Food Hygiene Surveillance in Italy: Is Food Ice a Public Health Risk?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ice Cube Collection
2.2. Determining Contamination Levels in Ice Samples
2.3. E. coli and Coliform Investigation
2.4. Enterococci Investigation
2.5. P. aeruginosa Investigation
2.6. S. aureus Investigation
2.7. Fungi Investigation
2.8. Enumeration of Culturable Micro-Organisms
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Settanni, L.; Gaglio, R.; Stucchi, C.; De Martino, S.; Francesca, N.; Moschetti, G. Presence of pathogenic bacteria in ice cubes and evaluation of their survival in different systems. Ann. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istituto Nazionale Ghiaccio Alimentare (INGA). Manuale di Corretta Prassi Operativa per la Produzione di Ghiaccio Alimentare. 2015. Available online: http://www.ghiaccioalimentare.it/ilmanuale/ (accessed on 10 January 2020).
- Portale Acque Ministero della Salute. Available online: http://www.portaleacque.salute.gov.it/PortaleAcquePubblico/noteInformative.do (accessed on 10 January 2020).
- Teixeira, P.; Brandão, J.; Silva, S.; Novak Babi, M.; Gunde-Cimerman, N.; Pires, J.; Costa, S.; Valério, E. Microbiological and chemical quality of ice used to preserve fish in Lisbon marketplaces. J. Food Saf. 2019, 39, e12641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decreto Legislativo 2 Febbraio 2001, n. 31 “Attuazione Della Direttiva 98/83/CE Relativa alla Qualità Delle Acque Destinate al Consumo Umano” Gazzetta Ufficiale n. 52 del 3 Marzo 2001—Supplemento Ordinario n. 41. Available online: https://www.camera.it/parlam/leggi/deleghe/01031dl.htm (accessed on 10 January 2020).
- Francesca, N.; Gaglio, R.; Stucchi, C.; De Martino, S.; Moschetti, G.; Settanni, L. Yeasts and moulds contaminants of food ice cubes and their survival in different drinks. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 124, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaglio, R.; Francesca, N.; Di Gerlando, R.; Mahony, J.; De Martino, S.; Stucchi, C.; Moschetti, G.; Settanni, L. Enteric bacteria of food ice and their survival in alcoholic beverages and soft drinks. Food Microbiol. 2017, 67, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerokomou, V.; Voidarou, C.; Vatopoulos, A.; Velonakis, E.; Rozos, G.; Alexopoulos, A.; Plessas, S.; Stavropoulou, E.; Bezirtzoglou, E.; Demertzis, P.G.; et al. Physical, chemical and microbiological quality of ice used to cool drinks and foods in Greece and its public health implications. Anaerobe 2011, 17, 351–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellou, K.; Katsioulis, A.; Potamiti-Komi, M.; Pournaras, S.; Kyritsi, M.; Katsiaflaka, A.; Kallimania, A.; Kokkinos, P.; Petinaki, E.; Sideroglou, T.; et al. A large waterborne gastroenteritis outbreak in central Greece, March 2012: Challenges for the investigation and management. Epidemiol. Infect. 2014, 142, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draper, A.D.K.; Morton, C.N.; Heath, J.N.I.; Lim, J.A.; Markey, P.G. An outbreak of Salmonella Saintpaul gastroenteritis after attending a school camp in the Northern Territory, Australia. Commun. Dis. Intell. 2017, 41, E10–E15. [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama, T.; Ha, N.C.; Quoc Le, P.; Kawahara, R.; Kumeda, Y.; Sumimura, Y.; Yamamoto, Y. Consumption of edible ice contaminated with Acinetobacter, Pseudomonas, and Stenotrophomonas is a risk factor for fecal colonization with extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli in Vietnam. J. Water Health 2017, 15, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.V.; Pham, Q.D.; Do, Q.K.; Diep, T.T.; Phan, H.C.; Ho, T.V.; Do, H.T.; Phan, L.T.; Tran, H.N. Cholera returns to southern Vietnam in an outbreak associated with consuming unsafe water through iced tea: A matched case-control study. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, W.C.; Stephenson, W.T.; Craun, G.F. Waterborne disease outbreaks, 1986–1988. J. Food Prot. 1991, 54, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qualità Dell’acqua—Conta di Escherichia coli e Batteri Coliformi—Parte 1: Metodo per Filtrazione su Membrana; UNI EN ISO 9308-1; UNI: Milan, Italy, 2017.
- Qualità Dell’acqua—Ricerca ed Enumerazione di Enterococchi Intestinali—Metodo di Filtrazione su Membrana; UNI EN ISO 7899-2; UNI: Milan, Italy, 2003.
- Water Quality—Detection and Enumeration of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Most Probable Number Method; ISO 16266-2; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018.
- RAPPORTI ISTISAN 07/5. Metodi analitici per le acque destinate al consumo umano ai sensi del DL.vo 31/2001. (ISS A 018B rev. 00. Determinazione Stafilococchi Patogeni); Metodi microbiologici Istituto Superiore di Sanità: Roma, Italy, 2007; Available online: http://old.iss.it/binary/publ/cont/07-5.1178787574.pdf (accessed on 27 January 2020).
- De Hoog, G.S.; Guarro, J.; Gené, J.; Figueras, M.J. Atlas of Clinical Fungi: Electronic Version 3.1; Centraalbureau voor Schimmelcultures (CBS): Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP) System and Guidelines for Its Application—Annex to CAC/RCP 1–1969 . 2003. Available online: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/english/topics/importedfoods/guideline/dl/05.pdf (accessed on 25 January 2020).
- Hampikyan, H.; Bingol, E.B.; Cetin, O.; Colak, H. Microbiological quality of ice and ice machines used in food establishments. J. Water Health 2017, 15, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noor Izani, N.J.; Zulaikha, A.R.; Mohamad Noor, M.R.; Amri, M.A.; Mahat, N.A. Contamination of faecal coliforms in ice cubes sampled from food outlets in Kubang Kerian, Kelantan. Trop. Biomed. 2012, 29, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Falcão, J.P.; Falcão, D.P.; Gomes, T.A. Ice as a vehicle for diarrheagenic Escherichia coli. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 91, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waturangi, D.E.; Pradita, N.; Linarta, J.; Banerjee, S. Prevalence and molecular characterization of Vibrio cholerae from ice and beverages sold in Jakarta, Indonesia, using most probable number and multiplex PCR. J. Food Prot. 2012, 75, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cava, R.; Sangronis, E.; Marin-Iniesta, F. Comparison of methods for recovering Vibrio cholerae O1 from ice. J. Food Prot. 2006, 69, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caggiano, G.; Dambrosio, A.; Ioanna, F.; Balbino, S.; Barbuti, G.; De Giglio, O.; Diella, G.; Lovero, G.; Rutigliano, S.; Scarafile, G.; et al. Prevalence and characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates in food industry workers. Ann. Ig. 2016, 28, 8–14. [Google Scholar]
- Kanwar, A.; Cadnum, J.L.; Xu, D.; Jencson, A.L.; Donskey, C.J. Hiding in plain sight: Contaminated ice machines are a potential source for dissemination of Gram-negative bacteria and Candida species in healthcare facilities. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2018, 39, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yorioka, K.; Oie, S.; Hayashi, K.; Kimoto, H.; Furukawa, H. Microbial contamination of ice machines is mediated by activated charcoal filtration systems in a city hospital. J. Environ. Health 2016, 78, 32–35. [Google Scholar]
- Worthington, H.V.; Clarkson, J.E.; Eden, O.B. Interventions for preventing oral mucositis for patients with cancer receiving treatment. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2007, 4, CD000978. Review. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010, 12, CD000978. [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach, A.S.; Riley, P.A.; Shad, S.; Jownally, S.M.; Law, R.; Chin, P.C.; Kaufmann, M.E.; Smith, E.J. An outbreak of wound infection in cardiac surgery patients caused by Enterobacter cloacae arising from cardioplegia ice. J. Hosp. Infect. 2006, 64, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montagna, M.T.; Lovero, G.; De Giglio, O.; Iatta, R.; Caggiano, G.; Montagna, O.; Laforgia, N. Invasive fungal Infections in Neonatal Intensive Care Units of Southern Italy: A multicenter regional active surveillance (AURORA Project). J. Prev. Med. Hyg. 2010, 51, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Montagna, M.T.; De Giglio, O.; Napoli, C.; Lovero, G.; Caggiano, G.; Delia, M.; Pastore, D.; Santoro, N.; Specchia, G. Invasive fungal infections in patients with hematologic malignancies (Aurora Project): Lights and shadows during 18-months surveillance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 774–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caggiano, G.; Lovero, G.; De Giglio, O.; Barbuti, G.; Montagna, O.; Laforgia, N.; Montagna, M.T. Candidemia in the neonatal intensive care unit: A retrospective, observational survey and analysis of literature data. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montagna, M.T.; Lovero, G.; Coretti, C.; De Giglio, O.; Martinelli, D.; Bedini, A.; Delia, M.; Rosato, A.; Codeluppi, M.; Caggiano, G. In vitro activities of amphotericin B deoxycholate and liposomal amphotericin B against 604 clinical yeast isolates. J. Med. Microbiol. 2014, 63, 1638–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality, 4th ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011; Available online: https://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/publications/dwq-guidelines-4/en/ (accessed on 27 March 2020).
- Bonadonna, L.; Cannarozzi de Grazia, M.; Capolongo, S.; Casini, B.; Cristina, M.L.; Daniele, G.; D'Alessandro, D.; De Giglio, O.; Di Benedetto, A.; Di Vittorio, G.; et al. Water Safety in Healthcare Facilities. The Vieste Charter. Ann. Ig. 2017, 29, 92–100. [Google Scholar]
- Guidelines for the Assessment and Management of Risk in the System of Distribution of Water for Human Consumption According to the Model of the Water Safety Plans; ISTISAN 14/21 Reports; Istituto Superiore di Sanità: Roma, Italy, 2014; Available online: http://old.iss.it/binary/publ/cont/14_21_web.pdf (accessed on 27 March 2020).
- Puglia Regional Regulation No. 1 of 9 January. In Regulations for the Quality Assessment, Surveillance and Control of Water for Human Consumption; Regione Puglia: Bari, Italy, 2014.

| Food Ice Samples | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| No (%) | No (%) | p-values | |
| Compliant 54/99 (54.5) | Non-Compliant 45/99 (45.5) | ||
| Additional parameters | 52 (96.2) | 43 (95.5) | 0.5405 |
| P.aeruginosa | 8 (14.8) | 18 (40) | 0.0144 * |
| S.aureus | 11 (11.1) | 4 (6.7) | 0.669 * |
| Fungi | 52 (96.2) | 43 (95.5) | 0.8867 * |
| median (range) | median (range) | ||
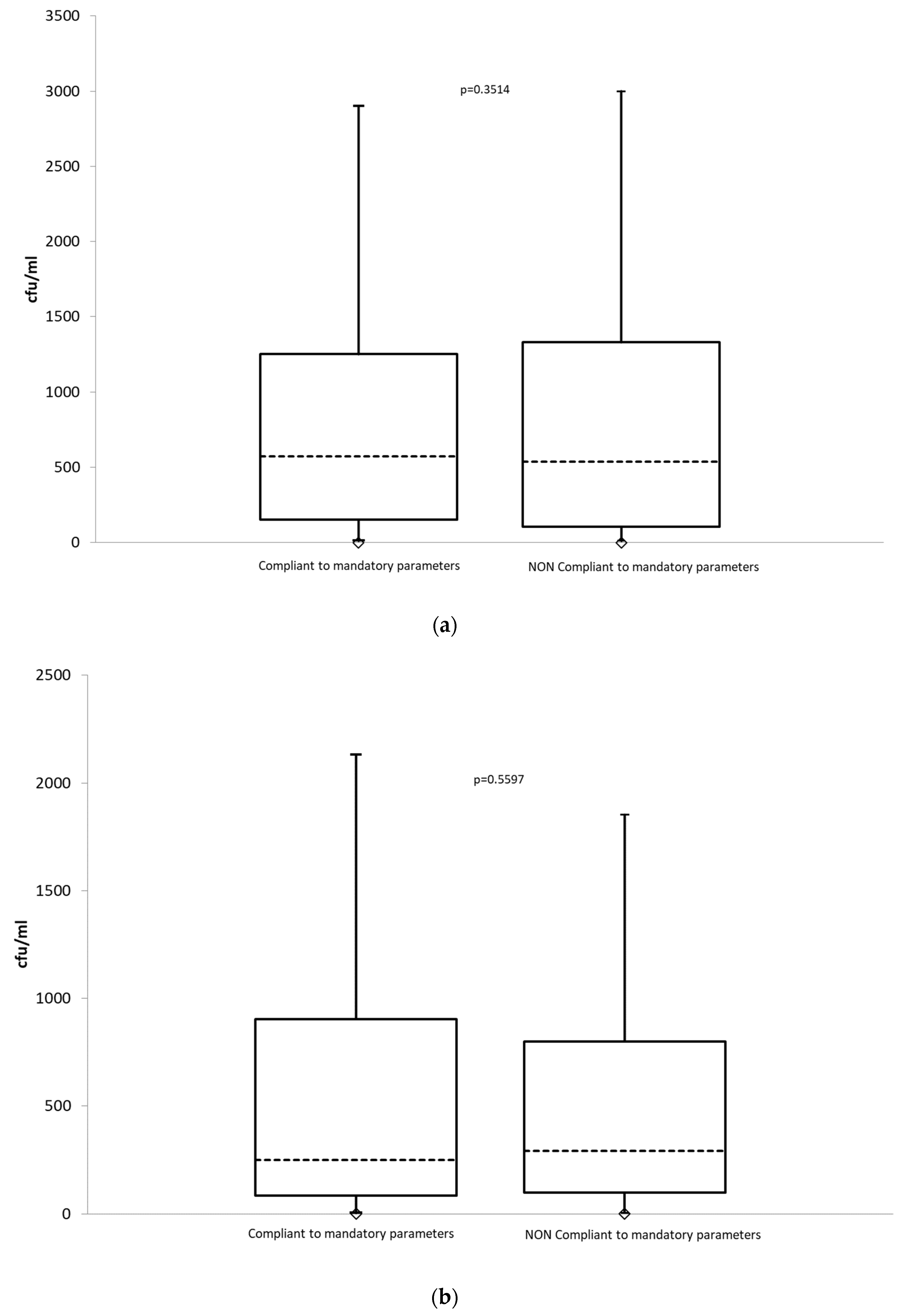
| Total microbial count at 22 °C (cfu/mL) | 574 (11–3000) | 536 (11–3000) | 0.3514 |
| Total microbial count at 37 °C (cfu/mL) | 292 (5–3000) | 250 (4–3000) | 0.5597 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Caggiano, G.; Marcotrigiano, V.; Trerotoli, P.; Diella, G.; Rutigliano, S.; Apollonio, F.; Marzella, A.; Triggiano, F.; Gramegna, M.; Lagravinese, D.; et al. Food Hygiene Surveillance in Italy: Is Food Ice a Public Health Risk? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2408. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17072408
Caggiano G, Marcotrigiano V, Trerotoli P, Diella G, Rutigliano S, Apollonio F, Marzella A, Triggiano F, Gramegna M, Lagravinese D, et al. Food Hygiene Surveillance in Italy: Is Food Ice a Public Health Risk? International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(7):2408. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17072408
Chicago/Turabian StyleCaggiano, Giuseppina, Vincenzo Marcotrigiano, Paolo Trerotoli, Giusy Diella, Serafina Rutigliano, Francesca Apollonio, Angelo Marzella, Francesco Triggiano, Matilde Gramegna, Domenico Lagravinese, and et al. 2020. "Food Hygiene Surveillance in Italy: Is Food Ice a Public Health Risk?" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 7: 2408. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17072408
APA StyleCaggiano, G., Marcotrigiano, V., Trerotoli, P., Diella, G., Rutigliano, S., Apollonio, F., Marzella, A., Triggiano, F., Gramegna, M., Lagravinese, D., Sorrenti, G. T., Magarelli, P., Moscato, U., & Montagna, M. T. (2020). Food Hygiene Surveillance in Italy: Is Food Ice a Public Health Risk? International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(7), 2408. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17072408








