Stomach Cancer and Exposure to Talc Powder without Asbestos via Chinese Herbal Medicine: A Population-Based Cohort Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Setting
- Registry for Beneficiaries contains the registration data of all beneficiaries.
- Registry for drug prescriptions contains the names of all approved medications and related information including the drug codes issued by the National Health Insurance Administration (NHI)
- Ambulatory Care Expenditures by Visits contains the physician billing claims data, including the diagnosis, the medical orders and the names of medication prescribed.
- Details of Ambulatory Care Orders connects the Ambulatory Care Expenditures by Visits to show the details of drug prescription record, including the days of prescription, the frequency of usage, and the total amount prescribed by a physician.
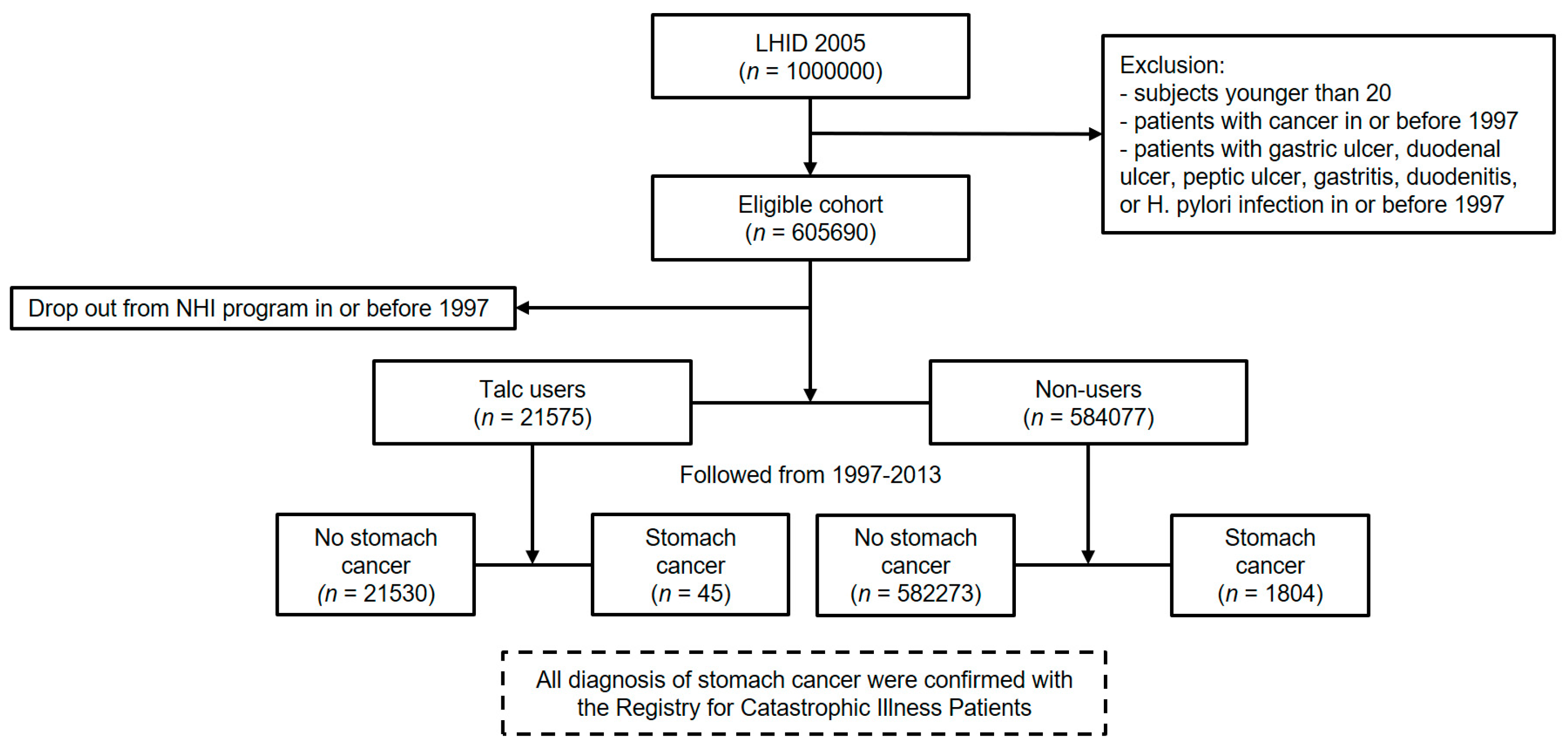
2.2. Participants
- patients younger than 20 on 1 January 1997,
- patients with diagnosis of cancer in or before 1997,
- patients with gastric ulcer, duodenal ulcer, peptic ulcer, gastritis, duodenitis, or Helicobacter pylori infection in or before 1997
2.3. Variables
2.4. Exposure Assessment
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
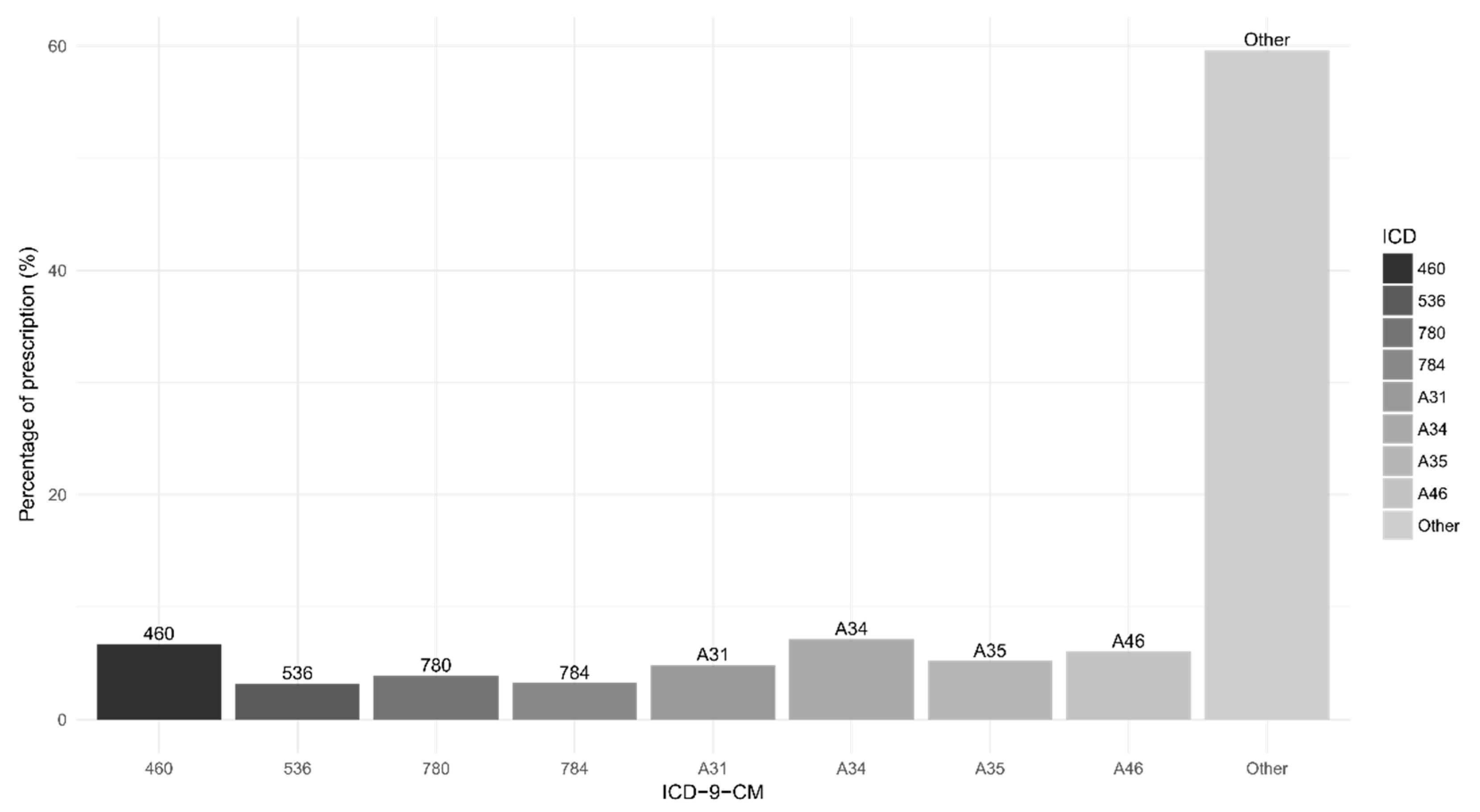
3.1. Descriptive Data
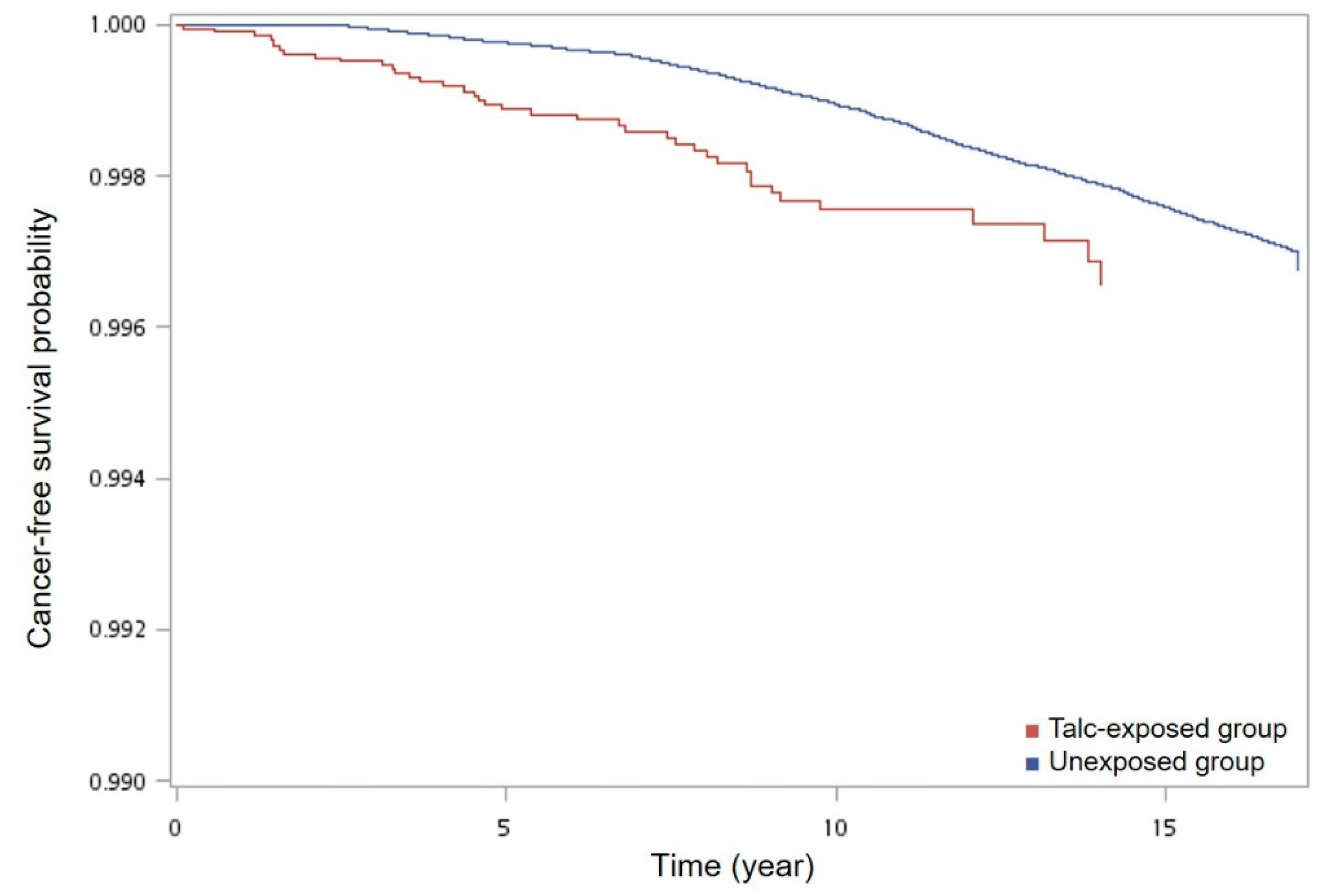
3.2. Main Results
3.3. Other Analyses
4. Discussion
4.1. Key Results
4.2. Mineral Analysis of Talc in Taiwan
- (1)
- Fourier Transform Infrared spectrometry (FTIR)
- (2)
- X-ray Powder Diffraction (XRD)
- (3)
- Microscopy of asbestos
4.3. Limitations
4.4. Interpretation
4.5. Generalisability
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, S.Z. Ben Cao Gang Mu [Compendium of Materia Medica]; Shanghai Ancient Books Publishing House: Shanghai, China, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Merliss, R.R. Talc-treated rice and Japanese stomach cancer. Science 1971, 173, 1141–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). Evaluation of the carcinogenic risk of chemicals to humans: Silica and some silicates. IARC Monog. 1987, 42, 13–32. [Google Scholar]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). Carbon black, titanium dioxide, and talc. IARC Monog. Eval. Carcinog. Risks Hum. 2010, 93, 1–413. [Google Scholar]
- Vandenbroucke, J.P.; Von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Pocock, S.J.; Poole, C.; Schlesselman, J.J.; Egger, M.; Initiative, S. Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE): Explanation and elaboration. PLoS Med. 2007, 4, e297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Health Insurance Administration, Ministry of Health and Welfare. National Health Insurance Annual Report 2016–2017; National Health Insurance Administration, Ministry of Health and Welfare: Taipei, Taiwan, 2017.
- National Health Insurance Research Database, Taiwan. Available online: https://nhird.nhri.org.tw/en/index.html (accessed on 24 October 2017).
- Patients with Catastrophic Illnesses or Rare Diseases. Available online: https://www.nhi.gov.tw/english/Content_List.aspx?n=F5B8E49CB4548C60&topn=1D1ECC54F86E9050 (accessed on 28th October 2017).
- The List of Catastrophic Illnesses (Revised). Available online: https://www.nhi.gov.tw/DL.aspx?sitessn=292&u=LzAwMS9VcGxvYWQvT2xkRmlsZS9OaGlQdWJXZWIvcmVzb3VyY2UvV2ViZGF0YS8zMDI1MF8xX%2bmHjeWkp%2bWCt%2beXhemgheebrigxMDXlubQx5pyIMeaXpei1t%2bmBqeeUqCkub2R0&n=MzAyNTBfMV%2fph43lpKflgrfnl4XpoIXnm64oMTA15bm0MeaciDHml6XotbfpgannlKgpLm9kdA%3d%3d&ico%20=.odt (accessed on 28 October 2017).
- Charlson, M.E.; Pompei, P.; Ales, K.L.; MacKenzie, C.R. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: Development and validation. J. Chronic Dis. 1987, 40, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klabunde, C.N.; Potosky, A.L.; Legler, J.M.; Warren, J.L. Development of a comorbidity index using physician claims data. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2000, 53, 1258–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Definition of an Older or Elderly Person. Available online: http://www.who.int/healthinfo/survey/ageingdefnolder/en/ (accessed on 28 October 2016).
- Liu, C.-Y.; Hung, Y.; Chuang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Weng, W.; Liu, J.; Liang, K. Incorporating development stratification of Taiwan townships into sampling design of large scale health interview survey. J. Health Manag. 2006, 4, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Charlson, M.; Szatrowski, T.P.; Peterson, J.; Gold, J. Validation of a combined comorbidity index. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1994, 47, 1245–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Hoore, W.; Bouckaert, A.; Tilquin, C. Practical considerations on the use of the Charlson comorbidity index with administrative data bases. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1996, 49, 1429–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lévesque, L.E.; Hanley, J.A.; Kezouh, A.; Suissa, S. Problem of immortal time bias in cohort studies: Example using statins for preventing progression of diabetes. BMJ 2010, 340, b5087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelley, J.R.; Duggan, J.M. Gastric cancer epidemiology and risk factors. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2003, 56, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, R.E.; Fitzgerald, S.; Millette, J. Asbestos in commercial cosmetic talcum powder as a cause of mesothelioma in women. Int. J. Occup. Environ. Health 2014, 20, 318–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- TFDA Regulation of Drugs No. 0940338432. Available online: https://www.fda.gov.tw/tc/includes/GetFile.ashx?id=f636694164952134262 (accessed on 9 February 2019).
- Zhong Hua Yao Dian [Chinese Pharmacopoeia], 8th ed.; TFDA: Taipei, Taiwan, 2016.
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Ambient Air–Determination of Numerical Concentration of Inorganic Fibrous Particles, Scanning Electron Microscopy Method, ISO 14966: 2002; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.-C.; Lai, J.-N.; Chen, P.-C.; Wang, J.-D. Concurrent use of conventional drugs with Chinese herbal products in Taiwan: A population-based study. J. Tradit. Complementary Med. 2013, 3, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, A. Association or Causation? Proc. R. Soc. Med. 1965, 58, 295–300. [Google Scholar]
- Forman, D. Helicobacter pylori and gastric cancer. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1996, 31, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-J.; Tu, Y.-K.; Chen, P.-C.; Yang, H.-Y. Talc exposure and risk of stomach cancer: Systematic review and meta-analysis of occupational cohort studies. J. Formosan Med. Assoc. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NTP (National Toxicology Program). NTP Toxicology and Carcinogenesis Studies of Talc (CAS No. 14807-96-6)(Non-Asbestiform) in F344/N Rats and B6C3F1 Mice (Inhalation Studies). Nat. Toxicol. Program Tech. Rep. Ser. 1993, 421, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, R.; Skidmore, J.; Griffiths, D.; Moncrieff, C. Cytotoxicity of talc for macrophages in vitro. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1983, 21, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Non-Users N = 584,077 | Talc Users N = 21,575 |
|---|---|---|
| Gender | ||
| Female | 292,319 (50.1%) | 13,180 (61.1%) |
| Male | 291,758 (49.9%) | 8395 (38.9%) |
| Age (year) a | 40.2 ± 14.7 | 39.0 ± 13.2 |
| Monthly Income b | 21,822 ± 12,575 | 21,630 ± 11,380 |
| Urbanization c | ||
| Level 1 (high) | 173,513 (29.9%) | 5,486 (25.1%) |
| Level 2 (medium) | 249,744 (43.0%) | 9602 (44.7%) |
| Level 3 (low) | 157,831 (27.2%) | 6414 (29.8%) |
| Charlson Comorbidity Index d | ||
| 0–2 | 583,744 (99.94%) | 21,558 (99.92%) |
| >2 | 333 (0.06%) | 17 (0.08%) |
| Follow-up time in month | 196.2 ± 21.7 | 200.3 ± 13.4 |
| Variable | Person-Years | No. of Stomach Cancer | Rate/10,000 Person-Years (95% CI a) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | |||
| <65 | 9,171,234 | 1202 | 1.31 (1.24–1.39) |
| ≥65 | 737,872 | 647 | 8.77 (8.11–9.47) |
| Gender | |||
| Female | 5,024,262 | 715 | 1.42 (1.32–1.53) |
| Male | 4,884,844 | 1134 | 2.32 (2.19–2.46) |
| Urbanization | |||
| Level 1 (high) | 2,944,130 | 519 | 1.76 (1.61–1.92) |
| Level 2 (medium) | 4,247,016 | 796 | 1.87 (1.75–2.01) |
| Level 3 (low) | 2,668,495 | 516 | 1.93 (1.77–2.11) |
| Charlson Comorbidity Index b | |||
| 0–2 | 9,904,066 | 1848 | 1.87 (1.78–1.95) |
| >2 | 5040 | 1 | 1.98 (0.05–11.06) |
| Exposure of talc c | |||
| Unexposed period | 9,728,639 | 1804 | 1.85 (1.77–1.94) |
| Talc-exposed period | 180,467 | 45 | 2.49 (1.82–3.34) |
| Cumulative talc exposure c | |||
| Low to none (≤ 6 g) | 9,774,552 | 1816 | 1.86 (1.77–1.95) |
| Medium (6–21 g) | 87,550 | 23 | 2.63 (1.67–3.94) |
| High (>21 g) | 47,004 | 10 | 2.13 (1.02–3.91) |
| Risk Factor | Person-Years (Cases) | Crude Hazard Ratio a | Adjusted Hazard Ratio b | Ten-Year Absolute Risk/1000 Persons (95% CI) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | p-Value | HR (95% CI) | p-Value | |||
| Exposure of talc | ||||||
| Unexposed period | 9,728,639 (1804) | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.07 (0.99–1.15) | ||
| Talc-exposed period | 180,467 (45) | 1.83 (1.32–2.52) | <0.001 | 2.13 (1.54–2.94) | <0.001 | 1.95 (1.33–2.57) |
| Cumulative talc exposure | ||||||
| Low to none (≤6 g) | 9,774,552 (1816) | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.07 (0.99–1.16) | ||
| Medium (6–21 g) | 87,550 (23) | 1.99 (1.28–3.09) | 0.002 | 2.30 (1.48–3.57) | <0.001 | 2.13 (1.19–3.07) |
| High (>21 g) | 47,004 (10) | 1.43 (0.71–2.87) | 0.31 | 1.58 (0.79–3.17) | 0.19 | 1.54 (0.47–2.60) |
| Model | Person-Years (Cases) | Adjusted Hazard Ratio | |
|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | p-Value | ||
| Original model | |||
| Cumulative talc exposure | |||
| Low to none (≤ 6g) | 9,774,552 (1816) | 1.00 | |
| Medium (6~21g) | 87,550 (23) | 2.30 (1.48–3.57) | <0.001 |
| High (>21g) | 47,004 (10) | 1.58 (0.79–3.17) | 0.19 |
| Changing the cut-off points for levels of talc exposure a | |||
| Cumulative talc exposure | |||
| Unexposed | 9,728,639 (1804) | 1.00 | |
| Low (≤10.5 g) | 88,312 (23) | 2.40 (1.54–3.73) | 0.007 |
| High (>10.5 g) | 92,155 (22) | 1.89 (1.19–3.01) | <0.001 |
| Excluding time to event less than five years b | |||
| Cumulative talc exposure | |||
| Low to none (≤6 g) | 9,755,288 (1671) | 1.00 | |
| Medium (6–21 g) | 78,828 (6) | 0.86 (0.39–1.93) | 0.72 |
| High (>21 g) | 43,288 (7) | 1.99 (0.81–3.59) | 0.16 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, C.-J.; Yang, Y.-H.; Chen, P.-C.; Peng, H.-Y.; Lu, Y.-C.; Song, S.-R.; Yang, H.-Y. Stomach Cancer and Exposure to Talc Powder without Asbestos via Chinese Herbal Medicine: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 717. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16050717
Chang C-J, Yang Y-H, Chen P-C, Peng H-Y, Lu Y-C, Song S-R, Yang H-Y. Stomach Cancer and Exposure to Talc Powder without Asbestos via Chinese Herbal Medicine: A Population-Based Cohort Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(5):717. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16050717
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Che-Jui, Yao-Hsu Yang, Pau-Chung Chen, Hsin-Yi Peng, Yi-Chia Lu, Sheng-Rong Song, and Hsiao-Yu Yang. 2019. "Stomach Cancer and Exposure to Talc Powder without Asbestos via Chinese Herbal Medicine: A Population-Based Cohort Study" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 5: 717. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16050717
APA StyleChang, C.-J., Yang, Y.-H., Chen, P.-C., Peng, H.-Y., Lu, Y.-C., Song, S.-R., & Yang, H.-Y. (2019). Stomach Cancer and Exposure to Talc Powder without Asbestos via Chinese Herbal Medicine: A Population-Based Cohort Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(5), 717. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16050717





