Effects of Hearing Disability on the Employment Status Using WHODAS 2.0 in Taiwan
Abstract
1. Introduction
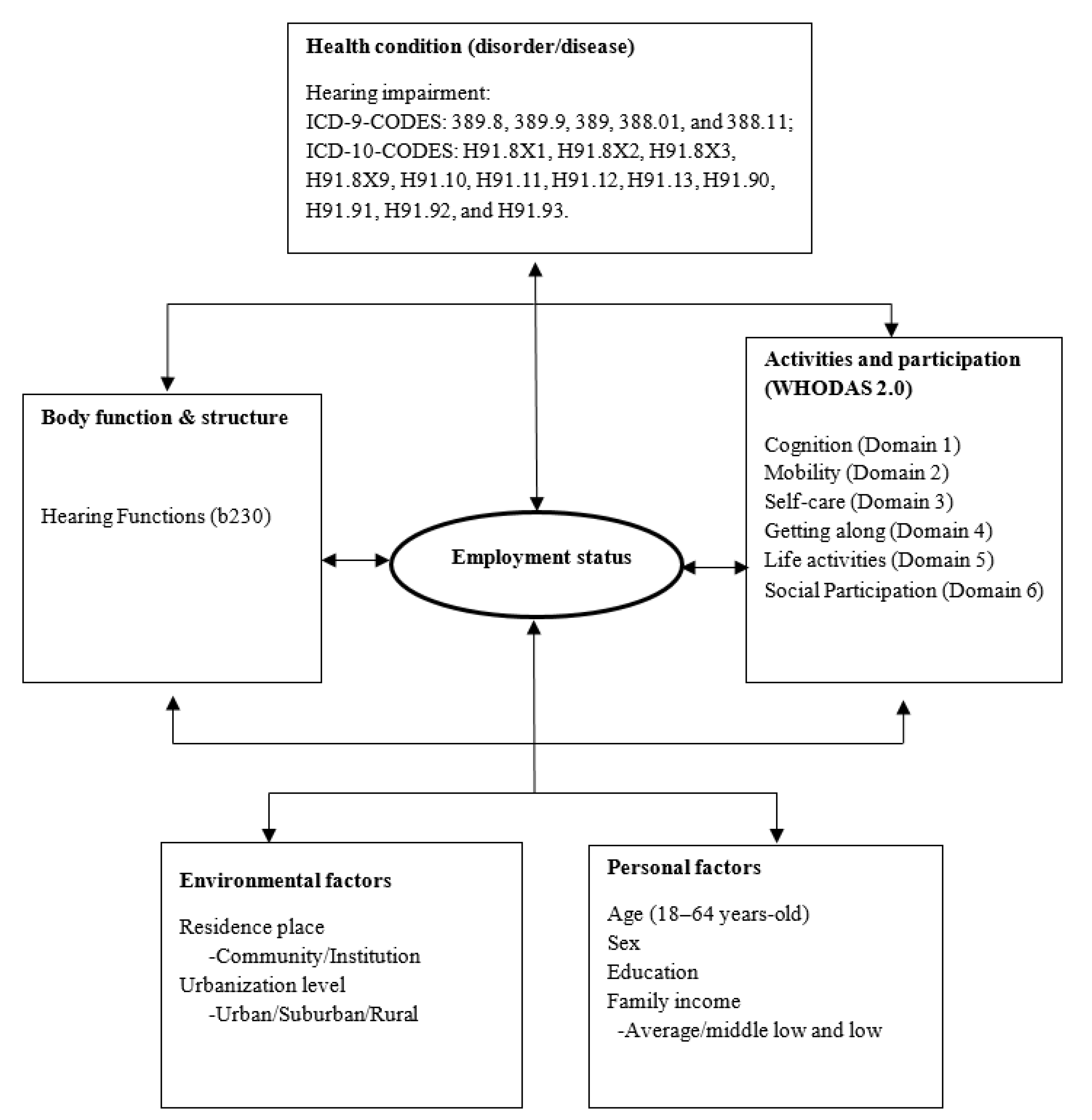
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Outcome Measurements
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Deafness and Hearing Loss. Available online: https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/deafness-and-hearing-loss (accessed on 25 November 2020).
- Wilson, B.S.; Tucci, D.L.; Merson, M.H.; O’Donoghue, G.M. Global hearing health care: New findings and perspectives. Lancet 2017, 390, 2503–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vos, T.; Allen, C.; Arora, M.; Barber, R.M.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Brown, A.; Carter, A.; Casey, D.C.; Charlson, F.J.; Chen, A.Z.; et al. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990–2015: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet 2016, 388, 1545–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Health and Welfare. Health Statistics. Available online: https://www.mohw.gov.tw/np-127-2.html (accessed on 25 November 2020).
- World Health Organization. Global Costs of Unaddressed Hearing Loss and Cost-Effectiveness of Interventions: Executive Summary. Available online: http://www.who.int/pbd/deafness/world-hearing-day/CostOfUnaddressedHearingLossExecSummary.pdf (accessed on 25 November 2020).
- Ustun, T.B.; Chatterji, S.; Bickenbach, J.; Kostanjsek, N.; Schneider, M. The International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health: A new tool for understanding disability and health. Disabil. Rehabil. 2003, 25, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selb, M.; Escorpizo, R.; Kostanjsek, N.; Stucki, G.; Ustun, B.; Cieza, A. A guide on how to develop an International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health Core Set. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2015, 51, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stephens, D.; Gianopoulos, I.; Kerr, P. Determination and classification of the problems experienced by hearing-impaired elderly people. Audiol. Off. Organ Int. Soc. Audiol. 2001, 40, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, G.H.; Chisolm, T.H.; Abrams, H.B. Measuring hearing aid outcomes—Not as easy as it seems. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2005, 42, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hickson, L.; Scarinci, N. Older adults with acquired hearing impairment: Applying the ICF in rehabilitation. Semin. Speech Lang. 2007, 28, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danermark, B.; Cieza, A.; Gange, J.P.; Gimigliano, F.; Granberg, S.; Hickson, L.; Kramer, S.E.; McPherson, B.; Moller, C.; Russo, I.; et al. International classification of functioning, disability, and health core sets for hearing loss: A discussion paper and invitation. Int. J. Audiol. 2010, 49, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustun, T.B.; Chatterji, S.; Kostanjsek, N.; Rehm, J.; Kennedy, C.; Epping-Jordan, J.; Saxena, S.; von Korff, M.; Pull, C. Developing the World Health Organization Disability Assessment Schedule 2.0. Bull. World Health Organ. 2010, 88, 815–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutlay, S.; Kucukdeveci, A.A.; Elhan, A.H.; Oztuna, D.; Koc, N.; Tennant, A. Validation of the World Health Organization disability assessment schedule II (WHODAS-II) in patients with osteoarthritis. Rheumatol. Int. 2011, 31, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucukdeveci, A.A.; Kutlay, S.; Yildizlar, D.; Oztuna, D.; Elhan, A.H.; Tennant, A. The reliability and validity of the World Health Organization Disability Assessment Schedule (WHODAS-II) in stroke. Disabil. Rehabil. 2013, 35, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guilera, G.; Gomez-Benito, J.; Pino, O.; Rojo, J.E.; Cuesta, M.J.; Martinez-Aran, A.; Safont, G.; Tabares-Seisdedos, R.; Vieta, E.; Bernardo, M.; et al. Utility of the World Health Organization Disability Assessment Schedule II in schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2012, 138, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.P.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.L.; Ma, L.; Zhang, Y.J.; Wang, J. Activity limitation and participation restrictions of breast cancer patients receiving chemotherapy: Psychometric properties and validation of the Chinese version of the WHODAS 2.0. Qual. Life Res. Int. J. Qual. Life Asp. Treat. Care Rehabil. 2013, 22, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chisolm, T.H.; Abrams, H.B.; McArdle, R.; Wilson, R.H.; Doyle, P.J. The WHO-DAS II: Psychometric properties in the measurement of functional health status in adults with acquired hearing loss. Trends Amplif. 2005, 9, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Federici, S.; Bracalenti, M.; Meloni, F.; Luciano, J.V. World Health Organization disability assessment schedule 2.0: An international systematic review. Disabil. Rehabil. 2017, 39, 2347–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelius, L.R.; van der Klink, J.J.; de Boer, M.R.; Groothoff, J.W.; Brouwer, S. Predictors of functional improvement and future work status after the disability benefit claim: A prospective cohort study. J. Occup. Rehabil. 2014, 24, 680–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.F.; Chang, K.H.; Chi, W.C.; Huang, S.W.; Yen, C.F.; Liao, H.F.; Liou, T.H.; Chao, P.Z.; Lin, I.C. Influence of visual impairment and hearing impairment on functional dependence status among people in Taiwan-An evaluation using the WHODAS 2.0 score. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. JCMA 2018, 81, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.J.; Liou, T.H.; Yen, C.F.; Chang, F.H.; Chen, Y.L.; Escorpizo, R.; Strauser, D.R.; Pan, A.W. Determinants of Employment Outcome for the People with Schizophrenia Using the WHODAS 2.0. J. Occup. Rehabil. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.W.; Chi, W.C.; Chang, K.H.; Yen, C.F.; Liao, H.F.; Escorpizo, R.; Liou, T.H. World health organization disability assessment schedule 2.0 as an objective assessment tool for predicting return to work after a stroke. Disabil. Rehabil. 2018, 40, 2592–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Chang, K.H.; Escorpizo, R.; Chi, W.C.; Yen, C.F.; Liao, H.F.; Huang, S.W.; Liou, T.H. Accuracy of the World Health Organization Disability Assessment Schedule 2.0 (WHODAS 2.0) score as an objective assessment tool for predicting return-to-work status after head and neck cancer in male survivors. Supportive Care Cancer Off. J. Multinatl. Assoc. Supportive Care Cancer 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, D.; Bhattacharyya, N. Association of hearing loss with decreased employment and income among adults in the United States. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2012, 121, 771–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, H.L.; Hoffmeister, R.; Bahan, B.J. A Journey Into the Deaf-World; DawnSignPress: San Diego, CA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Chiu, W.T.; Yen, C.F.; Teng, S.W.; Liao, H.F.; Chang, K.H.; Chi, W.C.; Wang, Y.H.; Liou, T.H. Implementing disability evaluation and welfare services based on the framework of the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health: Experiences in Taiwan. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2013, 13, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, T.Y.; Yen, C.F.; Chou, C.H.; Lin, J.D.; Hwang, A.W.; Liao, H.F.; Chi, W.C. Development of traditional Chinese version of World Health Organization disability assessment schedule 2.0 36--item (WHODAS 2.0) in Taiwan: Validity and reliability analyses. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2014, 35, 2812–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavanagh, K.T. Evaluation of hearing handicaps and presbyacusis using World Wide Web-based calculators. J. Am. Acad. Audiol. 2001, 12, 497–505. [Google Scholar]
- Yen, C.F.; Hwang, A.W.; Liou, T.H.; Chiu, T.Y.; Hsu, H.Y.; Chi, W.C.; Wu, T.F.; Chang, B.S.; Lu, S.J.; Liao, H.F.; et al. Validity and reliability of the Functioning Disability Evaluation Scale-Adult Version based on the WHODAS 2.0--36 items. J. Formos. Med Assoc. 2014, 113, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF); WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, J.; Sathiyandra, S.; Rochfordv, M.; Jones, D.; Krishnan, V.; McLeod, K. Work Participation among People with Disabilities: Does the Type of Disability Influence the Outcome? Soc. Policy J. N. Z. 2005, 24, 134–159. [Google Scholar]
- Kramer, S.E.; Kapteyn, T.S.; Kuik, D.J.; Deeg, D.J. The association of hearing impairment and chronic diseases with psychosocial health status in older age. J. Aging Health 2002, 14, 122–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton, D.S.; Cruickshanks, K.J.; Klein, B.E.; Klein, R.; Wiley, T.L.; Nondahl, D.M. The impact of hearing loss on quality of life in older adults. Gerontologist 2003, 43, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachtegaal, J.; Festen, J.M.; Kramer, S.E. Hearing ability in working life and its relationship with sick leave and self-reported work productivity. Ear Hear. 2012, 33, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feeny, D.; Huguet, N.; McFarland, B.H.; Kaplan, M.S.; Orpana, H.; Eckstrom, E. Hearing, mobility, and pain predict mortality: A longitudinal population-based study. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2012, 65, 764–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fischer, M.E.; Cruickshanks, K.J.; Klein, B.E.; Klein, R.; Schubert, C.R.; Wiley, T.L. Multiple sensory impairment and quality of life. Ophthalmic Epidemiol. 2009, 16, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emmett, S.D.; Francis, H.W. The socioeconomic impact of hearing loss in U.S. adults. Otol. Neurotol. Off. Publ. Am. Otol. Soc. Am. Neurotol. Soc. Eur. Acad. Otol. Neurotol. 2015, 36, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruben, R.J. Redefining the survival of the fittest: Communication disorders in the 21st century. Laryngoscope 2000, 110, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hetu, R.; Jones, L.; Getty, L. The impact of acquired hearing impairment on intimate relationships: Implications for rehabilitation. Audiol. Off. Organ Int. Soc. Audiol. 1993, 32, 363–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, H.; Thornton, P.; Campbell, S.M. Disabled People and Employment. A Review of Research and Development Work; Policy Press: London, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Hogan, A.; O’Loughlin, K.; Davis, A.; Kendig, H. Hearing loss and paid employment: Australian population survey findings. Int. J. Audiol. 2009, 48, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogan, A.; O’Loughlin, K.; Miller, P.; Kendig, H. The health impact of a hearing disability on older people in Australia. J. Aging Health 2009, 21, 1098–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, L.; Kyle, J.; Wood, P. Words Apart: Losing Your Hearing as an Adult; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.C.; Chan, S.J. Is Higher Education Expansion Related to Increasing Unemployment Rates? A Comparative Analysis of Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan. Int. J. Chin. Educ. 2017, 5, 162–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Directorate-General of Budget Accounting and Statistics of Taiwan Executive Yuan, Taiwan. Available online: https://eng.dgbas.gov.tw/mp.asp?mp=2 (accessed on 25 November 2020).
- Ho, E.C. Utility of WHODAS 2.0 (Quality of Life Assessment) in detecting Changes in Quality of Life in Hearing Impairment. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2016, 130, S176–S177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Svinndal, E.V.; Jensen, C.; Rise, M.B. Employees with hearing impairment. A qualitative study exploring managers’ experiences. Disabil. Rehabil. 2020, 42, 1855–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, A.; Taylor, A.; Doyle, J.; Osborn, R.; Fitzmaurice, K.; Kendig, H.A.L. The Communication and Health Needs of Older People with Hearing Loss: Are Hearing Aids Enough? Aust. N. Z. J. Audiol. 2001, 23, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variables | Men n = 10,155 | Women n = 8418 | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | % | No. | % | ||
| Age (years) | <0.001 | ||||
| Mean, SD | 53.76 | 10.834 | 52.96 | 10.990 | |
| Education | <0.001 | ||||
| ≥College | 497 | 4.89 | 263 | 3.12 | |
| Senior High | 1782 | 17.55 | 1260 | 14.97 | |
| Junior High | 4977 | 49.01 | 3926 | 46.64 | |
| ≤Primary | 2899 | 28.55 | 2969 | 35.27 | |
| Residence | <0.001 | ||||
| Community dwelling | 10,094 | 99.40 | 8400 | 99.79 | |
| Institution | 61 | 0.60 | 18 | 0.21 | |
| Urbanization level | <0.001 | ||||
| Rural | 1501 | 14.78 | 1065 | 12.65 | |
| Suburban | 4271 | 42.06 | 3541 | 42.06 | |
| Urban | 4383 | 43.16 | 3812 | 45.28 | |
| Family income | 0.1352 | ||||
| Average | 10,057 | 99.03 | 8354 | 99.24 | |
| Middle low and low | 98 | 0.97 | 64 | 0.76 | |
| Severity of Hearing functions | 0.0830 | ||||
| Mild | 6351 | 62.54 | 5316 | 63.15 | |
| Moderate | 2574 | 25.35 | 2026 | 24.07 | |
| Severe | 1230 | 12.11 | 1076 | 12.78 | |
| Work Status | <0.001 | ||||
| Employed | 4864 | 47.90 | 2570 | 30.53 | |
| Unemployed | 5291 | 52.10 | 5848 | 69.47 | |
| Variable | Employment (n = 7434) | Unemployment (n = 11,139) | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | ||
| Cognition | 18.15 | 16.001 | 25.05 | 20.568 | <0.001 |
| Mobility | 4.91 | 11.311 | 12.44 | 19.353 | <0.001 |
| Self-care | 2.04 | 7.054 | 5.40 | 12.738 | <0.001 |
| Getting along | 30.85 | 24.991 | 39.24 | 28.194 | <0.001 |
| Life activities | 9.18 | 18.245 | 19.03 | 27.560 | <0.001 |
| Social Participation | 24.10 | 18.933 | 30.22 | 21.768 | <0.001 |
| Summary | 16.33 | 12.315 | 23.27 | 16.898 | <0.001 |
| Univariate Model | Multivariate Model | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | Beta (β) | OR | 99% CI | p Value | Beta (β) | OR (Adjusted) | 99% CI | p Value | ||
| Age (year) | 0.044 | 1.045 | 1.042 | 1.048 | <0.001 | 0.037 | 1.038 | 1.035 | 1.041 | <0.001 |
| Sex (ref. = Male) | ||||||||||
| Female | 0.738 | 2.092 | 1.969 | 2.222 | <0.001 | 0.796 | 2.216 | 2.079 | 2.363 | <0.001 |
| Education (ref. ≥ College) | ||||||||||
| Senior High | 0.301 | 1.351 | 1.151 | 1.586 | <0.001 | 0.185 | 1.203 | 1.019 | 1.420 | 0.0288 |
| Junior high | 0.467 | 1.596 | 1.374 | 1.853 | <0.001 | 0.286 | 1.331 | 1.140 | 1.554 | <0.001 |
| ≤Primary | 1.451 | 4.267 | 3.651 | 4.986 | <0.001 | 0.948 | 2.579 | 2.189 | 3.039 | <0.001 |
| Residence (ref. = Community dwelling) | ||||||||||
| Institution | 1.781 | 5.936 | 2.859 | 12.325 | <0.001 | 1.966 | 7.140 | 3.368 | 15.138 | <0.001 |
| Urbanization level (ref. = urban) | ||||||||||
| Suburban | 0.072 | 1.074 | 1.009 | 1.144 | 0.0260 | 0.061 | 1.253 | 1.137 | 1.382 | 0.0746 |
| Rural | 0.224 | 1.252 | 1.142 | 1.372 | <0.001 | 0.226 | 1.063 | 0.994 | 1.137 | <0.001 |
| Family Income (ref. = Average) | ||||||||||
| Middle Low and Low | 1.338 | 0.291 | 0.964 | 1.857 | 0.0818 | 0.376 | 1.457 | 1.024 | 2.072 | 0.0364 |
| Severity (ref. = Mild) | ||||||||||
| Moderate | 0.156 | 1.169 | 1.090 | 1.254 | <0.001 | 0.154 | 1.167 | 1.083 | 1.257 | <0.001 |
| Severe | 0.308 | 1.360 | 1.239 | 1.493 | <0.001 | 0.424 | 1.528 | 1.384 | 1.688 | <0.001 |
| Domain Score | ||||||||||
| Cognition | 0.358 | 1.431 | 1.319 | 1.553 | <0.001 | |||||
| Mobility | 0.917 | 2.501 | 2.346 | 2.666 | <0.001 | |||||
| Self-care | 0.834 | 2.304 | 2.122 | 2.501 | <0.001 | |||||
| Getting along | 0.338 | 1.401 | 1.305 | 1.505 | <0.001 | |||||
| Life activities | 0.735 | 2.085 | 1.957 | 2.221 | <0.001 | |||||
| Social Participation | 0.406 | 1.500 | 1.390 | 1.620 | <0.001 | |||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chao, P.-Z.; Huang, S.-W.; Escorpizo, R.; Chi, W.-C.; Yen, C.-F.; Liao, H.-F.; Chen, Y.-W.; Liou, T.-H. Effects of Hearing Disability on the Employment Status Using WHODAS 2.0 in Taiwan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9374. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17249374
Chao P-Z, Huang S-W, Escorpizo R, Chi W-C, Yen C-F, Liao H-F, Chen Y-W, Liou T-H. Effects of Hearing Disability on the Employment Status Using WHODAS 2.0 in Taiwan. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(24):9374. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17249374
Chicago/Turabian StyleChao, Pin-Zhir, Shih-Wei Huang, Reuben Escorpizo, Wen-Chou Chi, Chia-Feng Yen, Hua-Fang Liao, Yi-Wen Chen, and Tsan-Hon Liou. 2020. "Effects of Hearing Disability on the Employment Status Using WHODAS 2.0 in Taiwan" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 24: 9374. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17249374
APA StyleChao, P.-Z., Huang, S.-W., Escorpizo, R., Chi, W.-C., Yen, C.-F., Liao, H.-F., Chen, Y.-W., & Liou, T.-H. (2020). Effects of Hearing Disability on the Employment Status Using WHODAS 2.0 in Taiwan. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(24), 9374. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17249374






