Value Assessment of Health Losses Caused by PM2.5 Pollution in Cities of Atmospheric Pollution Transmission Channel in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Region, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
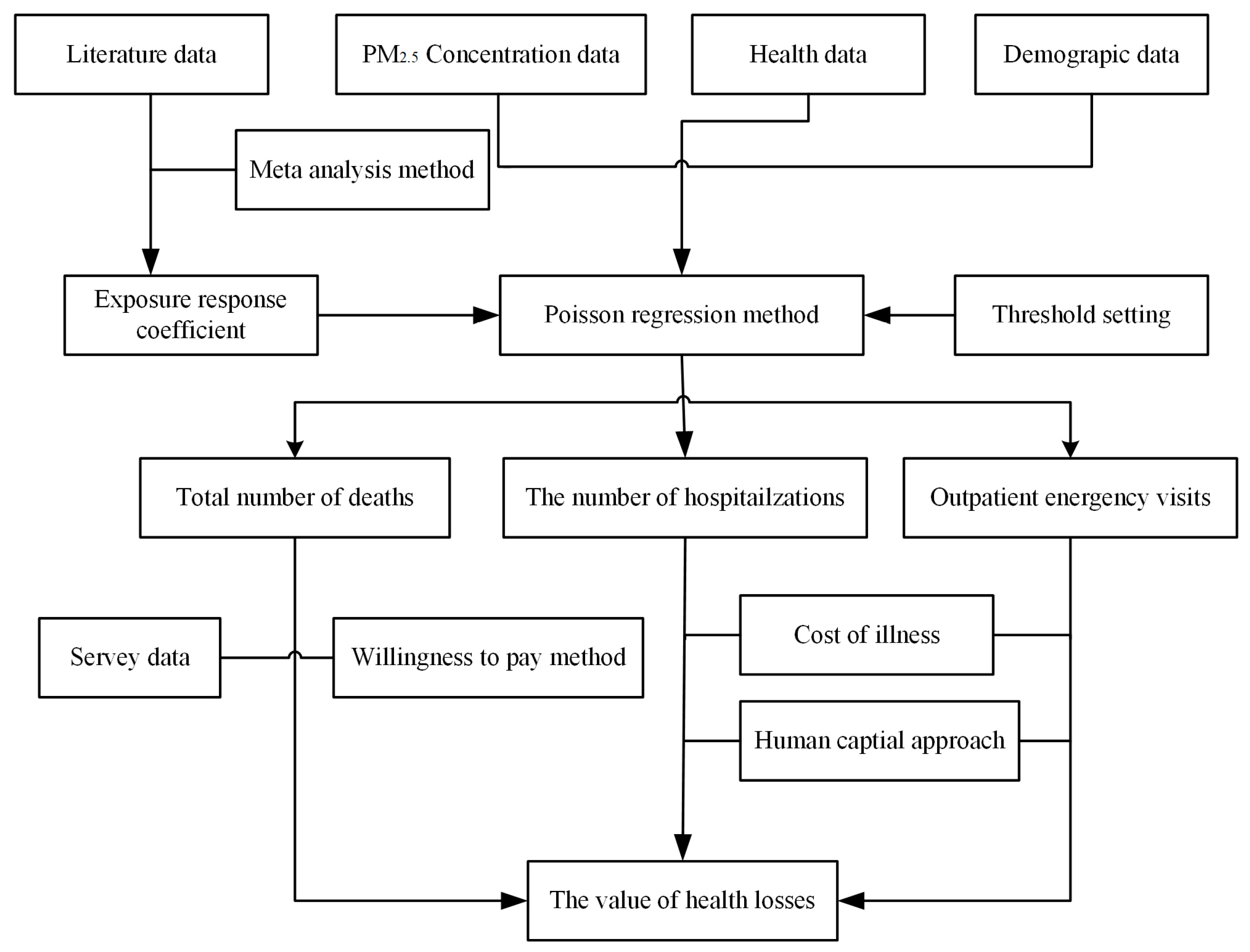
2.1. Research Framework
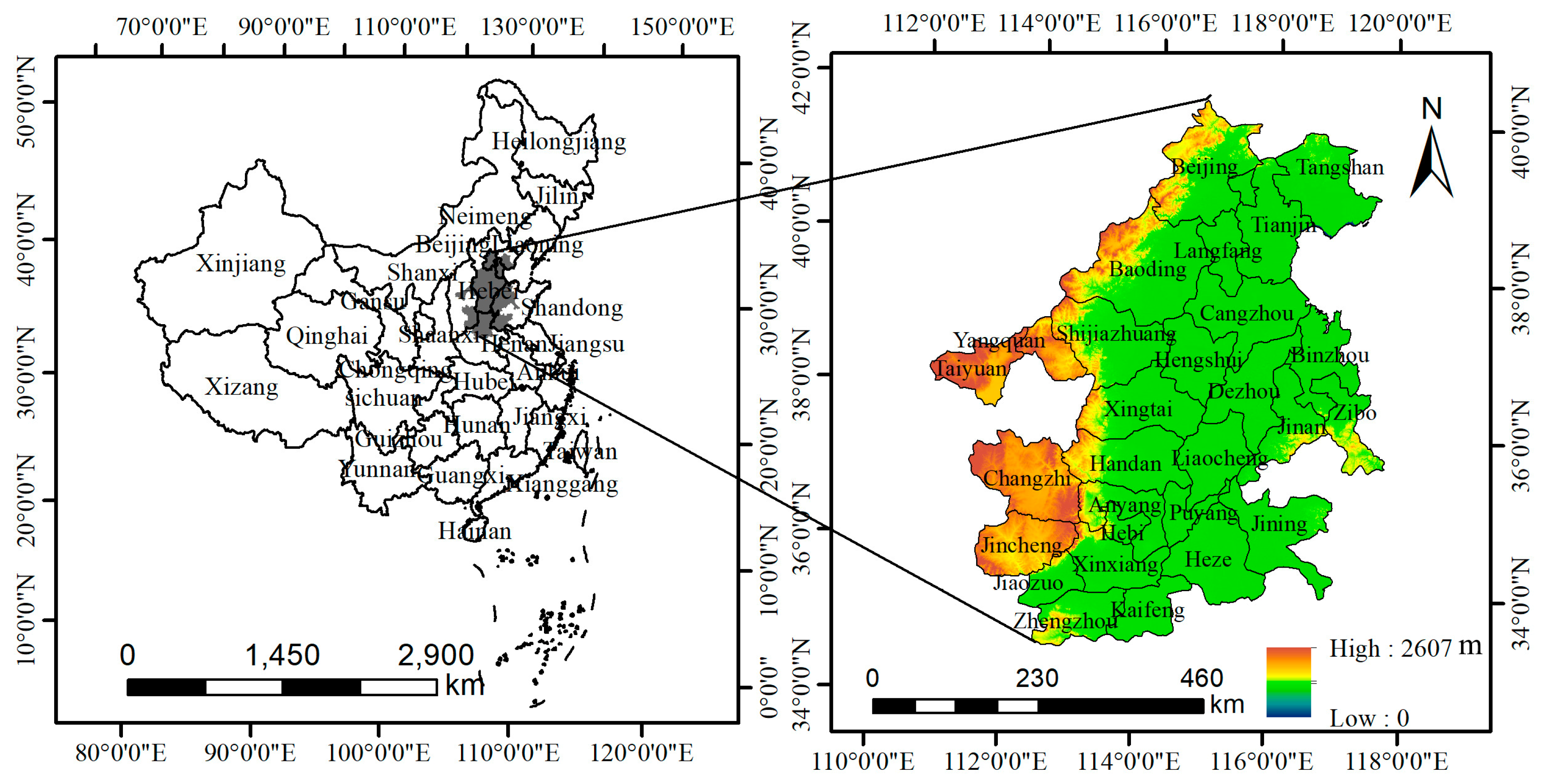
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Research Methods
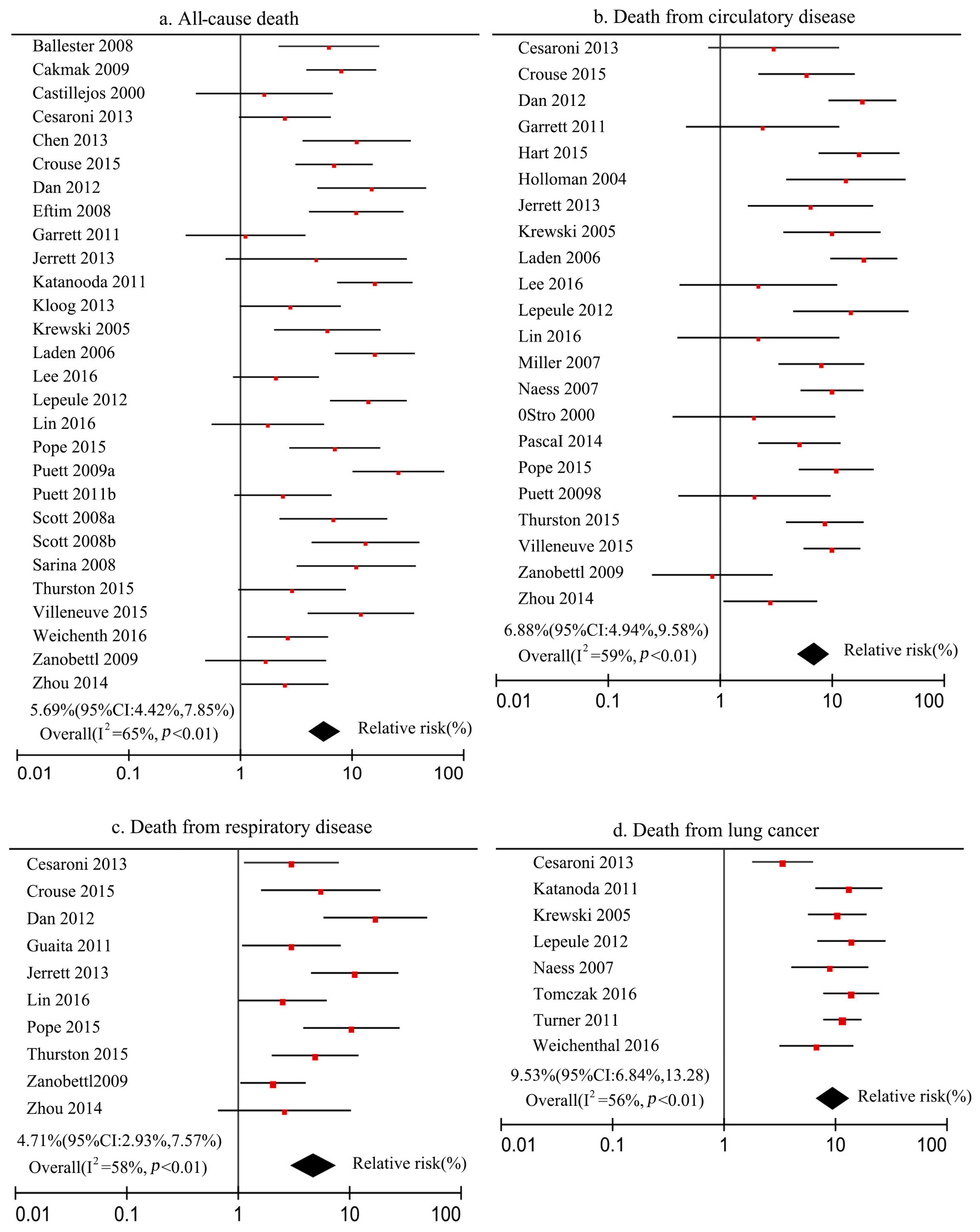
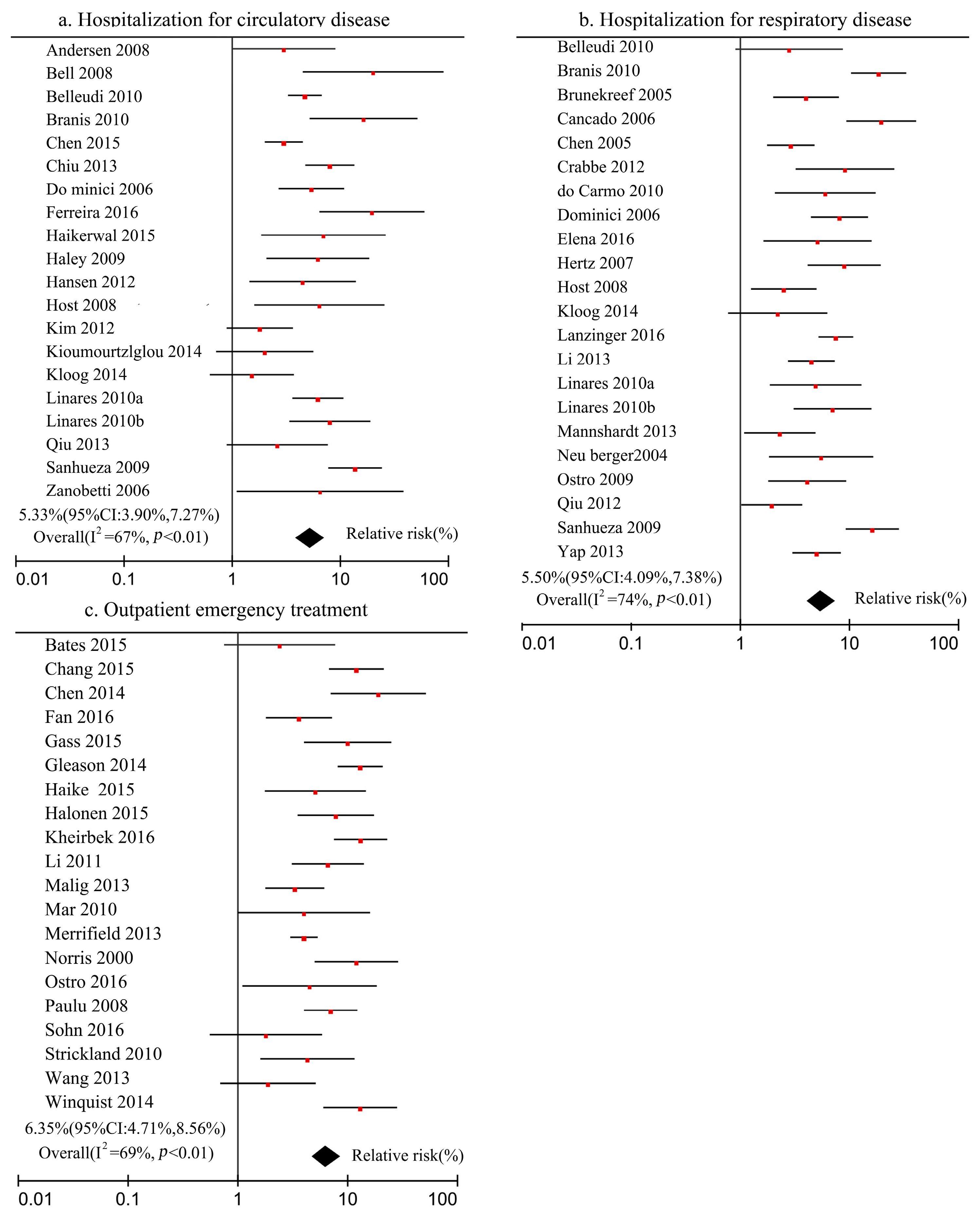
2.3.1. Meta-Analysis Method
2.3.2. Poisson Regression Model
2.3.3. Environmental Value Assessment Method
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Determination of Exposure–Response Coefficients
3.2. Accounting of Residents’ Health Losses
3.3. Value Assessment of Residents’ Health Losses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ajmal, M.; Tarar, M.A.; Arshad, M.I.; Gulshan, A.B.; Iqbal, M.A.; Tanvir, F. Atmospheric pollution and its effect on human health: A case study in Dera Ghazi Khan urban areas, Pakistan. J. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 6, 87–93. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, S.S.; Chang, C.C.; Liou, S.H.; Yang, C.Y. The effects of fine particulate atmospheric pollution on daily mortality: A case-crossover study in a subtropical city, Taipei, Taiwan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 5081–5093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Zhou, W.; Li, W.; Qian, Y. Global population exposed to fine particulate pollution by population increase and pollution expansion. Air. Qual. Atmos. Health 2017, 10, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.X.; Qin, Y.C.; Li, Y.N.; Shen, W. Evaluation of haze press risk in China based on PM2.5. Acta. Sci. Circumst. 2017, 37, 4503–4510. [Google Scholar]
- Younossi, Z.; Anstee, Q.M.; Marietti, M.; Hardy, T.; Henry, L.; Eslam, M.; George, J.; Bugianesi, E. Global burden of NAFLD and NASH: Trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, R. Death effects assessment of PM2.5 Pollution in China. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2018, 27, 1813–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.Z.; Wu, L.Y.; Chen, J.B.; Song, Y.X.; Chen, R.R. A CGE-based analysis on PM2.5-induced health-related economic effect in Beijing. China Environ. Sci. 2017, 37, 2779–2785. [Google Scholar]
- Ridker, R.G. Economic Costs of Atmospheric Pollution: Studies in Measurement; F.A. Praeger: New York, NY, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Dockery, D.W.; Pope, C.A.; Xu, X.; Spengler, J.D. An association between atmospheric pollution and mortality in six U.S. cities. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 329, 1753–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, C.A.; Thun, M.J.; Namboodiri, M.M.; Dockery, D.W.; Evans, J.S.; Speizer, F.E.; Heath, C.W.J. Particulate atmospheric pollution as a predictor of mortality in a prospective study of US adults. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care 1995, 151, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katanoda, K.; Sobue, T.; Satoh, H.; Tajima, K.; Suzuki, T.; Nakayama, T.; Nitta, H.; Tanabe, K.; Tominaqa, S. An association between long-term exposure to ambient atmospheric pollution and mortality from lung cancer and respiratory diseases in Japan. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 21, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, R.W.; Anderson, H.R.; Sunyer, J.; Ayres, J.G. Acute effects of particulate atmospheric pollution on respiratory admissions: Results from APHEA-2 project. Atmospheric pollution and health: A European approach. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care 2001, 164, 1860–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seethaler, R.K.; Künzli, N.; Sommer, H.; Chanel, O.; Herry, M.; Masson, S.; Vernaud, J.C.; Filliger, P.; Horak, F.J.; Kaiser, R.; et al. Economic costs of air pollution-related health impacts: An impact assessment project of Austria, France and Switzerland. Clean Air Environ. Qual. 2003, 37, 35–43. [Google Scholar]
- Quah, E.; Boon, T.L. The economic cost of particulate atmospheric pollution on health in Singapore. J. Asian Econ. 2003, 14, 73–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.M.; Zhang, H.Q.; Li, P. The calculation of economic losses from environmental pollution in China. China Environ. Sci. 1990, 10, 51–59. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.J.; Chen, B.H.; Kan, H.D. A health-based economic assessment of particulate atmospheric pollution in 113 Chinese cities. China Environ. Sci. 2010, 30, 410–415. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, D.S.; Zhang, S.Q. Health benefit evaluation for PM2.5 pollution control in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region in China. China Environ. Sci. 2013, 33, 166–174. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.Z.; Gu, S.J.; Chen, J.B. Assessment of the indirect economic loss caused by heavy haze in Beijing based on input-output model. Environ. Eng. 2016, 34, 121–125. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Dai, H.C.; Tatsuya, H.; Toshihiko, M. Health and economic impacts of PM2.5 pollution in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei area. China Popul. Res. Environ. 2016, 26, 19–27. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.L.; Fan, C.Y.; Wang, Y.X. Evaluation of health losses by atmospheric pollution in Beijing: A study based on corrected human capital method. China Popul. Res. Environ. 2014, 24, 169–176. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Han, Y.; Tang, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, T. Estimating adult mortality attributable to PM2.5 exposure in China with assimilated PM2.5 concentrations based on a ground monitoring network. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 568, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, D.; Wang, Q.; Li, H.; Yu, H.; Lu, Y.; Qian, X. Mortality effects assessment of ambient PM2.5 pollution in the 74 leading cities of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569, 1545–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, T.; Li, G.X.; Xu, M.M.; Wang, X.Y.; Liang, F.C.; Zeng, Q.; Pan, X.C. Health economic loss evaluation of ambient PM2.5 pollution based on willingness to pay. J. Environ. Health 2015, 32, 697–700. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, X.G.; Jiang, Y. Evaluation of value of statistical life in health costs attributable to atmospheric pollution. China Environ. Sci. 2010, 30, 284–288. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.J.; Zhou, D.Q.; Wei, Y.J. An assessment of PM2.5–related health risks and associated economic losses in Chinese cities. Environ. Sci. 2018, 39, 3467–3475. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, G.R.; Shi, X.M. Evaluation the extent of health damage caused by PM2.5 particulate in Xi’an city. Environ. Sci. 2018, 39, 3014–3021. [Google Scholar]
- National Bureau of Statistics of the People’s Republic of China. China Statistical Yearbook of 2017; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Wang, Y.C.; Jiang, C.L.; He, J.Y.; Zhong, Y.Z.; Song, X.H.; Lei, Y.; Yan, L. Atmospheric pollution emissions reduction potential from burning coal in cities of atmospheric pollution transmission in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei area. China Environ. Sci. 2018, 38, 2401–2405. [Google Scholar]
- Van, D.A.; Martin, R.V.; Brauer, M.; Hsu, N.C.; Kahn, R.A.; Lew, R.C.; Lyapustin, A.; Sayer, A.M.; Winker, D.M. Global estimates of fine particulate matter using a combined geophysical-statistical method with information from satellites, models, and monitors. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 3762–3772. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Matsunaga, T.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Zhao, A. Long-term trends and spatial patterns of satellite-retrieved PM2.5, concentrations in South and Southeast Asia from 1999 to 2014. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 615, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Bureau of Statistics of the People’s Republic of China. China City Statistical Yearbook of 2017; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2017.
- National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China. China Health and Family Planning Statistical Yearbook of 2017; Beijing Union Medical University Press: Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Glass, G.V. Primary, secondary, and meta-analysis of research. Educ. Res. 1976, 5, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoek, G.; Krishnan, R.M.; Beelen, R.; Peters, A.; Ostro, B.; Brunekreef, B.; Kaufman, J.D. Long-term atmospheric pollution exposure and cardio- respiratory mortality: A review. Environ. Health 2013, 12, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, R.T.; Pope, C.A.; Ezzati, M.; Olives, C.; Lim, S.S.; Mehta, S.; Shin, H.H.; Singh, G.; Hubbell, B.; Brauer, M. An integrated risk function for estimating the global burden of disease attributable to ambient fine particulate matter exposure. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.G.; Xie, F.; Zong, Q. Behavior selection and willingness to pay of reducing PM2.5 health risk: Taking residents in Beijing as an example. China Popul. Res. Environ. 2015, 25, 127–133. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Song, G.J. Evaluation of PM2.5′s adverse human health effect in cities. Acta Sci. Circumst. 2016, 36, 1468–1476. [Google Scholar]
- Hart, J.E.; Garshick, E.; Smith, T.J.; Davis, M.E.; Laden, F. Ischaemic heart disease mortality and years of work in trucking industry workers. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2013, 70, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Hammitt, J.K. Compensating wage differentials with unemployment: Evidence from China. Environ. Res. Econ. 2009, 42, 187–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
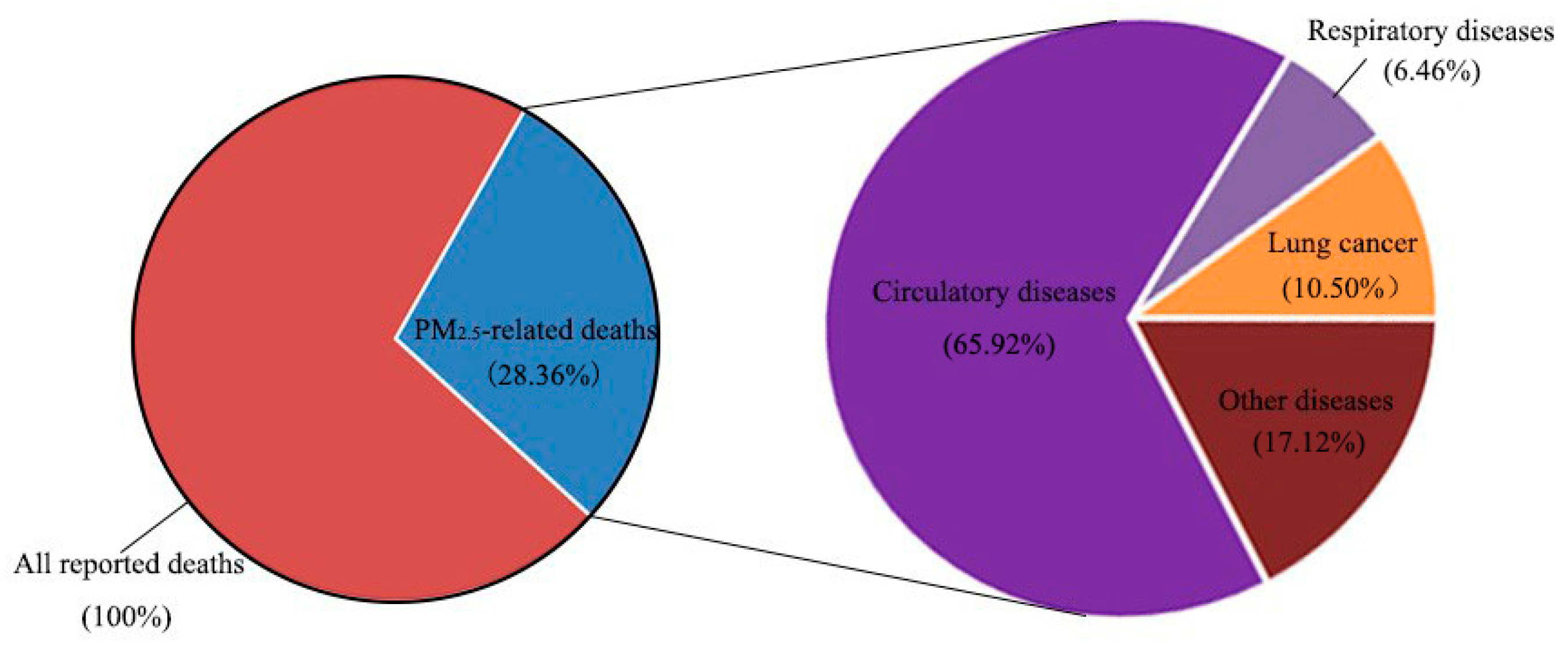
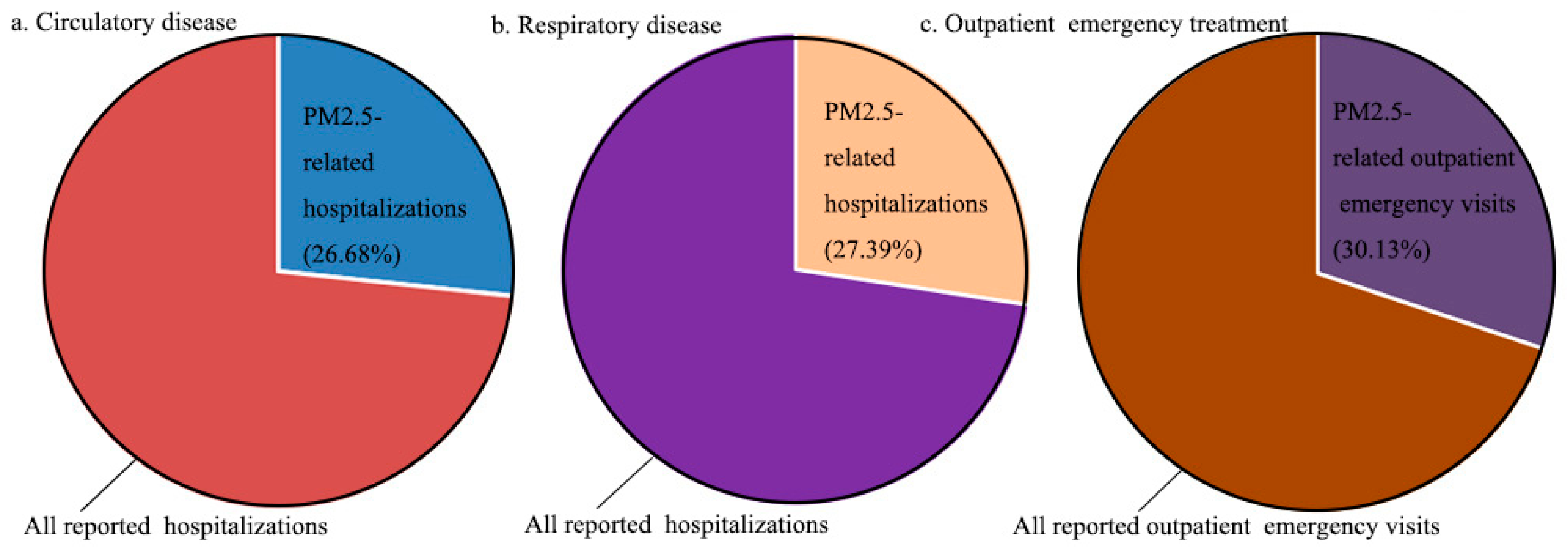
| Variable | Option | Proportion | Variable | Option | Proportion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Man | 49.5% | Daily outdoor time | <2 h | 26.0% |
| Woman | 50.5% | 2–4 h | 32.8% | ||
| Age | Youth (≤44) | 36.6% | 4–6 h | 18.7% | |
| Middle (45–59) | 39.6% | >6 h | 22.5% | ||
| Old (≥60) | 23.8% | Health condition | Very good | 28.2% | |
| Education | ≤Middle school | 24.7% | Good | 41.3% | |
| High school | 29.0% | General | 26.7% | ||
| Junior college | 23.5% | Poor | 3.1% | ||
| Undergraduate | 19.4% | Very poor | 0.7% | ||
| Postgraduate | 3.4% | Possibility of living in Zhengzhou city | Very high | 64.3% | |
| Monthly income | <$453 | 27.1% | High | 22.1% | |
| $453–$906 | 41.4% | General | 6.7% | ||
| $906–$1360 | 17.6% | Small | 0.6% | ||
| $1360–$1813 | 10.7% | Very small | 1.5% | ||
| >$1813 | 3.2% | Uncertainty | 4.8% |
| Payment Interval (dollars/month) | Annual Payment Currency (dollars) | Number of Residents (persons) | Statistical Life Value (dollars) | Proportion (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 1053 | 0 | 29.44 |
| 0–3.02 | 18.13 | 403 | 730.80 | 11.27 |
| 3.02–6.04 | 54.40 | 450 | 2448.09 | 12.58 |
| 6.04–9.07 | 90.67 | 428 | 3880.68 | 11.97 |
| 9.07–12.09 | 126.94 | 411 | 5217.15 | 11.49 |
| 12.09–15.11 | 163.21 | 412 | 6724.09 | 11.52 |
| 15.11–18.13 | 199.47 | 229 | 4567.96 | 6.40 |
| 18.13–21.16 | 235.74 | 115 | 2711.03 | 3.21 |
| 21.16–24.18 | 272.01 | 29 | 788.83 | 0.81 |
| 24.18–27.20 | 308.28 | 22 | 678.21 | 0.62 |
| 27.20–30.22 | 344.55 | 16 | 551.27 | 0.45 |
| >30.22 | 362.68 | 9 | 326.41 | 0.25 |
| City | SLV (104 dollar/person) | HC (dollar/person) | OETC (dollar/person-time) | City | SLV (104 dollar/person) | HC (dollar/person) | OETC (dollar/person-time) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | 14.42 | 3108.59 | 69.28 | Jinan | 9.31 | 1849.57 | 49.85 |
| Tianjin | 10.19 | 2361.37 | 45.06 | Zibo | 8.09 | 1607.00 | 43.30 |
| Shijiazhuang | 6.22 | 1347.47 | 37.16 | Jining | 6.00 | 1192.03 | 32.13 |
| Tangshan | 7.01 | 1518.92 | 41.88 | Dezhou | 4.80 | 952.74 | 25.67 |
| Langfang | 6.88 | 1491.31 | 41.12 | Liaocheng | 4.56 | 905.83 | 24.40 |
| Baoding | 4.89 | 1058.97 | 29.21 | Binzhou | 6.21 | 1232.89 | 33.23 |
| Cangzhou | 5.36 | 1161.22 | 32.02 | Heze | 4.30 | 854.24 | 23.02 |
| Hengshui | 4.47 | 969.38 | 26.72 | Zhengzhou | 7.70 | 1621.73 | 39.41 |
| Xingtai | 4.48 | 970.81 | 26.77 | Kaifeng | 4.56 | 960.51 | 23.35 |
| Handan | 5.46 | 1183.05 | 32.62 | Anyang | 5.31 | 1117.49 | 27.16 |
| Taiyuan | 7.46 | 1731.92 | 51.04 | Hebi | 5.57 | 1173.42 | 28.51 |
| Yangquan | 6.03 | 1399.29 | 41.24 | Xinxiang | 5.25 | 1105.58 | 26.87 |
| Changzhi | 5.25 | 1218.61 | 35.91 | Jiaozuo | 5.75 | 1211.25 | 29.43 |
| Jincheng | 5.65 | 1311.76 | 38.66 | Puyang | 4.51 | 950.51 | 23.09 |
| City | All-Cause Death (persons) | Death from Circulatory Disease (persons) | Death from Respiratory Disease (persons) | Death from Lung Cancer (persons) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | 25,045 | 13,461 | 2076 | 4767 |
| Tianjin | 28,097 | 16,942 | 1733 | 3989 |
| Shijiazhuang | 18,657 | 12,452 | 1104 | 1342 |
| Tangshan | 8748 | 5883 | 519 | 608 |
| Langfang | 8651 | 5740 | 511 | 599 |
| Baoding | 18,557 | 12,384 | 1092 | 1332 |
| Cangzhou | 16,725 | 11,031 | 996 | 1163 |
| Hengshui | 9778 | 6445 | 580 | 681 |
| Xingtai | 14,777 | 9811 | 880 | 1039 |
| Handan | 18,154 | 12,067 | 1084 | 1291 |
| Taiyuan | 2114 | 1143 | 205 | 354 |
| Yangquan | 846 | 503 | 50 | 102 |
| Changzhi | 2647 | 1318 | 159 | 317 |
| Jincheng | 1885 | 1118 | 114 | 227 |
| Jinan | 15,256 | 11,480 | 999 | 1869 |
| Zibo | 7305 | 5520 | 483 | 912 |
| Jining | 10,632 | 8033 | 688 | 1319 |
| Dezhou | 10,785 | 8086 | 717 | 1314 |
| Liaocheng | 15,336 | 11,516 | 1008 | 1845 |
| Binzhou | 6873 | 5181 | 448 | 836 |
| Heze | 13,463 | 10,200 | 889 | 1682 |
| Zhengzhou | 12,583 | 7051 | 1116 | 1031 |
| Kaifeng | 7947 | 4983 | 473 | 731 |
| Anyang | 8935 | 5607 | 531 | 817 |
| Hebi | 2592 | 1626 | 156 | 235 |
| Xinxiang | 10,517 | 6591 | 631 | 963 |
| Jiaozuo | 4813 | 3041 | 287 | 449 |
| Puyang | 7925 | 4946 | 483 | 704 |
| City | Hospitalization for Circulatory Disease (persons) | Hospitalization for Respiratory Disease (persons) | Outpatient Emergency Visit (person-time) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | 96,722 | 90,112 | 11,327,305 |
| Tianjin | 72,583 | 67,478 | 9,660,363 |
| Shijiazhuang | 51,777 | 48,187 | 1,732,705 |
| Tangshan | 36,976 | 34,409 | 1,237,717 |
| Langfang | 26,262 | 24,433 | 873,788 |
| Baoding | 54,978 | 51,167 | 1,840,382 |
| Cangzhou | 46,493 | 43,199 | 1,541,968 |
| Hengshui | 28,314 | 26,294 | 937,885 |
| Xingtai | 39,394 | 36,630 | 1,313,009 |
| Handan | 48,588 | 45,191 | 1,622,251 |
| Taiyuan | 7478 | 6972 | 235,741 |
| Yangquan | 2432 | 2263 | 76,676 |
| Changzhi | 6428 | 5998 | 202,697 |
| Jincheng | 4727 | 4421 | 148,945 |
| Jinan | 46,759 | 43,492 | 1,530,678 |
| Zibo | 27,169 | 25,281 | 892,821 |
| Jining | 49,927 | 46,409 | 1,638,365 |
| Dezhou | 40,210 | 37,371 | 1,312,459 |
| Liaocheng | 41,862 | 38,897 | 1,365,983 |
| Binzhou | 24,011 | 22,331 | 786,991 |
| Heze | 48,835 | 45,439 | 1,605,797 |
| Zhengzhou | 42,746 | 39,803 | 1,496,117 |
| Kaifeng | 22,861 | 21,294 | 797,537 |
| Anyang | 26,297 | 24,482 | 916,369 |
| Hebi | 8491 | 7890 | 295,713 |
| Xinxiang | 28,655 | 26,685 | 999,651 |
| Jiaozuo | 14,949 | 13,910 | 523,525 |
| Puyang | 21,377 | 19,901 | 741,967 |
| City | All-Cause Death (108 dollars) | Hospitalizations for Circulatory Disease (108 dollars) | Hospitalizations for Respiratory Disease (108 dollars) | Outpatient Emergency Treatment (108 dollars) | Values of Health Losses (108 dollars) | Percentage of GDP (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | 36.13 | 3.50 | 3.26 | 13.36 | 56.24 | 1.46 |
| Tianjin | 28.63 | 2.07 | 1.92 | 8.92 | 41.54 | 1.54 |
| Shijiazhuang | 11.61 | 0.80 | 0.75 | 1.04 | 14.20 | 1.59 |
| Tangshan | 6.13 | 0.67 | 0.62 | 0.93 | 8.36 | 0.87 |
| Langfang | 5.95 | 0.45 | 0.42 | 0.57 | 7.39 | 1.81 |
| Baoding | 9.07 | 0.64 | 0.60 | 0.76 | 11.07 | 2.12 |
| Cangzhou | 8.96 | 0.62 | 0.58 | 0.79 | 10.95 | 2.05 |
| Hengshui | 4.37 | 0.31 | 0.29 | 0.37 | 5.34 | 2.50 |
| Xingtai | 6.62 | 0.42 | 0.39 | 0.50 | 7.93 | 2.67 |
| Handan | 9.91 | 0.64 | 0.59 | 0.76 | 11.91 | 2.37 |
| Taiyuan | 1.58 | 0.15 | 0.14 | 0.19 | 2.06 | 0.46 |
| Yangquan | 0.51 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.63 | 0.67 |
| Changzhi | 1.39 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.10 | 1.67 | 0.87 |
| Jincheng | 1.06 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 1.29 | 0.81 |
| Jinan | 14.21 | 1.02 | 0.95 | 1.34 | 17.51 | 1.78 |
| Zibo | 5.91 | 0.53 | 0.49 | 0.73 | 7.67 | 1.15 |
| Jining | 6.38 | 0.69 | 0.64 | 0.87 | 8.59 | 1.33 |
| Dezhou | 5.17 | 0.46 | 0.43 | 0.61 | 6.67 | 1.51 |
| Liaocheng | 6.99 | 0.45 | 0.42 | 0.60 | 8.47 | 1.97 |
| Binzhou | 4.27 | 0.35 | 0.33 | 0.47 | 5.41 | 1.46 |
| Heze | 5.79 | 0.47 | 0.44 | 0.57 | 7.27 | 1.88 |
| Zhengzhou | 9.69 | 0.84 | 0.78 | 1.11 | 12.41 | 1.02 |
| Kaifeng | 3.62 | 0.25 | 0.24 | 0.31 | 4.43 | 1.68 |
| Anyang | 4.74 | 0.34 | 0.31 | 0.40 | 5.79 | 1.89 |
| Hebi | 1.44 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.14 | 1.81 | 1.56 |
| Xinxiang | 5.52 | 0.36 | 0.34 | 0.42 | 6.64 | 2.04 |
| Jiaozuo | 2.77 | 0.22 | 0.20 | 0.28 | 3.47 | 1.10 |
| Puyang | 3.58 | 0.24 | 0.22 | 0.29 | 4.33 | 1.98 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, Z.; Li, Y.; Qin, Y.; Rong, P. Value Assessment of Health Losses Caused by PM2.5 Pollution in Cities of Atmospheric Pollution Transmission Channel in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Region, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16061012
Xie Z, Li Y, Qin Y, Rong P. Value Assessment of Health Losses Caused by PM2.5 Pollution in Cities of Atmospheric Pollution Transmission Channel in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Region, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(6):1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16061012
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Zhixiang, Yang Li, Yaochen Qin, and Peijun Rong. 2019. "Value Assessment of Health Losses Caused by PM2.5 Pollution in Cities of Atmospheric Pollution Transmission Channel in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Region, China" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 6: 1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16061012
APA StyleXie, Z., Li, Y., Qin, Y., & Rong, P. (2019). Value Assessment of Health Losses Caused by PM2.5 Pollution in Cities of Atmospheric Pollution Transmission Channel in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Region, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(6), 1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16061012





