Bibliometric Analysis of Current Status on Bioremediation of Petroleum Contaminated Soils during 2000–2019
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology and Data
Data Collection
3. Results and Discussion
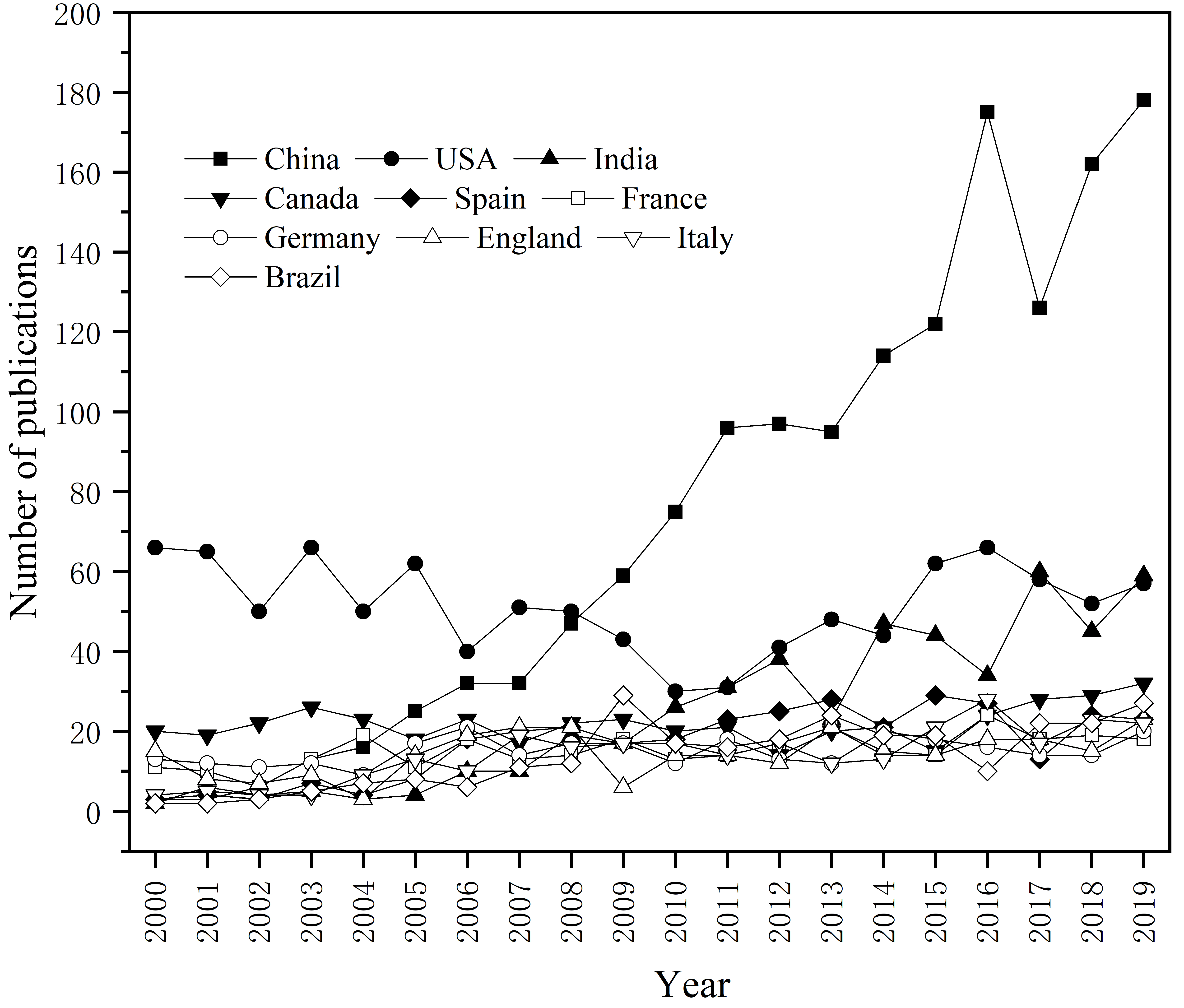
3.1. Growth Trend of Publications
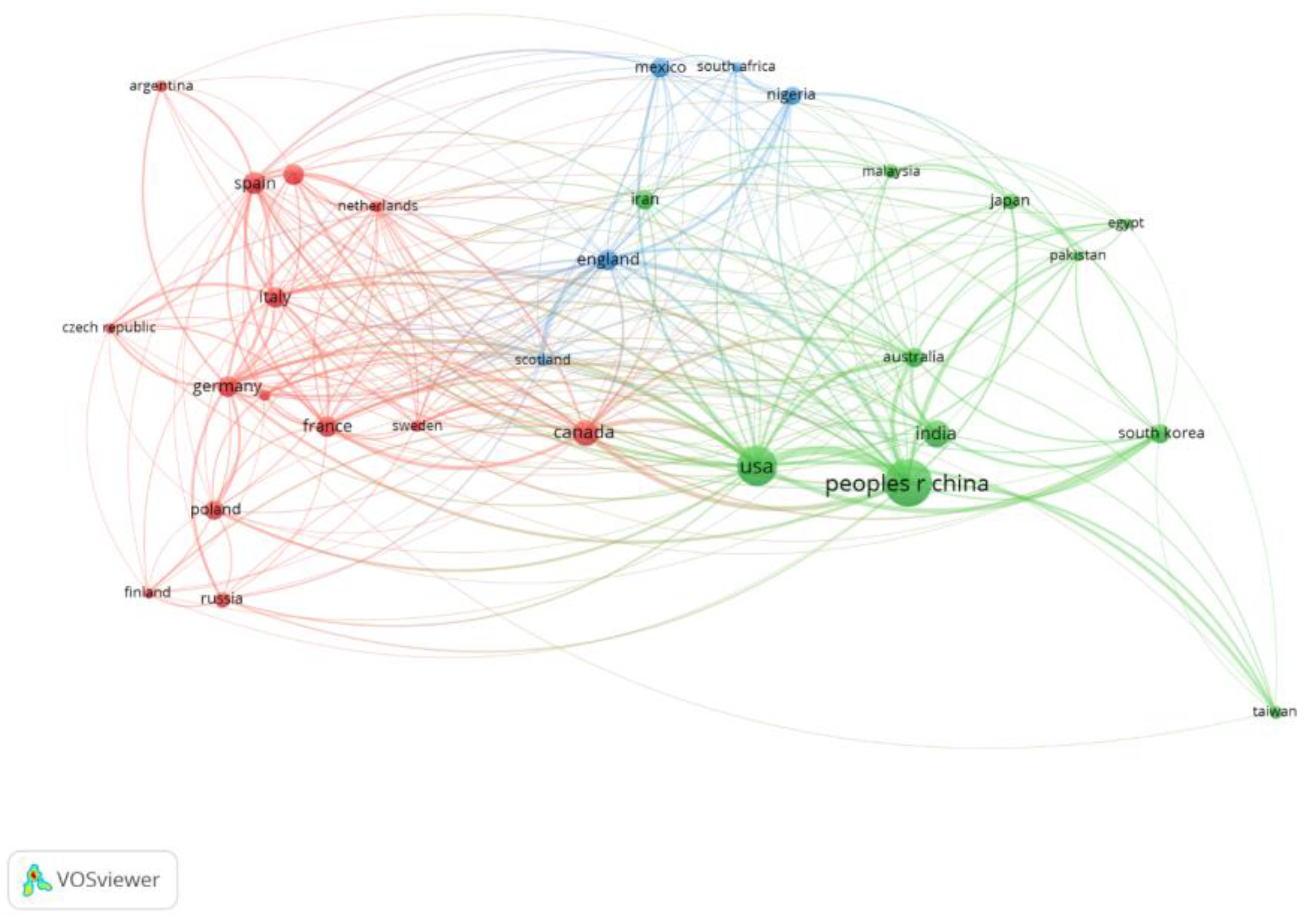
3.2. Publication Distribution of Countries/Territories
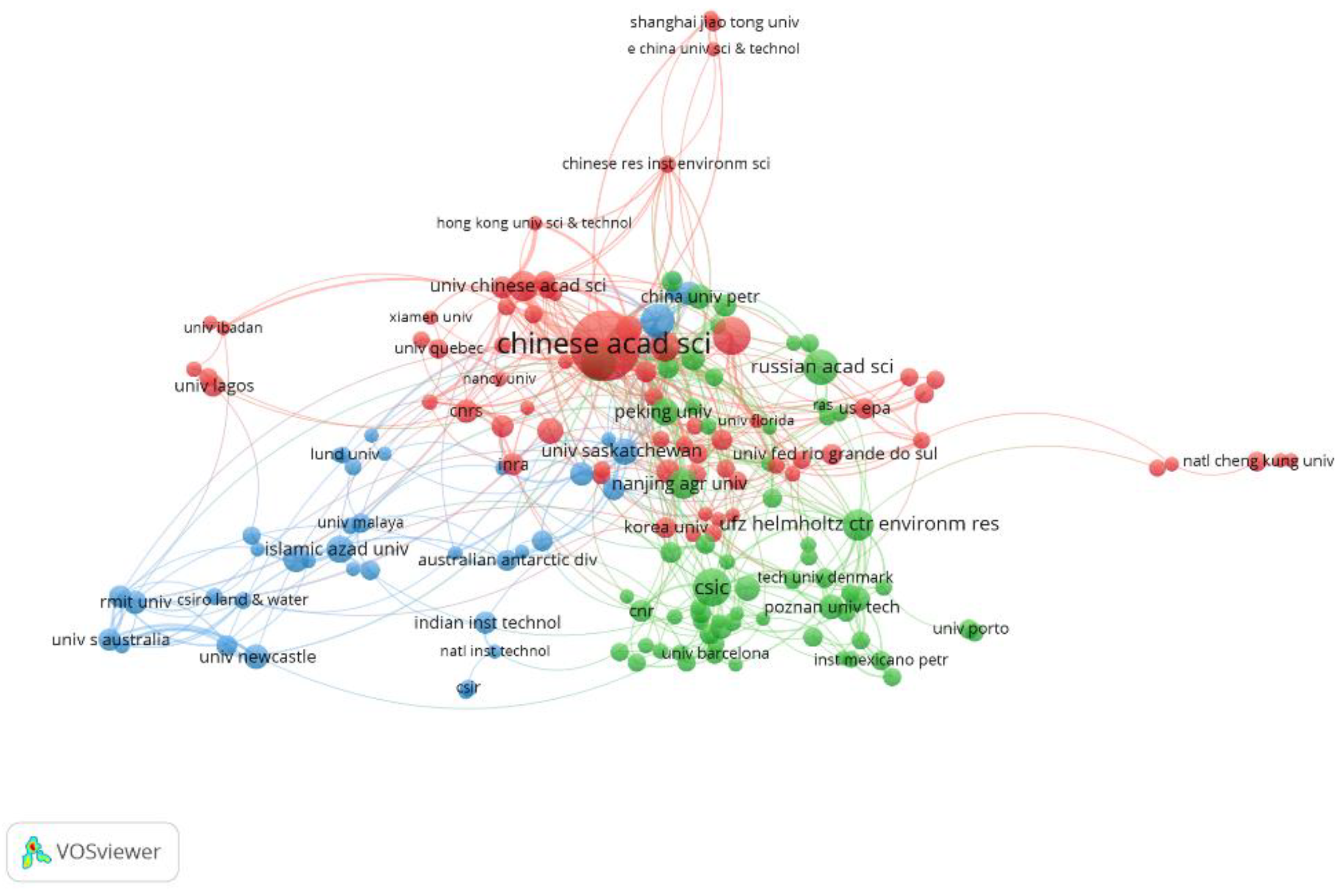
3.3. Publication Distribution of Institutions
3.4. Publication Distribution of Journals
3.5. The Most Highly Cited Articles
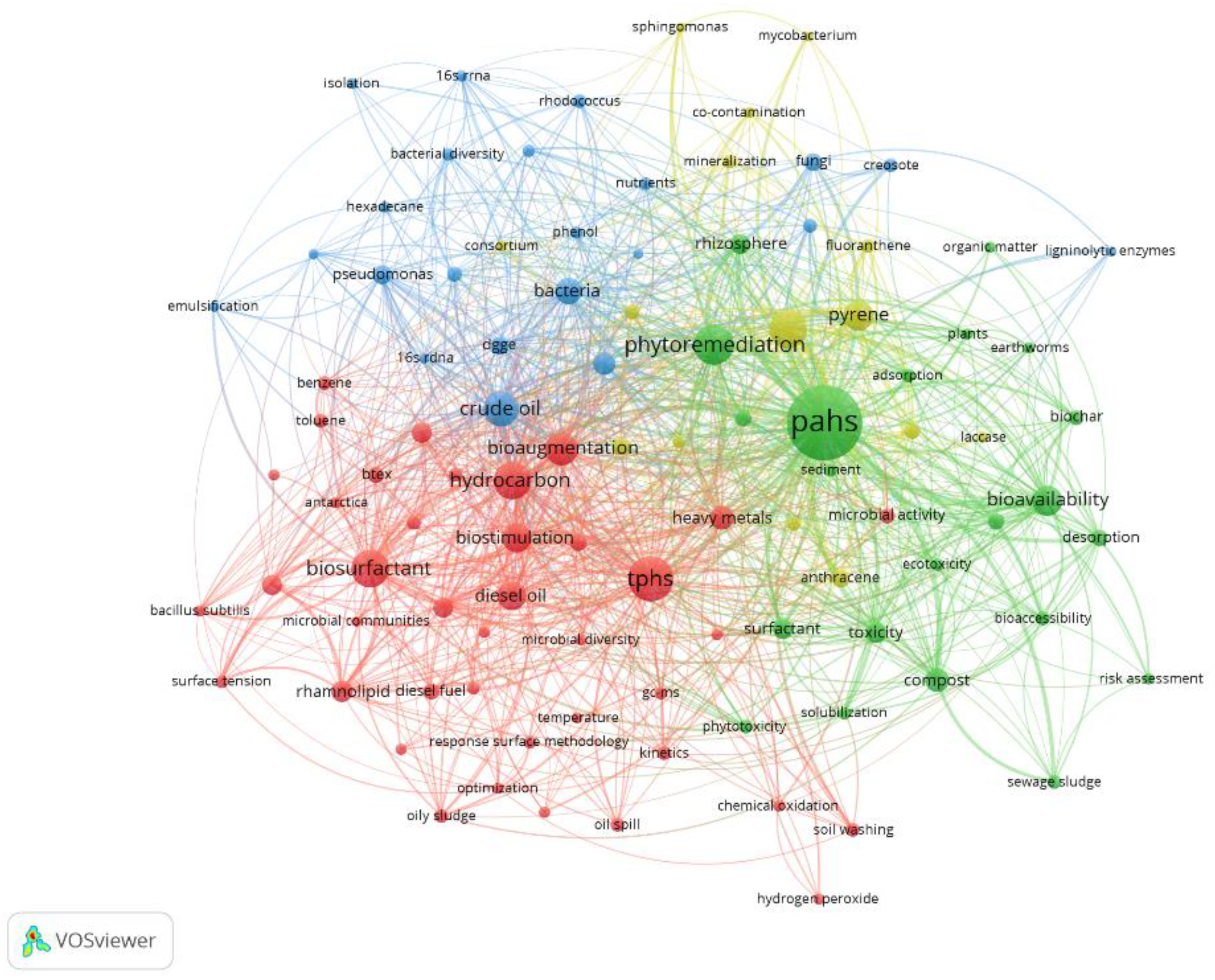
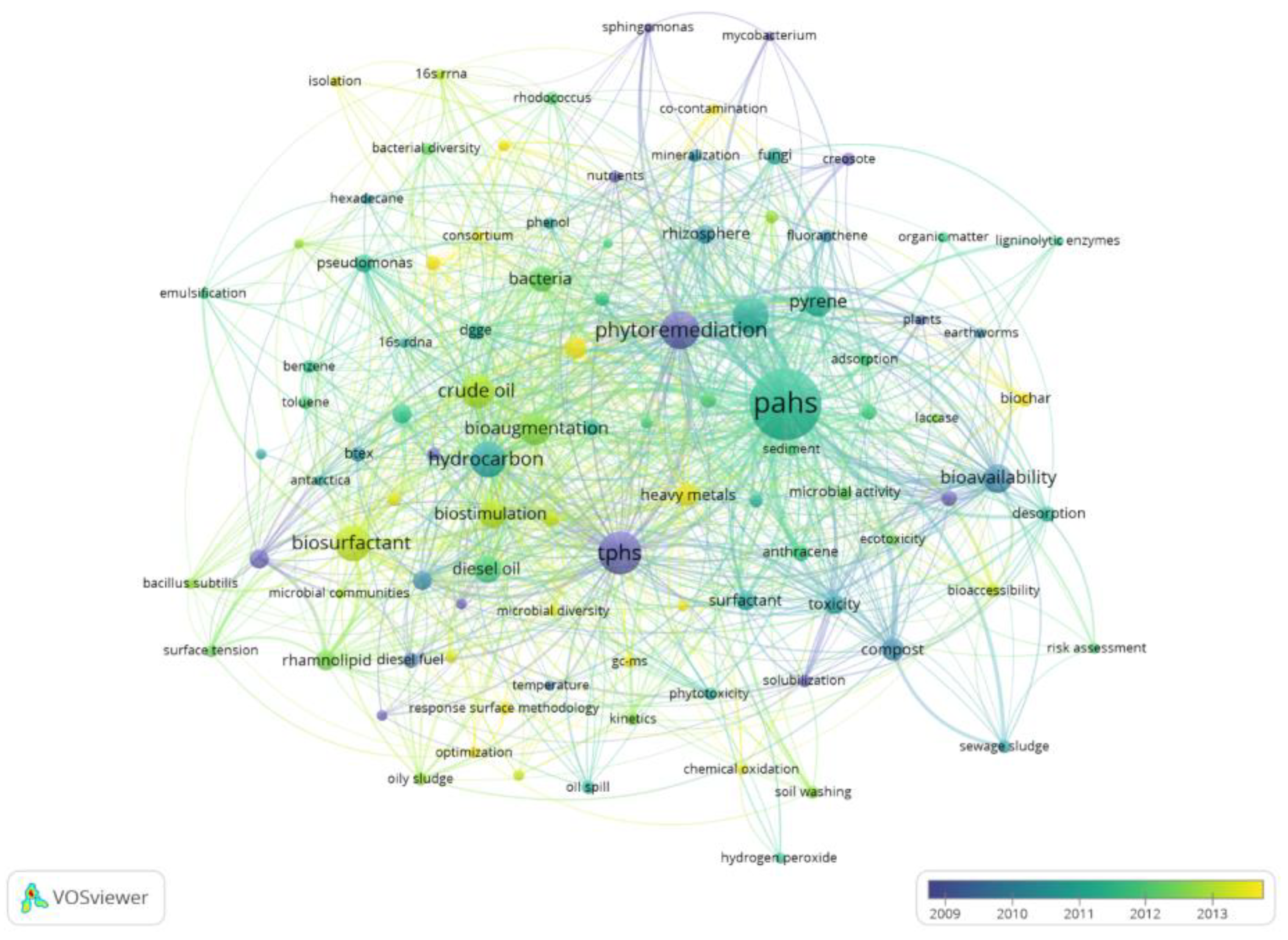
3.6. Keyword Analysis
3.7. Hot Issues
3.7.1. Research on the Composite Pollution System of Oil and Heavy Metals
3.7.2. Research on the Succession of Soil Microbial Community in the Process of Bioremediation
3.7.3. Application of BS in Bioremediation
3.7.4. Application of Biological Combined Remediation Technology
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- A steady increase was observed in publication output, with extensive international collaboration in the past 20 years. The growth rate in the number of articles published from 2000 to 2019 was 21.7%.
- (2)
- China was the country with the highest number of articles (1476), and the United States had the highest h-index (86). The Chinese Academy of Sciences was the institution with the largest number of papers (347) and cooperative relations (52).
- (3)
- Chemosphere was the most productive journal, with 360 records. The most highly cited article was on applying biochar and compost in soil remediation and was published by the Liverpool John Moores University in Environmental Pollution in 2010, with 683 citations.
- (4)
- According to the analysis of high-frequency keywords, the research on PCS bioremediation was basically steady. Phytoremediation and microbial remediation were the main remediation methods.
- (5)
- More study on the following research areas can be conducted: clarifying the biodegradation mechanism of TPHs under heavy metal stress; monitoring microbial community dynamics during bioremediation; expounding the relationship between BS, microorganisms, and pollutants; and carrying out field studies on biological combined remediation of PCS.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Wu, M.; Dick, W.A.; Li, W.; Wang, X.; Yang, Q.; Wang, T.; Xu, L.; Zhang, M.; Chen, L. Bioaugmentation and biostimulation of hydrocarbon degradation and the microbial community in a petroleum-contaminated soil. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2016, 107, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, W.A.; Farid, W.A.; Al-Salman, A.N.K. Bioremediation of Agricultural Soil Contaminated by a Crude Oil Spill. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2020, 18, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezza, F.A.; Chirwa, E.M.N. Production and applications of lipopeptide biosurfactant for bioremediation and oil recovery by Bacillus subtilis CN2. Biochem. Eng. J. 2015, 101, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, D.K.; Kim, J. New insights into bioremediation strategies for oil-contaminated soil in cold environments. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2019, 142, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, M.W.; Von Lau, E.; Poh, P.E. A comprehensive guide of remediation technologies for oil contaminated soil—Present works and future directions. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 109, 14–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, G.; Zou, H.; Chen, G.; Du, H.; Zuo, J. Past, current and future of biomass energy research: A bibliometric analysis. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 52, 1823–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, S.R.; Jones, K.C. Polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons in the United Kingdom environment: A preliminary source inventory and budget. Environ. Pollut. 1995, 88, 91–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisic, L.; Mesic, S.; Basic, F.; Brkic, V.; Mesic, M.; Durn, G.; Zgorelec, Z.; Bertovic, L. The effect of drilling fluids and crude oil on some chemical characteristics of soil and crops. Geoderma 2009, 149, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truskewycz, A.; Gundry, T.D.; Khudur, L.S.; Kolobaric, A.; Taha, M.; Aburto-Medina, A.; Ball, A.S.; Shahsavari, E. Petroleum Hydrocarbon Contamination in Terrestrial Ecosystems-Fate and Microbial Responses. Molecules 2019, 24, 3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okoh, E.; Yelebe, Z.R.; Oruabena, B.; Nelson, E.S.; Indiamaowei, O.P. Clean-up of crude oil-contaminated soils: Bioremediation option. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 17, 1185–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, N.; Flora, G.; Yadav, M.; Tiwari, A. A review with recent advancements on bioremediation-based abolition of heavy metals. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts. 2014, 16, 180–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshlaf, E.; Ball, A.S. Soil bioremediation approaches for petroleum hydrocarbon polluted environments. AIMS Microbiol. 2017, 3, 25–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.C.; Pan, P.T.; Cheng, S.S. Ex situ bioremediation of oil-contaminated soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 176, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, S. Development of bioremediation in China—A review. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao Chin. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 31, 901–916. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, W.; Zhu, N.; Cui, J.; Wang, H.; Dang, Z.; Wu, P.; Luo, Y.; Shi, C. Ecotoxicity monitoring and bioindicator screening of oil-contaminated soil during bioremediation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 124, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abtahi, H.; Parhamfar, M.; Saeedi, R.; Villasenor, J.; Sartaj, M.; Kumar, V.; Coulon, F.; Parhamfar, M.; Didehdar, M.; Hamed, S.; et al. Effect of competition between petroleum-degrading bacteria and indigenous compost microorganisms on the efficiency of petroleum sludge bioremediation: Field application of mineral-based culture in the composting process. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 258, 110013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boopathy, R. Factors limiting bioremediation technologies. Bioresour. Technol. 2000, 74, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; Li, F.; Guo, G. Bioremediation of oil sludge contaminated soil by landfarming with added cotton stalks. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2016, 106, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, W.L.; Wahab Mohammad, A.; Johnson, D.; Hilal, N. Forward osmosis research trends in desalination and wastewater treatment: A review of research trends over the past decade. J. Water Process. Eng. 2019, 31, 100886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, W. Global Trends of Compost Research from 1997 to 2012: A Bibliometric Analysis Based on SCI Database. Asian J. Chem. 2014, 26, 5242–5248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Han, R.; Lu, X. Bibliometric analysis of research trends on solid waste reuse and recycling during 1992–2016. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 130, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Li, C.; Reniers, G.; Yang, F. Safety and security of oil and gas pipeline transportation: A systematic analysis of research trends and future needs using WoS. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 279, 123583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Liu, Z.; Luo, Z.; Webber, M.; Chen, J. Bibliometric and visualized analysis of emergy research. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 90, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Liang, Q.-M. Recent progress of cooperation on climate mitigation: A bibliometric analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 277, 123495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Hong, S. Global biodiversity research during 1900–2009: A bibliometric analysis. Biodivers. Conserv. 2011, 20, 807–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhao, X.; Tang, O.; Price, L.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, W. Supply chain collaboration for sustainability: A literature review and future research agenda. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2017, 194, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.Z.; Ho, Y.S.; Sui, Y.M.; Li, Z.S. A bibliometric analysis of solid waste research during the period 1993–2008. Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 2410–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintella, C.M.; Mata, A.M.T.; Lima, L.C.P. Overview of bioremediation with technology assessment and emphasis on fungal bioremediation of oil contaminated soils. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 241, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arfaoui, A.; Ibrahimi, K.; Trabelsi, F. Biochar application to soil under arid conditions: A bibliometric study of research status and trends. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhai, X.; He, Y.; Chen, R.; Zhou, J.; Li, M.; Wang, Q. Publication trends of research on diabetes mellitus and T cells (1997–2016): A 20-year bibliometric study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 2010, 84, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biresselioglu, M.E.; Demir, M.H.; Solak, B.; Kayacan, A.; Altinci, S. Investigating the trends in arctic research: The increasing role of social sciences and humanities. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 729, 139027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, N. Status and Trend of Control over Livestock and Poultry Pollution Based on Bibliometrics. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2014, 33, 429–434. [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch, J.E. An index to quantify an individual’s scientific research output. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 16569–16572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hirsch, J.E. An index to quantify an individual’s scientific research output that takes into account the effect of multiple coauthorship. Scientometrics 2010, 85, 741–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mao, G.; Shi, T.; Zhang, S.; Crittenden, J.; Guo, S.; Du, H. Bibliometric analysis of insights into soil remediation. J. Soils Sed. 2018, 18, 2520–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lai, N.; Zuo, J.; Chen, G.; Du, H. Characteristics and trends of research on waste-to-energy incineration: A bibliometric analysis, 1999–2015. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 66, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beesley, L.; Moreno-Jimenez, E.; Gomez-Eyles, J.L. Effects of biochar and greenwaste compost amendments on mobility, bioavailability and toxicity of inorganic and organic contaminants in a multi-element polluted soil. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 2282–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulligan, C.N.; Yong, R.N.; Gibbs, B.F. Surfactant-enhanced remediation of contaminated soil: A review. Eng. Geol. 2001, 60, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, K.Y.; Huang, Y.L.; Ho, Y.S. A bibliometric and citation analysis of stroke-related research in Taiwan. Scientometrics 2007, 72, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, M.; Tang, J.; Li, C.; Sun, H. Rhamnolipid-modified biochar-enhanced bioremediation of crude oil-contaminated soil and mediated regulation of greenhouse gas emission in soil. J. Soils Sed. 2021, 21, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Chen, D.; Zhou, Y. Research progress on microbial remediation of petroleum contaminated soil. Environ. Eng. 2014, 32, 157–161. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, M.; Li, W.; Dick, W.A.; Ye, X.; Chen, K.; Kost, D.; Chen, L. Bioremediation of hydrocarbon degradation in a petroleum contaminated soil and microbial population and activity determination. Chemosphere 2017, 169, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Sinkko, H.; Penttinen, P.; Lindstrom, K. Characterization of successional changes in bacterial community composition during bioremediation of used motor oil-contaminated soil in a boreal climate. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 542, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Novakovic, M.; Ramadan, M.M.A.; Knudsen, T.S.; Antic, M.; Beskoski, V.; Gojgic-Cvijovic, G.; Vrvic, M.M.; Jovancicevic, B. Degradation of methyl-phenanthrene isomers during bioremediation of soil contaminated by residual fuel oil. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2012, 10, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simarro, R.; Gonzalez, N.; Bautista, L.F.; Molina, M.C. Assessment of the efficiency of in situ bioremediation techniques in a creosote polluted soil: Change in bacterial community. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 262, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whelan, M.J.; Coulon, F.; Hince, G.; Rayner, J.; Mcwatters, R.; Spedding, T.; Snape, I. Fate and transport of petroleum hydrocarbons in engineered biopiles in polar regions. Chemosphere 2015, 131, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dua, M.; Singh, A.; Sethunathan, N.; Johri, A.K. Biotechnology and bioremediation: Successes and limitations. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2002, 59, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ramadass, K.; Megharaj, M.; Venkateswarlu, K.; Naidu, R. Bioavailability of weathered hydrocarbons in engine oil-contaminated soil: Impact of bioaugmentation mediated by Pseudomonas spp. on bioremediation. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 968–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerniglia, C.E.; Yang, S.K. Stereoselective metabolism of anthracene and phenanthrene by the fungus Cunninghamella elegans. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1984, 47, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davies, J.I.; Evans, W.C. Oxidative metabolism of naphthalene by soil pseudomonads. The ring-fission mechanism. Biochem. J. 1964, 91, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastner, M.; Mahro, B. Microbial degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soils affected by the organic matrix of compost. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1996, 44, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agamuthu, P.; Abioye, O.P.; Aziz, A.A. Phytoremediation of soil contaminated with used lubricating oil using Jatropha curcas. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 179, 891–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, C.; Xu, W.; Lu, G.; Deng, F.; Liang, X.; Guo, C.; Dang, Z. Biosurfactant-enhanced phytoremediation of soils contaminated by crude oil using maize (Zea mays L.). Ecol. Eng. 2016, 92, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiltse, C.C.; Rooney, W.L.; Chen, Z.; Schwab, A.P.; Banks, M.K. Greenhouse evaluation of agronomic and crude oil phytoremediation potential among alfalfa genotypes. J. Environ. Qual. 1998, 27, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahar, A.; Wang, P.; Ali, A.; Awasthi, M.K.; Lahori, A.H.; Wang, Q.; Li, R.; Zhang, Z. Challenges and opportunities in the phytoremediation of heavy metals contaminated soils: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 126, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwitzguebel, J.P.; Comino, E.; Plata, N.; Khalvati, M. Is phytoremediation a sustainable and reliable approach to clean-up contaminated water and soil in Alpine areas? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2011, 18, 842–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashraf, S.; Ali, Q.; Zahir, Z.A.; Ashraf, S.; Asghar, H.N. Phytoremediation: Environmentally sustainable way for reclamation of heavy metal polluted soils. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 174, 714–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Ling, W.; Kong, H.; Zhu, X. Gradient Distribution of Root Exudates and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Rhizosphere Soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2011, 75, 1694–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Crowley, D.E. Biostimulation of PAH degradation with plants containing high concentrations of linoleic acid. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 4382–4388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siciliano, S.D.; Germida, J.J.; Banks, K.; Greer, C.W. Changes in microbial community composition and function during a polyaromatic hydrocarbon phytoremediation field trial. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shirdam, R.; Zand, A.D.; Bidhendi, G.N.; Mehrdadi, N. Phytoremediation of hydrocarbon-contaminated soils with emphasis on the effect of petroleum hydrocarbons on the growth of plant species. Phytoprotection 2008, 89, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merkl, N.; Schultze-Kraft, R.; Infante, C. Assessment of tropical grasses and legumes for phytoremediation of petroleum-contaminated soils. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2005, 165, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyak, Y.M.; Bakina, L.G.; Chugunova, M.V.; Mayachkina, N.V.; Gerasimov, A.O.; Bure, V.M. Effect of remediation strategies on biological activity of oil-contaminated soil—A field study. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2018, 126, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Delgado, C.; Alfaro-Barta, I.; Eymar, E. Combination of biochar amendment and mycoremediation for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons immobilization and biodegradation in creosote-contaminated soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 285, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domingo, J.L.; Nadal, M. Human dietary exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: A review of the scientific literature. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 86, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hou, L.; Liu, M.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Y.; Lin, X. Abundance and diversity of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degradation bacteria in urban roadside soils in Shanghai. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 3639–3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerin, T.F. Bioremediation of phenols and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in creosote contaminated soil using ex-situ landtreatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 1999, 65, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, M.; Da Fonseca MM, R.; De Carvalho, C.C.C.R. Bioaugmentation and biostimulation strategies to improve the effectiveness of bioremediation processes. Biodegradation 2011, 22, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bento, F.M.; De Oliveira Camargo, F.A.; Okeke, B.; Frankenberger-Junior, W.T. Bioremediation of soil contaminated by diesel oil. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2003, 34, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suja, F.; Rahim, F.; Taha, M.R.; Hambali, N.; Razali, M.R.; Khalid, A.; Hamzah, A. Effects of local microbial bioaugmentation and biostimulation on the bioremediation of total petroleum hydrocarbons (TPH) in crude oil contaminated soil based on laboratory. and field observations. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2014, 90, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bento, F.M.; Camargo, F.A.; Okeke, B.C.; Frankenberger, W.T. Comparative bioremediation of soils contaminated with diesel oil by natural attenuation, biostimulation and bioaugmentation. Bioresour Technol. 2005, 96, 1049–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.S.H.; Wong, A.H.Y.; Yau, K.W.Y.; Wong, Y.S.; Tam, N.F.Y. Natural attenuation, biostimulation and bioaugmentation on biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in mangrove sediments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 51, 1071–1077. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abdulsalam, S.; Bugaje, I.M.; Adefila, S.S.; Ibrahim, S. Comparison of biostimulation and bioaugmentation for remediation of soil contaminated with spent motor oil. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 8, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kauppi, S.; Sinkkonen, A.; Romantschuk, M. Enhancing bioremediation of diesel-fuel-contaminated soil in a boreal climate: Comparison of biostimulation and bioaugmentation. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2011, 65, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geissen, V.; Gomez-Rivera, P.; Huerta Lwanga, E.; Mendoza, R.B.; Narcías, A.T.; Marcías, E.B. Using earthworms to test the efficiency of remediation of oil-polluted soil in tropical Mexico. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2008, 71, 638–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nano, G.; Borroni, A.; Rota, R. Combined slurry and solid-phase bioremediation of diesel contaminated soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2003, 100, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dangi, A.K.; Sharma, B.; Hill, R.T.; Shukla, P. Bioremediation through microbes: Systems biology and metabolic engineering approach. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol 2019, 39, 79–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megharaj, M.; Ramakrishnan, B.; Venkateswarlu, K.; Sethunathan, N.; Naidu, R. Bioremediation approaches for organic pollutants: A critical perspective. Environ. Int. 2011, 37, 1362–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essiett, U.A.; Effiong, G.S.; Ogbemudia, F.O.; Bruno, E.J. Heavy metal concentrations in plants growing in crude oil contaminated soil in Akwa Ibom State, South-Eastern Nigeria. Afr. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2010, 4, 465–470. [Google Scholar]
- Nadal, M.; Schuhmacher, M.; Domingo, J.L. Long-term environmental monitoring of persistent organic pollutants and metals in a chemical/petrochemical area: Human health risks. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 1769–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaiser, M.S.H.; Ahmad, I.; Ahmad, S.R.; Afzal, M.; Qayyum, A. Assessing Heavy Metal Contamination in Oil and Gas Well Drilling Waste and Soil in Pakistan. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2019, 28, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Guo, H.; Zhang, S.; Fan, H.; Shi, J.A. Are oil spills an important source of heavy metal contamination in the Bohai Sea, China? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 3449–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiedler, S.; Siebe, C.; Herre, A.; Roth, B.; Cram, S.; Stahr, K. Contribution of Oil Industry Activities to Environmental Loads of Heavy Metals in the Tabasco Lowlands, Mexico. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2009, 197, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzyzanowski, J. Environmental pathways of potential impacts to human health from oil and gas development in northeast British Columbia, Canada. Environ. Rev. 2012, 20, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carls, E.G.; Fenn, D.B.; Chaffey, S.A. Soil Contamination by Oil and Gas Drilling and Production Operations in Padre Island National Seashore, Texas, U.S.A. J. Environ. Manag. 1995, 45, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, F.; Huertas, R.; Danulat, E. Heavy metal levels in fish from coastal waters of Uruguay. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2005, 48, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.W.; Wang, F.Y.; Huang, Z.H.; Wang, H. Simultaneous removal of 2,4-dichlorophenol and Cd from soils by electrokinetic remediation combined with activated bamboo charcoal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 176, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprocati, A.R.; Alisi, C.; Tasso, F.; Marconi, P.; Sciullo, A.; Pinto, V.; Chiavarini, S.; Ubaldi, C.; Cremisini, C. Effectiveness of a microbial formula, as a bioaugmentation agent, tailored for bioremediation of diesel oil and heavy metal co-contaminated soil. Process. Biochem. 2012, 47, 1649–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Jyot, J.; Kuhad, R.C.; Lal, B. Evaluation of inoculum addition to stimulate in situ bioremediation of oily-sludge-contaminated soil. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 1675–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Camacho-Montealegre, C.M.; Rodrigues, E.M.; Totola, M.R. Microbial diversity and bioremediation of rhizospheric soils from Trindade Island—Brazil. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 236, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ros, M.; Rodriguez, I.; Garcia, C.; Teresa Hernandez, M. Bacterial community in semiarid hydrocarbon contaminated soils treated by aeration and organic amendments. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2014, 94, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Dong, Y.; Gao, P.; Fu, M.; Ta, K.; Li, J. Microbial communities inhabiting oil-contaminated soils from two major oilfields in Northern China: Implications for active petroleum-degrading capacity. J. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eddouaouda, K.; Mnif, S.; Badis, A.; Younes, S.B.; Cherif, S.; Ferhat, S.; Mhiri, N.; Chamkha, M.; Sayadi, S. Characterization of a novel biosurfactant produced by Staphylococcus sp. strain 1E with potential application on hydrocarbon bioremediation. J. Basic Microbiol. 2012, 52, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, E.C.; Vessoni-Penna, T.C.; De Souza Oliveira, R.P. Biosurfactant-enhanced hydrocarbon bioremediation: An overview. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2014, 89, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.J.; Kumar, R. Bioremediation of petroleum contaminated soil to combat toxicity on Withania somnifera through seed priming with biosurfactant producing plant growth promoting rhizobacteria. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 174, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, V.G.; Kalil, S.J.; Costa, J.A.V. In situ bioremediation using biosurfactant produced by solid state fermentation. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 25, 843–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadrasnia, A.; Ismail, S. Biosurfactant Production by Bacillus salmalaya for Lubricating Oil Solubilization and Biodegradation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 9848–9863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jorfi, S.; Rezaee, A.; Mobeh-Ali, G.-A.; Jaafarzadeh, N.A. Application of Biosurfactants Produced byPseudomonas aeruginosa SP4for Bioremediation of Soils Contaminated by Pyrene. Soil Sediment. Contam. 2013, 22, 890–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawniczak, L.; Marecik, R.; Chrzanowski, L. Contributions of biosurfactants to natural or induced bioremediation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 2327–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szulc, A.; Ambrozewicz, D.; Sydow, M.; Lawniczak, L.; Piotrowska-Cyplik, A.; Marecik, R.; Chrzanowski, L. The influence of bioaugmentation and biosurfactant addition on bioremediation efficiency of diesel-oil contaminated soil: Feasibility during field studies. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 132, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Hong, P.K.A.; Wavrek, D.A. Chemical-biological treatment of pyrene. Water Res. 2000, 34, 1157–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, R.; Guo, M.; Zhao, X.; Gong, Z.; Jia, C.; Li, X.; Zhuang, J. Response of soil bacterial communities to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons during the phyto-microbial remediation of a contaminated soil. Chemosphere 2020, 261, 127779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Yang, L.; Chu, Y. Research on Progress in Combined Remediation Technologies of Heavy Metal Polluted Sediment. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 5098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koolivand, A.; Naddafi, K.; Nabizadeh, R.; Saeedi, R. Optimization of combined in-vessel composting process and chemical oxidation for remediation of bottom sludge of crude oil storage tanks. Environ. Technol. 2018, 39, 2597–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, D.; Wang, J.; Zeng, H.; Liu, M.; Miao, Y.; Wu, H.; Kardol, P. The nutrient absorption–transportation hypothesis: Optimizing structural traits in absorptive roots. New Phytol. 2017, 213, 1569–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnoor, J.L.; Licht, L.A.; Mccutcheon, S.C.; Wolfe, N.L.; Carreira, L.H. Phytoremediation of organic and nutrient contaminants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1995, 29, 318A–323A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liste, H.H.; Alexander, M. Plant-promoted pyrene degradation in soil. Chemosphere 2000, 40, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xun, F.; Xie, B.; Liu, S.; Guo, C. Effect of plant growth-promoting bacteria (PGPR) and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) inoculation on oats in saline-alkali soil contaminated by petroleum to enhance phytoremediation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 598–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valderrama, C.; Alessandri, R.; Aunola, T.; Cortina, J.L.; Gamisans, X.; Tuhkanen, T. Oxidation by Fenton’s reagent combined with biological treatment applied to a creosote-comtaminated soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 166, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, X.B. Remediation of weathered petroleum oil-contaminated soil using a combination of biostimulation and modified Fenton oxidation. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2012, 70, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| PY | TP | AU | AU/TP | PG | PG/TP | NR | NR/TP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 191 | 592 | 3.1 | 1801 | 9.4 | 5862 | 30.7 |
| 2001 | 195 | 578 | 3.0 | 1813 | 9.3 | 5556 | 28.5 |
| 2002 | 168 | 544 | 3.2 | 1572 | 9.4 | 4858 | 28.9 |
| 2003 | 221 | 737 | 3.3 | 2139 | 9.7 | 6873 | 31.1 |
| 2004 | 215 | 699 | 3.3 | 2010 | 9.3 | 7252 | 33.7 |
| 2005 | 252 | 867 | 3.4 | 2334 | 9.3 | 8420 | 33.4 |
| 2006 | 286 | 988 | 3.5 | 2626 | 9.2 | 9719 | 34.0 |
| 2007 | 309 | 1057 | 3.4 | 2681 | 8.7 | 10,403 | 33.7 |
| 2008 | 372 | 1312 | 3.5 | 3186 | 8.6 | 12,955 | 34.8 |
| 2009 | 367 | 1402 | 3.8 | 3087 | 8.4 | 13,011 | 35.5 |
| 2010 | 366 | 1386 | 3.8 | 3279 | 9.0 | 14,287 | 39.0 |
| 2011 | 390 | 1527 | 3.9 | 3360 | 8.6 | 15,259 | 39.1 |
| 2012 | 441 | 1688 | 3.8 | 3878 | 8.8 | 17,440 | 39.5 |
| 2013 | 427 | 1651 | 3.9 | 4067 | 9.5 | 18,254 | 42.7 |
| 2014 | 459 | 1856 | 4.0 | 4287 | 9.3 | 19,012 | 41.4 |
| 2015 | 537 | 2179 | 4.1 | 5394 | 10.0 | 23,173 | 43.2 |
| 2016 | 597 | 2435 | 4.1 | 5972 | 10.0 | 27,340 | 45.8 |
| 2017 | 542 | 2290 | 4.2 | 5543 | 10.2 | 25,725 | 47.5 |
| 2018 | 616 | 2611 | 4.2 | 6354 | 10.3 | 29,952 | 48.6 |
| 2019 | 624 | 2815 | 4.5 | 6609 | 10.6 | 31,681 | 50.8 |
| Total | 7575 | 29,214 | 3.7 | 71,992 | 9.4 | 307,032 | 38.1 |
| No. | Country | TP | R/% | NC | NC/TP | h-Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | China | 1476 | 19.485 | 33,997 | 23 | 78 |
| 2 | USA | 1032 | 13.624 | 32,212 | 31.2 | 86 |
| 3 | India | 487 | 6.429 | 11,685 | 24 | 53 |
| 4 | Canada | 437 | 5.769 | 13,104 | 30 | 60 |
| 5 | Spain | 336 | 4.436 | 11,942 | 35.5 | 56 |
| 6 | France | 305 | 4.026 | 10,656 | 34.9 | 51 |
| 7 | Germany | 300 | 3.96 | 9677 | 32.3 | 49 |
| 8 | UK | 287 | 3.789 | 9299 | 32.4 | 52 |
| 9 | Italy | 285 | 3.762 | 7236 | 25.4 | 46 |
| 10 | Brazil | 277 | 3.657 | 6176 | 22.3 | 39 |
| No. | Institutions | TP | R/% | NC | NC/TP | h-Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Chinese Academy of Sciences | 347 | 4.581 | 8994 | 25.9 | 47 |
| 2 | Center National De La Recherche Scientifique | 163 | 2.152 | 6390 | 39.2 | 40 |
| 3 | Helmholtz Association | 132 | 1.743 | 3701 | 28 | 35 |
| 4 | Consejo Superior De Investigaciones Cientificas | 126 | 1.663 | 4698 | 37.3 | 43 |
| 5 | Russian Academy of Sciences | 111 | 1.465 | 1266 | 11.4 | 19 |
| 6 | Zhejiang University | 98 | 1.294 | 3316 | 33.8 | 31 |
| 7 | University of Chinese Academy of Sciences | 94 | 1.241 | 2454 | 26.1 | 28 |
| 8 | Council of Scientific Industrial Research | 87 | 1.149 | 2224 | 25.6 | 27 |
| 9 | Tsinghua University | 86 | 1.135 | 2054 | 23.9 | 27 |
| 10 | Universite De Lorraine | 85 | 1.122 | 3369 | 39.6 | 33 |
| Rank | Journals | TP | R/% | NC | NC/TP | IF (5 Years) | Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Chemosphere | 360 | 4.752 | 14,828 | 41.19 | 5.705 | UK |
| 2 | Journal of Hazardous Materials | 307 | 4.053 | 12,773 | 41.61 | 8.512 | Netherlands |
| 3 | International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation | 278 | 3.67 | 8607 | 30.96 | 4.046 | UK |
| 4 | Environmental Science and Pollution Research | 224 | 2.957 | 3792 | 16.93 | 3.306 | Germany |
| 5 | Environmental Science & Technology | 177 | 2.337 | 8402 | 47.47 | 8.543 | USA |
| 6 | Water Air and Soil Pollution | 164 | 2.165 | 2748 | 16.76 | 2.041 | Netherlands |
| 7 | Science of The Total Environment | 162 | 2.139 | 4120 | 25.43 | 6.419 | Netherlands |
| 8 | Environmental Pollution | 157 | 2.073 | 7252 | 46.19 | 6.939 | USA |
| 9 | Bioresource Technology | 139 | 1.835 | 7779 | 55.96 | 7.27 | Netherlands |
| 10 | Biodegradation | 127 | 1.677 | 3625 | 28.54 | 2.575 | Netherlands |
| Rank | Title | Country of Corresponding Author | Publication Year | Journal | NC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Effects of biochar and greenwaste compost amendments on mobility, bioavailability and toxicity of inorganic and organic contaminants in a multi-element polluted soil | England | 2010 | Environmental Pollution | 683 |
| 2 | Surfactant-enhanced remediation of contaminated soil: a review | Canada | 2001 | Engineering Geology | 680 |
| 3 | An overview on olive mill wastes and their valorisation methods | Spain | 2006 | Waste Management | 451 |
| 4 | Comparative bioremediation of soils contaminated with diesel oil by natural attenuation, biostimulation and bioaugmentation | USA | 2005 | Bioresource Technology | 405 |
| 5 | Bioavailability of hydrophobic organic contaminants in soils: fundamental concepts and techniques for analysis | England | 2003 | European Journal of Soil Science | 386 |
| 6 | Degradation and mineralization of high-molecular-weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by defined fungal-bacterial cocultures | Australia | 2000 | Applied and Environmental Microbiology | 385 |
| 7 | Crude petroleum-oil biodegradation efficiency of Bacillus subtilis and Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated from a petroleum-oil contaminated soil from North-East India | India | 2007 | Bioresource Technology | 362 |
| 8 | Plant uptake, accumulation and translocation of phenanthrene and pyrene in soils | China | 2004 | Chemosphere | 348 |
| 9 | Two complementary sides of bioavailability: Accessibility and chemical activity of organic contaminants in sediments and soils | Denmark | 2006 | Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry | 343 |
| 10 | Bioremediation of heavy metals from soil and aquatic environment: An overview of principles and criteria of fundamental processes | South Korea | 2015 | Sustainability | 342 |
| Keywords | Frequency | Keywords | Frequency | Keywords | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons | 1199 | Diesel oil | 182 | Rhizosphere | 85 |
| Total petroleum hydrocarbons | 449 | Biostimulation | 179 | Toxicity | 85 |
| Phytoremediation | 342 | Bacteria | 152 | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 84 |
| Hydrocarbons | 314 | Compost | 121 | Pseudomonas | 81 |
| Biosurfactant | 307 | Heavy metals | 119 | Anthracene | 72 |
| Phenanthrene | 296 | Microbial community | 116 | Fungi | 72 |
| Crude oil | 259 | Rhamnolipid | 99 | DGGE | 69 |
| Bioaugmentation | 237 | Natural attenuation | 88 | Naphthalene | 69 |
| Pyrene | 204 | Surfactant | 88 | Sorption | 61 |
| Bioavailability | 199 | Groundwater | 87 | Microorganisms | 60 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, Y.; Li, R.; Chen, G.; Yan, B.; Zhong, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y. Bibliometric Analysis of Current Status on Bioremediation of Petroleum Contaminated Soils during 2000–2019. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8859. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18168859
Song Y, Li R, Chen G, Yan B, Zhong L, Wang Y, Li Y, Li J, Zhang Y. Bibliometric Analysis of Current Status on Bioremediation of Petroleum Contaminated Soils during 2000–2019. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(16):8859. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18168859
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Yingjin, Ruiyi Li, Guanyi Chen, Beibei Yan, Lei Zhong, Yuxin Wang, Yihang Li, Jinlei Li, and Yingxiu Zhang. 2021. "Bibliometric Analysis of Current Status on Bioremediation of Petroleum Contaminated Soils during 2000–2019" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 16: 8859. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18168859
APA StyleSong, Y., Li, R., Chen, G., Yan, B., Zhong, L., Wang, Y., Li, Y., Li, J., & Zhang, Y. (2021). Bibliometric Analysis of Current Status on Bioremediation of Petroleum Contaminated Soils during 2000–2019. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(16), 8859. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18168859







