Sensation Seeking and Gambling Behavior in Adolescence: Can Externalizing Problems Moderate this Relationship?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Procedure
2.3. Measures
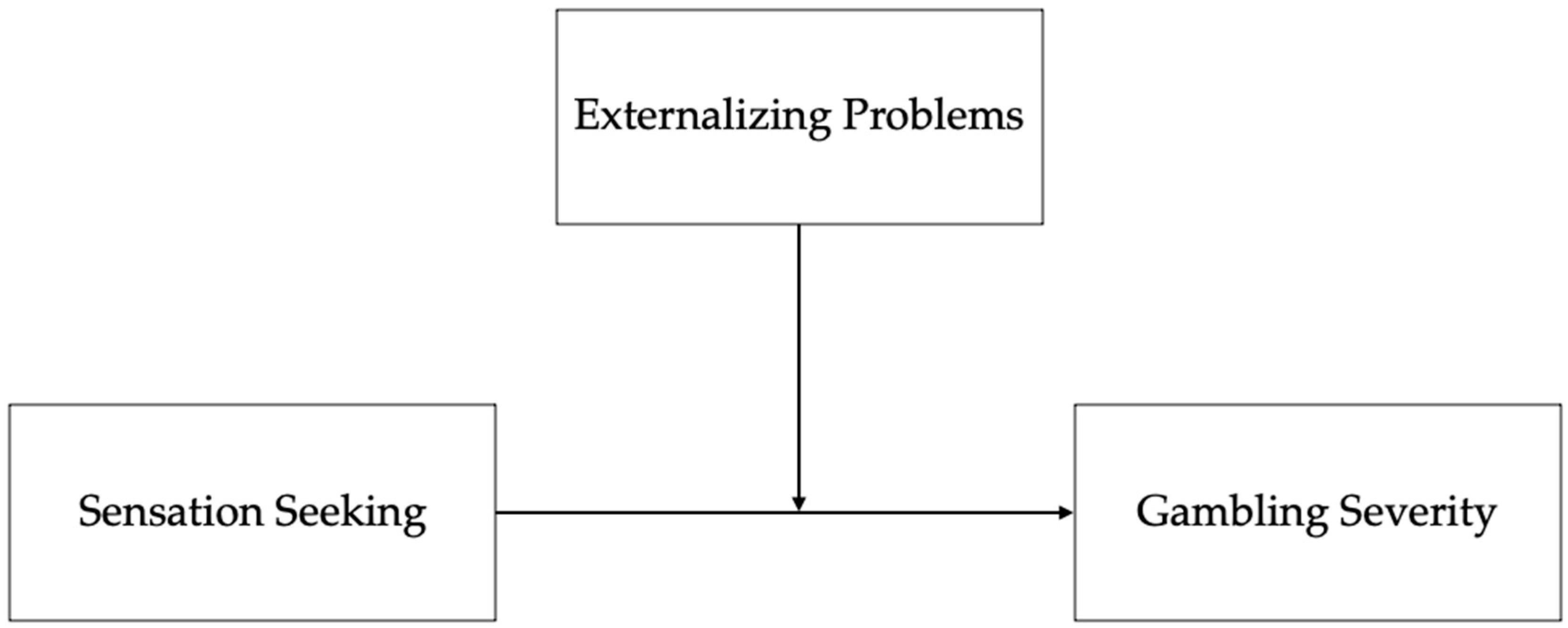
2.4. Data Analysis
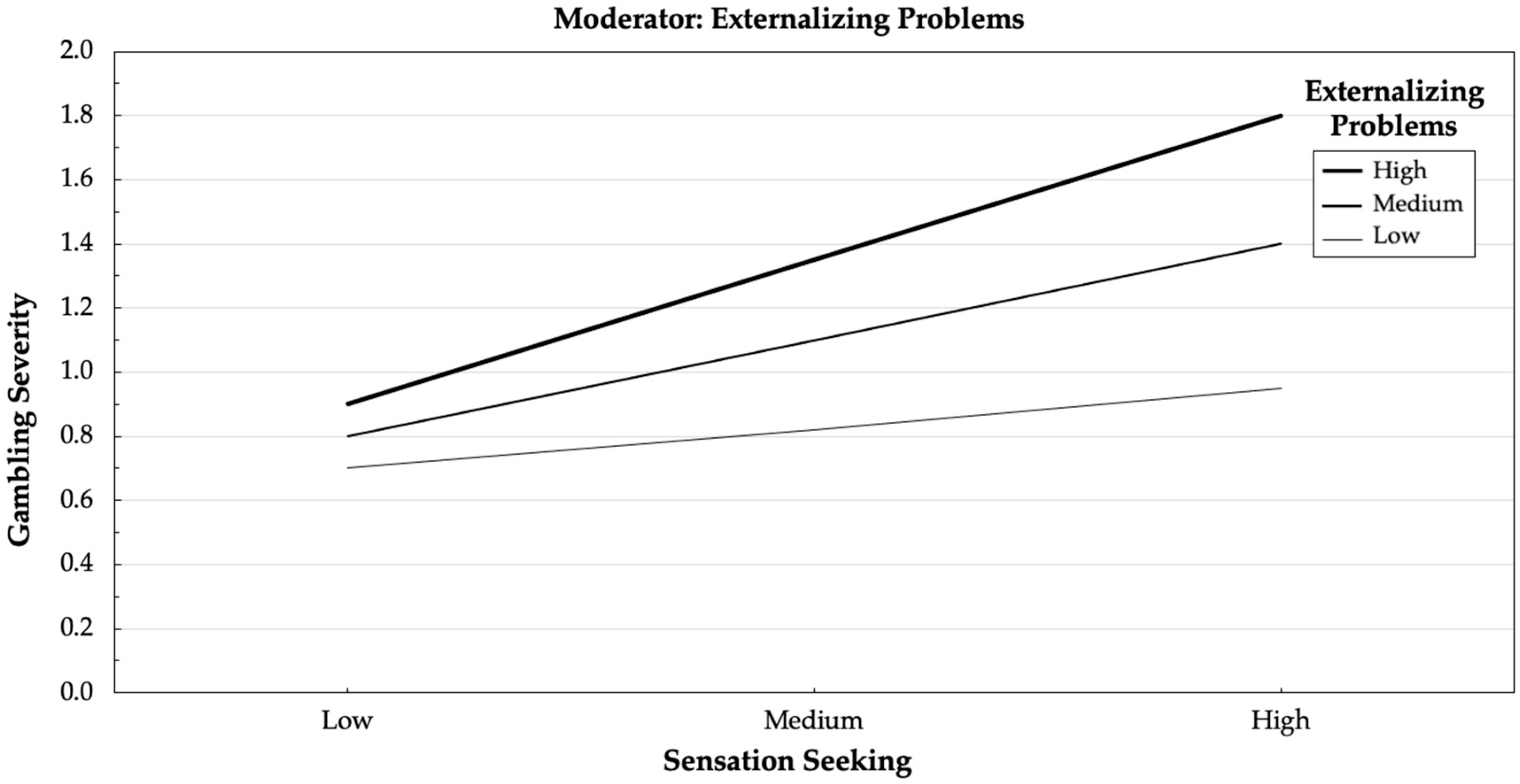
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Erikson, E.H. Identity: Youth and Crisis; Norton: New York, NY, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Corsano, P.; Majorano, M.; Musetti, A.; Antonioni, M.C. Autonomia emotiva e solitudine in adolescenti con abuso di sostanze Emotional autonomy and solitude in adolescent substance abusers. Psicologia Clinica dello Sviluppo 2014, 18, 257–278. [Google Scholar]
- Derevensky, J.L.; Gilbeau, L. Preventing adolescent gambling problems. In Gambling Disorder; Heinz, A., Romanczuk-Seiferth, N., Potenza, M.N., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 297–311. [Google Scholar]
- Guzzo, G.; Cascio, V.L.; Pace, U. The role of individual and relational characteristics on alcohol consumption among Italian adolescents: A discriminant function analysis. Child Ind. Res. 2013, 6, 605–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derevensky, J.L.; Gupta, R.; Winters, K. Prevalence rates of youth gambling problems: Are the current rates inflated? J. Gambl. Stud. 2003, 19, 405–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potenza, M.N. Neurobiology of gambling behaviors. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2013, 23, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyna, V.F.; Chapman, S.B.; Dougherty, M.R.; Confrey, J. The Adolescent Brain: Learning, Reasoning, and Decision Making; American Psychological Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Tozzi, L.; Akre, C.; Fleury-Schubert, A.; Surís, J.C. Gambling among youths in Switzerland and its association with other addictive behaviours: A population-based study. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2013, 143, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, R.J.; Volberg, R.A.; Stevens, R.M.G.; Williams, L.A.; Arthur, J.N. The Definition, Dimensionalization, and Assessment of Gambling Participation; Report for the Canadian Consortium for Gambling Research: Guelph, ON, Canada, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Andrie, E.K.; Tzavara, C.K.; Tzavela, E.; Richardson, C.; Greydanus, D.; Tsolia, M.; Tsitsika, A.K. Gambling involvement and problem gambling correlates among European adolescents: Results from the European Network for Addictive Behavior study. Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 2019, 54, 1429–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calado, F.; Alexandre, J.; Griffiths, M.D. Prevalence of adolescent problem gambling: A systematic review of recent research. J. Gambl. Stud. 2017, 33, 397–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floros, G.D. Gambling disorder in adolescents: Prevalence, new developments, and treatment challenges. Adolesc. Health Med. Ther. 2018, 9, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tani, F.; Ponti, L.; Ghinassi, S. Gambling behaviors in adolescent male and female regular and non-regular gamblers: A study of Central Italian adolescents. J. Gambl. Stud. 2020, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Derevensky, J. Reflections on underage gambling. Responsible Gambl. Rev. 2014, 1, 37–50. [Google Scholar]
- Livazović, G.; Bojčić, K. Problem gambling in adolescents: What are the psychological, social and financial consequences? BMC Psychiatry 2019, 19, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiesi, F.; Donati, M.A.; Galli, S.; Primi, C. The suitability of the South Oaks Gambling Screen–Revised for Adolescents (SOGS-RA) as a screening tool: IRT-based evidence. Psychol. Addict. Behav. 2013, 27, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canale, N.; Vieno, A.; Griffiths, M.D.; Marino, C.; Francesca Chieco, F.; Disperati, F.; Andriolo, S.; Santinello, M. The efficacy of a web-based gambling intervention program for high school students: A preliminary randomized study. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 55, 946–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosenza, M.; Ciccarelli, M.; Nigro, G. The steamy mirror of adolescent gamblers: Mentalization, impulsivity, and time horizon. Addict. Behav. 2019, 89, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allami, Y.; Vitaro, F.; Brendgen, M.; Carbonneau, R.; Tremblay, R.E. Identifying at-risk profiles and protective factors for problem gambling: A longitudinal study across adolescence and early adulthood. Psychol. Addict. Behav. 2018, 32, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowling, N.A.; Merkouris, S.S.; Greenwood, C.J.; Oldenhof, E.; Toumbourou, J.W.; Youssef, G.J. Early risk and protective factors for problem gambling: A systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2017, 51, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passanisi, A.; D’Urso, G.; Pace, U. The Interplay Between Maladaptive Personality Traits and Mindfulness Deficits Among Adolescent Regular Gamblers: A Mediation Model. J. Gambl. Stud. 2019, 35, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passanisi, A.; D’Urso, G.; Schimmenti, A.; Ruggieri, S.; Pace, U. Coping Strategies, Creativity, Social Self-Efficacy, and Hypercompetitiveness in Gambling Behaviors: A Study on Male Adolescent Regular Gamblers. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuckerman, M. Behavioral Expression and Biosocial Bases of Sensation Seeking; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Donati, M.A.; Chiesi, F.; Primi, C. A model to explain at-risk/problem gambling among male and female adolescents: Gender similarities and differences. J. Adolesc. 2013, 36, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estevez, A.; Herrero-Fernández, D.; Sarabia, I.; Jauregui, P. The impulsivity and sensation-seeking mediators of the psychological consequences of pathological gambling in adolescence. J. Gambl. Stud. 2015, 31, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reardon, K.W.; Wang, M.; Neighbors, C.; Tackett, J.L. The Personality Context of Adolescent Gambling: Better Explained by the Big Five or Sensation-Seeking? J. Psychopathol. Behav. Assess. 2019, 41, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollén, L.; Dörner, R.; Griffiths, M.D.; Emond, A. Gambling in young adults aged 17-24 years: A population-based study. J. Gambl. Stud. 2020, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donati, M.A.; Primi, C.; Mazzarese, M.; Sanson, F.; Leone, L. Immigrant status and problem-gambling severity in adolescents: Evidence for moderation by sensation seeking. Addict. Behav. 2020, 107, 106395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tani, F.; Ilari, A. Il gioco d’azzardo tra attività ludica e patologia The spiral of the game. Gambling between ludic activity and pathology. In La Spirale Del Gioco; University Press: Florence, Italy, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zuckerman, M. Faites vos jeux anouveau: Still another look at sensation seeking and pathological gambling. Pers. Individ. Differ. 2005, 39, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canale, N.; Scacchi, L.; Griffiths, M.D. Adolescent gambling and impulsivity: Does employment during high school moderate the association? Addict. Behav. 2016, 60, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeman, R.F.; Hoff, R.A.; Krishnan-Sarin, S.; Patock-Peckham, J.A.; Potenza, M.N. Impulsivity, sensation-seeking, and part-time job status in relation to substance use and gambling in adolescents. J. Adolesc. Health 2014, 54, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldeira, K.M.; Arria, A.M.; O’Grady, K.E.; Vincent, K.B.; Robertson, C.; Welsh, C.J. Risk factors for gambling and substance use among recent college students. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2017, 179, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achenbach, T.M. Manual for The Youth Self-Report and 1991 Profile; Department of Psychiatry, University of Vermont: Burlington, VT, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Masten, A.S.; Roisman, G.I.; Long, J.D.; Burt, K.B.; Obradović, J.; Riley, J.R.; Boelcke-Stennes, K.; Tellegen, A. Developmental cascades: Linking academic achievement and externalizing and internalizing symptoms over 20 years. Dev. Psychol. 2005, 41, 733–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffitt, T.E. Adolescence-limited and life-course-persistent antisocial behavior: A developmental taxonomy. Psychol. Rev. 1993, 100, 674–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuckerman, M. Sensation Seeking and Risky Behavior; American Psychological Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, F.D.; Engelhardt, L.; Briley, D.A.; Grotzinger, A.D.; Patterson, M.W.; Tackett, J.L.; Statham, D.J.; Heath, A.; Lynskey, M.T.; Slutske, W.G.; et al. Sensation seeking and impulsive traits as personality endophenotypes for antisocial behavior: Evidence from two independent samples. Pers. Individ. Differ. 2017, 105, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, F.D.; Kretsch, N.; Tackett, J.L.; Harden, K.P.; Tucker-Drob, E.M. Person× environment interactions on adolescent delinquency: Sensation seeking, peer deviance and parental monitoring. Pers. Individ. Differ. 2015, 76, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peach, H.D.; Gaultney, J.F. Sleep, impulse control, and sensation-seeking predict delinquent behavior in adolescents, emerging adults, and adults. J. Adolesc. Health 2013, 53, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, S.S.; Liu, W.; Hedden, S.L.; Goldweber, A.; Storr, C.L.; Derevensky, J.L.; Stinchfield, R.; Ialongo, N.S.; Petras, H. Youth aggressive/disruptive behavior trajectories and subsequent gambling among urban male youth. J. Clin. Child Adolesc. Psychol. 2013, 42, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winters, K.C.; Stinchfield, R.; Fulkerson, J. Patterns and characteristics of adolescent gambling. J. Gambl. Stud. 1993, 9, 371–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, D.; Mallery, P. SPSS for Windows Step by Step: A Simple Guide and Reference. 11.0 Update, 4th ed.; Allyn & Bacon: Boston, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Pastorelli, C.; Gerbino, M.; Vecchio, G.M.; Steca, P.; Picconi, L.; Paciello, M. School failure: Risk and protective factors during preadolescence. Età Evol. 2002, 71, 84–91. [Google Scholar]
- Primi, C.; Narducci, R.; Benedetti, D.; Donati, M.; Chiesi, F. Validity and reliability of the Italian version of the Brief Sensation Seeking Scale (BSSS) and its invariance across age and gender. Test Psychom. Methodol. Appl. Psychol. 2011, 18, 231–241. [Google Scholar]
- Zuckerman, M.; Eysenck, S.; Eysenck, H.J. Sensation seeking in England and America: Cross-cultural age and sex comparisons. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 1978, 46, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran, P.J.; West, S.G.; Finch, J.F. The robustness of test statistics to nonnormality and specification error in confirmatory factor analysis. Psychol. Methods 1996, 1, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Erlbaum: Hillsdale, MI, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Aiken, L.S.; West, S.G. Multiple Regression: Testing and Interpreting Interactions; Sage: Newbury Park, CA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Joseé, P.E. Doing Statistical Mediation and Moderation, 1st ed.; Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Donati, M.A.; Sottili, E.; Morsanyi, K.; Primi, C. Time perspectives and gambling in adolescent boys: Differential effects of present-and future-orientation. J. Gambl. Stud. 2019, 35, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans-Polce, R.J.; Schuler, M.S.; Schulenberg, J.E.; Patrick, M.E. Gender-and age-varying associations of sensation seeking and substance use across young adulthood. Addict. Behav. 2018, 84, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innamorati, M.; Parolin, L.; Tagini, A.; Santona, A.; Bosco, A.; De Carli, P.; Palmisano, G.L.; Pergola, F.; Sarracino, D. Attachment, social value orientation, sensation seeking, and bullying in early adolescence. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiire, S.; Matsumoto, N.; Yoshida, E. Discrimination of Dark Triad traits using the UPPS-P model of impulsivity. Pers. Individ. Differ. 2020, 167, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionio, C.; Camisasca, E.; Milani, L.; Miragoli, S.; Di Blasio, P. Facing Death in Adolescence: What Leads to Internalization and Externalization Problems? J. Child Adolesc. Trauma 2018, 11, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca-Pedrero, E.; Sierra-Baigrie, S.; Lemos-Giráldez, S.; Paino, M.; Muñiz, J. Dimensional structure and measurement invariance of the Youth Self-Report across gender and age. J. Adolesc. Health 2012, 50, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rescorla, L.; Achenbach, T.M.; Ivanova, M.Y.; Dumenci, L.; Almqvist, F.; Bilenberg, N.; Bird, H.; Hector Broberg, A.; Dobrean, A.; Döpfner, M.; et al. Epidemiological comparisons of problems and positive qualities reported by adolescents in 24 countries. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 2007, 75, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canale, N.; Vieno, A.; Lenzi, M.; Griffiths, M.D.; Borraccino, A.; Lazzeri, G.; Lemma, P.; Scacchi, L.; Santinello, M. Income inequality and adolescent gambling severity: Findings from a large-scale Italian representative survey. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, J.; Sundqvist, K. Gambling among Swedish youth: Predictors and prevalence among 15-and 17-year-old students. Nord. Stud. Alcohol Drugs 2019, 36, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidberg, S.; González-Roz, A.; Fernández-Hermida, J.R.; Martínez-Loredo, V.; Grande-Gosende, A.; García-Pérez, Á.; Secades-Villa, R. Gender differences among adolescent gamblers. Pers. Individ. Differ. 2018, 125, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blinn-Pike, L.; Worthy, S.L.; Jonkman, J.N. Adolescent gambling: A review of an emerging field of research. J. Adolesc. Health 2010, 47, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magoon, M.E.; Ingersoll, G.M. Parental modeling, attachment, and supervision as moderators of adolescent gambling. J. Gambl. Stud. 2006, 22, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbonneau, R.; Vitaro, F.; Brendgen, M.; Tremblay, R.E. Trajectories of gambling problems from mid-adolescence to age 30 in a general population cohort. Psychol. Addict. Behav. 2015, 29, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granero, R.; Penelo, E.; Stinchfield, R.; Fernandez-Aranda, F.; Savvidou, L.G.; Fröberg, F.; Aymamì, N.; Gómez-Peña, M.; Pérez-Serrano, M.; del Pino-Gutiérrez, A.; et al. Is pathological gambling moderated by age? J. Gambl. Stud. 2014, 30, 475–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volberg, R.A.; Gupta, R.; Griffiths, M.D.; Olason, D.T.; Delfabbro, P. An international perspective on youth gambling prevalence studies. Int. J. Adolesc. Med. Health 2010, 2, 3–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| M | SD | Skewness | Kurtosis | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Externalizing problems | 10.91 | 6.75 | 1.00 | 1.17 | - | 0.44 ** | 0.29 ** |
| 2. Sensation seeking | 25.64 | 5.84 | −0.09 | −0.30 | - | 0.27 ** | |
| 3. Gambling | 0.82 | 1.48 | 2.05 | 3.74 | - |
| ß | t | p | 95% CI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | |||||
| Gender | −0.37 | −7.58 | 0.000 | −1.43 | −0.84 |
| Step 2 | |||||
| Gender | −0.33 | −6.67 | 0.024 | −1.30 | −0.71 |
| Sensation seeking | 0.20 | 4.00 | 0.000 | 0.03 | 0.07 |
| Step 3 | |||||
| Gender | −0.31 | −6.45 | 0.000 | −1.26 | −0.67 |
| Sensation seeking | 0.12 | 2.26 | 0.024 | 0.01 | 0.06 |
| Externalizing problems | 0.18 | 3.37 | 0.001 | 0.02 | 0.06 |
| Step 4 | |||||
| Gender | −0.31 | −0.46 | 0.000 | −1.25 | −0.66 |
| Sensation seeking | −0.08 | −0.88 | 0.382 | −0.07 | 0.03 |
| Externalizing problems | 0.13 | 2.43 | 0.016 | 0.01 | 0.05 |
| Sensation seeking X Externalizing problems | 0.26 | 2.72 | 0.007 | 0.00 | 0.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tani, F.; Ponti, L.; Ghinassi, S. Sensation Seeking and Gambling Behavior in Adolescence: Can Externalizing Problems Moderate this Relationship? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8986. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17238986
Tani F, Ponti L, Ghinassi S. Sensation Seeking and Gambling Behavior in Adolescence: Can Externalizing Problems Moderate this Relationship? International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(23):8986. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17238986
Chicago/Turabian StyleTani, Franca, Lucia Ponti, and Simon Ghinassi. 2020. "Sensation Seeking and Gambling Behavior in Adolescence: Can Externalizing Problems Moderate this Relationship?" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 23: 8986. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17238986
APA StyleTani, F., Ponti, L., & Ghinassi, S. (2020). Sensation Seeking and Gambling Behavior in Adolescence: Can Externalizing Problems Moderate this Relationship? International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(23), 8986. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17238986





