Clinical, Neuroimaging, and Neurophysiological Findings in Children with Microcephaly Related to Congenital Zika Virus Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Paticipants and Procedures
2.2. Assessment
2.3. Ethics Principles
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Campos, G.S.; Bandeira, A.C.; Sardi, S.I. Zika virus outbreak, Bahia, Brazil. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 1885–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, G.W.; Kitchen, S.F.; Haddow, A.J. Zika virus (I). Isolations and serological specificity. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1952, 46, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, R.; Barcellos, C.; Brasil, P.; Cruz, O.G.; Alves Honório, N.; Kuper, H.; Carvalho, M.S. The Zika Virus Epidemic in Brazil: From Discovery to Future Implications. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, M.R.; Chen, T.H.; Hancock, W.T.; Powers, A.M.; Kool, J.L.; Lanciotti, R.S.; Pretrick, M.; Marfel, M.; Holzbauer, S.; Dubray, C.; et al. Zika virus outbreak on Yap Island, Federated States of Micronesia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 2536–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasil, P.; Pereira, J.P., Jr.; Moreira, M.E.; Ribeiro Nogueira, R.M.; Damasceno, L.; Wakimoto, M.; Rabello, R.S.; Valderramos, S.G.; Halai, U.-A.; Salles, T.S.; et al. Zika virus infection in pregnant women in Rio de Janeiro. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 2016, 2321–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Araújo, T.V.B.; Rodrigues, L.C.; de Alencar Ximenes, R.A.; de Barros Miranda-Filho, D.; Montarroyos, U.R.; de Melo, A.P.L.; Valongueiro, S.; Souza, W.V.; Braga, C.; Brandão Filho, S.P.; et al. Association between Zika virus infection and microcephaly in Brazil, January to May, 2016: Preliminary report of a case-control study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 1356–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noronha, L.D.; Zanluca, C.; Azevedo, M.L.; Luz, K.G.; Santos, C.N. Zika virus damages the human placental barrier and presents marked fetal neurotropism. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz. 2016, 111, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC Zika and Pregnancy. Congenital Zika Syndrome & Other Birth Defects. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/pregnancy/zika/testing-follow-up/zika-syndrome-birth-defects.html (accessed on 20 August 2018).
- De Fatima Vasco Aragao, M.; van der Linden, V.; Brainer-Lima, A.M.; Coeli, R.R.; Rocha, M.A.; Sobral da Silva, P.; Durce Costa Gomes de Carvalho, M.; van der Linden, A.; Cesario de Holanda, A.; Valenca, M.M. Clinical features and neuroimaging (CT and MRI) findings in presumed Zika virus related congenital infection and microcephaly: Retrospective case series study. BMJ 2016, 353, i1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honein, M.A.; Dawson, A.; Petersen, E.E.; Jones, A.M.; Lee, E.H.; Yazdy, A.M.; Ahmad, N.; Macdonald, J.M.; Evert, N.; Bingham, A.; et al. Birth defects among fetuses and infants of US women with evidence of possible Zika virus infection during pregnancy. JAMA 2017, 317, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Linden, V.; Filho, E.L.R.; Lins, O.G.; Vand de Linden, A.; Aragão, M.d.F.; Brainer-Lima, A.M.; Cruz, D.D.; Rocha, M.A.; Sobral da Silva, P.F.; Carvalho, M.D.; et al. Congenital Zika syndrome with arthogryposis: Retroscpective case series study. BMJ. 2016, 354, i3899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessoa, A.; Van der Linden, V.; Yeargin-Allsopp, M.; Carvalho, C.G.; Ribeiro, E.M.; Van Naarden Braun, K.; Durkin, M.S.; Pastula, D.M.; Moore, J.D.; Moore, C.A. Motor abnormalities and epilepsy in infants and children with evidence of congenital Zika virus infection. Pediatrics 2018, 141, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura da Silva, A.A.; Ganz, J.S.; Souza, P.D.; Doriqui, M.J.; Ribeiro, M.R.; Branco, M.D.; Queiroz, R.C.; Pacheco, M.J.; Vieira da Costa, F.R.; Silva, F.S.; et al. Early growth and neurologic outcomes of infants with probable congenital Zika virus syndrome. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 1953–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leal, M.C.; Muniz, L.F.; Ferreira, T.S.; Santos, C.M.; Almeida, L.C.; Van der Linden, V.; Ramos, R.C.; Rodrigues, L.C.; Neto, S.S. Hearing Loss in Infants with microcephaly and evidence of congenital Zika virus infection-Brazil, November 2015-May 2016. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2015, 65, 917–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira-Filho, J.; Felzemburgh, R.; Costa, F.; Nery, N.; Mattos, A.; Henrique, D.F.; Ko, A. Seizures as a complication of congenital zika syndrome in early infancy. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2018, 98, 1860–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventura, L.C.; Ventura, C.V.; Dias, N.C.; Vilar, I.G.; Goies, A.L.; Arantes, T.E.; Fernandes, L.C.; Chiang, M.F.; Miller, M.T.; Lawrence, L. Visual impairment evaluation in 119 children with congenital Zika syndrome. J. AAPOS. 2018, 22, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, M.C.; Van der Linden, V.; Bezerra, T.P.; de Valois, L.; Borges, A.C.G.; Antunes, M.M.C.; Brandt, K.G.; Moura, C.X.; Rodrigues, L.C.; Ximenes, C.R. Characteristics of dysphagia in infants with microcephaly caused by congenital Zika infection, Brazil, 2015. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 1253–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villar, J.; Cheikh Ismail, L.; Victora, C.G.; Chuma, E.C.; Bertino, E.; Altman, D.G.; Lambert, A.; Papageorghiou, A.T.; Carvalho, M.; Jaffer, Y.A.; et al. International standards for newborn weight, length, and head circumference by gestational age and sex: The Newborn Cross-Sectional Study of the INTERGROWTH-21st Project. Lancet 2014, 384, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashwal, S.; Michelson, D.; Plawner, L.; Dobyns, W.B. Practice parameter: Evaluation of the child wilt microcephaly (an evidence-based review): Report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the Practice Committee of the Child Neurology Society. Neurology 2009, 73, 887–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebanjo, T.; Godfred-Cato, S.; Viens, L.; Fischer, M.; Staples, J.E.; Kuhnert-Tallman, W.; Walke, H.; Oduyebo, T.; Polen, K.; Peacock, G.; et al. Update: Interim Guidance for the diagnosis, Evaluation and management of infants with possible congenital zika virus infection- United States, October 2017. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2017, 66, 1089–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domas, C.F.; Andrews, D.; Goulden, K.J. Evidence-based milestone ages as a framework for developmental surveillance. Paediatr. Child Health 2012, 17, 561–568. [Google Scholar]
- França, T.L.B.; Medeiros, W.R.; Saouza, N.L.; Longo, E.; Pereira, S.A.; França, T.B.O.; Souza, K.G. Growth and development of children with microcephaly associated with congenital Zika Virus Syndrome in Brazil. Int. Resp. Public Health 2018, 15, 1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, H.N.C.; Schiariti, V.; Regalado, I.C.R.; Souza, K.G.; Pereira, S.A.; Fechine, C.P.N.D.; Longo, E. Functioning and disability profile of children with microcephaly associated with congenital Zika virus infection. Int. J. Environ. Resp. Public Heath 2018, 29, 1107. [Google Scholar]
- Hazin, A.N.; Poretti, A.; Cavalcanti Souza Cruz, O.; Tenorio, M.; Van der Linden, A.; Pena, L.J.; Brito, C.; Gil, L.H.; de Barros Miranda-Filho, D.; Marques, E.T.; et al. Computed Tomographic finding in microcephaly associated with zika virus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 2193–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares de Oliveira-Szejnfeld, P.; Levine, D.; Melo, A.S.; Amorim, M.M.; Batista, A.G.; Chimelli, L.; Tanuri, A.; Aguair, R.S.; Malinger, G.; Ximenes, R.; et al. Congenital brain abnormali] and zika virus: What the radiologist can expect to see prenatally and postnatally. Radiology 2016, 281, 202–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragao, MF.V.V.; Holanda, A.C.; Brainer-Lima, A.M.; Petribu, N.C.L.; Castillo, M.; Ven der Linder, V.; Serpa, S.C.; Teório, A.G.; Travassos, P.T.C.; Cordeiro, M.T.; et al. Nonmicrocephalic Infants with Congenital Zika syndrome suspected only after neuroimaging evaluation compared with those with microcephaly at birth and postnally: How large is the Zika Virus “iceberg”? AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2017, 38, 1427–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, A.M.; Hughes, B.l. Detection and Prevention of Perinatal Infection cytomegalovirus and zika virus. Clin. Perinatol. 2018, 45, 307–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frenkel, L.D.; Gomez, F.; Sabari, F. The pathogenesis of microcephaly resulting from congenital infection: Why is my baby’s headson small? Euro. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 37, 209–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcez, P.P.; Loiola, E.C.; Madeiro da Costa, R.; Higa, L.M.; Trindade, P.; Delvecchio, R.; Nascimento, J.M.; Brinderiro, R.; Tanuri, A.; Rehen, S.K. Zika virus impairs growth in human neurospheres and brain organoids. Science 2016, 352, 816–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Armstrong, N.; Zhao, H.; Hou, W.; Liu, J.; Chen, C.; Wan, J.; Zhong, C.; Liu, C.; Zhu, H.; et al. Zika virus fatally infects wild type neonatal mice and replicates in central nervous system. Viruses 2018, 10, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbaum, P.; Paneth, N.; Leviton, A.; Goldstein, M.; Baz, M. A report: The definition and classification of cerebral palsy April 2006. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2007, 109, 8–14. [Google Scholar]
- Brazilian Ministry of Heath. Ministério da Saúde: Ministério da Saúde vai distribuir teste rápido de Zika. Available online: http://combateaedes.saude.gov.br/pt/noticias/645-saude-acompanha-avaliacao-de-qualidade-de-teste-de-zik. 2016 (accessed on 20 August 2018).
| Findings | Mean | SD |
|---|---|---|
| At birth | ||
| Gestational age, weeks | 38.4 | 1.7 |
| Weight, Kg | 2.6 | 0.5 |
| Length, cm | 45.0 | 3.4 |
| HC, cm | 28.6 | 1.7 |
| At admission | ||
| Age, months | 4.1 | 2.3 |
| Weight, Kg | 5.4 | 1.7 |
| HC, cm | 33.1 | 4.4 |
| Age in which neurological exam was performed, months | 4.6 | 2.4 |
| Number of Evaluated Infants | Frequency (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Female | 102 | 56 (54.9) |
| Severe microcephaly * | 102 | 56 (54.9) |
| Premature † (34.2 ± 0.8 weeks) | 102 | 09 (8.8) |
| Delivered by caesarean section | 100 | 58 (58.0) |
| Apgar score 5 min between 7 and 10 | 84 | 82 (97.6) |
| Apgar score 5 min between 5 and 6 | 84 | 02 (2.4) |
| Neonatal complications ‡ | 100 | 38 (38.0) |
| Evaluation Findings | Number of Evaluated Infants * | Frequency (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Neuroimaging * | ||
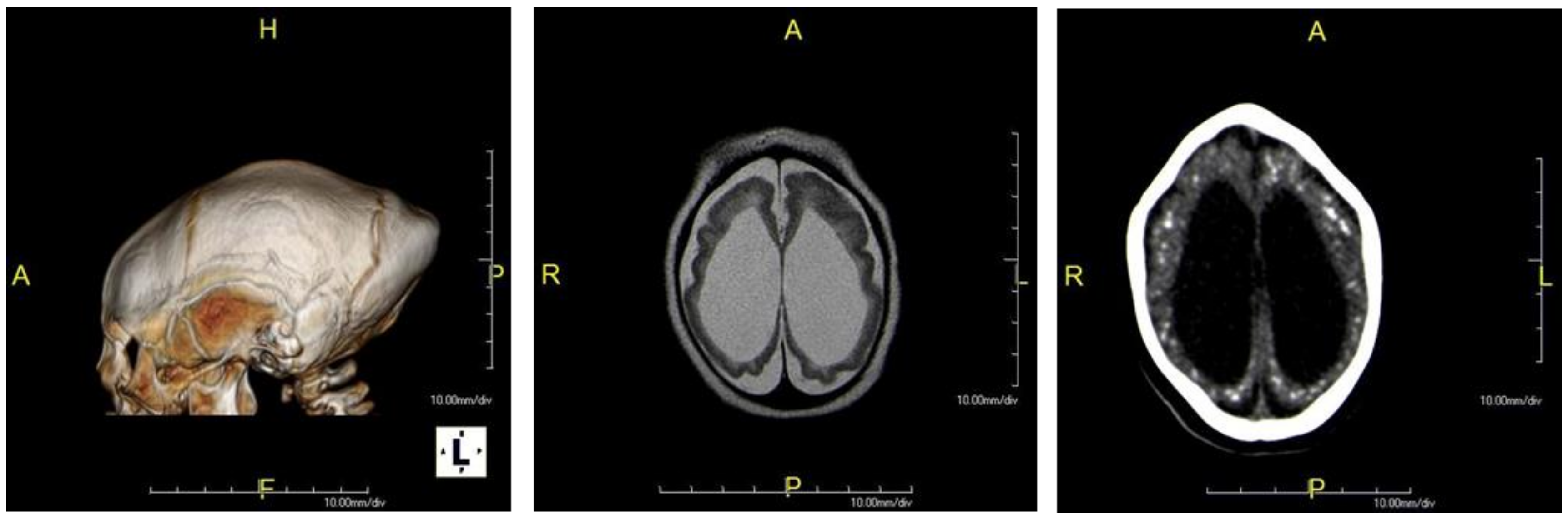
| Cerebral atrophy | 102 | 94 (92.1) |
| Ventriculomegaly | 101 | 93 (92.1) |
| Malformation of cortical development | 101 | 86 (85.1) |
| Location of calcifications | ||
| • Cortical and subcortical | 101 | 81(80.2) |
| • Basal ganglia | 101 | 62 (61.4) |
| • Periventricular | 101 | 30 (29.7) |
| • Brainstem | 101 | 10 (9.9) |
| • Cerebellum | 101 | 3 (2.9) |
| Corpus callosum abnormalities | 102 | 76 (74.6) |
| Enlarged subarachnoid space | 101 | 51 (50.5) |
| Cerebellum hypoplasia | 101 | 24(23.7) |
| Brainstem hypoplasia | 101 | 20 (19.8) |
| Enlarged cisterna magna | 101 | 19 (18.8) |
| Delayed myelination | 97 | 5 (5.1) |
| Intraparenchymal cysts | 101 | 2 (1.9) |
| Videoeletroencephalogram | ||
| Epileptogenic activity | 96 | 54 (56.3) |
| Slow activity | 96 | 8 (8.5) |
| Normal activity | 96 | 34 (35.4) |
| Neurological findings | ||
| Hypertonia/spasticity | 101 | 98 (97.0) |
| Neurodevelopmental milestones delay | 101 | 91 (92.8) |
| Hyperreflexia | 101 | 74 (73.3) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
C. Lage, M.-L.; Carvalho, A.L.d.; Ventura, P.A.; Taguchi, T.B.; Fernandes, A.S.; Pinho, S.F.; Santos-Junior, O.T.; Ramos, C.L.; Nascimento-Carvalho, C.M. Clinical, Neuroimaging, and Neurophysiological Findings in Children with Microcephaly Related to Congenital Zika Virus Infection. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 309. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16030309
C. Lage M-L, Carvalho ALd, Ventura PA, Taguchi TB, Fernandes AS, Pinho SF, Santos-Junior OT, Ramos CL, Nascimento-Carvalho CM. Clinical, Neuroimaging, and Neurophysiological Findings in Children with Microcephaly Related to Congenital Zika Virus Infection. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(3):309. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16030309
Chicago/Turabian StyleC. Lage, Maria-Lucia, Alessandra L. de Carvalho, Paloma A. Ventura, Tania B. Taguchi, Adriana S. Fernandes, Suely F. Pinho, Onildo T. Santos-Junior, Clara L. Ramos, and Cristiana M. Nascimento-Carvalho. 2019. "Clinical, Neuroimaging, and Neurophysiological Findings in Children with Microcephaly Related to Congenital Zika Virus Infection" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 3: 309. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16030309
APA StyleC. Lage, M.-L., Carvalho, A. L. d., Ventura, P. A., Taguchi, T. B., Fernandes, A. S., Pinho, S. F., Santos-Junior, O. T., Ramos, C. L., & Nascimento-Carvalho, C. M. (2019). Clinical, Neuroimaging, and Neurophysiological Findings in Children with Microcephaly Related to Congenital Zika Virus Infection. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(3), 309. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16030309





