Urinary Arsenic Species are Detectable in Urban Underserved Hispanic/Latino Populations: A Pilot Study from the Study of Latinos: Nutrition & Physical Activity Assessment Study (SOLNAS)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Laboratory Analyses
2.2. Statistical Analyses
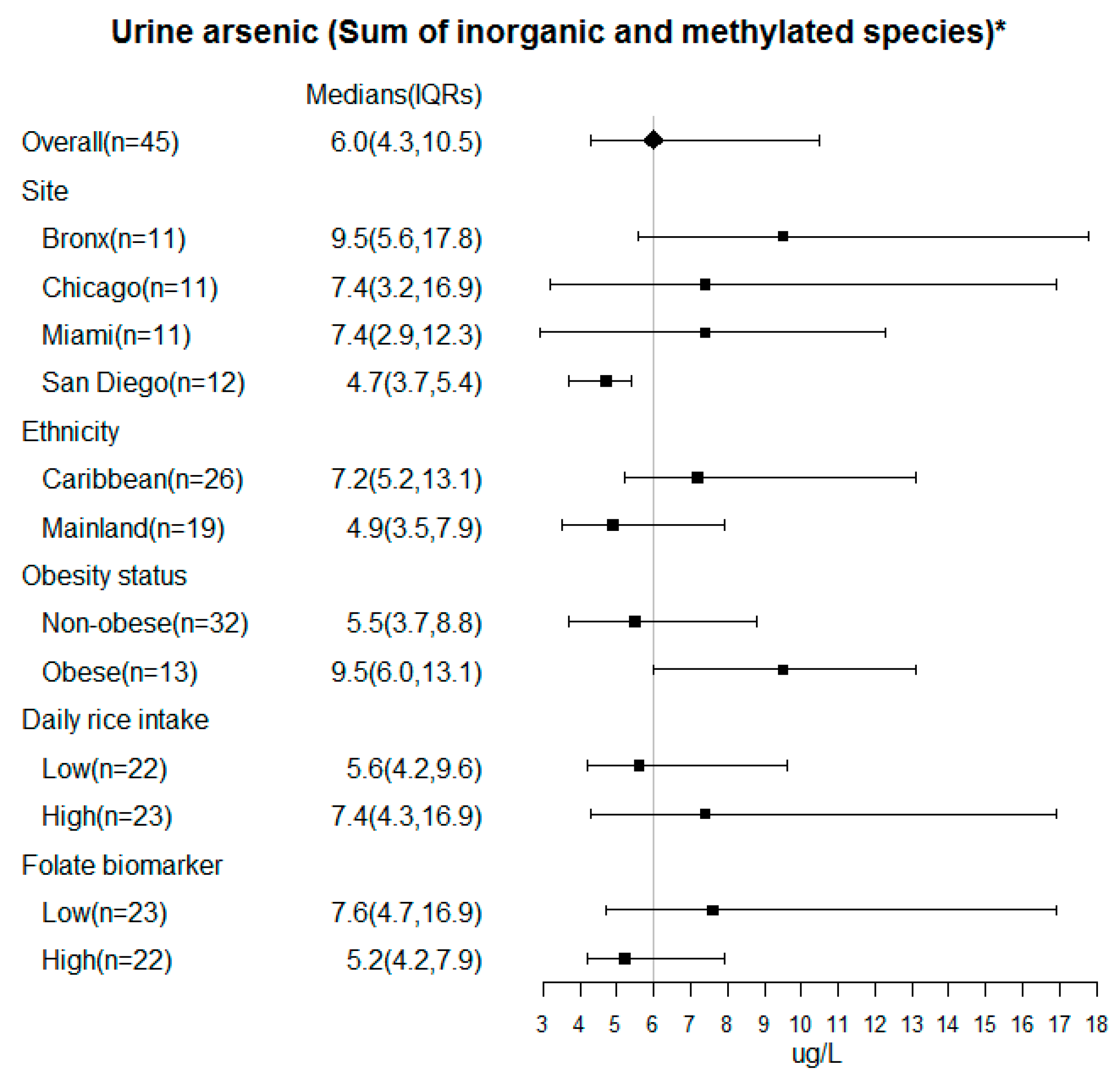
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kuo, C.C.; Moon, K.A.; Wang, S.L.; Silbergeld, E.; Navas-Acien, A. The Association of Arsenic Metabolism with Cancer, Cardiovascular Disease, and Diabetes: A Systematic Review of the Epidemiological Evidence. Environ. Health Perspect. 2017, 125, 087001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Arsenic, metals, fibres, and dusts. IARC Monogr. Eval. Carcinog. Risks Hum. 2012, 100 Pt C, 11–465. [Google Scholar]
- Micha, R.; Penalvo, J.L.; Cudhea, F.; Imamura, F.; Rehm, C.D.; Mozaffarian, D. Association Between Dietary Factors and Mortality From Heart Disease, Stroke, and Type 2 Diabetes in the United States. JAMA 2017, 317, 912–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corsino, L.; Sotres-Alvarez, D.; Butera, N.M.; Siega-Riz, A.M.; Palacios, C.; Perez, C.M.; Albrecht, S.S.; Espinoza Giacinto, R.A.; Perera, M.J.; Horn, L.V.; et al. Association of the DASH dietary pattern with insulin resistance and diabetes in US Hispanic/Latino adults: Results from the Hispanic Community Health Study/Study of Latinos (HCHS/SOL). BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2017, 5, e000402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, E.M.; Acevedo, J.; López, F.G.; Cortés, S.; Ferreccio, C.; Smith, A.H.; Steinmaus, C.M. Hypertension among adults exposed to drinking water arsenic in Northern Chile. Environ. Res. 2017, 153, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Marshall, G.; Ferreccio, C.; Steinmaus, C.; Selvin, S.; Liaw, J.; Bates, M.N.; Smith, A.H. Acute myocardial infarction mortality in comparison with lung and bladder cancer mortality in arsenic-exposed region II of Chile from 1950 to 2000. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2007, 166, 1381–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mozaffarian, D.; Benjamin, E.J.; Go, A.S.; Arnett, D.K.; Blaha, M.J.; Cushman, M.; de Ferranti, S.; Despres, J.P.; Fullerton, H.J.; Howard, V.J.; et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics--2015 update: A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2015, 131, e29–e322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geiss, L.S.; Wang, J.; Cheng, Y.J.; Thompson, T.J.; Barker, L.; Li, Y.; Albright, A.L.; Gregg, E.W. Prevalence and incidence trends for diagnosed diabetes among adults aged 20 to 79 years, United States, 1980–2012. JAMA 2014, 312, 1218–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Castro, B.R.; Caldwell, K.L.; Jones, R.L.; Blount, B.C.; Pan, Y.; Ward, C.; Mortensen, M.E. Dietary sources of methylated arsenic species in urine of the United States population, NHANES 2003–2010. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borak, J.; Hosgood, H.D. Seafood arsenic: Implications for human risk assessment. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2007, 47, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sams, R., 2nd; Wolf, D.C.; Ramasamy, S.; Ohanian, E.; Chen, J.; Lowit, A. Workshop overview: Arsenic research and risk assessment. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2007, 222, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, V.; Goodale, B.; Raab, A.; Schwerdtle, T.; Reimer, K.; Conklin, S.; Karagas, M.R.; Francesconi, K.A. Human exposure to organic arsenic species from seafood. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 580, 266–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, M.R.; Tellez-Plaza, M.; Vaidya, D.; Grau, M.; Francesconi, K.A.; Goessler, W.; Guallar, E.; Post, W.S.; Kaufman, J.D.; Navas-Acien, A. Estimation of Inorganic Arsenic Exposure in Populations With Frequent Seafood Intake: Evidence From MESA and NHANES. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 184, 590–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, M.R.; Tellez-Plaza, M.; Vaidya, D.; Grau-Perez, M.; Post, W.S.; Kaufman, J.D.; Guallar, E.; Francesconi, K.A.; Goessler, W.; Nachman, K.E.; et al. Ethnic, geographic and dietary differences in arsenic exposure in the multi-Ethnic study of atherosclerosis (MESA). J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavange, L.M.; Kalsbeek, W.D.; Sorlie, P.D.; Aviles-Santa, L.M.; Kaplan, R.C.; Barnhart, J.; Liu, K.; Giachello, A.; Lee, D.J.; Ryan, J.; et al. Sample design and cohort selection in the Hispanic Community Health Study/Study of Latinos. Ann. Epidemiol. 2010, 20, 642–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mossavar-Rahmani, Y.; Shaw, P.A.; Wong, W.W.; Sotres-Alvarez, D.; Gellman, M.D.; Van Horn, L.; Stoutenberg, M.; Daviglus, M.L.; Wylie-Rosett, J.; Siega-Riz, A.M.; et al. Applying Recovery Biomarkers to Calibrate Self-Report Measures of Energy and Protein in the Hispanic Community Health Study/Study of Latinos. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 181, 996–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheer, J.; Findenig, S.; Goessler, W.; Francesconi, K.A.; Howard, B.; Umans, J.G.; Pollak, J.; Tellez-Plaza, M.; Silbergeld, E.K.; Guallar, E.; et al. Arsenic species and selected metals in human urine: Validation of HPLC/ICPMS and ICPMS procedures for a long-Term population-Based epidemiological study. Anal. Methods 2012, 4, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamble, M.V.; Liu, X.; Slavkovich, V.; Pilsner, J.R.; Ilievski, V.; Factor-Litvak, P.; Levy, D.; Alam, S.; Islam, M.; Parvez, F.; et al. Folic acid supplementation lowers blood arsenic. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 86, 1202–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, B.A.; Hall, M.N.; Liu, X.; Parvez, F.; Sanchez, T.R.; van Geen, A.; Mey, J.L.; Siddique, A.B.; Shahriar, H.; Uddin, M.N.; et al. Folic Acid and Creatine as Therapeutic Approaches to Lower Blood Arsenic: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 123, 1294–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristic | Women | Men | All |
|---|---|---|---|
| n = 22 | n = 23 | n = 45 | |
| Age (years), Median (IQR) | 45.0 (36.0, 57.5) | 45.0 (37.5, 50.0) | 45.0 (36.0, 51.0) |
| BMI (kg/m2), Median (IQR) | 28.6 (25.8, 29.8) | 27.4 (24.8, 30.8) | 28.3 (25.0, 30.4) |
| Center, n (%) | |||
| Bronx | 4 (18.2) | 7 (30.4) | 11 (24.4) |
| Chicago | 6 (27.3) | 5 (21.7) | 11 (24.4) |
| Miami | 4 (18.2) | 7 (30.4) | 11 (24.4) |
| San Diego | 8 (36.4) | 4 (17.4) | 12 (26.7) |
| Hispanic/Latino Background, n (%) | |||
| Central American | 2 (9.1) | 1 (4.3) | 3 (6.7) |
| Cuban | 4 (18.2) | 6 (26.1) | 10 (22.2) |
| Dominican | 2 (9.1) | 2 (8.7) | 4 (8.9) |
| Mexican | 8 (36.4) | 6 (26.1) | 14 (31.1) |
| Puerto Rican | 5 (22.7) | 7 (30.4) | 12 (26.7) |
| South American | 1 (4.5) | 1 (4.3) | 2 (4.4) |
| Nativity, n (%) | |||
| Not born in 50 US States | 17 (77.3) | 16 (69.6) | 33 (73.3) |
| Born in 50 US States | 5 (22.7) | 7 (30.4) | 12 (26.7) |
| Arsenic | SOLNAS Visit | Mean (SD) | Median (IQR) | Minimum | Max | # Below LOD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| u∑As †, µg/L | 1 | 28.46 (47.42) | 16.20 (7.20, 24.40) | 2.20 | 227.20 | 0 |
| 2 | 11.71 (8.00) | 11.90 (4.38, 17.28) | 1.30 | 26.20 | 0 | |
| 3 | 20.50 (18.71) | 12.65 (10.00, 26.32) | 2.10 | 78.90 | 0 | |
| ∑As ¥, µg/L | 1 | 9.58 (10.75) | 6.04 (4.30, 10.46) | 1.99 | 69.30 | N/A |
| 2 | 7.34 (5.94) | 5.43 (2.77, 12.77) | 1.03 | 19.18 | N/A | |
| 3 | 9.80 (5.94) | 8.54 (5.75, 11.99) | 2.70 | 24.84 | N/A | |
| Inorganic As (iAs), µg/L | 1 | 0.91 (0.83) | 0.60 (0.40, 0.97) | <LOD | 3.37 | 1 |
| 2 | 0.71 (0.64) | 0.58 (0.18, 0.87) | <LOD | 2.19 | 2 | |
| 3 | 1.11 (0.94) | 0.74 (0.58, 1.31) | 0.19 | 4.11 | 0 | |
| Monomethylated As (MMA), µg/L | 1 | 2.08 (5.32) | 1.16 (0.69, 1.86) | 0.19 | 36.41 | 0 |
| 2 | 1.09 (0.98) | 0.86 (0.44, 1.45) | 0.13 | 4.11 | 0 | |
| 3 | 1.75 (1.21) | 1.38 (0.92, 2.13) | 0.39 | 4.83 | 0 | |
| Dimethylated As (DMA), µg/L | 1 | 13.26 (22.01) | 7.18 (4.29, 15.27) | 1.25 | 148.86 | 0 |
| 2 | 7.05 (5.17) | 5.69 (3.13, 11.32) | 0.78 | 18.95 | 0 | |
| 3 | 10.26 (6.24) | 9.02 (6.36, 10.71) | 1.73 | 26.76 | 0 | |
| iAs % | 1 | 8.78 (3.73) | 8.28 (6.51, 11.03) | 0.22 | 20.09 | N/A |
| 2 | 8.67 (4.07) | 8.98 (6.28, 10.00) | 0.50 | 20.86 | N/A | |
| 3 | 9.58 (3.84) | 8.26 (7.37, 11.24) | 5.36 | 21.30 | N/A | |
| MMA% | 1 | 12.26 (4.96) | 12.25 (9.12, 14.69) | 2.49 | 26.32 | N/A |
| 2 | 12.69 (4.28) | 11.59 (9.75, 13.71) | 7.47 | 21.85 | N/A | |
| 3 | 13.60 (5.22) | 13.21 (10.51, 17.23) | 5.84 | 23.12 | N/A | |
| DMA% | 1 | 80.31 (7.66) | 79.56 (76.22, 83.93) | 59.81 | 96.09 | N/A |
| 2 | 79.69 (5.95) | 80.13 (77.34, 83.21) | 68.20 | 89.79 | N/A | |
| 3 | 78.12 (7.89) | 78.59 (73.14, 83.75) | 64.36 | 89.78 | N/A |
| As Species | All Visits † (n = 85) | Second vs. First (n = 65) | Third vs. First (n = 65) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Log-∑As * | 0.48 (0.27–0.70) | 0.62 (0.37–0.82) | 0.42 (0.15–0.76) |
| Inorganic As (iAs) % | 0.36 (0.15–0.63) | 0.20 (0.02–0.75) | 0.65 (0.41–0.84) |
| Monomethylarsonic acid (MMA) % | 0.74 (0.57–0.85) | 0.71 (0.48–0.86) | 0.72 (0.50–0.87) |
| Dimethylarsinic acid (DMA) % | 0.67 (0.49–0.81) | 0.57 (0.31–0.8) | 0.71 (0.49–0.86) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hosgood, H.D.; Slavkovich, V.; Hua, S.; Klugman, M.; Grau-Perez, M.; Thyagarajan, B.; Graziano, J.; Cai, J.; Shaw, P.A.; Kaplan, R.; et al. Urinary Arsenic Species are Detectable in Urban Underserved Hispanic/Latino Populations: A Pilot Study from the Study of Latinos: Nutrition & Physical Activity Assessment Study (SOLNAS). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2247. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17072247
Hosgood HD, Slavkovich V, Hua S, Klugman M, Grau-Perez M, Thyagarajan B, Graziano J, Cai J, Shaw PA, Kaplan R, et al. Urinary Arsenic Species are Detectable in Urban Underserved Hispanic/Latino Populations: A Pilot Study from the Study of Latinos: Nutrition & Physical Activity Assessment Study (SOLNAS). International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(7):2247. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17072247
Chicago/Turabian StyleHosgood, H. Dean, Vesna Slavkovich, Simin Hua, Madelyn Klugman, Maria Grau-Perez, Bharat Thyagarajan, Joseph Graziano, Jianwen Cai, Pamela A Shaw, Robert Kaplan, and et al. 2020. "Urinary Arsenic Species are Detectable in Urban Underserved Hispanic/Latino Populations: A Pilot Study from the Study of Latinos: Nutrition & Physical Activity Assessment Study (SOLNAS)" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 7: 2247. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17072247
APA StyleHosgood, H. D., Slavkovich, V., Hua, S., Klugman, M., Grau-Perez, M., Thyagarajan, B., Graziano, J., Cai, J., Shaw, P. A., Kaplan, R., Navas-Acien, A., & Mossavar-Rahmani, Y. (2020). Urinary Arsenic Species are Detectable in Urban Underserved Hispanic/Latino Populations: A Pilot Study from the Study of Latinos: Nutrition & Physical Activity Assessment Study (SOLNAS). International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(7), 2247. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17072247






