The Effect of Physical Activity and High Body Mass Index on Health-Related Quality of Life in Individuals with Metabolic Syndrome
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Ethical Considerations
2.3. Participants
2.4. HRQoL
2.5. PA and BMI
2.6. Other Covariables
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Steering Committee
Executive Committee
Dietary and Lifestyle Intervention Committee
Clinical Event Ascertainment Committee
Independent Data and Safety Monitoring Board:
Rovira i Virgili University, Department of Biochemistry and Biotechnology, Human Nutrition Unit, University Hospital of Sant Joan de Reus, Pere Virgili Institute for Health Research, Reus, Spain
Department of Preventive Medicine and Public Health, University of Navarra-Navarra Institute for Health Research (IdiSNA), Pamplona, Spain
Department of Preventive Medicine, University of Valencia, University Jaume I, Conselleria de Sanitat de la Generalitat Valenciana, Valencia, Spain
Cardiovascular Risk and Nutrition Research Group, Endocrinology Service, Neurosciences Programme, Clinical Research Unit at the Hospital del Mar Medical Research Institute (IMIM), Barcelona. Medicine Departament, Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain
Nutritional Epidemiology Unit, Miguel Hernandez University, ISABIAL-FISABIO, Alicante, Spain
Hospital Son Espases (HUSE) and Institute for Health Research Illes Balears (IdISBa), Palma de Mallorca, Spain
Department of Nutrition, Food Sciences, and Physiology, Center for Nutrition Research, University of Navarra, Pamplona, Spain
University of Málaga and Institute of Biomedical Research in Malaga (IBIMA), Málaga, Spain
Lipids and Atherosclerosis Unit, Department of Internal Medicine, Maimonides Biomedical Research Institute of Cordoba (IMIBIC), Reina Sofia University Hospital, University of Cordoba, Cordoba, Spain
Department of Internal Medicine, Institut d’Investigacions Biomèdiques August Pi i Sunyer (IDIBAPS), Hospital Clínic, University of Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain
Departament of Preventive Medicine and Public Health, University of Granada, Granada, Spain
Bioaraba Health Research Institute, Cardiovascular, Respiratory and Metabolic Area; Osakidetza Basque Health Service, Araba University Hospital; University of the Basque Country UPV/EHU, Vitoria-Gasteiz, Spain
Research Group on Community Nutrition & Oxidative Stress, University of Balearic Islands and Institute for Health Research Illes Balears (IdISBa), Palma de Mallorca, Spain
Virgen de la Victoria Hospital, University of Málaga, Málaga, Spain
University of Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Las Palmas, Spain
Biomedicine Institute (IBIOMED); University of León, and Primary Health Care Management of León (Sacyl), León, Spain: Biomedicine Institute (IBIOMED); University of León, and Primary Health Care Management of León (Sacyl), León, Spain
Department of Family Medicine, Distrito Sanitario Atención Primaria Sevilla, Sevilla, Spain
Department of Endocrinology and Nutrition, Hospital Fundación Jimenez Díaz. Instituto de Investigaciones Biomédicas IISFJD. University Autonoma, Madrid, Spain
Department of Endocrinology, IDIBAPS, Hospital Clinic, University of Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain
Nutritional Control of the Epigenome Group. Precision Nutrition and Obesity Program, Institute IMDEA-Food, CEI UAM+CSIC, Madrid, Spain
Division of Preventive Medicine, University of Jaén, Jaén, Spain
Department of Endocrinology and Nutrition, Hospital Clínico San Carlos, Instituto de Investigación Sanitaria del Hospital Clínico San Carlos (IdISSC), Madrid, España (Spain para internacionales)
Department of Basic and Clinical Psychology and Psychobiology, University Jaume I, Castellón de la Plana, Spain
Oxidative Pathology Unit. Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, School of Medicine-INCLIVA, Service of Clinical Analyses, University Hospital Doctor Peset, Valencia, Spain. University of Valencia, Valencia Spain
Department of Preventive Medicine, University of Malaga, Malaga, Spain
Department of Psychiatry, University Hospital of Bellvitge, Barcelona, Spain
References
- Bray, G.A.; Kim, K.K.; Wilding, J.P.H. Obesity: A chronic relapsing progressive disease process. A position statement of the World Obesity Federation. Obes. Rev. 2017, 18, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Obesity Observatory. Available online: https://www.worldobesitydata.org/country-profiles/ (accessed on 4 February 2020).
- WHO. Obesity: Preventing and Managing the Global Epidemic; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Catenacci, V.A.; Hill, J.O.; Wyatt, H.R. The obesity epidemic. Clin. Chest Med. 2009, 30, 415–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentham, J.; Di Cesare, M.; Bilano, V.; Bixby, H.; Zhou, B.; Stevens, G.A.; Riley, L.M.; Taddei, C.; Hajifathalian, K.; Lu, Y.; et al. Worldwide trends in body-mass index, underweight, overweight, and obesity from 1975 to 2016: A pooled analysis of 2416 population-based measurement studies in 128·9 million children, adolescents, and adults. Lancet 2017, 390, 2627–2642. [Google Scholar]
- Berrington de Gonzalez, A.; Hartge, P.; Cerhan, J.R.; Flint, A.J.; Hannan, L.; MacInnis, R.J.; Moore, S.C.; Tobias, G.S.; Anton-Culver, H.; Freeman, L.B.; et al. Body-Mass Index and Mortality among 1.46 Million White Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 2211–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerhan, J.R.; Moore, S.C.; Jacobs, E.J.; Kitahara, C.M.; Rosenberg, P.S.; Adami, H.-O.; Ebbert, J.O.; English, D.R.; Gapstur, S.M.; Giles, G.G.; et al. A pooled analysis of waist circumference and mortality in 650,000 adults. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2014, 89, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFronzo, R.A.; Ferrannini, E.; Groop, L.; Henry, R.R.; Herman, W.H.; Holst, J.J.; Hu, F.B.; Kahn, C.R.; Raz, I.; Shulman, G.I.; et al. Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2015, 1, 15019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seravalle, G.; Grassi, G. Obesity and hypertension. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 122, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Estevez, L.; Moreno-Bueno, G. Updating the role of obesity and cholesterol in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2019, 21, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puhl, R.; Suh, Y. Health Consequences of Weight Stigma: Implications for Obesity Prevention and Treatment. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2015, 4, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, S.V.; Hicks, G.E.; Zhang, Y.; Niu, J.; Apovian, C.M.; White, D.K. The association of waist circumference with walking difficulty among adults with or at risk of knee osteoarthritis: The Osteoarthritis Initiative. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2017, 25, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, S.V.; Walsh, M.K.; Pratt, J.A.; Toosizadeh, N.; Najafi, B.; Travison, T.G. Changes in spatiotemporal gait patterns during flat ground walking and obstacle crossing 1 year after bariatric surgery. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2016, 12, 1080–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Yan, Z.; Chen, Y.; Liu, F. A social contagious model of the obesity epidemic. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Encuesta Europea de Salud 2014. Instituto Nacional de Estadística. Gobierno De España. Número De Días Por Semana De Ejercicio Físico Durante El Tiempo De Ocio Según Sexo y Grupo De Edad. Población De 15 y Más Años. Available online: https://www.ine.es/jaxi/Tabla.htm?path=/t15/p420/a2014/p06/l0/&file=04022.px&L=0 (accessed on 3 March 2020).
- Kolotkin, R.L.; Andersen, J.R. A systematic review of reviews: Exploring the relationship between obesity, weight loss and health-related quality of life. Clin. Obes. 2017, 7, 273–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillison, F.B.; Skevington, S.M.; Sato, A.; Standage, M.; Evangelidou, S. The effects of exercise interventions on quality of life in clinical and healthy populations; a meta-analysis. Soc. Sci. Med. 2009, 68, 1700–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The WHOQOL Group. The World Health Organization quality of life assessment (WHOQOL): Position paper from the World Health Organization. Soc. Sci. Med. 1995, 41, 1403–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, C.; Calvo, D.; María, C.; Sampedro, G. Health related to quality of life and their relationship with adherence to the mediterranean diet and physical activity at the university in Galicia. Nutr. Clín. Diet. Hosp. 2017, 37, 42–49. [Google Scholar]
- Piercy, K.L.; Troiano, R.P.; Ballard, R.M.; Carlson, S.A.; Fulton, J.E.; Galuska, D.A.; George, S.M.; Olson, R.D. The physical activity guidelines for Americans. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2018, 320, 2020–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galilea-Zabalza, I.; Buil-Cosiales, P.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Toledo, E.; Ortega-Azorín, C.; Díez-Espino, J.; Vázquez-Ruiz, Z.; Zomeño, M.D.; Vioque, J.; Martínez, J.A.; et al. Mediterranean diet and quality of life: Baseline cross-sectional analysis of the PREDIMED-PLUS trial. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanning, J.; Walkup, M.P.; Ambrosius, W.T.; Brawley, L.R.; Ip, E.H.; Marsh, A.P.; Rejeski, W.J. Change in health-related quality of life and social cognitive outcomes in obese, older adults in a randomized controlled weight loss trial: Does physical activity behavior matter? J. Behav. Med. 2018, 41, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, M.; Lee, S.; Kim, H.; Baek, W.-C.; Kimm, H. Effect of Aerobic Physical Activity on Health-Related Quality of Life in Middle Aged Women with Osteoarthritis: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2016–2017). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daimiel, L.; Martínez-González, M.A.; Corella, D.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Schröder, H.; Vioque, J.; Romaguera, D.; Martínez, J.A.; Wärnberg, J.; Lopez-Miranda, J.; et al. Physical fitness and physical activity association with cognitive function and quality of life: Baseline cross-sectional analysis of the PREDIMED-Plus trial. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saboya, P.P.; Bodanese, L.C.; Zimmermann, P.R.; da Silva Gustavo, A.; Assumpção, C.M.; Londero, F. Síndrome metabólica e qualidade de vida: Uma revisão sistemática. Rev. Lat. Am. Enferm. 2016, 24, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Heistaro, S.; Jousilahti, P.; Lahelma, E.; Vartiainen, E.; Puska, P. Self rated health and mortality: A long term prospective study in eastern Finland. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2001, 55, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slagter, S.N.; van Vliet-Ostaptchouk, J.V.; van Beek, A.P.; Keers, J.C.; Lutgers, H.L.; van der Klauw, M.M.; Wolffenbuttel, B.H.R. Health-Related Quality of Life in Relation to Obesity Grade, Type 2 Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Inflammation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estudio Predimed-Plus. Available online: https://www.predimedplus.com/ (accessed on 24 May 2019).
- Martínez-González, M.A.; Buil-Cosiales, P.; Corella, D.; Bulló, M.; Fitó, M.; Vioque, J.; Romaguera, D.; Martínez, J.A.; Wärnberg, J.; López-Miranda, J.; et al. Cohort Profile: Design and methods of the PREDIMED-Plus randomized trial. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2019, 48, 387–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas-Salvadó, J.; Díaz-López, A.; Ruiz-Canela, M.; Basora, J.; Fitó, M.; Corella, D.; Serra-Majem, L.; Wärnberg, J.; Romaguera, D.; Estruch, R.; et al. Effect of a Lifestyle Intervention Program With Energy-Restricted Mediterranean Diet and Exercise on Weight Loss and Cardiovascular Risk Factors: One-Year Results of the PREDIMED-Plus Trial. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 777–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, K.G.M.M.; Eckel, R.H.; Grundy, S.M.; Zimmet, P.Z.; Cleeman, J.I.; Donato, K.A.; Fruchart, J.C.; James, W.P.T.; Loria, C.M.; Smith, S.C. Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: A joint interim statement of the international diabetes federation task force on epidemiology and prevention; National heart, lung, and blood institute; American heart association; World heart federation; International atherosclerosis society; And international association for the study of obesity. Circulation 2009, 120, 1640–1645. [Google Scholar]
- Vilagut, G.; Ferrer, M.; Rajmil, L.; Rebollo, P.; Permanyer-Miralda, G.; Quintana, J.M.; Santed, R.; Valderas, J.M.; Ribera, A.; Domingo-Salvany, A.; et al. The Spanish version of the Short Form 36 Health Survey: A decade of experience and new developments. Gac. Sanit. 2005, 19, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, J.; Regidor, E.; Barrio, G.; Prieto, L.; Rodríguez, C.; de la Fuente, L. Population reference values of the Spanish version of the Health Questionnaire SF-36. Med. Clin. 1998, 111, 410–416. [Google Scholar]
- Molina, L.; Sarmiento, M.; Peñafiel, J.; Donaire, D.; Garcia-Aymerich, J.; Gomez, M.; Ble, M.; Ruiz, S.; Frances, A.; Schröder, H.; et al. Validation of the Regicor Short Physical Activity Questionnaire for the Adult Population. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0168148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainsworth, B.E.; Haskell, W.L.; Whitt, M.C.; Irwin, M.L.; Swartz, A.M.; Strath, S.J.; O’Brien, W.L.; Bassett, J.; Schmitz, K.H.; Emplaincourt, P.O.; et al. Compendium of physical activities: An update of activity codes and MET intensities. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2000, 32, S498–S516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Garcia, E.; Guallar-Castillón, P.; Garcia-Esquinas, E.; Rodríguez-Artalejo, F. Metabolically healthy obesity and health-related quality of life: A prospective cohort study. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pengpid, S.; Peltzer, K. High sedentary behaviour and low physical activity are associated with lower health related quality of life in Myanmar and Vietnam. Cogent Psychol. 2019, 6, 1601327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jantunen, H.; Wasenius, N.; Salonen, M.K.; Kautiainen, H.; von Bonsdorff, M.B.; Kajantie, E.; Eriksson, J.G. Change in physical activity and health-related quality of life in old age—A 10-year follow-up study. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2019, 29, 1797–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikkelsen, K.; Stojanovska, L.; Polenakovic, M.; Bosevski, M.; Apostolopoulos, V. Exercise and mental health. Maturitas 2017, 106, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsufiany, M.B.; Lohman, E.B.; Daher, N.S.; Gang, G.R.; Shallan, A.I.; Jaber, H.M. Non-specific chronic low back pain and physical activity. Medicine 2020, 99, e18544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahangiry, L.; Montazeri, A.; Najafi, M.; Yaseri, M.; Farhangi, M.A. An interactive web-based intervention on nutritional status, physical activity and health-related quality of life in patient with metabolic syndrome: A randomized-controlled trial (The Red Ruby Study). Nutr. Diabetes 2017, 7, e240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busutil, R.; Espallardo, O.; Torres, A.; Martínez-Galdeano, L.; Zozaya, N.; Hidalgo-Vega, Á. The impact of obesity on health-related quality of life in Spain. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2017, 15, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcones-Molero, M.F.; Sánchez-Villegas, A.; Martínez-González, M.A.; Bes-Rastrollo, M.; Martínez-Urbistondo, M.; Santabárbara, J.; Martínez, J.A. The influence of obesity and weight gain on quality of life according to the SF-36 for individuals of the dynamic follow-up cohort of the University of Navarra. Rev. Clínica Española 2018, 218, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayón-Orea, C.; Santiago, S.; Bes-Rastrollo, M.; Martínez-González, M.; Pastor, M.; Moreno-Aliaga, M.; Tur, J.; Garcia, A.; Martínez, J. Determinants of Self-Rated Health Perception in a Sample of a Physically Active Population: PLENUFAR VI Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, S.H.; Huang, W.L.; Akter, S.; Binks, M. Obesity and pain: A systematic review. Int. J. Obes. 2019, 44, 969–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tronieri, J.S.; Wurst, C.M.C.; Pearl, R.L.; Allison, K.C. Sex Differences in Obesity and Mental Health. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2017, 19, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sylliaas, H.; Brovold, T.; Wyller, T.B.; Bergland, A. Prolonged strength training in older patients after hip fracture: A randomised controlled trial. Age Ageing 2012, 41, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karinkanta, S.; Nupponen, R.; Heinonen, A.; Pasanen, M.; Sievänen, H.; Uusi-Rasi, K.; Fogelholm, M.; Kannus, P. Effects of exercise on health-related quality of life and fear of falling in home-dwelling older women. J. Aging Phys. Act. 2012, 20, 198–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awick, E.A.; Wójcicki, T.R.; Olson, E.A.; Fanning, J.; Chung, H.D.; Zuniga, K.; Mackenzie, M.; Kramer, A.F.; McAuley, E. Differential exercise effects on quality of life and health-related quality of life in older adults: A randomized controlled trial. Qual. Life Res. 2015, 24, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozas Saboya, P.; Bodanese, L.C.; Zimmermann, P.R.; da Silva Gustavo, A.; Macagnan, F.E.; Pandolfo Feoli, A.M.; da Silva Oliveira, M.; Lourega Chieza, F. Association between metabolic syndrome and quality of life. Sci. Med. 2016, 26, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hajian-Tilaki, K.; Heidari, B.; Hajian-Tilaki, A. Are gender differences in health-related quality of life attributable to sociodemographic characteristics and chronic disease conditions in elderly people? Int. J. Prev. Med. 2017, 8, 95. [Google Scholar]
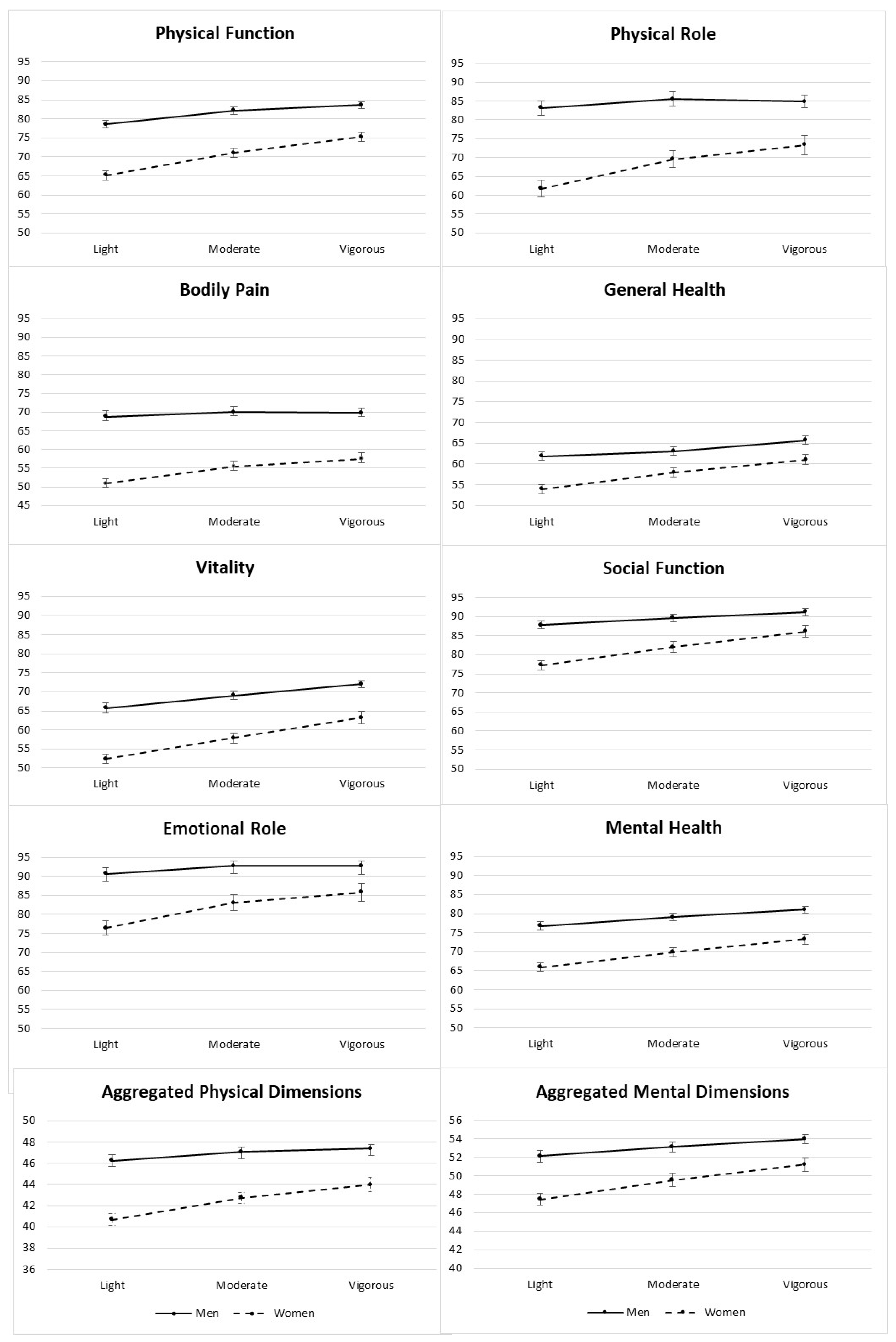
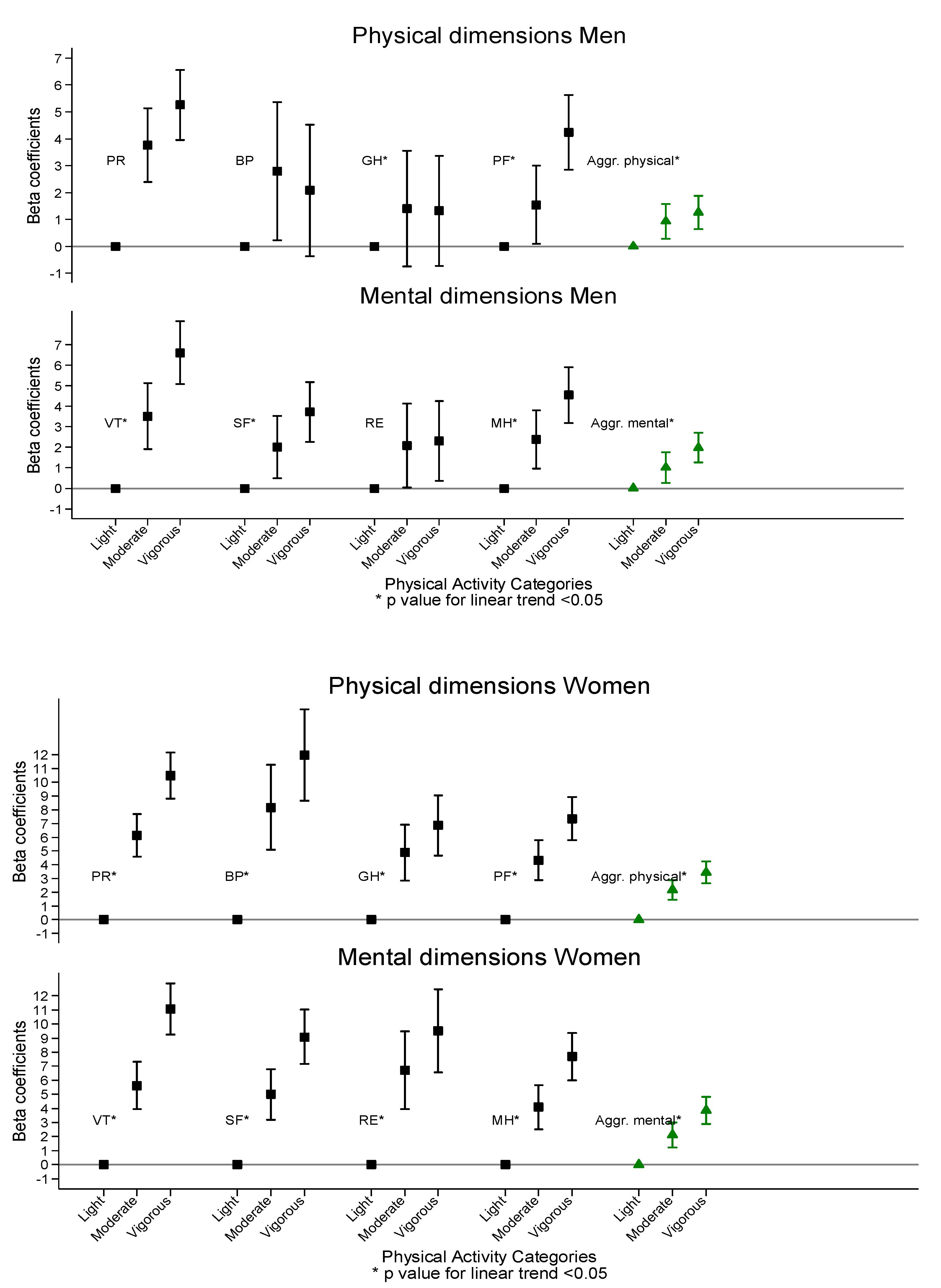
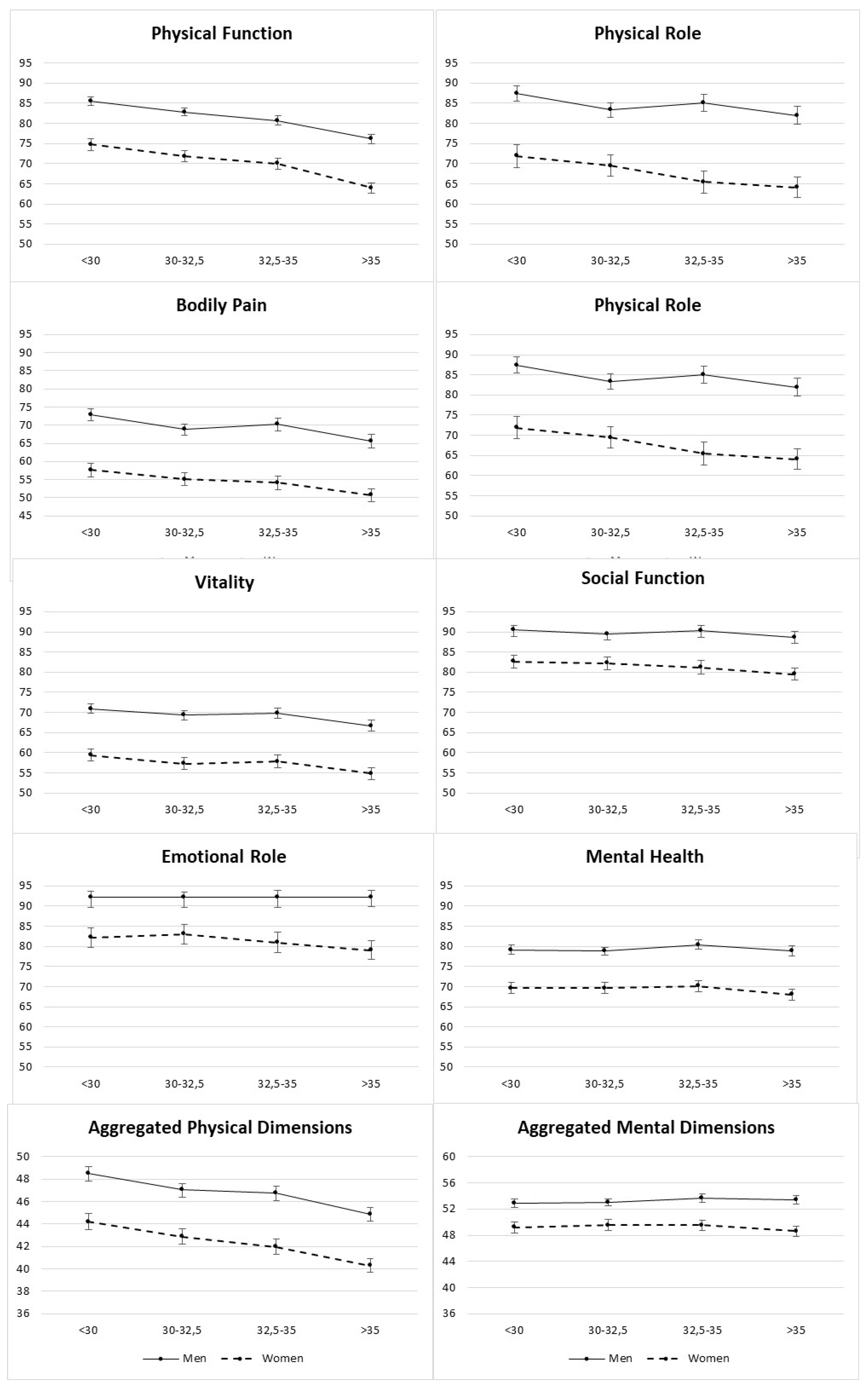
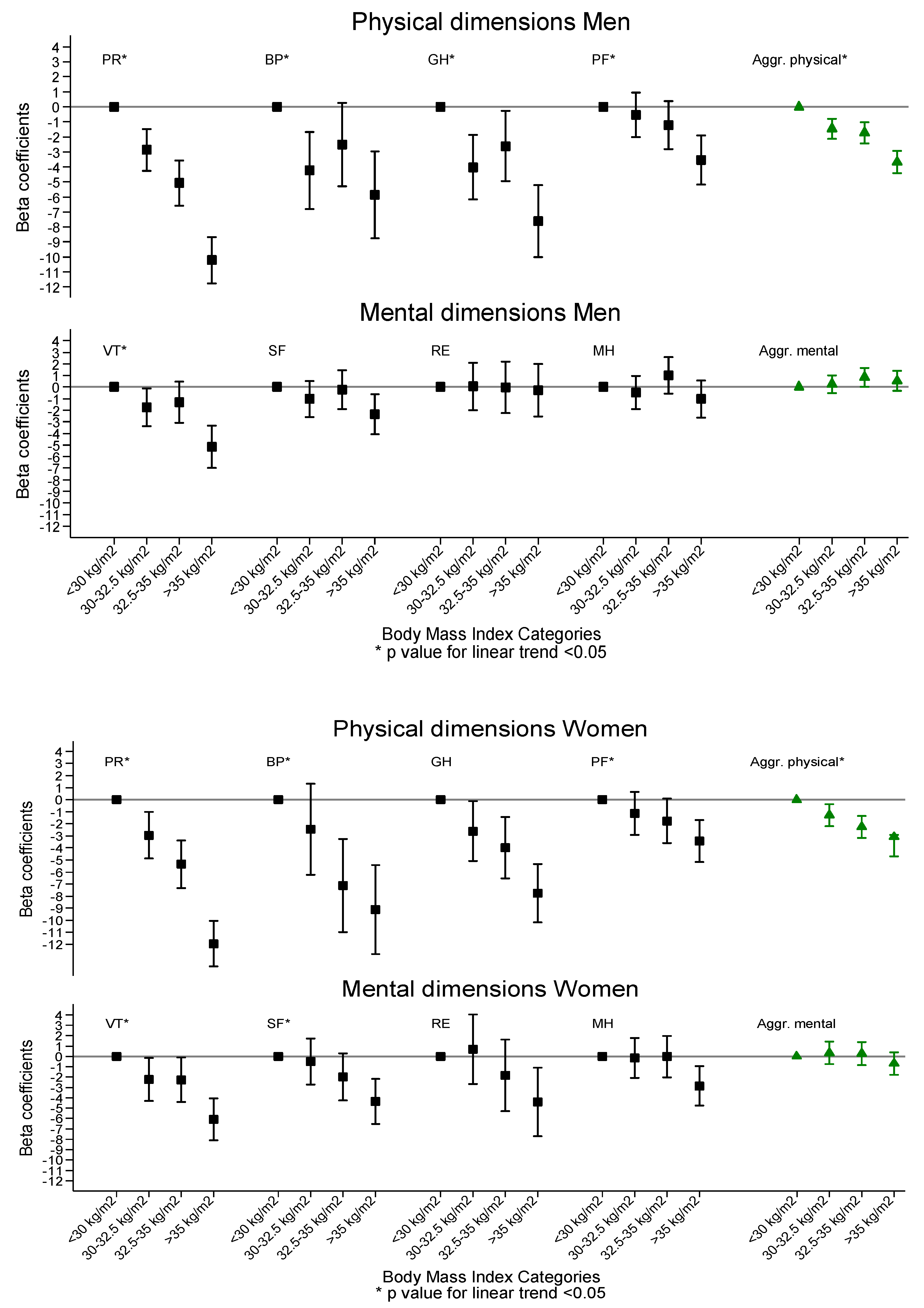
| PA | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Men | Women | |||||||||||
| Light | Moderate | Vigorous | p-Value | Light | Moderate | Vigorous | p-Value | Light | Moderate | Vigorous | p-Value | ||
| METs–min/week | 0–1200 | 1200–2800 | >2800 | 0–1200 | 1200–2800 | >2800 | 0–1200 | 1200–2800 | >2800 | ||||
| N | 2217 | 2206 | 2297 | 977 | 1079 | 1417 | 1240 | 1127 | 880 | ||||
| Age (y) | 64 (5) | 65 (5) | 65 (5) | <0.001 | 62 (5) | 64 (5) | 64 (5) | <0.001 | 66 (4) | 66 (4) | 66(4) | 0.356 | |
| Body-mass index (kg/m2) | 33.2 (3.5) | 32.4 (3.3) | 32.0 (3.1) | <0.001 | 33.0 (3.3) | 32.1 (3.1) | 31.9 (3.0) | <0.001 | 33.4 (3.6) | 33.7 (3.5) | 32.2 (3.3) | <0.001 | |
| Type 2 Diabetes at baseline (%) | 29.4 | 26.1 | 26.3 | 0.048 | 30.6 | 28.8 | 28.5 | 0.579 | 28.4 | 23.5 | 22.7 | 0.017 | |
| Depression at baseline (%) | 23.9 | 20.8 | 17.7 | <0.001 | 12.4 | 13.1 | 10.9 | 0.248 | 32.9 | 28.1 | 28.5 | 0.021 | |
| Systolic blood pressure ≥140 mmHg (%) | 44.4 | 47.7 | 48.6 | 0.013 | 46.3 | 51.5 | 53.3 | 0.003 | 43 | 44.1 | 41 | 0.382 | |
| Systolic blood pressure ≥90 mmHg (%) | 18.5 | 18.9 | 19.1 | 0.865 | 24.8 | 23.9 | 22.2 | 0.325 | 13.6 | 14.1 | 14.1 | 0.907 | |
| History of cancer (%) | 8.5 | 7.3 | 5.8 | 0.002 | 4 | 5.9 | 4.2 | 0.068 | 12.1 | 8.6 | 8.4 | 0.004 | |
| History of lung disease (%) | 5.2 | 4.1 | 4.3 | 0.157 | 5.7 | 4.5 | 4.7 | 0.415 | 4.9 | 3.7 | 3.5 | 0.238 | |
| Smoking status (%) | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.002 | ||||||||||
| Current smoker | 47.4 | 44.9 | 39.9 | 22.6 | 19.6 | 23.1 | 66.9 | 69 | 66.9 | ||||
| Former smoker | 37.8 | 43.4 | 48.9 | 56.4 | 63.8 | 62.5 | 23.2 | 24 | 27.2 | ||||
| Never smoker | 14.8 | 11.7 | 11.2 | 21 | 16.6 | 14.5 | 10 | 7 | 5.9 | ||||
| Marital status (%) | 0.004 | 0.150 | 10 | 0.234 | |||||||||
| Married | 74.7 | 75.8 | 78.9 | 82.8 | 84.7 | 86.5 | 68.3 | 67.2 | 66.8 | ||||
| Single | 5.4 | 5 | 5.1 | 5.6 | 4.3 | 4 | 5.2 | 5.6 | 7 | ||||
| Divorced | 9.1 | 7.6 | 7.1 | 8.7 | 7.6 | 6.3 | 9.4 | 7.5 | 8.4 | ||||
| Widowed/widower | 10.9 | 11.7 | 8.8 | 2.9 | 3.4 | 3.3 | 17.1 | 19.7 | 17.8 | ||||
| Educational level (%) | 0.939 | 0.006 | 0.468 | ||||||||||
| Primary school or less | 49.7 | 48.9 | 48.4 | 35.2 | 37.5 | 42 | 61.1 | 59.8 | 58.8 | ||||
| Secondary school | 28.6 | 29.1 | 29.2 | 33.9 | 32.3 | 32 | 24.4 | 26.1 | 24.7 | ||||
| High school or university | 21.7 | 22 | 22.4 | 30.9 | 30.2 | 26 | 14.4 | 14.1 | 16.6 | ||||
| BMI | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Men | Women | |||||||||||||||
| kg/m2 | <30 | 30–32.4 | 32.5–34.9 | >35 | p-Value | <30 | 30–32.4 | 32.5–34.9 | ≥35 | p-Value | <30 | 30–32.4 | 32.5–34.9 | ≥35 | p-Value | ||
| N | 1.747 | 1.846 | 1.517 | 1.610 | 959 | 1.032 | 780 | 702 | 788 | 814 | 737 | 908 | |||||
| Age (SD) | 65 (5) | 65 (5) | 65 (5) | 65 (5) | 0.093 | 64 (5) | 64 (5) | 63 (5) | 63 (5) | 0.003 | 66 (4) | 67 (4) | 66 (4) | 66 (4) | 0.352 | ||
| PA (Mets-min/week) | 2724.6 (2309.4) | 2595.1 (2376.1) | 2473.1 (2381.4) | 2014.7 (2059.5) | <0.001 | 3108.9 (2524.7) | 2944.7 (2667.0) | 2852.5 (2711.9) | 2369.6 (2377.2) | <0.001 | 2256.8 (1916.9) | 2151.9 (1854.8) | 2071.6 (1893.0) | 1740.3 (1727.5) | <0.001 | ||
| Type 2 diabetes at baseline (%) | 26.3 | 26.1 | 27.5 | 29.4 | 0.116 | 29.7 | 27.8 | 29 | 30.8 | 0.192 | 22.1 | 23.8 | 25.9 | 28.4 | 0.121 | ||
| Depression at baseline (%) | 17.9 | 19.9 | 21.6 | 24 | <0.001 | 10.5 | 11.8 | 13.4 | 12.7 | 0.306 | 26.8 | 30 | 30.4 | 32.7 | 0.068 | ||
| Systolic blood pressure ≥140 mmHg (%) | 42.9 | 48.2 | 46 | 50.8 | <0.001 | 47.3 | 50.5 | 51.4 | 55.1 | 0.019 | 37.4 | 45.3 | 40.3 | 47.4 | <0.001 | ||
| Diastolic blood pressure ≥90 mmHg (%) | 15.3 | 19.1 | 20.4 | 20.9 | <0.001 | 19.7 | 23.6 | 25.5 | 26.2 | 0.006 | 9.9 | 13.5 | 15.1 | 16.7 | 0.001 | ||
| History of cancer (%) | 7.6 | 6.7 | 7.2 | 7.5 | 0.736 | 6 | 4.3 | 5.1 | 3.1 | 0.048 | 9.5 | 9.7 | 9.4 | 10.8 | 0.749 | ||
| History of lung disease (%) | 4.1 | 3.9 | 5 | 5.2 | 0.155 | 4.5 | 3.9 | 5.5 | 6.3 | 0.106 | 3.7 | 3.8 | 4.5 | 4.4 | 0.798 | ||
| Smoking status (%) | <0.001 | 0.120 | <0.001 | ||||||||||||||
| Current smoker | 42.6 | 40.5 | 44.7 | 48.8 | 23 | 21.5 | 20.6 | 22.2 | 66.4 | 64.7 | 70.2 | 69.3 | |||||
| Former smoker | 42.1 | 46.8 | 43.4 | 41.2 | 57.5 | 62.8 | 63.8 | 60.9 | 23.4 | 26.5 | 21.9 | 26 | |||||
| Never smoker | 15.3 | 12.7 | 11.9 | 10 | 19.5 | 15.7 | 15.7 | 16.9 | 10.2 | 8.9 | 7.9 | 4.8 | |||||
| Marital status (%) | 0.078 | 0.113 | 0.702 | ||||||||||||||
| Married | 77 | 77.8 | 77.5 | 73.6 | 84.5 | 85.1 | 86.7 | 83 | 67.7 | 68.4 | 67.8 | 66.3 | |||||
| Single | 5 | 4.9 | 4.8 | 5.9 | 3.2 | 5 | 4.3 | 6 | 7.1 | 4.9 | 5.4 | 5.8 | |||||
| Divorced | 8.7 | 7.6 | 7.3 | 8.1 | 8.6 | 7.2 | 5.9 | 7.6 | 8.7 | 8.1 | 8.7 | 8.5 | |||||
| Widowed/widower | 9.5 | 9.7 | 10.4 | 12.6 | 3.7 | 2.7 | 3.1 | 3.4 | 16.5 | 18.6 | 18.1 | 19.5 | |||||
| Educational level (%) | <0.001 | 0.259 | 0.003 | ||||||||||||||
| Primary school or less | 44.1 | 48.3 | 51.9 | 52.4 | 35.7 | 38.8 | 41 | 40.2 | 54.3 | 60.4 | 63.4 | 61.9 | |||||
| Secondary school | 30.2 | 29.4 | 27.9 | 28.3 | 33 | 32.8 | 32.1 | 32.6 | 26.8 | 25.1 | 23.5 | 24.9 | |||||
| High school or university | 25.8 | 22.3 | 20.2 | 19.3 | 31.4 | 28.5 | 26.9 | 27.2 | 18.9 | 14.5 | 13.2 | 13.2 | |||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marcos-Delgado, A.; Fernández-Villa, T.; Martínez-González, M.Á.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Corella, D.; Castañer, O.; Martínez, J.A.; Alonso-Gómez, Á.M.; Wärnberg, J.; Vioque, J.; et al. The Effect of Physical Activity and High Body Mass Index on Health-Related Quality of Life in Individuals with Metabolic Syndrome. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3728. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17103728
Marcos-Delgado A, Fernández-Villa T, Martínez-González MÁ, Salas-Salvadó J, Corella D, Castañer O, Martínez JA, Alonso-Gómez ÁM, Wärnberg J, Vioque J, et al. The Effect of Physical Activity and High Body Mass Index on Health-Related Quality of Life in Individuals with Metabolic Syndrome. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(10):3728. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17103728
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarcos-Delgado, Alba, Tania Fernández-Villa, Miguel Ángel Martínez-González, Jordi Salas-Salvadó, Dolores Corella, Olga Castañer, J. Alfredo Martínez, Ángel M. Alonso-Gómez, Julia Wärnberg, Jesús Vioque, and et al. 2020. "The Effect of Physical Activity and High Body Mass Index on Health-Related Quality of Life in Individuals with Metabolic Syndrome" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 10: 3728. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17103728
APA StyleMarcos-Delgado, A., Fernández-Villa, T., Martínez-González, M. Á., Salas-Salvadó, J., Corella, D., Castañer, O., Martínez, J. A., Alonso-Gómez, Á. M., Wärnberg, J., Vioque, J., Romaguera, D., López-Miranda, J., Estruch, R., Tinahones, F. J., Lapetra, J., Serra-Majem, J. L., García-Molina, L., Tur, J. A., de Paz, J. A., ... Martín, V., for the PREDIMED-Plus Investigators. (2020). The Effect of Physical Activity and High Body Mass Index on Health-Related Quality of Life in Individuals with Metabolic Syndrome. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(10), 3728. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17103728





















