Effects of Pyramid Resistance-Training System with Different Repetition Zones on Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Older Women: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Subjects
2.3. Body Composition
2.4. Biochemical Analysis
2.5. Resistance Training Program
2.6. Dietary Intake
2.7. Statistical Analyses
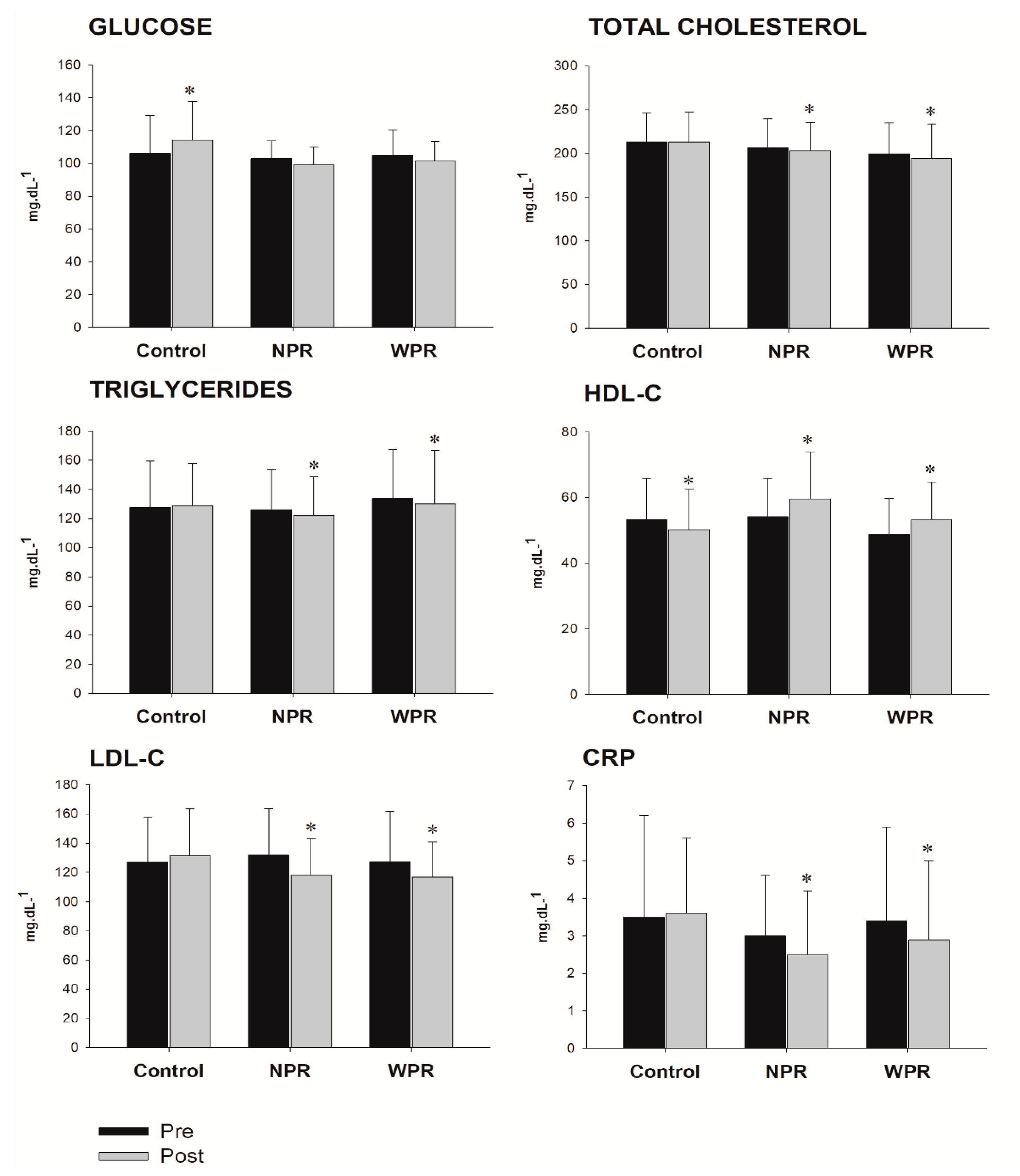
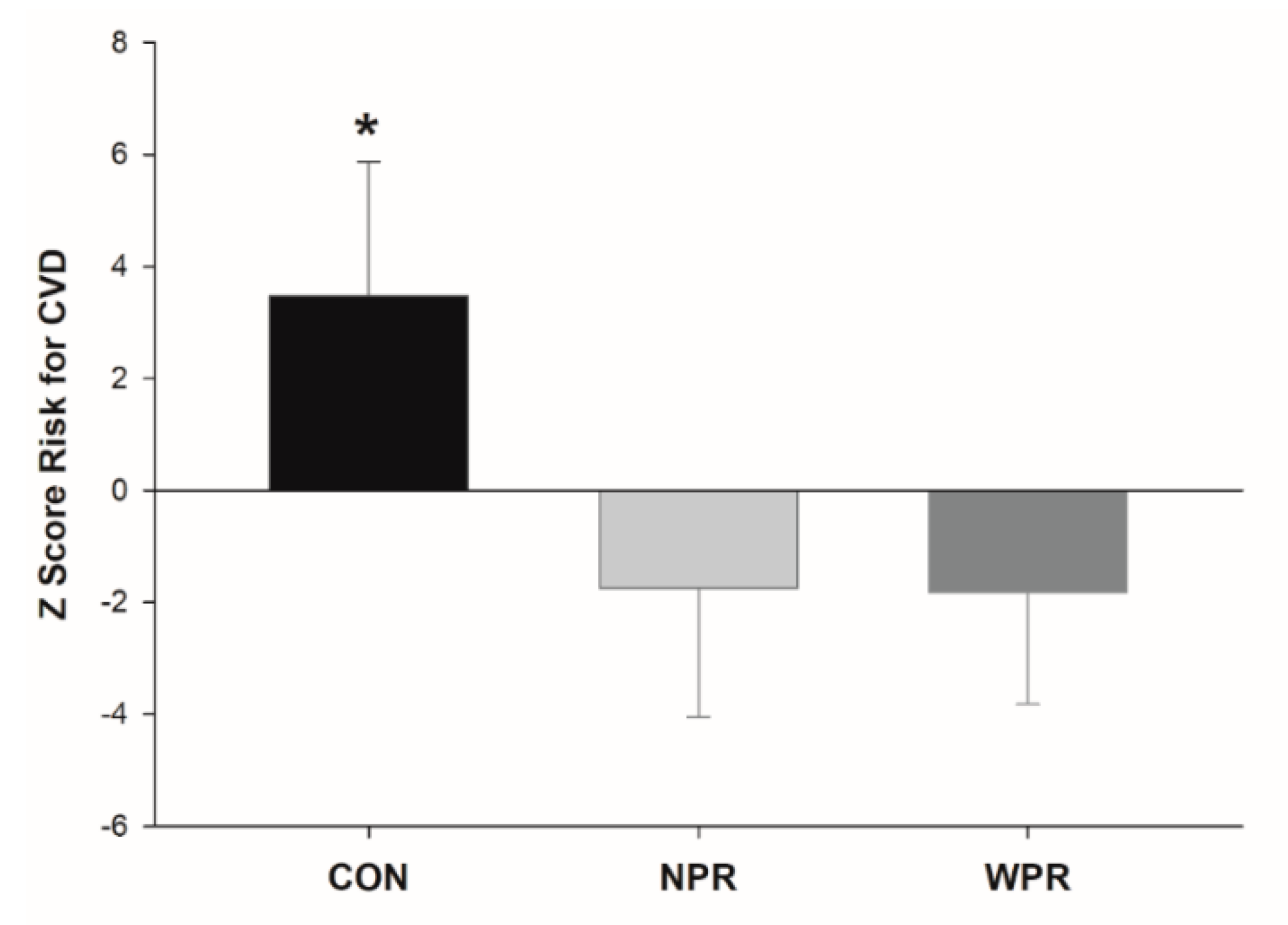
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Woodward, M. Cardiovascular disease and the female disadvantage. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Hong, X.; Wilker, E.; Li, Z.; Zhang, W.; Jin, D.; Liu, X.; Zang, T.; Xu, X.; Xu, X. Effects of age at menarche, reproductive years, and menopause on metabolic risk factors for cardiovascular diseases. Atherosclerosis 2008, 196, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, K.A.; Crawford, S.L.; Chae, C.U.; Everson-Rose, S.A.; Sowers, M.F.; Sternfeld, B.; Sutton-Tyrrell, K. Are changes in cardiovascular disease risk factors in midlife women due to chronological aging or to the menopausal transition? J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 54, 2366–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Leeuw, J.; Wassink, A.M.; van der Graaf, Y.; Westerveld, H.E.; Visseren, F.L. Second Manifestations of ARTerial Disease (SMART) Study Group. Age-related differences in abdominal fat distribution in premenopausal and postmenopausal women with cardiovascular disease. Menopause 2013, 20, 409–417. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.G.; Carr, M.C.; Murdoch, S.J.; Mitchell, E.; Woods, N.F.; Wener, M.H.; Chandler, W.L.; Boyko, E.J.; Brunzell, J.D. Adipokines, inflammation, and visceral adiposity across the menopausal transition: A prospective study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 1104–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragala, M.S.; Cadore, E.L.; Dorgo, S.; Izquierdo, M.; Kraemer, W.J.; Peterson, M.D.; Peterson, M.D.; Ryan, E.D. Resistance training for older adults: Position statement from the National Strength and Conditioning Association. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2019, 33, 2019–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westcott, W.L. Resistance training is medicine: Effects of strength training on health. Curr. Sports Med. Rep. 2012, 11, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ACSM. American College of Sports Medicine position stand. Quantity and quality of exercise for developing and maintaining cardiorespiratory, musculoskeletal, and neuromotor fitness in apparently healthy adults: Guidance for prescribing exercise. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2011, 43, 1334–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, L.J.O.; Davey, S.L.; Evans, W.J.; Campbell, W.W. Differential effect of resistance training on the body composition and lipoprotein-lipid profile in older men and women. Metabolism. 1999, 48, 1474–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ACSM. American College of Sports Medicine position stand. Progression models in resistance training for healthy adults. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2009, 41, 687–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toselli, S.; Badicu, G.; Bragonzoni, L.; Spiga, F.; Mazzuca, P.; Campa, F. Comparison of the effect of different resistance training frequencies on phase angle and handgrip strength in obese women: A randomized controlled trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunes, J.P.; Ribeiro, A.S.; Schoenfeld, B.J.; Cyrino, E.S. Comment on: “Comparison of periodized and non-periodized resistance training on maximal strength: A meta-analysis”. Sports Med. 2018, 48, 491–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoenfeld, B.J.; Grgic, J.; Ogborn, D.; Krieger, J.W. Strength and hypertrophy adaptations between low- versus high-load resistance training: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2017, 31, 3508–3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoenfeld, B.J.; Ogborn, D.; Krieger, J.W. Dose-response relationship between weekly resistance training volume and increases in muscle mass: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Sports Sci. 2017, 35, 1073–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, V.C.; de Salles, B.F.; Trajano, G.S. Volume for muscle hypertrophy and health outcomes: The most effective variable in resistance training. Sports Med. 2018, 48, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, R.W.; Colenso-Semple, L.; Phillips, S.M. Training for strength and hypertrophy: An evidence-based approach. Curr. Opin. Physiol. 2019, 10, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelissen, V.A.; Fagard, R.H.; Coeckelberghs, E.; Vanhees, L. Impact of resistance training on blood pressure and other cardiovascular risk factors: A meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials. Hypertension 2011, 58, 950–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, P.M.; Tomeleri, C.M.; Nascimento, M.A.; Mayhew, J.L.; Cavalcante, E.F.; Trindade, L.; Barbosa, D.S.; Venturini, D.; Cyrino, E.S. Comparation of low- and high-volume of resistance training on body fat, and blood biomarkers in untrained older women: A randomized clinical trial. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2019. Ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, P.M.; Ribeiro, A.S.; Nunes, J.P.; Tomeleri, C.M.; Nascimento, M.A.; Moraes, G.K.; Junior, P.S.; Barbosa, D.S.; Venturini, D.; Cyrino, E.S. Resistance training performed with single-set is sufficient to reduce cardiovascular risk factors in untrained older women: The randomized clinical trial. Active Aging Longitudinal. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2019, 81, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, A.S.; Schoenfeld, B.J.; Souza, M.F.; Tomeleri, C.M.; Venturini, D.; Barbosa, D.S.; Cyrino, E.S. Traditional and pyramidal resistance training systems improve muscle quality and metabolic biomarkers in older women: A randomized crossover study. Exp. Gerontol. 2016, 79, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, A.S.; Schoenfeld, B.J.; Aguiar, A.F.; Nunes, J.P.; Cavalcante, E.F.; Cadore, E.L.; Cyrino, E.S. Effects of different resistance training systems on muscular strength and hypertrophy in resistance-trained older women. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2018, 32, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos, L.; Ribeiro, A.S.; Cavalcante, E.F.; Nabuco, H.C.G.; Antunes, M.; Schoenfeld, B.J.; Cyrino, E.S. Effects of modified pyramid system on muscular strength and hypertrophy in older women. Int. J. Sports Med. 2018, 39, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos, L.; Ribeiro, A.S.; Gobbo, L.A.; Nunes, J.P.; Cunha, P.M.; Campa, F.; Toselli, S.; Schoenfeld, B.J.; Sardinha, L.B.; Cyrino, E.S. Effects of resistance training with different pyramid systems on bioimpedance vector patterns, body composition, and cellular health in older women: A randomized controlled trial. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pina, F.L.C.; Nunes, J.P.; Ribeiro, A.S.; Nascimento, M.A.; Cyrino, L.T.; Carneiro, N.H.; Venturini, D.; Barbosa, D.S.; Mayhew, J.L.; Cyrino, E.S. Comparison of the effects of different weekly frequencies of resistance training on metabolic health markers and body fat in older women. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fitness 2020, 60, 618–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedewald, W.T.; Levy, R.I.; Fredrickson, D.S. Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin. Chem. 1972, 18, 499–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J. A power primer. Psychol. Bull. 1992, 112, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sepe, A.; Tchkonia, T.; Thomou, T.; Zamboni, M.; Kirkland, J.L. Aging and regional differences in fat cell progenitors—A mini-review. Gerontology 2011, 57, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcante, E.F.; Ribeiro, A.S.; Do Nascimento, M.A.; Silva, A.M.; Tomeleri, C.M.; Nabuco, H.C.; Pina, F.L.; Mayhew, J.L.; Da Silva-Grigoletto, M.E.; da Silva, D.R.; et al. Effects of different resistance training frequencies on fat in overweight/obese older women. Int. J. Sports Med. 2018, 39, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, G.R.; Kekes-Szabo, T.; Treuth, M.S.; Williams, M.J.; Goran, M.; Pichon, C. Intra-abdominal adipose tissue, physical activity and cardiovascular risk in pre- and post-menopausal women. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 1996, 20, 860–865. [Google Scholar]
- Pina, F.L.C.; Nunes, J.P.; Schoenfeld, B.J.; Nascimento, M.A.; Gerage, A.M.; Januário, R.S.; Carneiro, N.H.; Cyrino, E.S.; Oliveira, A.R. Effects of different weekly sets-equated resistance training frequencies on muscular strength, muscle mass, and body fat in older women. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2019. Ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charro, M.A.; Aoki, M.S.; Coutts, A.J.; Araujo, R.C.; Bacurau, R.F. Hormonal, metabolic and perceptual responses to different resistance training systems. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fitness 2010, 50, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lambert, C.P.; Flynn, M.G. Fatigue during high-intensity intermittent exercise: Application to bodybuilding. Sports Med. 2002, 32, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Eckel, R.H. Lipoprotein lipase: From gene to obesity. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 297, E271–E288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Salles, B.F.; Simão, R.; Fleck, S.J.; Dias, I.; Kraemer-Aguiar, L.G.; Bouskela, E. Effects of resistance training on cytokines. Int. J. Sports Med. 2010, 31, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomeleri, C.M.; Souza, M.F.; Burini, R.C.; Cavaglieri, C.R.; Ribeiro, A.S.; Antunes, M.; Nunes, J.P.; Venturini, D.; Barbosa, D.S.; Sardinha, L.B.; et al. Resistance training reduces metabolic syndrome and inflammatory markers in older women: A randomized controlled trial. J. Diabetes. 2018, 10, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Fung, E.; Xu, A.; Lan, H.Y. C-reactive protein and ageing. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2017, 44, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | Control (n = 19) | Narrow Repetition Zone (n = 20) | Wide Repetition Zone (n = 20) | Interaction p−Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total body fat (kg) | Pre | 28.0 ± 10.5 | 26.8 ± 8.9 | 29.2 ± 7.9 | 0.14 |
| Post | 28.8 ± 11.8 | 26.4 ± 10.0 * | 28.6 ± 7.8 * | ||
| ∆% | +2.8 | −1.5 | −2.1 | ||
| Android body fat (kg) | Pre | 2.5 ± 1.2 | 2.6 ± 0.8 | 2.8 ± 1.0 | <0.01 |
| Post | 2.8 ± 1.0 * | 2.5 ± 0.9 * | 2.6 ± 1.2 * | ||
| ∆% | +10.8 | −4.3 | −8.1 | ||
| Gynoid body fat (kg) | Pre | 4.9 ± 1.5 | 5.1 ± 1.6 | 5.1 ± 1.3 | 0.63 |
| Post | 4.9 ± 1.7 | 5.0 ± 1.7 * | 5.0 ± 1.2 * | ||
| ∆% | +0.4 | −2.0 | −2.0 | ||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
dos Santos, L.; Ribeiro, A.S.; Nunes, J.P.; Tomeleri, C.M.; Nabuco, H.C.G.; Nascimento, M.A.; Sugihara Junior, P.; Fernandes, R.R.; Campa, F.; Toselli, S.; et al. Effects of Pyramid Resistance-Training System with Different Repetition Zones on Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Older Women: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6115. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17176115
dos Santos L, Ribeiro AS, Nunes JP, Tomeleri CM, Nabuco HCG, Nascimento MA, Sugihara Junior P, Fernandes RR, Campa F, Toselli S, et al. Effects of Pyramid Resistance-Training System with Different Repetition Zones on Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Older Women: A Randomized Controlled Trial. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(17):6115. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17176115
Chicago/Turabian Styledos Santos, Leandro, Alex S. Ribeiro, João Pedro Nunes, Crisieli M. Tomeleri, Hellen C. G. Nabuco, Matheus A. Nascimento, Paulo Sugihara Junior, Rodrigo R. Fernandes, Francesco Campa, Stefania Toselli, and et al. 2020. "Effects of Pyramid Resistance-Training System with Different Repetition Zones on Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Older Women: A Randomized Controlled Trial" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 17: 6115. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17176115
APA Styledos Santos, L., Ribeiro, A. S., Nunes, J. P., Tomeleri, C. M., Nabuco, H. C. G., Nascimento, M. A., Sugihara Junior, P., Fernandes, R. R., Campa, F., Toselli, S., Venturini, D., Barbosa, D. S., Sardinha, L. B., & Cyrino, E. S. (2020). Effects of Pyramid Resistance-Training System with Different Repetition Zones on Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Older Women: A Randomized Controlled Trial. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(17), 6115. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17176115










