Immediate Effects of Medially Posted Insoles on Lower Limb Joint Contact Forces in Adult Acquired Flatfoot: A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
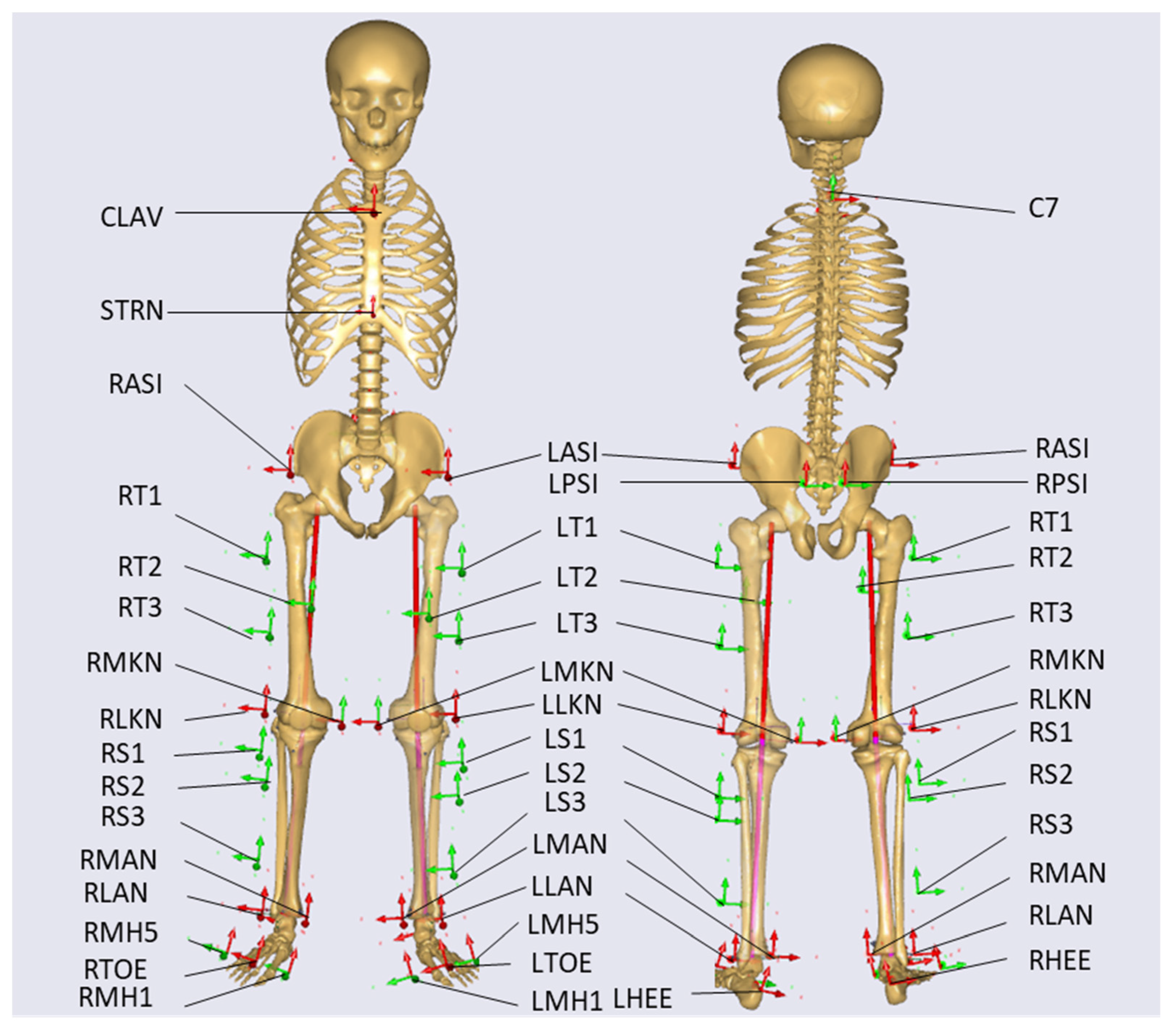
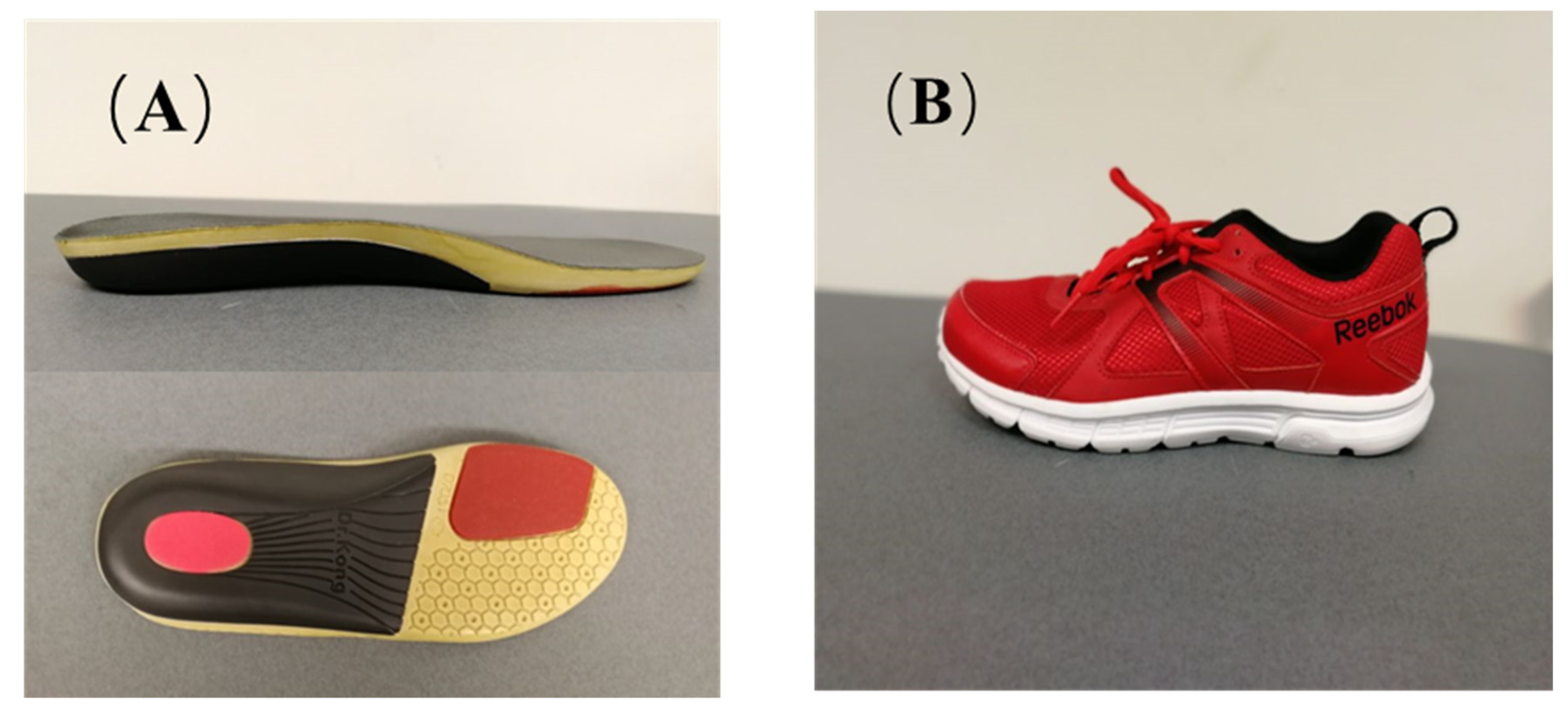
2.2. Equipment and Procedure
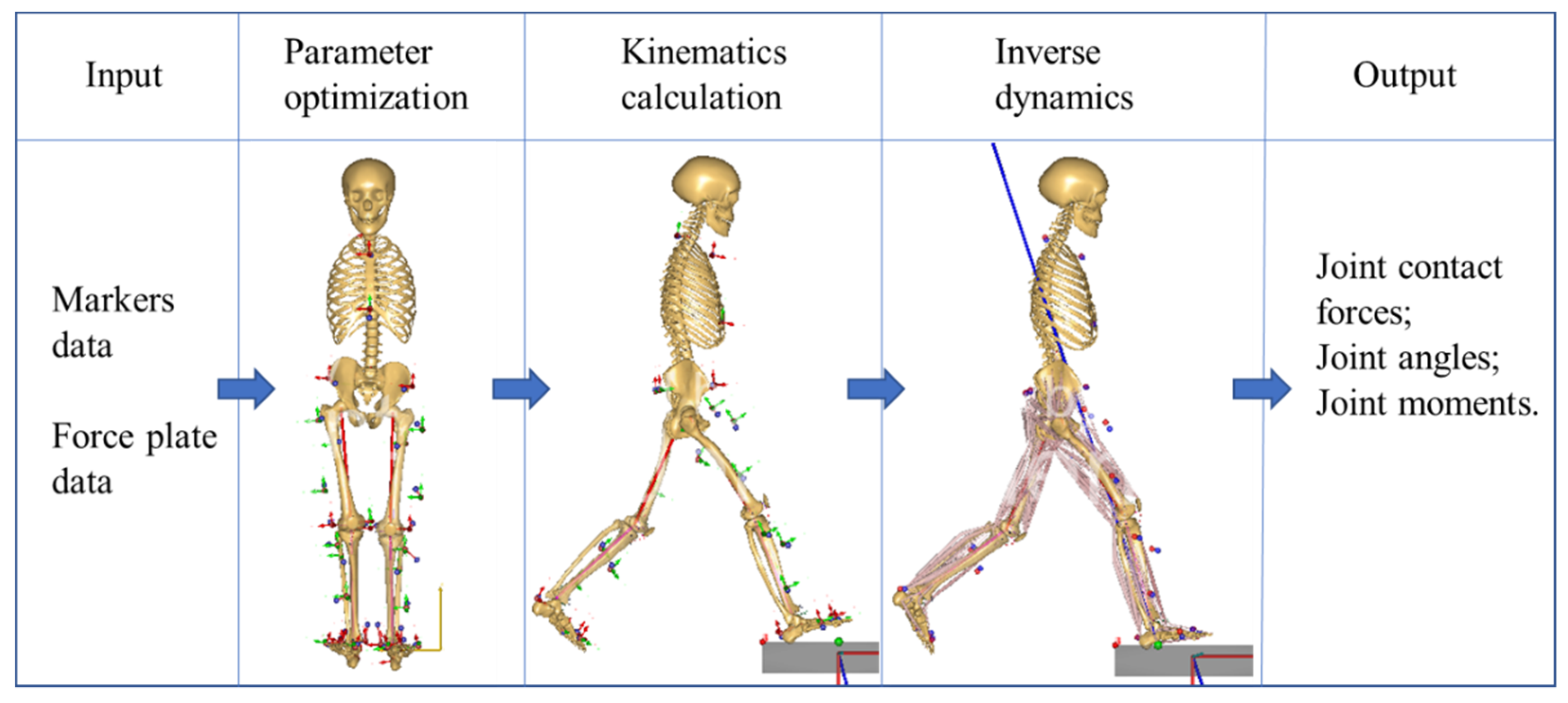
2.3. Musculoskeletal Model
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shibuya, N.; Jupiter, D.C.; Ciliberti, L.J.; VanBuren, V.; La Fontaine, J. Characteristics of adult flatfoot in the United States. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2010, 49, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golightly, Y.M.; Hannan, M.T.; Dufour, A.B.; Jordan, J.M. Racial differences in foot disorders and foot type. Arthritis Care Res. (Hoboken) 2012, 64, 1756–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-López, D.; Vilar-Fernández, J.M.; Barros-García, G.; Losa-Iglesias, M.E.; Palomo-López, P.; Becerro-de-Bengoa-Vallejo, R.; Calvo-Lobo, C. Foot arch height and quality of life in adults: A strobe observational study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banwell, H.A.; Mackintosh, S.; Thewlis, D. Foot orthoses for adults with flexible pes planus: A systematic review. J. Foot Ankle Res. 2014, 7, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angin, S.; Crofts, G.; Mickle, K.J.; Nester, C.J. Ultrasound evaluation of foot muscles and plantar fascia in pes planus. Gait Posture 2014, 40, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, K.A. Longitudinal arch load-sharing system of the foot. Revista Española de Podología 2017, 28, e18–e26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murley, G.S.; Tan, J.M.; Edwards, R.M.; De Luca, J.; Munteanu, S.E.; Cook, J.L. Foot posture is associated with morphometry of the peroneus longus muscle, tibialis anterior tendon, and Achilles tendon. Scand J. Med. Sci. Sports 2014, 24, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riskowski, J.L.; Dufour, A.B.; Hagedorn, T.J.; Hillstrom, H.J.; Casey, V.A.; Hannan, M.T. Associations of foot posture and function to lower extremity pain: Results from a population-based foot study. Arthritis Care Res. (Hoboken) 2013, 65, 1804–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squires, N.A.; Jeng, C.L. Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction. Oper. Tech. Orthop. 2006, 16, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levinger, P.; Gilleard, W. Tibia and rearfoot motion and ground reaction forces in subjects with patellofemoral pain syndrome during walking. Gait Posture 2007, 25, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razeghi, M.; Ebrahimi, S.; Yazdani, F. The comparison of patellofemoral joint forces between flat footed and normal subjects during stance phase of gait. Gait Posture 2012, S38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramappa, A.J.; Apreleva, M.; Harrold, F.R.; Fitzgibbons, P.G.; Wilson, D.R.; Gill, T.J. The effects of medialization and anteromedialization of the tibial tubercle on patellofemoral mechanics and kinematics. Am. J. Sports Med. 2006, 34, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahmkow, G.; Cassel, M.; Mayer, F.; Baur, H. Effects of different medial arch support heights on rearfoot kinematics. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosonen, J.; Kulmala, J.-P.; Müller, E.; Avela, J. Effects of medially posted insoles on foot and lower limb mechanics across walking and running in overpronating men. J. Biomech. 2017, 54, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafarnezhadgero, A.A.; Shad, M.M.; Majlesi, M. Effect of foot orthoses on the medial longitudinal arch in children with flexible flatfoot deformity: A three-dimensional moment analysis. Gait Posture 2017, 55, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telfer, S.; Abbott, M.; Steultjens, M.P.; Woodburn, J. Dose-response effects of customised foot orthoses on lower limb kinematics and kinetics in pronated foot type. J. Biomech. 2013, 46, 1489–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Nester, C.J.; Jones, R.K.; Lundgren, P.; Lundberg, A.; Arndt, A.; Wolf, P. Effect of an antipronation foot orthosis on ankle and subtalar kinematics. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2012, 44, 2384–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmyttere, G.; Hajizadeh, M.; Bleau, J.; Begon, M. Effect of foot orthosis design on lower limb joint kinematics and kinetics during walking in flexible pes planovalgus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Biomech. 2018, 59, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, W.-H.; Lewis, C.L.; Monaghan, G.M.; Saltzman, E.; Hamill, J.; Holt, K.G. Orthoses posted in both the forefoot and rearfoot reduce moments and angular impulses on lower extremity joints during walking. J. Biomech. 2014, 47, 2618–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, T.; Wada, M.; Kawahara, H.; Sato, M.; Baba, H.; Shimada, S. Dynamic load at baseline can predict radiographic disease progression in medial compartment knee osteoarthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2002, 61, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damsgaard, M.; Rasmussen, J.; Christensen, S.T.; Surma, E.; De Zee, M. Analysis of musculoskeletal systems in the AnyBody Modeling System. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 2006, 14, 1100–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modenese, L.; Montefiori, E.; Wang, A.; Wesarg, S.; Viceconti, M.; Mazza, C. Investigation of the dependence of joint contact forces on musculotendon parameters using a codified workflow for image-based modelling. J. Biomech. 2018, 73, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, H.X.; Diamond, L.E.; Lloyd, D.G.; Pizzolato, C. A calibrated EMG-informed neuromusculoskeletal model can appropriately account for muscle co-contraction in the estimation of hip joint contact forces in people with hip osteoarthritis. J. Biomech. 2019, 83, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.; Browning, R.C.; Lerner, Z.F. The effects of pediatric obesity on patellofemoral joint contact force during walking. Gait & Posture 2019, 73, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Walter, J.P.; Pandy, M.G. Predictive Simulations of Neuromuscular Coordination and Joint-Contact Loading in Human Gait. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 46, 1216–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, M.A.; Vanheule, V.; Fluit, R.; Koopman, B.H.; Rasmussen, J.; Verdonschot, N.; Andersen, M.S. A subject-specific musculoskeletal modeling framework to predict in vivo mechanics of total knee arthroplasty. J. Biomech. Eng. 2015, 137, 020904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, X.; Ardestani, M.M.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Lian, Q.; He, J.; Li, D.; Jin, Z. Prediction of in vivo joint mechanics of an artificial knee implant using rigid multi-body dynamics with elastic contacts. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. H 2014, 228, 564–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Lang, A.-G.; Buchner, A. G*Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav. Res. Methods 2007, 39, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.; Goonetilleke, R.S.; Witana, C.P.; Weerasinghe, T.W.; Au, E.Y.L. Foot Arch Characterization. J. Am. Podiat. Med. Assoc. 2010, 100, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, H.; Bhattacharya, K.; Deb, S.; Ray, K. Arch index: An easier approach for arch height (a regression analysis). Al Ameen J. Med. Sci. 2012, 5, 137–146. [Google Scholar]
- Jahss, M.H.; Kummer, F.; Michelson, J.D. Investigations into the fat pads of the sole of the foot: Heel pressure studies. Foot & Ankle 1992, 13, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lower body modeling with Plug-in Gait. 2002. Available online: https://docs.vicon.com/display/Nexus25/Lower+body+modeling+with+Plug-in+Gait (accessed on 25 March 2020).
- Horsman, M.K.; Koopman, H.F.; van der Helm, F.C.; Prosé, L.P.; Veeger, H. Morphological muscle and joint parameters for musculoskeletal modelling of the lower extremity. Clin. Biomech. 2007, 22, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xin, H.; Zhang, Q.; Fan, X.; Jin, Z. Concurrent prediction of ground reaction forces and moments and tibiofemoral contact forces during walking using musculoskeletal modelling. Med. Eng. Phys. 2018, 52, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, R.E.; Andersen, M.S.; Harlaar, J.; van den Noort, J.C. Relationship between knee joint contact forces and external knee joint moments in patients with medial knee osteoarthritis: Effects of gait modifications. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2018, 26, 1203–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannisi, M.; Dell’Isola, A.; Andersen, M.S.; Woodburn, J. Effect of lateral wedged insoles on the knee internal contact forces in medial knee osteoarthritis. Gait Posture 2019, 68, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGough, J.J.; Faraone, S.V. Estimating the size of treatment effects: Moving beyond p values. Psychiatry (Edgmont (Pa. Township)) 2009, 6, 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, D.W.-C.; Zhang, M.; Yu, J.; Leung, A.K.-L. Biomechanics of first ray hypermobility: An investigation on joint force during walking using finite element analysis. Med. Eng. Phys. 2014, 36, 1388–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brognara, L.; Navarro-Flores, E.; Iachemet, L.; Serra-Catalá, N.; Cauli, O. Beneficial Effect of Foot Plantar Stimulation in Gait Parameters in Individuals with Parkinson’s Disease. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, R.G.; Marini, A.; Schmitt, C.; Saltzman, C.L. Stage I and II Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Treated by a Structured Nonoperative Management Protocol: An Orthosis and Exercise Program. Foot Ankle Int. 2006, 27, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohls-Gatzoulis, J.; Angel, J.C.; Singh, D.; Haddad, F.; Livingstone, J.; Berry, G. Tibialis posterior dysfunction: A common and treatable cause of adult acquired flatfoot. Brit. Med. J. 2004, 329, 1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D.W.-C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, T.L.-W.; Leung, A.K.-L.; Zhang, M. Biomechanical consequences of subtalar joint arthroereisis in treating posterior tibial tendon dysfunction: A theoretical analysis using finite element analysis. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 20, 1525–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D.W.-C.; Wang, Y.; Leung, A.K.-L.; Yang, M.; Zhang, M. Finite element simulation on posterior tibial tendinopathy: Load transfer alteration and implications to the onset of pes planus. Clin. Biomech. 2018, 51, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabbito, M.; Pohl, M.B.; Humble, N.; Ferber, R. Biomechanical and clinical factors related to stage I posterior tibial tendon dysfunction. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2011, 41, 776–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murley, G.S.; Buldt, A.K.; Trump, P.J.; Wickham, J.B. Tibialis posterior EMG activity during barefoot walking in people with neutral foot posture. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2009, 19, e69–e77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutzner, I.; Trepczynski, A.; Heller, M.O.; Bergmann, G. Knee adduction moment and medial contact force--facts about their correlation during gait. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxby, D.J.; Modenese, L.; Bryant, A.L.; Gerus, P.; Killen, B.; Fortin, K.; Wrigley, T.V.; Bennell, K.L.; Cicuttini, F.M.; Lloyd, D.G. Tibiofemoral contact forces during walking, running and sidestepping. Gait Posture 2016, 49, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banwell, H.A.; Thewlis, D.; Mackintosh, S. Adults with flexible pes planus and the approach to the prescription of customised foot orthoses in clinical practice: A clinical records audit. The Foot 2015, 25, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.F.; Chen, C.H.; Wu, C.K.; Hong, W.H.; Chen, K.J.; Chen, C.K. The effects of total contact insole with forefoot medial posting on rearfoot movement and foot pressure distributions in patients with flexible flatfoot. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2015, 129, S8–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.P.; Donatelli, R.; Catlin, P.A.; Wooden, M.J. The effect of two types of foot orthoses on rearfoot mechanics. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 1995, 21, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Leung, A.K.; Mak, A.F.; Evans, J.H. Biomedical gait evaluation of the immediate effect of orthotic treatment for flexible flat foot. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 1998, 22, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stacoff, A.; Quervain, I.K.-d.; Dettwyler, M.; Wolf, P.; List, R.; Ukelo, T.; Stüssi, E. Biomechanical effects of foot orthoses during walking. The Foot 2007, 17, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wong, D.W.-C.; Zhang, M. Computational Models of the Foot and Ankle for Pathomechanics and Clinical Applications: A Review. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 44, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Wong, D.W.-C.; Zhang, H.; Luo, Z.-P.; Zhang, M. The influence of high-heeled shoes on strain and tension force of the anterior talofibular ligament and plantar fascia during balanced standing and walking. Med. Eng. Phys. 2016, 38, 1152–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, J.T.-M.; Yu, J.; Wong, D.W.-C.; Zhang, M. Current methods in computer-aided engineering for footwear design. Footwear Sci. 2009, 1, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Sanz, D.; Tovaruela-Carrión, N.; López-López, D.; Palomo-López, P.; Romero-Morales, C.; Navarro-Flores, E.; Calvo-Lobo, C. Foot disorders in the elderly: A mini-review. Disease-a-Month 2018, 64, 64–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
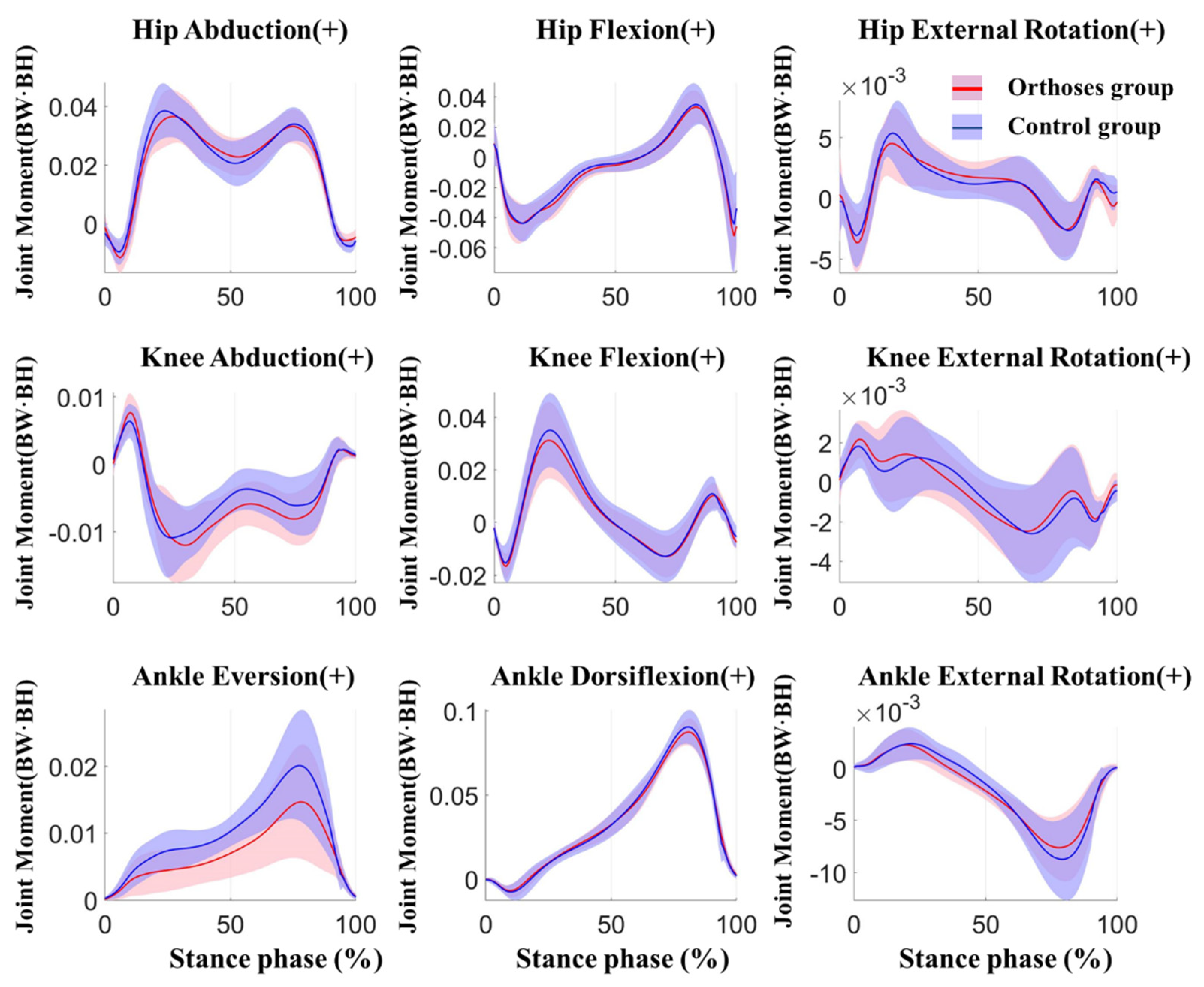
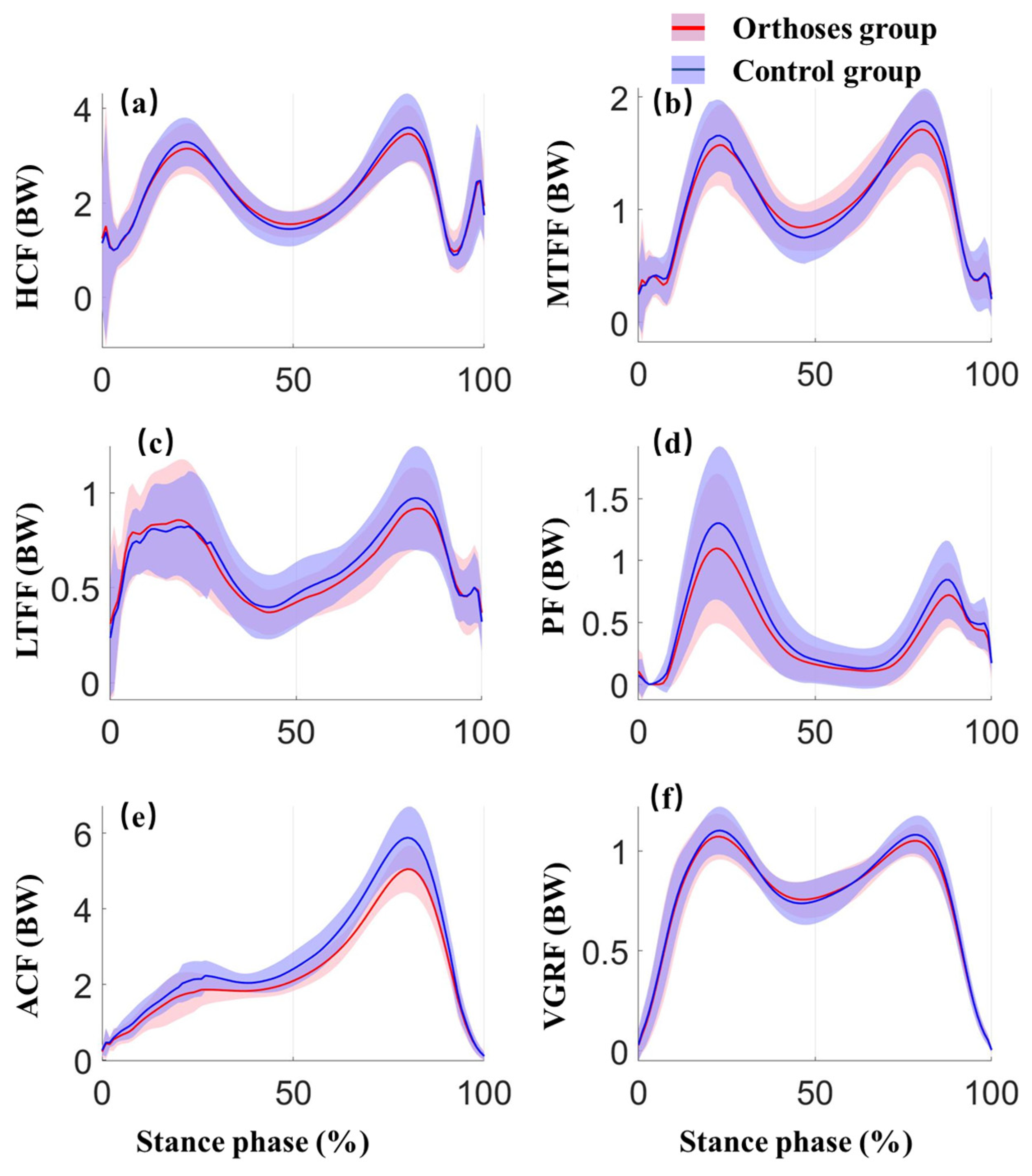
| Parameter | WSFO Mean (SD) | WS Mean (SD) | p−Value | ES (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hip flexion | 26.827 (6.373) | 27.256 (5.948) | 0.443 | 0.204 (−0.736,1.593) |
| Hip extension | −14.222 (7.347) | −15.025 (5.884) | 0.257 | 0.305 (−2.263,0.656) |
| Hip abduction | 5.868 (2.796) | 6.095 (2.318) | 0.421 | 0.214 (−0.361,0.815) |
| Hip adduction | −5.563 (2.449) | −5.957 (2.355) | 0.072 | 0.502 (−0.828,0.041) |
| Hip external rotation | 5.181 (4.157) | 6.225 (4.622) | 0.145 | 0.398 (−0.407,2.494) |
| Hip internal rotation | −2.212 (4.909) | −2.309 (4.547) | 0.871 | 0.043 (−1.361,1.167) |
| Knee flexion | 47.687 (4.112) | 46.82 (4.539) | 0.223 | 0.329 (−2.326,0.592) |
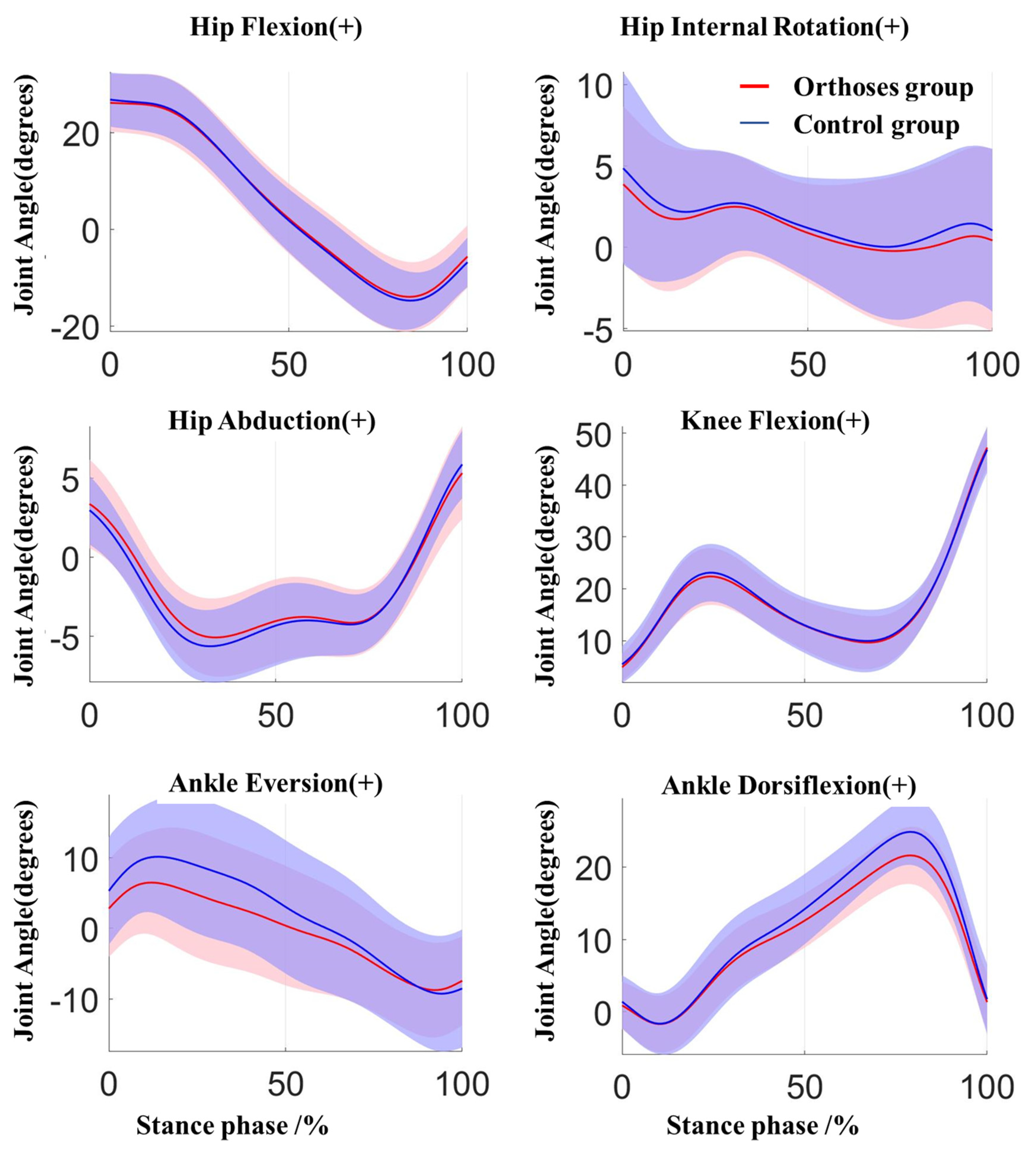
| Ankle dorsiflexion | 22.848 (4.163) | 24.734 (4.576) | 0.002 1 | 1.015 (0.857,2.915) |
| Ankle plantarflexion | −2.514 (3.917) | −2.663 (4.612) | 0.81 | 0.063 (−1.454,1.155) |
| Ankle eversion | 7.06 (6.675) | 10.886 (6.764) | 0.001 1 | 1.468 (2.382,5.27) |
| Ankle inversion | −9.521 (6.931) | −9.734 (8.737) | 0.85 | 0.05 (−2.588,2.161) |
| Parameter | WSFO Mean (SD) | WS Mean (SD) | p−Value | ES (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hip | First Abduction | −0.039 (0.01) | −0.041 (0.009) | 0.106 | 0.446 (−0.003,0) |
| Second Abduction | −0.034 (0.006) | −0.034 (0.006) | 0.193 | 0.353 (−0.001,0) | |
| External Rotation | 0.006 (0.003) | 0.005 (0.002) | 0.362 | 0.243 (−0.002,0.001) | |
| Internal Rotation | −0.006 (0.002) | −0.006 (0.002) | 0.357 | 0.246 (−0.001,0) | |
| Flexion Rotation | 0.061 (0.016) | 0.058 (0.017) | 0.443 | 0.204 (−0.013,0.006) | |
| Extension Rotation | −0.037 (0.007) | −0.039 (0.01) | 0.191 | 0.355 (−0.005,0.001) | |
| Knee | First Adduction | −0.015 (0.004) | −0.013 (0.004) | 0.007 1 | 0.822 (0,0.003) |
| Second Adduction | −0.009 (0.004) | −0.008 (0.003) | 0.016 1 | 0.707 (0,0.002) | |
| External Rotation | 0.003 (0.002) | 0.003 (0.001) | 0.592 | 0.142 (0,0) | |
| Internal Rotation | −0.003 (0.002) | −0.003 (0.002) | 0.224 | 0.329 (0,0) | |
| Flexion | 0.019 (0.006) | 0.019 (0.007) | 0.932 | 0.022 (−0.002,0.002) | |
| Extension | −0.032 (0.015) | −0.036 (0.015) | 0.18 | 0.364 (−0.009,0.002) | |
| Ankle | Eversion | 0.015 (0.008) | 0.021 (0.008) | 0.002 1 | 1.627 (0.003,0.007) |
| Inversion | 0.001 (0.001) | 0.002 (0.001) | 0.101 | 0.453 (0,0.001) | |
| External | 0.002 (0.001) | 0.003 (0.001) | 0.083 | 0.482 (0,0) | |
| Internal | −0.008 (0.003) | −0.009 (0.004) | 0.014 1 | 0.728 (−0.002,0) | |
| Dorsiflexion | 0.089 (0.008) | 0.091 (0.01) | 0.08 | 0.487 (0,0.005) | |
| Plantarflexion | −0.008 (0.004) | −0.009 (0.005) | 0.182 | 0.363 (−0.002,0.001) | |
| Parameter | WSFO Mean (SD) | WS Mean (SD) | p−Value | ES (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hip | First peak | 3.286 (0.502) | 3.355 (0.523) | 0.42 | 0.215 (−0.109,0.248) |
| Second peak | 3.562 (0.527) | 3.666 (0.675) | 0.201 | 0.347 (−0.062,0.269) | |
| Tibiofemoral joint | First medial peak | 1.617 (0.324) | 1.684 (0.356) | 0.249 | 0.31 (−0.052,0.185) |
| Second medial peak | 1.737 (0.318) | 1.81 (0.313) | 0.262 | 0.302 (−0.061,0.208) | |
| First lateral peak | 0.894 (0.292) | 0.927 (0.264) | 0.503 | 0.177 (−0.07,0.136) | |
| Second lateral peak | 0.904 (0.224) | 0.994 (0.291) | 0.095 | 0.462 (−0.018,0.199) | |
| Patellofemoral joint | First peak | 1.179 (0.63) | 1.324 (0.686) | 0.153 | 0.391 (−0.061,0.352) |
| Second peak | 0.78 (0.259) | 0.869 (0.334) | 0.022 1 | 0.663 (0.015,0.164) | |
| Ankle | Peak | 5.521 (0.627) | 5.925 (0.882) | 0.004 1 | 1.03 (0.187,0.621) |
| Ground force | First peak | 1.099 (0.127) | 1.113 (0.128) | 0.458 | 0.197 (−0.025,0.053) |
| Second peak | 1.066 (0.081) | 1.074 (0.08) | 0.238 | 0.318 (−0.006,0.023) | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, Y.; Wong, D.W.-C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, T.L.-W.; Tan, Q.; Chen, Z.; Jin, Z.; Zhang, M. Immediate Effects of Medially Posted Insoles on Lower Limb Joint Contact Forces in Adult Acquired Flatfoot: A Pilot Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2226. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17072226
Peng Y, Wong DW-C, Wang Y, Chen TL-W, Tan Q, Chen Z, Jin Z, Zhang M. Immediate Effects of Medially Posted Insoles on Lower Limb Joint Contact Forces in Adult Acquired Flatfoot: A Pilot Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(7):2226. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17072226
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Yinghu, Duo Wai-Chi Wong, Yan Wang, Tony Lin-Wei Chen, Qitao Tan, Zhenxian Chen, Zhongmin Jin, and Ming Zhang. 2020. "Immediate Effects of Medially Posted Insoles on Lower Limb Joint Contact Forces in Adult Acquired Flatfoot: A Pilot Study" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 7: 2226. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17072226
APA StylePeng, Y., Wong, D. W.-C., Wang, Y., Chen, T. L.-W., Tan, Q., Chen, Z., Jin, Z., & Zhang, M. (2020). Immediate Effects of Medially Posted Insoles on Lower Limb Joint Contact Forces in Adult Acquired Flatfoot: A Pilot Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(7), 2226. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17072226







