Ecotoxicity Evaluation of Pure Peracetic Acid (PAA) after Eliminating Hydrogen Peroxide from Commercial PAA
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Chemical Analyses
2.2. Peracetic Acid Concentration Profiles
2.3. Bioassays
2.3.1. Microbial Toxicity
2.3.2. Crustaceans Immobilization Test
2.3.3. Algal Growth Inhibition Test
2.3.4. Statistical Analyses of Bioassays
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation of Pure PAA
3.2. Toxicity Values
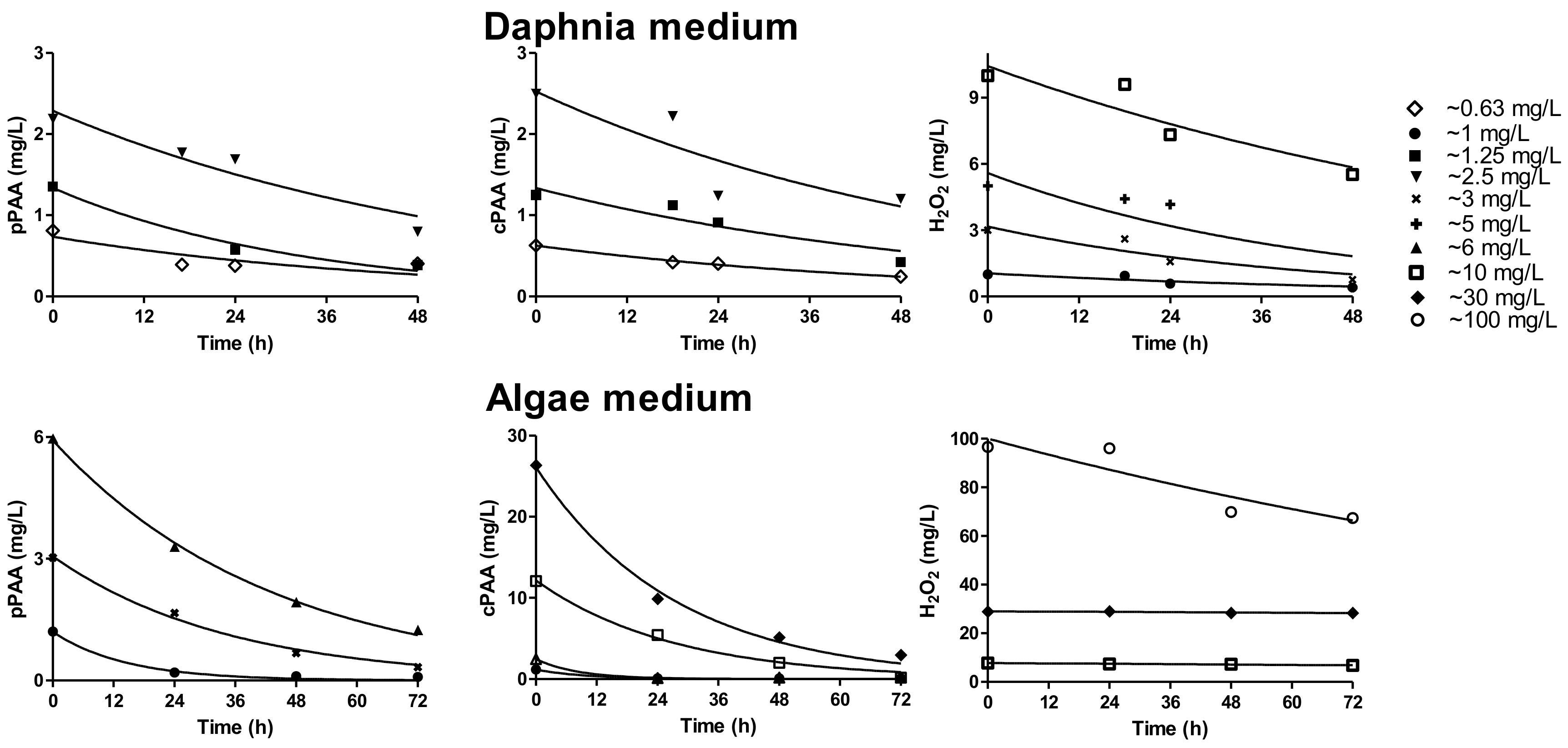
3.3. Concentration Profiles in Test Media
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- White, G.C. Handbook of Chlorination and Alternative Disinfectants, 5th ed.; John Wiley and Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bayo, J.; Angosto, J.M.; Gómez-López, M.D. Ecotoxicological screening of reclaimed disinfected wastewater by Vibrio fischeri bioassay after a chlorination-dechlorination process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 172, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurizzo, C.; Antonelli, M.; Profaizer, M.; Romele, L. By-Products in surface and reclaimed water disinfected with various agents. Desalination 2005, 176, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrudey, S.E.; Charrois, W.J. Disinfection By-Products and Human Health; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2012; ISBN 9781843395195. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, K.; Shaw, G.; Leusch, F.D.L.; Knight, N.L. Chlorine disinfection by-products in wastewater effluent: Bioassay-Based assessment of toxicological impact. Water Res. 2012, 46, 6069–6083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falsanisi, D.; Gehr, R.; Santoro, D.; Dell’Erba, A.; Notarnicola, M.; Liberti, L.; Dell’Erba, A.; Notarnicola, M.; Liberti, L. Kinetics of PAA demand and its implications on disinfection of wastewaters. Water Qual. Res. J. Can. 2006, 41, 398–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, S.; Antonelli, M.; Mezzanotte, V.; Nurizzo, C. Peracetic acid disinfection: A feasible alternative to wastewater chlorination. Water Environ. Res. 2007, 79, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoro, D.; Gehr, R.; Bartrand, T.A.; Liberti, L.; Notarnicola, M.; Dell’Erba, A.; Falsanisi, D.; Haas, C.N. Wastewater Disinfection by Peracetic Acid: Assessment of Models for Tracking Residual Measurements and Inactivation. Water Environ. Res. 2007, 79, 775–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonelli, M.; Turolla, A.; Mezzanotte, V.; Nurizzo, C. Peracetic acid for secondary effluent disinfection: A comprehensive performance assessment. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 68, 2638–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez Henao, L.; Turolla, A.; Antonelli, M. Disinfection by-products formation and ecotoxicological effects of effluents treated with peracetic acid: A review. Chemosphere 2018, 213, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhetri, R.K.; Bonnerup, A.; Andersen, H.R. Combined Sewer Overflow pretreatment with chemical coagulation and a particle settler for improved peracetic acid disinfection. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 37, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jussila, J.; Makkonen, J.; Kokko, H. Peracetic acid (PAA) treatment is an effective disinfectant against crayfish plague (Aphanomyces astaci) spores in aquaculture. Aquaculture 2011, 320, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, L.-F.; Pedersen, P.B.; Nielsen, J.L.; Nielsen, P.H. Peracetic acid degradation and effects on nitrification in recirculating aquaculture systems. Aquaculture 2009, 296, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhetri, R.K.; Thornberg, D.; Berner, J.; Gramstad, R.; Ojstedt, U.; Sharma, A.K.; Andersen, H.R. Chemical disinfection of combined sewer overflow waters using performic acid or peracetic acids. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 490, 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, M.; Brumelis, D.; Gehr, R. Disinfection of Wastewater by Hydrogen Peroxide or Peracetic Acid: Development of Procedures for Measurement of Residual Disinfectant and Application to a Physicochemically Treated Municipal Effluent. Water Environ. Res. 2002, 74, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FRODO. Forbedret Rensning og Desinfektion af Overløbsvand. Available online: http://www.udviklingssamarbejdet.dk/en/projekter/frodo (accessed on 2 January 2014).
- Antonelli, M.; Mezzanotte, V.; Panouillères, M. Assessment of peracetic acid disinfected effluents by microbiotests. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 6579–6584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Straus, D.L.; Pedersen, L.-F.; Meinelt, T. Comparison of the toxicity of wofasteril peracetic acid formulations E400, E250, and lspez to daphnia magna, with emphasis on the effect of hydrogen peroxide. N. Am. J. Aquac. 2015, 77, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhetri, R.K.; Kaarsholm, K.M.S.; Andersen, H.R. Colorimetric quantification methods for peracetic acid together with hydrogen peroxide for water disinfection process control. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO. 11348–3 Water Quality—Determination of the İnhibitory Effect of Water Samples on the Light Emission of Vibrio Fischeri (Luminescent Bacteria Test)—Part 3: Method Using Freeze-Dried Bacteria. Available online: http://www.iso.org/iso/iso_catalogue/catalogue_tc/catalogue_detail.htm?csnumber=40518 (accessed on 26 May 2016).
- ISO. 6341: 2012 Water Quality—Determination of the İnhibition of the Mobility of Daphnia Magna Straus (Cladocera, Crustacea)—Acute Toxicity Test. Available online: http://www.iso.org/iso/home/store/catalogue_tc/catalogue_detail.htm?csnumber=54614 (accessed on 26 May 2016).
- ISO. 8692 Water Quality—Fresh Water Algal Growth İnhibition Test with Unicellular Green Algae. Available online: http://www.iso.org/iso/home/store/catalogue_tc/catalogue_detail.htm?csnumber=54150 (accessed on 26 May 2016).
- Arensberg, P.; Hemmingsen, V.H.; Nyholm, N. A miniscale algal toxicity test. Chemosphere 1995, 30, 2103–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, P.; Cuhel, R.; Nyholm, N. A simple in vitro fluorescence method for biomass measurements in algal growth inhibition tests. Water Res. 1997, 31, 2525–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, E.R.; Kusk, K.O.; Nyholm, N. Dose-Response regressions for algal growth and similar continuous endpoints: Calculation of effective concentrations. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2009, 28, 826–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhetri, R.K.; Baun, A.; Andersen, H.R. Acute toxicity and risk evaluation of the CSO disinfectants performic acid, peracetic acid, chlorine dioxide and their by-products hydrogen peroxide and chlorite. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 677, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhetri, R.K.; Baun, A.; Andersen, H.R. Algal toxicity of the alternative disinfectants performic acid (PFA), peracetic acid (PAA), chlorine dioxide (ClO2) and their by-products hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and chlorite (ClO2−). Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2017, 220, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ECETOC. Joint Assessment of Commodity Chemicals (JACC) Report No. 40. Peracetic Acid (CAS No. 79-21-0) and Its Equilibrium Solutions; ECETOC: Brussels, Belgium, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Flores, M.J.; Lescano, M.R.; Brandi, R.J.; Cassano, A.E.; Labas, M.D. A novel approach to explain the inactivation mechanism of Escherichia coli employing a commercially available peracetic acid. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 69, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EU Commission. Regulation (EU) No 286/2011 10.03.2011. Amending Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council on Classification, Labelling and Packaging of Substances and Mixtures; EU Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. Guidance Document on Aquatic Toxicity Testing of Difficult Substances and Mixtures; OECD: Paris, France, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Hey, G.; Ledin, A.; Jansen, J.L.C.; Andersen, H.R. Removal of pharmaceuticals in biologically treated wastewater by chlorine dioxide or peracetic acid. Environ. Technol. 2012, 33, 1041–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- TGD-EQS. Technical Guidance for Deriving Environmental Quality Standards, Guidance Document Number 27. Common Implementation Strategy for the Water Framework Directive (2000/60/EC); TGD-EQS, European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2011. [Google Scholar]
| KMnO4 (mg/L) | PAA (mg/L) | HP (mg/L) | Removal-PAA | Removal-HP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1160 | 150 | 0% | 0% |
| 16 | 1148 | 6 | 1 ± 2% | 96 ± 0.6% |
| 31 | 1079 | 1.5 | 7 ± 1% | 99 ± 0.2% |
| 62 | 974 | 1.5 | 16 ± 1% | 99 ± 0.1% |
| 92 | 835 | 1.5 | 28 ± 3% | 99 ± 0.1% |
| Test Organism | pPAA Nominal Concentration (mg/L) | pPAA Median Concentration (mg/L) | Area under the Curve (mg × min/L) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vibrio fischeri | EC10 | 0.47 (0.38–0.58) | N/A | N/A |
| EC50 | 0.84 (0.78–0.91) | N/A | N/A | |
| Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata | EC10 | 1.43 (1.25–1.63) | 0.30 (0.22–0.41) | 36.8 (29.5–45.9) |
| EC50 | 2.46 (2.35–2.58) | 0.88 (0.83–0.94) | 77.2 (70.6–84.3) | |
| Daphnia magna | LC10 | 0.45 (0.20–0.59) | 0.32 (0.18–0.38) | 17.4 (8.7–21.1) |
| LC50 | 0.74 (0.55–0.91) | 0.43 (0.36–0.49) | 24.7 (19.6–28.3) |
| Assay Medium | Disinfectants | Nominal Concentration (mg/L) | Cinitial (mg/L) | k × (h−1) | R2 | t½ (h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Daphnia | pPAA | 0.6 | 0.7 | 2.1 × 10−2 | 0.67 | 33 |
| 1.3 | 1.3 | 3.0 × 10−2 | 0.98 | 23 | ||
| 2.5 | 2.3 | 1.8 × 10−2 | 0.91 | 40 | ||
| cPAA | 0.6 | 0.6 | 2.0 × 10−2 | 0.99 | 35 | |
| 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.8 × 10−2 | 0.87 | 38 | ||
| 2.5 | 2.5 | 1.7 × 10−2 | 0.75 | 40 | ||
| HP | 1 | 1.0 | 1.8 × 10−2 | 0.81 | 39 | |
| 3 | 3.2 | 2.4 × 10−2 | 0.86 | 29 | ||
| 5 | 5.6 | 2.3 × 10−2 | 0.71 | 30 | ||
| 10 | 10.4 | 1.2 × 10−2 | 0.85 | 57 | ||
| Algae | pPAA | 1 | 1.2 | 6.9 × 10−2 | 0.99 | 10 |
| 3 | 3.0 | 2.8 × 10−2 | 0.98 | 24 | ||
| 6 | 5.9 | 2.3 × 10−2 | 0.99 | 30 | ||
| cPAA | 1 | 1.2 | 9.9 × 10−2 | 0.98 | 7 | |
| 2 | 2.5 | 1.2 × 10−1 | 0.99 | 6 | ||
| 10 | 12.2 | 3.7 × 10−2 | 0.99 | 19 | ||
| 30 | 26 | 3.6 × 10−2 | 0.99 | 19 | ||
| HP | 10 | 7.8 | 1.8 × 10−3 | 0.94 | 394 | |
| 30 | 29 | 3.4 × 10−4 | 0.71 | 2000 | ||
| 100 | 100 | 5.6 × 10−3 | 0.83 | 122 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chhetri, R.K.; Di Gaetano, S.; Turolla, A.; Antonelli, M.; Andersen, H.R. Ecotoxicity Evaluation of Pure Peracetic Acid (PAA) after Eliminating Hydrogen Peroxide from Commercial PAA. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5031. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17145031
Chhetri RK, Di Gaetano S, Turolla A, Antonelli M, Andersen HR. Ecotoxicity Evaluation of Pure Peracetic Acid (PAA) after Eliminating Hydrogen Peroxide from Commercial PAA. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(14):5031. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17145031
Chicago/Turabian StyleChhetri, Ravi Kumar, Silvia Di Gaetano, Andrea Turolla, Manuela Antonelli, and Henrik Rasmus Andersen. 2020. "Ecotoxicity Evaluation of Pure Peracetic Acid (PAA) after Eliminating Hydrogen Peroxide from Commercial PAA" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 14: 5031. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17145031
APA StyleChhetri, R. K., Di Gaetano, S., Turolla, A., Antonelli, M., & Andersen, H. R. (2020). Ecotoxicity Evaluation of Pure Peracetic Acid (PAA) after Eliminating Hydrogen Peroxide from Commercial PAA. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(14), 5031. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17145031







