Determination of Selenium in Common and Selenium-Rich Rice from Different Areas in China and Assessment of Their Dietary Intake
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Selection of Sampling Sites and Sampling
2.2. Sample Pretreatment for Total Selenium Detection
2.3. Sample Pretreatment for Inorganic Selenium Detection
2.4. Detection of Organic Selenium
2.5. Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS) Working Conditions
2.6. Quality Assurance and Quality Control Data
2.7. Precision and Stability of the Detection Method
2.8. Assessment Model of Daily Dietary Selenium Intake
2.9. Risk index Calculation
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Selenium Content of Common/Selenium-Rich Rice Samples from Different Areas in China
3.2. Distribution of Inorganic and Organic Selenium in Selenium-Rich Rice Samples
3.3. Dietary Selenium Intake and Risk Index of Common/Selenium-Rich Rice in Different Areas
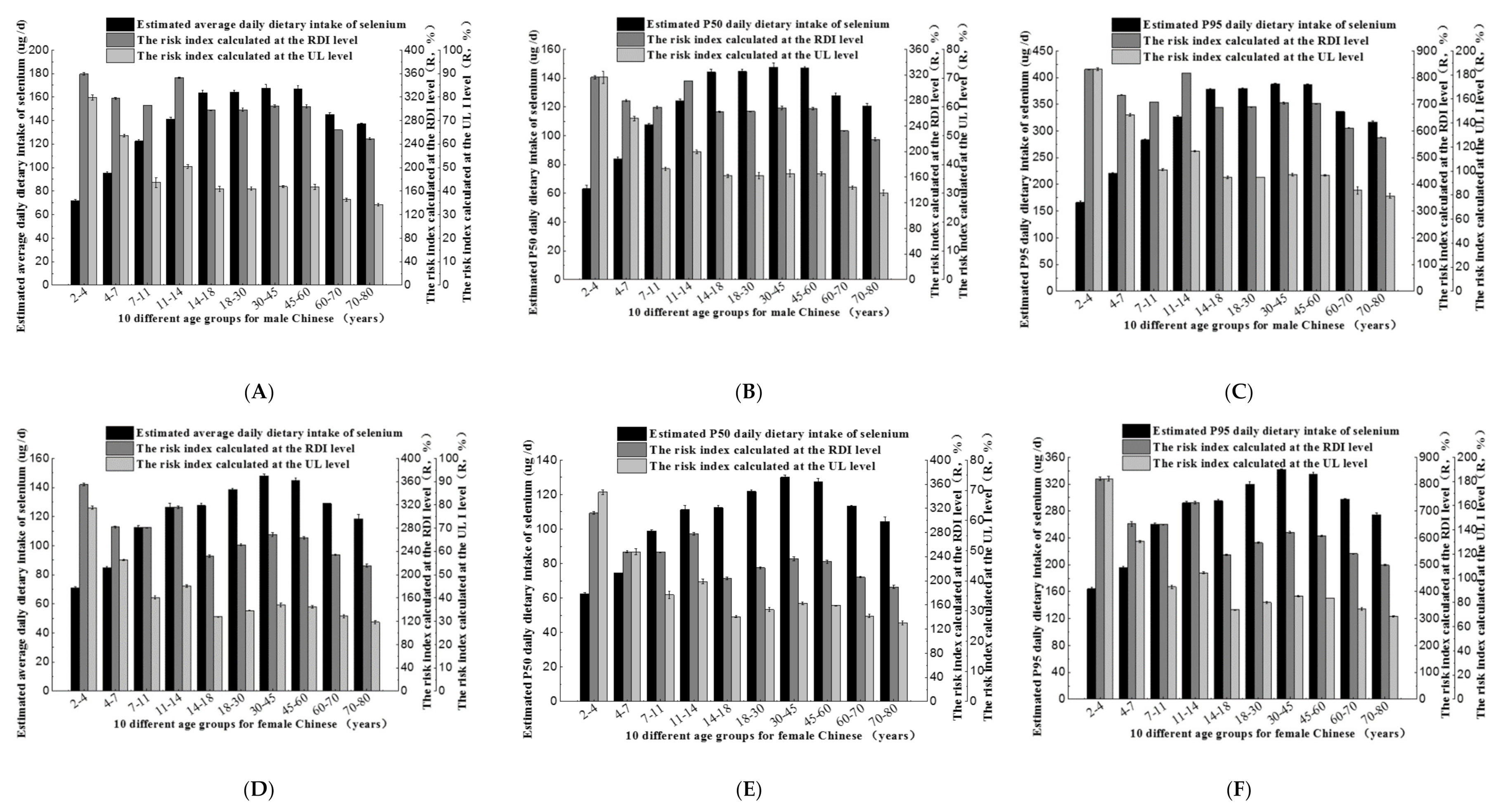
3.4. Dietary Selenium Intake and Risk Index of Common Rice Consumed by Different Age and Genders Groups
3.5. Dietary Selenium Intake and Risk Index of Selenium-Rich Rice Consumed by the Population in Different Ages and Genders
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Avissar, N.; Kerl, E.A.; Baker, S.S.; Cohen, H.J. Extracellular Glutathione-Peroxidase Messenger-Rna and Protein in Human Cell-Lines. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1994, 309, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tinggi, U. Essentiality and toxicity of selenium and its status in Australia: A review. Toxicol. Lett. 2003, 137, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoffaneller, R.; Morse, N.L. A Review of Dietary Selenium Intake and Selenium Status in Europe and the Middle East. Nutrients 2015, 7, 1494–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.S.; Shyu, Y.C.; Chen, H.Y.; Lin, L.M.; Lo, C.Y.; Yuan, S.S.; Chen, P.J. Effect of Parenteral Selenium Supplementation in Critically Ill Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.Q.; Xu, Y.M.; Liu, Y.Y.; Qin, X.; Huang, R.; Liang, X.F. Selenium application alters soil cadmium bioavailability and reduces its accumulation in rice grown in Cd-contaminated soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 31175–31182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrauzer, G.N. Selenium and Cancer—Review. Bioinorg. Chem. 1976, 5, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.Y.; Yuan, X.Y.; Song, Y.X.; Chen, H.Y.; Liu, Q.; Hu, S. Influence of Heavy Metals and Nutrient Concentrations on Selenium Geochemical Behavior in Soil-Rice System. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2016, 25, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.L.; Chen, F.S.; Zhao, Y.; Gu, Z.X.; Yang, H.S. Selenium accumulation in protein fractions during germination of Se-enriched brown rice and molecular weights distribution of Se-containing proteins. Food Chem. 2011, 127, 1526–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, D.W.; Christian, R.G.; Whenham, G.R.; Howell, J. Review of Some Aspects of Vitamin-E-Selenium Responsive Diseases with a Note on Their Possible Incidence in Alberta. Can. Vet. J. 1976, 17, 61–71. [Google Scholar]
- Uchwal, P.; Juszczak, M.; Bakowska, M. Content of Selenium in Selected Food Products on the Markets of North-Western Poland. J. Elementol. 2019, 24, 111–123. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Ahmary, K.M. Selenium content in selected foods from the Saudi Arabia market and estimation of the daily intake. Arab. J. Chem. 2009, 2, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulah, R.; Miyazaki, K.; Nakazawa, M.; Koyama, H. Low contribution of rice and vegetables to the daily intake of selenium in Japan. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2005, 56, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.H.; Hu, B.; Deng, K.; Gao, X.K.; Sun, G.X.; Zhang, Z.L.; Li, P.; Wang, W.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z.H.; et al. NRT1.1B improves selenium concentrations in rice grains by facilitating selenomethinone translocation. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2019, 17, 1058–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Xing, G.F.; Tang, S.H.; Pang, Y.W.; Yi, Q.; Huang, Q.Y.; Huang, X.; Huang, J.F.; Li, P.; Fu, H.T. Improving soil selenium availability as a strategy to promote selenium uptake by high-Se rice cultivar. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2019, 163, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, K.L.; Chen, F.S.; Cheng, Y.Q. Comparative proteomics analysis reveals the effect of germination and selenium enrichment on the quality of brown rice during storage. Food Chem. 2018, 269, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNaughton, S.A.; Marks, G.C. Selenium content of Australian foods: A review of literature values. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2002, 15, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.W.; Wei, C.Y.; Tu, S.X.; Tang, S.R.; Wu, F.C. Detoxification of antimony by selenium and their interaction in paddy rice under hydroponic conditions. Microchem. J. 2011, 97, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.Q.; Ma, L.; Li, J.H.; Wang, F.H.; Sisak, I.; Zhang, F.S. Phosphorus flows and use efficiencies in production and consumption of wheat, rice, and maize in China. Chemosphere 2011, 84, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.D.; Wang, X.; Wong, Y.S. Generation of selenium-enriched rice with enhanced grain yield, selenium content and bioavailability through fertilisation with selenite. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 2385–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Zhou, W.H.; Dai, H.X.; Cao, F.B.; Zhang, G.P.; Wu, F.B. Selenium reduces cadmium uptake and mitigates cadmium toxicity in rice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 235, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, R.Y.; Ai, C.Y.; Zhang, B.J.; Cheng, X.L. Effect of selenite on organic selenium speciation and selenium bioaccessibility in rice grains of two Se-enriched rice cultivars. Food Chem. 2018, 264, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.H.; Shi, W.M.; Wang, X.C. Difference in selenium accumulation in shoots of two rice cultivars. Pedosphere 2006, 16, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.Y.; Cheng, Y.X.; Suzuki, N.; Guo, X.P.; Xiong, H.; Ogra, Y. Speciation of Selenium in Brown Rice Fertilized with Selenite and Effects of Selenium Fertilization on Rice Proteins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.X.; Ding, C.F.; Yu, X.Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, T.L.; Wang, X.X. Characteristics of Time-Dependent Selenium Biofortification of Rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 12490–12497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norton, G.J.; Deacon, C.M.; Xiong, L.Z.; Huang, S.Y.; Meharg, A.A.; Price, A.H. Genetic mapping of the rice ionome in leaves and grain: Identification of QTLs for 17 elements including arsenic, cadmium, iron and selenium. Plant Soil 2010, 329, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falandysz, J. Review: On published data and methods for selenium in mushrooms. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehner, J.P.; Meyer, F.; Juillet, Y.; XVI, T.R.N.d.G. Transparency of communication of the risk-benefit assessment: The example of medications. Therapie 2001, 56, 335–339. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, J.N.; Huang, Y.J. Selenium in Geo-Ecosystem and Its Relation To Endemic Diseases in China. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1991, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.Y.; Kuang, L.X.; Li, Z.X.; Pang, R.L.; Yang, L.; Chen, Q.S.; Li, A.; Zhao, X.B.; Xu, W.H. Selenium content of main deciduous fruits from China and its dietary exposure assessment. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2015, 48, 3015–3026. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.L.; Gu, Z.X. Selenium Accumulation in Different Brown Rice Cultivars and Its Distribution in Fractions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amato, R.; Fontanella, M.C.; Falcinelli, B.; Beone, G.M.; Bravi, E.; Marconi, O.; Benincasa, P.; Businelli, D. Selenium Biofortification in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Sprouting: Effects on Se Yield and Nutritional Traits with Focus on Phenolic Acid Profile. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 4082–4090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pappa, E.C.; Pappas, A.C.; Surai, P.F. Selenium content in selected foods from the Greek market and estimation of the daily intake. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 372, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussein, L.; Bruggeman, J. Selenium analysis of selected Egyptian foods and estimated daily intakes among a population group. Food Chem. 1999, 65, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Goyal, R.; Singh Sadana, U. Selenium Accumulation and Antioxidant Status of Rice Plants Grown on Seleniferous Soil from Northwestern India. Rice Sci. 2014, 21, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.C.; Yang, F.M.; Xu, J.; Hu, Y.; Hu, Q.H.; Zhang, Y.L.; Pan, G.X. Determination of selenium concentration of rice in China and effect of fertilization of selenite and selenate on selenium content of rice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 5128–5130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munehiro Yoshida, K.Y. Selenium Contents of Rice Grown at Various Sites in Japan. J. Food Compos. Anal. 1987, 1, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panigati, M.; Falciola, L.; Mussini, P.; Beretta, G.; Facino, R.M. Determination of selenium in Italian rices by differential pulse cathodic stripping voltammetry. Food Chem. 2007, 105, 1091–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.F.; Hu, Z.Q.; Yu, Y.H.; Mou, R.X.; Zhu, Z.W.; Beta, T. Phenolic acids, anthocyanins, proanthocyanidins, antioxidant activity, minerals and their correlations in non-pigmented, red, and black rice. Food Chem. 2018, 239, 733–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Testing Index | Background Value of the Sample Being Tested (mg/kg) | Amount of Reference Substance Added to 0.2 g Sample (μg) | Average Recovery (%) | Relative Standard Deviation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total selenium | 0.126 | 0.020 | 98.17 | 4.15 |
| 0.040 | 99.98 | 3.74 | ||
| 0.060 | 99.17 | 0.50 | ||
| Inorganic selenium | 0.057 | 0.024 | 95.11 | 7.22 |
| 0.030 | 98.93 | 0.02 | ||
| 0.036 | 83.19 | 4.67 |
| Food Samples | n | Mean | Relative Standard Deviation | Range | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rice | —— | 70.25 | 7.5 | 62.70–87.00 | USA [32] |
| 4 | 1.83 | 9.0 | 2.01 ± 0.18 (white rice) | Italy [37] | |
| 5 | 4.52 | 4.7 | 5.30 ± 0.10 (red rice) | Italy [37] | |
| 3 | 2.05 | 1.9 | 2.67 ±0.13 (black rice) | Italy [37] | |
| 4 | 3.41 | 9.0 | 4.53 ± 0.41 (white rice hull) | Italy [37] | |
| 27 | 1.80 | —— | 1.20–2.40 | Spain [31] | |
| 69 | 0.35 | 8.5 | 0.05–0.12 | Iran [33] | |
| 58 | —— | —— | 1.40–3.60 | China [35] | |
| 24 | 1.85 | 5.6 | 1.77–2.05 | Greece f | |
| 69 | —— | —— | 1.60–7.00 | Japan [36] | |
| —— | 4.58 | 5.7 | 0.50–9.50 | India [34] | |
| 15 | 6.50 | 4.8 | 1.50–13.00 | Bangladesh [30] | |
| —— | —— | —— | 1.30–9.90 | Ireland [32] | |
| 16 | 19.30 | 5.9 | —— | Egypt [33] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Guo, Y.; Liang, K.; Hu, Z.; Sun, X.; Fang, Y.; Mei, X.; Yin, H.; Liu, X.; Lu, B. Determination of Selenium in Common and Selenium-Rich Rice from Different Areas in China and Assessment of Their Dietary Intake. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4596. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17124596
Zhang L, Guo Y, Liang K, Hu Z, Sun X, Fang Y, Mei X, Yin H, Liu X, Lu B. Determination of Selenium in Common and Selenium-Rich Rice from Different Areas in China and Assessment of Their Dietary Intake. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(12):4596. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17124596
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Liuquan, Yanbin Guo, Kehong Liang, Zhongqiu Hu, Xiangdong Sun, Yong Fang, Xiaohong Mei, Hongqing Yin, Xianjin Liu, and Baiyi Lu. 2020. "Determination of Selenium in Common and Selenium-Rich Rice from Different Areas in China and Assessment of Their Dietary Intake" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 12: 4596. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17124596
APA StyleZhang, L., Guo, Y., Liang, K., Hu, Z., Sun, X., Fang, Y., Mei, X., Yin, H., Liu, X., & Lu, B. (2020). Determination of Selenium in Common and Selenium-Rich Rice from Different Areas in China and Assessment of Their Dietary Intake. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(12), 4596. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17124596






