Correlation of Pre-Hypertension with Carotid Artery Damage in Middle-Aged and Older Adults
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. Body Composition and Blood Pressure Assessment
2.3. Carotid Artery Characteristics Assessment
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murakami, S.; Otsuka, K.; Hotta, N.; Yamanaka, G.; Kubo, Y.; Matsuoka, O.; Yamanaka, T.; Shinagawa, M.; Nunoda, S.; Nishimura, Y.; et al. Common carotid intima-media thickness is predictive of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in elderly community-dwelling people: Longitudinal Investigation for the Longevity and Aging in Hokkaido County (LILAC) study. Biomed. Pharm. 2005, 59, S49–S53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijk, J.M.; van der Graaf, Y.; Bots, M.L.; Grobbee, D.E.; Algra, A. Carotid intima-media thickness and the risk of new vascular events in patients with manifest atherosclerotic disease: The SMART study. Eur. Heart J. 2006, 27, 1971–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenz, M.W.; von Kegler, S.; Steinmetz, H.; Markus, H.S.; Sitzer, M. Carotid intima-media thickening indicates a higher vascular risk across a wide age range: Prospective data from the Carotid Atherosclerosis Progression Study (CAPS). Stroke 2006, 37, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokubo, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Higashiyama, A.; Nakao, Y.M.; Nakamura, F.; Miyamoto, Y. Impact of Intima-Media Thickness Progression in the Common Carotid Arteries on the Risk of Incident Cardiovascular Disease in the Suita Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e007720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kablak-Ziembicka, A.; Przewlocki, T.; Tracz, W.; Pieniazek, P.; Musialek, P.; Sokolowski, A.; Drwila, R.; Rzeznik, D. Carotid intima-media thickness in pre- and postmenopausal women with suspected coronary artery disease. Heart Vessel. 2008, 23, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polak, J.F.; Pencina, M.J.; Pencina, K.M.; O’Donnell, C.J.; Wolf, P.A.; D’Agostino, R.B., Sr. Carotid-wall intima-media thickness and cardiovascular events. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.H.; Chen, J.R.; Chiu, H.C.; Pan, W.H. Lower blood flow velocity, higher resistance index, and larger diameter of extracranial carotid arteries are associated with ischemic stroke independently of carotid atherosclerosis and cardiovascular risk factors. J. Clin. Ultrasound Jcu 2007, 35, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozakova, M.; Morizzo, C.; La Carrubba, S.; Fabiani, I.; Della Latta, D.; Jamagidze, J.; Chiappino, D.; Di Bello, V.; Palombo, C. Associations between common carotid artery diameter, Framingham risk score and cardiovascular events. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. Nmcd 2017, 27, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, S.Y.; Bai, C.H.; Cheng, H.M.; Chen, J.R.; Yeh, W.T.; Hsu, P.F.; Liu, W.L.; Pan, W.H. Common carotid artery end-diastolic velocity is independently associated with future cardiovascular events. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2016, 23, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellinazzi, V.R.; Cipolli, J.A.; Pimenta, M.V.; Guimaraes, P.V.; Pio-Magalhaes, J.A.; Coelho-Filho, O.R.; Biering-Sorensen, T.; Matos-Souza, J.R.; Sposito, A.C.; Nadruz, W., Jr. Carotid flow velocity/diameter ratio is a predictor of cardiovascular events in hypertensive patients. J. Hypertens 2015, 33, 2054–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoving, A.M.; de Vries, E.E.; Mikhal, J.; de Borst, G.J.; Slump, C.H. A Systematic Review for the Design of In Vitro Flow Studies of the Carotid Artery Bifurcation. Cardiovasc. Eng. Technol. 2020, 11, 111–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zouggari, L.; Bou-said, B.; Massi, F.; Culla, A.; Millon, A. The Role of Biomechanics in the Assessment of Carotid Atherosclerosis Severity: A Numerical Approach. World J. Vasc. Surg. 2018, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Khakpour, S.; Abas, W.A.B.W.; Razak, N.A.A.; Osman, N.A.A. Carotid atherosclerosis disease: A review of diagnosis, risk factors and simulations. Clin. Case Rep. Rev. 2016, 2, 537–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neupane, D.; McLachlan, C.S.; Sharma, R.; Gyawali, B.; Khanal, V.; Mishra, S.R.; Christensen, B.; Kallestrup, P. Prevalence of hypertension in member countries of South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC): Systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2014, 93, e74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Wang, H.; Liao, H. Prehypertension is associated with increased carotid atherosclerotic plaque in the community population of Southern China. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2013, 13, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamoto, R.; Kohara, K.; Tabara, Y.; Abe, M.; Kusunoki, T.; Miki, T. Insulin resistance and prevalence of prehypertension and hypertension among community-dwelling persons. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2010, 17, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Khanam, M.A.; Lindeboom, W.; Razzaque, A.; Niessen, L.; Milton, A.H. Prevalence and determinants of pre-hypertension and hypertension among the adults in rural Bangladesh: Findings from a community-based study. BMC Public Health 2015, 15, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmanian, K.; Shojaie, M. The prevalence of pre-hypertension and its association to established cardiovascular risk factors in south of Iran. BMC Res. Notes 2012, 5, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbina, E.M.; Khoury, P.R.; McCoy, C.; Daniels, S.R.; Kimball, T.R.; Dolan, L.M. Cardiac and vascular consequences of pre-hypertension in youth. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2011, 13, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuspidi, C.; Sala, C.; Tadic, M.; Gherbesi, E.; Grassi, G.; Mancia, G. Pre-hypertension and subclinical cardiac damage: A meta-analysis of echocardiographic studies. Int. J. Cardiol. 2018, 270, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manios, E.; Tsivgoulis, G.; Koroboki, E.; Stamatelopoulos, K.; Papamichael, C.; Toumanidis, S.; Stamboulis, E.; Vemmos, K.; Zakopoulos, N. Impact of prehypertension on common carotid artery intima-media thickness and left ventricular mass. Stroke 2009, 40, 1515–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.L.; Shiel, L.M.; Teede, H.; Kotsopoulos, D.; McNeil, J.; Cameron, J.D.; McGrath, B.P. Effects of Blood Pressure, Smoking, and Their Interaction on Carotid Artery Structure and Function. Hypertension 2001, 37, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tan, J.R.; Chen, Y.H.; Bi, Y.F.; Xu, M.; Huang, Y.; Dai, M.; Ning, G.; Li, X.Y. Prehypertension is associated with atherosclerosis in Type 2 diabetes. J. Diabetes 2010, 2, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannami, T.; Baba, S.; Ogata, J. Potential of carotid enlargement as a useful indicator affected by high blood pressure in a large general population of a Japanese city: The Suita study. Stroke 2000, 31, 2958–2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verwoert, G.C.; Franco, O.H.; Hoeks, A.P.; Reneman, R.S.; Hofman, A.; CM, V.D.; Sijbrands, E.J.; Witteman, J.C.; Mattace-Raso, F.U. Arterial stiffness and hypertension in a large population of untreated individuals: The Rotterdam Study. J. Hypertens 2014, 32, 1606–1612, discussion 1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Park, J.B.; Kim, K.I.; Kim, J.H.; Yang, D.H.; Pyun, W.B.; Kim, Y.G.; Kim, G.H.; Chae, S.C.; Guideline Committee of the Korean Society of Hypertension. 2013 Korean Society of Hypertension guidelines for the management of hypertension: Part I-epidemiology and diagnosis of hypertension. Clin. Hypertens. 2015, 21, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ihm, S.H.; Bakris, G.; Sakuma, I.; Sohn, I.S.; Koh, K.K. Controversies in the 2017 ACC/AHA Hypertension Guidelines: Who Can Be Eligible for Treatments under the New Guidelines?—An Asian Perspective. Circ. J. Off. J. Jpn. Circ. Soc. 2019, 83, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, H.K.; Ram, C.V.S. Recent Guidelines for Hypertension. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 984–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Park, H. Effects of 6 months of aerobic and resistance exercise training on carotid artery intima media thickness in overweight and obese older women. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2017, 17, 2304–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyaki, A.; Maeda, S.; Yoshizawa, M.; Misono, M.; Saito, Y.; Sasai, H.; Kim, M.K.; Nakata, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Ajisaka, R. Effect of habitual aerobic exercise on body weight and arterial function in overweight and obese men. Am. J. Cardiol. 2009, 104, 823–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambless, L.E.; Heiss, G.; Folsom, A.R.; Rosamond, W.; Szklo, M.; Sharrett, A.R.; Clegg, L.X. Association of coronary heart disease incidence with carotid arterial wall thickness and major risk factors: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study, 1987–1993. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1997, 146, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, C.R.L.; Salles, G.C.; Leite, N.C.; Salles, G.F. Prognostic impact of carotid intima-media thickness and carotid plaques on the development of micro- and macrovascular complications in individuals with type 2 diabetes: The Rio de Janeiro type 2 diabetes cohort study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2019, 18, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romanens, M.; Sudano, I.; Adams, A.; Warmuth, W. Advanced carotid atherosclerosis in middle-aged subjects: Comparison with PROCAM and SCORE risk categories, the potential for reclassification and cost-efficiency of carotid ultrasound in the setting of primary care. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2019, 149, w20006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katakami, N.; Kaneto, H.; Shimomura, I. Carotid ultrasonography: A potent tool for better clinical practice in diagnosis of atherosclerosis in diabetic patients. J. Diabetes Investig. 2014, 5, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasha, S.M.; Wiria, A.E.; Wammes, L.J.; Smit, J.W.; Partono, F.; Supali, T.; Yazdanbakhsh, M.; Tamsma, J.T. Blood pressure class and carotid artery intima-media thickness in a population at the secondary epidemiological transition. J. Hypertens. 2011, 29, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.C.; Jeng, J.S.; Chien, K.L.; Sung, F.C.; Hsu, H.C.; Lee, Y.T. Hypertension status is the major determinant of carotid atherosclerosis: A community-based study in Taiwan. Stroke 2001, 32, 2265–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaussier, H.; Masson, I.; Collin, C.; Bozec, E.; Laloux, B.; Calvet, D.; Zidi, M.; Boutouyrie, P.; Laurent, S. Carotid plaque, arterial stiffness gradient, and remodeling in hypertension. Hypertension 2008, 52, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myredal, A.; Gan, L.M.; Osika, W.; Friberg, P.; Johansson, M. Increased intima thickness of the radial artery in individuals with prehypertension and hypertension. Atherosclerosis 2010, 209, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijk, J.M.; Algra, A.; van der Graaf, Y.; Grobbee, D.E.; Bots, M.L.; SMART Study Group. Carotid stiffness and the risk of new vascular events in patients with manifest cardiovascular disease. The SMART study. Eur. Heart J. 2005, 26, 1213–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Sloten, T.T.; Sedaghat, S.; Laurent, S.; London, G.M.; Pannier, B.; Ikram, M.A.; Kavousi, M.; Mattace-Raso, F.; Franco, O.H.; Boutouyrie, P.; et al. Carotid stiffness is associated with incident stroke: A systematic review and individual participant data meta-analysis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 66, 2116–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Dinenno, F.A.; Monahan, K.D.; DeSouza, C.A.; Seals, D.R. Carotid artery wall hypertrophy with age is related to local systolic blood pressure in healthy men. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2001, 21, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gando, Y.; Yamamoto, K.; Kawano, H.; Murakami, H.; Ohmori, Y.; Kawakami, R.; Sanada, K.; Higuchi, M.; Tabata, I.; Miyachi, M. Attenuated age-related carotid arterial remodeling in adults with a high level of cardiorespiratory fitness. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2011, 18, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirata, K.; Yaginuma, T.; O’Rourke, M.F.; Kawakami, M. Age-related changes in carotid artery flow and pressure pulses: Possible implications for cerebral microvascular disease. Stroke 2006, 37, 2552–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeersch, S.J.; Rietzschel, E.R.; De Buyzere, M.L.; De Bacquer, D.; De Backer, G.; Van Bortel, L.M.; Gillebert, T.C.; Verdonck, P.R.; Segers, P. Age and gender related patterns in carotid-femoral PWV and carotid and femoral stiffness in a large healthy, middle-aged population. J. Hypertens. 2008, 26, 1411–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, S.Y.; Bai, C.H.; Chen, J.R.; Yeh, W.T.; Chen, H.J.; Chiu, H.C.; Shiu, R.S.; Pan, W.H. Common carotid end-diastolic velocity and intima-media thickness jointly predict ischemic stroke in Taiwan. Stroke 2011, 42, 1338–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.; Pearman, M.E.; Park, W.; Alkatan, M.; Machin, D.R.; Tanaka, H. Impact of blood pressure perturbations on arterial stiffness. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2015, 309, R1540–R1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt-Trucksass, A.; Grathwohl, D.; Schmid, A.; Boragk, R.; Upmeier, C.; Keul, J.; Huonker, M. Structural, functional, and hemodynamic changes of the common carotid artery with age in male subjects. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1999, 19, 1091–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, Y.; Saxena, V.; Mittal, M.; Srivastava, M.; Raghuvanshi, S. Age-Wise Association of Carotid Intima Media Thickness in Ischemic Stroke. Ann. Neurosci. 2017, 24, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, K.D.; Barinas-Mitchell, E.; Kuller, L.H.; Mackey, R.H.; Wong, E.A.; Sutton-Tyrrell, K. Common carotid artery diameter and cardiovascular risk factors in overweight or obese postmenopausal women. Int. J. Vasc. Med. 2012, 2012, 169323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Total (n = 544) | Normotensive (n = 274) | Pre-Hypertensive (n = 150) | Hypertensive (n = 120) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, male/female | 83/461 | 43/231 | 17/133 | 23/97 | |
| Age, years | 55.2 ± 18.2 | 46.3 ± 16.3 | 62.0 ± 16.4 # | 67.0 ± 13.7 # ƒ | <0.001 |
| Height, cm | 158.7 ± 7.2 | 159.9 ± 7.7 | 157.8 ± 6.8 # | 157.1 ± 6.5 # | <0.001 |
| Body mass, kg | 60.3 ± 9.2 | 59.5 ± 9.1 | 61.3 ± 9.4 | 60.8 ± 8.8 | |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 23.9 ± 3.0 | 23.2 ± 2.9 | 24.6 ± 3.1 # | 24.6 ± 2.9 # | <0.001 |
| Body fat mass, % | 32.0 ± 8.2 | 29.7 ± 7.6 | 33.8 ± 8.1 # | 35.3 ± 7.7 # ƒ | <0.001 |
| Lean body mass, kg | 40.8 ± 7.8 | 41.7 ± 8.2 | 40.4 ± 7.6 | 39.0 ± 6.7 # | <0.001 |
| Waist to hip ratio | 0.89 ± 0.1 | 0.86 ± 0.1 | 0.90 ± 0.1 # | 0.92 ± 0.1 # ƒ | <0.001 |
| Systolic blood pressure, mmHg | 123.8 ± 14.5 | 112.5 ± 5.0 | 129.9 ± 6.3 # | 142.1 ± 13.1 # ƒ | <0.001 |
| Diastolic blood pressure, mmHg | 76.3 ± 8.1 | 72.4 ± 5.5 | 79.0 ± 7.2 # | 81.8 ± 9.7 # ƒ | <0.001 |
| Physical activity, Mets min/week | 1923.0 ± 2195.3 | 2935.4 ± 2497.5 | 1667.4 ± 1849.7 # | 1163.9 ± 1490.1 # ƒ | <0.001 |
| Cardiovascular disease, n | 10 | 6 | 2 | 2 | |
| Stroke, n | 6 | 3 | 1 | 2 | |
| Lung disease, n | 7 | 4 | 1 | 1 | |
| Musculoskeletal disorders, n | 78 | 10 | 32 | 36 | <0.001 |
| Hypertension, n | 120 | 120 | <0.001 | ||
| Diabetes, n | 33 | 11 | 29 | 6 | <0.001 |
| Hyperlipidemia, n | 52 | 28 | 12 | 12 | <0.042 |
| * Alcohol drinking, n | 403 | 217 | 107 | 79 | <0.014 |
| * Smoking, n | 81 | 33 | 18 | 30 | <0.002 |
| Variable | Systolic Blood Pressure, mmHg | Diastolic Blood Pressure, mmHg |
|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 0.464 *** | 0.093 * |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 0.257 *** | 0.203 *** |
| Body fat mass percent, % | 0.276 *** | 0.149 *** |
| Lean body mass, kg | −0.069 | 0.007 |
| Waist to hip ratio | 0.372 *** | 0.181 *** |
| Physical activity, Mets min/week | 0.200 *** | 0.026 |
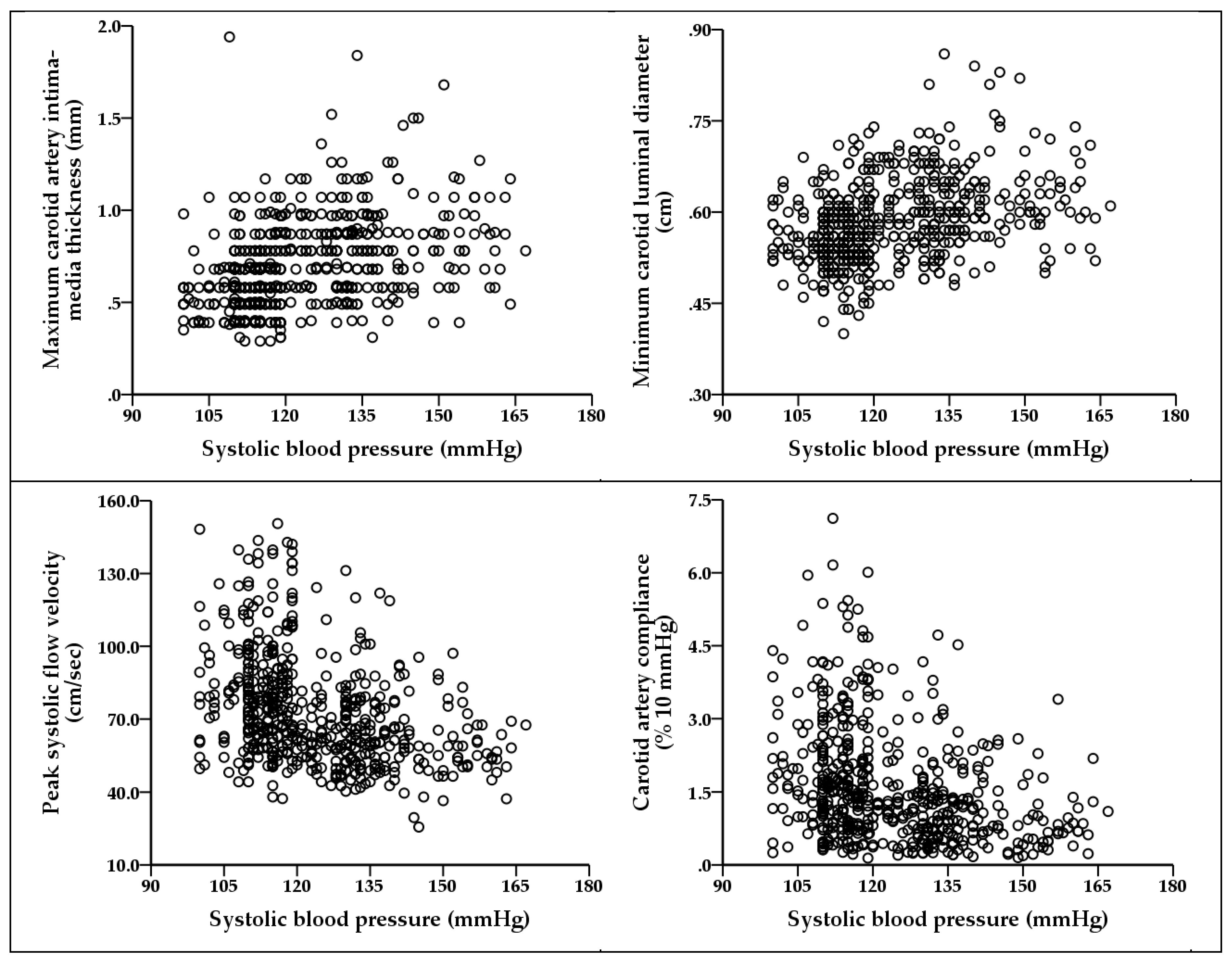
| Intima-media thickness max, mm | 0.400 *** | 0.115 ** |
| Intima-media thickness min, mm | 0.423 *** | 0.136 ** |
| Intima-media thickness mean, mm | 0.421 *** | 0.127 ** |
| Luminal diameter max, cm | 0.308 *** | 0.080 |
| Luminal diameter min, cm | 0.367 *** | 0.138 ** |
| IMT/luminal diameter max | 0.330 *** | 0.069 |
| Peak-systolic flow velocity, cm/sec | −0.361 *** | −0.184 *** |
| End-diastolic flow velocity, cm/sec | −0.366 *** | −0.070 |
| PFV/luminal diameter max, s−1 | −0.400 *** | −0.205 *** |
| EFV/luminal diameter min, s−1 | −0.393 *** | −0.091 * |
| Carotid artery compliance, % 10 mmHg | −0.307 ** | −0.166 *** |
| β-stiffness index, AU | 0.231 *** | 0.023 |
| Variable | ANOVA | ANCOVA | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normotensive (n = 274) | Pre-Hypertensive (n= 150) | Hypertensive (n = 120) | Crude | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | ||||
| p-Value | F-Value | p-Value | F-Value | p-Value | F-Value | p-Value | ||||
| IMTmax, mm | 0.59 ± 0.2 | 0.77 ± 0.2 # | 0.85 ± 0.2 # ƒ | <0.001 | 40.689 | <0.001 | 25.505 | <0.001 | 8.780 | <0.001 |
| IMTmean, mm | 0.55 ± 0.2 | 0.71 ± 0.2 # | 0.77 ± 0.2 # ƒ | <0.001 | 44.797 | <0.001 | 28.356 | <0.001 | 10.153 | <0.001 |
| IMTmin, mm | 0.51 ± 0.1 | 0.65 ± 0.2 # | 0.70 ± 0.2 # ƒ | <0.001 | 43.694 | <0.001 | 27.439 | <0.001 | 10.240 | <0.001 |
| LDmax, cm | 0.60 ± 0.1 | 0.64 ± 0.1 # | 0.67 ± 0.1 # ƒ | <0.001 | 22.772 | <0.001 | 16.159 | <0.001 | 11.829 | <0.001 |
| LDmin, cm | 0.56 ± 0.1 | 0.60 ± 0.1 # | 0.63 ± 0.1 # ƒ | <0.001 | 35.800 | <0.001 | 24.619 | <0.001 | 15.531 | <0.001 |
| IMTmax/LDmax | 0.93 ± 0.3 | 1.19 ± 0.4 # | 1.25 ± 0.4 # | <0.001 | 23.055 | 0.097 | 13.687 | <0.001 | 2.557 | 0.078 |
| PFV, cm/s | 83.1 ± 23.5 | 66.1 ± 17.1 # | 61.5 ± 14.5 # | <0.001 | 39.778 | 0.001 | 25.341 | <0.001 | 7.760 | <0.001 |
| EFV, cm/s | 25.0 ± 4.7 | 21.3 ± 5.1 # | 19.7 ± 5.9 # ƒ | <0.001 | 25.959 | <0.001 | 16.944 | <0.001 | 9.284 | <0.001 |
| PFV/LDmin, s−1 | 151.8 ± 49.6 | 112.8 ± 35.5 # | 100.5 ± 29.5 # | <0.001 | 48.966 | <0 001 | 31.493 | <0.001 | 12.261 | <0.001 |
| EFV/LDmax, s−1 | 41.9 ± 9.4 | 34.1 ± 9.9 # | 30.4 ± 10.9 # ƒ | <0.001 | 34.334 | <0.001 | 23.197 | <0.001 | 14.141 | <0.001 |
| CAC, % 10 mmHg | 1.95 ± 1.3 | 1.31 ± 1.0 # | 1.15 ± 0.8 # | <0.001 | 18.218 | <0.001 | 10.614 | <0.001 | 2.731 | 0.066 |
| β-stiffness index, AU | 8.9 ± 8.2 | 12.5 ± 10.0 # | 14.1 ± 12.1 # | <0.001 | 8.487 | <0.001 | 5.513 | 0.004 | 1.815 | 0.164 |
| Variable | 19–39 Years | 40–59 Years | ≥60 Years | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normotensive (n = 78) | Pre-Hypertensive (n = 12) | Hypertensive (n = 6) | p-Value | Normotensive (n = 144) | Pre-Hypertensive (n= 49) | Hypertensive (n = 35) | p-Value | Normotensive (n = 52) | Pre-Hypertensive (n = 89) | Hypertensive (n = 79) | p-Value | |
| IMTmax, mm | 0.45 ± 0.1 | 0.54 ± 0.2 | 0.55 ± 0.0 | 0.001 | 0.60 ± 0.1 | 0.64 ± 0.1 | 0.68 ± 0.1 | 0.016 | 0.78 ± 0.2 | 0.88 ± 0.2 | 0.95 ± 0.2 | <0.001 |
| IMTmean, mm | 0.42 ± 0.1 | 0.52 ± 0.1 | 0.51 ± 0.0 | <0.001 | 0.56 ± 0.1 | 0.60 ± 0.1 | 0.63 ± 0.1 | 0.020 | 0.70 ± 0.1 | 0.80 ± 0.2 | 0.86 ± 0.2 | <0.001 |
| IMTmin, mm | 0.39 ± 0.1 | 0.49 ± 0.1 | 0.48 ± 0.1 | <0.001 | 0.52 ± 0.1 | 0.55 ± 0.1 | 0.58 ± 0.1 | 0.048 | 0.63 ± 0.1 | 0.72 ± 0.1 | 0.77 ± 0.2 | <0.001 |
| LDmax, cm | 0.60 ± 0.1 | 0.62 ± 0.0 | 0.64 ± 0.0 | 0.168 | 0.60 ± 0.1 | 0.62 ± 0.1 | 0.63 ± 0.1 | 0.008 | 0.62 ± 0.1 | 0.65 ± 0.1 | 0.68 ± 0.1 | <0.001 |
| LDmin, cm | 0.53 ± 0.1 | 0.57 ± 0.0 | 0.59 ± 0.0 | 0.004 | 0.56 ± 0.1 | 0.58 ± 0.1 | 0.60 ± 0.1 | <0.001 | 0.58 ± 0.07 | 0.61 ± 0.07 | 0.64 ± 0.08 | <0.001 |
| IMTmax/LDmax | 0.72 ± 0.1 | 0.76 ± 0.2 | 0.82 ± 0.2 | 0.026 | 0.96 ± 0.3 | 0.98 ± 0.3 | 1.01 ± 0.3 | 0.528 | 1.20 ± 0.30 | 1.40 ± 0.33 | 1.40 ± 0.41 | 0.008 |
| PFV, cm/s | 104.2 ± 23.1 | 98.1 ± 18.6 | 81.0 ± 17.2 | 0.044 | 77.4 ± 18.2 | 69.1 ± 17.3 | 69.6 ± 14.1 | 0.004 | 67.1 ± 13.9 | 60.1 ± 10.4 | 56.5 ± 11.5 | <0.001 |
| EFV, cm/s | 25.3 ± 4.1 | 25.4 ± 2.2 | 24.0 ± 5.4 | 0.733 | 25.7 ± 4.4 | 23.0 ± 4.9 | 24.1 ± 3.7 | 0.001 | 22.4 ± 4.9 | 19.8 ± 5.0 | 17.4 ± 5.5 | <0.001 |
| PFV/LDmin, s−1 | 196.6 ± 47.4 | 174.1 ± 32.8 | 138.5 ± 33.1 | 0.006 | 139.8 ± 38.5 | 121.4 ± 37.8 | 117.8 ± 28.0 | <0.001 | 118.2 ± 31.7 | 99.8 ± 22.2 | 89.9 ± 23.7 | <0.001 |
| EFV/LDmax, s−1 | 42.5 ± 8.3 | 40.8 ± 4.1 | 37.7 ± 9.1 | 0.320 | 43.2 ± 8.9 | 37.5 ± 9.1 | 38.6 ± 7.3 | <0.001 | 36.9 ± 10.2 | 31.3 ± 10.0 | 26.1 ± 9.9 | <0.001 |
| CAC, % 10 mmHg | 2.9 ± 1.5 | 2.2 ± 1.3 | 1.8 ± 0.9 | 0.100 | 1.7 ± 1.1 | 1.5 ± 1.0 | 1.3 ± 0.9 | 0.087 | 1.4 ± 0.8 | 1.1 ± 0.7 | 1.1 ± 0.7 | 0.047 |
| β-stiffness index, AU | 5.5 ± 5.2 | 7.0 ± 6.9 | 7.2 ± 4.1 | 0.557 | 9.4 ± 7.3 | 9.5 ± 5.6 | 13.1 ± 9.5 | 0.023 | 12.7 ± 11.8 | 14.9 ± 11.4 | 15.1 ± 13.2 | 0.509 |
| Variables | Model 1 OR (95% CI) | Model 2 OR (95% CI) | Model 3 OR (95% CI) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normotensive | Pre-Hypertensive | Hypertensive | Normotensive | Pre-Hypertensive | Hypertensive | Normotensive | Pre-Hypertensive | Hypertensive | |
| IMTmax (cut-off: ≥1.00 mm) | 1.0 (ref.) | 5.40 ** (1.786–16.536) | 14.72 *** (4.952–43.730) | 1.0 (ref.) | 4.20 *** (1.292–13.652) | 10.65 *** (3.426–33.118) | 1.0 (ref.) | 2.30 (0.688–7.714) | 5.90 ** (1.833–18.968) |
| LDmax (cut-off: ≥0.68 cm) | 1.0 (ref.) | 3.32 *** (1.897–5.807) | 3.73 *** (2.043–6.798) | 1.0 (ref.) | 2.70 ** (1.494–4.885) | 3.04 ** (1.606–5.770) | 1.0 (ref.) | 2.10 * (1.133–3.888) | 2.38 * (1.226–4.614) |
| LDmin (cut-off: ≥0.63 cm) | 1.0 (ref.) | 6.01 *** (2.527–7.756) | 4.43 *** (3.304–10.938) | 1.0 (ref.) | 3.52 *** (1.953–6.353) | 4.69 *** (2.486–8.828) | 1.0 (ref.) | 2.55 *** (1.7902–6.632) | 3.45 ** (1.380–4.713) |
| PFV (cut-off: ≤57.5 cm/s) | 1.0 (ref.) | 3.14 *** (2.262–5.669) | 3.18 *** (2.312–6.493) | 1.0 (ref.) | 2.41 ** (1.332–4.373) | 2.64 ** (1.519–4.597) | 1.0 (ref.) | 1.68 (0.931–3.025) | 1.62 (0.871–3.029) |
| EFV (cut-off: ≤19.5 cm/s) | 1.0 (ref.) | 3.78 *** (2.221–6.434) | 4.53 *** (2.558–8.036) | 1.0 (ref.) | 3.06 *** (1.751–5.331) | 3.36 *** (1.845–6.106) | 1.0 (ref.) | 1.96 * (1.086–3.545) | 2.29 * (1.220–4.286) |
| PFV/LDmin (cut-off: ≤94.0 s−1) | 1.0 (ref.) | 4.38 *** (2.527–7.605) | 5.16 *** (2.863–9.316) | 1.0 (ref.) | 3.56 *** (2.004–6.306) | 3.90 *** (2.116–7.178) | 1.0 (ref.) | 2.20 * (1.194–4.035) | 2.55 ** (1.341–4.832) |
| EFV/LDmax (cut-off: ≤30.0 s−1) | 1.0 (ref.) | 4.25 *** (2.377–7.597) | 7.06 *** (3.848–12.967) | 1.0 (ref.) | 3.29 *** (1.793–6.034) | 5.32 *** (2.826–10.015) | 1.0 (ref.) | 2.04 * (1.077–3.870) | 3.58 *** (1.852–6.921) |
| CAC, % 10 mmHg (cut-off: ≤0.75 % 10 mmHg) | 1.0 (ref.) | 2.27 ** (1.373–3.738) | 3.22 *** (1.870–5.534) | 1.0 (ref.) | 2.02 ** (1.192–3.404) | 2.93 *** (1.657–5.179) | 1.0 (ref.) | 1.50 (0.865–2.590) | 2.17 * (1.204–3.915) |
| β-stiffness index, AU (cut-off: ≥12.9 AU) | 1.0 (ref.) | 1.94 ** (1.183–3.186) | 2.68 *** (1.563–4.588) | 1.0 (ref.) | 1.84 * (1.089–3.094) | 2.65 ** (1.495–4.670) | 1.0 (ref.) | 1.41 (0.815–2.422) | 2.02 * (1.120–3.628) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, J.; Na, Y.; Jang, Y.; Park, S.-Y.; Park, H. Correlation of Pre-Hypertension with Carotid Artery Damage in Middle-Aged and Older Adults. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7686. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17207686
Park J, Na Y, Jang Y, Park S-Y, Park H. Correlation of Pre-Hypertension with Carotid Artery Damage in Middle-Aged and Older Adults. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(20):7686. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17207686
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Jinkee, Yongseong Na, Yunjung Jang, Song-Young Park, and Hyuntae Park. 2020. "Correlation of Pre-Hypertension with Carotid Artery Damage in Middle-Aged and Older Adults" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 20: 7686. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17207686
APA StylePark, J., Na, Y., Jang, Y., Park, S.-Y., & Park, H. (2020). Correlation of Pre-Hypertension with Carotid Artery Damage in Middle-Aged and Older Adults. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(20), 7686. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17207686






