Evaluating Transmission Heterogeneity and Super-Spreading Event of COVID-19 in a Metropolis of China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Analytical Approach
2.2.1. Inference of Transmission Characteristics
2.2.2. Assessment of Control Measures
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of COVID-19 Cases
3.2. Reconstructed Transmission Chains
3.3. Estimation of R and k
3.4. Super Spreading Event in Tianjin
3.5. Effect of Government Control Measures
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SARS | Severe acute respiratory syndrome |
| 2019-nCoV | 2019 novel coronavirus |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| SARS-CoV-2 | Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 |
| COVID-19 | Corona Virus Disease 2019 |
| NHC | National Health Commission |
| SSEs | Super-spreading events |
| EM algorithm | Expectation-maximization algorithm |
References
- W.H.O. Statement on the Second Meeting of the International Health Regulations (2005) Emergency Committee Regarding the Outbreak of Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV); WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd-Smith, J.O.; Schreiber, S.J.; Kopp, P.E.; Getz, W.M. Superspreading and the effect of individual variation on disease emergence. Nature 2005, 438, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucharski, A.; Althaus, C. The role of supersprea ding in Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) transmission. Eurosurveillance 2015, 20, 21167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, G.; Liu, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, B.; Bi, Y.; Gao, G.F. MERS, SARS, and Ebola: The Role of Super-Spreaders in Infectious Disease. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 18, 398–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, R.A. Super-spreaders in infectious diseases. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 15, e510–e513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, M.S.Y.; Dalziel, B.D.; Funk, S.; McClelland, A.; Tiffany, A.; Riley, S.; Metcalf, C.J.E.; Grenfell, B.T. Spatial and temporal dynamics of superspreading events in the 2014–2015 West Africa Ebola epidemic. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 2337–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faye, O.; Boëlle, P.Y.; Heleze, E.; Faye, O.; Loucoubar, C.; Magassouba, N.; Soropogui, B.; Keita, S.; Gakou, T.; Bah, E.H.I.; et al. Chains of transmission and control of Ebola virus disease in Conakry, Guinea, in 2014: An observational study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Guan, X.; Wu, P.; Wang, X.; Zhou, L.; Tong, Y.; Ren, R.; Leung, K.S.; Lau, E.H.; Wong, J.Y.; et al. Early transmission dynamics in Wuhan, China, of novel coronavirus–infected pneumonia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riou, J.; Althaus, C.L. Pattern of early human-to-human transmission of Wuhan 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV), December 2019 to January 2020. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25, 2000058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Gayle, A.A.; Wilder-Smith, A.; Rocklöv, J. The reproductive number of COVID-19 is higher compared to SARS coronavirus. J. Travel Med. 2020, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tariq, A.; Lee, Y.; Roosa, K.; Blumberg, S.; Yan, P.; Ma, S.; Chowell, G. Real-time monitoring the transmission potential of COVID-19 in Singapore, February 2020. medRxiv 2020. Available online: https://www.medrxiv.org/content/early/2020/03/12/2020.02.21.20026435.full.pdf (accessed on 21 February 2020). [CrossRef]
- Bi, Q.; Wu, Y.; Mei, S.; Ye, C.; Zou, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Wei, L.; Truelove, S.A.; Zhang, T.; et al. Epidemiology and Transmission of COVID-19 in Shenzhen China: Analysis of 391 cases and 1286 of their close contacts. MedRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, A.; Abbott, S.; Kucharski, A.J.; Funk, S. Estimating the overdispersion in COVID-19 transmission using outbreak sizes outside China. Wellcome Open Res. 2020, 5, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Eggo, R.M.; Kucharski, A.J. Secondary attack rate and superspreading events for SARS-CoV-2. Lancet 2020, 395, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Li, Y.; Wei, Z.; Zhou, P.; Lyu, L.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, Y.; He, H.; Li, X.; Gao, L.; et al. Investigation and analysis on characteristics of a cluster of COVID-19 associated with exposure in a department store in Tianjin. Zhonghua liu Xing Bing xue za zhi = Zhonghua Liuxingbingxue Zazhi 2020, 41, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Blumberg, S.; Lloyd-Smith, J.O. Inference of R 0 and transmission heterogeneity from the size distribution of stuttering chains. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2013, 9, e1002993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Proposal of New Coronavirus Pneumonia Prevention (Sixth Edition). Available online: http://www.chinacdc.cn/jkzt/crb/zl/szkb_11803/jszl_11815/202003/W020200309376009304000.pdf (accessed on 9 March 2020).
- Tianjin Municipal People’s Government. Available online: http://www.tj.gov.cn/xw/ztzl/tjsyqfk/yqtb/ (accessed on 21 January 2020).
- Tianjin: Come up with 18 Policies for Epidemic Prevention and Control. Available online: http://www.tj.gov.cn/xw/spxw/202001/t20200129_3668285.html (accessed on 29 January 2020).
- Lauer, S.A.; Grantz, K.H.; Bi, Q.; Jones, F.K.; Zheng, Q.; Meredith, H.R.; Azman, A.S.; Reich, N.G.; Lessler, J. The Incubation Period of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) From Publicly Reported Confirmed Cases: Estimation and Application. Ann. Internal Med. 2020, 172, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Health Commission of Ningbo. Available online: http://wjw.ningbo.gov.cn/col/col142/index.html (accessed on 22 January 2020).
- All 9 Family Members in New Year’s Eve Dinners in Heilongjiang Were Confirmed. Available online: http://hlj.people.com.cn/GB/n2/2020/0205/c220024-33767665.html (accessed on 5 February 2020).
- Nine Members of Hongkong Family Feared Infected After Sharing Hotpot. Available online: https://www.straitstimes.com/asia/east-asia/coronavirus-nine-members-of-hong-kong-family-feared-infected-after-sharing-hotpot (accessed on 9 February 2020).
- Fraser, C.; Riley, S.; Anderson, R.M.; Ferguson, N.M. Factors That Make an Infectious Disease Outbreak Controllable. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 6146–6151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Health Commission of Heilongjiang Province. Available online: http://yiqing.ljjk.org.cn/index/patients/newsinfo/id/1887.html (accessed on 21 April 2020).
- Lloyd-Smith, J.O. Maximum likelihood estimation of the negative binomial dispersion parameter for highly overdispersed data, with applications to infectious diseases. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
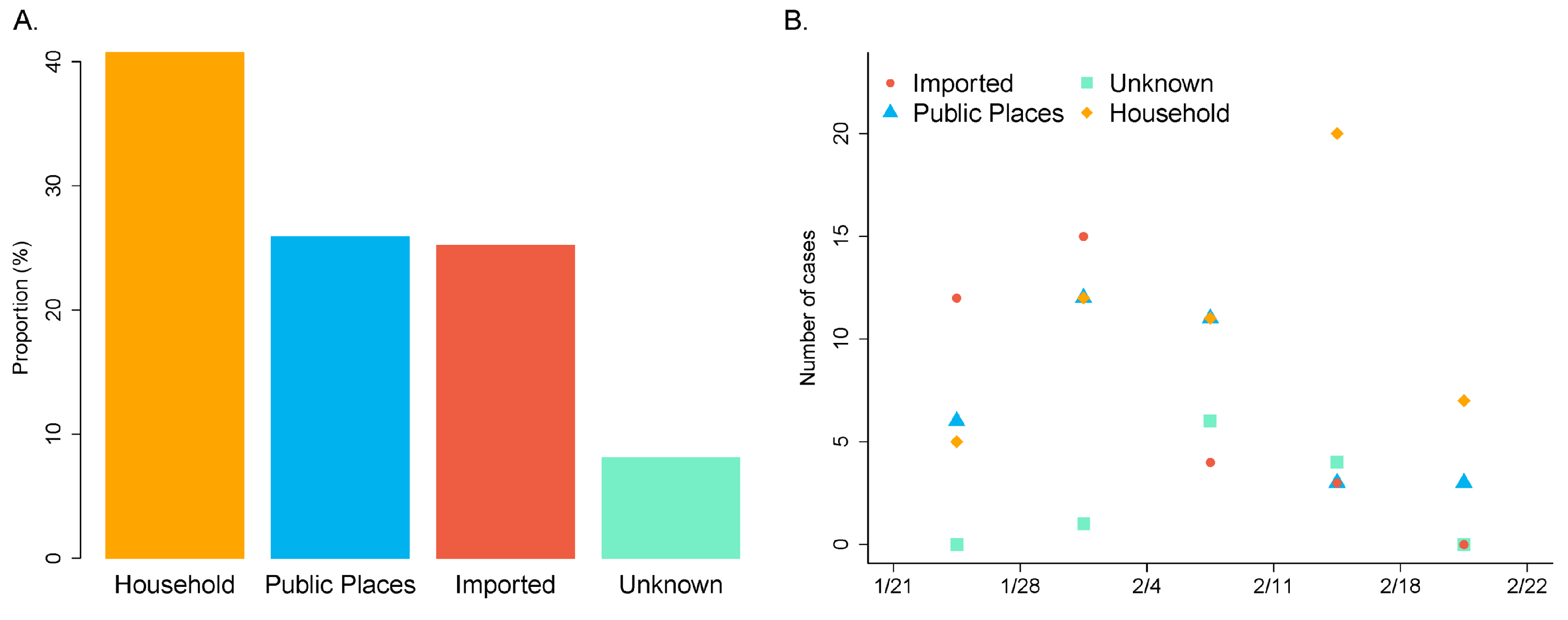
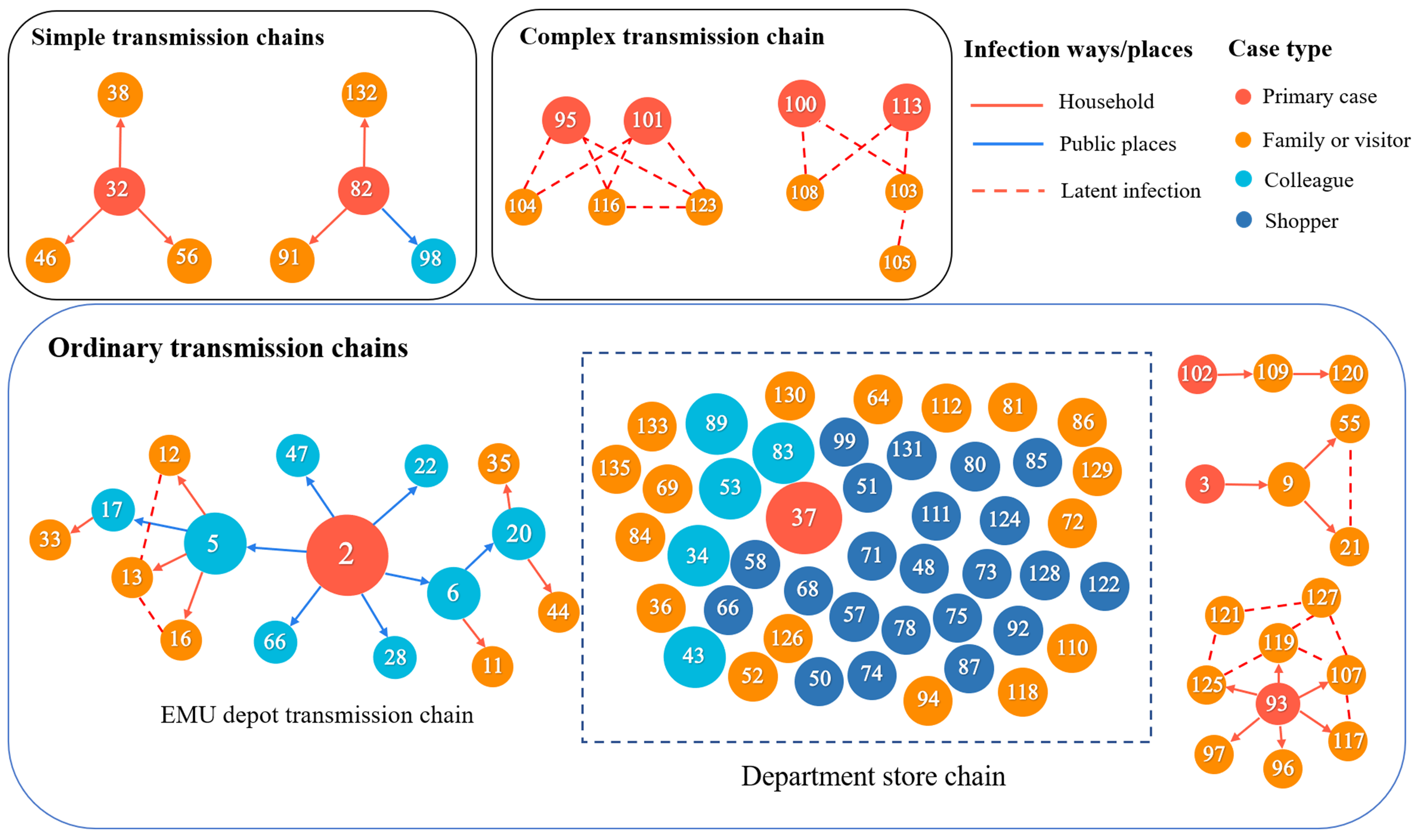
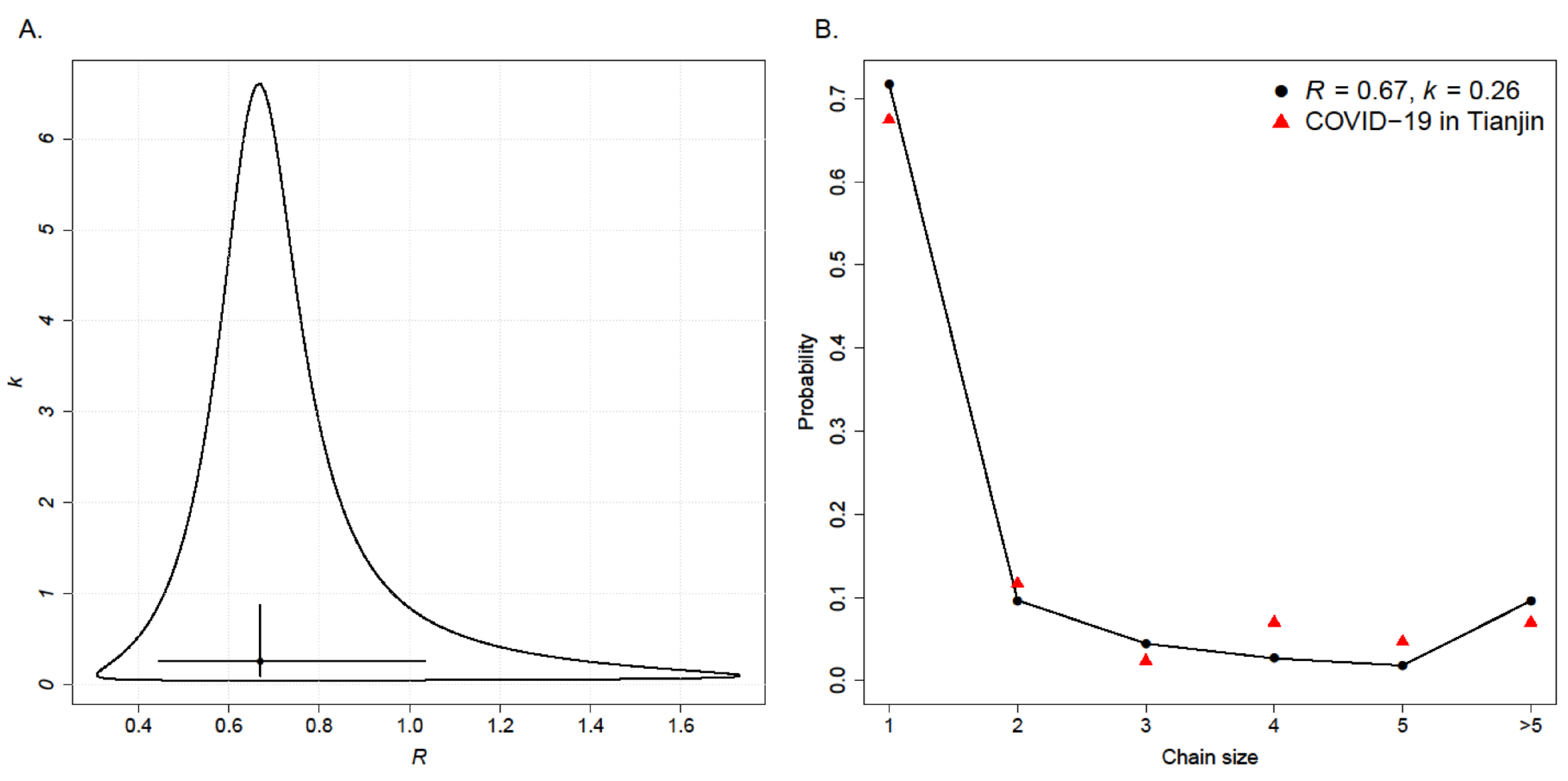
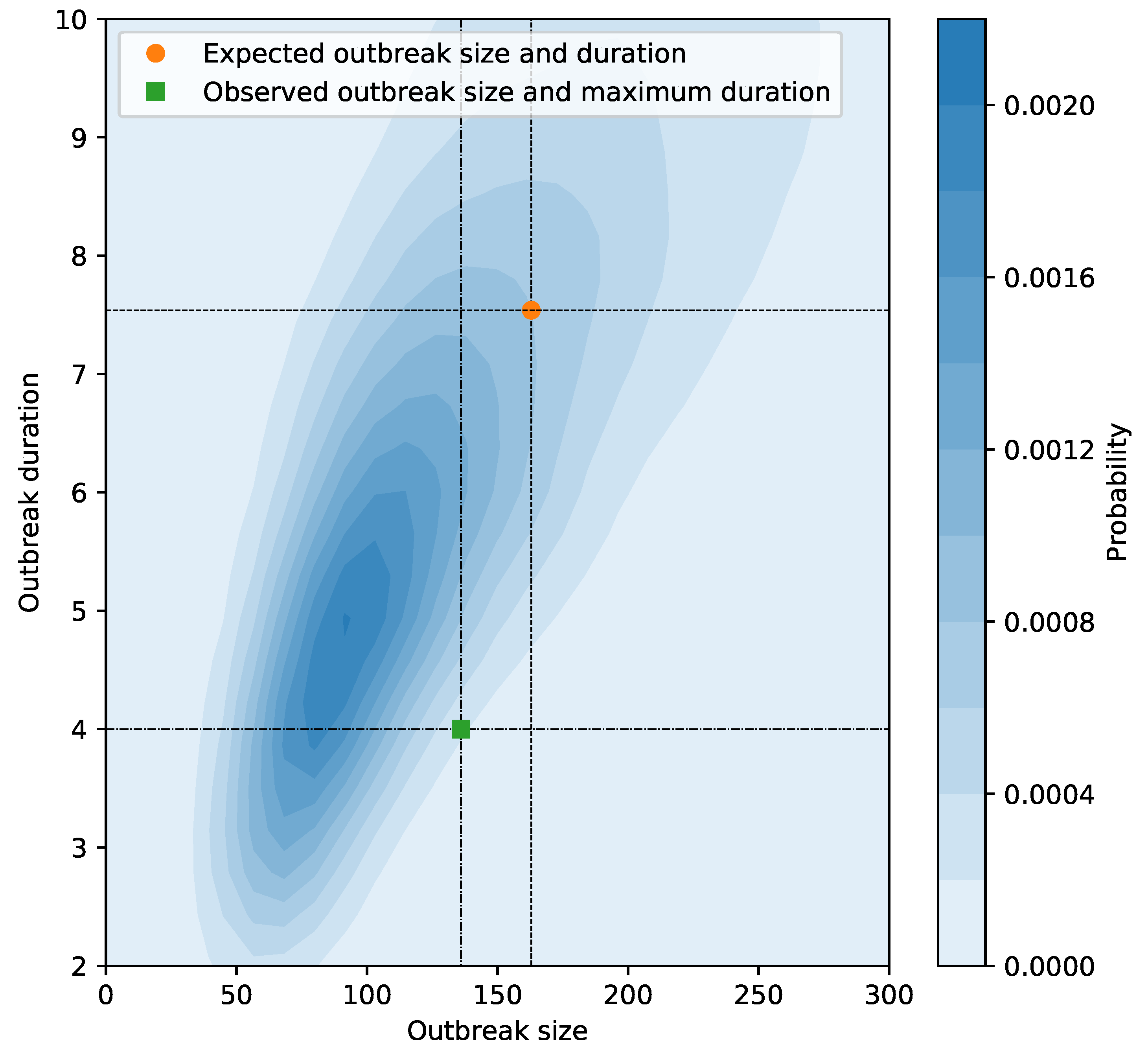
| Chain Type | Amount | Total Number | Average | Range of |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| of Chains | of Cases | Chain Size | Chain Size | |
| Simple transmission chain | 36 | 47 | 1.3 | 1–4 |
| Ordinary transmission chain | 5 | 78 | 15.6 | 3–45 |
| Complex transmission chain | 2 | 10 | 5 | 5–5 |
| Combinatorial Method (95% CI) | EM (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|
| R | 0.67 (0.44, 1.03) | 0.67 (0.54, 0.84) |
| k | 0.26 (0.10, 0.88) | 0.25 (0.13, 0.88) |
| Before 1 February (95% CI) | After 1 February (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|
| R | 0.74 (0.39, 1.61) | 0.53 (0.29, 0.96) |
| k | 0.14 (0.04, 0.63) | 0.77 (0.14, 31.47) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, M.; Zhou, X. Evaluating Transmission Heterogeneity and Super-Spreading Event of COVID-19 in a Metropolis of China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3705. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17103705
Zhang Y, Li Y, Wang L, Li M, Zhou X. Evaluating Transmission Heterogeneity and Super-Spreading Event of COVID-19 in a Metropolis of China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(10):3705. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17103705
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yunjun, Yuying Li, Lu Wang, Mingyuan Li, and Xiaohua Zhou. 2020. "Evaluating Transmission Heterogeneity and Super-Spreading Event of COVID-19 in a Metropolis of China" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 10: 3705. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17103705
APA StyleZhang, Y., Li, Y., Wang, L., Li, M., & Zhou, X. (2020). Evaluating Transmission Heterogeneity and Super-Spreading Event of COVID-19 in a Metropolis of China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(10), 3705. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17103705




