The Role of Motor Imagery in Predicting Motor Skills in Young Male Soccer Players
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Measures
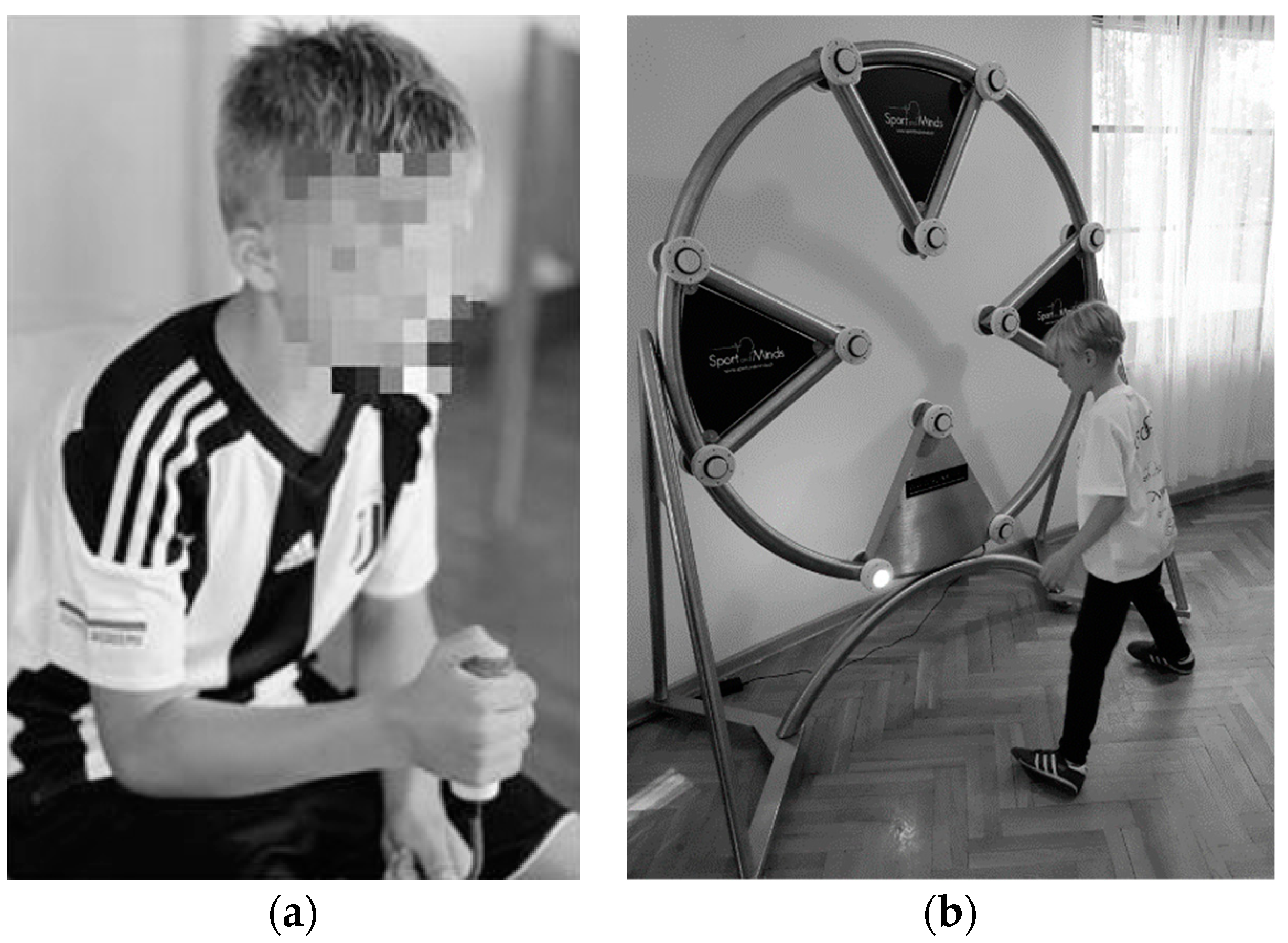
2.2.1. Reaction Time Task
2.2.2. Eye–Hand Coordination Task
2.2.3. Motor Imagery Questionnaire–Revised
2.2.4. Short Survey
2.3. Procedure
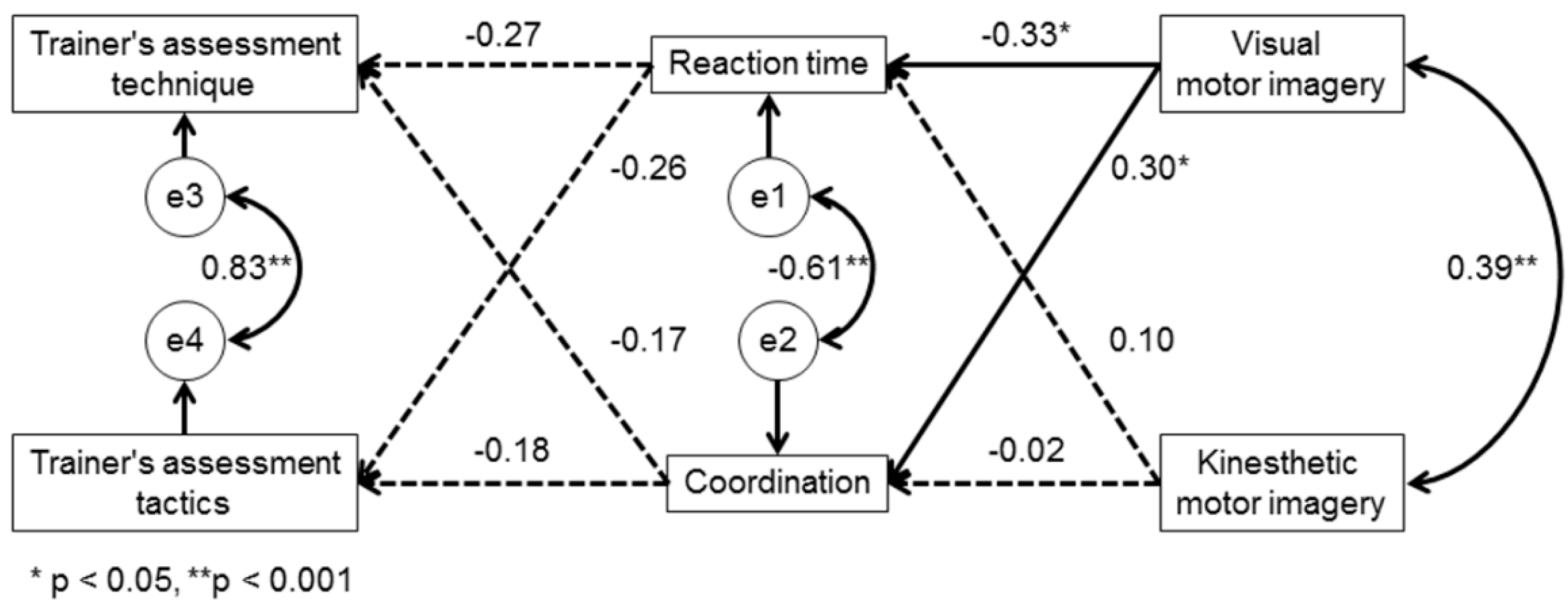
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| The Trainer’s Assessment Tactics and Technique | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
References
- Jeannerod, M. Neural simulation of action: A unifying mechanism for motor cognition. Neuroimage 2001, 14, S103–S109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, C.R.; Rodgers, W.M.; Barr, K.A. The use of imagery by athletes in selected sports. Sport Psychol. 1990, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, C.; Land, W.M.; Popp, C.; Schack, T. Mental Representation and Mental Practice: Experimental Investigation on the Functional Links between Motor Memory and Motor Imagery. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, C.; Land, W.M.; Schack, T. Perceptual-Cognitive Changes during Motor Learning: The Influence of Mental and Physical Practice on Mental Representation, Gaze Behavior, and Performance of a Complex Action. Front. Psychol. 2016, 6, 1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suinn, R.M. Mental Practice in Sport Psychology: Where Have We Been, Where Do We Go? Clin. Psychol. 1997, 4, 189–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, L.; Stuth, G. The Uses of Mental Imagery in Athletics an Overview. Appl. Prev. Psychol. 1997, 6, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridderinkhof, K.R.; Brass, M. How kinesthetic motor imagery works: A predictive-processing theory of visualization in sports and motor expertise. J. Physiol. Paris 2015, 109, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotze, M.; Halsband, U. Motor imagery. J. Physiol. Paris 2006, 99, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ungerleider, S.; Golding, J.M. Mental practice among Olympic athletes. Percept. Mot. Ski. 1991, 72, 1007–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebon, F.; Collet, C.; Guillot, A. Benefits of motor imagery training on muscle strength. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2010, 24, 1680–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosprêtre, S.; Jacquet, T.; Lebon, F.; Papaxanthis, C.; Martin, A. Neural mechanisms of strength increase after one-week motor imagery training. EJSS 2018, 18, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yágüez, L.; Nagel, D.; Hoffman, H.; Canavan, A.G.M.; Wist, E.; Hömberg, V. A mental route to motor learning: Improving trajectorial kinematics through imagery training. Behav. Brain Res. 1998, 90, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuper, C.; Scherer, R.; Reiner, M.; Pfurtscheller, G. Imagery of motor actions: Differential effects of kinesthetic and visual-motor mode of imagery in single-trial EEG. Cogn. Brain Res. 2005, 25, 668–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumming, J.; Nordin, S.M.; Horton, R.; Reynolds, S. Examining the direction of imagery and self-talk on dart-throwing performance and self efficacy. Sport Psychol. 2006, 20, 257–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filgueiras, A. Imagery for the Improvement of Serving in Beach Volleyball: A Single Case Study. Rev. Bras. Psicol. Esporte 2017, 6, 57–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Féry, Y.A.; Morizot, P. Kinesthetic and visual image in modeling closed motor skills: The example of the tennis serve. Percept. Mot. Ski. 2000, 90, 707–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hétu, S.; Grégoire, M.; Saimpont, A.; Coll, M.P.; Eugène, F.; Michon, P.E.; Jackson, P.L. The neural network of motor imagery: An ALE meta-analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2013, 37, 930–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filgueiras, A.; Conde, E.F.Q.; Hall, C.R. The neural basis of kinesthetic and visual imagery in sports: An ALE meta-analysis. Brain Imaging Behav. 2017, 12, 1513–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillot, A.; Collet, C.; Nguyen, V.A.; Malouin, F.; Richards, C.; Doyon, J. Brain activity during visual versus kinesthetic imagery: An fMRI study. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2008, 30, 2157–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, M.; Brugger, P.; Wilkening, F. Motor processes in children’s imagery: The case of mental rotation of hands. Dev. Sci. 2005, 8, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krüger, M.; Krist, H. Imagery and motor processes—When are they connected? The mental rotation of body parts in development. Cogn. Dev. 2009, 10, 239–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, M.; Tijus, C.; Jouen, F. The Emergence of Motor Imagery in Children. J. Exp. Child Psychol. 2008, 99, 196–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smits-Engelsman, B.; Wilson, P. Age-related changes in motor imagery from early childhood to adulthood: Probing the internal representation of speed-accuracy trade-offs. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2012, 32, 1151–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spruijt, S.; van der Kamp, J.; Steenbergen, B. Current insights in the development of children’s motor imagery ability. Front. Psychol. 2015, 10, 6–787. [Google Scholar]
- Butson, M.; Hyde, C.; Steenbergen, B.; Williams, J. Assessing motor imagery using the hand rotation task: Does performance change across childhood? Hum. Mov. Sci. 2014, 35, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caeyenberghs, K.; Tsoupas, J.; Wilson, P.H.; Smits-Engelsman, B.C. Motor imagery development in primary school children. Dev. Neuropsychol. 2009, 34, 103–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyek, N.; Champely, S.; Collet, C.; Fargier, P.; Guillot, A. Age and gender-related differences in the temporal congruence between motor imagery and motor performance. Learn. Individ. Differ. 2009, 19, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoura, X.; Vinter, A.; Papaxanthis, C. Mentally simulated motor actions in children. Dev. Neuropsychol. 2009, 34, 356–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhury, S.; Charman, T.; Bird, V.; Blakemore, S.-J. Development of action representation during adolescence. Neuropsychologia 2007, 45, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregg, M.; Strachan, L. Examining Developmental Differences in Imagery Use with Youth Soccer Players. J. Imag. Res. Sport Phys. Act. 2015, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, R.; Carter, M.J.; Yoxon, E.; Cumming, J.; Ste-Marie, D.M. Development and validation of the Movement Imagery Questionnaire for Children (MIQ-C). Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2016, 22, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonsmeier, B.A.; Frank, C.; Gubelmann, H.; Schneider, M. The effects of motor imagery training on performance and mental representation of 7-to 15-year-old gymnasts of different levels of expertise. Sport Exerc. Perform. Psychol. 2018, 7, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li-Wei, Z.; Qi-Wei, M.; Orlick, T.; Zitzelsberger, L. The effect of mental-imagery training on performance enhancement with 7–10-year-old children. Sport Psychol. 1992, 6, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.; Wright, C.; Allsopp, A.; Westhead, H. It’s all in the mind: PETTLEP-based imagery and sports performance. J. Appl. Sport Psychol. 2007, 19, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, S.; Ohtani, Y.; Imanaka, K. Reaction times and anticipatory skills of karate athletes. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2002, 21, 213–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, V.; Rodrigues, L.; Maia, J.A.; Malina, R.M. Motor coordination as predictor of physical activity in childhood. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2011, 21, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandorpe, B.; Vandendriessche, J.B.; Vaeyens, R.; Pion, J.; Lefevre, J.; Philippaerts, R.M.; Lenoir, M. The value of a non-sport-specific motor test battery in predicting performance in young female gymnasts. J. Sports Sci. 2012, 30, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuri, L.; Shadmehr, A.; Ghotbi, N.; Attarbashi Moghadam, B. Reaction time and anticipatory skill of athletes in open and closed skill-dominated sport. EJSS 2013, 13, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zazzo, R. Manuel Pour L’examen Psychologique De L’enfant. In Tome 1; Delachaux Et Niestlé: Paris, France, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Bogdanowicz, M. Diagnosis and Treatment of Children with Reading and Writing Difficulties in Poland. Int. J. Disabil. Dev. Educ. 1989, 36, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregg, M.; Hall, C.; Butler, A. The MIQ-RS: A Suitable Option for Examining Movement Imagery Ability. eCAM 2010, 7, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naglak, Z. Metodyka Trenowania Sportowca; Wydawnictwo AWF Wrocław: Wrocław, Poland, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Nevitt, J.; Hancock, G.R. Evaluating small sample approaches for model test statistics in structural equation modeling. Multivar. Behav. Res. 2004, 39, 439–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kline, R.B. Principles and Practice of Structural Equation Modeling; Kline, R.B., Ed.; The Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Byrne, B.M. Structural Equation Modeling with AMOS: Basic Concepts, Applications, and Programming; Byrne, B.M., Ed.; Taylor & Francis Group: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kwiatkowski, M.; Borek, D.; Żukowski, N. Norm klasyfikacyjne czasów reakcji dla grupy sportowców. Sport Wyczyn. 2006, 1112, 3545. [Google Scholar]
- Fitts, P.M.; Peterson, J.R. Information capacity of discrete motor responses. J. Exp. Psychol. 1964, 67, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleishman, E.A.; Rich, S. Role of kinesthetic and spatial-visual abilities in perceptual-motor learning. J. Exp. Psychol. 1963, 66, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebon, F.; Horn, U.; Domin, M.; Lotze, M. Motor imagery training: Kinesthetic imagery strategy and inferior parietal f MRI activation. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2018, 39, 1805–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolas, R.; Laurent, D.; Toussaint, L.; Blandin, Y. Effects of motor imagery training on service return accuracy in tennis: The role of imagery ability. Int. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2007, 5, 175. [Google Scholar]
- Féry, Y.A. Differentiating visual and kinesthetic imagery in mental practice. Can. J. Exp. Psychol. Rev. Can. Psychol. Exp. 2003, 57, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veraksa, A.; Gorovaya, A. Imagery training efficacy among novice soccer players. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2012, 33, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Johnson, B.; Jobst, C.; Al-Loos, R.; He, W.; Cheyne, D. Developmental Changes in Movement Related Brain Activity in Early Childhood. BioRxiv 2019, 531905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slimani, M.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Tod, D.; Dellal, A.; Hue, O.; Cheour, F.; Taylor, L.; Chamari, K. Do cognitive training strategies improve motor and positive psychological skills development in soccer players? Insights from a systematic review. J. Sports Sci. 2016, 34, 2338–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahmani, M.; Babak, M.; Land, W.M.; Howard, J.T.; Diekfuss, J.A.; Abdollahipour, R. Children’s motor imagery modality dominance modulates the role of attentional focus in motor skill learning. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2021, 75, 102742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.H.; Fu, A.S.; Kho, A.; Li, J.; Sun, X.H.; Chan, C.C. Imagery perspective among young athletes: Differentiation between external and internal visual imagery. J. Sport Health Sci. 2016, 5, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callow, N.; Jiang, D.; Roberts, R.; Edwards, M.G. Kinesthetic imagery provides additive benefits to internal visual imagery on slalom task performance. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2017, 39, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zapała, D.; Zabielska-Mendyk, E.; Cudo, A.; Jaśkiewicz, M.; Kwiatkowski, M.; Kwiatkowska, A. The Role of Motor Imagery in Predicting Motor Skills in Young Male Soccer Players. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6316. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18126316
Zapała D, Zabielska-Mendyk E, Cudo A, Jaśkiewicz M, Kwiatkowski M, Kwiatkowska A. The Role of Motor Imagery in Predicting Motor Skills in Young Male Soccer Players. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(12):6316. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18126316
Chicago/Turabian StyleZapała, Dariusz, Emilia Zabielska-Mendyk, Andrzej Cudo, Marta Jaśkiewicz, Marcin Kwiatkowski, and Agnieszka Kwiatkowska. 2021. "The Role of Motor Imagery in Predicting Motor Skills in Young Male Soccer Players" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 12: 6316. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18126316
APA StyleZapała, D., Zabielska-Mendyk, E., Cudo, A., Jaśkiewicz, M., Kwiatkowski, M., & Kwiatkowska, A. (2021). The Role of Motor Imagery in Predicting Motor Skills in Young Male Soccer Players. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(12), 6316. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18126316






