Analysis of the Healthcare MERS-CoV Outbreak in King Abdulaziz Medical Center, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, June–August 2015 Using a SEIR Ward Transmission Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Summary of the June 2015 Healthcare MERS-CoV Outbreak
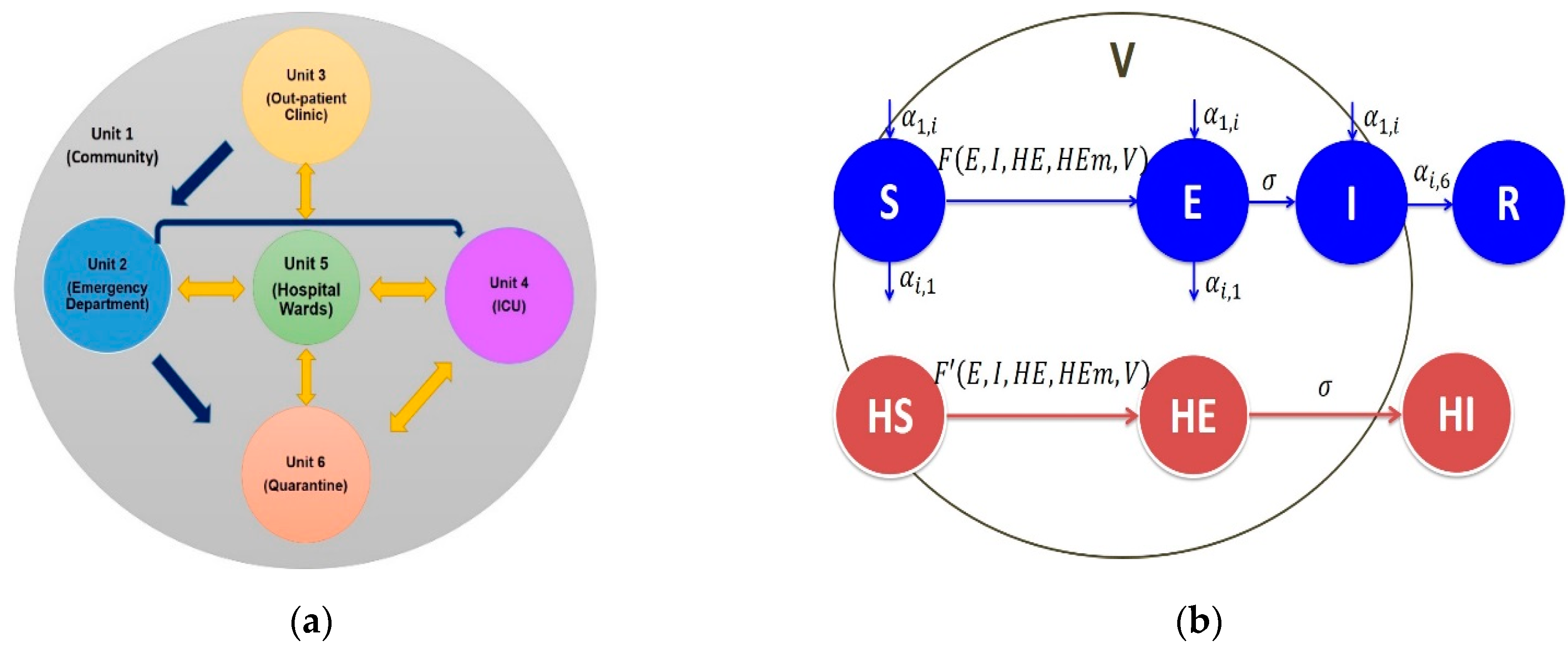
2.2. Model Description
2.3. Calculating
2.4. Model Calibration by Data Fitting
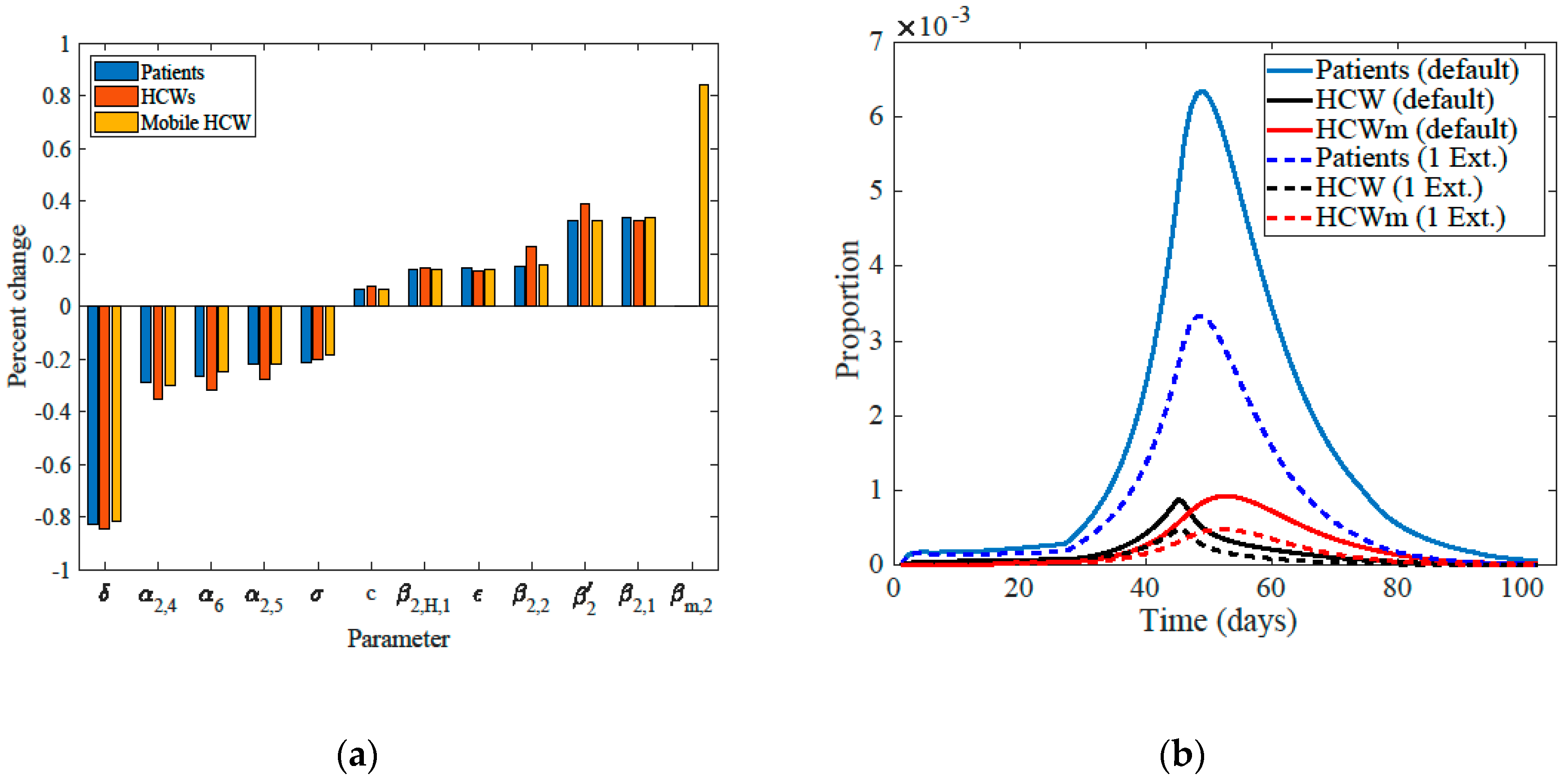
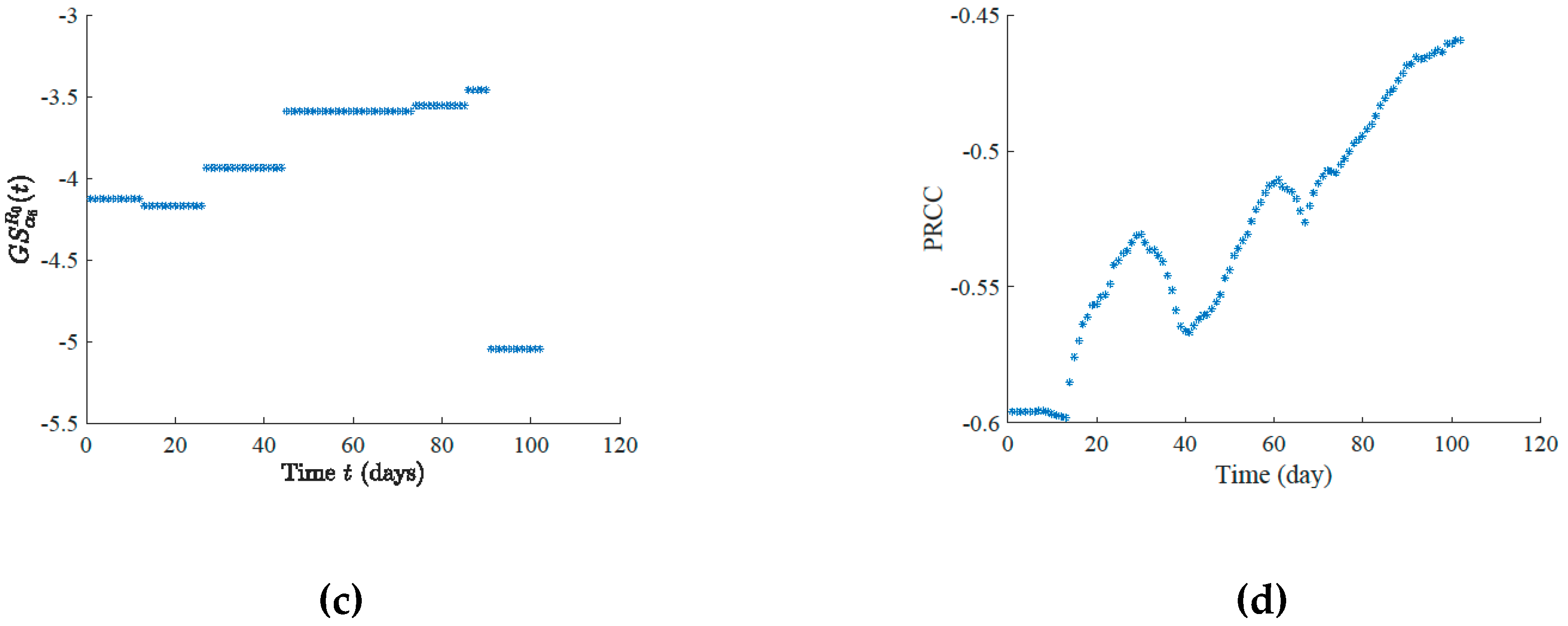
2.5. Sensitivity Analysis
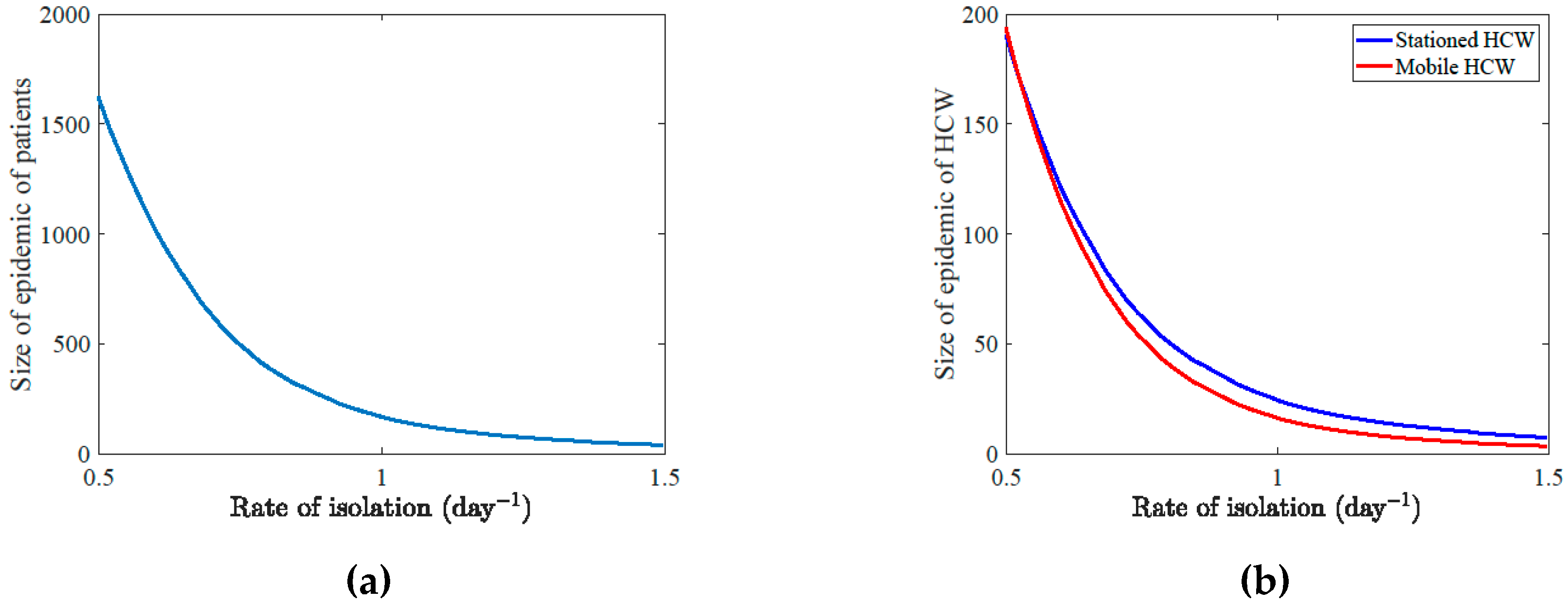
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gardner, L.; Chughtai, A.A.; MacIntyre, C.R. Risk of global spread of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) via the air transport network. J. Travel Med. 2016, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Tandi, T.; Choi, J.; Moon, J.; Kim, M. Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) outbreak in South Korea, 2015: Epidemiology, characteristics and public health implications. J. Hosp. Infect. 2017, 95, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Control ECfDPa. Severe Respiratory Disease Associated with Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV) 21st Update. 21 October 2015. Available online: https://ecdc.europa.eu/sites/portal/files/media/en/publications/Publications/MERS-rapid-risk-assessment-update-october-2015.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2019).
- World Health Organization. Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV). 2018. Available online: http://www.who.int/emergencies/mers-cov/en/ (accessed on 1 September 2019).
- Assiri, A.; Al-Tawfiq, J.A.; Al-Rabeeah, A.; Al-Rabiah, F.; Al-Hajjar, S.; Al-Barrak, A.; Flemban, H.; Al-Nassir, W.N.; Balkhy, H.H.; Al-Hakeem, R.F.; et al. Epidemiological, demographic, and clinical characteristics of 47 cases of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus disease from Saudi Arabia: A descriptive study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 752–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Center for Disease Control and Prevention. CDC Laboratory Testing for Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV). 2018. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/mers/lab/lab-testing.html (accessed on 1 September 2019).
- Arabi, Y.M.; Omran, A.; Balkhy, H.H.; Najm, H.; Aldawood, A.S.; Ghabashi, A.; Hawa, H.; Alothman, A.; Khaldi, A.; Al Raiy, B. Clinical Course and Outcomes of Critically Ill Patients With Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Infection. Ann. Intern. Med. 2014, 160, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Dorzi, H.M.; Al-Dawood, A.; Khan, R.; Baharoon, S.; Alchin, J.D.; Matroud, A.; Al Johany, S.M.; Balkhy, H.H.; Arabi, Y.M. The critical care response to a hospital outbreak of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) infection: An observational study. Ann. Intensive Care 2016, 6, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkhy, H.H.; Alenazi, T.H.; Alshamrani, M.M.; Baffoe-Bonnie, H.; Al-Abdely, H.M.; El-Saed, A.; Al Arbash, H.A.; Al Mayahi, Z.K.; Assiri, A.M.; Bin Saeed, A. Notes from the Field: Nosocomial Outbreak of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome in a Large Tertiary Care Hospital--Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. 2015. MMWR Morb. Mortal Wkly. Rep. 2016, 65, 163–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, S.; Fraser, C.; Donnelly, C.A.; Ghani, A.C.; Abu-Raddad, L.J.; Hedley, A.J.; Leung, G.M.; Ho, L.-M.; Lam, T.H.; Thach, T.Q.; et al. Transmission Dynamics of the Etiological Agent of SARS in Hong Kong: Impact of Public Health Interventions. Science 2003, 300, 1961–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipsitch, M.; Cohen, T.; Cooper, B.; Robins, J.M.; Ma, S.; James, L.; Gopalakrishna, G.; Chew, S.K.; Tan, C.C.; Samore, M.H.; et al. Transmission Dynamics and Control of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome. Science 2003, 300, 1966–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowell, G.; Blumberg, S.; Simonsen, L.; Miller, M.A.; Viboud, C. Synthesizing data and models for the spread of MERS-CoV, 2013: Key role of index cases and hospital transmission. Epidemics 2014, 9, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Kim, Y.-S.; Jung, Y.; Choi, S.Y.; Cho, N.-H.; Jeong, H.W.; Heo, J.Y.; Yoon, J.H.; Lee, J.; Cheon, S.; et al. Outbreaks of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome in Two Hospitals Initiated by a Single Patient in Daejeon, South Korea. Infect. Chemother. 2016, 48, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowell, G.; Abdirizak, F.; Lee, S.; Lee, J.; Jung, E.; Nishiura, H.; Viboud, C. Transmission characteristics of MERS and SARS in the healthcare setting: A comparative study. BMC Med. 2015, 13, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowell, G.; Sattenspiel, L.; Bansal, S.; Viboud, C. Mathematical models to characterize early epidemic growth: A review. Phys. Life Rev. 2016, 18, 66–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driessche, P.V.D.; Watmough, J. Reproduction numbers and sub-threshold endemic equilibria for compartmental models of disease transmission. Math. Biosci. 2002, 180, 29–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.C. Uncertainty Quantification: Theory, Implementation, and Applications; SIAM-Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2013; 382p, ISBN 978-1-611973-21-1. [Google Scholar]
- Mackay, I.M.; Arden, K.E. MERS coronavirus: Diagnostics, epidemiology and transmission. Virol. J. 2015, 12, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hastings, D.L.; Tokars, J.I.; Aziz, I.Z.A.A.; AlKhaldi, K.Z.; Bensadek, A.T.; Alraddadi, B.M.; Jokhdar, H.; Jernigan, J.A.; Garout, M.A.; Tomczyk, S.M.; et al. Outbreak of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome at Tertiary Care Hospital, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, 2014. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 794–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Tawfiq, J.A.; Perl, T.M. Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus in healthcare settings. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 28, 392–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.-H. Structural Factors of the Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Outbreak as a Public Health Crisis in Korea and Future Response Strategies. J. Prev. Med. Public Health 2015, 48, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kim, K.M.; Ki, M.; Cho, S.-I.; Sung, M.; Hong, J.K.; Cheong, H.-K.; Kim, J.-H.; Lee, S.-E.; Lee, C.; Lee, K.-J.; et al. Epidemiologic features of the first MERS outbreak in Korea: Focus on Pyeongtaek St. Mary’s Hospital. Epidemiol. Health 2015, 37, e2015041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.-C. Post-MERS: The Strategies to Minimize the Risks from New Epidemics. J. Korean Med Assoc. 2015, 58, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breban, R.; Riou, J.; Fontanet, A. Interhuman transmissibility of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus: Estimation of pandemic risk. Lancet 2013, 382, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd-Smith, J.O.; George, D.; Pepin, K.M.; Pitzer, V.E.; Pulliam, J.R.C.; Dobson, A.P.; Hudson, P.J.; Grenfell, B.T. Epidemic Dynamics at the Human-Animal Interface. Science 2009, 326, 1362–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotten, M.; Watson, S.J.; Zumla, A.; Makhdoom, H.Q.; Palser, A.L.; Ong, S.H.; Al Rabeeah, A.A.; AlHakeem, R.F.; Assiri, A.; Al-Tawfiq, J.A.; et al. Spread, Circulation, and Evolution of the Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus. mBio 2014, 14, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauch, C.T.; Oraby, T. Assessing the pandemic potential of MERS-CoV. Lancet 2013, 382, 662–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oraby, T.; Tyshenko, M.G.; Balkhy, H.H.; Tasnif, Y.; Quiroz-Gaspar, A.; Mohamed, Z.; Araya, A.; Elsaadany, S.; Al-Mazroa, E.; Alhelail, M.A.; et al. Analysis of the Healthcare MERS-CoV Outbreak in King Abdulaziz Medical Center, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, June–August 2015 Using a SEIR Ward Transmission Model. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2936. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17082936
Oraby T, Tyshenko MG, Balkhy HH, Tasnif Y, Quiroz-Gaspar A, Mohamed Z, Araya A, Elsaadany S, Al-Mazroa E, Alhelail MA, et al. Analysis of the Healthcare MERS-CoV Outbreak in King Abdulaziz Medical Center, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, June–August 2015 Using a SEIR Ward Transmission Model. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(8):2936. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17082936
Chicago/Turabian StyleOraby, Tamer, Michael G. Tyshenko, Hanan H. Balkhy, Yasar Tasnif, Adriana Quiroz-Gaspar, Zeinab Mohamed, Ayesha Araya, Susie Elsaadany, Eman Al-Mazroa, Mohammed A. Alhelail, and et al. 2020. "Analysis of the Healthcare MERS-CoV Outbreak in King Abdulaziz Medical Center, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, June–August 2015 Using a SEIR Ward Transmission Model" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 8: 2936. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17082936
APA StyleOraby, T., Tyshenko, M. G., Balkhy, H. H., Tasnif, Y., Quiroz-Gaspar, A., Mohamed, Z., Araya, A., Elsaadany, S., Al-Mazroa, E., Alhelail, M. A., Arabi, Y. M., & Al-Zoughool, M. (2020). Analysis of the Healthcare MERS-CoV Outbreak in King Abdulaziz Medical Center, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, June–August 2015 Using a SEIR Ward Transmission Model. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(8), 2936. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17082936





