Association between Reflux Esophagitis Incidence and Palmar Hyperhidrosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Database
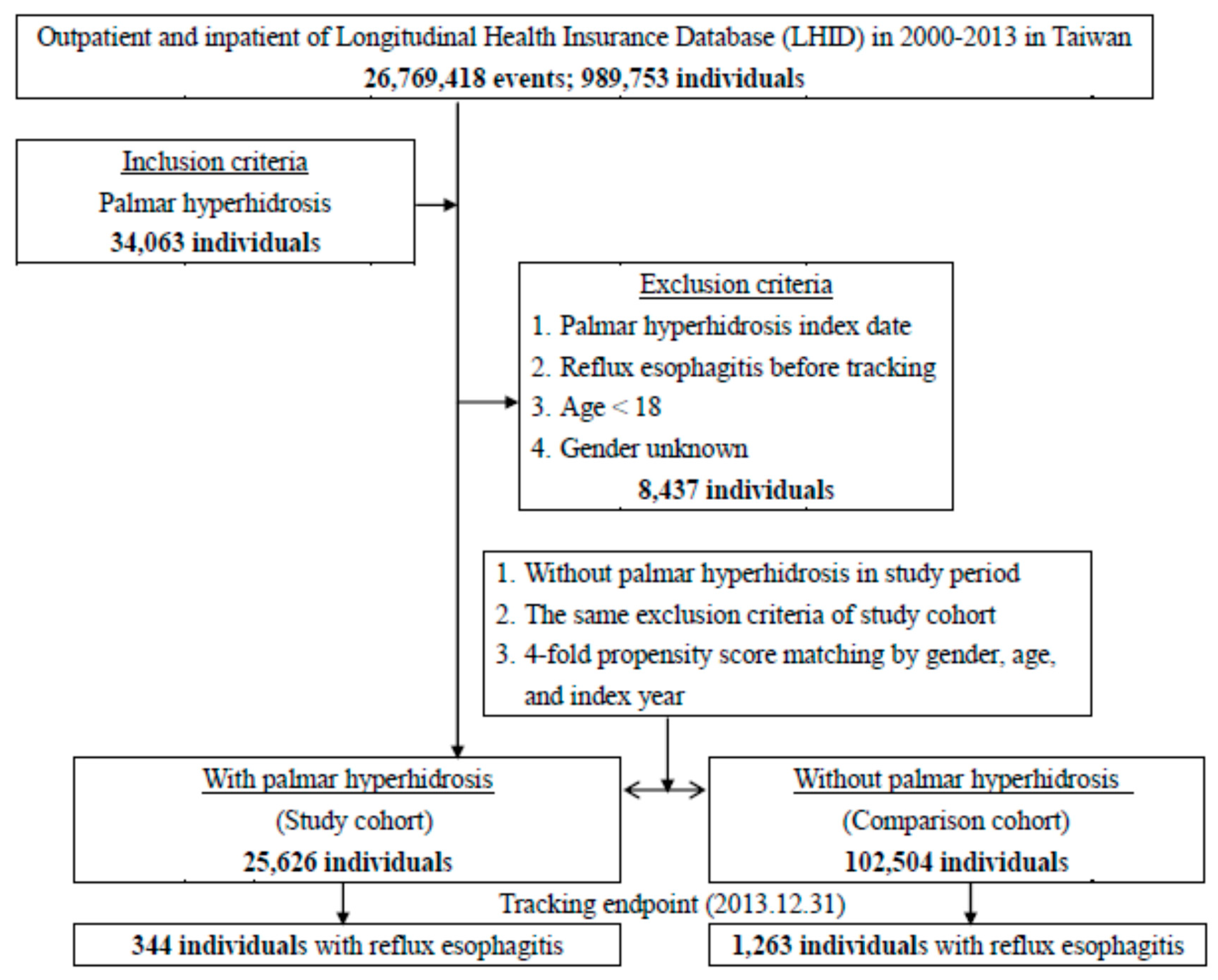
2.2. Design
2.3. Statistical Analysis
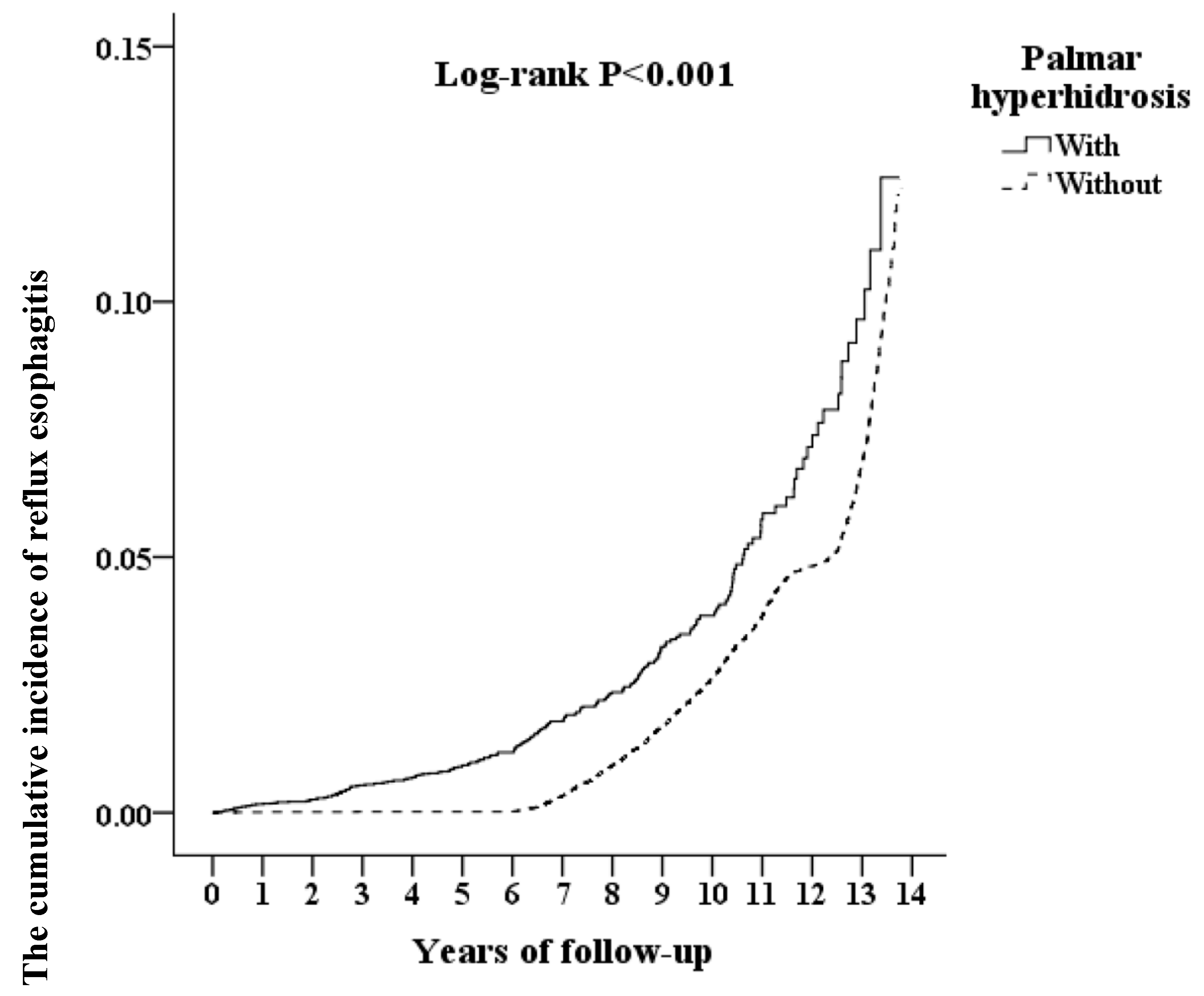
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Iwase, S.; Ikeda, T.; Kitazawa, H.; Hakusui, S.; Sugenoya, J.; Mano, T. Altered response in cutaneous sympathetic outflow to mental and thermal stimuli in primary palmoplantar hyperhidrosis. J. Auton. Nerv. Syst. 1997, 64, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birner, P.; Heinzl, H.; Schindl, M.; Pumprla, J.; Schnider, P. Cardiac autonomic function in patients suffering from primary focal hyperhidrosis. Eur. Neurol. 2000, 44, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.G.; Cheng, C.A.; Chien, W.C.; Chung, C.H.; Lee, J.T. Associated With Ischemic Stroke Risk Reduction After Endoscopic Thoracic Sympathectomy for Palmar Sweating. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2018, 27, 2235–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.A.; Cheng, C.G.; Chu, H.; Lin, H.C.; Chung, C.H.; Chiu, H.W.; Chien, W.C. Risk Reduction of Long-Term Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events After Endoscopic Thoracic Sympathectomy in Palmar Hyperhidrosis. Clin. Auton. Res. 2017, 27, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.M.; Moon, D.H.; Lee, H.S.; Park, J.Y.; Lee, J.W.; Lee, S. Hyperhidrosis, Endoscopic Thoracic Sympathectomy, and Cardiovascular Outcomes: A Cohort Study Based on the Korean Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service Database. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madisch, A.; Kulich, K.; Malfertheiner, P.; Ziegler, K.; Bayerdörffer, E.; Miehlke, S.; Labenz, J.; Carlsson, J.; Wiklund, I. Impact of reflux disease on general and disease-related quality of life-evidence from a recent comparative methodological study in Germany. Z. Gastroenterol. 2003, 41, 1137–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza Cury, M.; Ferrari, A.; Ciconelli, R.; Ferraz, M.; Moraes-Filho, J.P.P. Evaluation of health-related quality of life in gastroesophageal reflux disease patients before and after treatment with pantoprazole. Dis. Esophagus 2006, 19, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, D.S.; Kadish, S.L. The diagnosis and management of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Med. Clin. N. Am. 1996, 80, 411–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djeddi, D.-D.; Kongolo, G.; Stéphan-Blanchard, E.; Ammari, M.; Léké, A.; Delanaud, S.; Bach, V.; Telliez, F. Involvement of autonomic nervous activity changes in gastroesophageal reflux in neonates during sleep and wakefulness. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milovanovic, B.; Filipovic, B.; Mutavdzin, S.; Zdravkovic, M.; Gligorijevic, T.; Paunovic, J.; Arsic, M. Cardiac autonomic dysfunction in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 6982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, R.K.; Holloway, R.; Dent, J. Effect of atropine on the frequency of reflux and transient lower esophageal sphincter relaxation in normal subjects. Gastroenterology 1995, 109, 1547–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordenstedt, H.; Lagergren, J. Environmental Factors in the Etiology of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 2, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, P.-H.; Lin, C.-C.; Lin, C.-H.; Tsai, C.-J.; Cheng, C.; Chuo, Y.-P.; Chan, C.-H.; Lan, T.-H. Prevalence of gastroesophageal reflux disease in major depressive disorder: A population-based study. Psychosomatics 2014, 55, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.-S.; Chang, F.-Y. The prevalence and risk factors of reflux esophagitis among adult Chinese population in Taiwan. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2007, 41, 819–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, J.-L.; Tu, C.-C.; Hsu, P.-I.; Pan, M.-H.; Lee, C.-C.; Tsay, F.-W.; Wang, H.-M.; Cheng, L.-C.; Lai, K.-H.; Yu, H.-C. Prevalence and risk factors of erosive esophagitis in Taiwan. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2012, 75, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Dodds, W.J.; Dent, J.; Hogan, W.J.; Helm, J.F.; Hauser, R.; Patel, G.K.; Egide, M.S. Mechanisms of gastroesophageal reflux in patients with reflux esophagitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1982, 307, 1547–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, J.H.; Küper, M.A.; Königsrainer, A.; Brücher, B.L. Transient lower esophageal sphincter relaxation and esophageal motor response. J. Surg. Res. 2010, 159, 714–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boeckxstaens, G.E.; Rohof, W.O. Pathophysiology of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2014, 43, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyawali, C.; Roman, S.; Bredenoord, A.; Fox, M.; Keller, J.; Pandolfino, J.; Sifrim, D.; Tatum, R.; Yadlapati, R.; Savarino, E. Classification of esophageal motor findings in gastro-esophageal reflux disease: Conclusions from an international consensus group. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaker, R. Gastroesophageal reflux disease: Beyond mucosal injury. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2007, 41, S160–S162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes-Filho, J.P.P.; Navarro-Rodriguez, T.; Eisig, J.N.; Barbuti, R.C.; Chinzon, D.; Quigley, E.M. Comorbidities are frequent in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease in a tertiary health care hospital. Clinics 2009, 64, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H.; Yu, C.-H.; Li, Y.-M. Risk factors for gastroesophageal reflux disease, reflux esophagitis and non-erosive reflux disease among Chinese patients undergoing upper gastrointestinal endoscopic examination. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 6009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.L.; Goldstein, R.S. Gastroesophageal reflux disease in COPD: Links and risks. Int. J. Chron. Obstruct. Pulmon. Dis. 2015, 10, 1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.-M.; Tan, J.-C.; Zhu, Y.; Lin, L. Association between diabetes mellitus and gastroesophageal reflux disease: A meta-analysis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haug, T.T.; Mykletun, A.; Dahl, A. Are anxiety and depression related to gastrointestinal symptoms in the general population? Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2002, 37, 294–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, M.L.; Gregory, L.J.; Cullen, S.; Cohen, S.; Ng, V.; Andrew, C.; Giampietro, V.; Bullmore, E.; Zelaya, F.; Amaro, E. The effect of negative emotional context on neural and behavioural responses to oesophageal stimulation. Brain 2003, 126, 669–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, Y.; Mine, T.; Kawana, I.; Yasuzaki, H.; Kokuho, T.; Toya, Y.; Ohnishi, T.; Umemura, S. Gastroesophageal reflux disease in chronic renal failure patients: Evaluation by endoscopic examination. Tokai J. Exp. Clin. Med. 2009, 34, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lien, H.-C.; Chang, C.-S.; Yeh, H.-Z.; Ko, C.-W.; Chang, H.-Y.; Cheng, K.; Sung, F.-C. Increasing prevalence of erosive esophagitis among Taiwanese aged 40 years and above: A comparison between two time periods. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2009, 43, 926–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, D.; Chen, R.-C.; Lee, C.-H.; Yang, N.-P.; Chou, P. Incidence and frequency of endoscopic sympathectomy for the treatment of hyperhidrosis palmaris in Taiwan. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2010, 26, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Serag, H.B.; Graham, D.Y.; Satia, J.A.; Rabeneck, L. Obesity is an independent risk factor for GERD symptoms and erosive esophagitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 100, 1243–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karason, K.; Mølgaard, H.; Wikstrand, J.; Sjöström, L. Heart rate variability in obesity and the effect of weight loss. Am. J. Cardiol. 1999, 83, 1242–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarasiri, D.L.; Pathmeswaran, A.; de Silva, H.J.; Ranasinha, C.D. Response of the airways and autonomic nervous system to acid perfusion of the esophagus in patients with asthma: A laboratory study. BMC Pulm. Med. 2013, 13, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuribayashi, S.; Kusano, M.; Kawamura, O.; Shimoyama, Y.; Maeda, M.; Hisada, T.; Ishizuka, T.; Dobashi, K.; Mori, M. Mechanism of gastroesophageal reflux in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2010, 22, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bygstad, E.; Terkelsen, A.J.; Pilegaard, H.K.; Hansen, J.; Mølgaard, H.; Hjortdal, V.E. Thoracoscopic sympathectomy increases efferent cardiac vagal activity and baroreceptor sensitivity. Eur. J. Cardio-Thorac Surg. 2013, 44, e193–e199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staunton, E.; Smid, S.D.; Dent, J.; Blackshaw, L.A. Triggering of transient LES relaxations in ferrets: Role of sympathetic pathways and effects of baclofen. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2000, 279, G157–G162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, E.; Perring, S.; Khattab, A.; Allenby-Smith, O. The effects of proton pump inhibitors on autonomic tone in patients with erosive and non-erosive esophagitis. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2016, 28, 659–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | PH (%) | Non-PH (%) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 25,626 | 102,504 | |
| Gender (Male) | 12,131 (47.34) | 48,524 (47.34) | 0.999 |
| Age (years) | 28.16 ± 9.57 | 28.21 ± 9.79 | 0.999 |
| Catastrophic illness | 88 (0.34) | 5245 (5.12) | <0.001 * |
| Insured premium ($USD) | <0.001 * | ||
| <600 | 19,900 (77.66) | 76,864 (74.99) | |
| 600–1167 | 3434 (13.4) | 15,537 (15.16) | |
| ≥1167 | 2292 (8.94) | 10,103 (9.86) | |
| Hypertension | 142 (0.55) | 2456 (2.4) | <0.001 * |
| Hyperlipidemia | 29 (0.11) | 1661 (1.62) | <0.001 * |
| Obesity | 4 (0.02) | 51 (0.05) | 0.017 * |
| Diabetes mellitus | 75 (0.29) | 2648 (2.58) | <0.001 * |
| Depression | 38 (0.15) | 309 (0.3) | <0.001 * |
| Asthma | 32 (0.12) | 682 (0.67) | <0.001 * |
| Constipation | 10 (0.04) | 132 (0.13) | <0.001 * |
| Allergic rhinitis | 4 (0.02) | 109 (0.11) | <0.001 * |
| Obstructive sleep apnea | 2 (0.01) | 45 (0.04) | 0.005 * |
| Osteoarthritis | 3 (0.01) | 381 (0.37) | <0.001 * |
| Osteoporosis | 0 | 84 (0.08) | <0.001 * |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | 70 (0.27) | 1200 (1.17) | <0.001 * |
| Anxiety | 35 (0.14) | 305 (0.3) | <0.001 * |
| Congestive heart failure | 13 (0.05) | 282 (0.28) | <0.001 * |
| Chronic kidney disease | 15 (0.06) | 1094 (1.07) | <0.001 * |
| Thyrotoxicosis | 25 (0.1) | 397 (0.39) | <0.001 * |
| Season | <0.001 * | ||
| Spring (3–5) | 7819 (30.51) | 26,354 (25.71) | |
| Summer (6–8) | 8996 (35.1) | 25,633 (25.01) | |
| Autumn (9–11) | 4531 (17.68) | 24,831 (24.22) | |
| Winter (12,1,2) | 4280 (16.7) | 25,686 (25.06) | |
| Location | <0.001 * | ||
| Northern | 9915 (38.69) | 42,264 (41.23) | |
| Middle | 8714 (34) | 28,514 (27.82) | |
| Southern | 6081 (23.73) | 25,825 (25.19) | |
| Eastern | 834 (3.25) | 5375 (5.24) | |
| Outlets islands | 82 (0.32) | 526 (0.51) | |
| Urbanization level | <0.001 * | ||
| 1 (The highest) | 8498 (33.16) | 37,100 (36.19) | |
| 2 | 11,186 (43.65) | 41,349 (40.34) | |
| 3 | 3783 (14.76) | 9194 (8.97) | |
| 4 (The lowest) | 2159 (8.43) | 14,861 (14.5) | |
| Hospital levels | <0.001 * | ||
| Medical center | 6896 (26.91) | 26,362 (25.72) | |
| Regional hospital | 10,729 (41.87) | 28,252 (27.56) | |
| Local hospital | 8001 (31.22) | 47,890 (46.72) |
| Variables | Crude HR | 95% CI | p | Adjusted HR | 95% CI | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Palmar hyperhidrosis | 2.903 | 2.569–3.279 | <0.001 * | 3.457 | 3.043–3.928 | <0.001 * |
| Gender (Female) | Reference | Reference | ||||
| Male | 2.167 | 1.454–2.667 | <0.001 * | 2.376 | 2.129–2.651 | <0.001 * |
| Age (years) | 1.002 | 0.948–1.068 | 0.245 | 0.997 | 0.992–1.001 | 0.161 |
| Catastrophic illness | 0.897 | 0.601–0.972 | 0.008 * | 0.814 | 0.704–0.901 | 0.006 * |
| Insured premium ($USD) | ||||||
| <600 | Reference | Reference | ||||
| 600–1167 | 1.024 | 0.467–1.464 | 0.802 | 0.959 | 0.672–1.368 | 0.816 |
| ≥1167 | 1.805 | 0.225–2.401 | 0.554 | 1.766 | 0.384–2.598 | 0.453 |
| Hypertension | 1.567 | 1.005–2.842 | <0.001 * | 1.730 | 1.161–2.864 | <0.001 * |
| Hyperlipidemia | 0.799 | 0.264–1.985 | 0.465 | 0.972 | 0.486–1.597 | 0.462 |
| Obesity | 2.297 | 0.446–5.012 | 0.246 | 2.208 | 0.985–4.95 | 0.154 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 1.454 | 1.121–1.77 | 0.001 * | 1.479 | 1.272–1.714 | <0.001 * |
| Depression | 1.498 | 1.064–1.932 | 0.007 * | 1.512 | 1.112–2.005 | <0.001 * |
| Asthma | 0.952 | 0.454–1.701 | 0.465 | 0.880 | 0.555–1.396 | 0.588 |
| Constipation | 0.882 | 0.498–1.985 | 0.703 | 0.934 | 0.67–1.588 | 0.879 |
| Allergic rhinitis | 0.468 | 0.105–2.345 | 0.154 | 0.537 | 0.119–2.888 | 0.101 |
| Obstructive sleep apnea | 9.565 | 0.099–78.452 | 0.875 | 11.245 | 0.167–197.752 | 0.786 |
| Osteoarthritis | 2.085 | 0.498–7.017 | 0.452 | 1.974 | 0.628–6.054 | 0.297 |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | 1.442 | 1.154–2.448 | 0.003 * | 1.842 | 1.34–2.537 | <0.001 * |
| Anxiety | 2.989 | 1.498–3.902 | <0.001 * | 2.031 | 1.301–3.172 | <0.001 * |
| Congestive heart failure | 1.454 | 0.598–3.012 | 0.678 | 1.795 | 0.798–2.454 | 0.295 |
| Chronic kidney disease | 1.227 | 1.005–1.704 | 0.041 * | 1.363 | 1.039–1.788 | 0.025 * |
| Thyrotoxicosis | 0.996 | 0.124–1.642 | 0.564 | 1.088 | 0.157–1.516 | 0.215 |
| Season | ||||||
| Spring | Reference | Reference | ||||
| Summer | 1.452 | 0.742–1.897 | 0.872 | 1.045 | 0.597–1.787 | 0.842 |
| Autumn | 0.804 | 0.512–0.911 | 0.002 * | 0.779 | 0.678–0.893 | 0.003 * |
| Winter | 0.667 | 0.334–0.876 | 0.004 * | 0.564 | 0.487–0.642 | 0.001 * |
| Urbanization level | ||||||
| 1 (The highest) | 0.795 | 0.642 | 0.053 | 0.889 | 0.743–1.063 | 0.197 |
| 2 | 0.701 | 0.611 | 0.025 * | 0.861 | 0.754–0.984 | 0.028 * |
| 3 | 0.685 | 0.572 | 0.001 * | 0.676 | 0.575–0.796 | <0.001 * |
| 4 (The lowest) | Reference | Reference | ||||
| Hospital levels | ||||||
| Hospital center | 1.756 | 0.425–2.905 | 0.498 | 1.295 | 0.498–1.795 | 0.540 |
| Regional hospital | 1.015 | 0.375–1.785 | 0.811 | 0.884 | 0.331–1.454 | 0.735 |
| Local hospital | Reference | Reference |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, C.-G.; Chien, W.-C.; Yu, C.-P.; Chung, C.-H.; Cheng, C.-A. Association between Reflux Esophagitis Incidence and Palmar Hyperhidrosis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4502. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17124502
Cheng C-G, Chien W-C, Yu C-P, Chung C-H, Cheng C-A. Association between Reflux Esophagitis Incidence and Palmar Hyperhidrosis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(12):4502. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17124502
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Chun-Gu, Wu-Chien Chien, Chia-Peng Yu, Chi-Hsiang Chung, and Chun-An Cheng. 2020. "Association between Reflux Esophagitis Incidence and Palmar Hyperhidrosis" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 12: 4502. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17124502
APA StyleCheng, C.-G., Chien, W.-C., Yu, C.-P., Chung, C.-H., & Cheng, C.-A. (2020). Association between Reflux Esophagitis Incidence and Palmar Hyperhidrosis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(12), 4502. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17124502





