Multiple Health Risk Factors in Vocational Education Students: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
- The co-occurrence of key multiple health risk factors responsible for NCDs (i.e., at least two of smoking tobacco, inadequate fruit intake, inadequate vegetable intake, risky alcohol consumption, physical inactivity, obesity, anxiety and depression);
- Clustering patterns of these health risk factors;
- Socio-demographic characteristics associated with co-occurrence of health risk factors or identified clusters.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design and Registration
2.2. Literature Search
2.3. Inclusion Criteria
2.3.1. Type of Studies
2.3.2. Study Design
2.3.3. Participants
2.3.4. Outcomes
- Smoking tobacco: any measure assessing current tobacco smoking behaviours (e.g., cigarette smoking);
- Fruit intake: any measure assessing fruit intake (e.g., daily serves of fruits);
- Vegetable intake: any measure assessing vegetable intake (e.g., daily serves of vegetables);
- Alcohol use: any measure assessing alcohol consumption (e.g., standard drinks per day);
- Physical activity: any measure of physical activity (e.g., minutes of moderate or vigorous physical activity);
- Obesity: any measure of obesity (e.g., body mass index, waist circumference);
- Depression: any measure of depression (e.g., having low interest in doing things);
- Anxiety: any measure of anxiety (e.g., feeling nervous or on edge).
2.4. Study Exclusion Criteria
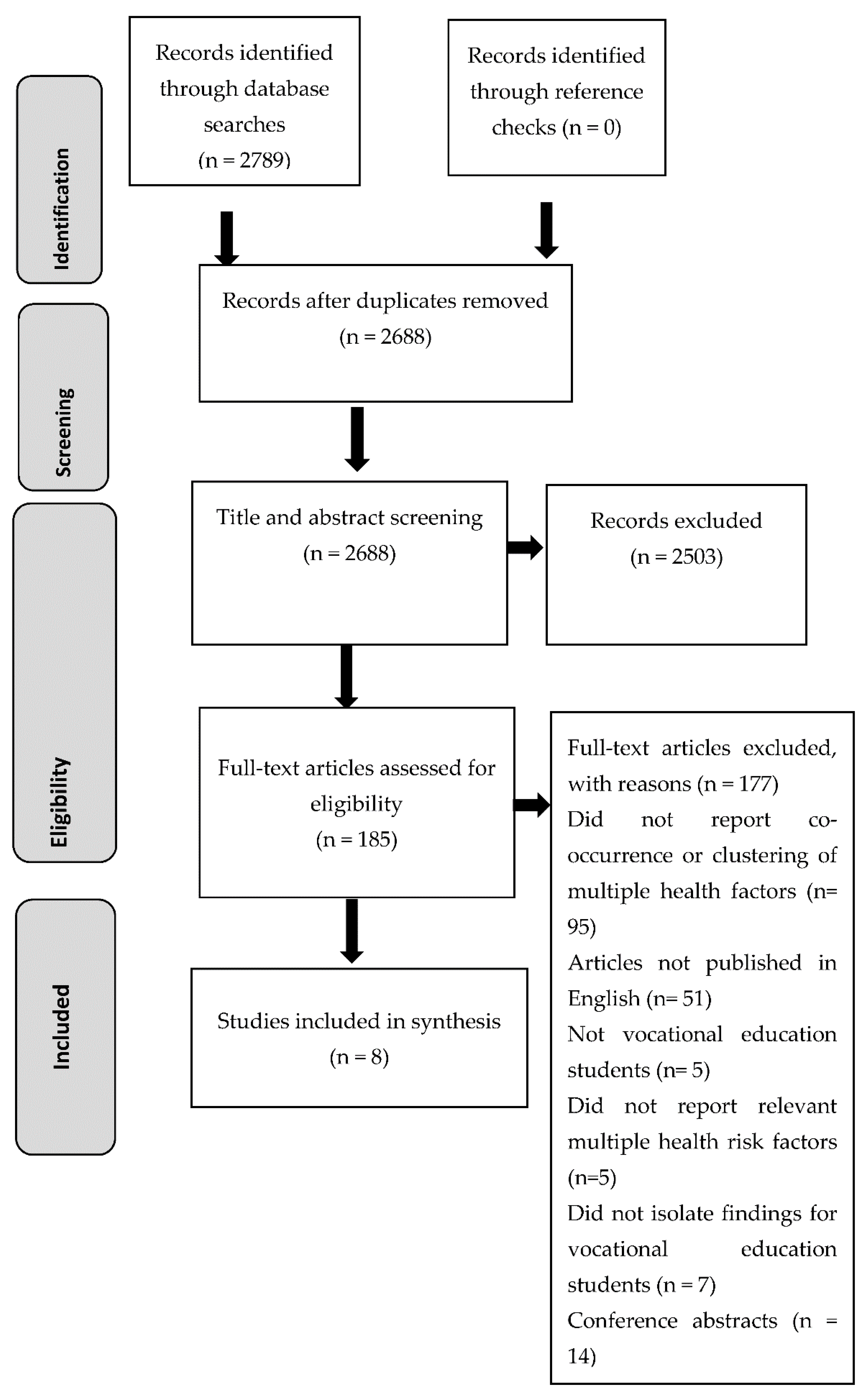
2.5. Screening
2.6. Data Extraction
- Publication details: author(s), publication year, country of study and year data were collected;
- Study setting: type of vocational education setting;
- Study design: cross-sectional studies, longitudinal studies, and baseline data from randomised controlled trials;
- Sample characteristics: socio-demographic characteristics (e.g., age, gender, education, employment status, socio-economic status, marital status, country of birth, area of residence), sample size, recruitment methods used, eligibility criteria, consent rates;
- Measures: type of tobacco smoking, fruit intake, vegetable intake, alcohol use, physical activity, obesity, depression, and anxiety measures used;
- Outcomes: co-occurrence of two or more health risk factors, clustering of multiple health risk factors and socio-demographic characteristics associated with co-occurrence of multiple health risk factors and/or identified clusters.
2.7. Methodological Quality Assessment
2.8. Data Analysis and Synthesis
3. Results
3.1. Study Characteristics
3.2. Combinations of Health Risk Factors Measured
3.3. Co-Occurrence of Multiple Health Risk Factors
3.4. Clustering Patterns of Health Risk Factors
3.5. Socio-Demographic Characteristics Associated with Co-Occurrence of Multiple Health Risk Factors and/or Identified Clusters
3.5.1. Gender
3.5.2. Age
3.5.3. Socio-Economic Status (SES)
3.5.4. Education
3.5.5. Ethnicity
3.6. Methodological Quality Assessment
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Noncommunicable Diseases Country Profiles 2018. 2018. Available online: https://www.who.int/nmh/publications/ncd-profiles-2018/en/ (accessed on 1 October 2020).
- Myint, P.K.; Luben, R.N.; Wareham, N.J.; Bingham, S.A.; Khaw, K.T. Combined effect of health behaviours and risk of first ever stroke in 20,040 men and women over 11 years’ follow-up in Norfolk cohort of European Prospective Investigation of Cancer (EPIC Norfolk): Prospective population study. BMJ 2009, 338, b349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kvaavik, E.; Batty, G.D.; Ursin, G.; Huxley, R.; Gale, C.R. Influence of individual and combined health behaviors on total and cause-specific mortality in men and women: The United Kingdom health and lifestyle survey. Arch. Internet Med. 2010, 170, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webber, L.; Divajeva, D.; Marsh, T.; McPherson, K.; Brown, M.; Galea, G.; Breda, J. The future burden of obesity-related diseases in the 53 WHO European-Region countries and the impact of effective interventions: A modelling study. BMJ Open 2014, 4, e004787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webber, L.; Kilpi, F.; Marsh, T.; Rtveladze, K.; Brown, M.; McPherson, K. High rates of obesity and non-communicable diseases predicted across Latin America. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Champion, K.E.; Mather, M.; Spring, B.; Kay-Lambkin, F.; Teesson, M.; Newton, N.C. Clustering of Multiple Risk Behaviors Among a Sample of 18-Year-Old Australians and Associations with Mental Health Outcomes: A Latent Class Analysis. Front. Public Health 2018, 6, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennasar-Veny, M.; Yanez, A.M.; Pericas, J.; Ballester, L.; Fernandez-Dominguez, J.C.; Tauler, P.; Aguilo, A. Cluster Analysis of Health-Related Lifestyles in University Students. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, K.; Nilsson, E.; Festin, K.; Henriksson, P.; Lowen, M.; Lof, M.; Kristenson, M. Associations of Psychosocial Factors with Multiple Health Behaviors: A Population-Based Study of Middle-Aged Men and Women. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardner, L.A.; Champion, K.E.; Parmenter, B.; Grummitt, L.; Chapman, C.; Sunderland, M.; Thornton, L.; McBride, N.; The Health Life, T.; Newton, N.C. Clustering of Six Key Risk Behaviors for Chronic Disease among Adolescent Females. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAloney, K.; Graham, H.; Law, C.; Platt, L. A scoping review of statistical approaches to the analysis of multiple health-related behaviours. Prev. Med. 2013, 56, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaw, K.T.; Wareham, N.; Bingham, S.; Welch, A.; Luben, R.; Day, N. Combined impact of health behaviours and mortality in men and women: The EPIC-Norfolk prospective population study. PLoS Med. 2008, 5, e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prochaska, J.J.; Nigg, C.R.; Spring, B.; Velicer, W.F.; Prochaska, J.O. The benefits and challenges of multiple health behavior change in research and in practice. Prev. Med. 2010, 50, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prochaska, J.J.; Spring, B.; Nigg, C.R. Multiple health behavior change research: An introduction and overview. Prev. Med. 2008, 46, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prochaska, J.O.; Evers, K.E.; Castle, P.H.; Johnson, J.L.; Prochaska, J.M.; Rula, E.Y.; Coberley, C.; Pope, J.E. Enhancing multiple domains of well-being by decreasing multiple health risk behaviors: A randomized clinical trial. Popul. Health Manag. 2012, 15, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwan, M.Y.; Cairney, J.; Faulkner, G.E.; Pullenayegum, E.E. Physical activity and other health-risk behaviors during the transition into early adulthood: A longitudinal cohort study. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2012, 42, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hale, D.R.; Viner, R.M. Policy responses to multiple risk behaviours in adolescents. J. Public Health 2012, 34 (Suppl. 1), i11–i19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development. Education at a Glance 2018: OECD Indicatiors; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suciati, P. Why Do Students Choose Vocational School? Lesson Learned from Indonesian Vocational Education. KnE Soc. Sci. 2018, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, M.Y.; Arbour-Nicitopoulos, K.P.; Duku, E.; Faulkner, G.E. Patterns of multiple health risk–behaviours in university students and their association with mental health: Application of latent class analysis. Health Promot. Chronic Dis. Prev. Can. Res. Policy Pract. 2016, 36, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patton, G.C.; Coffey, C.; Romaniuk, H.; Mackinnon, A.; Carlin, J.B.; Degenhardt, L.; Olsson, C.A.; Moran, P. The prognosis of common mental disorders in adolescents: A 14-year prospective cohort study. Lancet 2014, 383, 1404–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, V. Reducing the burden of depression in youth: What are the implications of neuroscience and genetics on policies and programs? J. Adolesc. Health 2013, 52, S36–S38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashton, L.M.; Hutchesson, M.J.; Rollo, M.E.; Morgan, P.J.; Thompson, D.I.; Collins, C.E. Young adult males’ motivators and perceived barriers towards eating healthily and being active: A qualitative study. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2015, 12, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aceijas, C.; Waldhausl, S.; Lambert, N.; Cassar, S.; Bello-Corassa, R. Determinants of health-related lifestyles among university students. Perspect. Public Health 2017, 137, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, M.M.; Mathijssen, J.J.; van Bon-Martens, M.J.; Van Oers, H.A.; Garretsen, H.F. A qualitative exploration of attitudes towards alcohol, and the role of parents and peers of two alcohol-attitude-based segments of the adolescent population. Subst. Abus. Treat. Prev. Policy 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Laska, M.N.; Sevcik, S.M.; Moe, S.G.; Petrich, C.A.; Nanney, M.S.; Linde, J.A.; Lytle, L.A. A 2-year young adult obesity prevention trial in the US: Process evaluation results. Health Promot. Int. 2016, 31, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, M.C.; Larson, N.I.; Barr-Anderson, D.; Neumark-Sztainer, D.; Story, M. Disparities in dietary intake, meal patterning, and home food environments among young adult nonstudents and 2- and 4-year college students. Am. J. Public Health 2009, 99, 1216–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenberg, D.; Hunt, J.; Speer, N. Help seeking for mental health on college campuses: Review of evidence and next steps for research and practice. Harv. Rev. Psychiatry 2012, 20, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vankim, N.A.; Ehlinger, E.; Lust, K.; Story, M.; Laska, M.N. Understanding young adult physical activity, alcohol and tobacco use in community colleges and 4-year post-secondary institutions: A cross-sectional analysis of epidemiological surveillance data. BMC Public Health 2010, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, N.; Paul, C.; Turon, H.; Oldmeadow, C. Which modifiable health risk behaviours are related? A systematic review of the clustering of Smoking, Nutrition, Alcohol and Physical activity (‘SNAP’) health risk factors. Prev. Med. 2015, 81, 16–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meader, N.; King, K.; Moe-Byrne, T.; Wright, K.; Graham, H.; Petticrew, M.; Power, C.; White, M.; Sowden, A.J. A systematic review on the clustering and co-occurrence of multiple risk behaviours. BMC Public Health 2016, 16, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Heart Lung and Blood Institute. Background: Development and Use of Study Quality Assessment Tools. Available online: http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-pro/guidelines/in-develop/cardiovascular-risk-reduction/tools/background (accessed on 1 February 2018).
- Popay, J.; Roberts, H.; Sowden, A.; Petticrew, M.; Arai, L.; Rodgers, M.; Britten, N.; Roen, K.; Duffy, S. Guidance on the conduct of narrative synthesis in systematic reviews. Prod. ESRC Methods Programme Version 2006, 1, b92. [Google Scholar]
- Bannink, R.; Broeren, S.; Heydelberg, J.; van’t Klooster, E.; Raat, H. Depressive symptoms and clustering of risk behaviours among adolescents and young adults attending vocational education: A cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health 2015, 15, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonevski, B.; Guillaumier, A.; Paul, C.; Walsh, R. The vocational education setting for health promotion: A survey of students’ health risk behaviours and preferences for help. Health Promot. J. Austr. 2013, 24, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadigan, J.M.; Lee, C.M. Identifying Barriers to Mental Health Service Utilization Among Heavy Drinking Community College Students. Community Coll. J. Res. Pract. 2019, 43, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chyderiotis, S.; Benmarhnia, T.; Spilka, S.; Beck, F.; Andler, R.; Legleye, S.; Menvielle, G. Why do apprentices smoke much more than high school students? Understanding educational disparities in smoking with a Oaxaca-blinder decomposition analysis. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffries, J.K.; Lytle, L.; Sotres-Alvarez, D.; Golden, S.; Aiello, A.E.; Linnan, L. Chronic Disease Risk Typologies among Young Adults in Community College. Am. J. Health Behav. 2018, 42, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczyk, S.; Pedersen, A.; Hanewinkel, R.; Isensee, B.; Morgenstern, M. Polysubstance use patterns and trajectories in vocational students--a latent transition analysis. Addict. Behav. 2016, 58, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Underwood, B.; Hackshaw, A.; Fox, K. Smoking, alcohol and drug use among vocational dental practitioners in 2000 and 2005. Br. Dent. J. 2007, 203, 701–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haug, S.; Schaub, M.P.; Salis Gross, C.; John, U.; Meyer, C. Predictors of hazardous drinking, tobacco smoking and physical inactivity in vocational school students. BMC Public Health 2013, 13, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laska, M.N.; Pasch, K.E.; Lust, K.; Story, M.; Ehlinger, E. Latent class analysis of lifestyle characteristics and health risk behaviors among college youth. Prev. Sci. 2009, 10, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintiliani, L.; Allen, J.; Marino, M.; Kelly-Weeder, S.; Li, Y. Multiple health behavior clusters among female college students. Patient Educ. Couns. 2010, 79, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodd, L.J.; Al-Nakeeb, Y.; Nevill, A.; Forshaw, M.J. Lifestyle risk factors of students: A cluster analytical approach. Prev. Med. 2010, 51, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plotnikoff, R.C.; Costigan, S.A.; Williams, R.L.; Hutchesson, M.J.; Kennedy, S.G.; Robards, S.L.; Allen, J.; Collins, C.E.; Callister, R.; Germov, J. Effectiveness of interventions targeting physical activity, nutrition and healthy weight for university and college students: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2015, 12, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| # | Searches |
|---|---|
| 1 | smoke/or smoking cessation/or smoking/or cigarette smoking/or smok*.mp. or tobacco/ |
| 2 | smoking.mp. or smoking/ |
| 3 | 1 or 2 |
| 4 | nutrition/or nutrition.mp. |
| 5 | unhealthy diet/or diet.mp. or healthy diet/or diet/ |
| 6 | fruit*.mp. or fruit/ |
| 7 | vegetable/or vegetable*.mp. |
| 8 | 4 or 5 or 6 or 7 |
| 9 | Alcohol*.mp. or alcohol intoxication/or alcohol/ or alcohol consumption/ |
| 10 | binge drinking.mp. or drinking behavior/ or binge drinking/ |
| 11 | 9 or 10 |
| 12 | exercise/or physical activity/or physical activ*.mp. |
| 13 | physical inactivity/or physical inactiv*.mp. |
| 14 | sedentary lifestyle/or sedentary*.mp. |
| 15 | 12 or 13 or 14 |
| 16 | obesity/or obesity.mp. |
| 17 | body weight.mp. or body weight/ |
| 18 | weight loss.mp. or body weight loss/ |
| 19 | weight control.mp. or body weight control/ |
| 20 | overweight.mp. |
| 21 | body mass index.mp. or body mass/ |
| 22 | 16 or 17 or 18 or 19 or 20 or 21 |
| 23 | multiple health risk behavio?r*.mp. |
| 24 | multiple behavio?r*.mp. |
| 25 | multiple risk behavio?r*.mp. |
| 26 | multiple lifestyle behavio?r*.mp. |
| 27 | multiple health behavio?r*.mp. |
| 28 | 23 or 24 or 25 or 26 or 27 |
| 29 | mental health.mp. or mental health/ |
| 30 | psychological distress.mp. |
| 31 | depression/or depression.mp. |
| 32 | anxiety.mp. or anxiety/ |
| 33 | 29 or 30 or 31 or 32 |
| 34 | vocational education.mp. or vocational education/ |
| 35 | technical education.mp. |
| 36 | polytechnic*.mp. |
| 37 | apprentice.mp. |
| 38 | Technical Schools.mp. |
| 39 | community colleges.mp. |
| 40 | further education.mp. |
| 41 | vocational education and training.mp. |
| 42 | Technical and Vocational Education Training.mp. |
| 43 | vocational training.mp. |
| 44 | TAFE.mp. |
| 45 | 34 or 35 or 36 or 37 or 38 or 39 or 40 or 41 or 42 or 43 or 44 |
| 46 | 3 and (8 or 11 or 15 or 22 or 33) |
| 47 | 8 and (3 or 11 or 15 or 22 or 33) |
| 48 | 11 and (3 or 8 or 15 or 22 or 33) |
| 49 | 15 and (3 or 8 or 11 or 22 or 33) |
| 50 | 22 and (3 or 8 or 11 or 15 or 33) |
| 51 | 33 and (3 or 8 or 11 or 15 or 22) |
| 52 | 46 or 47 or 48 or 49 or 50 or 51 |
| 53 | 28 or 52 |
| 54 | 53 and 45 |
| Author, Country, Year of Data Collection | (i) Study Design (ii) Setting | Sample Characteristics | (i) Recruitment Method (ii) Eligibility Criteria (iii) Response Rate | Measures Used | Co-Occurrence of Health Risk Factors | Description of Clusters Identified | Characteristics Associated with (i) Co-Occurrence of Health Risk Factors (ii) Clusters |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bannink et al. 2015 [35], Netherlands, 2012 | (i) Cross sectional (ii) 44 first-year classes from the two lowest levels of vocational education setting | N = 584 students Mean age = 18.3 ± 2.59 years 38.9% boys 27.9% Dutch 10.6% had a child | (i) Study information received by all students and parents a few weeks prior to study commencement (ii) Two lowest levels of vocational education (the easiest levels) (iii) 70.4% | Cigarette smoking: Frequency of smoking at the time of assessment (no smoking to every day) Alcohol use: number of alcoholic drinks consumed on a single occasion in the past 4 days Depression: Frequency of depressive symptoms using the Centre for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale (CES-D) * Frequency of cannabis use in the past 4 weeks also measured which is included in the co-occurrence of health risk factors results | 18.1% used two substances 11.0% used three substances. | 2 clusters: 1. “substance use” cluster: Binge drinking, cannabis use and cigarette smoking 2. “problem behaviour” cluster: delinquency, truancy and incurring debts | (i) Not reported (ii) Ethnicity and Depressive symptoms associated with “substance use” cluster |
| Bonevski et al. 2013 [36], Australia, 2010 | (i) Cross sectional (ii) One Technical and Further Education (TAFE) campus | N = 224 Age = 16 years and above 51.3% females 67.1% Australian-born, 80% spoke English at home, 55.6% lived with parent/guardian, 46.3% earned < $300 as personal weekly income, 59% attended TAFE full time | (i) Identified key contact distributed information letters to consenting teachers to give to eligible students 1 week before survey administration. (ii) Classes with high number of English-speaking students, on-campus classes and a high proportion of younger students (16–24 years). (iii) 97% | Smoking: Current smoking status Fruit and vegetable consumption: Number of daily fruit and vegetable serves Alcohol use: Number of standard drinks consumed on one occasion. Physical activity: Total times spent engaging in moderate and vigorous physical activity Body Mass index: Calculated based on self-reported height and weight * Sun tanning behaviour also measured which is included in the co-occurrence of health risk factors results | 98% reported two or more health risk behaviours. | Not reported | Not reported |
| Cadigan and Lee, 2019 [37], USA, not stated | (i) Cross sectional (ii) Three public community colleges | N = 142 Mean age = 22.75 ± 3.34 years 69.7% female 58.9% White 12.8% Asian 5.7% Black 14.9% multiracial 2.8% American Indian/Alaskan Native, 2.8% Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander, 2.1% other ethnicity | (i) Displayed posters and distributed handouts at campuses, ads in college newspapers and emails. (ii) 18- to 29-year-olds, enrolled full or part time at community colleges, engaged in heavy drinking (i.e., 4+/5+ drinks for women and men respectively or exceeding weekly National Institution on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism drinking recommendations of 8+/15+ for women and men respectively) and owned/used a cell phone (iii) 90% | Alcohol use: Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT) to measure the quantity and frequency of alcohol use and consequences of alcohol use. Depression: Depressive symptoms assessed using the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-8) Anxiety: Anxiety symptoms assessed using the Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7 (GAD-7) | 21.8% depression and anxiety 32% heavy drinking and depression 25% heavy drinking and anxiety | Not reported | Not reported |
| Chyderiotis et al. 2020 [38], France, 2008 and 2017 | (i) Cross- sectional (ii) Vocational students and apprentices | 2008 n = 4564 apprentices Mean age = 17.4 years 2017 sample A n = 877 apprentices Mean age = 17.4 years 73.7% boys 54.9% living with parents 53.1% grade repetition 2017 Sample B N = 949 Mean age = 17.4 years 73.8% boys 54.5% living with parents 55.8% grade repetition | (i) All adolescents who attended the National Defence and Citizenship Day (JDC) were invited to participate. (ii) Apprentices aged 17 in 2008 and 2017 (iii) >90% in 2008 and 2017 | Cigarette smoking: Smoking during the last 30 days. Alcohol use: Alcohol use in the past month | Sample A 2008 54.6% daily smoking and alcohol use in the past month 2017 sample A 51.1% daily smoking and alcohol use in the past month Sample B 2017 52.1% daily smoking and alcohol use in the past month | Not reported | Not reported |
| Haug et al. 2013 [42], Switzerland, 2011-2012 | (i) Cross-sectional (ii) 24 post-secondary vocational education campuses | (i) N = 2647 Median age = 18 years 50.9% females 78.8% had secondary school education 53.8% no immigrant background | (i) All students in participating classes invited by externally trained staff to participate in the survey during a health education lesson. (ii) Not stated (iii) 99.5% | Tobacco smoking: daily /occasional smokers Alcohol use: quantity consumed, frequency of consumption and binge drinking in the previous year Physical activity: hours spent engaging in moderate to vigorous physical activity in a week | 34% had two health risk factors 24.5% hazardous drinking and tobacco smoking 6.4% hazardous drinking and physical inactivity 3.1% tobacco smoking and physical inactivity 9.6% had all three health risk factors | Not reported | (i) Gender (ii) Age (iii) Education (iv) Ethnicity |
| Jeffries et al. 2018 [39], USA, 2011 and 2012 | (i) Cross sectional (ii) Three 2-year community colleges | N = 441 Mean age 22.7 ± 5 years 67.6% female 72.6% white Average BMI = 25.4 ± 3.8 54.4% living with parent | (i) Not stated (ii) Enrolled in the Choosing Healthy Options in College Environments and Settings (CHOICES) study and completed baseline assessments. (iii) 99.5% | Tobacco smoking: daily/occasional smokers Alcohol use: Binge drinking within the past 30 days Physical activity: Total minutes spent engaging in moderate-intensity aerobic activity in a week Body mass index: Height (metres) and weight (kg) measured by trained staff using height boards and scales. | Not reported | 3 classes Class 1 (13.1%): active, binge-drinkers with a healthy dietary intake Class 2 (38.2%): non-active, moderate-smokers and non-drinkers with poor dietary intake Class 3 (48.7%): moderately active, non-smoking and non-drinkers with moderately healthy dietary intake | (i) Body mass index (BMI) associated with class 2 membership Age associated with class 1 membership |
| Tomcyzk et al. 2016 [40] Germany Year of data collection not reported | (i) Longitudinal (ii) 49 vocational schools in seven German states | N = 5688 54% males Mean Age = 19.39 ± 3.92 years | (i) Not stated (ii) Not stated (iii) 79% | Substance use: frequency of use of alcohol and cigarettes * Other substances measured included: Cannabis/marijuana | Not reported | 3 classes Class 1 (43%) “low users” had low scores on all substance use Class 2 (50%) “alcohol users” had students with high scores for alcohol use and average scores on cigarette use Class 3 (7%) “polysubstance use” had students with high scores on all substance use | Job stress associated with class 3. |
| Underwood et al. 2007 [41], United Kingdom, 2000 and 2005 | (i) Cross-sectional (ii) 77 Vocational dental practitioners (VDP) | 2000 N = 534 2005 N = 502 No sample characteristics were reported. | (i) Questionnaire packs were sent to all UK VDP advisors, for distribution to their VDP groups at their next study day. (ii) Not reported (iii) 75% in 2000 and 66% in 2005 | Frequency and amount of tobacco smoking and alcohol use | 55% smoked tobacco and drank alcohol | Not reported | Not reported |
| Q1 Research Question | Q2 Study Population | Q3 Participation/Response Rate | Q4 Groups Recruited From the Same Population and Uniform Eligibility Criteria | Q5 Sample Size Justification | Q6 Exposure Assessed Prior to Outcome Measurement | Q7 Sufficient Timeframe to See an Effect | Q8 Different Levels of the Exposure of Interest | Q9 Exposure Measures and Assessment | Q10 Repeated Exposure Assessment | Q11 Outcome Measures | Q12 Blinding of Outcome Assessors | Q13 Follow-Up Rate | Q14 Measurement and Adjustment of Potential Confounders | Quality Rating | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bannink et al. [35] | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | CD | NR | NA | Yes | Fair |
| Bonevski et al. [36] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | CD | No | CD | NA | NA | No | Fair |
| Cadigan et al. [37] | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | NA | NA | No | Yes | NR | NA | No | Poor |
| Chyderiotis et al. [38] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | CD | No | CD | NA | NA | No | Fair |
| Haug et al. [42] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | CD | No | CD | NR | NA | Yes | Fair |
| Jeffries et al. [39] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | CD | No | Yes | NR | NA | Yes | Fair |
| Tomcyzk et al. [40] | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | CD | NR | No | Yes | Good |
| Underwoood et al. [41] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | NA | NA | No | CD | NA | NA | No | Fair |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Atorkey, P.; Byaruhanga, J.; Paul, C.; Wiggers, J.; Bonevski, B.; Tzelepis, F. Multiple Health Risk Factors in Vocational Education Students: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 637. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18020637
Atorkey P, Byaruhanga J, Paul C, Wiggers J, Bonevski B, Tzelepis F. Multiple Health Risk Factors in Vocational Education Students: A Systematic Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(2):637. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18020637
Chicago/Turabian StyleAtorkey, Prince, Judith Byaruhanga, Christine Paul, John Wiggers, Billie Bonevski, and Flora Tzelepis. 2021. "Multiple Health Risk Factors in Vocational Education Students: A Systematic Review" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 2: 637. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18020637
APA StyleAtorkey, P., Byaruhanga, J., Paul, C., Wiggers, J., Bonevski, B., & Tzelepis, F. (2021). Multiple Health Risk Factors in Vocational Education Students: A Systematic Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(2), 637. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18020637







