Seasonal Variation and Quality Assessment of the Major and Trace Elements of Atmospheric Dust in a Typical Karst City, Southwest China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
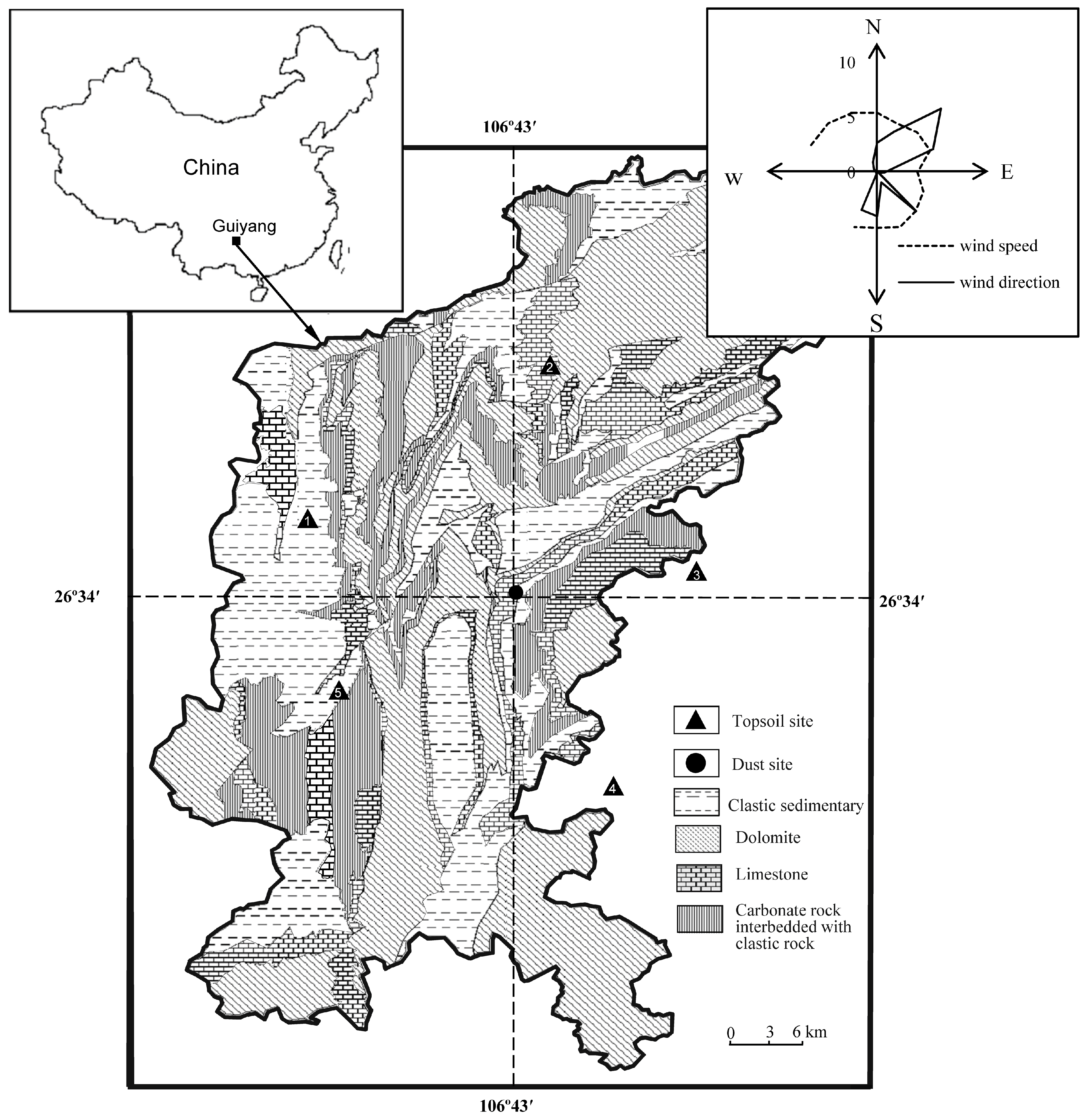
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling Methods
2.3. Analytical Methods
- (1)
- The accurate weighing 100 mg of powder samples were put into the 7 mL of Teflon digestion jar (Savillex, Eden Prairie, MN, US), then 1 mL HF and 2 mL HNO3 were added to the jar for digestion treatment at 140 °C for 7 days.
- (2)
- The same procedure of step 1 was reused to further dissolve the sample until the solution is thoroughly clarified.
- (3)
- After the samples are completely digested, add 2 mL HNO3 (1:1) two times to break up the fluorine compounds; then, dry and vaporize the samples on a hot plate.
- (4)
- Finally, dissolve the digested remainder in a 100-mL volumetric flask, using 3% HNO3. The digestion processes were performed in the Ultra-Clean Lab of the Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
3. Results
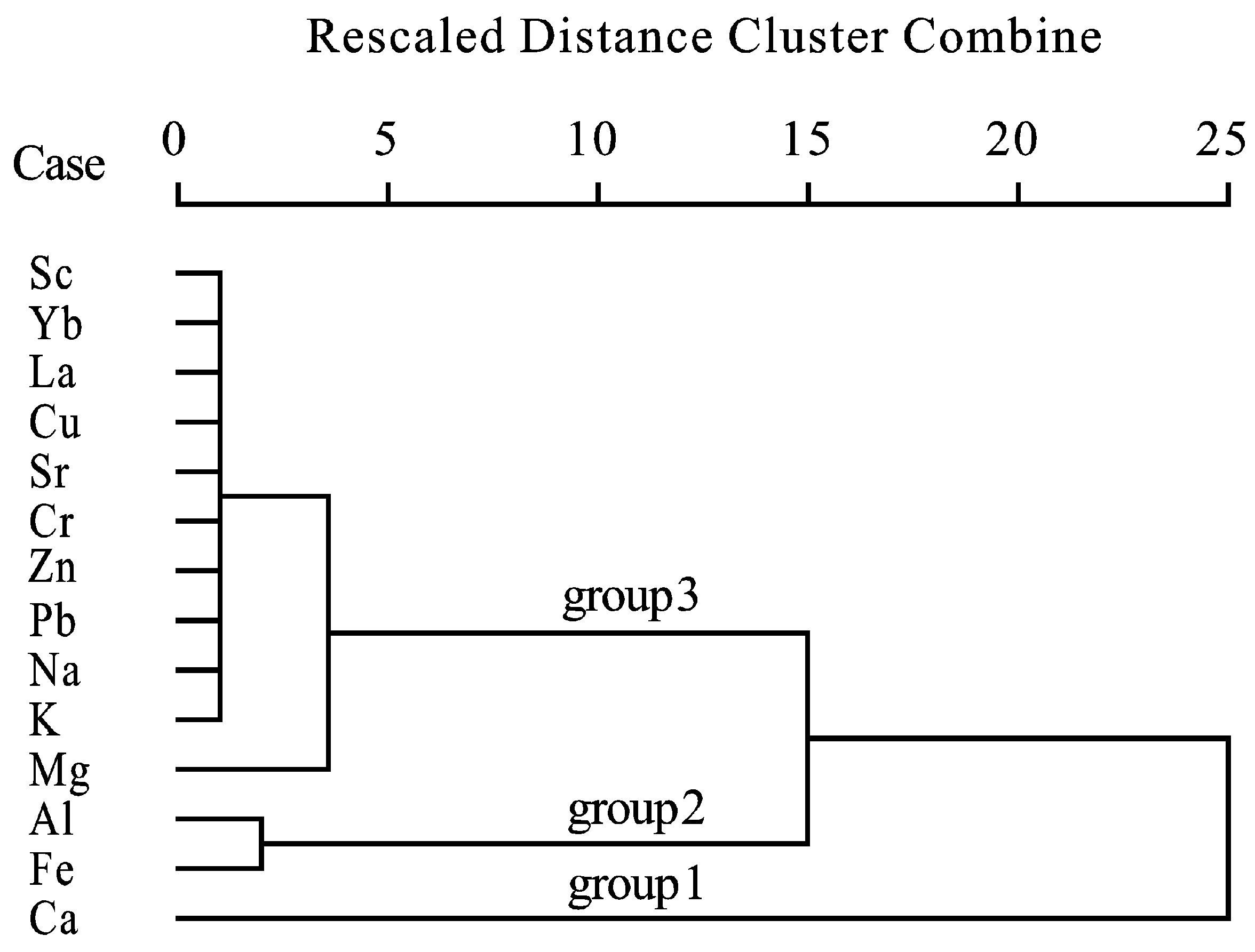
3.1. Element Content Characteristics of Atmospheric Dust
- Dust: Fe > Al > Ca > Mg > K > Na > Zn > Pb > Cr > Sr > Cu > La > Sc > Yb
- Topsoil: Fe > Al > Ca > K > Mg > Na > Zn > Cr > Pb > Cu > Sr > La > Sc > Yb
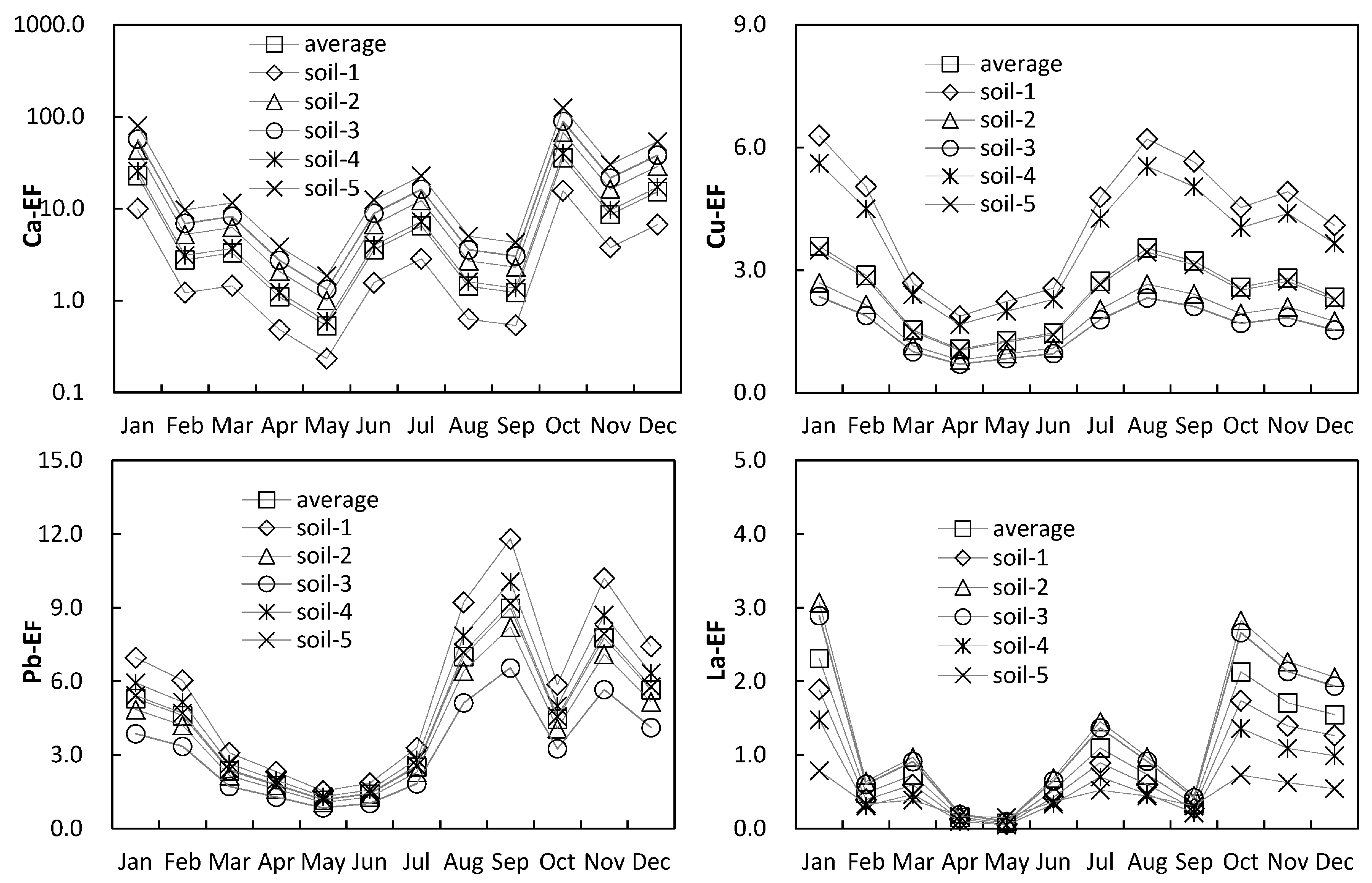
3.2. Seasonal Variation of Atmospheric Dust
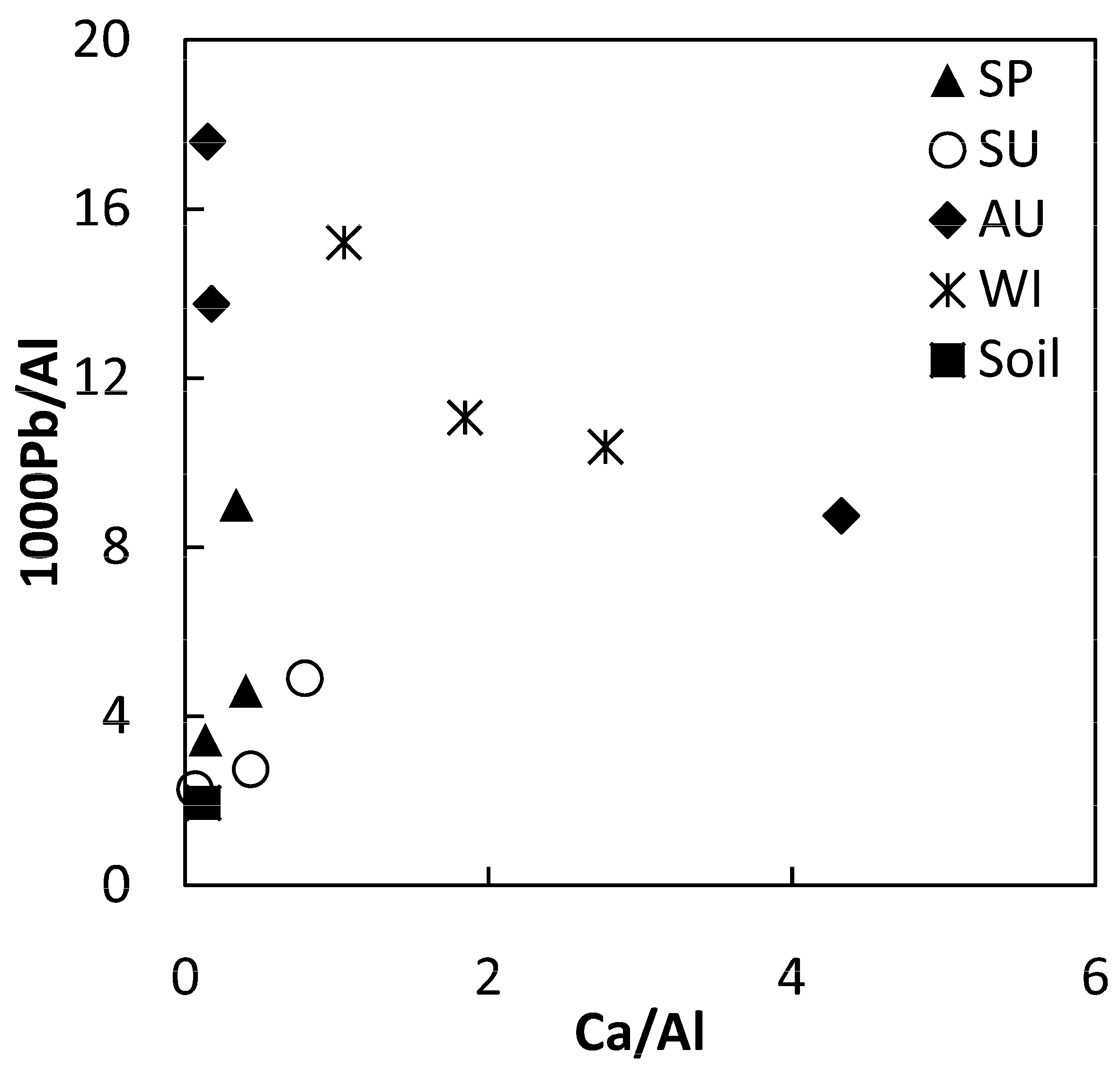
3.3. Assessment of Atmospheric Dust Pollution
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lawrence, C.R.; Neff, J.C. The Contemporary Physical and Chemical Flux of Aeolian Dust: A Synthesis of Direct Measurements of Dust Deposition. Chem. Geol. 2009, 267, 46–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelbrecht, J.P.; Derbyshire, E. Airborne Mineral Dust. Elements 2010, 6, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmer, A.M. The Effects of Dust on Vegetation—A Review. Environ. Pollut. 1993, 79, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, M.J.; Chadwick, O.A.; Vitousek, P.M.; Derry, L.A.; Hendricks, D.M. Changing Sources of Base Cations During Ecosystem Development, Hawaiian Islands. Geology 1998, 26, 1015–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soderberg, K.; Compton, J.S. Dust as a Nutrient Source for Fynbos Ecosystems, South Africa. Ecosystems 2007, 10, 550–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarà, G.; Milanese, M.; Prusina, I.; Sarà, A.; Angel, D.L.; Glamuzina, B.; Nitzan, T.; Freeman, S.; Rinaldi, A.; Palmeri, V. Interactions between Mineral Dust, Climate, and Ocean Ecosystems. Elements 2010, 6, 247–252. [Google Scholar]
- Prospero, J.M.; Collard, F.X.; Molinié, J.; Jeannot, A. Characterizing the Annual Cycle of African Dust Transport to the Caribbean Basin and South America and Its Impact on the Environment and Air Quality. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2015, 28, 757–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Z.S.; Kukla, G.; Porter, S.C.; Xiao, J.L. Late Quaternary Dust Flow on Chinese Loess Plateau. Catena 1991, 18, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J. Provenance of Loess Material and Formation of Loess Deposits on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2002, 203, 845–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arimoto, R. Eolian Dust and Climate: Relationships to Sources, Tropospheric Chemistry, Transport and Deposition. Earth Sci. Rev. 2001, 54, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neff, J.C.; Ballantyne, A.P.; Farmer, G.L.; Mahowald, N.M.; Conroy, J.L.; Landry, C.C.; Overpeck, J.T.; Painter, T.H.; Lawrence, C.R.; Reynolds, R.L. Increasing Eolian Dust Deposition in the Western United States Linked to Human Activity. Nat. Geosci. 2008, 1, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, I.S.; Peuckerehrenbrink, B. Anthropogenic Disturbance of Element Cycles at the Earth’s Surface. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 8601–8609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garnaud, S.; Mouchel, J.M.; Chebbo, G.; Thévenot, D.R. Heavy Metal Concentrations in Dry and Wet Atmospheric Deposits in Paris District: Comparison with Urban Runoff. Sci. Total Environ. 1999, 235, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onder, S.; Dursun, S. Air Borne Heavy Metal Pollution of Cedrus Libani (A. Rich.) in the City Centre of Konya (Turkey). Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 1122–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, I.; Salunkhe, A.; Kumar, R. Modelling 10-Year Trends of Pm10 and Related Toxic Heavy Metal Concentrations in Four Cities in India. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 179, 1084–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Duan, D.D.; Zhang, Y.L.; Cheng, H.F.; Ran, Y. Heavy Metals in Particulate and Colloidal Matter from Atmospheric Deposition of Urban Guangzhou, South China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 85, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birch, G.F.; Scollen, A. Heavy Metals in Road Dust, Gully Pots and Parkland Soils in a Highly Urbanised Sub-Catchment of Port Jackson, Australia. Soil Res. 2003, 41, 1329–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christoforidis, A.; Stamatis, N. Heavy Metal Contamination in Street Dust and Roadside Soil Along the Major National Road in Kavala’s Region, Greece. Geoderma 2009, 151, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.G.; Yang, L.S. A Review of Heavy Metal Contaminations in Urban Soils, Urban Road Dusts and Agricultural Soils from China. Microchem. J. 2010, 94, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhu, G.; Pan, H.; Shi, P.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Tong, H. Surface Dust Heavy Metals in the Major Cities, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 757. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Poon, C.S.; Liu, P.S. Heavy Metal Contamination of Urban Soils and Street Dusts in Hong Kong. Appl. Geochem. 2001, 16, 1361–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovmand, M.F.; Kemp, K.; Kystol, J.; Johnsen, I.; Riis-Nielsen, T.; Pacyna, J.M. Atmospheric Heavy Metal Deposition Accumulated in Rural Forest Soils of Southern Scandinavia. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 155, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, N.; Liu, J.H.; Wang, Q.C.; Liang, Z.Z. Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal Exposure to Street Dust in the Zinc Smelting District, Northeast of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 726–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yongming, H.; Peixuan, D.; Junji, C.; Posmentier, E.S. Multivariate Analysis of Heavy Metal Contamination in Urban Dusts of Xi’an, Central China. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 355, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Guan, D. Particulate Size and Heavy Metal Accumulation in Foliar Dust from Urban Vegetation in Rapidly Developing Cities. Acta Sci. Circumst. 2007, 27, 2080–2087. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, Q.; Huang, B.; Zhang, C.; Piper, J.D.A.; Pan, Y.; Sun, Y. Assessment of Heavy Metal Contamination of Dustfall in Northern China from Integrated Chemical and Magnetic Investigation. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 74, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, P.; Zhou, L.; Zheng, X.; Dong, Y.; Wang, Y. Magnetic Properties of Airborne Particulate Matter in Shanghai During Dust Storm Events and the Implications for Heavy Metal Contaminant Sources. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 4167–4178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Chen, Z.; Bi, C.; Wang, L.; Teng, J.; Li, Y.; Xu, S. A comparative study of health risk of potentially toxic metals in urban and suburban road dust in the most populated city of China. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, A.K.; Jin, H.P.; Won, J.H. Heavy Metal Distribution in Street Dust from Traditional Markets and the Human Health Implications. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 820. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China. 2013 Report on the State of the Environment in China; 27 May 2014. Available online: http://english.mee.gov.cn/Resources/Reports/soe/ (accessed on 21 December 2018).
- Ganor, E.; Foner, H.A.; Gravenhorst, G. The Amount and Nature of the Dustfall on Lake Kinneret (the Sea of Galilee), Israel: Flux and Fractionation. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 4301–4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.E.; Markert, B.; Chen, W.P.; Peng, C.; Ouyang, Z.Y. Identification of Heavy Metal Pollutants Using Multivariate Analysis and Effects of Land Uses on Their Accumulation in Urban Soils in Beijing, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 5889–5897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Han, G. Characteristics of Major Elements and Heavy Metals in Atmospheric Dust in Beijing, China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2015, 176, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Han, G.; Li, F.; Wu, Q. Natural and Anthropogenic Sources of Atmospheric Dust at a Remote Forest Area in Guizhou Karst Region, Southwest China. Geochem. Explor. Environ. Anal. 2016, 16, 2015–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
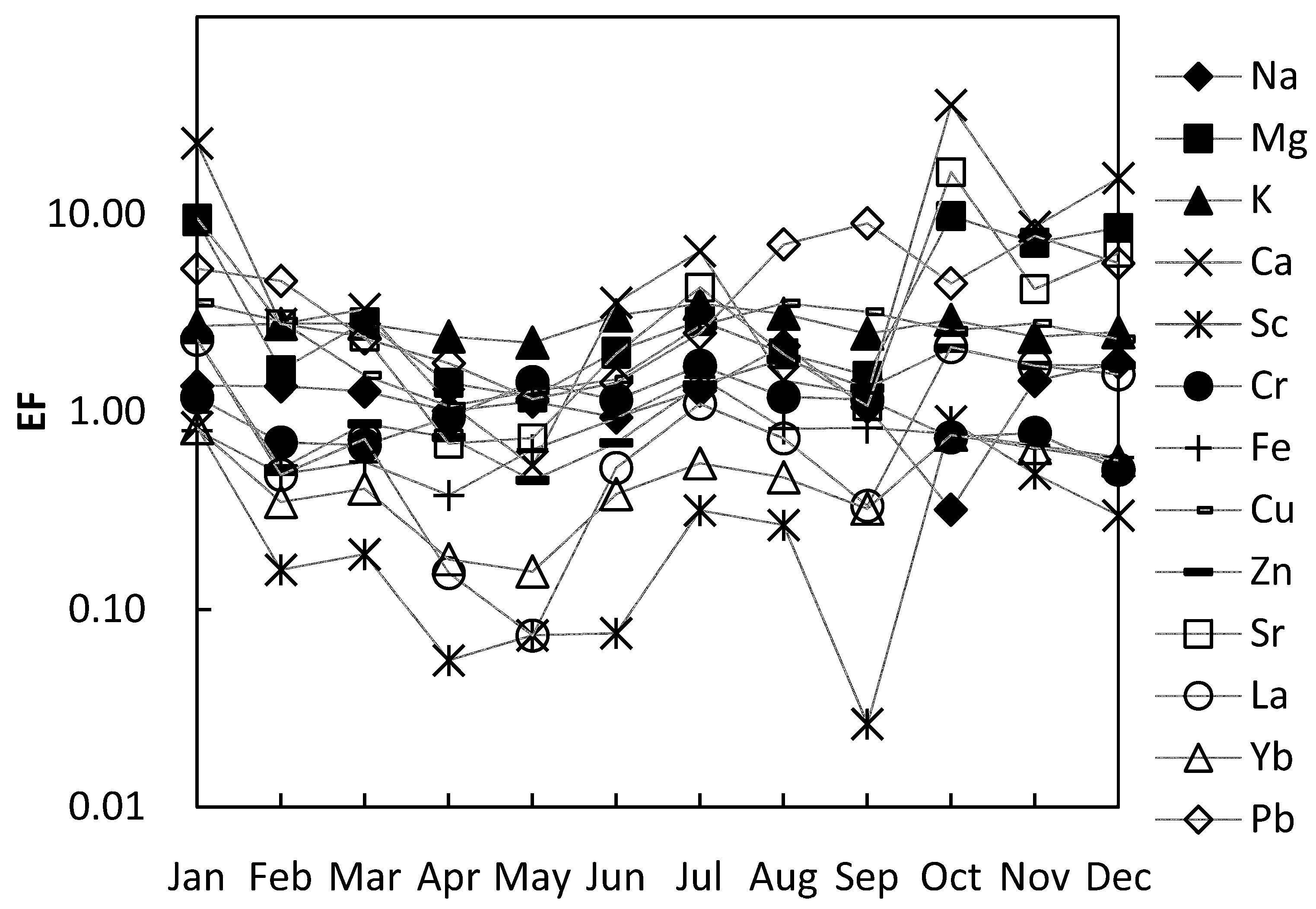
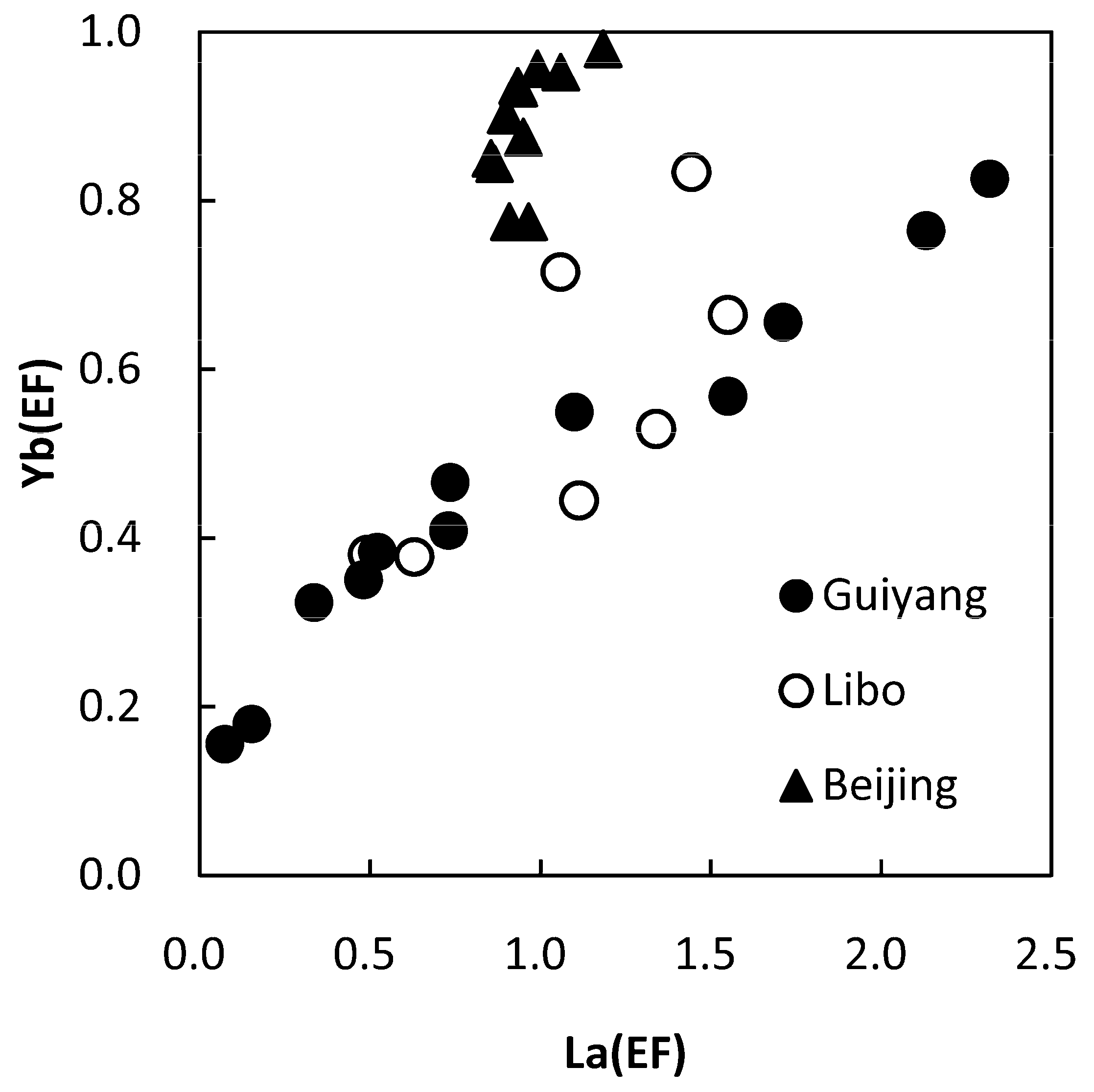
| Month | Na | Mg | Al | K | Ca | Fe | Sc | Cr | Cu | Zn | Sr | La | Yb | Pb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jan | 1.21 | 29.7 | 41.9 | 10.3 | 116 | 49.9 | 6.82 | 313 | 115 | 808 | 276 | 35.6 | 2.60 | 435 |
| Feb | 1.93 | 8.38 | 66.8 | 16.9 | 22.5 | 47.9 | 2.07 | 296 | 147 | 285 | 129 | 11.8 | 1.76 | 602 |
| Mar | 1.41 | 11.4 | 51.9 | 13.2 | 20.8 | 43.0 | 1.92 | 222 | 60.9 | 374 | 86.4 | 13.9 | 1.59 | 239 |
| Apr | 1.49 | 7.45 | 69.0 | 15.0 | 9.21 | 38.7 | 0.74 | 409 | 56.3 | 424 | 33.0 | 3.87 | 0.93 | 238 |
| May | 1.19 | 4.50 | 49.3 | 10.0 | 3.18 | 47.0 | 0.71 | 441 | 48.1 | 184 | 25.2 | 1.34 | 0.58 | 112 |
| Jun | 0.80 | 6.22 | 40.0 | 11.1 | 17.3 | 54.9 | 0.59 | 290 | 44.7 | 230 | 54.5 | 7.63 | 1.15 | 110 |
| Jul | 0.86 | 7.01 | 31.6 | 10.1 | 24.9 | 70.2 | 1.95 | 342 | 65.9 | 358 | 93.3 | 12.7 | 1.30 | 155 |
| Aug | 2.04 | 6.74 | 44.3 | 12.6 | 7.71 | 53.9 | 2.30 | 333 | 120 | 676 | 60.1 | 11.9 | 1.55 | 609 |
| Sep | 1.50 | 7.77 | 66.1 | 14.9 | 9.81 | 81.2 | 0.34 | 481 | 163 | 721 | 49.0 | 8.11 | 1.61 | 1163 |
| Oct | 0.27 | 29.8 | 39.5 | 10.5 | 171 | 45.3 | 6.89 | 186 | 78.1 | 688 | 448 | 30.9 | 2.27 | 345 |
| Nov | 1.86 | 33.5 | 60.6 | 13.2 | 63.4 | 60.6 | 5.73 | 300 | 130 | 865 | 176 | 38.0 | 2.99 | 922 |
| Dec | 2.21 | 38.2 | 58.2 | 13.4 | 108 | 50.8 | 3.39 | 188 | 104 | 831 | 258 | 33.1 | 2.49 | 644 |
| Soil * | 0.51 | 1.84 | 23.9 | 2.17 | 2.90 | 35.4 | 4.66 | 151 | 18.3 | 198 | 16.6 | 8.78 | 1.80 | 46.8 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, Y.; Han, G. Seasonal Variation and Quality Assessment of the Major and Trace Elements of Atmospheric Dust in a Typical Karst City, Southwest China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 325. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16030325
Tang Y, Han G. Seasonal Variation and Quality Assessment of the Major and Trace Elements of Atmospheric Dust in a Typical Karst City, Southwest China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(3):325. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16030325
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Yang, and Guilin Han. 2019. "Seasonal Variation and Quality Assessment of the Major and Trace Elements of Atmospheric Dust in a Typical Karst City, Southwest China" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 3: 325. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16030325
APA StyleTang, Y., & Han, G. (2019). Seasonal Variation and Quality Assessment of the Major and Trace Elements of Atmospheric Dust in a Typical Karst City, Southwest China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(3), 325. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16030325






