Heritability and Environmental Correlation of Phase Angle with Anthropometric Measurements: A Twin Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Measurements
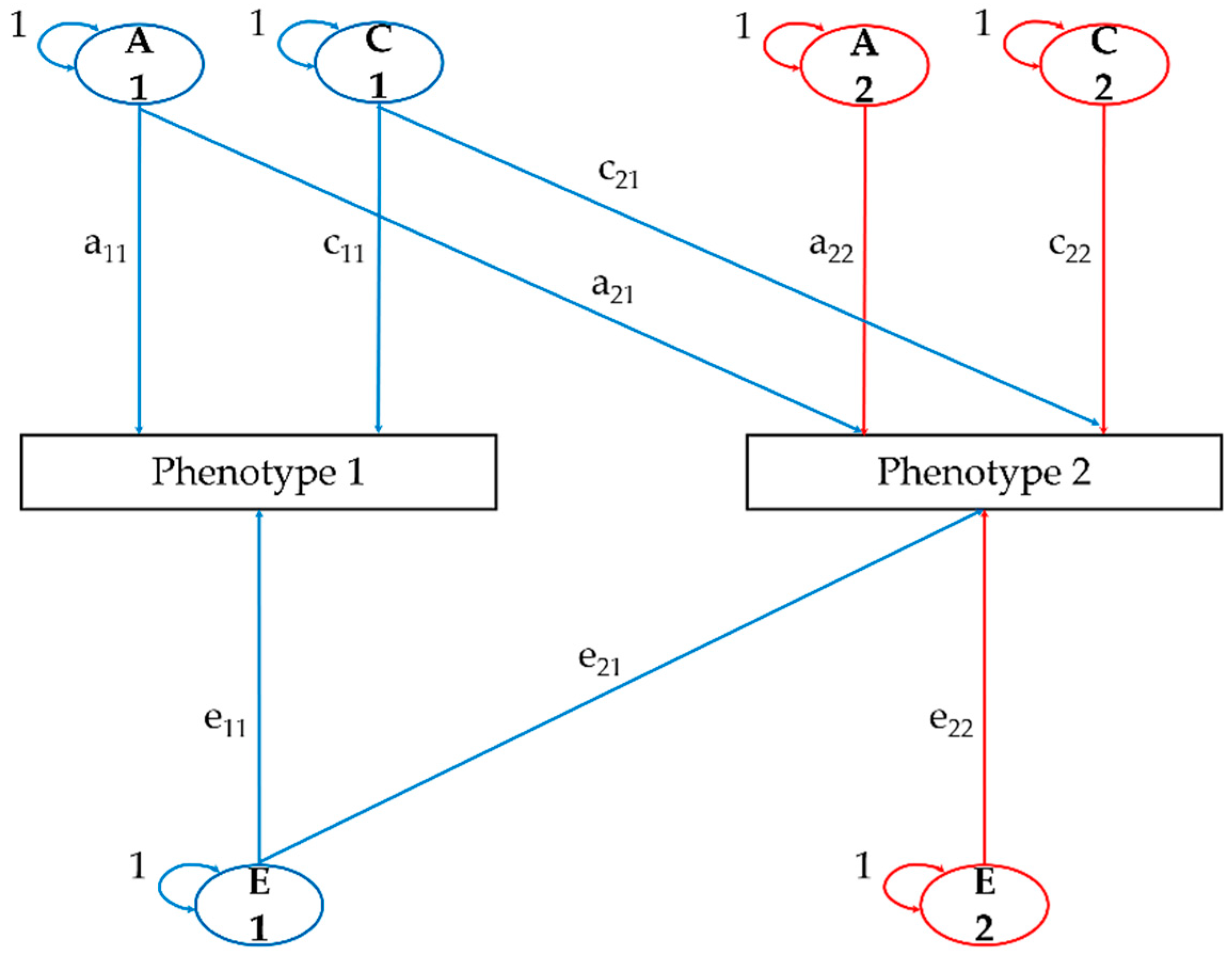
2.3. Statistical Analysis
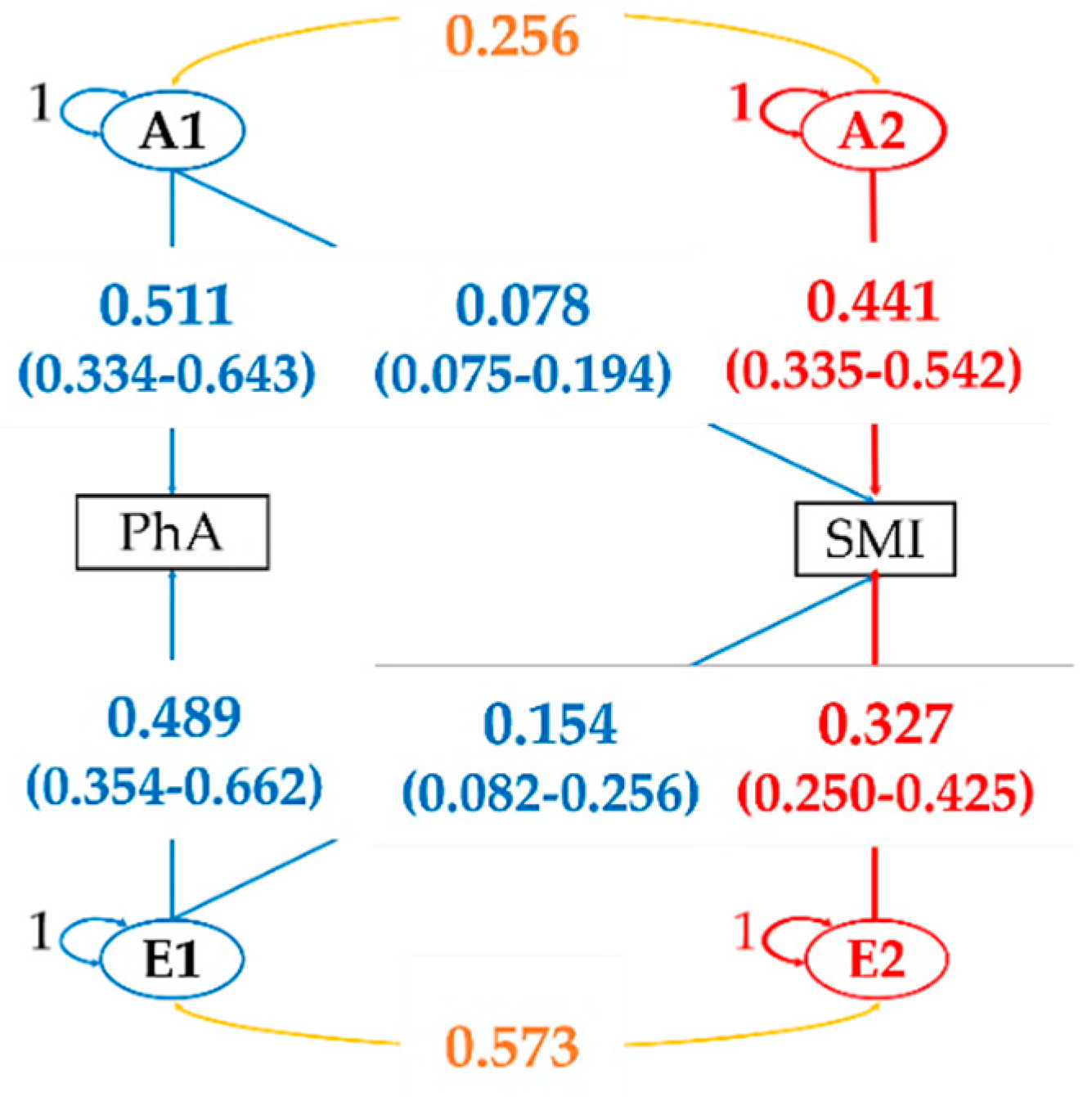
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Lorenzo, A.; Andreoli, A.; Matthie, J.; Withers, P. Predicting body cell mass with bioimpedance by using theoretical methods: A technological review. J. Appl. Physiol. 1997, 82, 1542–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyle, U.G.; Bosaeus, I.; De Lorenzo, A.D.; Deurenberg, P.; Elia, M.; Manuel Gomez, J.; Lilienthal Heitmann, B.; Kent-Smith, L.; Melchior, J.C.; Pirlich, M.; et al. Bioelectrical impedance analysis—Part II: Utilization in clinical practice. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 23, 1430–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyle, U.G.; Genton, L.; Pichard, C. Low phase angle determined by bioelectrical impedance analysis is associated with malnutrition and nutritional risk at hospital admission. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 32, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyle, U.G.; Soundar, E.P.; Genton, L.; Pichard, C. Can phase angle determined by bioelectrical impedance analysis assess nutritional risk? A comparison between healthy and hospitalized subjects. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 31, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Kwon, O.; Shin, C.S.; Lee, S.M. Use of bioelectrical impedance analysis for the assessment of nutritional status in critically ill patients. Clin. Nutr. Res. 2015, 4, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garlini, L.M.; Alves, F.D.; Ceretta, L.B.; Perry, I.S.; Souza, G.C.; Clausell, N.O. Phase angle and mortality: A systematic review. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 73, 495–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, M.; Kimura, Y.; Ishiyama, D.; Nishio, N.; Otobe, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Ohji, S.; Koyama, S.; Sato, A.; Suzuki, M.; et al. Phase angle is a useful indicator for muscle function in older adults. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2019, 23, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uemura, K.; Yamada, M.; Okamoto, H. Association of bioimpedance phase angle and prospective falls in older adults. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2019, 19, 503–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm-Leen, E.R.; Hall, Y.N.; Horwitz, R.I.; Chertow, G.M. Phase angle, frailty and mortality in older adults. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2014, 29, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uemura, K.; Doi, T.; Tsutsumimoto, K.; Nakakubo, S.; Kim, M.J.; Kurita, S.; Ishii, H.; Shimada, H. Predictivity of bioimpedance phase angle for incident disability in older adults. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2020, 11, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, K.; Wirth, R.; Neubauer, M.; Eckardt, R.; Stobaus, N. The bioimpedance phase angle predicts low muscle strength, impaired quality of life, and increased mortality in old patients with cancer. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2015, 16, 173.e17–173.e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, Y.; Buehring, B.; Krueger, D.; Anderson, R.M.; Schoeller, D.A.; Binkley, N. Electrical properties assessed by bioelectrical impedance spectroscopy as biomarkers of age-related loss of skeletal muscle quantity and quality. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2017, 72, 1180–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basile, C.; Della-Morte, D.; Cacciatore, F.; Gargiulo, G.; Galizia, G.; Roselli, M.; Curcio, F.; Bonaduce, D.; Abete, P. Phase angle as bioelectrical marker to identify elderly patients at risk of sarcopenia. Exp. Gerontol. 2014, 58, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, P.M.; Tomeleri, C.M.; Nascimento, M.A.D.; Nunes, J.P.; Antunes, M.; Nabuco, H.C.G.; Quadros, Y.; Cavalcante, E.F.; Mayhew, J.L.; Sardinha, L.B.; et al. Improvement of cellular health indicators and muscle quality in older women with different resistance training volumes. J. Sports Sci. 2018, 36, 2843–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heymsfield, S.B.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Lu, J.H.; Jia, G.; Zheng, J.N. Skeletal muscle mass and quality: Evolution of modern measurement concepts in the context of sarcopenia. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2015, 74, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyere, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A.; et al. Sarcopenia: Revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polderman, T.J.; Benyamin, B.; de Leeuw, C.A.; Sullivan, P.F.; van Bochoven, A.; Visscher, P.M.; Posthuma, D. Meta-analysis of the heritability of human traits based on fifty years of twin studies. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silventoinen, K.; Jelenkovic, A.; Sund, R.; Honda, C.; Aaltonen, S.; Yokoyama, Y.; Tarnoki, A.D.; Tarnoki, D.L.; Ning, F.; Ji, F.; et al. The CODATwins project: The cohort description of collaborative project of development of anthropometrical measures in twins to study macro-environmental variation in genetic and environmental effects on anthropometric traits. Twin Res. Hum. Genet. 2015, 18, 348–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silventoinen, K.; Jelenkovic, A.; Sund, R.; Yokoyama, Y.; Hur, Y.M.; Cozen, W.; Hwang, A.E.; Mack, T.M.; Honda, C.; Inui, F.; et al. Differences in genetic and environmental variation in adult BMI by sex, age, time period, and region: An individual-based pooled analysis of 40 twin cohorts. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 106, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elder, S.J.; Roberts, S.B.; McCrory, M.A.; Das, S.K.; Fuss, P.J.; Pittas, A.G.; Greenberg, A.S.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Dawson-Hughes, B.; Bouchard, T.J., Jr.; et al. Effect of body composition methodology on heritability estimation of body fatness. Open Nutr. J. 2012, 6, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tarnoki, A.D.; Tarnoki, D.L.; Medda, E.; Cotichini, R.; Stazi, M.A.; Fagnani, C.; Nistic, A.L.; Lucatelli, P.; Boatta, E.; Zini, C.; et al. Bioimpedance analysis of body composition in an international twin cohort. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2014, 8, e201–e298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, Y.; Nishizawa, M.; Uchiyama, T.; Kasahara, Y.; Shindo, M.; Miyachi, M.; Tanaka, S. Developing and validating an age-independent equation using multi-frequency bioelectrical impedance analysis for estimation of appendicular skeletal muscle mass and establishing a cutoff for Sarcopenia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dongen, J.; Slagboom, P.E.; Draisma, H.H.; Martin, N.G.; Boomsma, D.I. The continuing value of twin studies in the omics era. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 640–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijsdijk, F.V.; Sham, P.C. Analytic approaches to twin data using structural equation models. Brief. Bioinform. 2002, 3, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grayson, D.A. Twins reared together: Minimizing shared environmental effects. Behav. Genet. 1989, 19, 593–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akaike, H. Factor analysis and AIC. Psychometrika 1987, 52, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loehlin, J.C. The Cholesky approach: A cautionary note. Behav. Genet. 1996, 26, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neale, M.C.; Hunter, M.D.; Pritikin, J.N.; Zahery, M.; Brick, T.R.; Kirkpatrick, R.M.; Estabrook, R.; Bates, T.C.; Maes, H.H.; Boker, S.M. OpenMx 2.0: Extended structural equation and statistical modeling. Psychometrika 2016, 81, 535–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa-Silva, M.C.; Barros, A.J.; Wang, J.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Pierson, R.N., Jr. Bioelectrical impedance analysis population reference values for phase angle by age and sex. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 82, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosy-Westphal, A.; Danielzik, S.; Dorhofer, R.P.; Later, W.; Wiese, S.; Muller, M.J. Phase angle from bioelectrical impedance analysis: Population reference values by age, sex, and body mass index. J. Parenter. Enteral. Nutr. 2006, 30, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, N.M.; Pinho, C.P.S.; da Silva, C.P.; dos Santos, N.F.; Mendes, R.M.L. Phase angle as a sarcopenia marker in hospitalized elderly patients. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2018, 33, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilic, M.K.; Kizilarslanoglu, M.C.; Arik, G.; Bolayir, B.; Kara, O.; Dogan Varan, H.; Sumer, F.; Kuyumcu, M.E.; Halil, M.; Ulger, Z. Association of bioelectrical impedance analysis-derived phase angle and sarcopenia in older adults. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2017, 32, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, M.F.; Tomeleri, C.M.; Ribeiro, A.S.; Schoenfeld, B.J.; Silva, A.M.; Sardinha, L.B.; Cyrino, E.S. Effect of resistance training on phase angle in older women: A randomized controlled trial. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2017, 27, 1308–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, A.S.; Schoenfeld, B.J.; Souza, M.F.; Tomeleri, C.M.; Silva, A.M.; Teixeira, D.C.; Sardinha, L.B.; Cyrino, E.S. Resistance training prescription with different load-management methods improves phase angle in older women. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2017, 17, 913–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardinha, L.B. Physiology of exercise and phase angle: Another look at BIA. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 72, 1323–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, K.; Stobaus, N.; Pirlich, M.; Bosy-Westphal, A. Bioelectrical phase angle and impedance vector analysis—Clinical relevance and applicability of impedance parameters. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 31, 854–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadro, J.R.; Shirley, D.; Andrade, T.B.; Scurrah, K.J.; Bauman, A.; Ferreira, P.H. The beneficial effects of physical activity: Is it down to your genes? A systematic review and meta-analysis of twin and family studies. Sports Med. Open 2017, 3, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churchward-Venne, T.A.; Tieland, M.; Verdijk, L.B.; Leenders, M.; Dirks, M.L.; de Groot, L.C.; van Loon, L.J. There are no nonresponders to resistance-type exercise training in older men and women. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2015, 16, 400–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittmar, M. Reliability and variability of bioimpedance measures in normal adults: Effects of age, gender, and body mass. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 2003, 122, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variable | Total (n = 168) | Male (n = 54) | Female (n = 114) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | p-Value | |
| Age (years) | 61.0 | 16.5 | 60.7 | 20.9 | 61.1 | 14.0 | 0.903 |
| Height (cm) | 157.8 | 8.23 | 165.9 | 6.30 | 153.9 | 5.95 | <0.001 |
| Body Weight (kg) | 53.8 | 10.3 | 63.0 | 9.57 | 49.5 | 7.34 | <0.001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 21.5 | 3.19 | 22.9 | 3.32 | 20.9 | 2.93 | <0.001 |
| SMI (kg/m2) | 6.79 | 1.12 | 7.95 | 0.93 | 6.22 | 0.67 | <0.001 |
| PhA (°) | 5.46 | 0.88 | 5.94 | 0.92 | 5.24 | 0.76 | <0.001 |
| Variable | Body Weight | BMI | SMI | PhA | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | r | r | r | |||||
| Total (n = 168) | ||||||||
| Height (cm) | 0.387 | ** | −0.088 | −0.0550 | −0.082 | |||
| Body Weight (kg) | 0.879 | ** | 0.590 | ** | 0.151 | |||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 0.655 | ** | 0.189 | * | ||||
| SMI (kg/m2) | 0.467 | ** | ||||||
| MZ (n = 150) | ||||||||
| Height (cm) | 0.370 | ** | −0.094 | −0.066 | −0.107 | |||
| Body Weight (kg) | 0.885 | ** | 0.618 | ** | 0.127 | |||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 0.681 | ** | 0.163 | * | ||||
| SMI (kg/m2) | 0.390 | ** | ||||||
| DZ (n = 18) | ||||||||
| Height (cm) | 0.527 | * | −0.060 | −0.029 | −0.029 | |||
| Body Weight (kg) | 0.813 | ** | 0.376 | 0.171 | ||||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 0.464 | 0.232 | ||||||
| SMI (kg/m2) | 0.605 | ** | ||||||
| Variable | −2LL | AIC | p-Value | A (95% CI) | C (95% CI) | E (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Height (cm) | ||||||
| ACE | 1782 | 1119 | - | - | - | - |
| AE | 1783 | 1117 | 0.558 | 0.932 (0.908–0.950) | - | 0.068 (0.050–0.091) |
| CE | 1831 | 1165 | <0.01 | - | 0.888 (0.851–0.916) | 0.112 (0.084–0.149) |
| E | 2092 | 1424 | <0.01 | - | - | - |
| Body Weight (kg) | ||||||
| ACE | 2228 | 1564 | - | - | - | - |
| AE | 2228 | 1562 | 1.000 | 0.758 (0.682–0.817) | - | 0.242 (0.183–0.318) |
| CE | 2241 | 1575 | <0.01 | - | 0.704 (0.619–0.772) | 0.296 (0.228–0.381) |
| E | 2356 | 1688 | <0.01 | - | - | - |
| BMI (kg/m2) | ||||||
| ACE | 1568 | 904.0 | - | - | - | - |
| AE | 1568 | 902.0 | 1.000 | 0.718 (0.630–0.786) | - | 0.282 (0.214–0.370) |
| CE | 1585 | 919.1 | <0.01 | - | 0.645 (0.548–0.725) | 0.355 (0.275–0.451) |
| E | 1675 | 1007 | <0.01 | - | - | - |
| SMI (kg/m2) | ||||||
| ACE | 699.8 | 55.83 | - | - | - | - |
| AE | 700.4 | 54.43 | 0.439 | 0.513 (0.457–0.625) | - | 0.487 (0.375–0.543) |
| CE | 700.9 | 54.89 | 0.304 | - | 0.467 (0.337–0.579) | 0.533 (0.421–0.663) |
| E | 740.1 | 92.10 | <0.01 | - | - | - |
| PhA (°) | ||||||
| ACE | 1783 | 1119 | - | - | - | - |
| AE | 1783 | 1117 | 0.558 | 0.506 (0.341–0.642) | - | 0.494 (0.358–0.659) |
| CE | 1831 | 1165 | <0.01 | - | 0.281 (0.137–0.414) | 0.718 (0.585–0.863) |
| E | 2092 | 1424 | <0.01 | - | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matsumoto, D.; Inui, F.; Honda, C.; Tomizawa, R.; Watanabe, M.; Silventoinen, K.; Sakai, N. Heritability and Environmental Correlation of Phase Angle with Anthropometric Measurements: A Twin Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7810. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17217810
Matsumoto D, Inui F, Honda C, Tomizawa R, Watanabe M, Silventoinen K, Sakai N. Heritability and Environmental Correlation of Phase Angle with Anthropometric Measurements: A Twin Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(21):7810. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17217810
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatsumoto, Daisuke, Fujio Inui, Chika Honda, Rie Tomizawa, Mikio Watanabe, Karri Silventoinen, and Norio Sakai. 2020. "Heritability and Environmental Correlation of Phase Angle with Anthropometric Measurements: A Twin Study" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 21: 7810. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17217810
APA StyleMatsumoto, D., Inui, F., Honda, C., Tomizawa, R., Watanabe, M., Silventoinen, K., & Sakai, N. (2020). Heritability and Environmental Correlation of Phase Angle with Anthropometric Measurements: A Twin Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(21), 7810. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17217810






