.3) | (10–21.3) | (9.7–16.8) | (12.3–20.7) | (11.6–19.0) | (9.4–17.70) | (2–14) | (3–12.2) | (2–11.1) | |
| EC | 155.9 ± 49.1 | 153.5 ± 47.9 | 155.5 ± 53.8 | 169.8 ± 41.1 | 166.5 ± 47.9 | 167.7 ± 53.8 | 157.3 ± 25.6 | 153.0 ± 25.7 | 160.7 ± 27.0 | 157.0 ± 50.0 | 156.4 ± 50.0 | 157.6 ± 49.5 |
| (103–265) | (99–255) | (96–289) | (113–287) | (119–292) | (124–305) | (122–213) | (112–204) | (123–217) | (99–324) | (99–325) | (104–306) | |
| DO | 10.73 ± 0.85 | 10.70 ± 0.72 | 10.35 ± 0.62 | 7.21 ± 1.70 | 7.69 ± 1.45 | 7.89 ± 1.10 | 6.31 ± 1.18 | 5.97 ± 1.15 | 5.90 ± 1.24 | 9.76 ± 1.33 | 8.93 ± 1.72 | 8.31 ± 1.49 |
| (9.2–12.4) | (9.5–12.3) | (8.9–11.4) | (3.7–11.1) | (3.5–10.4) | (5.5–10.2) | (3.6–8.7) | (3.2–8.7) | (4.1–8.4) | (6.9–12.3) | (5.3–11.6) | (5.2–11.2) | |
| TSS | 0.79 ± 0.42 | 0.88 ± 0.47 | 0.87 ± 0.53 | 2.62 ± 1.94 | 2.01 ± 1.87 | 1.23 ± 0.9 | 2.39 ± 1.59 | 2.23 ± 1.65 | 1.31 ± 0.87 | 1.14 ± 0.75 | 1.25 ± 1.04 | 1.06 ± 0.82 |
| (0.2–1.8) | (0.1–1.8) | (0.2–2.2) | (0.2–17.6) | (0.2–13.2) | (0.2–8.3) | (0.1–15) | (0.2–15.4) | (0.3–4.1) | (0.3–3.5) | (0.2–5.3) | (0.2–4) | |
| BOD | 1.48 ± 0.43 | 1.45 ± 0.42 | 1.46 ± 0.43 | 1.47 ± 0.39 | 1.51 ± 0.31 | 1.45 ± 0.36 | 1.63 ± 0.28 | 1.57 ± 0.33 | 1.55 ± 0.31 | 1.44 ± 0.36 | 1.42 ± 0.37 | 1.34 ± 0.33 |
| (0.6–2.3) | (0.5–2.4) | (0.5–2.3) | (0.5–2.4) | (0.9–2.1) | (0.6–2.3) | (1–2.2) | (0.4–2.1) | (0.9–2.3) | (0.8–2.2) | (0.6–2.2) | (0.7–2.1) | |
| COD | 2.87 ± 0.30 | 2.83 ± 0.36 | 2.78 ± 0.28 | 2.94 ± 0.51 | 2.91 ± 0.48 | 2.77 ± 0.34 | 3.03 ± 0.75 | 2.87 ± 0.52 | 2.73 ± 0.70 | 2.73 ± 0.38 | 2.75 ± 0.46 | 2.71 ± 0.34 |
| (2.3–3.6) | (2.1–4.1) | (2.3–3.7) | (2.3–4.6) | (2.3–4.5) | (2.3–3.6) | (2.3–5.8) | (2.2–5) | (1.9–5.7) | (2.2–3.8) | (1.7–4.5) | (2.1–4) | |
| BOD:COD | 0.52 ± 0.16 | 0.52 ± 0.15 | 0.53 ± 0.16 | 0.52 ± 0.16 | 0.53 ± 0.14 | 0.54 ± 0.16 | 0.56 ± 0.14 | 0.56 ± 0.14 | 0.60 ± 0.19 | 0.54 ± 0.17 | 0.53 ± 0.16 | 0.51 ± 0.15 |
| (0.2–0.8) | (0.1–0.8) | (0.1–0.8) | (0.1–0.8) | (0.2–0.8) | (0.2–0.8) | (0.3–0.8) | (0.1–0.8) | (0.2–1.2) | (0.2–0.9) | (0.1–0.8) | (0.2–0.8) | |
| TP | 17.09 ± 5.0 | 16.79 ± 4.94 | 16.79 ± 5.77 | 23.48 ± 19.8 | 20.70 ± 10.9 | 18.39 ± 6.13 | 19.70 ± 6.24 | 19.82 ± 7.56 | 18.36 ± 4.04 | 16.94 ± 5.07 | 16.76 ± 5.27 | 17.15 ± 4.43 |
| (8–26) | (8–27) | (7–28) | (9–107) | (8–61) | (8–37) | (12–44) | (12–54) | (13–31) | (8–30) | (10–32) | (9–28) | |
| TN | 1.46 ± 0.22 | 1.43 ± 0.19 | 1.46 ± 0.18 | 1.58 ± 0.31 | 1.50 ± 0.27 | 1.48 ± 0.22 | 1.55 ± 0.30 | 1.53 ± 0.26 | 1.50 ± 0.26 | 1.54 ± 0.23 | 1.50 ± 0.23 | 1.49 ± 0.20 |
| (1.1–2) | (1.1–1.8) | (1.2–1.8) | (1.1–2.2) | (1.1–2.1) | (1–2) | (1.1–2.4) | (1.1–2) | (1–2) | (1–2) | (1–1.9) | (1–1.9) | |
| TN:TP | 92.27 ± 28.7 | 91.98 ± 31 | 97.48 ± 35.6 | 86.38 ± 34.7 | 82.21 ± 25.7 | 88.52 ± 31.9 | 83.10 ± 19.1 | 82.23 ± 18.3 | 83.64 ± 16.6 | 97.91 ± 31.2 | 95.41 ± 26.3 | 92.46 ± 27.5 |
| (49–160) | (50–201) | (44–200) | (20–188) | (33–174) | (39–201) | (44–110) | (36–116) | (52–115) | (61–195) | (53–155) | (47–164) | |
| Chl-a | 1.88 ± 0.29 | 1.82 ± 0.55 | 1.91 ± 0.34 | 2.88 ± 0.84 | 2.91 ± 0.89 | 2.19 ± 0.82 | 3.86 ± 0.55 | 3.34 ± 0.24 | 3.28 ± 0.45 | 1.65 ± 0.89 | 1.57 ± 0.89 | 1.68 ± 0.84 |
| (0.4–6.9) | (0.3–7.9) | (0.3–6.1) | (0.9–13.8) | (0.3–21.3) | (0.5–8.2) | (0.4–9.6) | (0.9–9.3) | (1–9.7) | (0.4–3.8) | (0.2–3.9) | (0.3–3.9) | |
| SD | 3.69 ± 1.17 | 3.85 ± 1.09 | 4.09 ± 1.18 | 4.08 ± 1.15 | 4.36 ± 1.42 | 4.65 ± 1.43 | 3.35 ± 1.30 | 3.65 ± 1.42 | 3.99 ± 1.51 | 3.78 ± 0.94 | 3.84 ± 0.96 | 4.06 ± 1.15 |
| (1.3–5.5) | (1.7–6) | (2.3–6.5) | (2–6) | (2–8) | (2–7.5) | (0.5–5.5) | (1–6) | (1–6.5) | (2–5.5) | (2.2–5.5) | (2.2–6) | |
| TCB | 49.76 ± 12 | 43.64 ± 14 | 32.21 ± 17 | 200.36 ± 25 | 229.52 ± 51 | 148.67 ± 46 | 276.33 ± 88 | 266.09 ± 33 | 765.00 ± 55 | 49.82 ± 12 | 79.12 ± 14 | 72.64 ± 16 |
| (0–345) | (0–180) | (0–136) | (1–1600) | (7–1600) | (5–920) | (2–5400) | (0–4300) | (1–16000) | (0–300) | (1–920) | (3–920) | |
| Condition of Reservoir | Chl-a (µgL−1) | Seasons | Chl-a (µgL−1) | ||
| Sites | |||||
| Lack of nutrients (LN) | <1 | S1 | S2 | S3 | |
| Poor nutrients (PN) | <2.5 | Spring | 1.88 (PN) | 1.82 (PN) | 1.91 (PN) |
| Average nutrients (AN) | 2.5–8.0 | Summer | 2.88 (AN) | 2.91 (AN) | 2.19 (PN) |
| Eutrophication (E) | 8.0–25.0 | Autumn | 3.86 (AN) | 3.34 (AN) | 3.28 (AN) |
| Super eutrophication (SE) | >25 | Winter | 1.65 (PN) | 1.57 (PN) | 1.68 (PN) |
| Water Quality Parameters | S Value | p Value | Slope | Intercept | Trend |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | −5 | 0.38 | −0.001 | 7.24 | No trend |
| WT | 36 | 0.00 | 0.15 | 10.02 | Increasing |
| EC | 31 | 0.00 | 8.38 | 108.95 | Increasing |
| DO | −1 | 0.50 | 0.0002 | 8.31 | No trend |
| TSS | −17 | 0.10 | −0.10 | 2.13 | No trend |
| BOD | −31 | 0.00 | −0.06 | 1.88 | Decreasing |
| COD | 25 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 2.44 | Increasing |
| TP | −10 | 0.24 | −0.13 | 19.29 | No trend |
| TN | −3 | 0.43 | 0.006 | 1.46 | No trend |
| TN:TP | 17 | 0.10 | 1.51 | 80.38 | No trend |
| TDP | 3 | 0.44 | 0.0001 | 0.01 | No trend |
| PO4-P | 5 | 0.38 | 0.0003 | 0.006 | No trend |
| NO3-N | 15 | 0.13 | 0.01 | 1.06 | No trend |
| NH4-N | −15 | 0.13 | −0.001 | 0.02 | No trend |
| TDN | −9 | 0.26 | 0.0001 | 1.36 | No trend |
| Chl-a | −35 | 0.00 | −0.26 | 4.0 | Decreasing |
| SD | 17 | 0.11 | 0.08 | 3.45 | No trend |
| TCB | −39 | 0.00 | −66.70 | 584.63 | Decreasing |
| Water Quality Factors | Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VF1 | VF2 | VF1 | VF2 | VF1 | VF2 | VF1 | VF2 | |
| pH | −0.05 | −0.25 | −0.33 | −0.02 | −0.22 | 0.03 | −0.17 | 0.01 |
| WT | −0.17 | −0.08 | 0.21 | 0.21 | 0.04 | 0.27 | −0.12 | 0.44 |
| DO | 0.24 | −0.06 | −0.10 | −0.14 | −0.33 | −0.26 | 0.19 | −0.43 |
| EC | −0.19 | −0.47 | −0.12 | −0.54 | 0.26 | −0.02 | 0.71 | 0.14 |
| TSS | 0.01 | 0.23 | 0.32 | 0.74 | −0.32 | 0.21 | −0.52 | 0.07 |
| BOD | 0.59 | 0.25 | −0.07 | 0.61 | −0.19 | 0.05 | −0.31 | 0.15 |
| COD | −0.07 | −0.26 | 0.26 | 0.00 | −0.23 | 0.53 | 0.16 | −0.07 |
| TN | −0.19 | 0.90 | 0.81 | −0.22 | 0.92 | 0.11 | 0.19 | 0.93 |
| TP | 0.82 | 0.41 | 0.80 | 0.47 | 0.32 | 0.88 | 0.83 | 0.12 |
| TN:TP | −0.89 | −0.06 | −0.28 | −0.71 | 0.36 | −0.84 | −0.68 | 0.40 |
| TDN | −0.17 | 0.92 | 0.78 | −0.20 | 0.90 | 0.05 | 0.12 | 0.94 |
| NH4-N | 0.03 | 0.24 | −0.02 | 0.61 | −0.15 | 0.12 | 0.21 | −0.41 |
| NO3-N | 0.11 | 0.52 | 0.86 | −0.23 | 0.91 | 0.16 | 0.49 | 0.73 |
| TDP | 0.84 | 0.17 | 0.79 | 0.44 | 0.18 | 0.91 | 0.90 | 0.06 |
| PO4-P | 0.75 | −0.32 | 0.65 | 0.43 | −0.12 | 0.81 | 0.76 | −0.18 |
| Chl-a | 0.00 | 0.43 | −0.18 | 0.62 | −0.56 | 0.00 | −0.43 | 0.06 |
| SD | 0.23 | 0.13 | 0.26 | −0.68 | 0.74 | −0.13 | 0.60 | 0.27 |
| TCB | 0.47 | −0.20 | −0.29 | 0.43 | −0.33 | −0.19 | −0.11 | −0.08 |
| Eigenvalues | 3.56 | 2.99 | 4.30 | 3.92 | 4.16 | 3.52 | 4.38 | 3.18 |
| % of variance | 19.80 | 16.64 | 23.87 | 21.75 | 23.10 | 19.57 | 24.34 | 17.65 |
| Cumulative % | 19.80 | 36.43 | 23.87 | 45.62 | 23.10 | 42.68 | 24.34 | 42.00 |
| % Correct | Season Assigned by the DA | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stepwise Mode | Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter | |
| Spring | 81.8 | 81 | 2 | 0 | 23 |
| Summer | 72.7 | 4 | 72 | 18 | 7 |
| Autumn | 77.8 | 0 | 25 | 77 | 6 |
| Winter | 63.6 | 14 | 0 | 4 | 63 |
| Total | 74 | 99 | 99 | 99 | 99 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mamun, M.; Atique, U.; Kim, J.Y.; An, K.-G. Seasonal Water Quality and Algal Responses to Monsoon-Mediated Nutrient Enrichment, Flow Regime, Drought, and Flood in a Drinking Water Reservoir. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 10714. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182010714
Mamun M, Atique U, Kim JY, An K-G. Seasonal Water Quality and Algal Responses to Monsoon-Mediated Nutrient Enrichment, Flow Regime, Drought, and Flood in a Drinking Water Reservoir. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(20):10714. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182010714
Chicago/Turabian StyleMamun, Md, Usman Atique, Ji Yoon Kim, and Kwang-Guk An. 2021. "Seasonal Water Quality and Algal Responses to Monsoon-Mediated Nutrient Enrichment, Flow Regime, Drought, and Flood in a Drinking Water Reservoir" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 20: 10714. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182010714
APA StyleMamun, M., Atique, U., Kim, J. Y., & An, K.-G. (2021). Seasonal Water Quality and Algal Responses to Monsoon-Mediated Nutrient Enrichment, Flow Regime, Drought, and Flood in a Drinking Water Reservoir. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(20), 10714. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182010714








