Bilateral Asymmetries Assessment in Elite and Sub-Elite Male Futsal Players
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Procedure
2.3. Experimental Protocol
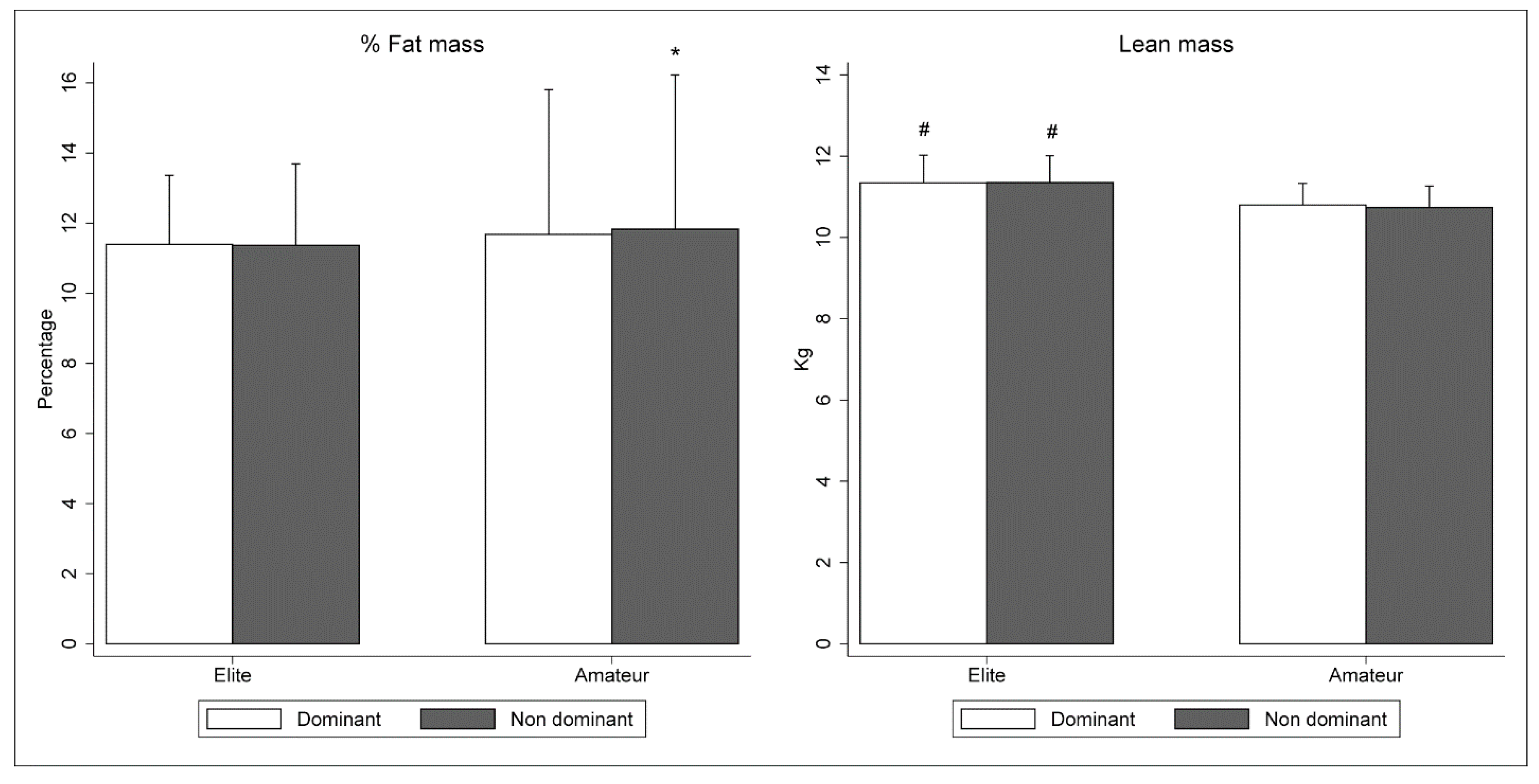
2.3.1. Tissue Composition of Lower Limbs
2.3.2. Postural Sway Test
2.3.3. Contractile Properties of Lower-Limb Muscles
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Junge, A.; Dvorak, J. Injury risk of playing football in Futsal World Cups. Br. J. Sports Med. 2010, 44, 1089–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angoorani, H.; Haratian, Z.; Mazaherinezhad, A.; Younespour, S. Injuries in Iran futsal national teams: A comparative study of incidence and characteristics. Asian J. Sports Med. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, M.S.A.; Jaafar, Z.; Ali, A.S.M. Incidence and characteristics of injuries during the 2010 FELDA/FAM national futsal league in Malaysia. PLoS ONE 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Martinez-Riaza, L.; Herrero-Gonzalez, H.; Lopez-Alcorocho, J.M.; Guillen-Garcia, P.; Fernandez-Jaen, T.F. Epidemiology of injuries in the Spanish national futsal male team: A five-season retrospective study. BMJ Open Sport Exerc. Med. 2017, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheldon, J.H. The effect of age on the control of sway. Gerontol. Clin. 1963, 5, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hespen, A.; Stege, J.P.; Stubbe, J.H. Soccer and futsal injuries in the netherlands. Br. J. Sports Med. 2011, 45, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahr, R. Why screening tests to predict injury do not work—And probably never will…: A critical review. Br. J. Sports Med. 2016, 50, 776–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maloney, S.J. The relationship between asymmetry and athletic performance: A critical review. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croisier, J.L.; Ganteaume, S.; Binet, J.; Genty, M.; Ferret, J.M. Strength imbalances and prevention of hamstring injury in professional soccer players: A prospective study. Am. J. Sports Med. 2008, 36, 1469–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiesel, K.B.; Butler, R.J.; Plisky, P.J. Prediction of injury by limited and asymmetrical fundamental movement patterns in American football players. J. Sport Rehabil. 2014, 2, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Söderman, K.; Werner, S.; Pietilä, T.; Engström, B.; Alfredson, H. Balance board training: Prevention of traumatic injuries of the lower extremities in female soccer players? Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2000, 8, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coratella, G.; Beato, M.; Schena, F. Correlation between quadriceps and hamstrings inter-limb strength asymmetry with change of direction and sprint in U21 elite soccer-players. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2018, 59, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, N.H.; Nimphius, S.; Spiteri, T.; Newton, R.U. Leg strength and lean mass symmetry influences kicking performance in Australian Football. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2014, 13, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kartal, A. Comparison of static balance in different athletes. Anthropologist 2014, 18, 811–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, L.A.; De Oliveira, D.L.; Romano, R.G.; Correa, S.C. Leg preference and interlateral asymmetry of balance stability in soccer players. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 2011, 82, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pau, M.; Arippa, F.; Leban, B.; Corona, F.; Ibba, G.; Todde, F.; Scorcu, M. Relationship between static and dynamic balance abilities in Italian professional and youth league soccer players. Phys. Ther. Sport 2015, 16, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pau, M.; Ibba, G.; Leban, B.; Scorcu, M. Characterization of static balance abilities in elite soccer players by playing position and age. Res. Sports Med. 2014, 22, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paillard, T.; Noe, F.; Riviere, T.; Marion, V.; Montoya, R.; Dupui, P. Postural performance and strategy in the unipedal stance of soccer players at different levels of competition. J. Athl. Train. 2006, 41, 172–176. [Google Scholar]
- Hrysomallis, C. Balance ability and athletic performance. Sports Med. 2011, 41, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, R.; Macaluso, F.; Traina, M.; Leonardi, V.; Farina, F.; Di Felice, V. Soccer players have a better standing balance in nondominant one-legged stance. Open Access. J. Sports Med. 2011, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, A.; Brown, S.; Abade, E. Evaluating injury risk in first and second league professional Portuguese soccer: Muscular strength and asymmetry. J. Hum. Kinet. 2016, 51, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bittencourt, N.F.N.; Meeuwisse, W.H.; Mendonça, L.D.; Nettel-Aguirre, A.; Ocarino, J.M.; Fonseca, S.T. Complex systems approach for sports injuries: Moving from risk factor identification to injury pattern recognition—Narrative review and new concept. Br. J. Sports Med. 2016, 50, 1309–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Dyk, N.; Bahr, R.; Burnett, A.F.; Whiteley, R.; Bakken, A.; Mosler, A.; Farooq, A.; Witvrouw, E. A comprehensive strength testing protocol offers no clinical value in predicting risk of hamstring injury: A prospective cohort study of 413 professional football players. Br. J. Sports Med. 2017, 51, 1695–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naser, N.; Ali, A.; Macadam, P. Physical and physiological demands of futsal. J. Exerc. Sci. Fit. 2017, 15, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, C.; Sánchez-Sánchez, J.; López-Fernández, J.; Hernando, E.; Gallardo, L. Influence of the playing surface on changes of direction and plantar pressures during an agility test in youth futsal players. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2019, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paillard, T. Effects of general and local fatigue on postural control: A review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2012, 36, 162–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pau, M.; Ibba, G.; Attene, G. Fatigue-induced balance impairment in young soccer players. J. Athl. Train. 2014, 49, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howerton, K. A comparison of postural stability in gymnasts, volleyball players, and non-athletes. Ursidae Undergrad. Res. J. Univ. North Colo 2016, 2, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Bressel, E.; Yonker, J.C.; Kras, J.; Heath, E.M. Comparison of static and dynamic balance in female collegiate soccer, basketball, and gymnastics athletes. J. Athl. Train. 2007, 42, 42–46. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda, S.; Demura, S.; Uchiyama, M. Centre of pressure sway characteristics during static one-legged stance of athletes from different sports. J. Sports Sci. 2008, 26, 775–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellis, S.; Gerodimos, V.; Kellis, E.; Manou, V. Bilateral isokinetic concentric and eccentric strength profiles of the knee extensors and flexors in young soccer players. Isokinet. Exerc. Sci. 2001, 9, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadczak, L.; Grygorowicz, M.; Dzudzinski, W.; Sliwowski, R. Comparison of static and dynamic balance at different levels of sport competition in professional and junior elite soccer player. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2019, 33, 3384–3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brito, J.; Fontes, I.; Ribeiro, F.; Raposo, A.; Krustrup, P.; Rebelo, A. Postural stability decreases in elite young soccer players after a competitive soccer match. Phys. Ther. Sport 2012, 13, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, D.R.; Sanfilippo, J.L.; Binkley, N.; Heiderscheit, B.C. Lean mass asymmetry influences force and power asymmetry during jumping in collegiate athletes. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2014, 28, 884–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slimani, M.; Znazen, H.; Hammami, A.; Bragazzi, N.L. Comparison of body fat percentage of male soccer players of different competitive levels, playing positions and age groups: A meta-analysis. J. Phys. Fit Sports Med. 2017, 58, 857–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milsom, J.; Naughton, R.; O’Boyle, A.; Iqbal, Z.; Morgans, R.; Drust, B.; Morton, J.P. Body composition assessment of English Premier League soccer players: A comparative DXA analysis of first team, U21 and U18 squads. J. Sports Sci. 2015, 33, 1706–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poliszczuk, T.; Mańkowska, M.; Poliszczuk, D.; Wiśniewski, A. Symmetry and asymmetry of reaction time and body tissue composition of upper limbs in young female basketball players. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. 2013, 19, 132–136. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, L.C. Segmental bioelectrical impedance analysis: An update. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2012, 15, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, E.; Lago-Peñas, C.; Lago-Ballesteros, J. Tensiomyography of selected lower-limb muscles in professional soccer players. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2012, 22, 866–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Matoso, D.; Rodríguez-Ruíz, D.; Quiroga, M.E.; Sarmiento, S.; De Saa, Y.; García-Manso, J.M. Tensiomygraphy, utility and methodology in the muscular assessment. Revista Int. Med. Cienc. Act. Fis Deporte 2010, 10, 620–629. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Ruiz, D.; Rodríguez-Matoso, D.; Quiroga, M.E.; Sarmiento, S.; García-Manso, J.M.; Da Silva-Grigoletto, M.E. Study of mechanical characteristics of the knee extensor and flexor musculature of volleyball players. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2012, 12, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Rodríguez, S.; Alentorn-Geli, E.; Tous-Fajardo, J.; Samuelsson, K.; Marín, M.; Álvarez-Díaz, P.; Cugat, R. Is tensiomyography a useful assessment tool in sports medicine? Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2017, 25, 3980–3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Rodríguez, S.; Loturco, I.; Hunter, A.M.; Rodríguez-Ruiz, D.; Munguia-Izquierdo, D. Reliability and measurement error of tensiomyography to assess mechanical muscle function: A systematic review. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2017, 31, 3524–3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benítez Jiménez, A.; Roldan, K.; Montero Doblas, J.M.; Romacho Castro, J. Fiabilidad de la tensiomiografía (tmg) como herramienta de valoración muscular/reliability of tensiomiography (tmg) as a muscle assessment tool. Revista Int. Med. Cienc. Act. Fis Deporte 2013, 13, 647–656. [Google Scholar]
- Krizaj, D.; Simunic, B.; Zagar, T. Short-term repeatability of parameters extracted from radial displacement of muscle belly. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2008, 18, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šimunič, B. Between-day reliability of a method for non-invasive estimation of muscle composition. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2012, 22, 527–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tous-Fajardo, J.; Moras, G.; Rodríguez-Jiménez, S.; Usach, R.; Moreno-Doutres, D.; Maffiuletti, N.A. Inter-rater reliability of muscle contractile property measurements using non-invasive tensiomyography. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2010, 20, 761–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Sánchez, J.; Bishop, D.; García-Unanue, J.; Ubago-Guisado, E.; Hernando, E.; López-Fernández, J.; Colino, E.; Gallardo, L. Effect of a repeated sprint ability test on the muscle contractile properties in elite futsal players. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, W.G.; Marshall, S.W.; Batterham, A.M.; Hanin, J. Progressive statistics for studies in sports medicine and exercise science. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2009, 41, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fousekis, K.; Tsepis, E.; Vagenas, G. Lower limb strength in professional soccer players: Profile, asymmetry, and training age. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2010, 9, 364–373. [Google Scholar]
- Ricotti, L. Static and dynamic balance in young athletes. J. Hum. Sport Exerc. 2011, 6, 616–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faude, O.; Junge, A.; Kindermann, W.; Dvorak, J. Risk factors for injuries in elite female soccer players. Br. J. Sports Med. 2006, 40, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hertel, J.; Gay, M.R.; Denegar, C.R. Differences in postural control during single-leg stance among healthy individuals with different foot types. J. Athl. Train. 2002, 37, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alentorn-Geli, E.; Alvarez-Diaz, P.; Ramon, S.; Marin, M.; Steinbacher, G.; Boffa, J.J.; Cuscó, X.; Ballester, J.; Cugat, R. Assessment of neuromuscular risk factors for anterior cruciate ligament injury through tensiomyography in male soccer players. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2015, 23, 2508–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, S.; Loturco, I.; Tricoli, V.; Ugrinowitsch, C.; Kobal, R.; Cal Abad, C.C.; Roschel, H. Tensiomyography parameters and jumping and sprinting performance in Brazilian elite soccer players. Sports Biomech. 2015, 14, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-García, O.; Serrano-Gómez, V.; Hernández-Mendo, A.; Morales-Sánchez, V. Baseline mechanical and neuromuscular profile of knee extensor and flexor muscles in professional soccer players at the start of the pre-season. J. Hum. Kinet. 2017, 58, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Valencic, V.; Knez, N.; Simunic, B. Tensiomyography: Detection of skeletal muscle response by means of radial muscle belly displacement. Biomed. Eng. 2001, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
| Dominant Leg | Non-Dominant Leg | Bilateral Asymmetry | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elite Players | Sub-Elite Players | Elite Players | Sub-Elite Players | Elite Players | Sub-Elite Players | |
| Sway path-total (mm) | 819.92 ± 207.44 | 880.77 ± 232.17 | 828.56 ± 222.46 | 844.31 ± 215.76 | −0.03 ± 0.19 | 0.03 ± 0.16 |
| Sway path-A-P (mm) | 507.88 ± 155.60 | 577.46 ± 180.25 | 522.52 ± 131.04 | 555.46 ± 160.87 | −0.07 ± 0.26 | 0.02 ± 0.17 |
| Sway path-M-L (mm) | 542.80 ± 138.76 | 551.69 ± 134.72 | 545.92 ± 169.14 | 526.08 ± 144.59 | −0.02 ± 0.17 | 0.04 ± 0.19 |
| Sway V-total (mm/s) | 40.97 ± 10.34 | 44.08 ± 11.68 | 41.46 ± 11.15 | 42.19 ± 10.77 | −0.03 ± 0.19 | 0.03 ± 0.16 |
| Sway V-A-P (mm/s) | 25.40 ± 7.79 | 28.88 ± 9.00 | 26.13 ± 6.56 | 27.78 ± 8.04 | −0.07 ± 0.26 | 0.02 ± 0.17 |
| Sway V-M-L (mm/s) | 27.14 ± 6.95 | 27.59 ± 6.75 | 27.31 ± 8.45 | 26.30 ± 7.24 | −0.02 ± 0.17 | 0.04 ± 0.19 |
| Sway average amplitude-A-P (mm) | 5.54 ± 1.91 | 6.28 ± 2.30 | 6.27 ± 2.04 | 5.84 ± 1.69 | −0.18 ± 0.41 | 0.01 ± 0.26 |
| Sway average amplitude-M-L (mm) | 6.34 ± 1.89 | 6.29 ± 2.12 | 6.28 ± 1.92 | 5.88 ± 2.37 | 0.00 ± 0.20 | 0.06 ± 0.23 |
| Sway maximal amplitude-A-P (mm) | 33.91 ± 7.02 | 35.15 ± 7.01 | 33.84 ± 8.98 | 36.40 ± 8.10 | −0.08 ± 0.42 | −0.07 ± 0.30 |
| Sway maximal amplitude-M-L (mm) | 25.36 ± 4.09 | 28.31 ± 5.08 | 25.03 ± 5.13 | 26.58 ± 4.24 | −0.01 ± 0.28 | 0.04 ± 0.18 |
| Sway area-total (mm2) | 2082.96 ± 782.15 | 2312.31 ± 855.88 | 2032.80 ± 660.08 | 2112.31 ± 639.90 | −0.08 ± 0.45 | 0.04 ± 0.28 |
| Sway area-A-P (mm·s) | 106.52 ± 27.25 | 114.59 ± 39.68 | 104.92 ± 28.48 | 107.41 ± 30.94 | −0.03 ± 0.38 | 0.00 ± 0.34 |
| Sway area-M-L (mm·s) | 79.79 ± 13.37 # | 91.90 ± 17.41 | 80.17 ± 16.52 | 83.62 ± 13.54 | 0.00 ± 0.24 | 0.07 ± 0.20 |
| Sway area per second-total (mm2/s) | 104.10 ± 38.98 | 115.79 ± 42.96 | 101.75 ± 33.08 | 105.68 ± 31.98 | −0.08 ± 0.45 | 0.04 ± 0.28 |
| Sway area per second-A-P (mm) | 5.33 ± 1.36 | 5.73 ± 1.98 | 5.25 ± 1.43 | 5.37 ± 1.55 | −0.03 ± 0.38 | 0.00 ± 0.34 |
| Sway area per second-M-L (mm) | 3.99 ± 0.67 # | 4.59 ± 0.86 | 4.01 ± 0.83 | 4.18 ± 0.67 | 0.00 ± 0.24 | 0.07 ± 0.19 |
| FRE from peaks-A-P (Hz) | 4.69 ± 0.60 | 4.86 ± 1.31 | 4.36 ± 0.94 | 4.87 ± 0.98 | 0.06 ± 0.14 | −0.04 ± 0.25 |
| FRE from peaks-M-L (Hz) | 4.41 ± 0.68 | 4.52 ± 0.61 | 4.47 ± 0.80 | 4.70 ± 0.71 | −0.03 ± 0.08 | −0.04 ± 0.10 |
| Dominant Leg | Non-Dominant Leg | Bilateral Asymmetry | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elite Players | Sub-Elite Players | Elite Players | Sub-Elite Players | Elite Players | Sub-Elite Players | ||
| RF | Td (ms) | 23.92 ± 2.24 | 23.21 ± 2.75 | 23.44 ± 1.78 | 26.03 ± 3.91 *,# | 0.02 ± 0.09 | −0.12 ± 0.11 # |
| Tc (ms) | 30.96 ± 8.37 | 30.99 ± 5.95 | 28.34 ± 6.06 | 31.40 ± 7.99 | 0.06 ± 0.18 | −0.02 ± 0.17 | |
| Dm (mm) | 6.86 ± 2.50 | 7.21 ± 2.07 | 7.43 ± 2.95 | 6.32 ± 2.83 | −0.10 ± 0.43 | 0.10 ± 0.35 | |
| BF | Td (ms) | 23.18 ± 1.62 | 25.40 ± 2.98 # | 22.37 ± 1.87 | 24.16 ± 2.10 # | 0.03 ± 0.11 | 0.04 ± 0.09 |
| Tc (ms) | 26.33 ± 5.90 | 33.96 ± 12.97 | 30.60 ± 14.59 | 33.27 ± 10.03 | −0.21 ± 0.68 | −0.09 ± 0.47 | |
| Dm (mm) | 5.84 ± 2.10 | 5.97 ± 2.12 | 5.56 ± 2.79 | 5.93 ± 2.52 | 0.00 ± 0.47 | −0.02 ± 0.36 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
López-Fernández, J.; García-Unanue, J.; Sánchez-Sánchez, J.; Colino, E.; Hernando, E.; Gallardo, L. Bilateral Asymmetries Assessment in Elite and Sub-Elite Male Futsal Players. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3169. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17093169
López-Fernández J, García-Unanue J, Sánchez-Sánchez J, Colino E, Hernando E, Gallardo L. Bilateral Asymmetries Assessment in Elite and Sub-Elite Male Futsal Players. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(9):3169. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17093169
Chicago/Turabian StyleLópez-Fernández, Jorge, Jorge García-Unanue, Javier Sánchez-Sánchez, Enrique Colino, Enrique Hernando, and Leonor Gallardo. 2020. "Bilateral Asymmetries Assessment in Elite and Sub-Elite Male Futsal Players" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 9: 3169. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17093169
APA StyleLópez-Fernández, J., García-Unanue, J., Sánchez-Sánchez, J., Colino, E., Hernando, E., & Gallardo, L. (2020). Bilateral Asymmetries Assessment in Elite and Sub-Elite Male Futsal Players. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(9), 3169. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17093169









