Tuberculosis Death Epidemiology and Its Associated Risk Factors in Sabah, Malaysia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
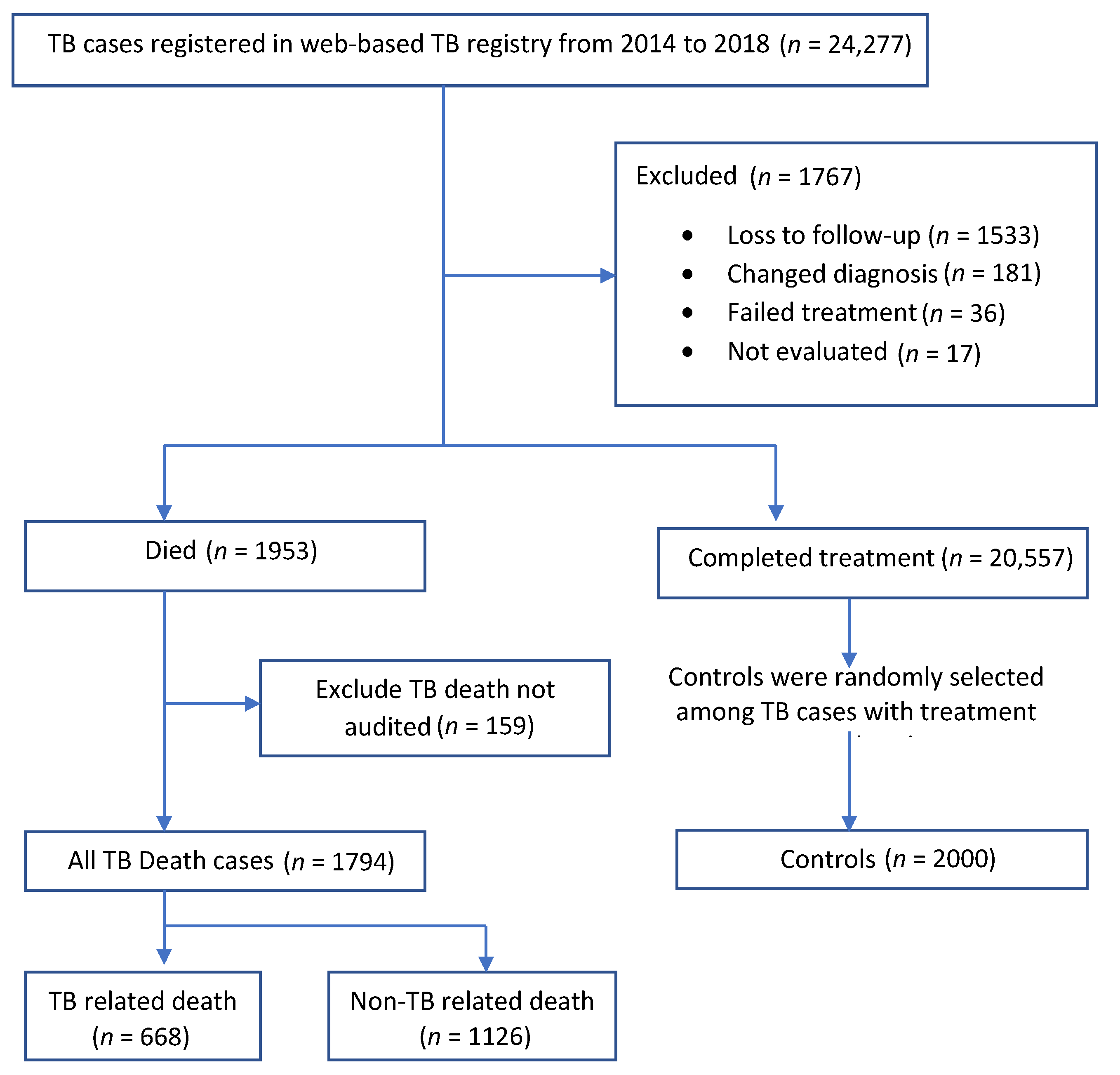
2. Methods
2.1. Study Population and Source of Data
2.2. Definitions
2.2.1. Outcome Variables
2.2.2. Explanatory Variables
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.4. Ethical Consideration
3. Results
3.1. Sample Characteristics
3.2. Trend of TB Death
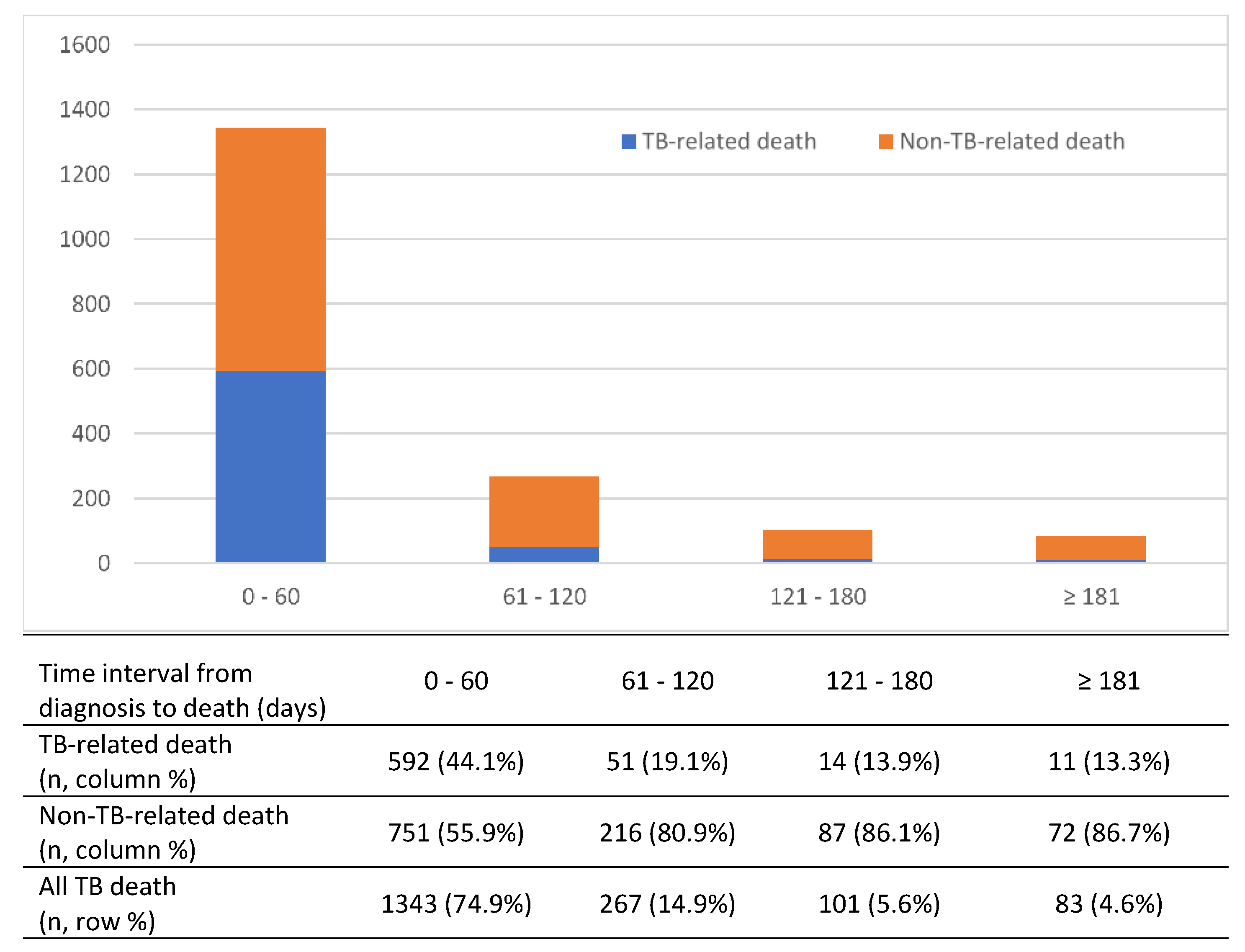
3.3. Timing of TB Death
3.4. Causes of TB Death
3.5. Risk Factors of TB Death
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report 2020; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organisation. The End TB Strategy; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Goroh, M.M.D.; Rajahram, G.S.; Avoi, R.; Boogaard, C.H.A.V.D.; William, T.; Ralph, A.P.; Lowbridge, C. Epidemiology of tuberculosis in Sabah, Malaysia, 2012–2018. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2020, 9, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waitt, C.J.; Squire, S. A systematic review of risk factors for death in adults during and after tuberculosis treatment [Review article]. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2011, 15, 871–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massavirov, S.; Akopyan, K.; Abdugapparov, F.; Ciobanu, A.; Hovhanessyan, A.; Khodjaeva, M.; Gadoev, J.; Parpieva, N. Risk Factors for Unfavorable Treatment Outcomes among the Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Associated Tuberculosis Population in Tashkent City, Uzbekistan: 2013–2017. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tok, P.S.K.; Liew, S.M.; Wong, L.P.; Razali, A.; Loganathan, T.; Chinna, K.; Ismail, N.; Kadir, N.A. Determinants of unsuccessful treatment outcomes and mortality among tuberculosis patients in Malaysia: A registry-based cohort study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, C.-H.; Kuo, Y.-W.; Wang, J.-Y.; Hsu, C.-L.; Chen, J.-M.; Cheng, W.-C.; Lee, L.-N. Tuberculosis mortality: Patient characteristics and causes. BMC Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Birlie, A.; Tesfaw, G.; Dejene, T.; Woldemichael, K. Time to Death and Associated Factors among Tuberculosis Patients in Dangila Woreda, Northwest Ethiopia. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Min, J.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, H.W.; Shin, A.Y.; Koo, H.-K.; Lee, S.-S.; Kim, Y.-K.; Shin, K.-C.; Chang, J.H.; Chun, G.; et al. Clinical profiles of early and tuberculosis-related mortality in South Korea between 2015 and 2017: A cross-sectional study. BMC Infect Dis. 2019, 19, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beavers, S.F.; Pascopella, L.; Davidow, A.; Mangan, J.M.; Hirsch-Moverman, Y.R.; Golub, J.E.; Blumberg, H.M.; Webb, R.M.; Royce, R.A.; Buskin, S.E.; et al. Tuberculosis Mortality in the United States: Epidemiology and Prevention Opportunities. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2018, 15, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, Y.-F.; Feng, J.-Y.; Pan, S.-W.; Chuang, P.-H.; Su, V.Y.-F.; Su, W.-J. Determinants of mortality in elderly patients with tuberculosis: A population-based follow-up study. Epidemiol. Infect. 2017, 145, 1374–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adamu, A.L.; Gadanya, M.A.; Abubakar, I.S.; Jibo, A.M.; Bello, M.M.; Gajida, A.U.; Babashani, M.M.; Abubakar, I. High mortality among tuberculosis patients on treatment in Nigeria: A retrospective cohort study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arcoverde, M.A.M.; Berra, T.Z.; Alves, L.S.; Dos Santos, D.T.; Belchior, A.D.S.; Ramos, A.C.V.; Arroyo, L.H.; De Assis, I.S.; Alves, J.D.; De Queiroz, A.A.R.; et al. How do social-economic differences in urban areas affect tuberculosis mortality in a city in the tri-border region of Brazil, Paraguay and Argentina. BMC Public Health 2018, 18, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhargava, A.; Bhargava, M. Tuberculosis deaths are predictable and preventable: Comprehensive assessment and clinical care is the key. J. Clin. Tuberc. Other Mycobact. Dis. 2020, 19, 100155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinsai, S. 1342. Impact of HIV Infection on Treatment Outcome of New Tuberculosis Patients Attending Tuberculosis and Antiretroviral Treatment Services in the Community-Based Hospital, Thailand: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2019, 6, S485–S486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Variables | TB Death | Control n (%) | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TB-Related n (%) | Non-TB Related n (%) | All TB Death n (%) | |||
| Sociodemographic Characteristics | |||||
| Age (mean ± SD), years | 44.6 ± 20.8 | 56.4 ± 17.8 | 52.0 ± 19.8 | 39.0 ± 17.6 | <0.001 ** |
| Age groups | |||||
| 0–14 | 34 (5.1) | 15 (1.3) | 49 (2.7) | 78 (3.9) | <0.001 |
| 15–44 | 303 (45.4) | 250 (22.2) | 553 (30.8) | 1156 (57.8) | |
| 45–64 | 202 (30.2) | 460 (40.9) | 662 (36.9) | 585 (29.3) | |
| ≥65 | 129 (19.3) | 401 (35.6) | 530 (29.5) | 181 (9.1) | |
| Gender | |||||
| Female | 265 (39.7) | 353 (31.3) | 618 (34.4) | 817 (40.9) | <0.001 |
| Male | 403 (60.3) | 773 (68.7) | 1176 (65.6) | 1183 (59.2) | |
| Place of residence | |||||
| Rural | 462 (70.0) | 778 (69.6) | 1240 (69.7) | 1462 (73.1) | 0.010 |
| Urban | 198 (30.0) | 340 (30.4) | 538 (30.3) | 527 (26.5) | |
| Nationality | |||||
| Malaysian | 379 (56.7) | 937 (83.2) | 1316 (73.4) | 1484 (74.2) | 0.555 |
| Non-Malaysian | 289 (43.3) | 189 (16.8) | 478 (26.6) | 516 (25.8) | |
| Education level | |||||
| Tertiary | 8 (1.2) | 16 (1.4) | 24 (1.3) | 49 (2.5) | <0.001 |
| Secondary | 136 (20.4) | 350 (31.1) | 486 (27.1) | 841 (42.1) | |
| Primary | 128 (19.2) | 291 (25.8) | 419 (23.4) | 462 (23.1) | |
| No formal education | 396 (59.3) | 469 (41.7) | 865 (48.2) | 648 (32.4) | |
| Income regular | |||||
| No | 504 (75.4) | 780 (69.3) | 1284 (71.6) | 1182 (59.1) | <0.001 |
| Yes | 164 (24.6) | 346 (30.7) | 510 (28.4) | 818 (40.9) | |
| Comorbid characteristics | |||||
| Smoking status | |||||
| No | 497 (74.4) | 777 (69.0) | 1274 (71.0) | 1405 (70.3) | 0.606 |
| Yes | 171 (25.6) | 349 (31.0) | 520 (29.0) | 595 (29.8) | |
| Diabetes mellitus status | |||||
| No | 620 (92.8) | 953 (84.6) | 1573 (87.7) | 1834 (91.7) | <0.001 |
| Yes | 48 (7.2) | 173 (15.4) | 221 (12.3) | 166 (8.3) | |
| HIV status | |||||
| Negative | 643 (97.4) | 1022 (92.2) | 1665 (94.1) | 1967 (98.4) | <0.001 |
| Positive | 17 (2.6) | 87 (7.8) | 104 (5.9) | 32 (1.6) | |
| Disease characteristics | |||||
| Category of TB | |||||
| New case | 613 (91.8) | 1003 (89.1) | 1616 (90.1) | 1884 (94.2) | <0.001 |
| Retreatment case | 55 (8.2) | 123 (10.9) | 178 (9.9) | 116 (5.8) | |
| Type of case detection | |||||
| Passive | 625 (93.6) | 1015 (90.1) | 1640 (91.4) | 1801 (90.1) | 0.148 |
| Active | 39 (5.8) | 111 (9.9) | 154 (8.6) | 199 (10.0) | |
| BCG scar | |||||
| No | 363 (54.3) | 482 (42.8) | 845 (47.1) | 604 (30.2) | <0.001 |
| Yes | 305 (45.7) | 644 (57.2) | 949 (52.9) | 1396 (69.8) | |
| TB anatomical site | |||||
| PTB | 602 (90.1) | 932 (82.8) | 1534 (85.5) | 1779 (89.0) | 0.001 |
| Extra PTB | 66 (9.9) | 194 (17.2) | 260 (14.5) | 221 (11.1) | |
| Initial sputum AFB | |||||
| Positive | 541 (82.7) | 681 (63.1) | 1222 (70.5) | 1434 (71.7) | 0.032 |
| Negative | 113 (17.3) | 398 (36.9) | 511 (29.5) | 512 (25.6) | |
| CXR status at diagnosis | |||||
| Minimal/normal | 181 (28.1) | 510 (46.8) | 691 (39.9) | 1103 (57.1) | <0.001 |
| Moderate | 336 (52.2) | 474 (43.5) | 810 (46.7) | 741 (38.4) | |
| Advanced | 127 (19.7) | 105 (9.6) | 232 (13.4) | 87 (4.5) | |
| MDRTB status | |||||
| No | 480 (99.6) | 839 (99.9) | 1319 (99.8) | 1691 (100.0) | 0.084 * |
| Yes | 2 (0.4) | 1 (0.1) | 3 (0.2) | 0 | |
| TB meningitis | |||||
| No | 67 (58.8) | 205 (77.9) | 272 (72.1) | 255 (93.1) | <0.001 |
| Yes | 47 (41.2) | 58 (22.1) | 105 (27.9) | 19 (6.9) | |
| TB miliary | |||||
| No | 93 (81.6) | 232 (88.2) | 325 (86.2) | 268 (97.8) | <0.001 |
| Yes | 21 (18.4) | 31 (11.8) | 52 (13.8) | 6 (2.2) | |
| Treatment characteristics | |||||
| Treatment regime (intensive phase) | |||||
| FDC | 341 (51.0) | 563 (50.0) | 904 (50.4) | 1428 (71.4) | <0.001 |
| Loose tablet | 327 (49.0) | 563 (50.0) | 890 (49.6) | 572 (28.6) | |
| Treatment delay (≥14 days) | |||||
| No | 659 (98.7) | 1105 (98.1) | 1764 (98.3) | 1975 (98.8) | 0.277 |
| Yes | 9 (1.3) | 21 (1.9) | 30 (1.7) | 25 (1.3) | |
| DOT achieved (intensive phase) | |||||
| No | 268 (41.4) | 329 (29.8) | 597 (34.1) | 7 (0.4) | <0.001 |
| Yes | 380 (58.6) | 774 (70.2) | 1154 (65.9) | 1993 (99.7) | |
| Year | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total TB cases registered | 4747 | 4464 | 4953 | 5105 | 5008 | 24,277 |
| Total TB death cases | 312 | 327 | 415 | 473 | 426 | 1953 |
| Non-TB-related death | 198 | 213 | 255 | 241 | 219 | 1126 |
| TB-related death | 114 | 110 | 148 | 168 | 128 | 668 |
| TB-related death (%) | 36.5% | 34.1% | 36.7% | 41.1% | 36.9% | 37.2% |
| TB notification rate (per 100,000 population) | 136.2 | 126.0 | 137.5 | 139.4 | 134.6 | 134.7 * |
| TB death rate (per 100,000 population) ** | 9.0 | 9.2 | 11.5 | 12.9 | 11.4 | 10.8 * |
| Case fatality rate (%) | 6.6% | 7.3% | 8.4% | 9.3% | 8.5% | 8.0% |
| Variables | Time of TB Death | Univariable Analysis | Multivariable Analysis | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| After Treatment Started, n (%) | Before Treatment Started, n (%) | cOR (95% CI) | aOR (95% CI) | |
| Age (mean ± SD), years | 45.2 ± 19.8 | 44.1 ± 19.8 | 0.99 (0.98–1.01) | |
| Age groups | ||||
| 0–14 | 43 (87.8) | 6 (12.2) | 1 | 1 |
| 15–44 | 487 (88.1) | 66 (11.9) | 0.95 (0.39–2.37) | 0.71 (0.27–1.84) |
| 45–64 | 618 (93.4) | 44 (6.6) | 0.51 (0.21–1.26) | 0.83 (0.31–2.21) |
| ≥65 | 504 (95.1) | 26 (4.9) | 0.37 (0.14–0.95) | 0.87 (0.30–2.48) |
| Gender | ||||
| Female | 562 (90.9) | 56 (9.1) | 1 | 1 |
| Male | 1090 (92.7) | 86 (7.3) | 0.79 (0.56–1.13) | 1.01 (0.68–1.50) |
| Place of residence | ||||
| Rural | 1147 (92.5) | 93 (7.5) | 1 | 1 |
| Urban | 493 (91.6) | 45 (8.4) | 1.13 (0.78–1.63) | 1.19 (0.79–1.78) |
| Nationality | ||||
| Malaysian | 1242 (94.4) | 74 (5.6) | 1 | 1 |
| Non-Malaysian | 410 (85.8) | 68 (14.2) | 2.78 (1.97–3.94) | 2.32 (1.44–3.72) |
| Diabetes mellitus status | ||||
| No | 1443 (91.7) | 130 (8.3) | 1 | 1 |
| Yes | 209 (94.6) | 12 (5.4) | 0.64 (0.35–1.17) | 0.76 (0.36–1.62) |
| HIV status | ||||
| Negative | 1543 (92.7) | 122 (7.3) | 1 | 1 |
| Positive | 93 (89.4) | 11 (10.6) | 1.50 (0.78–2.87) | 3.66 (1.80–7.43) |
| Type of case detection | ||||
| Passive | 1507 (91.9) | 133 (8.1) | 1 | 1 |
| Active | 145 (94.2) | 9 (5.8) | 0.70 (0.35–1.41) | 0.36 (0.13–0.99) |
| BCG scar | ||||
| No | 765 (90.5) | 80 (9.5) | 1 | 1 |
| Yes | 887 (93.5) | 62 (6.5) | 0.67 (0.47–0.94) | 0.78 (0.49–1.23) |
| CXR status at diagnosis | ||||
| Minimal/normal | 650 (94.1) | 41 (5.9) | 1 | 1 |
| Moderately advanced | 753 (93.0) | 57 (7.0) | 1.20 (0.79–1.82) | 1.53 (0.99–2.36) |
| Far-advanced | 203 (87.5) | 29 (12.5) | 2.27 (1.37–3.74) | 3.43 (2.02–5.84) |
| Cause of TB Death | Frequency | % |
|---|---|---|
| TB-related death | ||
| Advanced/disseminated | 420 | 62.9% |
| Sepsis | 149 | 22.3% |
| TB meningitis | 42 | 6.3% |
| TB miliary | 10 | 1.5% |
| Acute respiratory distress syndrome | 10 | 1.5% |
| Underlying HIV | 17 | 2.5% |
| Severe pneumonia | 6 | 0.9% |
| MDRTB | 2 | 0.3% |
| Others | 12 | 1.8% |
| Sub-total | 668 | 100.0% |
| Non-TB-related death | ||
| Sepsis | 201 | 17.9% |
| Pneumonia-HAP | 117 | 10.4% |
| Pneumonia-CAP | 48 | 4.3% |
| Pneumonia-other | 95 | 8.4% |
| Lung-other | 52 | 4.6% |
| Lung-COAD | 20 | 1.8% |
| Carcinoma-lung | 48 | 4.3% |
| Carcinoma-other | 93 | 8.3% |
| AIDS | 94 | 8.3% |
| Heart-acute coronary syndrome | 91 | 8.1% |
| Heart-congestive heart failure | 23 | 2.0% |
| Heart-other | 9 | 0.8% |
| Stroke | 29 | 2.6% |
| Meningitis-bacterial, other | 20 | 1.8% |
| Upper gastrointestinal bleeding | 25 | 2.2% |
| Liver failure–drug induced | 15 | 1.3% |
| End stage renal failure | 15 | 1.3% |
| Injury/accident | 9 | 0.8% |
| Other | 41 | 3.6% |
| Indetermined | 81 | 7.2% |
| Subtotal | 1126 | 100.0% |
| Variables | Univariable Analysis | Multivariable Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| cOR (95% CI) | aOR (95% CI) | |
| Age groups | ||
| 0–14 | 1 | 1 |
| 15–44 | 0.76 (0.53–1.10) | 0.97 (0.58–1.62) |
| 45–64 | 1.80 (1.24–2.62) | 2.61 (1.56–4.35) |
| ≥65 | 4.66 (3.14–6.92) | 7.46 (4.39–12.67) |
| Gender | ||
| Female | 1 | 1 |
| Male | 1.31 (1.15–1.50) | 1.17 (0.97–1.38) |
| Place of residence | ||
| Rural | 1 | 1 |
| Urban | 1.20 (1.04–1.39) | 1.47 (1.22–1.77) |
| Income regular | ||
| No | 1.74 (1.52–1.99) | 1.46 (1.22–1.77) |
| Yes | 1 | 1 |
| HIV status | ||
| Negative | 1 | 1 |
| Positive | 3.84 (2.57–5.74) | 5.61 (3.51–8.97) |
| Category of TB | ||
| New case | 1 | 1 |
| Retreatment case | 1.79 (1.40–2.28) | 1.63 (1.21–2.21) |
| TB anatomical site | ||
| PTB | 1 | 1 |
| Extra PTB | 1.36 (1.13–1.65) | 1.86 (1.43–2.42) |
| CXR status at diagnosis | ||
| Minimal/normal | 1 | 1 |
| Moderately advanced | 1.75 (1.52–2.00) | 1.71 (1.43–2.05) |
| Far-advanced | 4.26 (3.27–5.54) | 4.56 (3.31–6.28) |
| Treatment regime (intensive phase) | ||
| FDC | 1 | 1 |
| Loose tablet | 2.46 (2.15–2.81) | 2.11 (1.78–2.52) |
| DOT (intensive phase) | ||
| No | 1 | 1 |
| Yes | 0.007 (0.003–0.014) | 0.007 (0.003–0.014) |
| Variables | TB-Related Death | Non-TB Related Death | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Univariable Analysis | Multivariable Analysis | Univariable Analysis | Multivariable Analysis | |
| cOR (95% CI) | aOR (95% CI) | cOR (95% CI) | aOR (95% CI) | |
| Age groups | ||||
| 0–14 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 15–44 | 0.60 (0.39–0.92) | 0.87 (0.48–1.56) | 1.13 (0.64–1.99) | 1.53 (0.79–2.97) |
| 45–64 | 0.79 (0.51–1.22) | 1.31 (0.72–2.38) | 4.09 (2.32–7.20) | 5.26 (2.71–10.18) |
| ≥65 | 1.64 (1.03–2.59) | 3.18 (1.70–5.94) | 11.52 (6.45–20.57) | 14.89 (7.57–29.32) |
| Nationality | ||||
| Citizen | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Non-citizen | 2.19 (1.83–2.63) | 1.86 (1.46–2.37) | 0.58 (0.48–0.70) | 0.71 (0.56–0.89) |
| Place of residence | ||||
| Rural | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Urban | 1.19 (0.98–1.44) | 1.54 (1.21–1.94) | 1.21 (1.03–1.43) | 1.47 (1.20–1.79) |
| Income regular | ||||
| No | 2.13 (1.75–2.59) | 1.63 (1.28–2.07) | 1.56 (1.34–1.82) | 1.32 (1.08–1.60) |
| Yes | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Smoking | ||||
| No | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Yes | 0.81 (0.67–0.99) | 0.73 (0.57–0.93) | 1.06 (0.91–1.24) | 0.96 (0.78–1.17) |
| Category of TB | ||||
| New case | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Retreatment case | 1.46 (1.04–2.03) | 1.59 (1.08–2.36) | 1.99 (1.53–2.59) | 1.80 (1.31–2.47) |
| Type of case detection | ||||
| Active | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Passive | 1.61 (1.14–2.26) | 1.57 (1.02–2.40) | 0.99 (0.78–1.26) | 1.02 (0.75–1.40) |
| CXR status at diagnosis | ||||
| Minimal/normal | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Moderately advanced | 2.76 (2.26–3.39) | 2.27 (1.79–2.88) | 1.38 (1.18–1.62) | 1.23 (1.02–1.49) |
| Far-advanced | 8.89 (6.49–12.19) | 6.58 (4.56–9.50) | 2.61 (1.93–3.53) | 2.47 (1.74–3.53) |
| Treatment regime (intensive phase) | ||||
| FDC | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Loose tablet | 2.39 (2.00–2.87) | 2.15 (1.72–2.68) | 2.49 (2.15–2.91) | 2.41 (2.00–2.90) |
| DOT (intensive phase) | ||||
| No | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Yes | 0.005 (0.002–0.011) | 0.006 (0.003–0.013) | 0.008 (0.004–0.018) | 0.008 (0.004–0.018) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Avoi, R.; Liaw, Y.C. Tuberculosis Death Epidemiology and Its Associated Risk Factors in Sabah, Malaysia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9740. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18189740
Avoi R, Liaw YC. Tuberculosis Death Epidemiology and Its Associated Risk Factors in Sabah, Malaysia. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(18):9740. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18189740
Chicago/Turabian StyleAvoi, Richard, and Yau Chun Liaw. 2021. "Tuberculosis Death Epidemiology and Its Associated Risk Factors in Sabah, Malaysia" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 18: 9740. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18189740
APA StyleAvoi, R., & Liaw, Y. C. (2021). Tuberculosis Death Epidemiology and Its Associated Risk Factors in Sabah, Malaysia. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(18), 9740. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18189740






