Similarities between the Effects of Prenatal Chlorpyrifos and Valproic Acid on Ultrasonic Vocalization in Infant Wistar Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Animals
2.2. Administration Protocols
- CNT (n = 8): One subcutaneous injection of 1 mL/kg of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) for four days.
- CPF (n = 8): One subcutaneous injection of 1 mg/kg of CPF [O, O-dietil O-3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl phosphorothioate (Pestanal, Sigma Aldrich)] dissolved in DMSO, for four days.
- VPA (n = 9): One subcutaneous injection of 400 mg/kg body weight of VPA (with the aim of avoiding possible maternal death (Kim et al., 2011)), dissolved in 0.9% saline at a concentration of 250 mg/mL; and three daily subcutaneous injections with saline only.
2.3. Ultrasonic Vocalizations (PND7)
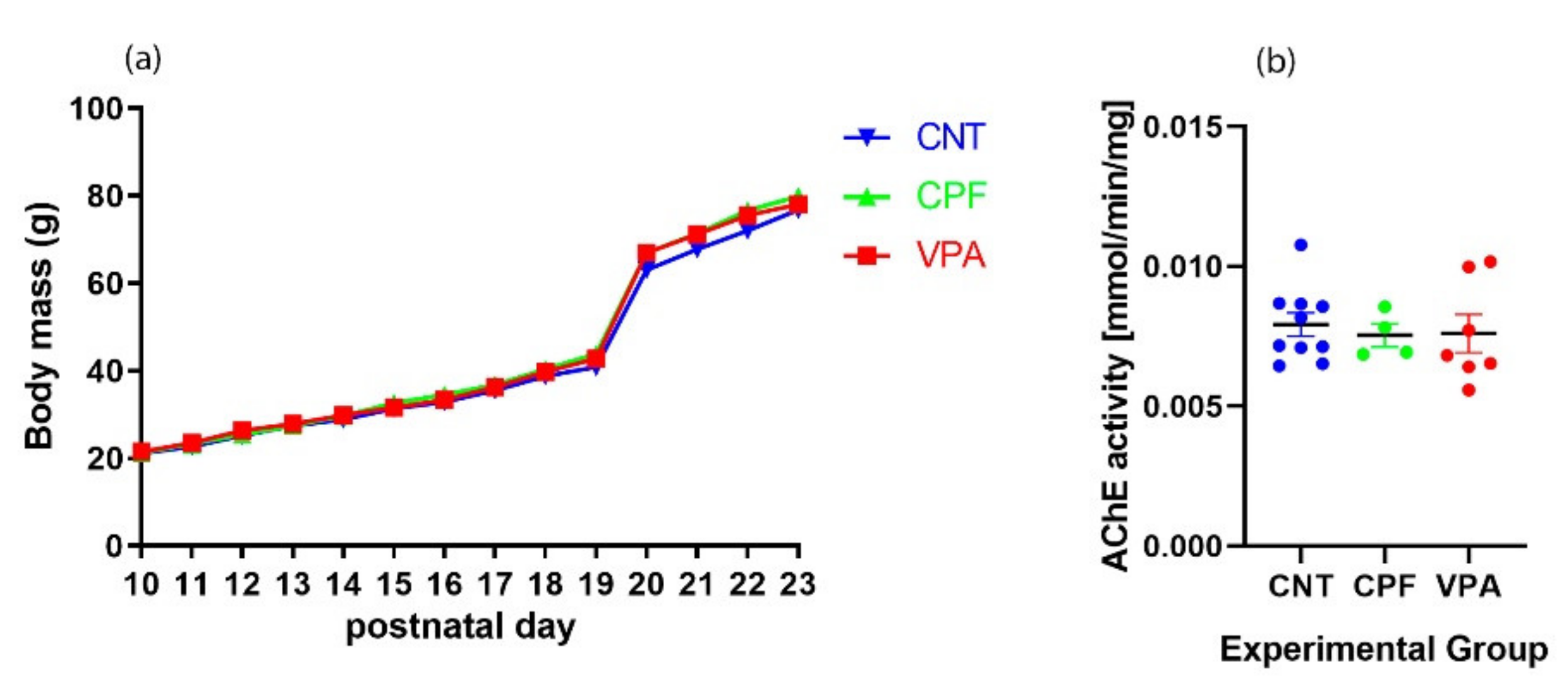
2.4. Acetylcholinesterase Activity
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
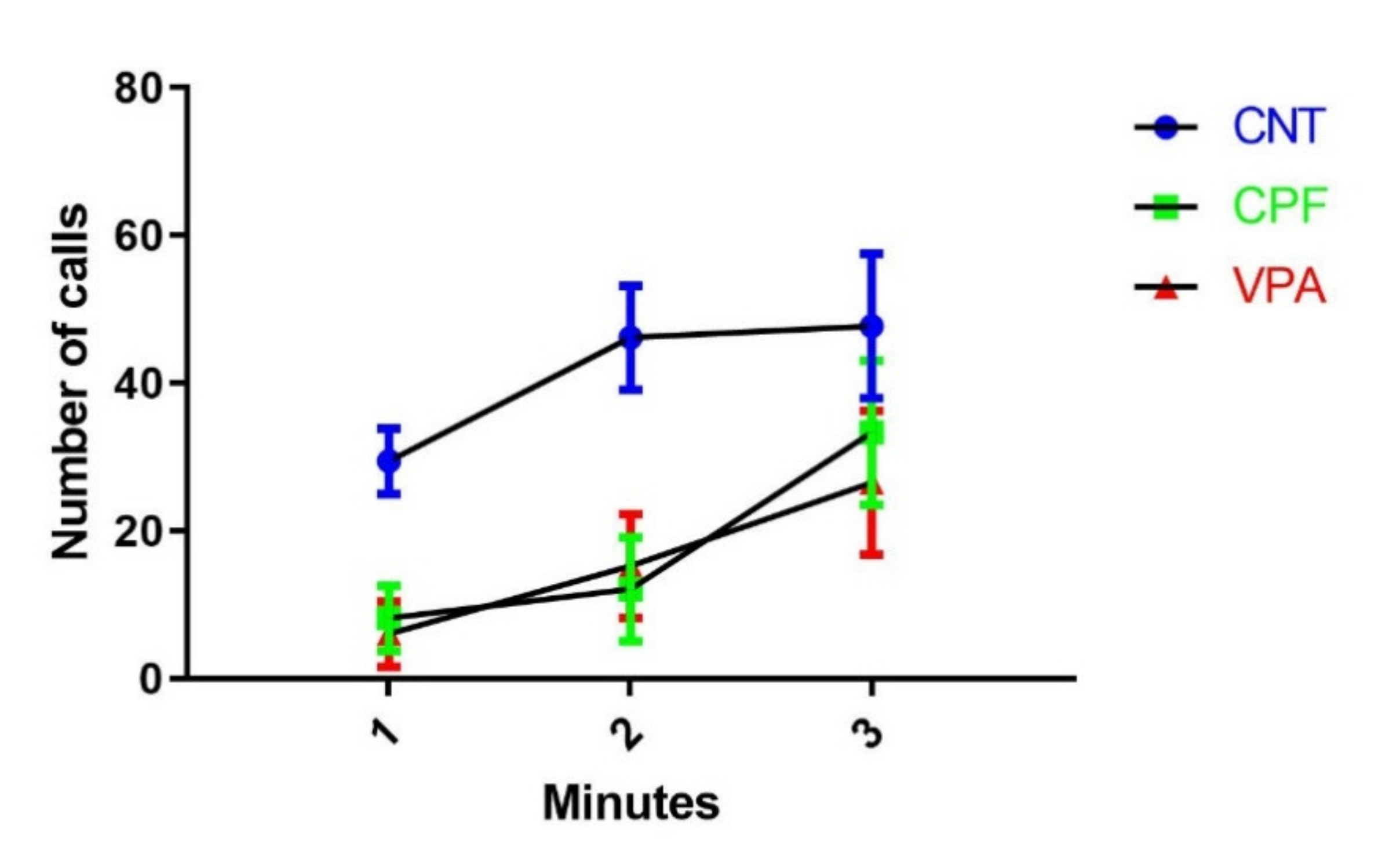
3.1. Developmental Markers
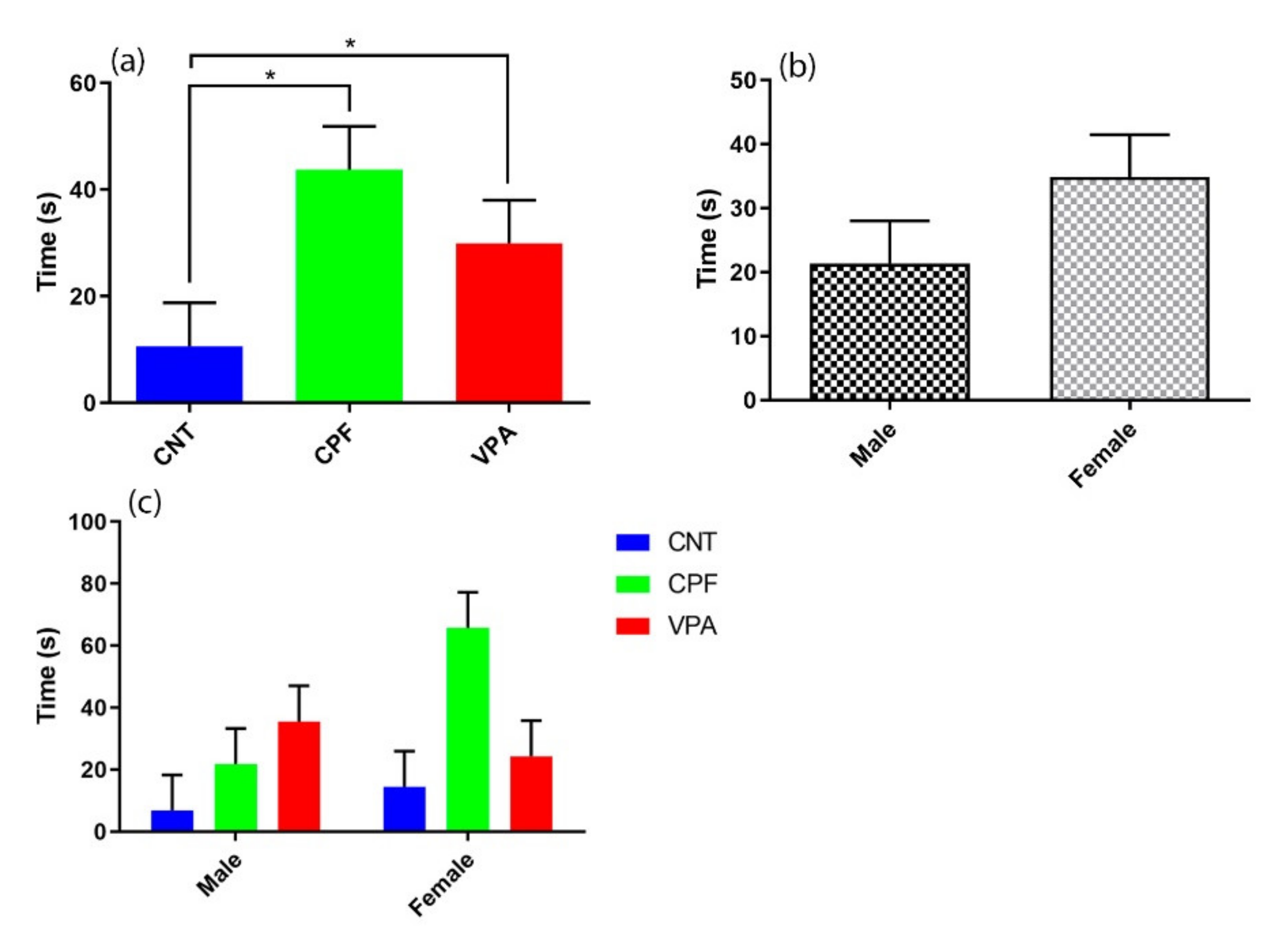
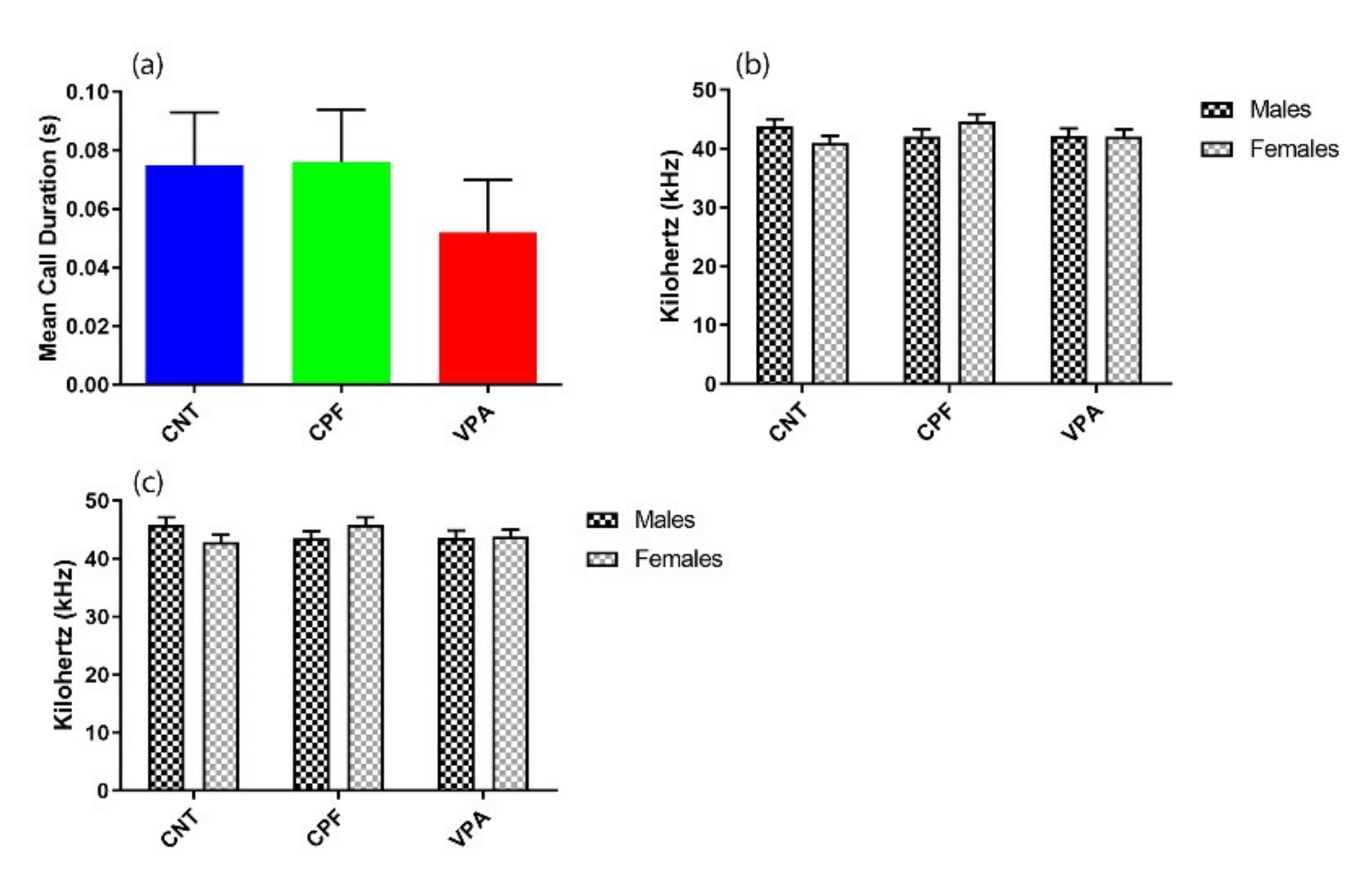
3.2. Ultrasonic Vocalization Recordings
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Zippelius, H.M.; Schleidt, W.M. Ultraschall-Laute bei jungen Mäusen. Naturwissenschaften 1956, 43, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolus, J.B.; Rincón-Cortés, M.; Sullivan, R.M.; Mouly, A.-M. Understanding pup affective state through ethologically significant ultrasonic vocalization frequency. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheinkopf, S.J.; Iverson, J.M.; Rinaldi, M.L.; Lester, B.M. Atypical Cry Acoustics in 6-Month-Old Infants at Risk for Autism Spectrum Disorder. Autism Res. 2012, 5, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gyawali, S.; Patra, B.N. Autism spectrum disorder: Trends in research exploring etiopathogenesis. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2019, 73, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persico, A.M.; Merelli, S. Environmental Factors in the Onset of Autism Spectrum Disorder. Curr. Dev. Disord. Rep. 2014, 1, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mabunga, D.F.N.; Gonzales, E.L.T.; Kim, J.-W.; Kim, K.C.; Shin, C.Y. Exploring the Validity of Valproic Acid Animal Model of Autism. Exp. Neurobiol. 2015, 24, 285–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bambini-Junior, V.; Zanatta, G.; Nunes, G.D.F.; de Melo, G.M.; Michels, M.; Fontes-Dutra, M.; Freire, V.N.; Riesgo, R.; Gottfried, C. Resveratrol prevents social deficts in animal model of autism induced by valproic acid. Neurosci. Lett. 2014, 583, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, T.; Przewłocki, R.; Przewłocki, R. Behavioral Alterations in Rats Prenatally Exposed to Valproic Acid: Animal Model of Autism. Neuropsychopharmacology 2005, 30, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellmann, K.A.; Varlinskaya, E.I.; Mooney, S.M. d-Cycloserine ameliorates social alterations that result from prenatal exposure to valproic acid. Brain Res. Bull. 2014, 108, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shelton, J.F.; Geraghty, E.M.; Tancredi, D.J.; Delwiche, L.D.; Schmidt, R.J.; Ritz, B.; Hansen, R.L.; Hertz-Picciotto, I. Neurodevelopmental Disorders and Prenatal Residential Proximity to Agricultural Pesticides: The CHARGE Study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 1103–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reserved, A.R. Ecological Risk Assessment for Chlorpyrifos in Terrestrial and Aquatic Systems in the United States; Giesy, J.P., Solomon, K.R., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; Volume 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, D.L.; Daroff, R.B.; Autrup, H.; Bridges, J.; Buffler, P.; Costa, L.G.; Coyle, J.; McKhann, G.; Mobley, W.C.; Nadel, L.; et al. Review of the Toxicology of Chlorpyrifos With an Emphasis on Human Exposure and Neurodevelopment. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2008, 38, 1–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saunders, M.; Magnanti, B.L.; Carreira, S.C.; Yang, A.; Álamo-Hernández, U.; Riojas-Rodríguez, H.; Calamandrei, G.; Koppe, J.G.; Von Krauss, M.K.; Keune, H.; et al. Chlorpyrifos and neurodevelopmental effects: A literature review and expert elicitation on research and policy. Environ. Health 2012, 11, S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roberts, E.M.; English, P.B.; Grether, J.K.; Windham, G.C.; Somberg, L.; Wolff, C. Maternal Residence Near Agricultural Pesticide Applications and Autism Spectrum Disorders among Children in the California Central Valley. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 1482–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Williams, A.L.; DeSesso, J.M. Gestational/Perinatal chlorpyrifos exposure is not associated with autistic-like behaviors in rodents. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2014, 44, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, A.; Kalimian, M.; Amram, B.; Kofman, O. Prenatal chlorpyrifos leads to autism-like deficits in C57Bl6/J mice. Environ. Health 2017, 16, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Venerosi, A.; Ricceri, L.; Scattoni, M.L.; Calamandrei, G. Prenatal chlorpyrifos exposure alters motor behavior and ultrasonic vocalization in cd-1 mouse pups. Environ. Health 2009, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Venerosi, A.; Tait, S.; Stecca, L.; Chiarotti, F.; De Felice, A.; Cometa, M.F.; Volpe, M.T.; Calamandrei, G.; Ricceri, L. Effects of maternal chlorpyrifos diet on social investigation and brain neuroendocrine markers in the offspring—A mouse study. Environ. Health 2015, 14, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Da Silva, J.G.; Boareto, A.C.; Schreiber, A.K.; Redivo, D.D.; Gambeta, E.; Vergara, F.; Morais, H.; Zanoveli, J.M.; Dalsenter, P.R. Chlorpyrifos induces anxiety-like behavior in offspring rats exposed during pregnancy. Neurosci. Lett. 2017, 641, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazevic, S.; Merkler, M.; Persic, D.; Hranilovic, D. Chronic postnatal monoamine oxidase inhibition affects affiliative behavior in rat pupso. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2017, 153, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofer, M.A.; Shair, H.N.; Brunelli, S.A. Ultrasonic Vocalizations in Rat and Mouse Pups. Curr. Protoc. Neurosci. 2001, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wöhr, M.; Schwarting, R.K. Maternal care, isolation-induced infant ultrasonic calling, and their relations to adult anxiety-related behavior in the rat. Behav. Neurosci. 2008, 122, 310–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, E.; Copping, N.A.; Rivera, J.K.; Pride, M.C.; Careaga, M.; Bauman, M.D.; Berman, R.F.; Lein, P.; Harony-Nicolas, H.; Buxbaum, J.D.; et al. Developmental social communication deficits in the Shank3 rat model of phelan-mcdermid syndrome and autism spectrum disorder. Autism Res. 2018, 11, 587–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, J.M.; Gourdon, J.C.; Clarke, P.B.S. Identification of multiple call categories within the rich repertoire of adult rat 50-kHz ultrasonic vocalizations: Effects of amphetamine and social context. Psychopharmacology 2010, 211, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffey, K.R.; Marx, R.G.; Neumaier, J.F. DeepSqueak: A deep learning-based system for detection and analysis of ultrasonic vocalizations. Neuropsychopharmacology 2019, 44, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ellman, G.L.; Courtney, K.; Andres, V.; Featherstone, R.M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1961, 7, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, E.J.; Graham, D.L.; Money, K.M.; Stanwood, G.D. Developmental Consequences of Fetal Exposure to Drugs: What We Know and What We Still Must Learn. Neuropsychopharmacology 2014, 40, 61–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breslin, W.J.; Liberacki, A.B.; Dittenber, D.A.; Quast, J.F. Evaluation of the developmental and reproductive toxicity of chlorpyrifos in the rat. Fundam. Appl. Toxicol. 1996, 29, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandal, M.J.; Edgar, J.C.; Ehrlichman, R.S.; Mehta, M.; Roberts, T.P.L.; Siegel, S.J. Validating γ Oscillations and Delayed Auditory Responses as Translational Biomarkers of Autism. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 68, 1100–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tyzio, R.; Nardou, R.; Ferrari, D.C.; Tsintsadze, T.; Shahrokhi, A.; Eftekhari, S.; Khalilov, I.; Brouchoud, C.; Chazal, G.; Lemonnier, E.; et al. Oxytocin-Mediated GABA Inhibition During Delivery Attenuates Autism Pathogenesis in Rodent Offspring. Science 2014, 343, 675–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieminska, E.; Toczyłowska, B.; Diamandakis, D.; Hilgier, W.; Filipkowski, R.K.; Polowy, R.; Orzel, J.; Gorka, M.; Lazarewicz, J.W. Glutamate, Glutamine and GABA Levels in Rat Brain Measured Using MRS, HPLC and NMR Methods in Study of Two Models of Autism. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vogel, A.P.; Tsanas, A.; Scattoni, M.L. Quantifying ultrasonic mouse vocalizations using acoustic analysis in a supervised statistical machine learning framework. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sagiv, S.K.; Harris, M.H.; Gunier, R.B.; Kogut, K.R.; Harley, K.G.; Deardorff, J.; Bradman, A.; Holland, N.; Eskenazi, B. Prenatal Organophosphate Pesticide Exposure and Traits Related to Autism Spectrum Disorders in a Population Living in Proximity to Agriculture. Environ. Health Perspect. 2018, 126, 047012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portfors, C.V. Types and functions of ultrasonic vocalizations in laboratory rats and mice. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2007, 46, 28–34. [Google Scholar]
- Sales, G.D. Strain Differences in the Ultrasonic Behavior of Rats (Rattus Norvegicus). Am. Zool. 1979, 19, 513–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wöhr, M.; Houx, B.; Schwarting, R.K.; Spruijt, B. Effects of experience and context on 50-kHz vocalizations in rats. Physiol. Behav. 2008, 93, 766–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, L.K.; Yoon, T.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, J.J. Strain and sex differences in fear conditioning: 22 kHz ultrasonic vocalizations and freezing in rats. Psychol. Neurosci. 2009, 2, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hill, A.P.; Zuckerman, K.; Fombonne, E. Epidemiology of Autism Spectrum Disorders. In Translational Approaches to Autism Spectrum Disorder; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 13–38. [Google Scholar]
- Posar, A.; Visconti, P. Autism in 2016: The need for answers. J. Pediatr. 2017, 93, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roy, T.S.; Seidler, F.J.; Slotkin, T.A. Morphologic effects of subtoxic neonatal chlorpyrifos exposure in developing rat brain: Regionally selective alterations in neurons and glia. Dev. Brain Res. 2004, 148, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, E.W.Y.; Winn, L.M. Valproic Acid Increases Formation of Reactive Oxygen Species and Induces Apoptosis in Postimplantation Embryos: A Role for Oxidative Stress in Valproic Acid-Induced Neural Tube Defects. Mol. Pharmacol. 2011, 80, 979–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldridge, J.E.; Meyer, A.; Seidler, F.J.; Slotkin, T.A. Alterations in Central Nervous System Serotonergic and Dopaminergic Synaptic Activity in Adulthood after Prenatal or Neonatal Chlorpyrifos Exposure. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyabu, A.; Narita, M.; Tashiro, Y. The effects of prenatal exposure to valproic acid on the initial development of serotonergic neurons. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2013, 31, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Group | PND12.5 | PND13.5 | PND14.5 | PND15.5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNT | DMSO | DMSO | DMSO | DMSO |
| CPF | CPF-Drug | CPF-Drug | CPF-Drug | CPF-Drug |
| VPA | VPA-Drug | Saline | Saline | Saline |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morales-Navas, M.; Castaño-Castaño, S.; Pérez-Fernández, C.; Sánchez-Gil, A.; Teresa Colomina, M.; Leinekugel, X.; Sánchez-Santed, F. Similarities between the Effects of Prenatal Chlorpyrifos and Valproic Acid on Ultrasonic Vocalization in Infant Wistar Rats. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6376. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17176376
Morales-Navas M, Castaño-Castaño S, Pérez-Fernández C, Sánchez-Gil A, Teresa Colomina M, Leinekugel X, Sánchez-Santed F. Similarities between the Effects of Prenatal Chlorpyrifos and Valproic Acid on Ultrasonic Vocalization in Infant Wistar Rats. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(17):6376. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17176376
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorales-Navas, Miguel, Sergio Castaño-Castaño, Cristian Pérez-Fernández, Ainhoa Sánchez-Gil, María Teresa Colomina, Xavier Leinekugel, and Fernando Sánchez-Santed. 2020. "Similarities between the Effects of Prenatal Chlorpyrifos and Valproic Acid on Ultrasonic Vocalization in Infant Wistar Rats" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 17: 6376. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17176376
APA StyleMorales-Navas, M., Castaño-Castaño, S., Pérez-Fernández, C., Sánchez-Gil, A., Teresa Colomina, M., Leinekugel, X., & Sánchez-Santed, F. (2020). Similarities between the Effects of Prenatal Chlorpyrifos and Valproic Acid on Ultrasonic Vocalization in Infant Wistar Rats. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(17), 6376. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17176376







